Submitted:
16 February 2024
Posted:
17 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Biochemical analyses
2.3. Calcification assessment
2.4. Brachial blood pressure
2.5. Statistical analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Study population
3.2. Laboratory analyses
3.3. Predictors of vascular calcification in studied groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Budoff, M.-J.; Rader, D.-J.; Reilly, M.-P.; Mohler, E.-R., 3rd.; Lash, J.; Yang, W.; Rosen, L.; Glenn, M.; Teal, V.; Feldman, H.-I.; CRIC Study Investigators. Relationship of estimated GFR and coronary artery calcification in the CRIC (Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort) Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011; Oct;58(4):519-26. Epub 2011 Jul 23. PMID: 21783289; PMCID: PMC3183168. [CrossRef]
- Kestenbaum, B.R.; Adeney, K.-L.; de Boer, I.-H.; Ix, J.-H.; Shlipak, M.-G.; Siscovick, D.-S. Incidence and progression of coronary calcification in chronic kidney disease: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2009; 76(9): 991-8. Epub 2009 Aug 19. PMID: 19692998; PMCID: PMC3039603. [CrossRef]
- Schlieper, G.; Schurgers, L.; Brandenburg, V.; Reutlings-Perger, C.; Floege, J. Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease: an update. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2016; 31: 31–9. Epub 2015 Apr 26. PMID: 25916871. [CrossRef]
- Gungor, O.; Kocyigit, I.; Yilmaz, M.-I.; Sezer, S. Role of vascular calcification inhibitors in preventing vascular dysfunction and mortality in hemodialysis patients. Semin Dial. 2018; 31(1):72-81. Epub 2017 Jun 13. PMID: 28608927. [CrossRef]
- Wolf M. Update on fibroblast growth factor 23 in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2012; 82: 737–47, doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.176. Epub 2012 May 23. PMID: 22622492; PMCID: PMC3434320. [CrossRef]
- London, G.-M.; Marchais, S.J.; Guérin, A.-P.; Métivier, F. Arteriosclerosis, vascular calcifications and cardiovascular disease in uremia. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2005; 14(6):525-31. PMID: 16205470. [CrossRef]
- Kakani, E.; Elyamny, M.; Ayach, T.; El-Husseini, A. Pathogenesis and management of vascular calcification in CKD and dialysis patients. Semin Dial. 2019; 32(6):553-561. Epub 2019 Aug 29. PMID: 31464003. [CrossRef]
- Werida, R. H., Abou-Madawy, S., Abdelsalam, M., & Helmy, M. W. Omega 3 fatty acids effect on the vascular calcification biomarkers fetuin A and osteoprotegerin in hemodialysis patients. Clin Exp Medicine, 2022; 22(2), 301–310. [CrossRef]
- Kestenbaum, B. R., Adeney, K. L., de Boer, I. H., Ix, J. H., Shlipak, M. G., & Siscovick, D. S. Incidence and progression of coronary calcification in chronic kidney disease: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Kidney Int, 2009; 76(9), 991–998. [CrossRef]
- Caluwé, R., Pyfferoen, L., De Boeck, K., & De Vriese, A. S. The effects of vitamin K supplementation and vitamin K antagonists on progression of vascular calcification: ongoing randomized controlled trials. Clinical kidney journal, 2016; 9(2), 273–279. [CrossRef]
