Submitted:
21 February 2024
Posted:
23 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Apparatus and Reagents
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Preparation of Solutions for HMF Determination
- Carrez I: 15 g of potassium hexacyanoferrate (II) trihydrate was dissolved in distilled water in a 100 mL volumetric flask;
- Carrez II: 30 g of zinc acetate dihydrate was dissolved in distilled water in a 100 mL volumetric flask;
- 0.2% sodium bisulfate (IV) solution: 0.1 g sodium bisulfate (IV) was dissolved in distilled water in a 50 mL volumetric flask (prepared immediately before use);
- p-toluidine solution: 10 g of p-toluidine was dissolved in propan-2-ol in a 100 mL volumetric flask. Preparation of the solution must take place 24 hours before use and can be used up to three days;
- 0.5 % barbituric acid solution: 0.5 g of barbituric acid was dissolved in distilled water in a 100 mL volumetric flask.
2.3.2. The White Spectrophotometric Method
2.3.3. The Winkler Spectrophotometric Method
2.3.4. The LC-MS/MS Method
2.3.5. Validation of the LC-MS/MS Method
2.3.6. Preparation of Honey for Determinations by LC-MS/MS
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation of the LC-MS/MS Method
3.2. Qualitative Analysis
3.3. Quantitative Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Missio da Silva, P.; Gauche, C.; Valdemiro Gonanza, L.; Oliveira Costa, A.C.; Fett, R. Honey: Chemical composition, stability and authenticity. Food Chemistry. 2016, 196, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarghandian, S.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samini, F. Honey and health: A review of recent clinical research. Pharmacognosy Research. 2017, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Shlyankevich, M.; Jeong, H.K.; Douglas, J.S.; Surh, Y.J. Bioactivation of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furaldehyde to an electrophilic and mutagenic allylic sulfuric acid ester. Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, Yale University School of Medicine. 1995, 209, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushina, Y.; Yagita, E.; Kuramochi, K.; Kuriyama, I.; Shimazaki, N.; Koiwai, O.; Uchiyama, Y.; Yomezawa, Y.; Sugawara, F.; Kobayashi, S.; Sakaguchi, K.; Yoshida, H. 5-(Hydroxymethyl)-2-furfural: A selective inhibitor of DNA polymerase λ and terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2008, 446, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, F.J. Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) and Related Compounds. Wiley. 2008, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Wu, L.Y.; Zhao, T.; Huang, X.; Liu, Z.H.; Fan, X.L.; Xiao, C.R.; Gao, Y.; Ma, Y.B.; Chen, J.J.; Zhu, L.L.; Fan, M. The protective role of 5-HMF against hypoxic injury. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011, 16, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.M.; Wu, L.Y.; Zhao, T.; Wu, K.W.; Xiong, L.; Zhu, L.L.; Fan, M. The protective role of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural (5-HMF) against acute hypobaric hypoxia. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011, 16, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapla, U.M.; Solayman, M.; Alam, N.; Khalil, M.I.; Gan, S.H. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) levels in honey and other food products: effects on bees and human health. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 35, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wed M.A.A.; Sraa A-M.; Rahaf M.H.A.; Badriah S. l-F.; Hamed A.G.; Al-Shehri B.M.A.; Bajaber M.A.; Khan K.A.; Alrooqi M.M.; Modawe G.A.; Mohammed M.E.A. Biochemical Reactions and Their Biological Contributions in Honey. Molecules 2022, 27, 4719. Molecules. [CrossRef]
- Tichonow, A.I.; Bondarenko, L.A.; Jarnych, T.G.; Szpyczak, O.S.; Kowal, W.M.; Skrypnik-Tichonow, R.I. Natural honey in medicine and pharmacy. Origin, properties, application, medicinal preparations. Sadecki Bartnik. 2017, ISBN: 978-83-61904-13-7.
- Khalil, M.I.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Gan, S.H. High 5-hydroxymethylfurfural concentrations are found in Malaysian honey samples stored for more than one year. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2010, 48, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Council of The European Union. Council Directive 2001/110/EC of 20 December 2001: relating to honey. Official Journal of the European Communities. 2001; L10: 47-52.. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2002:010:0047:0052:EN:PDF.
- Gokmen, V.; Acar, O.C.; Serpne, A.; Morales, A.F.J. Effect of leaving agents and sugars on the formation of hydroxymethylfurfural in cookies during baking. European Food Research and Technology. 2008, 226, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turhan, K. Effects of thermal treatment and storage on hydroxymethylfurfural (hmf) content and diastase activity of honeys collected from middle Anatolia on Turkey. Innovations in Chemical Biology. 2009, 23, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironescu, M.; Fratila, L.; Hupert, A.; Mironescu, I.D. Obtaining and Characterization of Starch-Based Edible Films Incorporating Honey, Propolis and Bee Bread. Acta Universitatis Cibiniensis. 2019, 23, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Su, J.; Li, L.; Hu, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.; Chen, T. In vitro antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2013, 61, 10604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappala, M.; Fallico, B.; Arena, E.; Verzera, A. Methods for the determination of HMF in honey: a comparison. Food Control. 2005, 16, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S. Harmonized Methods of the European Honey Commission. International Honey Commission. 2009. www.bee-hexagon.net.
