Submitted:
12 February 2024
Posted:
13 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
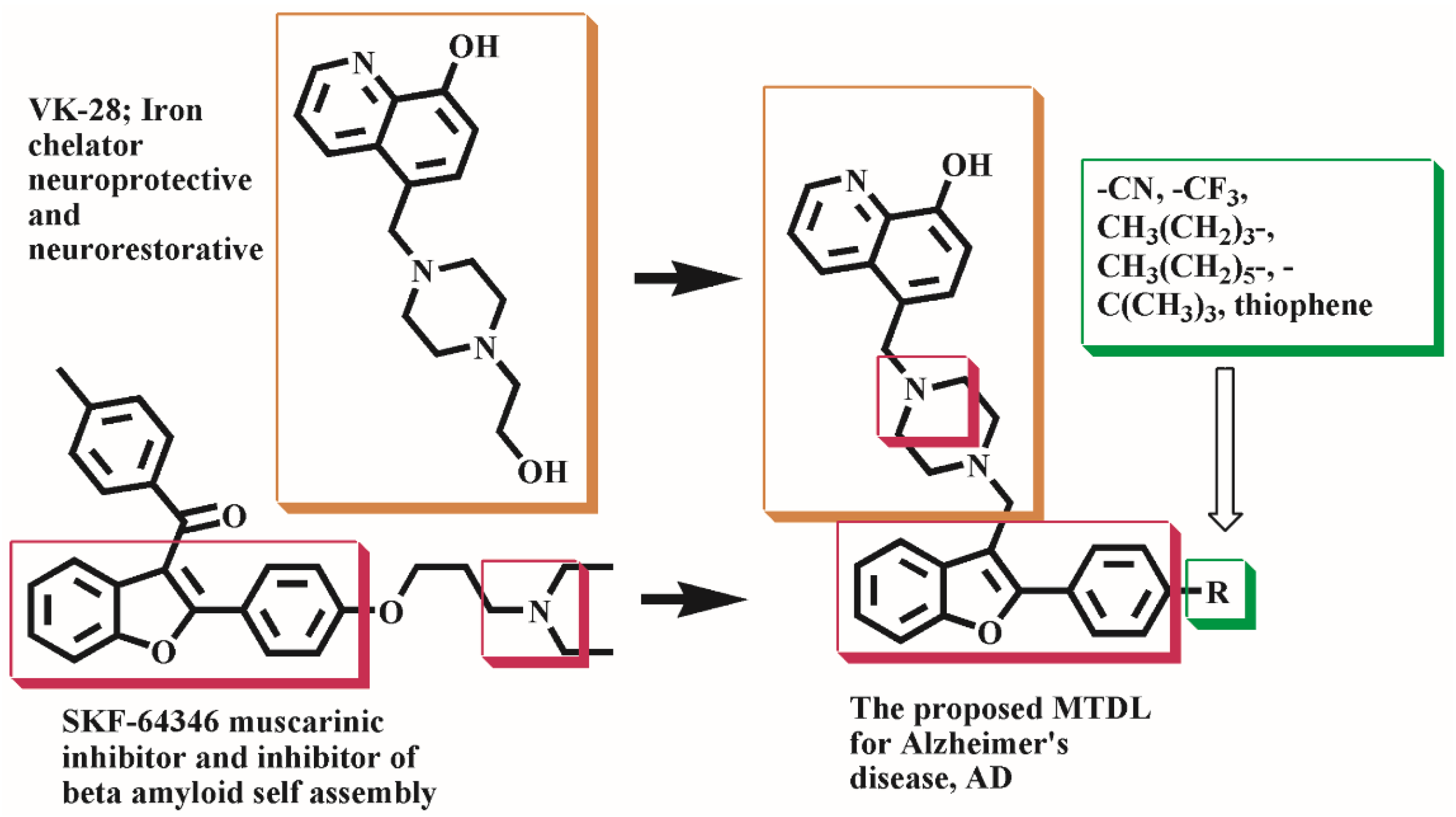
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Chemistry
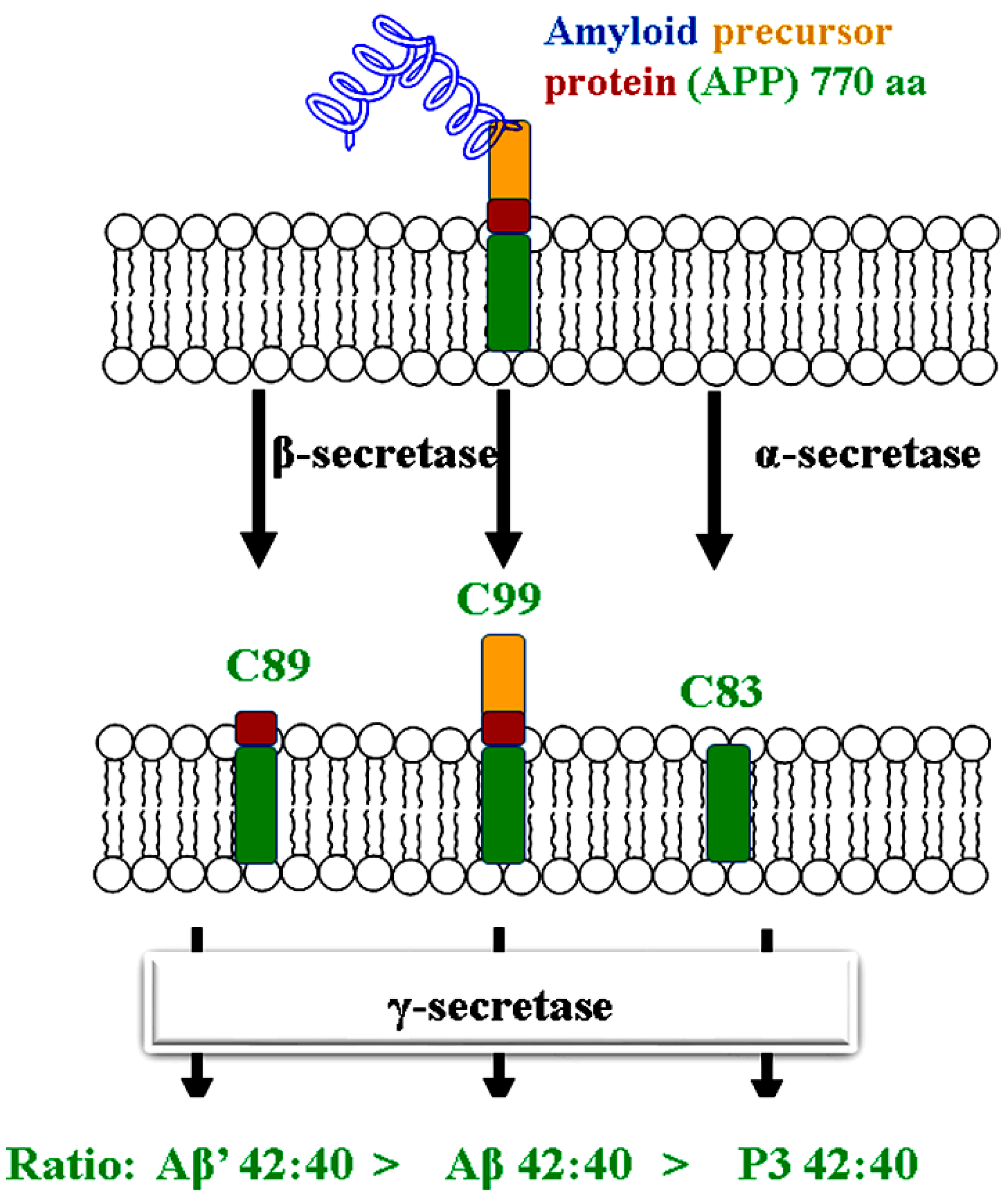
2.2. Inhibition of AChE, BChE and BACE1 Activities
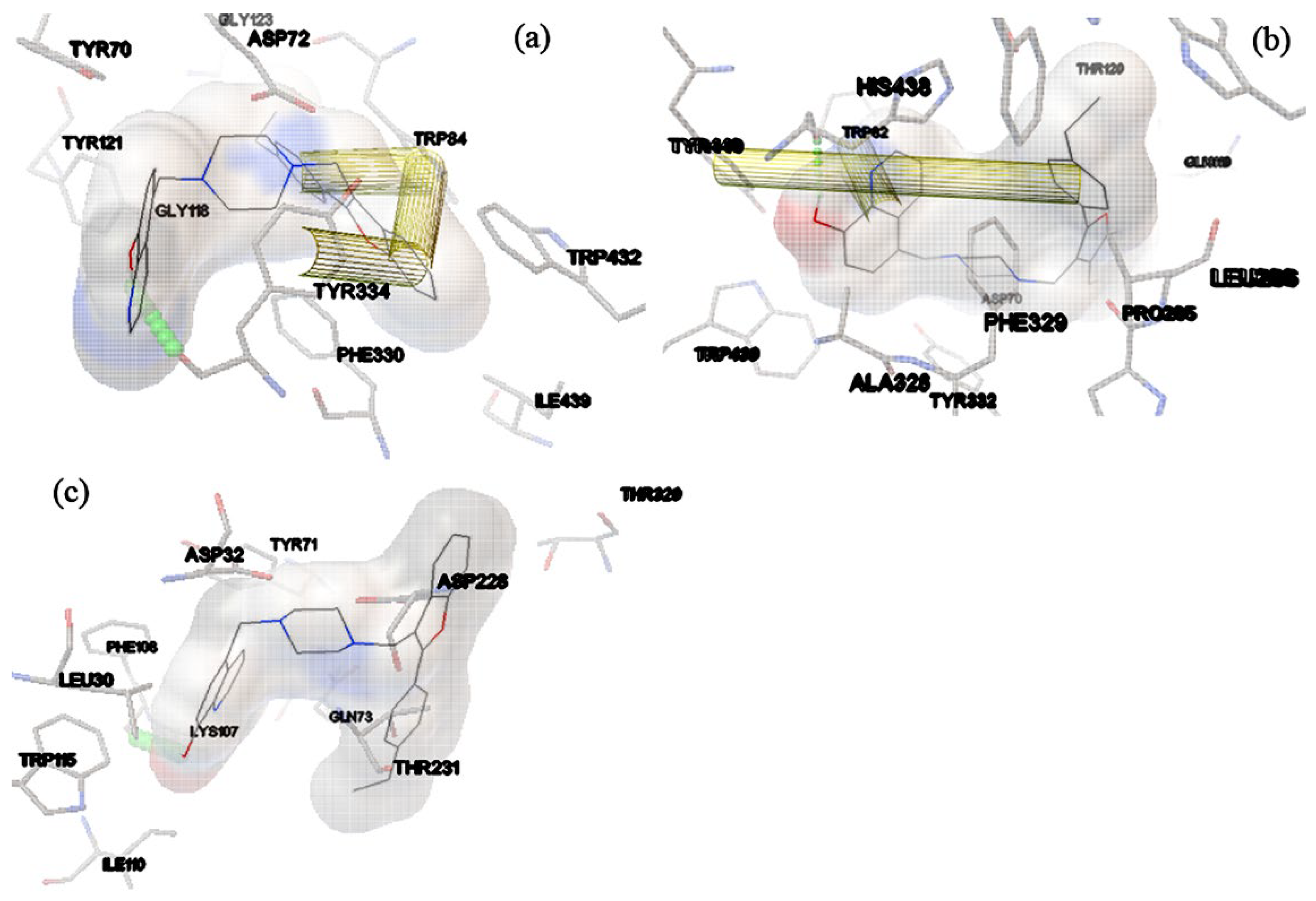
2.3. Docking Study of Compounds 15-28 against AChE and BChE Proteins Structures
| No. | Binding Energy Kcalmol-1 | Inhibition constant (Ki nmol) | Exp. inhibition % |
Binding residues | Hydrogen bonds (distance, Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | -12.54 | 0.638 | 83.4 | Leu30, Asp32, Tyr71, Gln73, Lys107, Ile110, Trp115, Asp228, Thr231, Thr320 | Phe108 |
| 16 | -13.16 | 0.227 | 87.0 | Gln12, Gly13, Leu30, Asp32, Tyr71, Gln73, Lys107, Phe108, Asp228,Gly230, Thr231, Thr282 | Thr72 |
| 17 | -12.86 | 0.376 | 63.1 | Gln12, Gly13, Leu30, Asp32, Tyr71, Gln73, Lys107, Phe108, Asp228,Gly230, Arg235, Thr282 | Thr72 |
| 18 | -13.65 | 0.099 | 74.5 | Gln12, Gly13, Leu30, Asp32, Tyr71, Gln73, Lys107, Phe108, Asp228,Gly230, Thr231, Thr282 | Thr72 |
