Submitted:
22 February 2024
Posted:
23 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Endpoints
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Assessment of Renal Function
2.6. Assessment of Complications and Mortality
3. Results
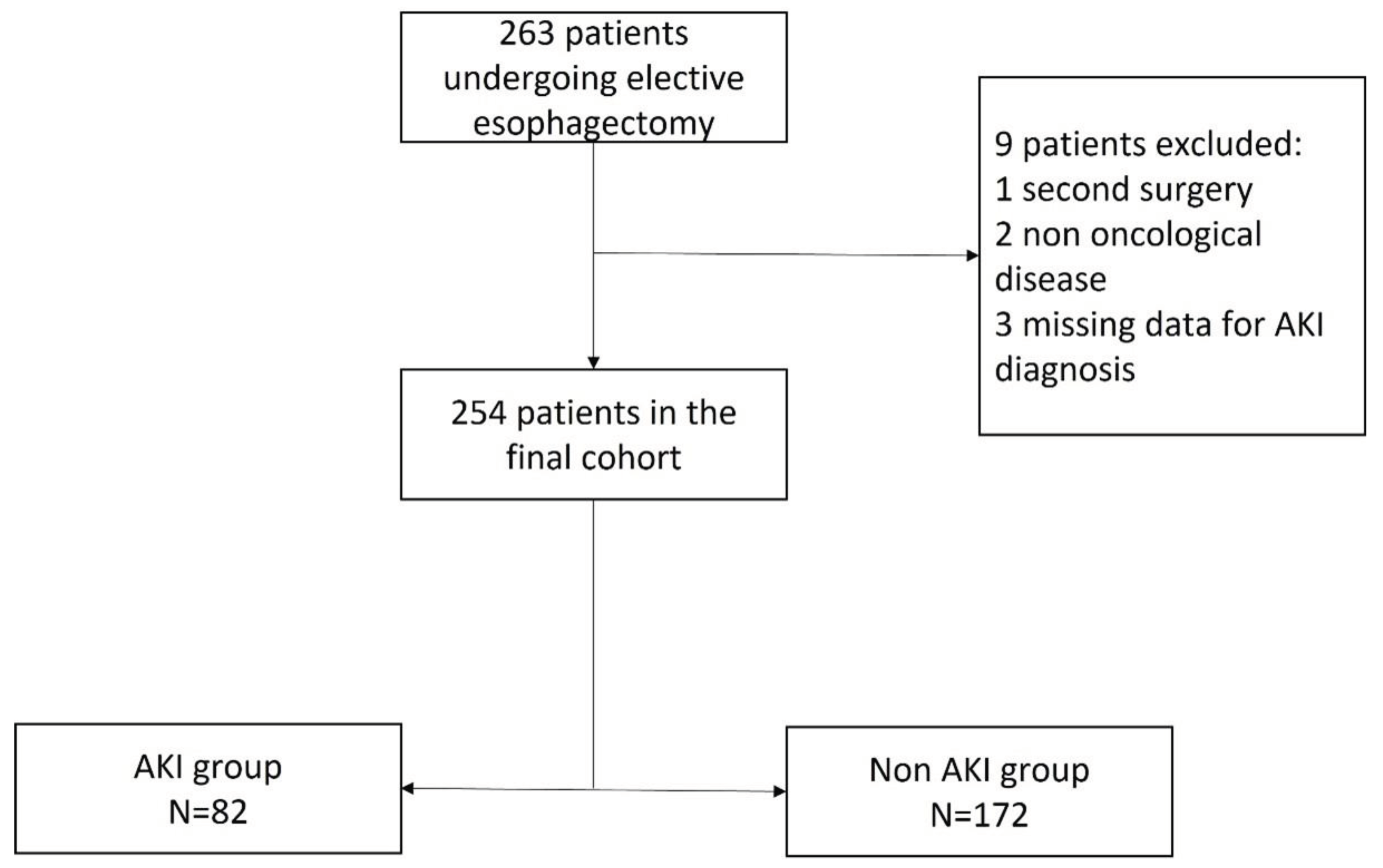
3.1. Participants
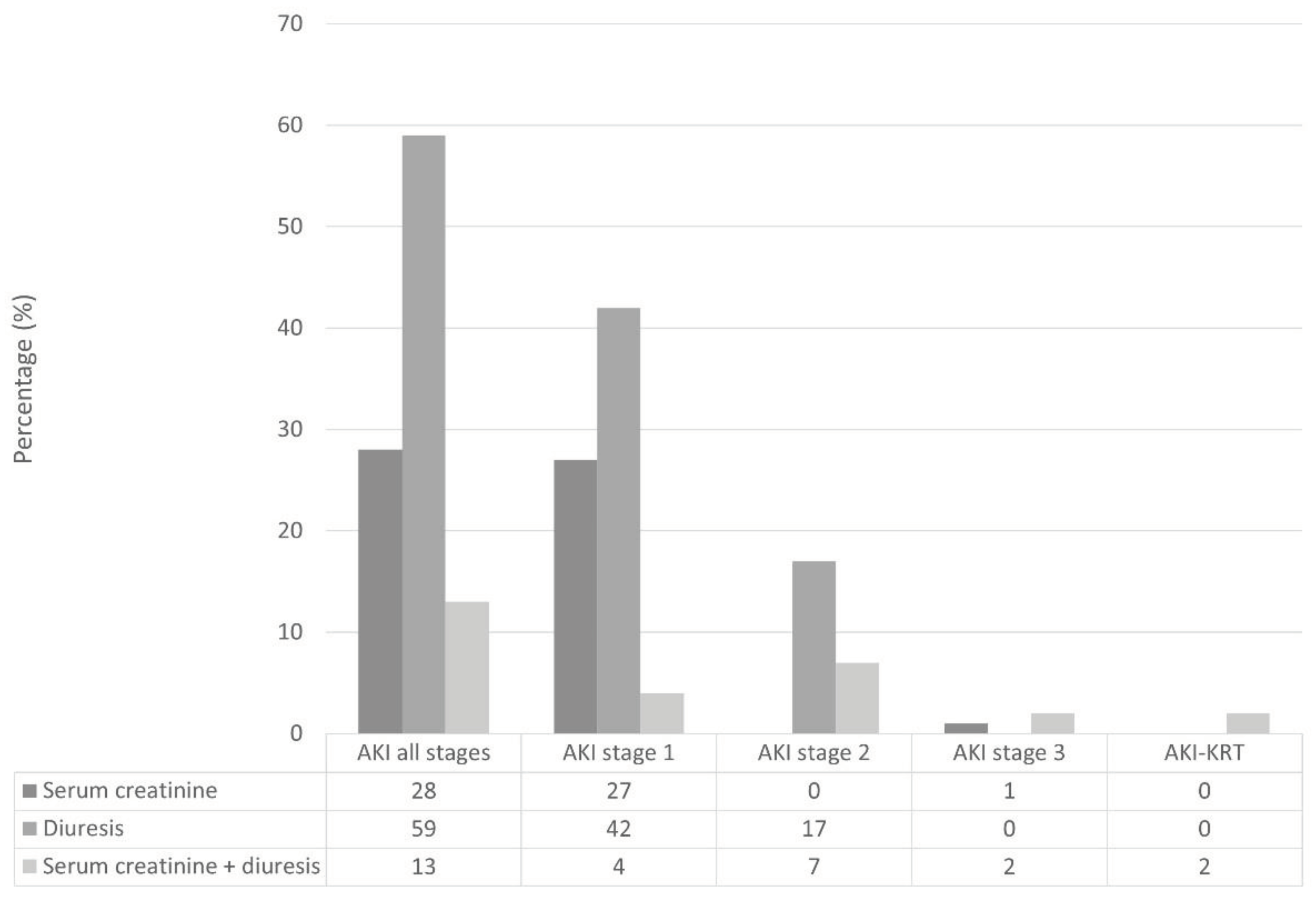
3.2. Incidence and Risk Factors of Postoperative AKI
3.3. Difference between Transient and Persistent Postoperative AKI
3.4. Postoperative Complications and Association with Kidney-Related Adverse Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Major Findings
4.2. Comparison with Previous Studies
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Hagen, P.; Hulshof, M.C.; van Lanschot, J.J.; et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 2012, 366, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, P.; Ward, J.; Tekkis, P.P.; et al. Mortality and morbidity in gastrooesophageal cancer surgery: initial results of ASCOT multicentre prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2003, 327, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.H.; Kim, H.R.; Baek, S.H.; et al. Risk factors of postoperative acute kidney injury in patients undergoing esophageal cancer surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2014, 28, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.M.; Hooker, C.M.; Molena, D.; et al. Complex Esophageal Reconstruction Procedures Have Acceptable Outcomes Compared With Routine Esophagectomy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konda, P.; Ai, D.; Guerra, C.E.; et al. Identification of Risk Factors Associated With Postoperative Acute Kidney Injury After Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2017, 31, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, T.; Feng, X.; Sun, L. Incidence and risk factors of acute kidney injury after esophageal cancer surgery: A nested case-control study. Int J Surg. 2017, 39, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.F.; Dunne, T.; Elliott, J.A.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury After Esophageal Cancer Surgery: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Impact on Oncologic Outcomes [published online ahead of print, 2020 Jul 24]. Ann Surg. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Sam D. Gumbert, Felix Kork, Maisie L. Jackson, Naveen Vanga, Semhar J. Ghebremichael, Christy Y. Wang, Holger K. Eltzschig; Perioperative Acute Kidney Injury. Anesthesiology 2020, 132, 180–204. [CrossRef]
