INTRODUCTION
Nurses are expected to be competent in practice based on ethics-legal, professional nursing, leadership-management, education-research,professional, personal and quality development in the era of globalization (Affara, 2009). Able to apply interpersonal soft skill as team work, leadership, interpersonal communication, discipline, self-confidence, honesty, ethical thinking, problem solving and adapting (Nursalam. Efendi, 2012 and Harmon, 2021). The placement of human resource is less evenly distributed in both number, composition and productivity (Cassiani et al., 2018), lack of knowledge and rejecting changes in nursing care (Camargo et al., 2018).
Hospital Nacional Guido Valadares (HNGV) Dili, nurses have misbehaved in patients (MONIZ, 2020), less responsible (Cote, 2014) in nursing practice (Rohi, 2019), (Price et al., 2016) and (Hou et al., 2016). Angry, yelling, rude to patients in Baucau (Bedford, 2014), patient hygiene is less important (Price et al., 2016), lack of ethics (Bertone et al., 2018), interpersonal communication (Rohi, 2019) and application of clinical skills (Luan et al., 2020). The use of Information Communication Technology (ICT) in learning is still lagging behind in Timor-Leste (Superhighway dan Paper, 2019). Interpersonal soft skills (ISS) learning digital-based model does not yet exist, so the division of nurse competency boundaries is not clear and not in accordance with ASEAN standards (Yupin Aungsuroch, 2015). Instituto Nacional de Saúde (INS) Timor-Leste was provide training in management, clinicals, communication, ethics and research to improve quality and efficiencies of services (Superhighway dan Paper, 2019), but the problem has not been resolved, due to the lack of clarity of learning standard. It is necessary to develop a suitable clinical learning model to ensure the quality of services (Caporiccio et al., 2019).
Data on 443 (20%) health workers (175 doctors, 150 nurses and 118 midwives) in Timor-Leste in Community health centers and hospitals showed that learning opportunities were not adequate 52%, physical assessment skills were 28% and average performance scores were 65% (Hou et al., 2016). The ability of HNGV nurses to do assessment 15 (47%), diagnoses 18 (56%), plan 11 (34%), implementation 10 (31%), evaluation 12 (37,5%) and 13 (41%) communication skills are still lacking (Rohi, 2019). Implementation clinical management-leadership 50%, ethics-right of the patients 27%, patient security and safety in HNGV 28% (Carter, 2020).
Factors of learning, culture, social environment support, facilities, ethical dimension, aesthetics, existence and technical greatly influence the application of nurse competence in achieving the perspective quality of nursing care (Moradi et al., 2019) and (Campbell-Voytal, 2010), use of ICT for communicating in nursing services (College of Nurses of Ontario, 2019). Therefore, nurses need to learn throughout life to prepare better skills, knowledge and attitudes in era of technological change and the professional development (Bartosiewicz et al., 2019). Develop of ISS learning model based TLTD can improve the competencies (Honkavuo, 2020).
Four stages apply in implementation are: pre-test, conventional learning, digitaly learning and post-test. A learning model to maintain collaboration-coordination of partisipants and facilitators were believed to creat positive changes in nurse competence. Competent nurses in the application of knowledge, skills, behaviors and creating environmentally friendly nursing services through digitalization learning (Steppingstones Partnership Inc.,2018). Current study aimed to develop an ISS learning model based on TLTD towards improving nurse competencies.
MATERIAL AND METHODE
Study Design: Design was used Explanatory research with cross sectional approach and adapted the STROBE Statement-Checklist specialy for Cross-Sectional model (Intarached & Chunuan, 2023).
Population, Sample and Sampling: The population consisted of 272 nurses practicioner who work at inpation room in HNGV Dili, Hospital Regional Eduardo Ximenes (HoREX) Baucau and Hospital Referal (HR) Maliana Timor-Leste. The sample was being nurse’s practitioner with the size selected technique was used the Rule of the Thumb: 5-10 x total indicators, and calculated: 5 x 38= 190 respondents and used simple random sampling. The inclusion chraiteria was: 1) Nurses practicioner in basic nursing education, 2) Nurse with civil service and contract status, 3) The work duration is at least 1 year, 4) Able to be respondents. Exlcusion chraiteria are: 1) Nurses who are on education, annual and maternity leave, 2) Physically-psychologically ill, 3) Working in administration unit.
Instruments: Questioner was composite by six types are: 1) Individual characteristic 16 item questions, 2) learning facilities 12 items, 3) social environment support 6 items, 4) TLTD 35 items, 5) ISS 31 items and 6) nurse competencies 37 items. Question was scored by a likert scale 1 to 5 were validity and reliability tested with SEM-PLS softwere.
Procedur: Author was conducted meeting with hospitals executive director to ask the permission to start data collection activities. Data was collected at three hospitals during 6 June to 10 August 2022, with 20 to 30 minutes for each responden to completed the checklist.