- Di Lullo, L., Tripepi, G., Ronco, C., D’Arrigo, G., Barbera, V., Russo, D., Di Iorio, B. R., Uguccioni, M., Paoletti, E., Ravera, M., Fusaro, M., & Bellasi, A. Cardiac valve calcification and use of anticoagulants: Preliminary observation of a potentially modifiable risk factor. Int J Cardiol, 2019; 278, 243–249. [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, Y., Hamano, T., Obi, Y., Monden, C., Oka, T., Yamaguchi, S., Matsui, I., Hashimoto, N., Matsumoto, A., Shimada, K., Takabatake, Y., Takahashi, A., Kaimori, J. Y., Moriyama, T., Yamamoto, R., Horio, M., Yamamoto, K., Sugimoto, K., Rakugi, H., & Isaka, Y. A Randomized Trial of Magnesium Oxide and Oral Carbon Adsorbent for Coronary Artery Calcification in Predialysis CKD. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2019; 30(6), 1073–1085. [CrossRef]
- Ketteler, M.; Block, G.-A.; Evenepoel, P.; Fukagawa, M.; Herzog, C.-A.; McCann, L.; Moe, S.-M.; Shroff, R.; Tonelli, M.-A.; Toussaint, N.-D.; Vervloet, M.-G.; Leonard, M.-B. Executive summary of the 2017 KDIGO chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD) guideline update: what’s changed and why it matters. Kidney Int. 2017; 92:26–36. [CrossRef]
- Adragao, T.; Pires, A.; Lucas, C.; Birne, R.; Magalhaes, L.;Gonçalves, M.; Negrao, A.-P. A simple vascularcalcification score predicts cardiovascular risk in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transpl2004; 19:1480–1488. Epub 2004 Mar 19. PMID: 15034154. [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G.; Fagard, R.; Narkiewicz, K.; Redon, J.; Zanchetti, A.; Böhm, M.; Christiaens, T.; Cifkova, R.; De-Backer, G.; Dominiczak, A.; Galderisi, M.; Grobbee, D.-E.; Jaarsma, T.; Kirchhof, P.; Kjeldsen, S.-E.; Laurent, S.; Manolis, A.-J.; Nilsson, P.-M.; Ruilope, L.-M.; Schmieder, R.E.; Sirnes, P.-A.; Sleight, P.; Viigimaa, M.; Waeber, B.; Zannad, F.; Redon, J.; Dominiczak, A.; Narkiewicz, K.; Nilsson, P.-M.; Burnier, M.; Viigimaa, M.; Ambrosioni, E.; Caufield, M.; Coca, A.; Olsen, M.-H.; Schmieder, R.-E.;Tsioufis, C.; van de Borne, P.; Zamorano, J.-L.; Achenbach, S.; Baumgartner, H.; Bax, J.-J.; Bueno, H.; Dean, V.; Deaton, C.; Erol, C.; Fagard, R.; Ferrari, R.; Hasdai, D.; Hoes, A.-W.; Kirchhof, P.; Knuuti, J.; Kolh, P.; Lancellotti, P.; Linhart, A.;Nihoyannopoulos, P.; Piepoli, M.-F.; Ponikowski, P.; Sirnes, P.-A.;Tamargo, J.-L.; Tendera, M.; Torbicki, A.; Wijns, W.; Windecker, S.;Clement, D.-L.; Coca, A.; Gillebert, T.-C.; Tendera, M.; Rosei, E.-A.; Ambrosioni, E.; Anker, S.-D.; Bauersachs, J.; Hitij, J.-B.; Caulfield, M.; De Buyzere, M.; De Geest, S.;Derumeaux, G.-A.; Erdine, S.; Farsang, C.;Funck-Brentano, C.; Gerc, V.; Germano, G.; Gielen, S.; Haller, H.; Hoes, A.-W.; Jordan, J.; Kahan, T.; Komajda, M.; Lovic, D.; Mahrholdt, H.; Olsen, M.-H.; Ostergren, J.;Parati, G.; Perk, J.;Polonia, J.; Popescu, B.-A.; Reiner, Z.; Rydén, L.; Sirenko, Y.; Stanton, A.; Struijker-Boudier, H.;Tsioufis, C.; van de Borne, P.; Vlachopoulos, C.; Volpe, M.; Wood, D.-A. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2013; 34(28):2159-2219. Epub 2013 Jun 14. PMID: 23771844. [CrossRef]
- Gorriz, J.-L.; Molina, P.; Cerveron, M.-J.; Vila, R.; Bover, J.; Nieto, J.; Barril, G.;Martínez-Castelao, A.;Fernández, E.; Escudero, V.; Piñera, C.; Adragao, T.; Navarro-Gonzalez, J.-F.; Molinero, L.-M.; Castro-Alonso, C.; Pallardó, L.-M.; Jamal, S.-A. Vascular calcification in patients with nondialysis CKD over 3 years. Clin J Am SocNephrol 2015;10: 654-666. [CrossRef]
- Damjanovic, T.; Djuric, Z.; Markovic, N.; Dimkovic, S.; Radojicic, Z.; Dimkovic, N. Screening of vascular calcifications in patients with end-stage renal diseases. Gen. Physiol. Biophys 2009; 28 Spec No: 277–283. [PubMed].