| 19 | -13.62 | 0.103 | 72.1 | Gln12, Gly13, Leu30, Asp32, Tyr71, Gln73, Lys107, Phe108, Asp228,Gly230, Thr231, Thr282 | Thr72 |
| 20 | -13.19 | 0.213 | 62.4 | Gly13, Asp32, Tyr71, Gln73, Gly74, Lys107, Phe108, Asp228,Gly230, Thr231, Thr282 | Thr72 |
| 21 | -11.32 | 5.02 | 60.5 | Gln12, Gly13, Tyr71, Gln73, Gly230, Thr231, Thr282 | Thr72 |
| 22 | -12.05 | 1.47 | 61.9 | Leu30, Tyr71,Thr72, Gln73, Lys107, Ile110, Trp115, Gly230, Thr231, Arg235 | Phe108 |
| 23 | -11.33 | 4.9 | 79.7 | Gln12, Gly13, Leu30, Tyr71, Gln73, Asp228, Gly230, Thr231, Arg235, Val232 | Thr72 |
| 24 | -10.12 | 38.3 | 89.2 | Gln12, Gly13, Tyr71, Gln73, Lys107, Phe108, Asp228,Gly230, Thr231, Thr282 | Thr72 |
| 25 | -11.82 | 2.16 | 83.1 | Leu30, Tyr71,Thr72, Gln73, Ile110, Ile118, Asp228, Thr229, Gly230, Thr231, Thr232 | Phe108 |
| 26 | -12.51 | 0.681 | 91.0 | Gln12, Gly13, Leu30, Tyr71, Thr72, Gln73, Phe108, Ile110, Trp115, Asp228,Gly230, Thr231, Arg235 | Lys107 |
