1. Introduction
Despite major advances in the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis, the incidence of coronary artery disease (CAD) is increasing in many regions of the world and is starting at an earlier age [
1,
2,
3,
4]. A significant percentage of younger patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) have premature CAD [
5,
6]. There is no universal definition of premature CAD [
3,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. Some authors have used an age cut-off of 45 years in men and 55 years in women [
11], whereas other authors have used the age cut-off of 65 years [
10]. Recently, an age cut-off of 50 years, for men, and 55 years, for women, has been suggested for defining premature CAD [
7,
10,
12,
13,
14].
Literature data indicate that premature CAD is present in around 30% of patients diagnosed with CAD [
11]. Patients with premature CAD are a population of particular concern because they may have a poor long-term outcome with a high likelihood for recurrence of the ischemic event [
1,
8,
15]. These patients generally have different risk factors, as compared to older patients (especially more frequent smoking, family history, and dyslipidemia), but also other so-called "unconventional" risk factors for coronary disease, such as psychosocial stress, obesity, use of psychoactive substances, etc. Also, more often than older patients, these patients have congenital or acquired disorders of hemostasis that can lead to arterial thrombosis and consequently to acute coronary syndrome (ACS) [
3,
5,
11,
15,
16,
17,
18].
Compared to elderly patients, younger patients (therefore, also patients with premature CAD) have a better prognosis after MI in terms of lower mortality, but it has often been reported that the occurrence of recurrent non-fatal ischemic events does not differ significantly, as compared to the population of older patients [
1,
6,
7,
8]. ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is more often the first manifestation of coronary disease in patients with premature CAD than is the case with the older population, where the first presentation of coronary disease is more often NSTEMI (non-STEMI) or unstable angina pectoris [
9]. Also, young patients with STEMI have a poorer prognosis, as compared to young patients with NSTEMI, especially in short-term follow-up [
19,
20]. Primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI) with stent implantation is currently considered the preferred treatment option for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) [
21]. Many of the earlier analyses dealing with the prognosis in patients with premature CAD and AMI also included patients with STEMI and NSTEMI, as patients who were not all treated with invasive procedures [
7]. To the best of our knowledge, so far, there are not many studies in literature that have analyzed the long-term prognosis of patients with STEMI who were treated with pPCI and who had premature CAD.
