Submitted:
20 February 2024
Posted:
21 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
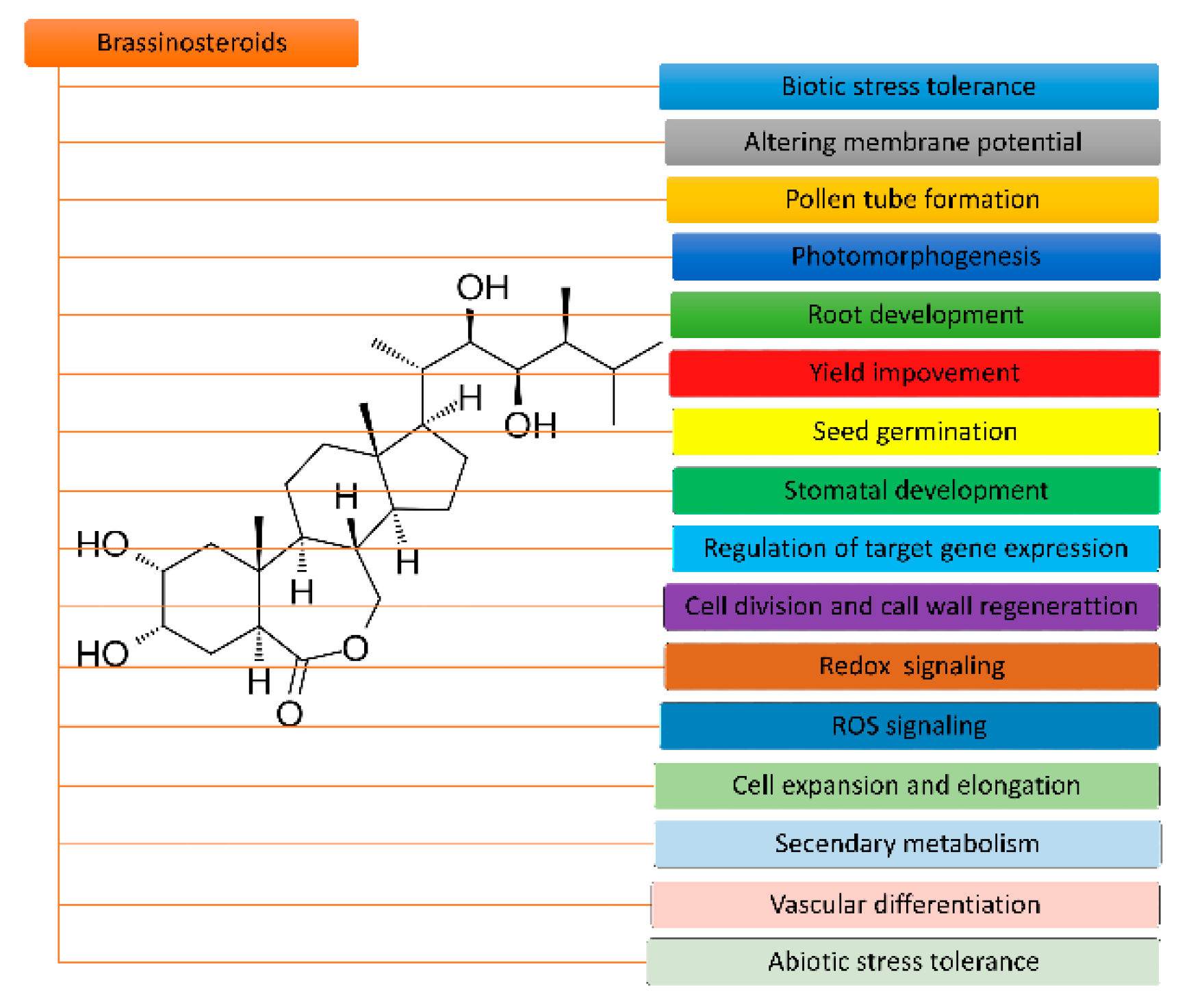
2. Structure and Functions of BR
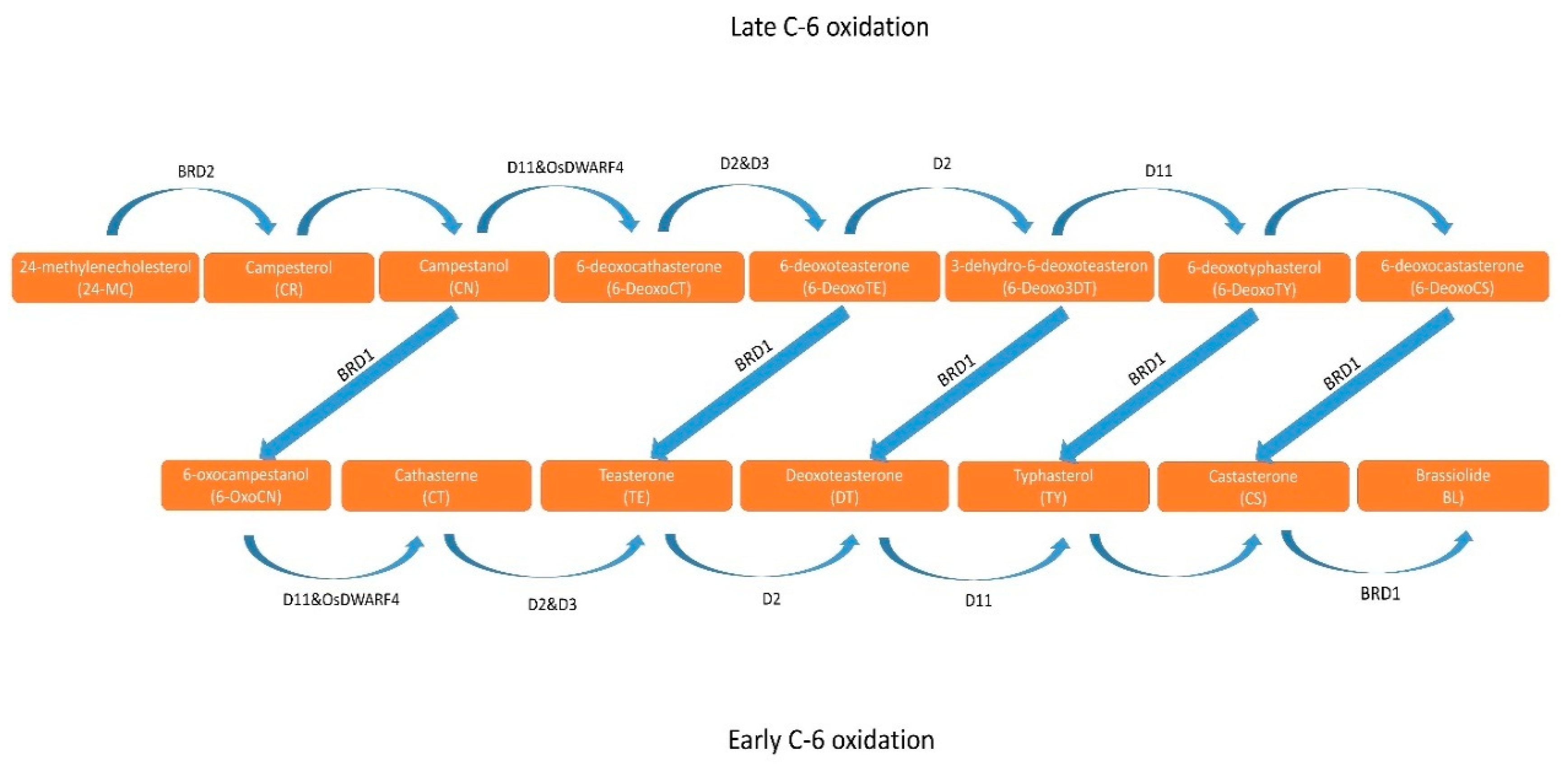
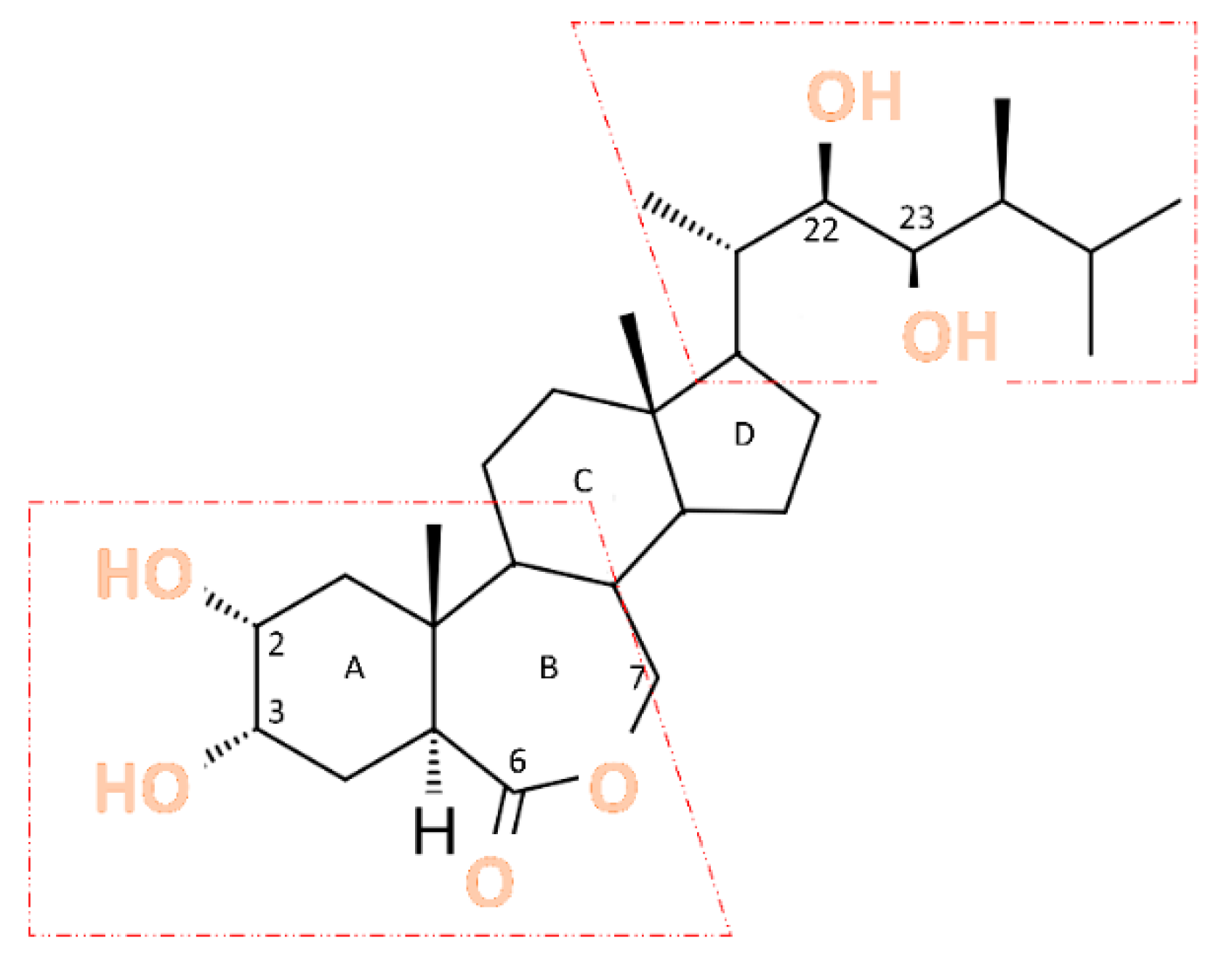
2.1. Structure and Biosynthesis of BR
- −
- −
- −
- −
- −
- a)
- Squalene -> campesterol by SQE.
- b)
- Campesterol -> obtusifoliol by CYP90B2.
- c)
- Obtusifoliol -> epicastasterone by CYP90D1.
- d)
- Epicastasterone -> teasterone by CYP85A2.
- e)
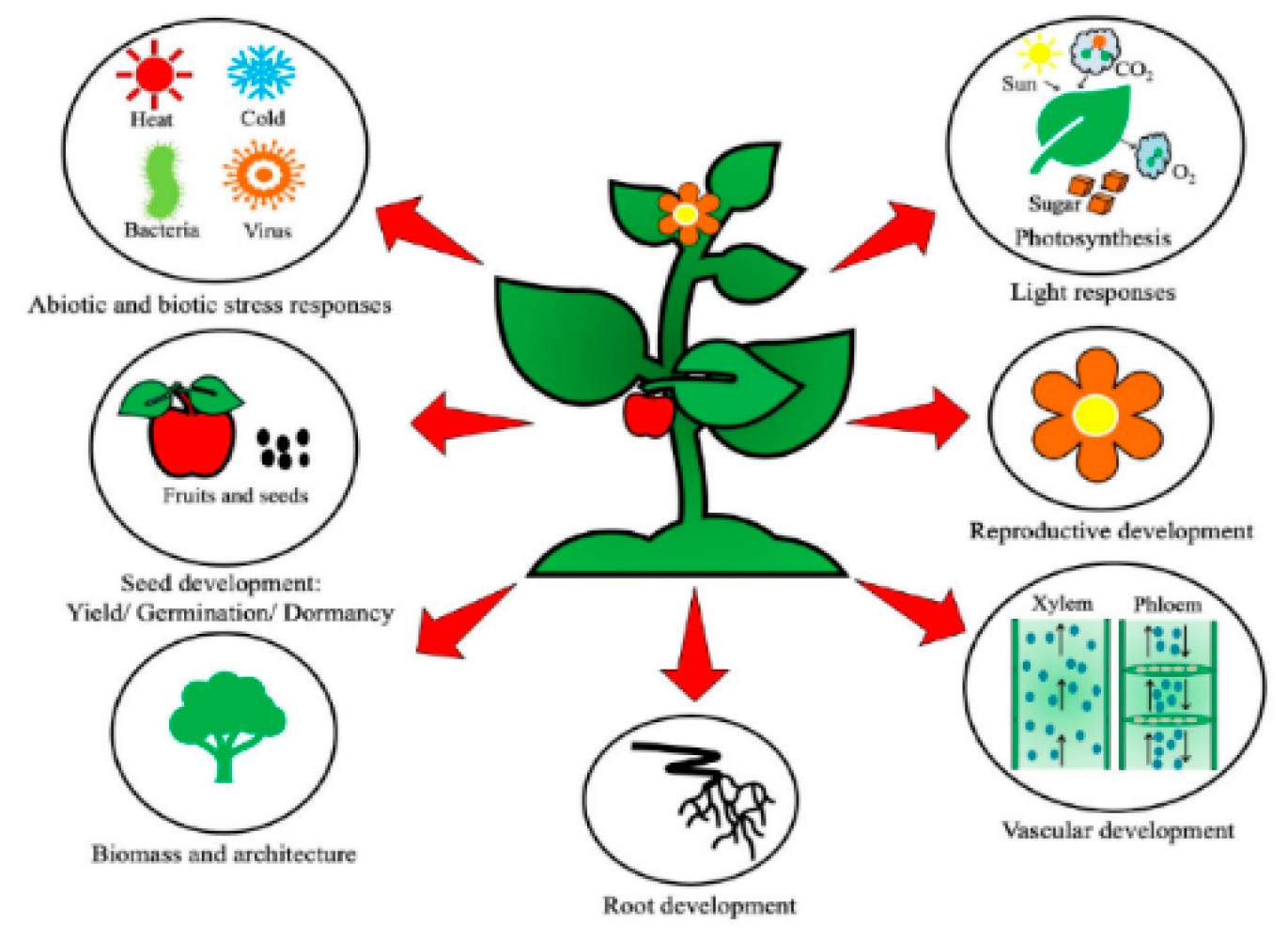
2.2. Physiological Functions of BR in Plant Growth and Development
- −
- −
- −
- −
- −
3. Mechanisms of Defense Related to BR
3.1. Impact of BR on the Expression of Genes Related to Plant Defense
3.2. Interactions between Electrical Signals and Plant Hormones
3.3. Regulation of Gene Expression Related to Immunity
- −
- −
- −
- −
- Expression of Defense Genes: Transcription factors like BZR1 and BES1 wield influence over the expression of defense-related genes. They orchestrate the activation of genes involved in plant defense against a spectrum of stresses, both biotic and abiotic. These genes encompass those encoding enzymes for synthesizing chemical compounds, receptors for pathogen recognition, and factors pivotal for the growth and development of defense cells. Consequently, BR-mediated signaling pathways modulate the expression of defense genes, bolstering plants’ resilience against stressors and pathogens. Nonetheless, the specific targets and mechanisms underlying these processes may vary contingent upon the plant species and the nature of the stressors [14,15,58].
3.4. Regulation of Water and Salt Economy
3.4.1. Drought Response
- −
- −
- Regulation of Stomatal Dynamics: BRs are involved in the regulation of stomatal opening and closing on leaf surfaces. This regulation is vital for managing water loss through transpiration and optimizing gas exchange. By modulating stomatal behavior, BRs help plants conserve water during drought stress [12,94,95].