- Ajlouni, S.; Sujirapinyokul, P. Hydroxymethyl-furfuraldehyde and amylase contents in Australian honey. Food Chemistry. 2010, 119, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixido, E.; Santos, F.J.; Puignou, L.; Galceran, M.T. Analysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in foods by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A. 2006, 1135, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizelioa, V.M.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Campelo Borges, G.S.; Micke, G.A.; Fetta R, Oliveira Costa, A.C. Development of a fast MECK method for determination of 5-HMF in honey samales. Food Chemistry. 2012, 133, 1640. [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Sales, E.O.; Manzanilla-Cano, J.A.; Barcelo-Quintal, M.H.; Juarez-Mendoza, D.; Reyes-Sales, M. Direct Electrochemical Determination of Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) and its Application to Honey Samples. Analytical Letters. 2007, 39, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, O.E.; Kukurová, K.; Dasko, L.; Stanciuc, N.; Ciesarová, Z.; Croitoru, C.; Râpeanu, G. Effect of Thermal Processing on Simultaneous Formation of Acrylamide and Hydroxymethylfurfural in Plum Purée. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences. 2019, 69(2), 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, M.; Zaguła, G.; Puchalski, C.; & Dżugan, M. Transfer of some toxic metals from soil to honey depending on bee habitat conditions. Acta Universitatis Cibiniensis. 2020, 24, 49. [CrossRef]
- Debska, J.; Kot-Wasik, A.; Namiesnik, J. Determination of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in water samples using liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector and mass spectrometry. Journal of Separation Science. 2005, 28, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anklam, E. A review of the analytical methods to determine the geographical and botanical origin of honey. Food Chemistry. 1998, 63, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