| 27 | -12.59 | 0.593 | 81.3 | Gly13, Asp32, Tyr71, Gln73, Phe108, Ile110, Ile226, Asp228,Gly230, Thr231,Thr232,Arg235, Val332, Thr329 | Lys107 |
| 28 | -9.98 | 56.95 | 78.6 | Tyr71, Lys107, Phe108, Ile110, Asp228,Thr229, Thr231, Arg235, Val332 | ---- |
| Xray | -11.45 | 4.0 | nd | Leu30, Asp32, Tyr71, Lys107, Phe108, Ile110, Trp115,Asp228,Thr229, Gly230, Arg235 | Gln73, Phe108, Asp228 |
| No | Binding residues | Hydrogen bonds (distance, Å) | Pi-pi interactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AChE | BChE | AChE | BChE | AChE | BChE | |
| 15 | Tyr70,Asp72,Gly118, Tyr121, Gly123, Phe330, Tyr334, Trp432, Ile439 | Asp70,Trp82,Gln119, Tyr120,Pro285,Leu286, Ala328,Phe329,Tyr332, Trp429 | Tyr334 | His438 | Trp84, Tyr334 | Tyr440 |
| 16 | Tyr70,Asp72,Gly118, Tyr121, Ser122, Phe330, Leu333, Trp432, Met436 | Asp70,Gly116, Gln119, Ser196,Pro285, Ser287, Asn289, Ala328, Phe329, Tyr332 | Tyr334 | His438 | Trp84 | Trp82, Tyr440 |
| 17 | Asp72, Gly118, Tyr121, Ser122, Gly123, Phe330 | Gly115,Gly117,Gln119, Gly121,Glu197,Ser198, Trp231, Pro285,Leu286, Ser287,Phe329, Phe398 | Tyr334 | His438 | Tyr70, Trp84, Trp432 | Trp82, Phe329, Phe398 |