- −
- Protection Against Oxidative Stress: Acting as antioxidants, BRs play a role in safeguarding plant cells from oxidative stress induced by drought. Oxidative damage often arises from an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and the cell’s antioxidant defense mechanisms. BRs contribute to maintaining cellular redox homeostasis, thereby protecting plants from oxidative injury [23,24,63,71].
- −
- Regulation of Drought-Responsive Gene Expression: BRs are implicated in the regulation of gene expression associated with drought response. Studies have identified genetic links between BR signaling and the activation of drought-responsive genes, highlighting the involvement of BRs in orchestrating molecular responses to water scarcity [56,99].
- −
- Enhanced Water Use Efficiency: Emerging evidence suggests that BR-treated plants may exhibit improved water use efficiency, allowing them to utilize available water resources more effectively. This enhanced efficiency can confer a competitive advantage to plants facing drought stress, enabling them to maintain essential physiological processes despite limited water availability [55,96,97].
3.4.2. Salinity Protection
- −
- −
- Stimulation of Root Development: BRs promote increased root development, enhancing the plant’s capacity to absorb water and nutrients from the soil, particularly crucial in saline environments where water availability is limited [23].
- −
- −
- −
- Osmotic Adjustment: BRs influence the accumulation of osmoprotectants such as proline and polyols, aiding in the maintenance of osmotic balance within cells under saline conditions, thus minimizing cellular damage [99].
- −
- Regulation of Gene Expression: BRs modulate the expression of stress-responsive genes, including those involved in salinity defense mechanisms, orchestrating molecular responses to mitigate the adverse effects of salinity stress [56].
- −
- −
- Ion Transport Regulation: BRs influence ion transport processes, including the uptake and translocation of ions such as sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+), crucial for maintaining ionic balance within plant cells and mitigating the harmful effects of excess salt accumulation [100].
3.5. Activation of Plant Defense System by BR
3.5.1. Mechanisms of Phytoalexin Induction by BR
3.5.2. BR Impact on Plant Defense Response
3.5.3. BR Modulation of Pathogen-Responsive Gene Expression
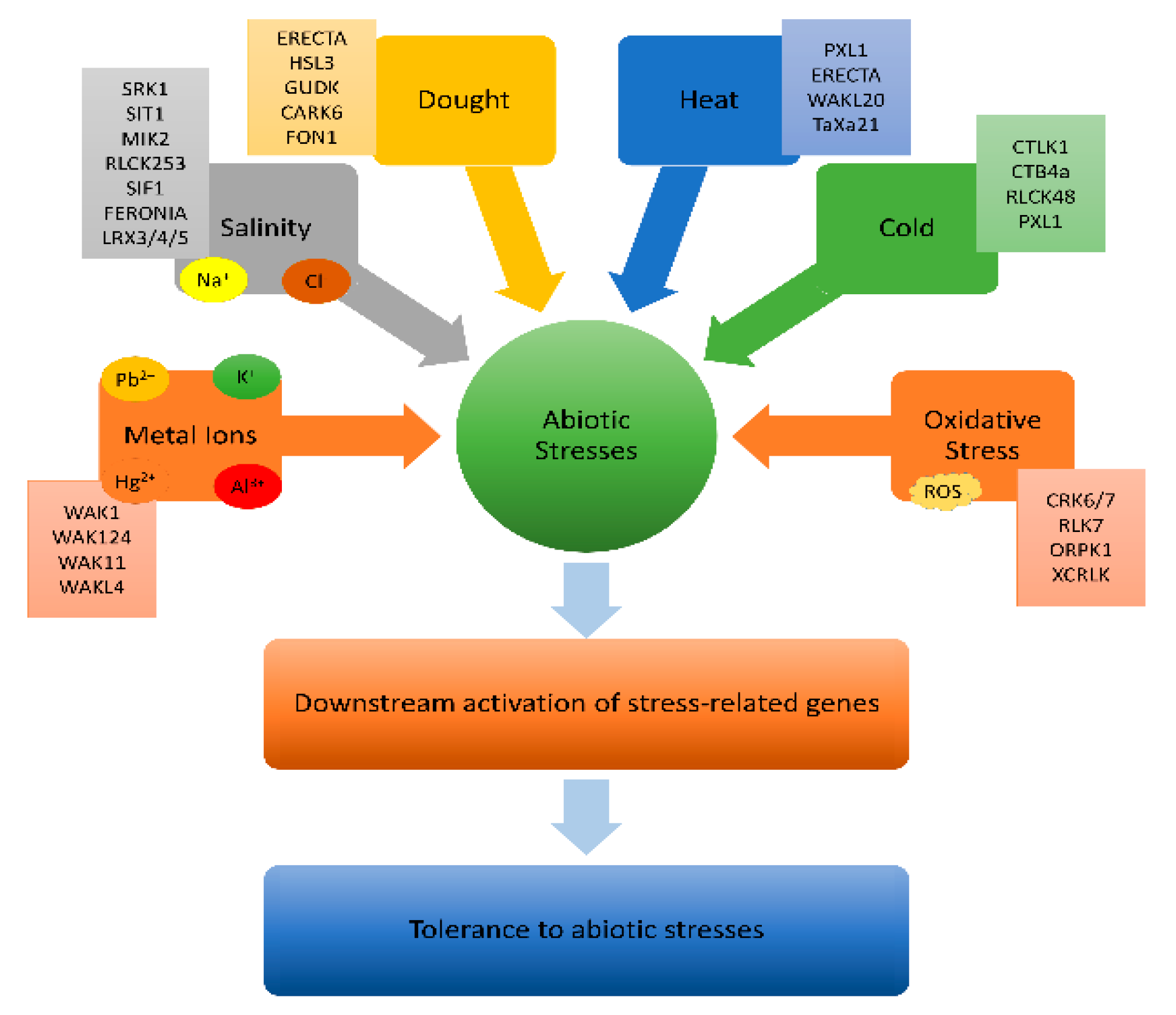
BR and Abiotic Stresses
4.1. Role of BR in Abiotic Stress Responses
- −
- Growth stimulation: BR promotes plant growth and aids in faster recovery from stress-induced damage by increasing cell length and numbers [38].
- −
- −
- −
- −
- −
4.1.1. Leaf Rust Kinase (LRK 10-like)
- −
- −
- −
- −
- Reducing oxidative stress by influencing antioxidant enzyme activity to neutralize reactive oxygen species [38].
- −
- −
4.2. BR and Plant Immune Activation through Antimicrobial Production
- −
- Stimulation of Phytohormone Production: BR stimulates the production of phytohormones like JA and SA, crucial for activating the plant immune system against pests and pathogens [124].
- −
- Regulation of Defensive Gene Expression: BR regulates the expression of genes encoding defensive proteins, including Pathogenesis-Related (PR) proteins and Resistance (R) proteins, aiding in combating pathogens [90].
- −
- −
- Regulation of Plant-Pathogen Interactions: BR influences interactions between plants and pathogens, affecting pathogen recognition mechanisms and intercellular communication [125].
- −
- −
4.3. Role of BR in Biotic Stresses
- Enhanced Pathogen Resistance: BR stimulates the production of phytoalexins, strengthening the plant’s defense system against infections [127].
- Reinforcement of Immunity: BR stimulates the production of chemical substances with anti-parasitic and antibacterial properties, enhancing overall plant immunity.
- Regulation of Defensive Cell Development: BR influences the development of defense cells like trichomes, aiding in defense against pests and pathogens [36].
Interactions Between Plant Hormones in Immunity
5.1. Abscisic Acid and Salicylic Acid
5.2. Interaction of ABA and JA
- −
- −
- −
- Gene Expression Regulation: Both BR and ABA influence gene expression in response to various stresses. In drought conditions, BR and ABA may regulate different sets of genes related to their absence. During drought, ABA levels increase, leading to the activation of signaling pathways controlling the expression of genes responsible for adapting to water deficiency. These genes may be associated with stomatal closure, activation of genes involved in osmotic compound synthesis, or maintaining water homeostasis. On the other hand, BR may be involved in regulating genes related to long-term stress adaptation, such as controlling the expression of genes associated with processes like stomatal closure, root growth, or activation of signaling pathways related to plant defense against stress, while ABA focuses on faster adaptive responses [69,81,84].
5.3. BR-JA Interactions
6. Practical Applications of BR
6.1. Potential Applications of BR in Agriculture and Horticulture
6.2. Significance of BR in Cell Division and Elongation
6.2.1. BR in Seed Development and Germination
6.2.2. BR in Root and Shoot Growth
6.2.3. BR Effects on Plant Growth, Photosynthesis, and Aging
6.3. BR under Salinity and Heavy Metal Concentrations
- −
- Activation of Stress Signaling Pathways: Upon exposure to salt stress, perennial ryegrass plants perceive the stress signals, leading to the activation of stress signaling pathways.