- Zhang, H.; Li, G.; Yu, X.; Yang, J.; Jiang, A.; Cheng, H.; Fu, J.; Liang, X.; Liu, J.; Lou, J.; Wang, M.; Xing, C.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Guan, T.; Peng, A.; Chen, N.; Hao, C.; Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, D.; Jia, Z.; Liu, Z. China Dialysis Calcification Study Group. Progression of Vascular Calcification and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Receiving Maintenance Dialysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(5):e2310909. PMID: 37126347; PMCID: PMC10152309. [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Nayeri, H.; Nasri, H. Association of fetuin-A with kidney disease; a review on current concepts and new data. J Nephropharmacol 2019; 8(2): e14.
- Ketteler, M.; Bongartz, P.; Westenfeld, R.; Wildberger, J.-E.; Mahnken, A.-H.; Böhm, R.; Metzger, T.; Wanner, C.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Floege, J. Association of low fetuin-A (AHSG) concentrations in serum with cardiovascular mortality in patients on dialysis: a cross-sectional study. Lancet 2003; 361:827–33. [CrossRef]
- Ulutas, O.; Taskapan, M.-C.; Dogan, A.;Baysal, T.; Taskapan, H. Vascular calcification is not related to serum fetuin-A and osteopontin levels in hemodialysis patients. Int Urol Nephrol 2018; 50(1):137-142. Epub 2017 Nov 13. PMID: 29134617. [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.-R.; Olauson, H.; Witasp, A.; Haarhaus, M.; Brandenburg, V.; Wernerson, A.; Lindholm, B.; Söderberg, M.; Wennberg, L.; Nordfors, L.; Ripsweden, J.; Barany, P.; Stenvinkel, P. Increased circulating sclerostin levels in end-stage renal disease predict biopsy-verified vascular medial calcification and coronary artery calcification. Kidney Int 2015; 88(6):1356-1364. Epub 2015 Sep 2. PMID: 26331407. 1356. [CrossRef]
- Claes, K.-J.; Viaene, L.; Heye, S.; Meijers, B.; d’Haese, P.; Evenepoel, P. Sclerostin: Another vascular calcification inhibitor? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013; 98(8):3221-8. Epub 2013 Jun 20. PMID: 23788689. 3221. [CrossRef]
- Isakova, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, W.; Xie, D.; Anderson, A.-H.; Scialla, J.; Wahl, P.; Gutiérrez, O.-M.; Steigerwalt, S.; He, J.; Schwartz, S.; Lo, J.; Ojo, A.; Sondheimer, J.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Lash, J.; Leonard, M.; Kusek, J.-W.; Feldman, H.-I.; Wolf, M. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and risks of mortality and end-stage renal disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. JAMA 2011; 305(23):2432-2439. [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, M.-M.; El-Shehaby, A.-R.; Salem, M.-M.; Osman, N.-A.; El Sheikh, E.; Sharaf, E.-l.; Din, U.-A. Fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF-23) is indepenently correlated to aortic calcification in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 2010; 25: 2679–2685. Epub 2010 Feb 22. PMID: 20176609. [CrossRef]
- Desjardins, L.; Liabeuf, S.; Renard, C.; Lenglet, A.; Lemke, H.-D.; Choukroun, G.; Drueke, T.-B.; Massy, Z.-A. European Uremic Toxin (EUTox) Work Group. FGF23 is independently associated with vascular calcification but not bone mineral density in patients at various CKD stages. Osteoporos Int 2012; 23: 2017–25. Epub 2011 Nov 23. PMID: 22109743s. 2020;32(10):1931-1940. [CrossRef]