The aims of this study were: 1) to analyze and compare all-cause mortality and the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), during eight-year follow-up, in patients with STEMI and premature and non-premature CAD; 2) to define independent predictors for eight-year all-cause mortality and MACE in patients with premature CAD.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Study population, data collection, and definitions
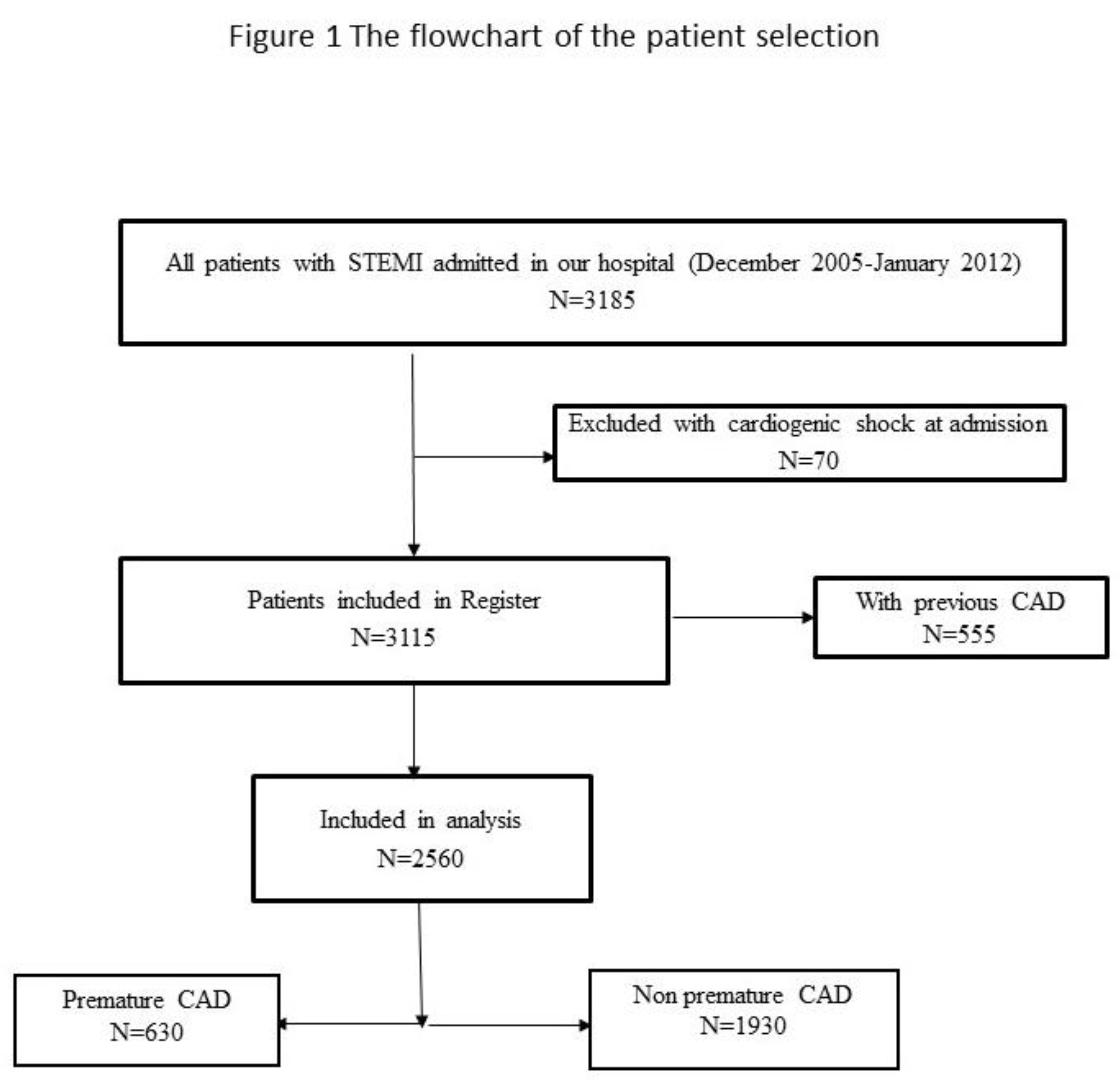
In the present study we included 2,560 consecutive patients without previous coronary artery disease (CAD), hospitalized between December 2005 and January 2012, who were included in the prospective University Clinical Center of Serbia STEMI Register. The purpose of the prospective University Clinical Center of Serbia STEMI Register has been published previously [
21].
The objective of the Register is to gather data on the management and short- and long-term outcomes of patients with STEMI, treated with primary PCI in the Center. All consecutive STEMI patients, aged 18 or older, who were admitted to the Coronary Care Unit after being treated with pPCI in the Center, were included in the Register. All included patients received written information of their participation in the Register and the long-term follow-up, and their verbal and written consent was obtained. Patients with cardiogenic shock at admission were excluded from the Register and, for the purpose of this study, we excluded patients with previous CAD. The flowchart of patient selection is presented in
Figure 1.
Coronary angiography was performed via the femoral approach. Primary PCI and stenting of the infarct-related artery (IRA) was performed using the standard technique. Loading doses of aspirin (300 mg) and clopidogrel (600 mg) were administered to all patients before pPCI. Selected patients were also given the GP IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitor during the intervention. Flow grades were assessed according to the thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) criteria. After pPCI, patients were treated according to the current guidelines.
Demographic, baseline clinical, laboratory, angiographic, and procedural data were collected and analyzed. Premature CAD was defined as the presence of CAD in men < 50 years and in women < 55 years. Echocardiographic examination was performed in the first three days after intervention (pPCI). The left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) was assessed according to the biplane method. We classified EF as preserved (EF ≥ 50%), moderately reduced (EF 40 – 49%), and reduced (EF < 40%). Baseline kidney function at admission was assessed using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease equation, and the value below 60 ml/min/m2 was considered as reduced kidney function. Obesity was defined as body mass index ≥ 30 kg/m2. Anemia was defined (according to the WHO criteria) as a baseline hemoglobin level below 120 g/l, in men, and below 110 g/l, in women.