- −
- Recognition and Uptake of EBR: Exogenous application of EBR to the plants allows for its recognition and uptake, either through the roots or foliar application.
- −
- Brassinosteroid Signaling Cascade Activation: EBR binds to its receptor, initiating a signaling cascade that involves various downstream components, such as BRASSINAZOLE-RESISTANT (BZR) transcription factors and BRI1-EMS-SUPPRESSOR 1 (BES1), leading to the activation of stress-responsive genes.
- −
- Enhanced Ion Homeostasis: EBR application modulates ion homeostasis by regulating the uptake and compartmentalization of ions, particularly sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-), thus preventing their toxic accumulation in plant tissues.
- −
- Osmotic Adjustment: EBR promotes osmotic adjustment by enhancing the accumulation of compatible solutes such as proline and sugars, which help maintain cellular turgor pressure and osmotic balance under salt stress conditions.
- −
- Antioxidant Defense Activation: EBR treatment boosts the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD), scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and minimizing oxidative damage to cellular components.
- −
- Maintenance of Photosynthetic Machinery: EBR application preserves the integrity and functionality of the photosynthetic apparatus by mitigating the adverse effects of salt stress on chlorophyll content, photosystem efficiency, and carbon assimilation rates.
- −
- Stimulation of Growth and Development: Despite salt stress, EBR promotes plant growth and development by modulating hormone signaling pathways, particularly auxins, cytokinin’s, and gibberellins, which contribute to enhanced root and shoot growth and biomass accumulation.
- −
- Regulation of Stress-Responsive Gene Expression: EBR-mediated regulation of stress-responsive genes involved in various physiological and biochemical processes helps orchestrate adaptive responses to salt stress, thereby improving overall stress tolerance in perennial ryegrass.
- −
- Overall Improvement in Salt Stress Tolerance: Through these mechanisms, EBR application confers enhanced salt stress tolerance in perennial ryegrass, enabling the plant to withstand adverse environmental conditions and maintain optimal growth and productivity [150].
- −
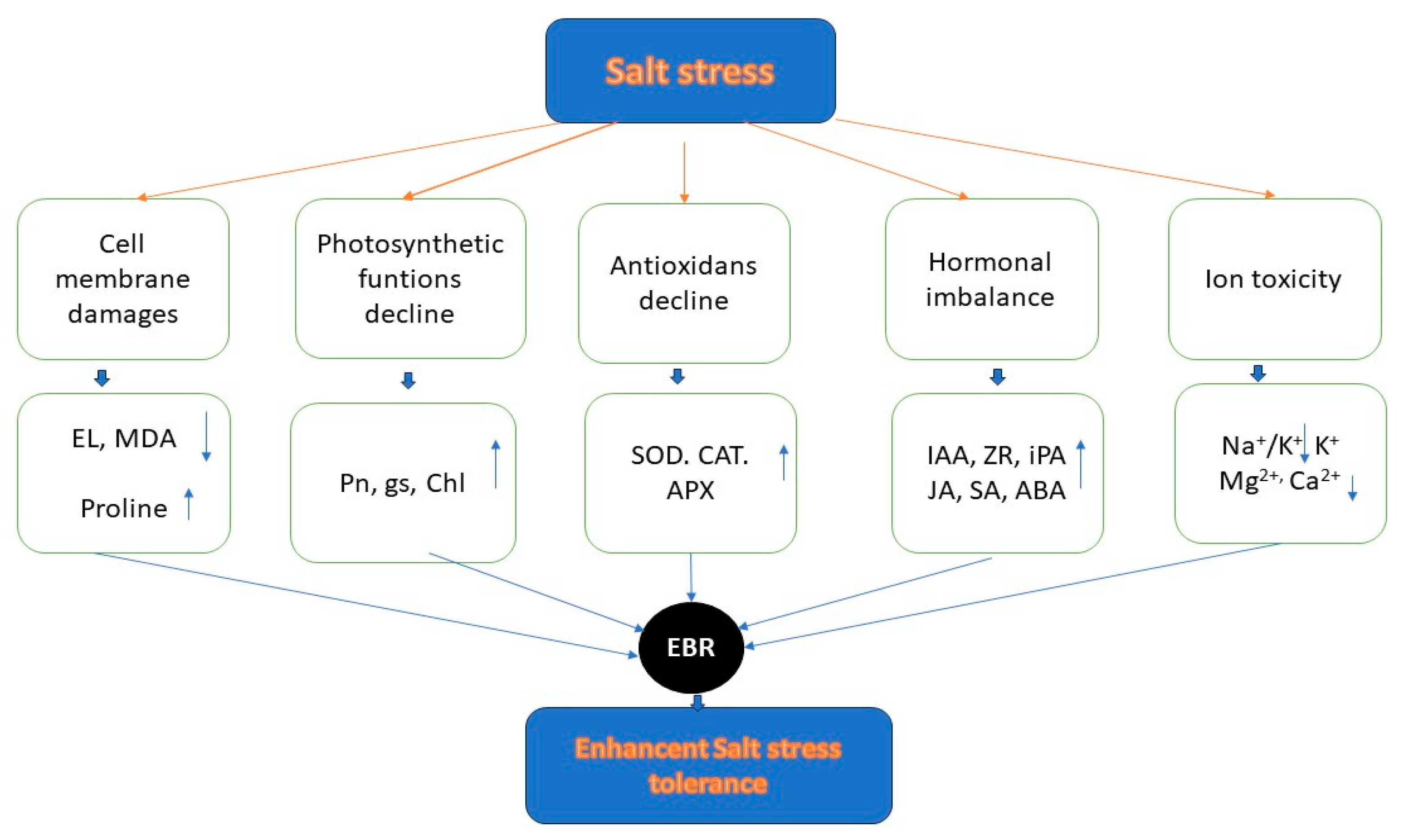
- As a result, exogenous 24-epibrassinolide (EBR) may: improve the integrity and stability of the cell membrane (lower MDA, EL, higher proline), enhance photosynthetic function (higher Pn, gs, and chlorophyll), enhance antioxidant defense (resulting in higher activity of SOD, CAT, and APX), increase hormonal metabolism (higher levels of IAA, ZR, iPA, JA, SA, and ABA), and reduce ion toxicity (lower Na+ and Na+/K+, higher K+, Mg2+, and Ca2+), leading to increased tolerance to salt stress and visual quality of plants [151] (Figure 8).
- −
- These studies collectively demonstrate the potential of BRs to alleviate the adverse effects of salinity and heavy metal stress on plants, highlighting their significance in enhancing plant resilience to environmental challenges.
6.4. Enhancing Crop Yield and Resilience with BR: Potential Strategies and Benefits
- −
- Growth Promotion: Elevating BR levels stimulates the growth of stems, leaves, and roots, potentially leading to increased yield mass [51].
- −
- −
- −
- −
- −
7. Towards the Future
- −
- Advanced Research Tools: Precision translatomics and fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) enable a deeper understanding of how plants respond to BR under stress, facilitating the mapping of BR interactions with other hormones.
- −
- Exogenous BR Application: Utilizing BR application can boost plant resilience, particularly in cereal crops. Genetic manipulation of BR-related genes can pave the way for developing transgenic varieties with heightened stress resistance.
- −
- Exploring Hormone Interactions: Investigating how exogenous BR impacts the synthesis and signaling of other hormones under stress conditions is crucial. Combining different plant hormones may offer synergistic strategies to enhance stress tolerance.
- −
- Genetic Engineering: Manipulating BR-related genes through genetic engineering, coupled with advanced research tools, holds promise for increasing crop yields by bolstering tolerance to abiotic stresses.
8. Conclusions
List abberavions
| ABA – Abscisic Acid BL – Brassinolide BR – Brassinosteroid BZR – Brasinozol CAT – Catalase CH4 - methane CK – Cytokinins CS – Castasterone EBL – benzylaminopurine EBL – Epibrassinolide EBR – 24-epibrassinolide ERF – Ethylene Response Factor FRK1 - Fusarium-Induced Receptor Kinase GA – Gibberelins HBR – Homobrassinolide IAA – indolyl-3-acetic acid IAN – indolylacetonitrile IBA – Indolyl-3-butyric acid IBA – indolyl-3-butyric acid IPA – indolyl-3-propionic acid JA – jasmonate MAPK – Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase MRW - indole-3-butyric acid NiRA – Nitrate Reductase PAA – phenylacetic acid, PAMPs – Pathogen-associated molecular proteins POD – Peroxidase PR - Pathogenesis-Related Genes PRRs – Pattern Recognition Receptors, PSII – photosystem II PTI – Pattern Triggered Immunity RLK – Receptor-Like Kinases ROS – Production of reactive oxygen species ROS – Reactive Oxygen Species SA – salicylic acid SERK – Somatic Embryogenesis Receptor-Like Kinase SOD – Superoxide Dismutase SQE – Squalene Monooxygenase Enzyme TZ – Tezasterone WRKY46, WRKY54, WRKY70 – regulators of proteins from the WRKY family activated by BR |
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability Statement
References
- Liu, X.; Igarashi, D.; Hillmer, R.A.; Stoddard, H.; Lu, Y.; Tsuda, K.; Myers, C.L.; Katagiri, F. Dynamic decomposition of transcriptome responses during plant effector-triggered immunity revealed conserved responses in two distinct cell populations. Preprint, 2022, Chrome.extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.12.30.522333v1.full.pdf.