- Bihorac, A.; Yavas, S.; Subbiah, S.; Hobson, C.E.; Schold, J.D.; Gabrielli, A.; Layon, A.J.; Segal, M.S. Long-term risk of mortality and acute kidney injury during hospitalization after major surgery. Ann Surg. 2009, 249, 851–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int Suppl 2012, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Macedo, E.; Bouchard, J.; Soroko, S.H.; et al. Fluid accumulation, recognition and staging of acute kidney injury in critically-ill patients. Crit Care 2010, 14, R82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, L.; Bellomo, R.; Bihorac, A.; et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat Rev Nephrol 2017, 13, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 14 Jammer, I.; Wickboldt, N.; Sander, M.; Smith, A.; Schultz, M.J.; Pelosi, P.; Leva, B.; Rhodes, A.; Hoeft, A.; Walder, B.; Chew, M.S.; Pearse, R.M.; European Society of Anaesthesiology (ESA) and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM); European Society of Anaesthesiology; European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Standards for definitions and use of outcome measures for clinical effectiveness research in perioperative medicine: European Perioperative Clinical Outcome (EPCO) definitions: a statement from the ESA-ESICM joint taskforce on perioperative outcome measures. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2015, 32, 88–105. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, D.E.; Alderson, D.; Cecconello, I.; Chang, A.C.; Darling, G.E.; DʼJourno, X.B.; Griffin, S.M.; Hölscher, A.H.; Hofstetter, W.L.; Jobe, B.A.; Kitagawa, Y.; Kucharczuk, J.C.; Law, S.Y.; Lerut, T.E.; Maynard, N.; Pera, M.; Peters, J.H.; Pramesh, C.S.; Reynolds, J.V.; Smithers, B.M.; van Lanschot, J.J. International Consensus on Standardization of Data Collection for Complications Associated With Esophagectomy: Esophagectomy Complications Consensus Group (ECCG). Ann Surg. 2015, 262, 286–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, T.E.; Helgason, D.; Helgadottir, S.; Palsson, R.; Gudbjartsson, T.; Sigurdsson, G.H.; Indridason, O.S.; Sigurdsson, M.I. Acute Kidney Injury After Abdominal Surgery: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcome. Anesth Analg. 