Data analysis: Was make clearning, codeing, entering the data to the computer and than analysis with Smart PLS for descriptive and inferential analysis to access the outer model, inner model and hyphotesis.
Ethical consideration: Ethical clearance was provided by Ethical committee from Instituto Nacional de Saúde (INS)-MoH Timor-Leste with RN.863 MS-INS/DE/V/2022, Dili, 31/05/2022. Researcher also was goted licencing by all hospital executive directors for access to nurses for take part in the study. Researcher was provided basic introduction about team compotition, objectives, duration and data collection mechanism to the participants and giving inform consent for signature requerment.
RESULT
1. Overview of Research Locations:
The result indicated that HNGV were located in Dili. It is still not clearly visible the professional nursing practice, standards of practice, management, research and educators. HoREX Baucau is Regional hospital, is lack of the ability of nurse’s care conducting based on standard, not been free to carry out nursing care, always depending on the instructions only. HR Maliana indicated that more of them perform collaborative functions only (ex. giving medicine), not conducting and using research finding in carrying out nursing care, room management is not clear so affected to the quality of care.
2. Individual character
In
Table 1 of 190 respondents with age 81.8% were young adults:25-49 years old, 67.9% female, education was a Bachelor’s degree 57.8% and 35% rated previous training as unsuccessful and 45.8% said previous learning did not live up to expectations.
3. Learning facilities
The results of the study in
Table 2 on 190 respondents mentioned that policy 23.7%, curriculum 23.4%, guideline 22.7%, module 27,9% and infrastructure 20,3% is still low.
4. Social environmental support factors
Based on the
Table 3 that 24.2% organizational support and peer support for nurses to keep up with learning 30,0% stated was still low. Family support 26,3% is low.
5. Frequency of TLTD in learning
Above