- Hewedy, O.A.; Elsheery, N.I.; Karkour, A.l.M.; Elhamouly, N.; Arafa, R.A.; Mahmoud, G.A.-E.; et al. Jasmonic acid regulates plant development and orchestrates stress response during tough times. Environmental and Experimental Botany 2023, 208, 105260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, T.M.; Vukašinović, N.; Liu, D.; Russinova, E.; Yin, Y. Brassinosteroids: multidimensional regulators of plant growth, development, and stress responses. The Plant Cell 2020, 32, 295–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Su, P.; Meng, X.; Liu, P. Phylogeny of the plant receptor-like kinase (RLK) gene family and expression analysis of wheat RLK genes in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. BMC Genomics 2023, 24, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.Y.; Xie, D.L.; Cao, J.J.; Xia, X.J.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; Foyer, C.H.; Yu, J.Q. Brassinosteroid-mediated reactive oxygen species are essential for tapetum degradation and pollen fertility in tomato. The Plant Journal 2020, 102, 931–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, Y. Roles of Brassinosteroids in Plant Reproduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, M.K.; Bajguz, A.; Zhou, J.; Bhardwaj, R. Analysis of brassinosteroids in plants. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 2017, 36, 1002–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, H.; Hayat, S.; Bajguz, A. Regulation of photosynthesis by brassinosteroids in plants. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 2018, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.H.; Honey, S.H.; Tax, F.E. The control of cell expansion, cell division, and vascular development by brassinosteroids: a historical perspective. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.; Zhu, J.Y.; Bai, M.Y.; Arenhart, R.A.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.Y. Cell elongation is regulated through a central circuit of interacting transcription factors in the Arabidopsis hypocotyl. Life 2014, 3, e03031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Li, J. Brassinosteroids regulate root growth, development, and symbiosis. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Fan, M.; Hua, W.; Tian, Y.; Chen, L.G.; Sun, Y.; Bai, M.Y. Brassinosteroid and hydrogen peroxide interdependently induce stomatal opening by promoting guard cell starch degradation. The Plant Cell 2020, 32, 984–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Feng, G.N.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C.Q.; Li, Q.F.; Liu, Q.Q. Brassinosteroid regulation in rice seed biology. Seed Biology 2022, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, R.; Fujioka, S.; Iwamoto, K.; Demura, T.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Fukuda, H. Co-regulation of brassinosteroid biosynthesis-related genes during xylem cell differentiation. Plant and Cell Physiology 2007, 48, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Bai, M.Y.; Oh, E.; Zhu, J.Y. Brassinosteroid signaling network and regulation of photomorphogenesis. Annual Review of Genetics 2012, 46, 701–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovtun, I.S.; Kukharenko, N.E.; Kusnetsov, V.V.; Khripach, V.A.; Efimova, M.V. Effect of lactone-and ketone-containing brassinosteroids on photosynthetic activity of barley leaves during aging. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology 2021, 68, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, T.; Fan, R.; Hussain, S.; Sattar, A.; Khalid, S.; Butt, M.; Shahzad, U.; Atif, H.M.; Batool, M.; Ullah, S.; Li, Y.; Al-Hashimi, A.; Elshikh, M.S.; Al-Yahyai, R. Protective effect of jasmonic acid and potassium against cadmium stress in peas (Pisum sativum L.). Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 2022, 29, 2626–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Ogiala, A., Carsjens, C., Diekmann, H., Fayyaz, P., Herrfurth, C., Feussner, I., Polle, A. Temperatureinduced lipocalin (TIL) is translocated under salt stress and protects chloroplasts from ion toxicity, Journal of Plant Physiology 2014, 171, 250–259, ISSN 0176-1617. [CrossRef]
- Aghaee, P.; Rahmani, F. Seed priming with 24-epibrassinolide alters growth and phenylpropanoid pathway in flax in response to water deficyt. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Ahammed, G.J.; Yu, J.Q. Role of Hormones in Plant Adaptation to Heat Stress. In: Plant Hormones under Challenging Environmental Factors, Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; 1–21.
- Ahammed, G.J.; Li, X.; Liu, A.; Chen, S. Brassinosteroids in plant tolerance to abiotic stress. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 2020, 39, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajguz, A. Brassinosteroids–occurence and chemical structures in plants. In Brassinosteroids: A Class of Plant Hormone; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Alzahrani, S.M.; Alaraidh, I.A.; Migdadi, H.; Alghamdi, S.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, P. Physiological, biochemical, and antioxidant properties of two genotypes of Vicia faba grown under salinity stress. Pakistan Journal of Botany 2019, 51, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.; Bhardwaj, R.; Kanwar, M.K. Effect of 24-epibrassinolide on growth, protein content and antioxidative defense system of Brassica juncea L. subjected to cobalt ion toxicity. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2012, 34, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariş, Ç.Ç.; Sağlam-Çağ, S. The effects of brassinosteroids on sequential leaf senescence occurring in Glycine max L. Int J Biotechnol. Res. 2016, 6, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bhanu, A.N. Bhanu, A.N. Brassinosteroids: Relevance in biological activities of plants and agriculture. J. Plant Sci. Res 2019, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.; Halder, K.; Abdin, M.Z.; Majee, M.; Datta, A. Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants: Brassinosteroids Navigate Competently, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kour, J.; Kohli, S.K.; Khannika, K.; Bakshi, P.; Sharma, P.; Singh, A.D.; Ibrahim, M.; Devi, K.; Sharma, N.; Ohri, P.; Skalicky, M.; Brestic, M.; Bhardwaj, R.; Landi, M.; Sharma, A. Brassinosteroid Signaling, Crosstalk and, Physiological Functions in Plants Under Heavy Metal Stress, Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Han, Z.; Chai, J. Q&A: what are brassinosteroids and how do they act in plants? BMC Biol 2016, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, V.; Diaz, K.; Soto, M.; Olea, A.F.; Cuellar, M.A.; Nuñez, M.; Espinoza-Catalán, L. New Brassinosteroid Analogs with 23,24-Dinorcholan Side Chain, and Benzoate Function at C-22: Synthesis, Assessment of Bioactivity on Plant Growth, and Molecular Docking Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.; Siddiqi, E.H.; Nawaz, I.; Nasir, N. 24-Epibrassinolide modulates biomass production, gas exchange characteristics and inorganic nutrients in canola (Brassica napus L.) under salt stress. Pak. J. Bot 2022, 54, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, T.; Ohnishi, T.; Shibata, K.; Asahina, M.; Nomura, T.; Fujita, T.; Ishizaki, K.; Kohchi, T. Occurrence of brassinosteroids in non-flowering land plants, liverwort, moss, lycophyte and fern. Phytochemistry 2017, 136, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.A.; Fahad, S.; Sharif, R.; Jan, M.F.; Mujtaba, M.; Ali, Q.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, H.; Amin, N.; Ajayo, B.S.; sun, C.; Gu, L.; Ahmad, I.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, J. Multifunctional role of brassinosteroid and its analogues in plants. Plant Growth Regulation 2020, 92, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafie, E. Physiological, Biochemical, Molecular and Hormonal Studies to Confirm Growth and Development Regulating Actions of Brassinosteroids in Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Bronco Seedlings. Life Science Journal 2014, 11, 974–991. [Google Scholar]