- Baralić, M.; Brković, V.; Stojanov, V.; Stanković, S.; Lalić, N.; Đurić, P.; Đukanović, Lj.; Kašiković, M.; Petrović, M.; Petrović, M.; Stošović, M.; Ležaić, V. al. Dual Roles of the Mineral Metabolism Disorders Biomarkers in Prevalent Hemodilysis Patients: In Renal Bone Disease and in Vascular Calcification. J Med Biochem2019; 38(2):134-144. PMID: 30867641; PMCID: PMC6411002. [CrossRef]
- Scialla, J.-J.; Lau, W.-L.; Reilly, M.-P.; Isakova, T.; Yang, H.-Y.; Crouthamel, M.-H.; Chavkin, N.-W.; Rahman, M.; Wahl, P.; Amaral, A.-P.; Hamano, T.; Master, S.-R.; Nessel, L.; Chai, B.; Xie, D.; Kallem, R.-R.; Chen, J.; Lash, J.-P.; Kusek, J.-W.; Budoff, M.-J.; Giachelli, C.-M.; Wolf, M. Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort Study Investigators. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is not associated with and does not induce arterial calcification. Kidney Int 2013;83: 1159–68. Epub 2013 Feb 6. PMID: 23389416; PMCID: PMC3672330. [CrossRef]
- Souberbielle, J. C., Roth, H., & Fouque, D. P. Parathyroid hormone measurement in CKD. Kidney Int 2010; 77(2), 93–100. [CrossRef]
- Cannata-Andia, J.-B.; Rodriguez, G.-M.; Gomez, A.-C. Osteoporosis and adynamic bone in chronic kidney disease. J Nephrol 2013; 26:73-80. PMID: 23023723. [CrossRef]
- Barreto, F. C., Barreto, D. V., Moysés, R. M., Neves, K. R., Canziani, M. E., Draibe, S. A., Jorgetti, V., & Carvalho, A. B. K/DOQI-recommended intact PTH levels do not prevent low-turnover bone disease in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int, 2008; 73(6), 771–777. [CrossRef]
- Ureña, P., & De Vernejoul, M. C. Circulating biochemical markers of bone remodeling in uremic patients. Kidney Int, 1999; 55(6), 2141–2156. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B., & Towler, D. A. Arterial calcification and bone physiology: role of the bone-vascular axis. Nature reviews. Endocrinology, 2012; 8(9), 529–543. [CrossRef]
- Hernandes, F. R., Canziani, M. E., Barreto, F. C., Santos, R. O., Moreira, V. M., Rochitte, C. E., & Carvalho, A. B. The shift from high to low turnover bone disease after parathyroidectomy is associated with the progression of vascular calcification in hemodialysis patients: A 12-month follow-up study. PloS one, 2017; 12(4), e0174811. [CrossRef]
- London, G. M., Marty, C., Marchais, S. J., Guerin, A. P., Metivier, F., & de Vernejoul, M. C. Arterial calcifications and bone histomorphometry in end-stage renal disease. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004; 15(7), 1943–1951. [CrossRef]
- Adragao, T., Ferreira, A., Frazao, J. M., Papoila, A. L., Pinto, I., Monier-Faugere, M. C., & Malluche, H. H. Higher mineralized bone volume is associated with a lower plain X-Ray vascular calcification score in hemodialysis patients. PloS one, 2017; 12(7), e0179868. [CrossRef]
- Persy, V., D’Haese, P. Vascular calcification and bone disease: the calcification paradox. Trends Mol Med 2009; 15: 405–416.
- Drüeke TB. Hyperparathyroidism in Chronic Kidney Disease. [Updated 2021 Oct 18]. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, et al., editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc. 2000. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK278975/.