Table 4 respondents stated that the development of self-reflection 38,4% high, strategy for critical reflection 44,7% high, supportive social environment 44,2% high, use of art, literature, film and drama 42,1% high, holistic, affective and spiritual processes 42,1% applied in previous training is still high. Basic skills of using computers 45,8%, internet 52,1%, smartphones 50,0% and reference search techniques 48,4 is already high.
6. Frequency of ISS in learning
Based on
Table 5, all indicators are already high; Teamwork 62,1%, leadership 54,2%, communication skill 56,3%, discipline in service 54,7%, confidence 52,6%, honesty 55,8%, ethical thinking 53,2%, problem-solving ability 52,6% and adaptability 53,7% high.
7. Description of Nurses competencies
Based of the
Table 6 above, indicated majiroty of indicators is already high: ethical and legal nursing practice 52,1%, Professional nursing practice 45,8%, leadership-management 37,9%, education and research 36,8%, professional, personal and quality development 51,1%. But also more mentioned that have categorized in low.
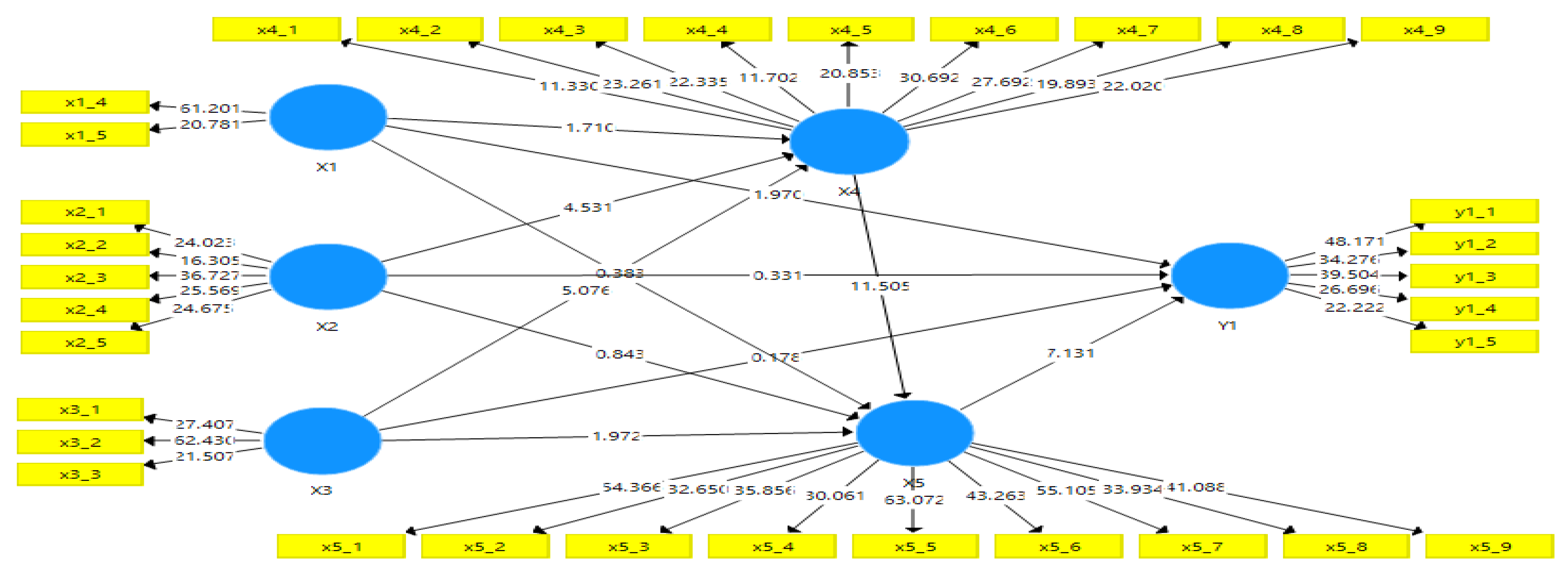
Outer Model: The analysis outer model intends to find out whether the indicator is valid to explain the latent variables in the study included: convergent validity, discriminant validity and reliability. The rule to read the test results is that if the loading factor (Outer loading) value > 0.05 it is mean the existing indicator is valid to explain the construct on the latent variable and if Cross loading value > 0.05 then it is mean the existing indicator is valid to explain the construct/latent variable. In the significance aspect test, if it appears that the statistical t value of the existing indicator > 1.96, it is mean significant.
Based on
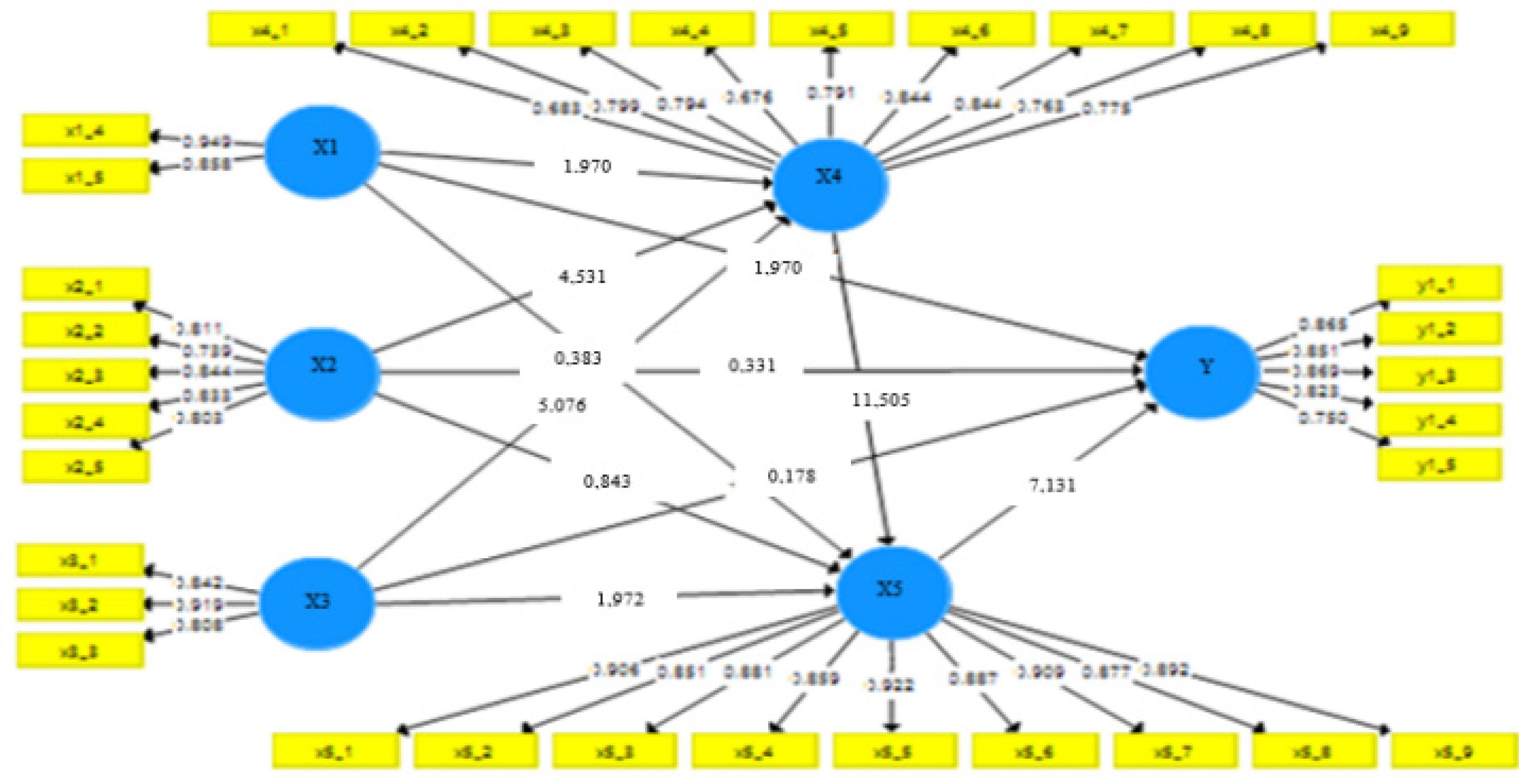
Figure 1 above the majority of existing indicators have an outer loading value greater than 0.05 but there are 5 indicators less than 0.05 (age factor X1.1), gender (X1.2), education level (X1.3), experience (duration) of work (X1.6) and location of work (X1.7), then these 5 indicators are excluded from the latent variable X1. After issuing the indicators mentioned above, further test results are as
Figure 2 follows.