- Bajguz, A. The effect of brassinosteroids on cultures of the alga Chlorella vulgaris exposed to selected phytohormones and stress factors. PhD Thesis, University in Białystok, Publishing House of the University of Białystok, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. Effects of brassinosteroids on the plant responses to environmental stresses. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2009, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Yuan, Y.; Du, J.; Sun, J.; Guo, S. Effects of 24-Epibrassinolide on Nitrogen Metabolism in Cucumber Seedlings under Ca[NO3]2 Stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 61, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, B.; Achard, B. Long-distance transport of phytohormones through the plant vascular system. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gawande, N.D.; Sankaranarayanan, S. Genome wide characterization and expression analysis of CrRLK1L gene family in wheat unravels their roles in development and stress-specific responses. BioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibañez, C.; Delker, C.; Martinez, C.; Bürstenbinder, K.; Janitza, P.; Lippmann, R.; Ludwig, W.; Sun, H.; James, G.V.; Klecker, M. Brassinosteroids dominate hormonal regulation of plant thermo morphogenesis via BZR1. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symons, G.M.; Ross, J.J.; Jager, C.E.; Reid, J.B. Brassinosteroid transport. J Exp Bot. 2008; 59(1):17-24. 59(1). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manghwar, H.; Hussain, A.; Ali, Q.; Liu, F. Brassinosteroids (BRs) role in plant development and coping with different stresses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Zhu, X.H.; Ding, H.D.; Yang, S.J.; Chen, Y.Y. Foliar Application of 24-Epibrassinolide Alleviates High-Temperature-Induced Inhibition of Photosynthesis in Seedlings of Two Melon Cultivars. Photosynthetica 2013, 51, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marková, H.; Tarkowská, D.; Čečetka, P.; Kočová, M.; Rothová Holá, D. Contents of endogenous brassinosteroids and the response to drought and/or exogenously applied 24-epibrassinolide in two different maize leaves. Frontiers in Plant Science 2023, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, A.; Oelmüller, R. Emerging Roles of Receptor-like Protein Kinases in Plant Response to Abiotic Stresses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 14762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Zheng, J.; Huang, R.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Fang, X. Phytohormones signaling and crosstalk regulating leaf angle in rice. Plant Cell Reports 2016, 2016. 35, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladeynova, M.; Mudrilov, M.; Berezina, E.; Kior, D.; Grinberg, M.; Brilkina, A.; Sukhov, V.; Vodeneev, V. Spatial and temporal dynamics of electrical and photosynthetic activity and the content of phytohormones induced by local stimulation of pea plants. Plants. 2020, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Fan, X.Y.; Cao, D.M.; Tang, W.; He, K.; Zhu, J.Y.; He, J.X.; Bai, M.Y.; Zhu, S.; Oh, E.; et al. Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction into the transcriptional network to regulate plant growth in Arabidopsis. Development Cell. 2010, 19, 765–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Han, S.; Lee, H.; Jeong, B.; Heo, T.; Hyun, T.K.; Kim, K.; Je, B.I.; Lee, H.; Shim, D.; et al. Brassinosteroids facilitate 1034 xylem differentiation and wood formation in tomato. Planta 2019, 249, 1391–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Cano-Delgado, A.; Seto, H.; Hiranuma, S.; Fujioka, S.; Yoshida, S.; Chory, J. Binding of brassinosteroids to 1036 the extracellular domain of plant receptor kinase BRI1. Nature 2005, 433, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, K.; Yu, X.; Ji, D. Genome-wide re-identification and analysis of crRLK1Ls in tomato. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Elena, F.; Caño-Delgado, A.I. Emerging roles of vascular brassinosteroid receptors of the BRI1-like family. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2019, 51, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, V.Q.; Messias, W.F.S.; Pereira, Y.C.; da Silva, B.R.S.; Lobato, E.M.S.G.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P.; Lobato, A.K.D.S. Pretreatment with 24- Epibrassinolide Synergistically Protects Root Structures and Chloroplastic Pigments and Upregulates Antioxidant Enzymes and Biomass in Na+-Stressed Tomato Plants. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.E.; Son, S.Y.; Lee, C.H. Comparison of Metabolome and Functional Properties of Three Korean Cucumber Cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.; Lobato, A. Brassinosteroids improve photosystem II efficiency, gas exchange, antioxidant enzymes and growth of cowpea plants exposed to water deficit. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2017, 23, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.; Amjad, H.; Qurban, A.; Fen, L. Brassinosteroids [BRs] Role in Plant Development and Coping with Different Stresses. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, W.; Wu, G.; Ali, K. An update on evolutionary, structural, and functional studies of receptor-like kinases in plants. Front. Plant Sci., Sec. Plant Pathogen Interactions 2024, 15. [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, S.; Ali, K.; Li, G.; Ren, H.; et al. The receptor-like kinase EMS1 and BRI1 coordinately regulate stamen elongation via the defense factors BES1/BZR1 in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2023, 331, 111673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, K.; Espinoza, L.; Carvajal, R.; Silva-Moreno, E.; Olea, A.F.; Rubio, J. Exogenous Application of Brassinosteroid 24-Norcholane 22(S)-23-Dihydroxy Type Analogs to Enhance Water Deficit Stress Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, C.; Cao, B.; Qin, G.; Wang, W.; Tian, S. Brassinolide enhances cold stress tolerance of fruit by regulating plasma membrane proteins and lipids. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 2469–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Assis-Gomes, M.D.M.; Pinheiro, D.T.; Bressan-Smith, R.; Campostrini, E. Exogenous brassinosteroid application delays senescence and promotes hyponasty in Carica papaya L. leaves. Theoretical and Experimental Plant Physiology 2018, 30, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, T. Recent advances in brassinosteroid biosynthetic pathway: Insight into novel brassinosteroid shortcut pathway. J. Pestic. Sci. 2018, 43, 159–167. [CrossRef]
- Basit, F.; Liu, J.; An, J.; Chen, M.; He, C.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Hu, J.; Guan, Y. Seed priming with brassinosteroids alleviates aluminum toxicity in rice via improving antioxidant defense system and suppressing aluminum uptake. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakma, S.P.; Chileshe, S.M.; Thomas, R.; Krishna, P. Cotton Seed Priming with Brassinosteroid Promotes Germination and Seedling Growth. Agronomy 2021, 11, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.; Korra, T.; Thakur, R.; Arutsel van, R.; Kashyap, A.S.; Nehela, Y.; Chaplygin, V.; Minkina, T.; Lacombe, C.K.; Achard, B.P. Role of plant secondary metabolites in defense and transcriptional regulation in response to biotic stress. Plant Stress 2023, 8, 100154. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, U.; Oba, S. The response of salinity stress-induced A. tricolor to growth, anatomy, physiology, non-enzymatic and enzymatic antioxidants. Front Plant Sci. 2020, 1354. [CrossRef]
- Dalio, R.J.D.; Pinheiro, H.P.; Sodek, L.; Haddad, C.R.B. The effect of 24-epibrassinolide and clotrimazole on the adaptation of Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. to salinity. Acta Physiol. Plant 2011, 33, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Alam, J.; Ahmad, I.; Ali, I.; Gul, H. Effects of exogenous and foliar applications of Brassinosteroid (BRs) and salt stress on the growth, yield and physiological parameters of Lycopersicon esculentum (Mill.). Plant Science Today 2017, 4, 88–10. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Yan, H.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, B.; Fan, C. Exogenous applications of brassinosteroids promote secondary xylem differentiation in Eucalyptus grandis. Peerj-16250 2024, 14. [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, S.; Azuma, T.; Kojima, K.; Inomura, K.; Hasegawa, M.; Nishimura, Y.; et al. Light-driven Proton Pumps as a Potential Regulator for Carbon Fixation in Marine Diatoms. Microbes Environ. 2023, 38. https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/browse/jsme2. /. [CrossRef]