Patients were followed-up at eight years after enrolment in the Register. Follow-up data were obtained through telephone interviews and at outpatient visits. We analyzed all-cause mortality and the composite endpoint- major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), which included cardiovascular death, non-fatal reinfarction, non-fatal ischemic stroke, and target vessel revascularization (TVR). The patients’ cause of death was obtained from death certificates or discharge forms (if the patient was hospitalized). Cardiovascular death included any death due to proximate cardiac cause (myocardial infarction, low-output heart failure, fatal arrhythmia, sudden death), and death caused by non-coronary vascular causes, such as cerebrovascular disease [
21]. Non-fatal recurrent myocardial infarction was defined according to the Fourth Universal Definition for Myocardial Infarction [
22]. Target vessel revascularization was defined as ischemia-driven percutaneous revascularization of the target vessel performed for restenosis or other complication. Stroke was defined as a new onset of focal or global neurological deficit lasting more than 24 hours. Computed tomography was used to diagnose (ischemic) stroke. The Emergency Hospital neurologist was responsible for the diagnosis and treatment of stroke [
21].
2.2. Ethics
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the University of Belgrade, Faculty of Medicine (approval number 470/II-4, February 21, 2008). The study was conducted in accordance with the principles set forth in the Helsinki Declaration. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients for their participation in the Register.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Categorical variables were expressed as frequency and percentage, while continuous variables were expressed as the median (med), with 25th and 75th quartiles (IQR). Analysis for normality of data was performed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Baseline differences between groups were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney test for continuous variables, and the Pearson χ² test for categorical variables. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for constructing the probability curves for eight-year mortality and the incidence of MACE, while the difference between patients with and without premature CAD was tested with the Log-Rank test. The Cox proportional hazard model (backward method, with p < 0.10 for entrance into the model) was used to identify univariable and multivariable predictors for the occurrence of eight-year all-cause mortality and MACE. Two-tailed p values of less than < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. We used the SPSS statistical software, version 19 for statistical analysis (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL).