1) Convergent validity
Table 7.
Convergent validity values June 2022 (N=190).
Table 7.
Convergent validity values June 2022 (N=190).
| |
Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
|
Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
| (X1) |
0.818 |
(X4) |
0.603 |
| (X2) |
0.651 |
(X5) |
0.787 |
| (X3) |
0.735 |
(Y1) |
0.693 |
Convergent validity above variables, all indicators already have outer loading and cross loadig values > 0.05. However, it met the requerments capable of effectively describing laten constructs of variables and better to be used in conducting further analysis in the development of soft skill learning models.
2) Discriminant validity
Table 8.
Description of the Discriminant Validity values for respondents, June 2022 (N=190).
Table 8.
Description of the Discriminant Validity values for respondents, June 2022 (N=190).
| |
X1 |
X2 |
X3 |
X4 |
X5 |
Y1 |
| X1: Individual character |
0.905 |
0.905 |
0.905 |
0.905 |
0.905 |
0.905 |
| X2: Learning facilities |
0.453 |
0.807 |
0.807 |
0.807 |
0.807 |
0.807 |
| X3: Social environmental support factor |
0.371 |
0.683 |
0.858 |
0.858 |
0.858 |
0.858 |
| X4: Transformative Learning Theory and Digitization (TLTD) |
0.422 |
0.689 |
0.677 |
0.777 |
0.777 |
0.777 |
| X5: Interpersonal soft skills learning |
0.284 |
0.500 |
0.424 |
0.710 |
0.887 |
0.887 |
| Y1: Nurses competence |
0.293 |
0.365 |
0.297 |
0.531 |
0.614 |
0.833 |
Discrimant validity outor loading values X1, X2, X3, X4, X5 and Y1 > of the cross loading values. The Heterotrait-Monotrait Ratio (HTMT) is values from all variables < 0.90. This means that the root of the AVE value: high validity and the AVE root value of each variable must be greater than the next latent variable. The root value of AVE meeting X1-X1: 0.905, X3-X3: 0.858, X2-X2: 0.807, X5-X5: 0.887, X4-X4: 0.777 and Y1-Y1: 0.833. It is all mean that discriminant validity value is already good or better.
Based on the above
Table 9 indicated that the analysis results of Cronbach’s Alpa, Composite Reliability, rho-A reliability indicated that 6 variables worth more than 0.7, it means all variables is reliable to be used and meet internal consistency. Variables also have an AVE value of more than 0.5 which means that the variable is valid convergent.
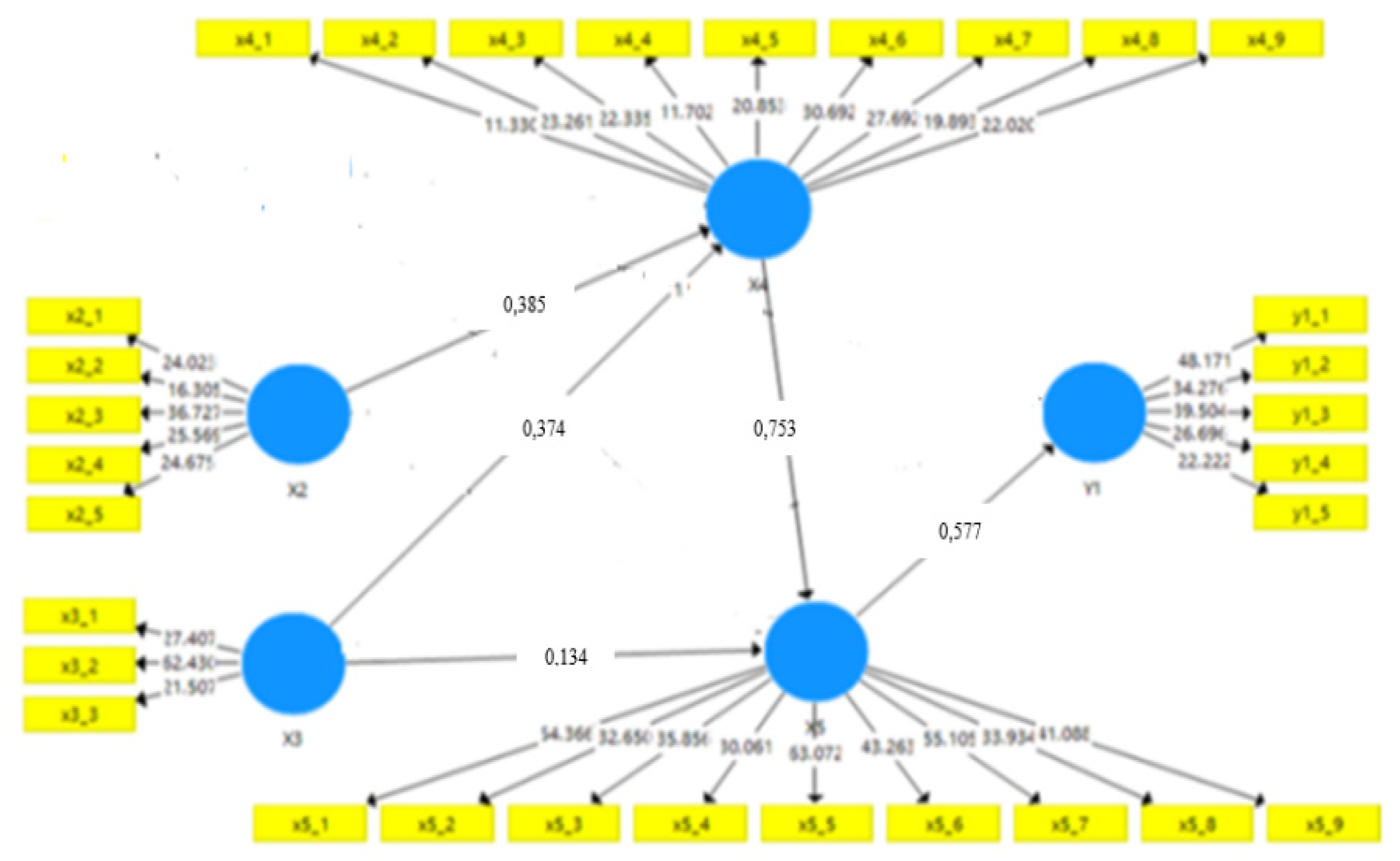
Figure 3.
Coefficients of determination (R2 /R Square).
Figure 3.
Coefficients of determination (R2 /R Square).
b. Inner Model