- Ogweno, J.O.; Song, X.S.; Shi, K.; Hu, W.H.; Mao, W.H.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yu, J.Q.; Nogués, S. Brassinosteroids Alleviate Heat-Induced Inhibition of Photosynthesis by Increasing Carboxylation Efficiency and Enhancing Antioxidant Systems in Lycopersicon esculentum. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 27, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariduddin, Q.; Yusuf, M.; Chalkoo, S.; Hayat, S.; Ahmad, A. 28-homobrassinolide improves growth and photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus L. through an enhanced antioxidant system in the presence of chilling stress. Photosynthetica 2011, 49, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururani, M.A.; Venkatesh, J.; Tran, L.S.P. Regulation of photosynthesis during abiotic stress-induced photoinhibition. Molecular Plant 2015, 8, 1304–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derks, A.; Schaven, K.; Bruce, D. Diverse mechanisms for photoprotection in photosynthesis. Dynamic regulation of photosystem II excitation in response to rapid environmental change. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 2015, 184, 468–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonjaroon, W.; Jutamanee, K.; Khamsuk, O.; Thussagunpanit, J.; Kaveeta, L.; Suksamrarn, A. Impact of brassinosteroid mimic on photosynthesis, carbohydrate content and rice seed set at reproductive stage under heat stress. Agriculture and Natural Resources 2018, 52, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sarwar, R.; Zhang, W.; Geng, R.; Zhu, K.-M.; Tan, X.-L. Research progress on the physiological response and molecular mechanism of cold response in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, Sec. Plant Abiotic Stress, 15 - 2024. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liang, W.; Cui, X.; Chen, M.; Yin, C.; Luo, Z.; Zhu, J.; Lucas, W.J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D. Brassinosteroids promote development of rice pollen grains and seeds by triggering expression of Carbon Starved Anther, a MYB domain protein. Plant J. 2015, 82, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, A.L.G.; Soares, J.S.; Tavares, R.G.; Righetto, G.; Zullo, M.A.; Mandava, N.B.; Menossi, M. Brassinosteroids, the sixth class of phytohormones: a molecular view from the discovery to hormonal interactions in plant development and stress adaptation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas-Riverola, A.; Gupta, A.; Betegón-Putze, I.; Bosch, N.; Ibañes, M.; Caño-Delgado, A.I. Brassinosteroid signaling in plant development and adaptation to stress. Development 2019, 146: dev151894. [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.-G.; Miller, G.; Wallace, I.; et al. Orchestrating rapid long-distance signaling in plants with Ca2+, ROS and electrical signals. Plant J. 2017, 90, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, F.; Li, J.; Iqbal, S.; Khan, U.; Ali, N.A.; Peng, Y.; Hong, L.; Asghar, S.; Javed, H.U.; Li, C.; et al. Hormonal Interactions Underlying Rootstock-Induced Vigor Control in Horticultural Crops. Applied Sci 2023, 13, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młodzińska-Michta, E. Regulacja wzrostu i rozwoju systemu korzeniowego przez wybrane czynniki zewnętrzne i wewnętrzne. Kosmos. Problemy Nauk Biologicznych 2018, 4, 801–811. (in Polish). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustakas, M. Plant photochemistry, reactive oxygen species, and photoprotection. Photochem 2022, 2, 5–8. [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, M.B.; Zahra, N.; Zahra, K.; Raza, A.; Batool, A.; Shaukat, K.; Khan, S. Brassinosteroids: Molecular and physiological responses in plant growth and abiotic stresses, Plant Stress 2021, 2, 100029, ISSN 2667-064X. [CrossRef]
- Golam, J.A.; Xiao-Jian, X.; Kai, S.; Jing-Quan, Y.; Yan-Hong, Z. Role of Brassinosteroid in Plant Adaptation to Abiotic Stresses and its Interplay with their Hormones. Current Protein & Peptide Science 2015, 16. [CrossRef]
- Reissig, G.N.; de Carvalho Oliveira, T.F.; Parise, A.G.; Costa, Á.V.L.; Posso, D.A.; Rombaldi, C.V.; Souza, G.M. Approximate entropy: a promising tool to understand the hidden electrical activity of fruit. Commun Integr Biol. 2023, 16, 2195236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheperd, V.A. From semi-conductors to the rhythms of sensitive plants: the research of J. C. Bose. Cell Mol Biol 2005, 51, 607–619. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhova, E.; Sukhov, V. Electrical signals, plant tolerance to actions of stressors, and programmed cell death: is interaction possible? Plants 2021, 10, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.J.; Fang, P.P.; Guo, X.; Qian, X.J.; Zhou, J.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yu, J.Q. Brassinosteroid-Mediated Apoplastic H2O2-Glutaredoxin 12/14 Cascade Regulates Antioxidant Capacity in Response to Chilling in Tomato. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, D.E.; Acuña, L.G.; Calderón, I.L. Stress response and virulence factors in bacterial pathogens relevant for Chilean aquaculture: current status and outlook of our knowledge. Biol Res 2022, 55, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.K.; Pretorius, T.; Naidoo, S. Mechanisms of systemic resistance to pathogen infection in plants and their potential application in forestry. BMC Plant Biology 2023, 23, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Kaur, N.; Pati, P.K. Phytohormones: Key players in the modulation of heavy metal stress tolerance in plants. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2021, 223, 112578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, M.B.; Raza, A.; Zahra, N.; Shaukat, K.; Akram, M.Z.; Iqbal, S.; Basra, S.M.A.; Irfana, L.; Syeda, F. Amjad, Nida Mansoora et al. Interactive effects of brassinosteroids and timber waste biochar enhances the drought tolerance capacity of wheat plant, 2022, PREPRINT (Version 2) available at Research Square. [CrossRef]
- Fricke, W. Fricke, W. Rapid and tissue-specific accumulation of solutes in the growth zone of barley leaves in response to salinity. Planta 2004, 219, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram et al. Role of Brassinosteroids in plants responses to salinity stress: A review. Journal of Applied and Natural Science 2022, 14, 582 -599. [CrossRef]
- Clauw, P.; Coppens, F.; Korte, A.; Herman, D.; Slabbinck, B.; Dhondt, S.; Van Daele, T.; De Milde, L.; Vermeersch, M.; Maleux, K.; Maere, S.; Gonzalez, N.; Inzé, D. Leaf growth response to mild drought: natural variation in Arabidopsis sheds light on trait architecture. The Plant Cell 2016, 28, 2417–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfana, L.; Syeda, F. Amjad, Mansoora N., et al. Interactive effects of brassinosteroids and timber waste biochar enhances the drought tolerance capacity of wheat plant, 2022, PREPRINT (Version 2) available at Research Square. [CrossRef]
- Kiliç, S.; Çavuşoğlu, K.; Kabar, K. Effects of 24-epibrassinolide on salinity stress induced inhibition of seed germination, seedling growth and leaf anatomy of barley. Süleyman Demirel University Faculty of Arts and Science. Journal of Science 2007, 2, 41–52. [Google Scholar]
- Safdar, H.; Amin, A.; Shafiq, Y.; Ali, A.; Yasin, R.; Shoukat, A.; Ul Hussan, M.; Sarwar, M.I. A review: Impact of salinity on plant growth. Nat. Sci 2019, 17, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Das, T.; Shukla, Y.M.; Poonia, T.C.; Meena, M.; Meena, M.D. Effects of brassinolide on physiological characteristics of rice (Oryza sativa L.) with different salinity levels. Ann. Biol 2013, 29, 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ranf, S. Pattern recognition receptors—versatile genetic tools for engineering broad-spectrum disease resistance in crops. Agronomy 2018, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Irving, H.R. Developing a model of plant hormone interactions. Plant Signaling & Behavior 2011, 6, 494–500. [Google Scholar]
- Sirangelo, T.M.; Ludlow, R.A.; Spadafora, N.D. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Potential Pathogen Resistance in Cannabis sativa. Plants. 2023, 12, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonimous 2023. Create Professional Science Figures in Minutes. https://www.biorender.com.