3. Results
Of the 2,560 patients analyzed, 630 (24.6%) patients had premature CAD. The mean age of all analyzed patients was 59 (51, 68) years, the mean age of patients with premature CAD was 45 (41, 48) years, and the mean age of patients with non-premature CAD was 62 (57, 71) years. As compared with patients with non-premature CAD, patients with premature CAD had fewer comorbidities; they were more likely to be smokers, to have hyperlipidemia and family history of CAD; they presented less often with heart failure, atrial fibrillation and complete atrioventricular (AV) block; they had a shorter period of time from symptom onset to presentation at the hospital; they less often had multivessel disease on the initial coronary angiogram. Procedural characteristics did not differ among the analyzed groups. Pre-discharge EF was significantly higher in patients with premature CAD. Baseline characteristics, laboratory, angiographic, and procedural characteristics, in-hospital mortality, and therapy at discharge, in patients with and without premature CAD, are presented in
Table 1.
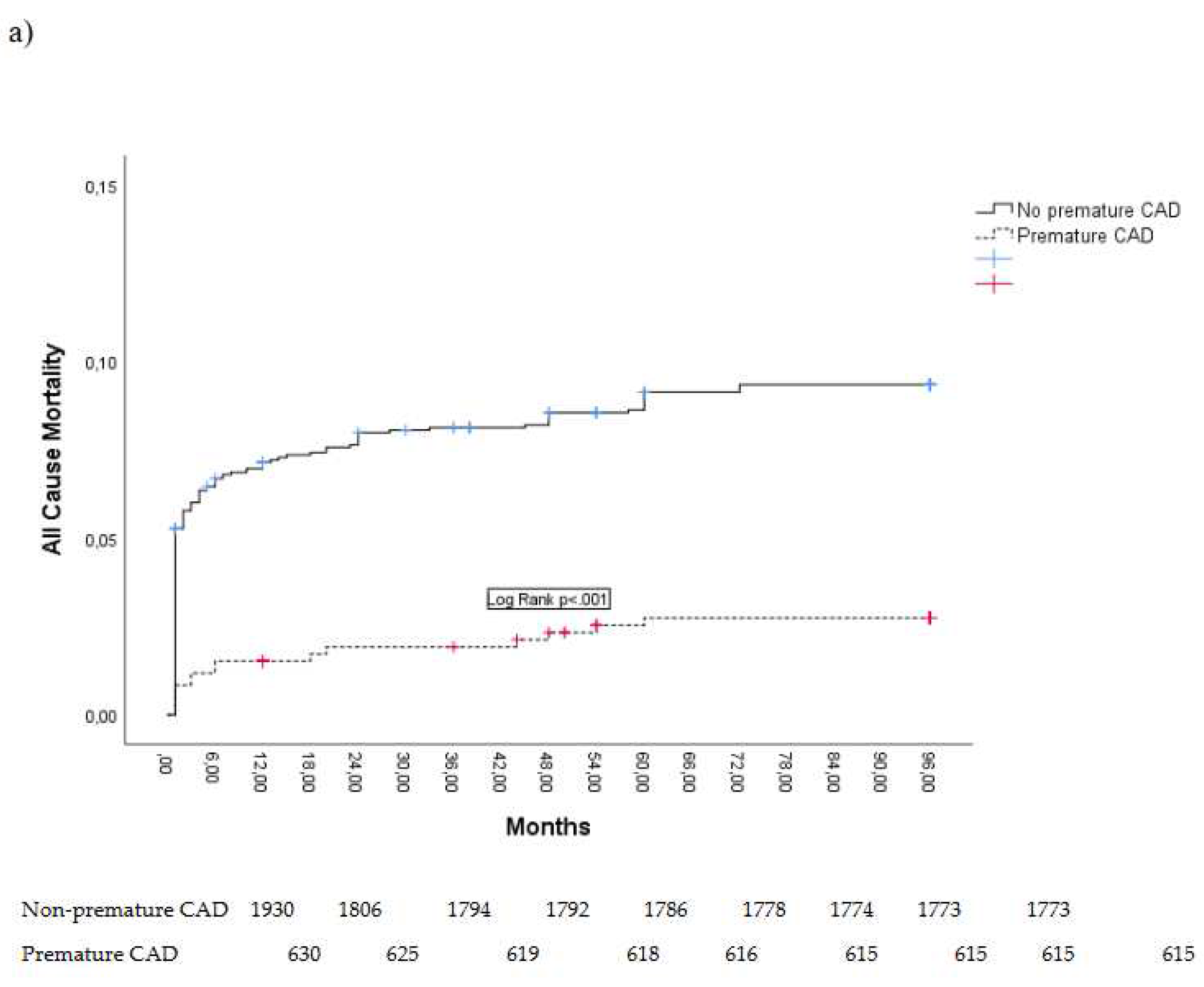
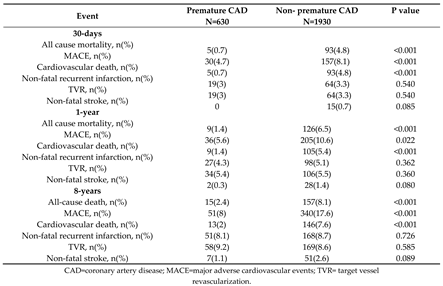
At eight-year follow-up, all-cause mortality and MACE were registered in a total of 172 (7.3%) patients and 391 (15.2%) patients, respectively. Causes of mortality were predominantly cardiovascular, while non-cardiovascular causes of death (cancer, ileus, pneumonia) were registered in a total of 13 patients (5.1% of all deaths).
Patients with premature CAD had lower all-cause mortality and lower composite endpoint MACE. Non-fatal recurrent infarction was related to a new lesion site in 39 (66.6%) patients with premature CAD and in 79 (46.7%) patients with non-premature CAD, p = 0.001.
All-cause mortality and MACE in patients with premature CAD and in patients with non-premature CAD are presented in
Table 2.
Kaplan Meier curves showing eight-year all-cause mortality and MACE are presented in
Figure 2.
After adjustment for confounders, premature CAD was associated with lower rates of all-cause mortality and MACE in eight-year follow-up. This is presented in
Table 3.
Independent predictors for eight-year all-cause mortality and MACE in patients with premature CAD are presented in
Table 4.