Structural model analysis (Inner model) that connects latent variables with the aim of assessing the goodness of fit through the following three ways:
1) Coefficients of determination (R2/R Square)
The coefficient of determination (R2/R Square) used to find out how much the contribution or strength of the exogenous variable is to the endogenous variable which is a force explaining the model that R2 overcomes as the predictive power in a sample. R2 values range from 0 to 1, which uses guidelines i.e., R2 values of 0.75, 0.50 and 0.25 can be considered substantial, medium and weak.
In the
Table 10 above shows that the three endogenous variables have a coefficient of determination (moderate). Where these three variables are already worthy of further use in building this research path model. R Square (R2) value in latent variavel TLTD (X4) with a value of 0.56 or 56.0%, it is mean that the TLTD variable can be decomposed by individual, facility and social environment support factors that have been available by 56.0% and the remaining 44.0% is a contribution from other variables that are not included in the model. R Square value (R2) on the latent variable ISS (X5) with a value of 0.51 or 51.0%. It can be explained that the variation of individual, facility and social environment support factors and TLTD variables contributed to the ISS learning variables by 51.0% and the remaining 49.0% contribution from other variables. R Square (R2) value on the Nurse Competency variable (Y1) of 0.39 (39.0%). Remaining 61.0% contributed other variables that were not studied. This means that variations of individual, facility, social environment support factors, ISS learning variables contributed to nurse competency variables by 39.0%.
2) Predictive relevance
Table 11 shows that the Q2>0 values, it means that ISS learning model based on TLTD is of medium predictive relevance and the model is already worth using in the study. Predictive relevance is tested through Blindfolding calculations which aims to assess the predictive relevance level of this structural model. Where viewed from the value of Q Square (Q2), which states that if the value of Q2 > from 0, then the configuration model is already relevant, (Hair et al., 2019). The rule of interpretation of the value of Q2, if the value of Q2 is 0 (a small predictive relevance), Q2 0.25 (medium predictive relevance) and Q2 0.50 (large predictive relevance) of the composed path model.