- Bisson, S. K., Ung, R. V., & Mac-Way, F. Role of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Renal Osteodystrophy. Int J Endocrinology, 2018; 5893514. [CrossRef]
- Pietrzyk, B.; Wyskida, K.; Ficek, J.; Kolonko, A.; Ficek, R.; Więcek, A.; Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M.; Chudek, J. Relationship between plasma levels of sclerostin, calcium-phosphate disturbances, established markers of bone turnover, and inflammation in haemodialysis patients. Int Urol Nephrol 2019; 51(3):519-526. Epub 2018 Dec 24. PMID: 30584645; PMCID: PMC6424932. [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Chang, K.-V.; Chao, C.-T.; Huang, J.-W. Gender-Related Differences in Chronic Kidney Disease-Associated Vascular Calcification Risk and Potential Risk Mediators: A Scoping Review. Healthcare (Basel) 2021; 9(8):979. PMID: 34442116; PMCID: PMC8394860. [CrossRef]
- Becs, G., Zarjou, A., Agarwal, A., Kovács, K. É., Becs, Á., Nyitrai, M., Balogh, E., Bányai, E., Eaton, J. W., Arosio, P., Poli, M., Jeney, V., Balla, J., & Balla, G. Pharmacological induction of ferritin prevents osteoblastic transformation of smooth muscle cells. J Cell Mol Med, 2016; 20(2), 217–230. [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y. C., Liu, W. C., Zheng, C. M., Zheng, J. Q., Yen, T. H., & Lu, K. C. Role of Vitamin D in Uremic Vascular Calcification. BioMed Res Int 2017, 2803579. [CrossRef]
- NKF-KDOQI Guidelines. Available from: http://www.kidney.org/professionals/KDOQI/guidelineupHDPDVA/index.htm [accessed 21.05.2023].
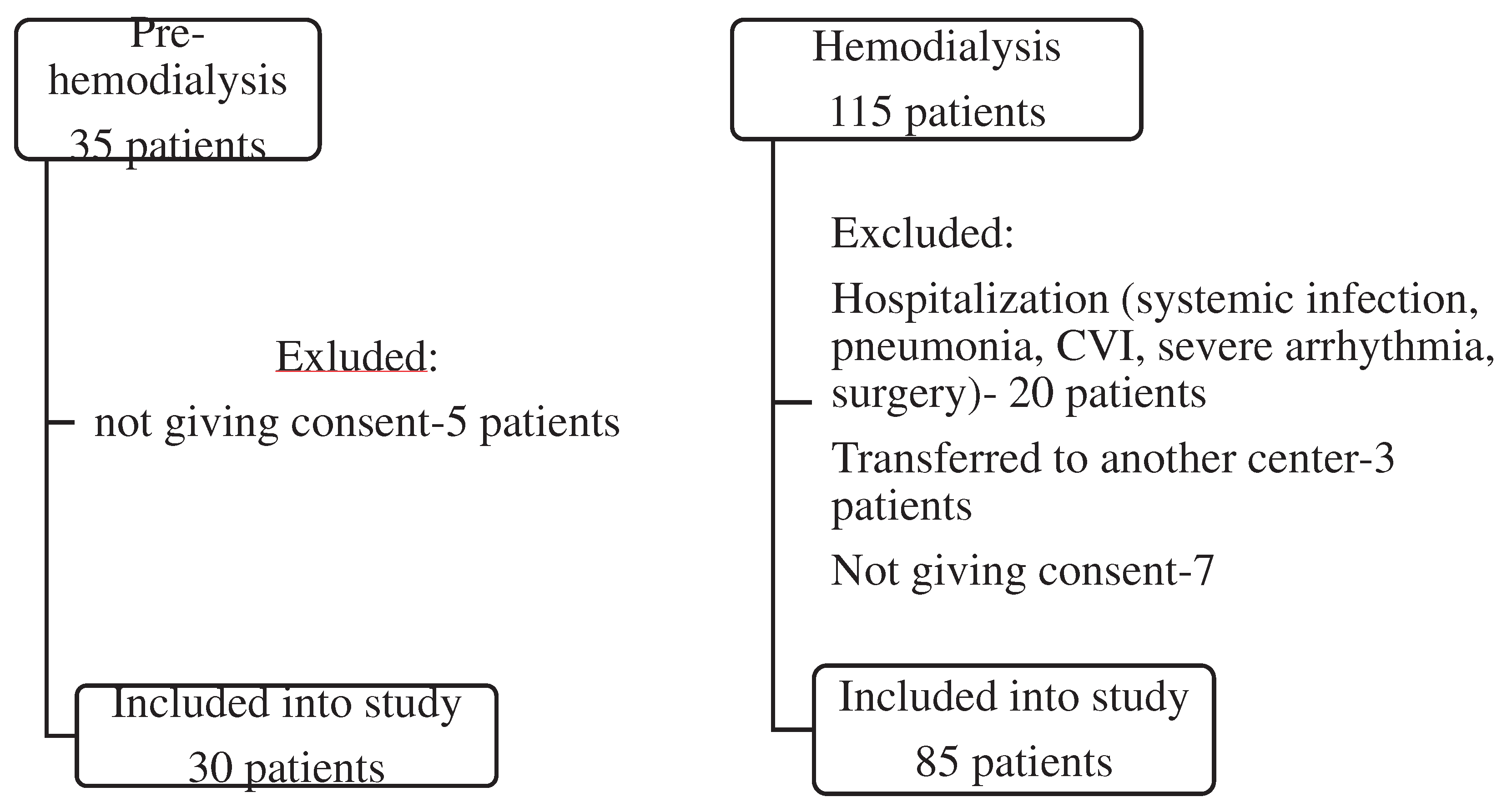
| Pre-HD (No=30) |
HD (No=85) |
p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics Age, years Sex, m/f |
66.7±2.76 19/11 |
57.72±1.49 40/45 |
0.003 0.141 |