| 18 | Tyr70, Asp72, Gly118, Tyr121, Ser122, Trp432, Met436 | Tpr82, Gly115,Gly117, Gln119,Ser198, Pro285, Leu286,Ser287, Ala328 | Tyr334 | His438 | Trp84, Phe330 | Tyr332 |
| 19 | Tyr70,Asp72,Gly118, Tyr121, Ser122, Phe330, Trp432, Met436 | Asp70,Gly117, Leu286, Ala328,Phe329,Tyr332, Trp430, Tyr440 | Tyr334 | His438 | Trp84 | Trp82, His438 |
| 20 | Tyr70,Asp72,Gly117, Gly118, Phe330, Trp432, Met436, Ile439, His440, Tyr442 | Gly115, Gly117, Gln119, Pro285, Ser287, Ala328 Tyr332, Trp430, Tyr440 | Tyr334 | His438 | Trp84 | Trp82, Tyr440 |
| 21 | Tyr70,Asp72, Asn85, Pro86,Gln89,Tyr121, Tyr334, Phe330, Tyr442, Ile439 | Gly116, Thr120, Glu197, Pro285, Ala328, Phe329, Tyr332, Trp430 | His440 | His438 | Trp84, Phe330, His440 | Trp82, Tyr128, Tyr332 |
| 22 | Asp72, Gly118, Tyr121, Phe290, Tyr334, Trp432, Ile439 | Gly117, Thr120, Trp231, Leu286, Phe398 | His440 | His438 | Trp84, Phe330, His440 | Trp82, Ala328 |
