Submitted:
23 February 2024
Posted:
23 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods and Materials
Instruments and Reagents
Animals
Experimental Design
Histology
ELISA Analysis of Kidney Tissue
Analysis of Physiological and Biochemical Indicators
Statistical Analysis
Results
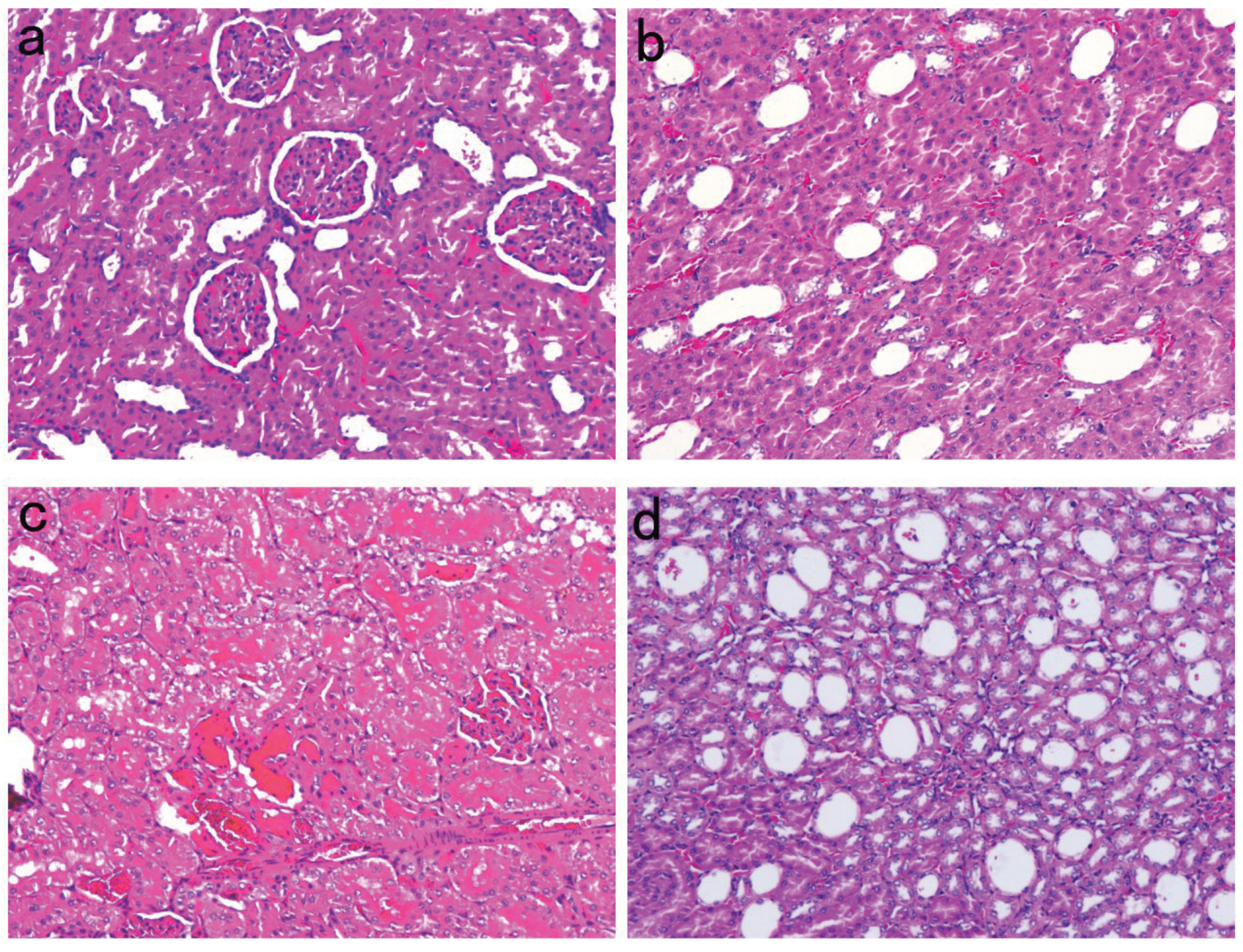
Renal Pathological Changes in SD Rats
Alterations in Serum Glucose and Urinary Protein Excretion in SD Rats
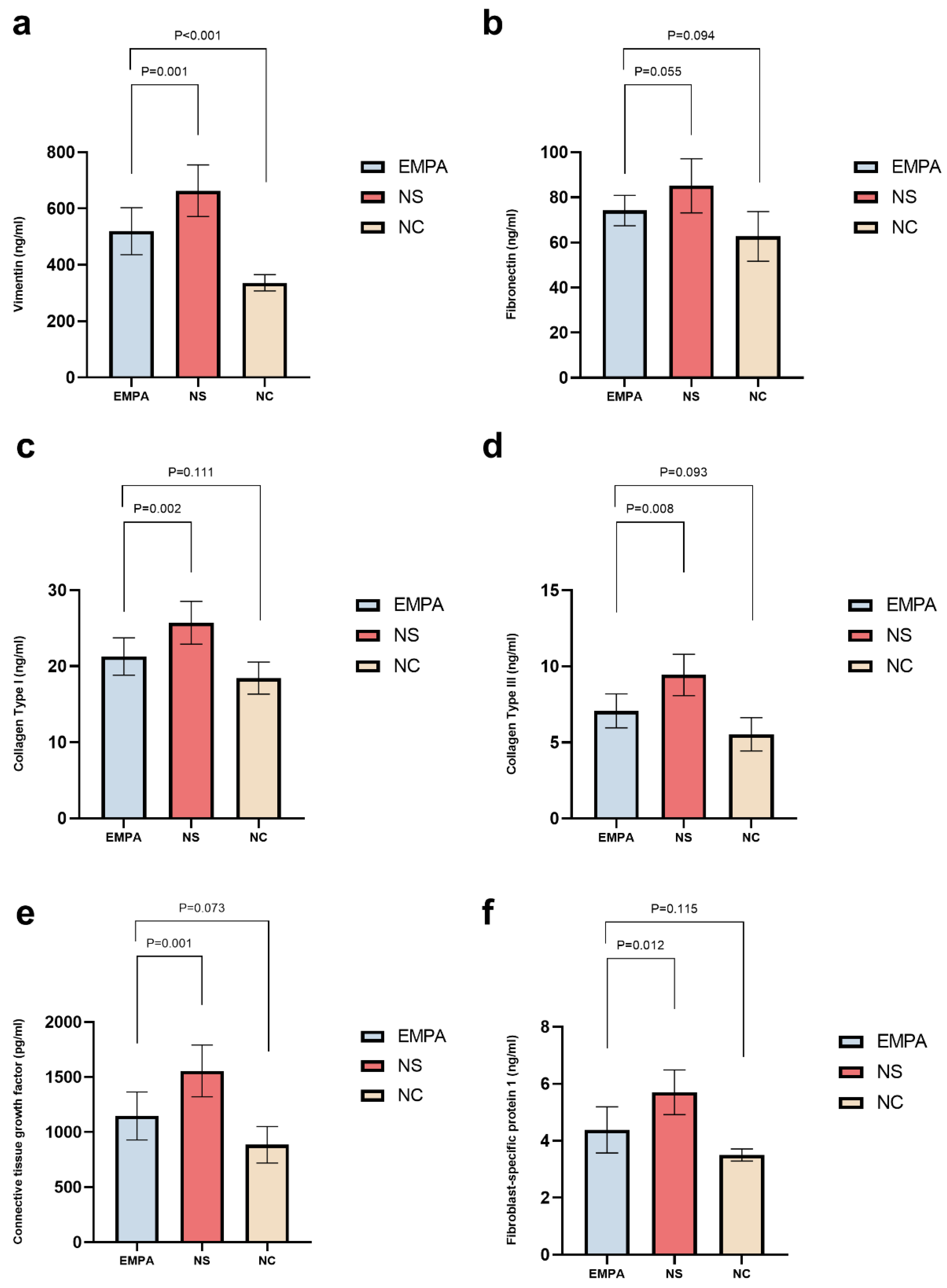
Empagliflozin Mitigates Renal Fibrosis-Associated Biomarkers Compare with NS Treatment in SD Diabetic Rats
The Impact of Empagliflozin on Renal Fibrosis-Associated Biomarkers Compared to NC Group after 4 Weeks of Treatment
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| Col-I | Collagen Type I |
| Col-III | Collagen Type III |
| CTGF | Connective Tissue Growth Factor |
| DKD | Diabetic Kidney Disease |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| EMPA | Empagliflozin |
| FN | Fibronectin |
| FSP-1 | Fibroblast-specific protein 1 |
| NC | Normal Control |
| NS | Normal Saline |
| SD | Sprague-Dawley |
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
| SGLT2i | Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors |
| VIM | Vimentin |
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Long, J.; Jiang, W.; Shi, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Yeung, R.O.; Wang, J.; Matsushita, K.; et al. Trends in Chronic Kidney Disease in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 905–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, S.; Munusamy, S. Renoprotective mechanisms of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors against the progression of diabetic kidney disease. J. Cell Physiol. 2022, 237, 1182–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, L.A.; Ward, M.S.; Fotheringham, A.K.; Zhuang, A.; Borg, D.J.; Flemming, N.B.; Harvie, B.M.; Kinneally, T.L.; Yeh, S.M.; McCarthy, D.A.; et al. Once daily administration of the SGLT2 inhibitor, empagliflozin, attenuates markers of renal fibrosis without improving albuminuria in diabetic db/db mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hillebrands, J.L.; van den Born, J.; Ji, L.; An, T.; Qin, G. Dapagliflozin Attenuates Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis Associated With Type 1 Diabetes by Regulating STAT1/TGFβ1 Signaling. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2019, 10, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, C.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; von Eynatten, M.; Mattheus, M.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Zinman, B. Empagliflozin and Progression of Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zou, H.; Lu, H.; Xiang, H.; Chen, S. Research progress of endothelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic kidney disease. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 3313–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, X.M.; Liang, X.M.; Wu, X.B.; Yao, C.M. SGLT2 inhibitors attenuate nephrin loss and enhance TGF-β(1) secretion in type 2 diabetes patients with albuminuria: A randomized clinical trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisho, Y. SGLT2 Inhibitors: The Star in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes? Diseases 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.J.; Iqbal, N.; T’Joen, C.; List, J.F. Dapagliflozin monotherapy in drug-naïve patients with diabetes: A randomized-controlled trial of low-dose range. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenlöf, K.; Cefalu, W.T.; Kim, K.A.; Alba, M.; Usiskin, K.; Tong, C.; Canovatchel, W.; Meininger, G. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin monotherapy in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2013, 15, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Arakawa, K.; Ueta, K.; Matsushita, Y.; Kuriyama, C.; Martin, T.; Du, F.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Conway, B.; et al. Effect of canagliflozin on renal threshold for glucose, glycemia, and body weight in normal and diabetic animal models. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terami, N.; Ogawa, D.; Tachibana, H.; Hatanaka, T.; Wada, J.; Nakatsuka, A.; Eguchi, J.; Horiguchi, C.S.; Nishii, N.; Yamada, H.; et al. Long-term treatment with the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, dapagliflozin, ameliorates glucose homeostasis and diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, A.; Takasu, T. Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor ipragliflozin on various diabetic symptoms and progression of overt nephropathy in type 2 diabetic mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2018, 391, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gembardt, F.; Bartaun, C.; Jarzebska, N.; Mayoux, E.; Todorov, V.T.; Hohenstein, B.; Hugo, C. The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin ameliorates early features of diabetic nephropathy in BTBR ob/ob type 2 diabetic mice with and without hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2014, 307, F317–F325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.; Perkins, B.A.; Soleymanlou, N.; Maione, M.; Lai, V.; Lee, A.; Fagan, N.M.; Woerle, H.J.; Johansen, O.E.; Broedl, U.C.; et al. Renal hemodynamic effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2014, 129, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.J.; Chung, S.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, E.M.; Yoo, Y.H.; Kim, J.W.; Ahn, Y.B.; Kim, E.S.; Moon, S.D.; Kim, M.J.; et al. Effect of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor, Dapagliflozin, on Renal Renin-Angiotensin System in an Animal Model of Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatanaka, T.; Ogawa, D.; Tachibana, H.; Eguchi, J.; Inoue, T.; Yamada, H.; Takei, K.; Makino, H.; Wada, J. Inhibition of SGLT2 alleviates diabetic nephropathy by suppressing high glucose-induced oxidative stress in type 1 diabetic mice. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2016, 4, e00239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradham, D.M.; Igarashi, A.; Potter, R.L.; Grotendorst, G.R. Connective tissue growth factor: A cysteine-rich mitogen secreted by human vascular endothelial cells is related to the SRC-induced immediate early gene product CEF-10. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 114, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Koka, V.; Lan, H.Y. Transforming growth factor-beta and Smad signalling in kidney diseases. Nephrology (Carlton) 2005, 10, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, N.; Mukoyama, M.; Yanagita, M.; Yokoi, H. CTGF in kidney fibrosis and glomerulonephritis. Inflamm. Regen. 2018, 38, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Denichilo, M.; Brubaker, C.; Hirschberg, R. Connective tissue growth factor in tubulointerstitial injury of diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.Y.; Ma, L.N.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X.L.; Shi, H.; Fan, Y.P.; Yang, B. Protection of CTGF Antibody Against Diabetic Nephropathy in Mice Via Reducing Glomerular β-Catenin Expression and Podocyte Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 3706–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R.C.; Pastar, I.; Ojeh, N.; Chen, V.; Liu, S.; Garzon, K.I.; Tomic-Canic, M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tissue repair and fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbiani, G. The myofibroblast in wound healing and fibrocontractive diseases. J. Pathol. 2003, 200, 500–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Capaldo, C.; Gumbiner, B.M.; Macara, I.G. The mammalian Scribble polarity protein regulates epithelial cell adhesion and migration through E-cadherin. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 171, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Dedhar, S.; Kalluri, R.; Thompson, E.W. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in signaling, development, and disease. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridge, K.M.; Eriksson, J.E.; Pekny, M.; Goldman, R.D. Roles of vimentin in health and disease. Genes. Dev. 2022, 36, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, M.G.; Kojima, S.; Goldman, R.D. Vimentin induces changes in cell shape, motility, and adhesion during the epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Faseb J. 2010, 24, 1838–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liang, M.; Huang, F.; Cheng, O.H.; Xiao, X.; Lee, T.H.; Truong, L.; Cheng, J. Notch Blockade Specifically in Bone Marrow-Derived FSP-1-Positive Cells Ameliorates Renal Fibrosis. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, H.; Danoff, T.M.; Kalluri, R.; Neilson, E.G. Early role of Fsp1 in epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, F563–F574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Fu, H.; Liu, Y. The fibrogenic niche in kidney fibrosis: Components and mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, A.D.; Manou, D.; Karamanos, N.K. The extracellular matrix as a multitasking player in disease. Febs J. 2019, 286, 2830–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, B.D. Mechanisms of Renal Fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2018, 80, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockey, D.C.; Bell, P.D.; Hill, J.A. Fibrosis--a common pathway to organ injury and failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1138–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
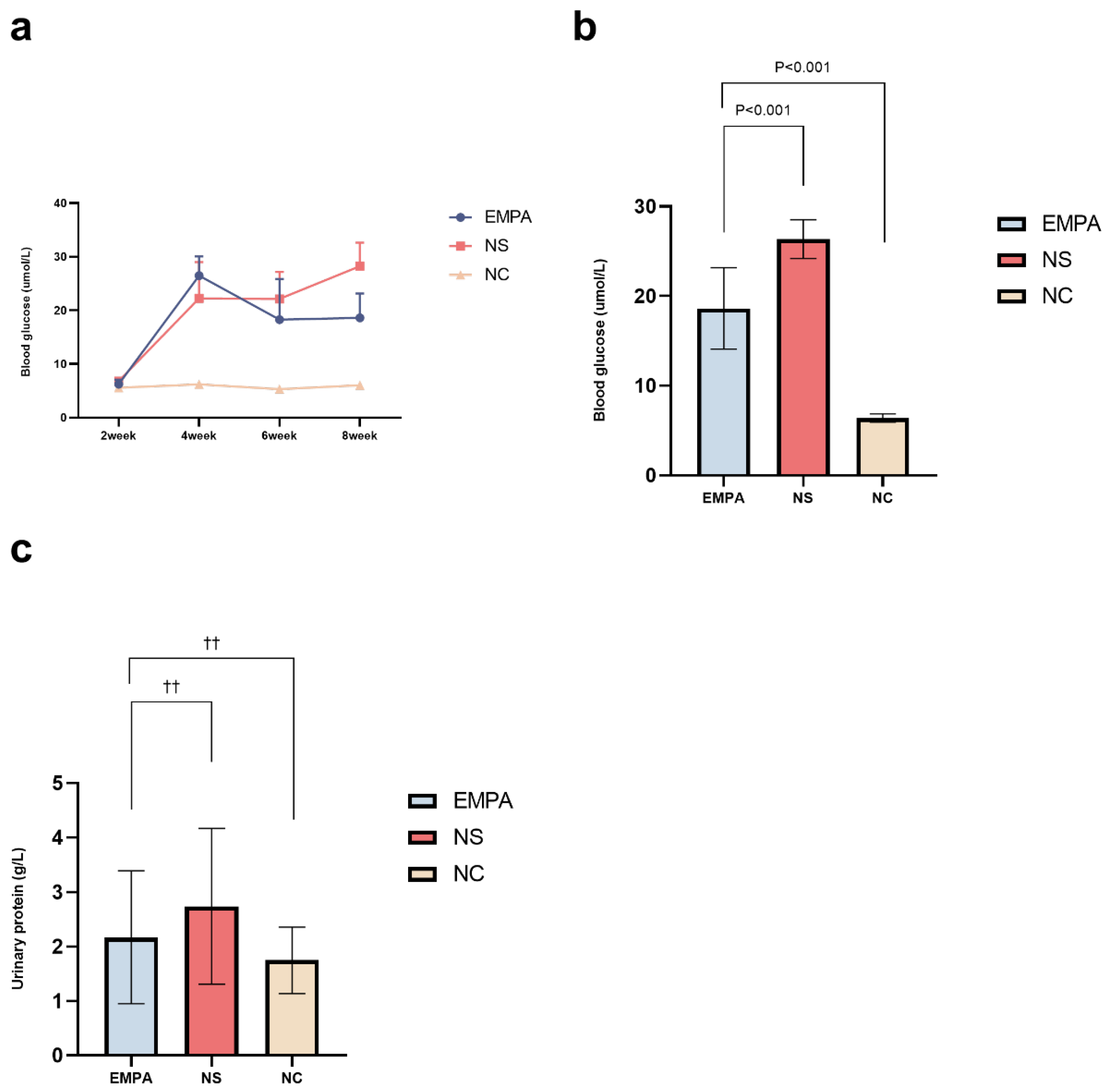
| Time line | NC n=6 | NS n=10 | EMPA n=11 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-week | 5.58±0.20 | 6.81±0.64 | 6.25±0.82 | 0.004 |
| 4-week | 6.20±0.40 | 22.25±6.78* | 26.48±3.60* | <0.001 |
| 6-week | 5.33±0.23 | 22.15±5.03* | 18.27±7.58* | <0.001 |
| 8-week | 6.05±0.48 | 28.26±4.34* | 18.62±4.54*† | <0.001 |
| Markers |
NC n=6 |
NS n=10 |
EMPA n=11 |
P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIM (ng/mL) | 336.66±28.87 | 663.27±91.84* | 519.84±83.37*† | < 0.001 |
| FN (ng/mL) | 62.69±10.98 | 85.11±11.99* | 74.17±6.71 | 0.001 |
| Col-I (ng/mL) | 18.43±2.11 | 25.71±2.82* | 21.27±2.46† | < 0.001 |
| Col-III (ng/mL) | 5.18(6.12, 8.53) | 9.95(7.97, 10.58)* | 6.51(6.22, 8.32)† | < 0.001 |
| CTGF (pg/mL) | 885.16±166.10 | 1555.81±234.80* | 1146.68±216.69† | < 0.001 |
| FSP-1 (ng/mL) | 3.50±0.21 | 5.70±0.78* | 4.38±0.81† | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