| Underlying kidney disease: (%) GN Nephroangiosclerosis APCD DM2 Nephrolithiasis Others |
3 (10) 6 (20) 2 (6.7) 5 (9.4) 1 (3.3) 13 (43.3) |
15 (17.6) 14 (16.5) 8 (9.4) 8 (9.4) 12 (14.1) 28 (32.9) |
0.394 0.779 1.000 0.442 0.178 0.376 |
| Co-morbidities, yes (%) DM2 Hypertension CVD CVI tumor |
4 (13.3) 27 (90) 14 (46.7) 2 (6.7) 1 (3.3) |
14 (16.4) 65 (76.7) 34 (34.1) 10 (10.6) 8 (8.2) |
0.778 0.029 0.527 0.728 0.442 |
| Treatment, no (%) | |||
| ESA Phosphate binder Alpha D3 Antihypertensive |
7 (23.3) 21 (70) 9 (30) 16 (53.3) |
36 (64.3) 80 (94.1) 25 (29.4) 62 (72.9) |
0.080 0.001 1.000 0.068 |
| VC score, no (%) 0 1-2 ≥ 3 ≥ 6 (8) |
16 (53.3) 4 (13.3) 10 (33.3) 1 (0) |
36 (42.35) 18 (21.2) 31 (37.47) 15 (6) |
0.393 0.384 0.756 0.030 |
| Pre-HD (N= 30) |
HD (N= 85) |
p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol, mmol/L Triglyceride, mmol/L Hemoglobin, g/L Glycaemia, mmol/L Creatinine, µmol/L Urea, mmol/L Urate, µmol/L Sodium, mmol/L Potassium, mmol/L Calcium, mmol/L Phosphate, mmol/L Feritin, µg/L |
4.83±0.15 1.4 (0.8) 106 (96.7-114.5) 5.2 (4.7-5.55) 552.5 (318-731.2) 23.4 (14.2-32.95) 386.70±24.2 139.87±0.7 4.85±0.1 2.16 (2.05-2.28) 1.53 (1.1-1.8) 84.3(50.75-231.87) |
4.59±1.16 1.65 (1.2-2.8) 108 (101.5-116.5) 4.9 (4.2-6.05) 808 (705.5-915) 21.0 (17.9-26.0) 342.1±10.2 137.86±0.33 5.29±0.08 2.19 (2.1-2.31) 1.65 (1.3-2.03) 355 (131.7-490.1) |
0.891 0.804 0.384 0.663 0.000 0.327 0.100 0.001 0.011 0.541 0.247 0.000 |
| Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L iPTH, pg/ml <100* 25(OH)D ng/ml <29 *(deficiency±insufficiency) |
73.5 (61.5-99.2) 200.9 (34.57) 11 (36.6%) 24.7 (46.22) 19 (64.28) |
87 (60-109) 118 (49.5-238.5) 36 (42.3%) 27.5 (19.2-48.05) 45 (53.6%) |
0.304 0.710 0.879 |
| Fetuin A, ng/ml | 520 (383-600) | 339.5 (244.5-432.6) | 0.000 |
| Sclerostin, pg/ml | 3190 (2550-4520) | 2105 (811-5105) | 0.103 |