2016, 122, 1912–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biteker, M.; Dayan, A.; Tekkeşin, A.İ.; Can, M.M.; Taycı, İ.; İlhan, E.; Şahin, G. Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of perioperative acute kidney injury in noncardiac and nonvascular surgery. Am J Surg. 2014, 207, 53–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gameiro, J.; Neves, J.B.; Rodrigues, N.; Bekerman, C.; Melo, M.J.; Pereira, M.; Teixeira, C.; Mendes, I.; Jorge, S.; Rosa, R.; Lopes, J.A. Acute kidney injury, long-term renal function and mortality in patients undergoing major abdominal surgery: a cohort analysis. Clin Kidney J. 2016, 9, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prowle, J.R.; Forni, L.G.; Bell, M.; et al. Postoperative acute kidney injury in adult non-cardiac surgery: joint consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative and PeriOperative Quality Initiative. Nat Rev Nephrol 2021, 17, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | N | Overall, N = 2541 |
Non-AKI, N = 1721 |
AKI, N = 821 |
| Age (years) | 254 | 66 (56, 72) | 65 (56, 71) | 66 (58, 73) |
| Gender | 254 | |||
| Male | 206 (81%) | 140 (81%) | 66 (80%) | |
| Female | 48 (19%) | 32 (19%) | 16 (20%) | |
| BMI (kg/h2) | 254 | 24.3 (22.4, 27.7) | 24.0 (22.0, 26.9) | 26.2 (23.1, 29.4) |
| Level of dependency | 254 | |||
| Independent | 247 (97%) | 168 (98%) | 79 (96%) | |
| Partially dependent | 7 (2.8%) | 4 (2.3%) | 3 (3.7%) | |
| ASA status | 254 | |||
| 1 | 1 (0.4%) | 1 (0.6%) | 0 (0%) | |
| 2 | 144 (57%) | 105 (61%) | 39 (48%) | |
| 3 | 106 (42%) | 64 (37%) | 42 (51%) | |
| 4 | 3 (1.2%) | 2 (1.2%) | 1 (1.2%) | |
| Chronic steroid use | 254 | |||
| No | 242 (95%) | 164 (95%) | 78 (95%) | |
| Yes | 12 (4.7%) | 8 (4.7%) | 4 (4.9%) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 254 | |||
| No | 209 (82%) | 145 (84%) | 64 (78%) | |
| Yes | 45 (18%) | 27 (16%) | 18 (22%) | |
| Hypertension | 254 | |||
| No | 153 (60%) | 112 (65%) | 41 (50%) | |
| Yes | 101 (40%) | 60 (35%) | 41 (50%) | |
| Current smoker within 1 year | 254 | |||
| No | 206 (81%) | 133 (77%) | 73 (89%) | |
| Yes | 48 (19%) | 39 (23%) | 9 (11%) | |
| Severe COPD | 254 | |||
| No | 226 (89%) | 156 (91%) | 70 (85%) | |
| Yes | 28 (11%) | 16 (9.3%) | 12 (15%) | |
| NSQIP | 254 | 9.00 (8.00, 11.50) | 9.00 (8.00, 11.50) | 10.50 (8.00, 11.50) |