4. Discussion
Our results of the analysis of the STEMI Register showed about a ¼ of patients with premature CAD. Patients with premature CAD have significantly fewer comorbidities and better initial angiographic findings, as compared to patients without premature CAD. During eight-year follow-up, mortality and composite endpoint MACE were significantly lower in patients with premature CAD, as compared to patients with non-premature CAD. The incidence of non-fatal recurrent ischemic events was not significantly different between these two groups of patients. In patients with premature CAD, only EF < 40% was an independent predictor of all-cause mortality and MACE during eight-year follow-up.4.1. The incidence and risk factors of premature CAD
The percentage of patients with premature CAD in our study is in keeping with the data from literature, which states that the percentage of patients with premature CAD ranges between 20% and 30%, depending on the analyzed patient population, as well as the age cut-off used for defining premature CAD [
7,
9,
10,
11,
16]. Since it is known that CAD generally occurs later in women, we used a different age cut-off for defining premature CAD in men and women, in our analysis [
7,
12,
13]. In our population of patients with premature CAD, 25% of the patients were women, which is in keeping with data from literature, where the reported percentage of women with premature CAD is around 20% – 30% [
7,
23]. A higher prevalence of smoking, hyperlipidemia, and existing family history of coronary disease in patients with premature CAD, and fewer comorbidities (primarily diabetes mellitus, hypertension, CKD) is also a common finding in all analyses dealing with these patients [
2,
6,
7].
4.2. Prognosis in patients with premature CAD
The relatively small number of studies analyzing patients with STEMI treated with primary PCI who have premature CAD makes it difficult to directly compare our results with those of other authors. It is well known that older age is one of the most important predictors of ACS outcomes, i.e., that younger age is a predictor of a more favorable prognosis [
6,
7,
19]. However, we should not forget that myocardial infarction in (young) patients with premature CAD is an aggressive disease with a relatively high rate of recurrence [
10].
In a study by Pinxterhuis et al., patients with premature CAD and the first presentation of coronary disease – STEMI and/or NSTEMI, were analyzed. In this study, it was found that premature CAD is a predictor of favorable prognosis during two-year follow-up, but also that the occurrence of non-fatal recurrent ischemic events does not differ between the group with premature CAD and the group without premature CAD [
7], which is identical to our findings.
The results of a study by Lv et al., which presents an analysis of data from the register of patients with STEMI and NSTEMI are similar. Significantly lower mortality and occurrence of MACE was found during two-year follow-up in patients aged ≤ 45 years, as compared with patients aged > 45 years. The incidence of non-fatal recurrent infarction did not differ between the two analyzed groups. Also, there was a "tendency" towards a lower incidence of non-fatal ischemic stroke in patients aged ≤ 45 years [
6].
In an analysis of the Norwegian Myocardial Infarction Registry, it was found that the rate of AMI was low amongst people < 45 years old, however, almost one in ten of these patients experienced a new cardiovascular event, while 4% of patients died during the 2.4 years of follow-up [
23]. In our study, the percentage of mortality and occurrence of MACE is lower, as compared to the analysis of this registry, and the differences are probably due to the different patient population that was analyzed (STEMI/NSTEMI), as well as the differently defined age cut-off.
In a prospective register analysis by Wittlinger et al., patients with STEMI and NSTEMI were included. In this study, younger patients under the age of 40 years had a better two-year survival, as compared to those older than 40 years, and the highest number of deaths occurred in the first 10 days after the initial event. In our study as well, the highest percentage of adverse events occurred in the first days/months of follow-up. However, unlike our study, this study also included patients with STEMI who were treated with both thrombolysis and rescue PCI [
3].
In a study by Noaman et al., data from the register of patients who underwent PCI due to chronic and acute coronary syndrome were analyzed. Patients younger than 45 years had a lower twelve-year mortality, as compared to middle aged (46 – 65 years) and elderly patients (> 65 years). The age of < 45 years was an independent predictor of better long-term survival, as compared to middle age (46 – 65 years) [
19].
The results of a study by Yang et al. analyzing young patients with MI showed no difference in one-year outcome and long-term mortality (more than 11 years), between patients younger than 40 years and patients aged 40 – 51 years [
16]. However, the fact remains that this study was generally focused on young patients, i.e., patients with premature CAD. In our study, as well, in the subgroup of patients with premature CAD, age was not a predictor of eight-year mortality and MACE.
In a study analyzing patients with premature CAD who underwent their first PCI due to STEMI or NSTEMI, it was found that patients with premature CAD had lower mortality, but a higher incidence of stent thrombosis and repeat revascularization than patients with non-premature CAD during three-year follow-up [
13]. In our study, the incidence of non-fatal adverse ischemic events during follow-up did not differ between the analyzed groups of patients, while the cause of non-fatal recurrent infarction in our patients was predominantly the appearance of new lesions in the coronary arteries, which was more frequent in comparison with patients with non-premature CAD.