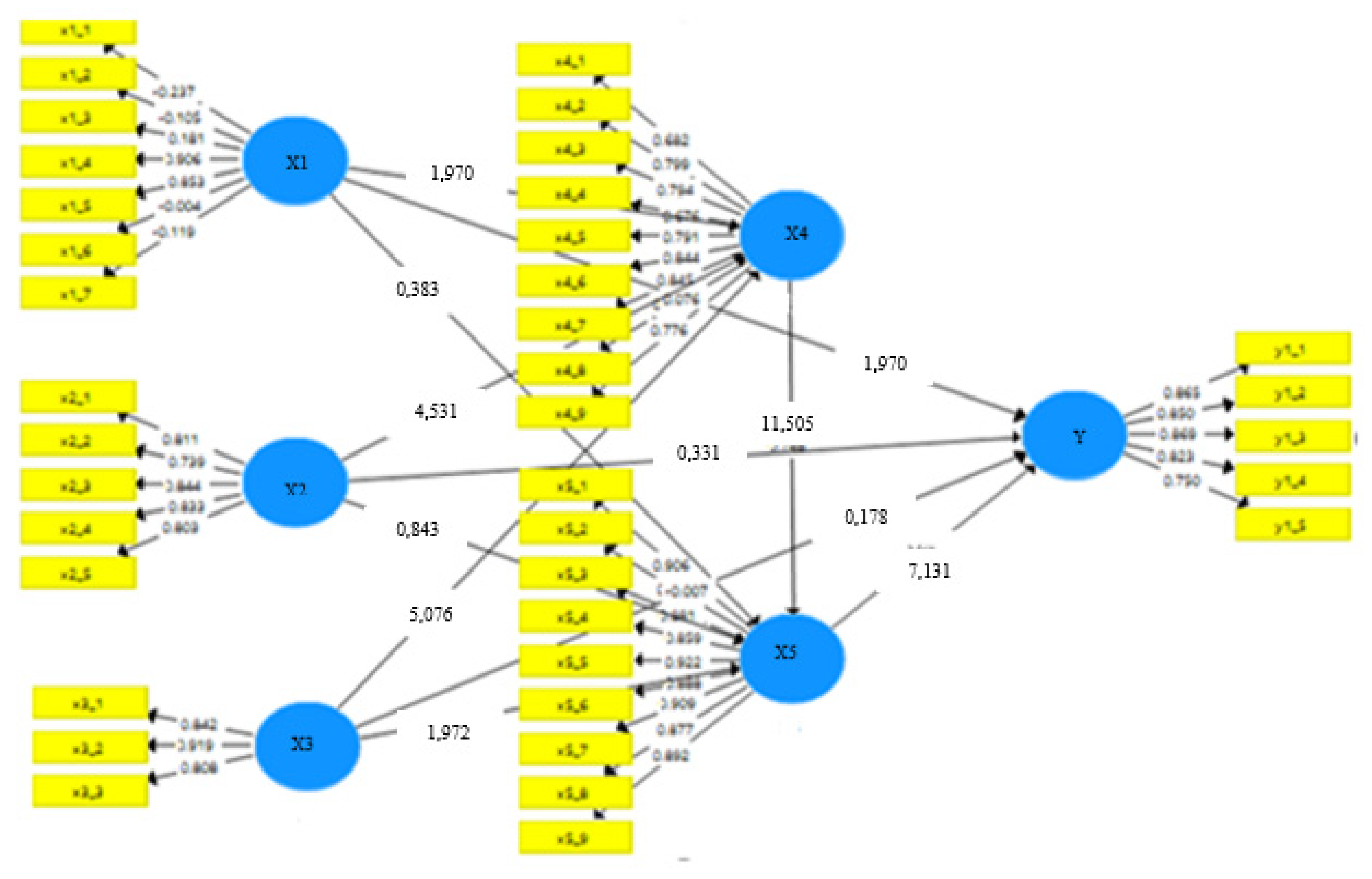
3) Hypothesis test
Table 13.
Hypothesis test results.
Table 13.
Hypothesis test results.
| |
Original Sample (O) |
Sample Mean (M) |
Standar Deviation (STDEV) |
T Statistics (|O/STDEVI) |
P Values |
Note |
| (X1) -> (X4) |
0.109 |
0.109 |
0.064 |
0.710 |
0.044 |
Insignificant |
| (X1) -> (X5) |
-0.022 |
-0.031 |
0.065 |
0.383 |
0.351 |
Insignificant |
| X1 -> Y1 |
0.121 |
0.126 |
0.062 |
1.970 |
0.025 |
Significant |
| X2 -> X4 |
0.385 |
0.386 |
0.085 |
4.531 |
0.000 |
Significant |
| X2 -> X5 |
0.083 |
0.086 |
0.098 |
0.843 |
0.200 |
Insignificant |
| X2 -> Y1 |
0.053 |
0.025 |
0.106 |
0.331 |
0.370 |
Insignificant |
| X3 -> X4 |
0.374 |
0.369 |
0.074 |
5.076 |
0.000 |
Significant |
| X3 -> X5 |
-0.134 |
-0.132 |
0.068 |
1.972 |
0.025 |
Significant |
| X3 -> Y1 |
-0.013 |
-0.017 |
0.071 |
0.178 |
0.430 |
Insignificant |
| X4 -> X5 |
0.753 |
0.750 |
0.065 |
11.505 |
0.000 |
Significant |
| X5 -> Y1 |
0.577 |
0.567 |
0.080 |
7.131 |
0.000 |
Significant |
The next path that has an indirect influence with the lowest contribution is the individual characteristic (X1) to the Nurse’s Competence with an estimated value of 0.121Significant means there is an influence between the variables, then the variables that affect each other.