| 23 | Tyr70, Val71, Asp72, Asn85, Tyr121, Ser122, Trp279, Phe331, Tyr334, His440, Gly441 | Asp70, Trp82, Gly115, Gly116, THR120, Tyr128, Pro285, Leu286, Ala328, Tyr332, Trp430 | Tyr334 | His438 | Trp84 | Tyr440 |
| 24 | Asp72, Gly118, Tyr121, Ser122, Leu127, Trp279, Trp432, Ile439 | Gly115, Gly116, Gly117, Gln119, Tyr128, Ser198, Pro285, Ala328, Phe329, Tyr332, Trp430, Tyr440 | Tyr334 | His438 | Trp84, Phe330 | Trp82, Trp430, Tyr440 |
| 25 | Asp72, Ser81, Trp84, Gly118, Gly119, Tyr121, Phe290, Phe330, Phe331, Trp432 | Gly117, Thr120, Trp198, Leu286, Ala328, Tyr332, Phe398, Trp430, Tyr440 | Tyr334 | His438 | Phe330 | Trp82, His438, Tyr440 |
| 26 | Val71, Asp72, Gly118, Gly119, Tyr121, Trp279, Phe290, Phe330,Tyr334, His440 | Asp70, Trp82, Gly116, THR120, Glu197, Ser198, Pro285, Ala328,Tyr332, Trp430 | Ser122 | His438 | Tyr70 | His438 |
| 27 | Asp72, Trp84, Gly118, Tyr121, Ser122, Trp279, Phe290, Phe330,Phe331,Tyr334, Gly335, His440 | Gly115, Gly116, THR120, Glu197, Ser198, Ser287, Ala328, Phe329, His438 | Tyr70 | Trp82 | Phe331 | Tyr332, Tyr440 |