According to the available literature data, up to 30% of younger patients develop new ischemic events after ACS in the first five years of follow-up, i.e. before the age of 60, and angiographic findings show that most often new lesions are found in the coronary arteries, which is different from the older population [
1,
8].
4.3. Independent predictors of mortality and MACE in patients with premature CAD
Predictors of mortality and of the occurrence of MACE in younger patients with ACS (which also include patients with premature CAD) differ depending on the study method, i.e., patient selection, as well as the type of ACS: STEMI, NSTEMI, or unstable angina [
6,
19,
24]. Our finding that reduced EF is an independent predictor of mortality and MACE in patients with premature CAD is in concordance with the findings of studies that analyzed the prognosis in younger patients (which also includes patients with premature CAD).
In the study by Lv et al., EF, creatinine level, and education level were independent predictors of two-year mortality in AMI patients aged ≤ 45 [
6]. In the study by Noaman et al., it was found that independent predictors of twelve-year mortality in patients aged ≤ 45 years with acute coronary syndrome are the following: poor angiographic findings, LM coronary intervention, severe CKD, EF < 30%, chronic lung disease, and diabetes mellitus [
19]. Unlike our study, in the cited study there were only 40% of patients with STEMI [
19], and patients with earlier CAD were also included, which can explain the differences in the results. In a study by Liang et al. in which patients with STEMI were analyzed, it was found that only diabetes mellitus was an independent predictor of thirty-month occurrence of MACE in patients younger than 45 years [
18]. In this study, only demographic characteristics, risk factors and angiographic findings were analyzed, and echocardiographic parameters were not presented/analyzed [
18].
4.4. Clinical implications
The results of our study can supplement existing knowledge regarding the prognosis in patients with STEMI, caused by premature CAD, who were treated with primary PCI. The prognosis of patients with premature CAD, although more favorable than the prognosis of older patients, is still not completely favorable and the occurrence of recurrent non-fatal myocardial infarction, caused predominantly by new lesions in the coronary arteries, indicates that more aggressive secondary prevention of coronary disease is necessary, as well as more frequent follow-up during monitoring, so as to improve the prognosis, and thus the quality of life [
1,
5,
10,
11,
19,
24]. In certain patients, investigation is indicated, in terms of the existence of congenital and acquired thrombophilic conditions [
7]. EF is the measure most commonly used to assess left ventricular systolic function. It is well known that EF is one of the most important predictors of prognosis after STEMI, and patients with reduced EF have a significantly worse prognosis, as compared to patients with preserved EF [
25]. The main reason for ventricular remodeling and reduced left ventricular systolic function (i. e. reduced EF) in patients with STEMI is the large zone of myocardial ischemia that leads to the necrosis of cardiomyocytes. Establishing normal blood flow through the infarcted artery (with primary PCI or less often with thrombolytic therapy) leads to a reduction in the myocardial necrotic zone and improves LV function and decreases LV remodeling [
26,
27]. Myocardial stunning is another mechanism that can cause left ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients treated with successful and timely reperfusion therapy (TIMI flow 3 through infarct-related artery). Myocardial necrosis and stunning lead to subsequent myocardial inflammation, hypertrophy, and fibrosis. In adition, different neurohumoral (such as renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, sympathetic system, etc) and mechanical changes contribute to decreasing in the systolic function of the left ventricle [
26,
28]. Before discharge from hospital, and especially during follow-up, special attention should be paid to young patients with premature CAD and reduced EF. In these patients, apart from secondary prevention of coronary disease, it is extremely important to include and titrate up to the target doses of therapy as early as possible, as this has proven to have a favorable effect on the prognosis in the presence of reduced EF after myocardial infarction [
28].
4.5. Study limitations
A number of limitations to our study should be mentioned. The study is unicentric, observational, but it is controlled, prospective, and has included consecutive patients. This can limit possible selection bias. Patients included in the study were hospitalized between 2005 and 2012. Patients with cardiogenic shock at admission were excluded from our Register. All patients were treated with clopidogrel. There were no patients treated with more recently developed antiplatelet drugs (ticagrelor and prasugrel were not available for routine administration to patients at the time of their entry into the Register). This may have influenced the patients’ prognosis, i.e. reduced the occurrence of cardiovascular mortality or the incidence of non-fatal ischemic events. Coronary angiography and concomitant PCI were performed via the femoral approach. The radial approach was not used in routine clinical practice at the time of the patients’ enrollment into the Register. We did not analyze "unconventional" risk factors for coronary disease in patients with premature CAD (congenital or acquired thrombophilia); the presence of menopause in women, the possible use of hormone replacement therapy, socioeconomic status, as well as possible substance abuse in patients with premature CAD [
10]. There are no data on follow-up echocardiographic examinations to show whether there has been a certain degree of recovery or deterioration in the myocardial contractility. The study was not designed to evaluate whether changing pharmacological treatment during follow-up would have an impact on long-term outcome in the analyzed patients.