DISCUSSION
Current study founded that HNGV, HoREX and HR Maliana are still not clearly visible the professional practice, lack of the ability to apply the nursing care process, problem in management, not clearce standards of practice, no conducting research and use the finding in the practice, all depends on the instructions and collaborative functions. This condition is still in line with previous research related that lack of nursing care, management and leadership processes (Rohi, 2019) and (Carter, 2020). The learning facility factor is still low, module does not yet exist, facilities and infrastructure to support the learning process still low. These reality is not in accordance with the opinion of (Ob, 2020) which states that teaching materials that are interesting for the five senses of students to be able to see, hear, smell, taste and touch, greatly facilitate facilitators and participants during learning process, so that it will run well, effectively and efficiently. Therefore, a training that is not supported by adequate facilities in terms of availability based on learning needs, learning objectives will be difficult to achieve.
The social environment support stated that organizational support and peer support for nurses to follow learning as still low. This fact is far from being an opinion that if the support of a conducive, comfortable, safe and harmonious environment, will have a positive stimulus impact on participants and be motivated and make it a reference for continuous learning (Nada, et al., 2019). The nurses’ situation and conditions in the hospitals, it is time to create social support from hospitals and the support of fellow nurses needs to be improved. Good and effective organizational, peer and family support will motivate a nurse in learn ISS to improve the competence of nurses.
The TLTD stated that it already a high level, but there are still some respondents mentioned it is still low such as: development of self-reflection, critical reflection strategies, social environment supportive, the use of art, literature, film and drama, holistic, affective and spiritual. It is according to the concept of (Enkhtur & Yamamoto, 2017) which encourages learning participants and facilitators to use the TLT steps. The causes are the facilitator has not been able to use the learning according to Mezirow stages in learning so far in the hospital.
All indicators of ISS in values upper then 74%, it is mean that ISS was doing well by nurses. This result strongly agrees with the opinion of (Nursalam. Efendi, 2012) and (Harmon, 2021) which can outline 9 indicators of ISS that need to be deepened by a health worker (nurses). So, we can see that it is subjectively the respondents stated that ISS is already high in implementation, but the objetivity may be have different. Therefore, it needs to be explored more deeply in the next research.
Nurses competencies indicated one indicator achieved 60,8% and other four is under then 60%, it is means that the nurses’s competences were applied in the hospital not yet maximally. The results of this nurse competency research are close to the ASEAN standards which concern 5 domains of competence (Yupin Aungsuroch, 2015). However, currently it still requires a more actively begin to learn and apply the ISS learning to improving the nurses’competence.
Five hypotheses such as X1-X4, X1-X5, X2-X5, X1-Y1. X3-Y1 no direct influence each other, but six hypotheses formed a new model for ISS learning based TLTD, such as: Facility factor (X2) on TLTD (X4), social environment support (X3) on TLTD (X4), TLTD (X4) on ISS learning (X5), social environment support (X3) on ISS learning (X5), facility factor variable (X2) on nurse competence (Y1). It is already according with the conceptual developed by (Honkavuo, 2020a) related to informatic nursing, blanded clinical education becomes an antecedent of the research developed by (Sayani, 2015). It is to improve the competence of nurses based on the ASEAN rule. Therefore, the variable components that have succeeded in forming a model of learning ISS are very reasonable and respond to existing realities. These six variables are interdependent with each other.
CONCLUSION
There are 11 hypotheses discussed in this study, was tested with SEM PLS met 6 hypotheses is significant a relationship. This able to build a model of interpersonal soft skills learning based on the TLTD. Lack of funding support and geographical chalanges.
Funding
Instituto Superior Cristal was provided partial funding during data collection
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank for all participant, INS Timor-Leste was provided approval letter for data collection and Instituto Superior Cristal for funding support.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
- Affara, F. (2009). ICN Framework of Competencies for the Nurse Specialist. In ICN Regulation Series.
- Bartosiewicz, A., Łuszczki, E., Różański, A., & Nagórska, M. (2019). Analysis of determinants of readiness for professional development among Polish nurses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(10), 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Bedford, D. G. J. D. J. (2014). Formative research, Reducing preventable child deaths from pneumonia, diarrhoea and newborn complications in Timor-Leste. Anthrological.