| Alohol use | 254 | |||
| No | 244 (96%) | 166 (97%) | 78 (95%) | |
| Yes | 10 (3.9%) | 6 (3.5%) | 4 (4.9%) | |
| Statins use | 254 | |||
| No | 208 (82%) | 142 (83%) | 66 (80%) | |
| Yes | 46 (18%) | 30 (17%) | 16 (20%) | |
| Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors use | 254 | |||
| No | 208 (82%) | 146 (85%) | 62 (76%) | |
| Yes | 46 (18%) | 26 (15%) | 20 (24%) | |
| Angiotensin-receptors blockers use | 254 | |||
| No | 223 (88%) | 156 (91%) | 67 (82%) | |
| Yes | 31 (12%) | 16 (9.3%) | 15 (18%) | |
| Beta blockers | 254 | |||
| No | 204 (80%) | 137 (80%) | 67 (82%) | |
| Yes | 50 (20%) | 35 (20%) | 15 (18%) | |
| Insulin use | 254 | |||
| No | 245 (96%) | 166 (97%) | 79 (96%) | |
| Yes | 9 (3.5%) | 6 (3.5%) | 3 (3.7%) | |
| Proton pump inhibitor use | 254 | |||
| No | 116 (46%) | 84 (49%) | 32 (39%) | |
| Yes | 138 (54%) | 88 (51%) | 50 (61%) | |
| Non-sterois-antinflammatory drugs use | 254 | |||
| No | 219 (86%) | 151 (88%) | 68 (83%) | |
| Yes | 35 (14%) | 21 (12%) | 14 (17%) | |
| Baseline serum creatinine (µmol/L) | 254 | 77 (67, 87) | 77 (66, 87) | 78 (69, 92) |
| Preoperative urea (mmol/L) | 230 | 5.55 (4.31, 7.00) | 5.60 (4.36, 6.88) | 5.50 (4.07, 7.53) |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate (ml/min/1.73m2) | 254 | 90 (79, 100) | 92 (81, 101) | 88 (72, 98) |
| Preoperative hemoglobin (g/dL) | 248 | 12.90 (11.70, 13.80) | 12.80 (11.70, 13.80) | 12.90 (11.80, 13.70) |
| Preoperative white blood cell count (x109/L) | 210 | 5.71 (4.48, 7.30) | 5.66 (4.50, 6.98) | 6.03 (4.46, 7.60) |
| Preoperative platelet count (x104/µL) | 244 | 207 (165, 252) | 205 (168, 247) | 216 (164, 258) |
| Preoperative atrial fibrillation | 254 | |||
| No | 244 (96%) | 166 (97%) | 78 (95%) | |
| Yes | 10 (3.9%) | 6 (3.5%) | 4 (4.9%) | |
| Preoperative ejection fraction < 45% | 254 | |||
| No | 247 (97%) | 168 (98%) | 79 (96%) | |
| Yes | 7 (2.8%) | 4 (2.3%) | 3 (3.7%) | |
| Surgical technique | 254 | |||
| Mini-invasive | 39 (15%) | 33 (19%) | 6 (7.3%) | |
| Partially-invasive | 9 (3.5%) | 4 (2.3%) | 5 (6.1%) | |
| Totally-invasive | 206 (81%) | 135 (78%) | 71 (87%) | |
| Tri-incisional surgery | 254 | |||
| No | 241 (95%) | 161 (94%) | 80 (98%) | |
| Yes | 13 (5.1%) | 11 (6.4%) | 2 (2.4%) | |
| Type of anesthesia | 248 | |||
| Inhaled | 2 (0.8%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (2.5%) | |