5. Conclusion
About 25% of the analyzed patients with STEMI had premature CAD. As compared with older patients, those with premature CAD had lower eight-year mortality and MACE. The incidence of non-fatal adverse ischemic events was similar to the incidence in older patients. Recurrent non-fatal myocardial infarction in patients with premature CAD was predominantly caused by the appearance of new lesions in the coronary arteries. In patients with premature CAD, only EF < 40% was an independent predictor of eight-year all-cause mortality and MACE. These findings indicate the great importance of the need for secondary prevention of coronary disease in patients with premature CAD, as well as early inclusion and titration to target doses of therapy, which has proven to have a beneficial effect on prognosis in the presence of reduced EF after myocardial infarction.
Author Contributions
LS and IM devised the study and participated in its design, acquisition of data and coordination. LS performed statistical analysis. MA, SS, GK, RL, DM, and DS participated in the design of the study and helped draft the manuscript. All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the ethics committee of the University of Belgrade, Faculty of Medicine (approval number 470/II-4, February 21, 2008).
Disclosure statement
The authors report that there are no competing interests to declare.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the physicians and nurses of the Coronary Unit and the Catheterization Laboratory who participated in the primary PCI program.
References
- Collet JP, Zeitouni M, Procopi N, Hulot JS, Silvain J, Kerneis M, et al.; ACTION Study Group. Long-Term Evolution of Premature Coronary Artery Disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;74(15):1868-78. [CrossRef]
- Bugiardini R, Badimon L; ISACS-TC Investigators and Coordinators. The International Survey of Acute Coronary Syndromes in Transitional Countries (ISACS-TC): 2010-2015. Int J Cardiol 2016;217:S1-6. [CrossRef]
- Wittlinger T, Seifert C, Simonis G, Gerlach M, Strasser RH. Prognosis in myocardial infarction of young patients: Results of a prospective registry. Int J Cardiol 2020;300:1-6. [CrossRef]
- Vasić A, Vasiljević Z, Mickovski-Katalina N, Mandić-Rajčević S, Soldatović I. Temporal Trends in Acute Coronary Syndrome Mortality in Serbia in 2005-2019: An Age-Period-Cohort Analysis Using Data from the Serbian Acute Coronary Syndrome Registry (RAACS). Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 4;19(21):14457. [CrossRef]
- Arora S, Stouffer GA, Kucharska-Newton AM, Qamar A, Vaduganathan M, Pandey A, et al. Twenty Year Trends and Sex Differences in Young Adults Hospitalized With Acute Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2019;139(8):1047-56. [CrossRef]
- Lv J, Ni L, Liu K, Gao X, Yang J, Zhang X, et al. Clinical Characteristics, Prognosis, and Gender Disparities in Young Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Aug 12;8:720378. [CrossRef]
- Pinxterhuis TH, Ploumen EH, Doggen CJM, Hartmann M, Schotborgh CE, Anthonio RL, et al. First myocardial infarction in patients with premature coronary artery disease: insights into patient characteristics and outcome after treatment with contemporary stents. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care 2023;12(11):774-781. [CrossRef]
- Smith CL, Seigerman M, Adusumalli S, Giri J, Fiorilli PN, Kolansky DM, et al. Evolution and Outcomes of Premature Coronary Artery Disease. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2021 Mar 8;23(4):36. [CrossRef]
- Sharma SK, Makkar JS, Bana A, Sharma K, Kasliwal A, Sidana SK,et al. Premature coronary artery disease, risk factors, clinical presentation, angiography and interventions: Hospital based registry. Indian Heart J 2022;74(5):391-7. [CrossRef]
- Rallidis LS, Xenogiannis I, Brilakis ES, Bhatt DL. Causes, Angiographic Characteristics, and Management of Premature Myocardial Infarction: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol 2022;79(24):2431-49.