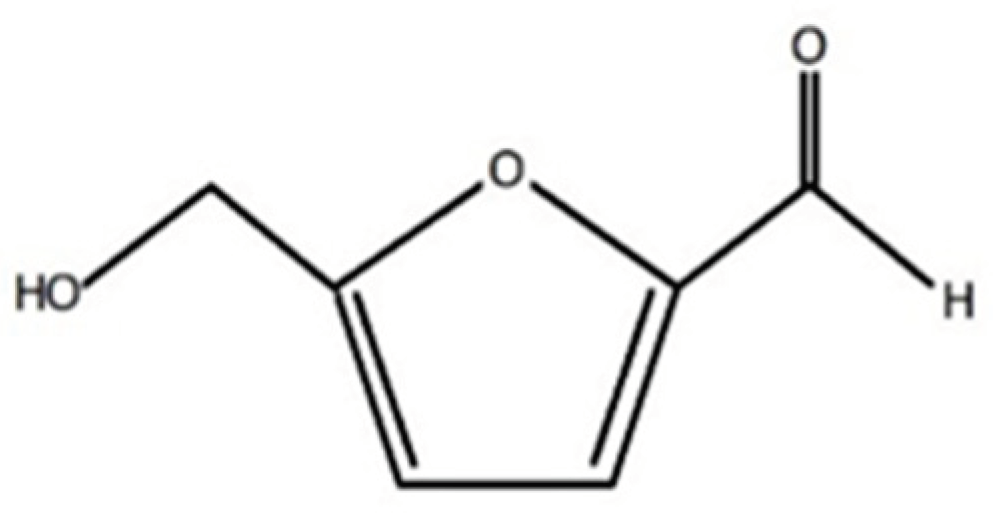
| Pseudo molecular ion [M+1]+ | DP [V] | MRM | CE [V] | CPX [V] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 127 | 46 | 127 → 109* | 15 | 8 |
| 127 | 81 | 127 → 81 | 23 | 6 |
| 127 | 53 | 127 → 53 | 31 | 8 |
| Linearity range | Curve equation | Correlation coefficient | LOD [μg/mL] | LOQ [μg/mL] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| From LOQ to 0.5 μg/mL |
y = 2E+07·x+ 35595 | 0.9992 | 0.0005 | 0.001 |
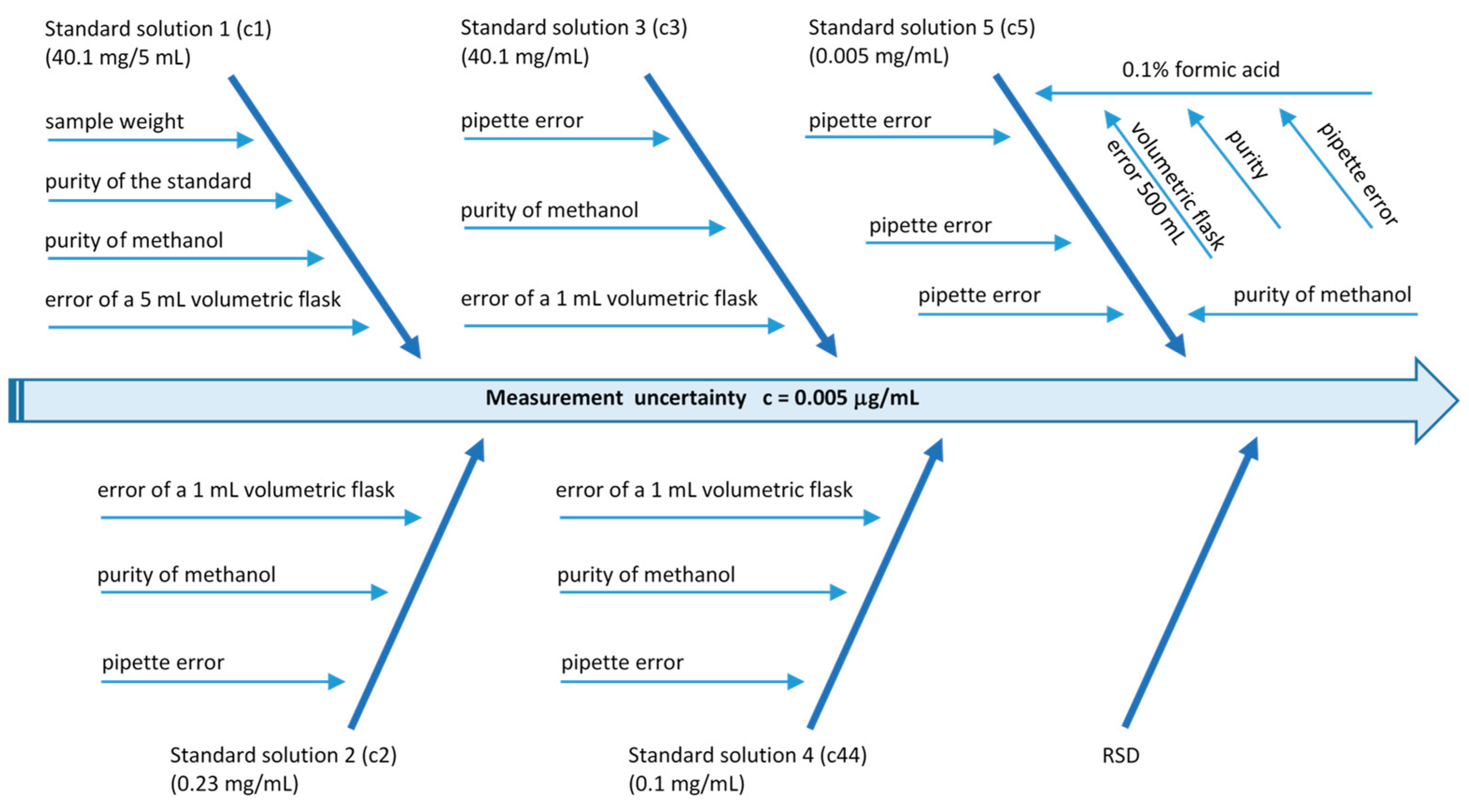
| Concentration [μg/mL] | Measurement uncertainty [μg/mL] |
|---|---|
| 0.001 | 7.60E-05 |
| 0.0025 | 2.16E-04 |
| 0.005 | 5.50E-04 |
| 0.010 | 7.97E-04 |
| 0.025 | 2.13E-03 |
| 0.050 | 2.59E-03 |
| 0.100 | 5.16E-03 |
| 0.250 | 1.32E-02 |
| 0.500 | 2.72E-02 |
| Honey sample number | HMF presence (LC-MS/MS) |
HMF presence (White) | HMF presence (Winkler) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | + | + | - |
| 2 | + | - | + |
| 3 | + | + | + |
| 4 | + | + | + |
| 5 | + | + | + |
| 6 | + | + | + |
| 7 | + | + | + |
| Honey sample number | HMF quantity [mg/kg] ± SD (LC-MS/MS) |
HMF quantity [mg/kg]± SD (White) |
HMF quantity [mg/kg]± SD (Winkler) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.4± 0.2 | 15.0 ±0.0 | 0.0 ±0.0 |
| 2 | 2.7± 0.4 | 0.0±0.0 | 3.7± 0.1 |
| 3 | 3.7± 0.2 | 4.5± 0.0 | 8.8± 1.6 |
| 4 | 2.6± 0.1 | 1.5± 0.0 | 3.7± 2.5 |
| 5 | 2.7± 0.2 | 1.5± 0.0 | 5.1± 1.3 |
| 6 | 3.0± 0.2 | 23.5± 1.7 | 23.4± 0.1 |
| 7 | 3.6± 0.2 | 28.5± 1.5 | 20.2± 1.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).