| Totally intravenous | 23 (9.3%) | 16 (9.5%) | 7 (8.9%) | |
| Inhaled + epidural | 18 (7.3%) | 9 (5.3%) | 9 (11%) | |
| Totally intravenous + epidural | 205 (83%) | 144 (85%) | 61 (77%) | |
| Anesthesia duration (hours) | 251 | 6.00 (5.20, 7.20) | 6.00 (5.20, 7.20) | 6.05 (5.95, 7.00) |
| Intraoperative minimal SpO2/FiO2 | 248 | 120 (98, 155) | 120 (96, 158) | 120 (107, 155) |
| Intraoperative minimal systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 247 | 100 (90, 100) | 100 (90, 100) | 100 (90, 110) |
| Intraoperative colloid use | 247 | |||
| No | 233 (94%) | 159 (95%) | 74 (94%) | |
| Yes | 14 (5.7%) | 9 (5.4%) | 5 (6.3%) | |
| Intraoperative blood loss (ml) | 246 | 150 (100, 200) | 100 (100, 200) | 200 (100, 215) |
| Intraoperative blood transfusion | 247 | |||
| No | 233 (94%) | 161 (96%) | 72 (91%) | |
| Yes | 14 (5.7%) | 7 (4.2%) | 7 (8.9%) | |
| Intraoperative volume infused (ml/kg/h) | 247 | 9.26 (7.68, 10.72) | 9.50 (7.67, 11.13) | 8.70 (7.74, 10.15) |
| End of surgery hemoglobin level (mg/dL) | 241 | 12.00 (11.00, 13.10) | 12.00 (11.10, 13.20) | 12.00 (10.90, 12.80) |
| End of surgery lactate level (mmol/L) | 74 | 1.16 (0.99, 1.78) | 1.10 (0.88, 2.03) | 1.25 (1.06, 1.65) |
| Intraoperative vasopressor use | 247 | |||
| No | 231 (94%) | 158 (94%) | 73 (92%) | |
| Yes | 16 (6.5%) | 10 (6.0%) | 6 (7.6%) | |
| Intraoperative inotrope use | 247 | |||
| No | 230 (93%) | 157 (93%) | 73 (92%) | |
| Yes | 17 (6.9%) | 11 (6.5%) | 6 (7.6%) | |
| Intraoperative arrhytmya | 248 | |||
| No | 242 (98%) | 166 (98%) | 76 (96%) | |
| Yes | 6 (2.4%) | 3 (1.8%) | 3 (3.8%) | |
| End of surgery diuresis (ml/kg/h) | 246 | 1.14 (0.76, 1.75) | 1.20 (0.81, 1.77) | 1.01 (0.63, 1.65) |
| Intraoperative use of diuretics | 248 | |||
| No | 223 (90%) | 154 (91%) | 69 (87%) | |
| Yes | 25 (10%) | 15 (8.9%) | 10 (13%) | |
| Intraoperative use of non-steroid-anti inflammatory drugs | 248 | |||
| No | 129 (52%) | 95 (56%) | 34 (43%) | |
| Yes | 119 (48%) | 74 (44%) | 45 (57%) | |
| End of surgery extubation | 253 | |||
| No | 117 (46%) | 80 (47%) | 37 (46%) | |
| Yes | 136 (54%) | 92 (53%) | 44 (54%) | |
| Intraoperative acute kidney injury | 246 | |||
| No | 219 (89%) | 153 (92%) | 66 (84%) | |
| Yes | 27 (11%) | 14 (8.4%) | 13 (16%) | |
| 1Median (IQR); n (%) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