- Khoja A, Andraweera PH, Lassi ZS, Ali A, Zheng M, Pathirana MM, et al. Risk Factors for Early Versus Late-Onset Coronary Heart Disease (CHD): Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Heart Lung Circ. 2023 Sep 28:S1443-9506(23)04288-9. [CrossRef]
- Abderrahman HA, Al-Abdallat IM, Idhair AK. Age threshold for proper definition of premature coronary artery disease in males. J Forensic Leg Med 2018;58:45-49. [CrossRef]
- Pinxterhuis TH, Ploumen EH, Zocca P, Doggen CJM, Schotborgh CE, Anthonio RL, et al. Impact of premature coronary artery disease on adverse event risk following first percutaneous coronary intervention. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Sep 7;10:1160201. [CrossRef]
- Vikulova DN, Grubisic M, Zhao Y, Lynch K, Humphries KH, Pimstone SN, et al. Premature atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: trends in incidence, risk factors, and sex-related differences, 2000 to 2016. J Am Heart Assoc. (2019) 8(14):e012178. [CrossRef]
- Gulati R, Behfar A, Narula J, Kanwar A, Lerman A, Cooper L, et al. Acute Myocardial Infarction in Young Individuals. Mayo Clin Proc 2020;95(1):136-56. [CrossRef]
- Yang J, Biery DW, Singh A, Divakaran S, DeFilippis EM, Wu WY, et al. Risk Factors and Outcomes of Very Young Adults Who Experience Myocardial Infarction: The Partners YOUNG-MI Registry. Am J Med 2020 ;133(5):605-12. [CrossRef]
- Malakar AK, Choudhury D, Halder B, Paul P, Uddin A, Chakraborty S. A review on coronary artery disease, its risk factors, and therapeutics. J Cell Physiol 2019;234(10):16812-23. [CrossRef]
- Liang MT, Pang Y, Gao LL, Han LJ, Yao HC. Clinical risk factors and outcomes of young patients with acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction: a retrospective study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Jul 17;23(1):353. [CrossRef]
- Noaman S, Dinh D, Reid CM, Brennan AL, Clark D, Shaw J, et al. Comparison of Outcomes of Coronary Artery Disease Treated by Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in 3 Different Age Groups (<45, 46-65, and >65 Years). Am J Cardiol 2021;152:19-26. [CrossRef]
- Biswas S, Andrianopoulos N, Papapostolou S, Noaman S, Duffy SJ, Lefkovits J, et al. Does the subtype of acute coronary syndrome treated by percutaneous coronary intervention predict long-term clinical outcomes? Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes 2018;4: 318-27. [CrossRef]
- Mrdovic I, Savic L, Lasica R, et al. Efficacy and safety of tirofiban-supported primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients pretreated with 600 mg clopidogrel: results of propensity analysis using the clinical center of serbia STEMI register. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2014;3(1):56–66. [CrossRef]
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Chaitman BR, Bax JJ, Morrow DA, White HD; ESC Scientific Document Group. Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018). Eur Heart J 2019;40(3):237-269. [CrossRef]
- Jortveit J, Pripp AH, Langørgen J, Halvorsen S. Incidence, risk factors and outcome of young patients with myocardial infarction. Heart 2020;106:1420–26. [CrossRef]
- Zheng R, Liu Y, Hao Z, Liao H, Xiao C. Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis of Young Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jul 1;26:e922957. [CrossRef]
- Savic L, Mrdovic I, Asanin M, Stankovic S, Krljanac G, Lasica R. Prognostic impact of renal dysfunction on long-term mortality in patients with preserved, moderately impaired, and severely impaired left ventricular systolic function following myocardial infarction. Anatol J Cardiol 2018;20(1):21-8. [CrossRef]
- Elgendy IY, Mahtta D, Pepine CJ. Medical Therapy for Heart Failure Caused by Ischemic Heart Disease. Circ Res. 2019 May 24;124(11):1520-1535. [CrossRef]
- Ng VG, Lansky AJ, Meller S, Witzenbichler B, Guagliumi G, Peruga JZ, et al. The prognostic importance of left ventricular function in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction:the HORIZONS-AMI trial. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2014;3:67–77. [CrossRef]
- Byrne RA, Rossello X, Coughlan JJ, Barbato E, Berry C, Chieffo A, et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J 2023;44(38):3720-826. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).