- Bertone, M. P., Martins, J. S., Pereira, S. M., Martineau, T., & Alonso-Garbayo, A. (2018). Understanding HRH recruitment in post-conflict settings: An analysis of central-level policies and processes in Timor-Leste (1999-2018). Human Resources for Health, 16(1), 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Camargo, F. C., Iwamoto, H. H., Galvão, C. M., Pereira, G. de A., Andrade, R. B., & Masso, G. C. (2018). Competences and Barriers for the Evidence-Based Practice in Nursing: an integrative review. Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem, 71(4), 2030–2038. [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Voytal, K. (2010). The role of theory in clinical prevention research. Family Practice, 27(4), 357–358. [CrossRef]
- Caporiccio, J., Louis, K. R., Connor, A. L., Son, K. Q., Raymond, N., Garcia-rodriguez, I. A., & Dollar, E. (2019). Pendidikan Berkelanjutan untuk Perawat Haiti : Bukti dari Pertanyaan Kualitatif dan Kuantitatif. 85(1), 1–7.
- Carter, J. (2020). Hospital Nacional Guido Valadares, Hospital Wide Survey Report.
- Cassiani, S. H. de B., Aguirre-Boza, F., Hoyos, M. C., Barreto, M. F. C., Peña, L. M., Mackay, M. C. C., & Silva, F. A. M. da. (2018). Competencies for training advanced practice nurses in primary health care. Acta Paulista de Enfermagem, 31(6), 572–584. [CrossRef]
- College of Nurses of Ontario (CNO). (2019). Entry-to-practice competencies for Registered Nurses (Pub. No. 41037). Cno, Pub. No. 41037, 16. https://www.cno.org/globalassets/docs/reg/41037-entry-to-practice-competencies-2020.pdf.
- Hair, J. F., Risher, J. J., Sarstedt, M., & Ringle, C. M. (2019). When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. European Business Review, 31(1), 2–24. [CrossRef]
- Harmon, D. T. (2021). Your Soft Skills are Showing: Organizational Efforts to Develop Sotf Skills. Rossier School of Education University of Southern California.
- Honkavuo, L. (2020). Digital Teaching in Nursing Education : A Quantitative Study on Nursing Students ’ Views. International Journal of Caring Sciences, 13(2), 837–846.
- Hou, X., Witter, S., Zaman, R. U., Engelhardt, K., Hafidz, F., Julia, F., Lemiere, C., Sullivan, E. B., Saldanha, E., Palu, T., & Lievens, T. (2016). What do health workers in Timor-Leste want, know and do Findings from a national health labour market survey. Human Resources for Health, 14(1), 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Intarached, P., & Chunuan, S. (2023). Factors Predicting Intention to Use Contraceptive Implants Among Pregnant Adolescents in Lower Southern Thailand: A Cross-sectional Study. Pacific Rim International Journal of Nursing Research, 27(1), 154–168. [CrossRef]
- Luan, B. M., Lopes, P., & Soares, D. (2020). Nurses’ Viewpoints on the Quality of Care: A Qualitative Study in Timor-Leste. 1–17. [CrossRef]
- MONIZ, O. (2020). FAKTOR-FAKTOR YANG MEMPENGARUHI PELAKSANAAN PERILAKU CARING PERAWAT DI RUANGAN PERINATOLOGIA HOSPITAL NASIONAL GUIDO VALADARES (HNGV) DILI TIMOR-LESTE. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 21(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101607%0Ahttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.02.034%0Ahttps://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/cjag.12228%0Ahttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104773%0Ahttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.011%0Ahttps://doi.o. [CrossRef]
- Moradi, Y., Ahmadi, F., Sadeghi, A., & Oshvandi, K. (2019). Conceptualizing and determining core clinical competencies in nursing students: a qualitative study. International Nursing Review, 66(4), 530–540. [CrossRef]
- Nursalam. Efendi. (2012). Pendidikan dalam Keperawatan. In Penerbit Salemba Medica (1 jil, p. 308).
- Price, J. A., Soares, A. I. F. S., Asante, A. D., Martins, J. S., Williams, K., & Wiseman, V. L. (2016). “I go I die, I stay I die, better to stay and die in my house”: understanding the barriers to accessing health care in Timor-Leste. BMC Health Services Research, 16(1), 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Steppingstones Partnership Inc. (n.d.). Learning in a Digital World : Applications to Nurse Learning and Education.
- Superhighway, A. I., & Paper, A. W. (2019). Regulatory Policies and ICT Trends : Insights from Timor-Leste.
- Yupin Aungsuroch, J. (2015). Nurse Preparation towards ASEAN Economic Community 2015. -. International Journal of Health Sciences and Research (IJHSR), 5(3), 365–372.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).