| FGF23, pg/ml | 154.5 (71.2-233.6) | 1108 (382-1500) | 0.000 |
| Pre HD group | HD group | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 VC + |
2 VC neg |
3 VC + |
4 VC neg |
||
| Number | 14 | 16 | 49 | 36 | |
| Age, years | 71.7±2.05 | 62.5±4.68 | 58.66±1,98 | 56.43±2.28 | 1 vs 3, 4 p< 0.001 |
| Sex, m/f | 12/2 | 7/9 | 23/26 | 17/19 | 1 vs 2, 3,4 p < 0.02 |
| ESA, yes /no | 2/12 | 5/11 | 20/29 | 16/20 | 1 vs 4 p= 0.05 |
| Phosphate binder, yes/ no | 9/5 | 12/4 | 47/2 | 33/3 | 1 vs 3,4 p<0.03 2 vs 3 p=0.028 |
| Phosphate, mmol/l | 1.57±0.16 | 1.51±0.11 | 1.54±0.06 | 1.87±0.08 | 4 vs 2, 3 p< 0.018 |
| Phosphate range, mmol/l <1.0 1.0 -1.8 ≥1.9 |
2 8 4* |
2 12 2* |
2 37 a 10 b, * |
0 18 a 18b, * |
a p=0.020 b p= 0.005 * 2+4 vs 1+3, p=0.057 |
| FGF 23, pg/ml | 140.75 (205) | 156 (165.7) | 1006 (1175) | 1500 (830) | 2 vs 3, 4 p< 0.0001 1 vs 3, 4 p< 0.004 |
| Fetuin A, ng/ml | 552.5(295) | 498 (162) | 326 (204) | 377 (193) | 1 vs 3, 4 p =0.001 2 vs 3, 4 p< 0.003 |
| B | OR | 95% CI for OR | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-HD group | ||||
| Fetuin-A | -0.0271 | -1.701 | -0.030- -0.024 | 0.001 |
| Sclerostin | 0.0023 | 1.463 | 0.002- 0.003 | 0.001 |
| Gender | -7.465 | -1.607 | -8.128- -6.803 | 0.000 |
| Age | 0.162 | 1.269 | 0.148-0.177 | 0.000 |
| Ferritin | -0.0048 | -0.252 | -0.007- -0.002 | 0.014 |
| Vit D treatment | -0.766 | -0.187 | -1.259- -0.274 | 0.022 |
| (Constant) | 0.236 | 0.263 | ||
| HD Group | ||||
| Sclerostin | 0.0005 | 0.389 | 0.000-0.001 | 0.012 |
| FGF 23 | 0.0015 | 0.315 | 0.000-0.003 | 0.036 |
| Urea | 0.193 | 0.446 | 0.069- 0.318 | 0.004 |
| iPTH | -0.0054 | -0.553 | -0.008- 0.003 | 0.001 |
| (Constant) | 10.908 | 3.295 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