- Kan, Y.; Mu, X.R.; Gao, J.; Lin, H.-X.; Lin, Y. The molecular basis of heat stress responses in plants. Molecular Plant 2023, 16, 1612–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremina, M.; Unterholzner, S.J.; Rathnayake, A.I.; Castellanos, M.; Khan, M.; Kugler, K.G.; May, S.T.; Mayer, K.F.; Rozhon, W.; Poppenberger, B. Brassinosteroids participate in the control of basal and acquired freezing tolerance of plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5982–E5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Deng, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, L.; Zou, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, D.; Lin, H. Ethylene and hydrogen peroxide are involved in brassinosteroid-induced salt tolerance in tomato. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajewska, I.; Talarek, M.; Bajguz, A. Brassinosteroids and response of plants to heavy metals action. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, M.; Chu, L.; Li, Q.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fan, X.; Zhao, D.; Yan, C.; Liu, Q. Brassinosteroid and gibberellin coordinate rice seed germination and embryo growth by regulating glutelin mobilization. The Crop Journal 2021, 9, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Chen, Z.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Duan, B.B.; Xi, Z.M. Involvement of ABA and Antioxidant System in Brassinosteroid-Induced Water Stress Tolerance of Grapevine [Vitis vinifera L.]. Sci. Hortic 2019, 256, 108596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazorraa, L.M.; Holtonb, N.; Bishopb, G.J.; Ineza, M. Heat shock response in tomato brassinosteroid mutants indicates that thermotolerance is independent of brassinosteroid homeostasis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 49, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Khan, T.A.; Yusuf, M.; Fariduddin, Q. Silicon-Mediated Role of 24-Epibrassinolide in Wheat under High-Temperature Stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 17163–17172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Wang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Deng, M.; Zhang, Z. Effects of 24-Epibrassinolide on Antioxidation Defense and Osmoregulation Systems of Young Grapevines (V. vinifera L.) under Chilling Stress. Plant Growth Regul 2013, 71, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicka, B.; Kalembasa, D. Annual Variability of Some Toxic Element Contents (Cd, Cr, Co, Ni, and Pb) and Response of Two Jerusalem Artichoke Varieties to Increasing Nitrogen Fertilizer at Constant PK Levels. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 22, 861–871. [Google Scholar]
- Biziewska, I.; Talarek, M.; Bajguz, A. Rola brassinosteroidów w odpowiedzi roślin na stres metali ciężkich. [w:] A. Bajguz, I. Ciereszko [red.] Różnorodność biologiczna – od komórki do ekosystemu Funkcjonowanie roślin i grzybów. Środowisko – eksperyment – edukacja, Polskie Towarzystwo Botaniczne 2015, 253–263. (in Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, I.; Pati, P.K.; Bhardwaj, R. Effect of 28-homobrassinolide on antioxidant defense system in Raphanus sativus L. under chromium toxicity. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, S.; Maheshwari, P.; Wani, A.S.; Irfan, M.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, A. Comparative effect of 28 homobrassinolide and salicylic acid in the amelioration of NaCl stress in Brassica juncea L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 53, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampelotto, P.H.; Giannakos, N.R.O.; Mena Canata, D.A.; Pereira, F.D.; Hackenhaar, F.S.; Pereira, M.J.R.; Benfato, M.S. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense in the Brain of Bat Species with Different Feeding Habits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuillet, C.; Schachermayr, G.; Keller, B. Molecular cloning of a new receptor-like kinase gene encoded at the Lr10 disease resistance locus of wheat. The Plant Journal 1997, 11, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.W.; Lee, S.C. Arabidopsis abscisic acid receptors play an important role in disease resistance. Plant Molecular Biology 2015, 88, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veley, K.M.; Michaels, S.D. Functional redundancy and new roles for genes of the autonomous floral-promotion pathway. Plant Physiology 2008, 147, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.A.; Pervez, M.A.; Balal, R.M.; Mattson, N.S.; Rashid, A.; Ahmad, R.; Ayyub, C.M.; Abbas, T. Brassinosteroid (24-epibrassinolide) enhances growth and alleviates the deleterious effects induced by salt stress in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Australian Journal of Crop Science 2011, 5, 500–510. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, M.; Elkelish, A.; Souad, T.; Alhaithloul, H.; Farooq, M. Brassinosteroid seed priming with nitrogen supplementation improves salt tolerance in soybean. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants 2020, 26, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawicka, B.; Barbaś, P.; Skiba, D.; Pszczółkowski, P.; Yeganehpoor, F. Oxylipins in Plant Protection/Disease Management. [in:] Phyto-Oxylipins. 1st Edition, First Published 2023, Imprint: CRC Press, pp. 19; eBook ISBN: 9781003316558.
- Tang, K.W.K.; Millar, B.C.; Moore, J.E. Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Br J Biomed Sci. 2023, 80, 11387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, T.; Sharma, P.; Chandra, S.; et al. A spotlight on the recent advances in bacterial plant diseases and their footprint on crop production [in:] Recent Advancements in Microbial Diversity, Editor(s): Surajit De Mandal, Pankaj Bhatt, Academic Press, 2020, 37-56, ISBN: 9780128212653. [CrossRef]
- Manghwar, H.; Zaman, W. Plant Biotic and Abiotic Stresses — Volume II. Editors H. Manghwar & W. Zaman. Editorial Office: MDPI, Basel, Switzerland, 2023, ISBN: 978-3-0365-8538-3(Hbk); ISBN: 978-3-0365-8539-0(PDF). [CrossRef]
- Thussagunpanit, J.; Jutamanee, K.; Sonjaroon, W.; Kaveeta, L.; Chai-Arree, W.; Pankean, P.; Suksamrarn, A. Effects of brassinosteroid and brassinosteroid mimic on photosynthetic efficiency and rice yield under heat stress. Photosynthetica 2015, 53, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, C.; Sanchez, D.L.; Lipka, A.E.; Liu, P.; Yin, Y.; Blanco, M.; Lübberstedt, T. Gibberellins Promote Brassinosteroids Action and Both Increase Heterosis for Plant Height in Maize (Zea mays L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, Sec. Plant Breeding, 8 - 2017. [CrossRef]
- Mmbando, G.S. The recent relationship between ultraviolet-B radiation and biotic resistance in plants: a novel non-chemical strategy for managing biotic stresses. Plant Signaling & Behavior 2023. [CrossRef]
- Das, S.R.; Rout, GR. Role of Brassinosteroids on Plant Growth and Development. [In book:] Jasmonates and Brassinosteroids in Plants: Metabolisms, signaling and Biotechnological applications. Edited by Akul Ramakrishna, Geetika Sirhindi. Publisher: CRC Press, pp. 246. 2023.
- Divi, U.K.; Krishna, P. Brassinosteroid: A biotechnological target for enhancing crop yield and stress tolerance. New Biotechnol. 2009, 26, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Sharma, V.; Kaur, G.; Lata, C.; Dasila, H.; Perveen, K.; Khan, F.; Gupta, V.K.; Khanam, M.N. Brassinosteroids as promoters of seedling growth and antioxidant activity under heavy metal zinc stress in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.). Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1259103. [CrossRef]
- Bajguz, A.; Chmur, M.; Gruszka, D. Comprehensive Overview of the Brassinosteroid Biosynthesis Pathways: Substrates, Products, Inhibitors, and Connections. Frontiers in Plant Science 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelissen, H.; Gonzalez, N.; Inze, D. Leaf growth in dicots and monocots: so different yet so alike. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2016, 33, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hua, J.; Hou, X.; et al. Brassinosteroids is involved in methane-induced adventitious root formation via inducing cell wall relaxation in marigold. BMC Plant Biol 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, F.P.; Núñez, M.G.; Rosado-Abón, A.; Amesty, Á.; Estévez-Braun, A.; Díaz, K.; Espinoza, L.C.; Iglesias-Arteaga, M.A. Methyl esters of 23,24-Dinor-5α-cholan-22-oic acids as brassinosteroid Analogues. Synthesis, evaluation of plant growth promoting activity and Molecular docking. Steroids 2023, 196, 109248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Yao, L.; Hu, Y. Determination and analysis of solubility of brassinolide in different solvent systems at different temperatures (T = 278.15–323.15 K). Journal of Molecular Liquids 2021, 340, 117316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, C.L.; Kepka, M.; Wunschel, C.; Rajagopalan, N.; Nelson, K.M.; Christmann, A.; Abrams, S.R.; Grill, E.; Loewen, M.C. Abscisic acid analogs as chemical probes for dissection of abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry 2015, 113, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongsri, K.; Teingtham, K.; Duangpatra, J.; Romkaew, J. Effects of brassinosteroids and gibberellin on water uptake and performance of soya bean seeds under different temperatures. Seed Science and Technology 2021, 49, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, S.; Ahmad, A. 28-Homobrassinolide induced changes favored germinability of wheat grains. Bulg. J., Plant Physiol 2003, 29, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Che, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, S.; Han, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Tang, M. Brassinosteroids benefit plants performance by augmenting arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Microbiology Spectrum 2021, 9, e01645–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nováková, O.; Kuneš, I.; Gallo, J.; Baláš, M. Effects of brassinosteroids on prosperity of Scots pine seedlings. Journal of Forest Science 2014, 60, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, M.; Mekala, N.R.; Aro, E.M. Photosystem II photoinhibition-repair cycle protects Photosystem I from irreversible damage. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 2014, 837, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Murata, N. Revised scheme for the mechanism of photoinhibition and its application to enhance the abiotic stress tolerance of the photosynthetic machinery. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2014, 98, 8777–8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Rozhon, W.; Poppenberger, B. The role of hormones in the aging of plants-a mini-review. Gerontology 2013, 60, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan-Dalyan, E.; Sağlam-Çağ, S. The effect of epibrassinolide on senescence in horizontal sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) seedlings. European Journal of Biology 2013, 72, 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Efimova, M.V.; Savchuk, A.L.; Hasan, J.A.K.; Litvinovskaya, R.P.; Khripach, V.A.; Kholodova, V.P.; Kuznetsov, V.V. Physiological mechanisms of enhancing salt tolerance of oilseed rape plants with brassinosteroids. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology 2014, 61, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houimli, S.I.M.; Denden, M.; Mouhandes, B.D. Effects of 24-epibrassinolide on growth, chlorophyll, electrolyte leakage and proline by pepper plants under NaCl-stress. EurAsian Journal of BioSciences 2010, 4, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Awan, S.A.; Ikram, R.; Rizwan, M.; Akhtar, N.; Yasmin, H.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Ali, S.; Ilyas, N. Effects of 24-epibrassinolide on plant growth, antioxidants defense system, and endogenous hormones in two wheat varieties under drought stress. Physiol Plant. 2021, 172, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, S.; Båga, M.; Chibbar, R.N. Brassinosteroid receptor mutation influences starch granule size distribution in barley grains. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 154, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