| 28 | Tyr70, Asp72, Trp84, Asn85,Gly118,Tyr121, Ser122, Trp279, Tyr334 | Gly116, Ser198, Thr284, Pro285, Ala328, Tyr332, Tyr440 | His440 | His438 | Phe330 | Trp82, Tyr440 |
| Xray | Tyr70, Asp72, Tyr121, Trp279, Phe330, Tyr334, Gly335, Trp432, Met436, Ile439, His440, Gly441, | Asp70, Gly115,Gln119, Ser196, Glu197 Ser198, Pro285,Leu286,Ala328, Phe329, Trp430, Met437, Tyr440 | Tyr121 | His438 | Trp84 | Ala328,Tyr440 |
2.4. Docking study of compounds 15-28 against BAC1 enzyme structures
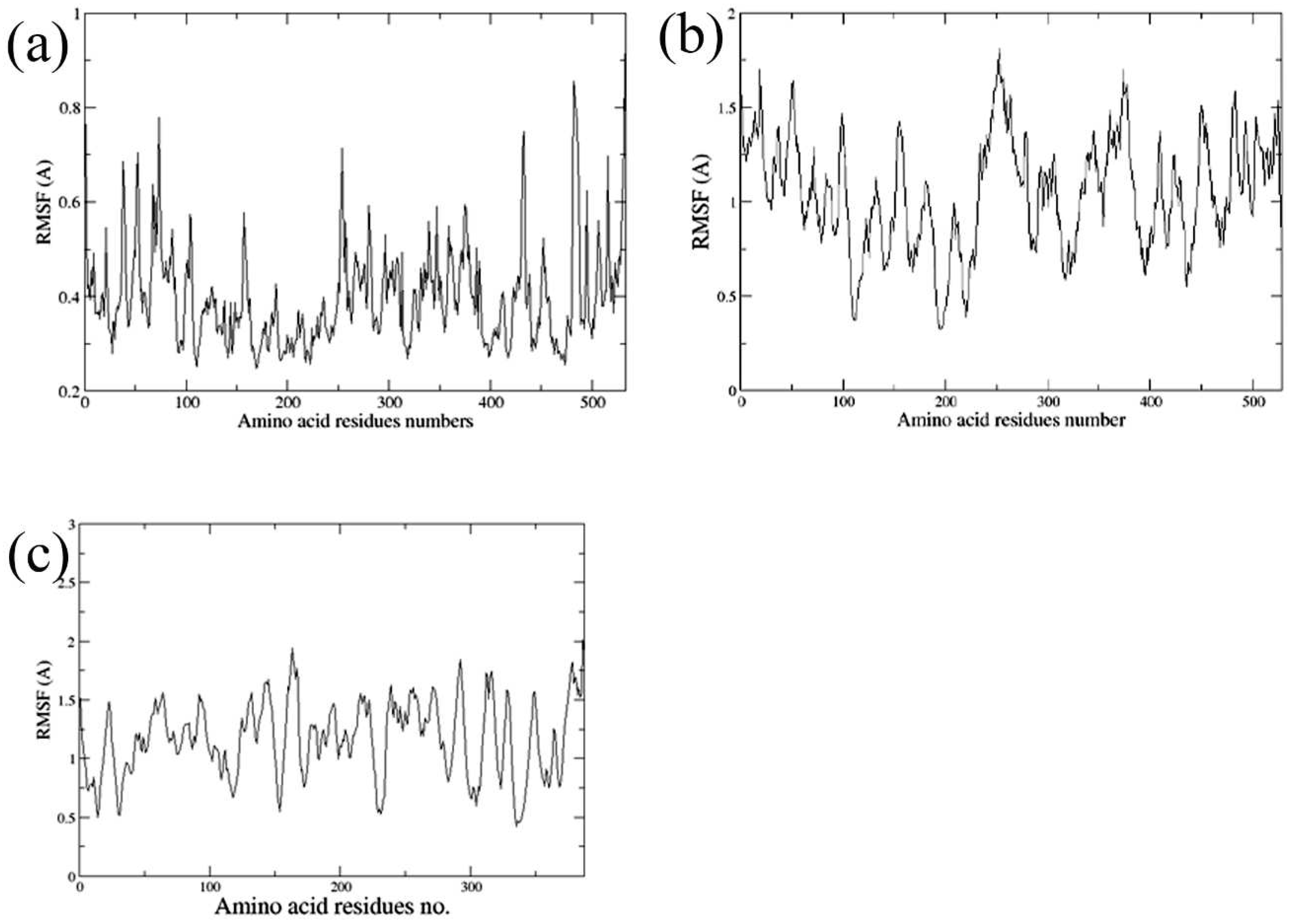
2.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3. Experiment and procedures
3.1. Chemistry
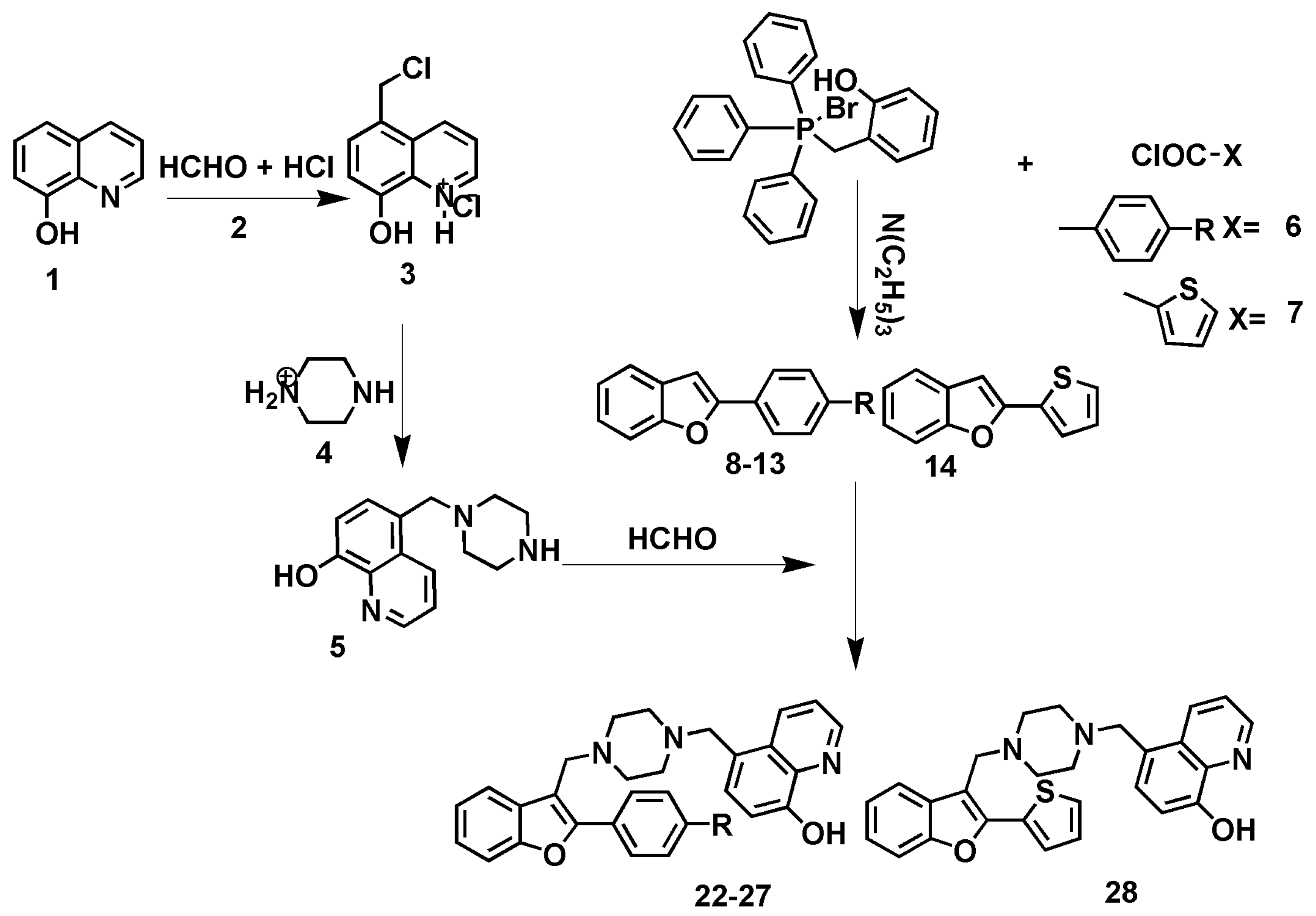
3.1.1. General synthesis of 2-(4-substitutedphenyl)benzofuran derivatives (8-14)
3.1.2. General synthesis of 5-((4-((2-(4-substitutedphenyl)benzofuran-3-yl)methyl)piperazin-1-yl)methyl)quinolin-8-ol derivatives (22-28)
3.2. AChE/BChE screening experiment.
3.3. BACE-1 Screening Experiment
3.4. Molecular Docking
3.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, H.D.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.B.; Young, L.D. History of Alzheimer’s disease. Dement. Neurocogn. Disord. 2016, 15, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maramai, S.; Benchekroun, M.; Gabr, M.T.; Yahiaoui, S. Multitarget therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease: Review on emerging target combinations. BioMed. Res. Int. 2020, 5120230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraji, A.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Firuzi, O.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Edraki, N. Novel small molecule therapeutic agents for Alzheimer disease: focusing on BACE1 and multi-target directed ligands. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 97, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, Z.; Mahdavi, M.; Saeedi, M.; Karimpour-Razkenari, E.; Asatouri, R.; Vafadarnejad, F.; Moghadam, F.H.; Khanavi, M.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Akbarzadeh, T. Novel tacrine-1,2,3-triazole hybrids: in vitro, in vivo biological evaluation and docking study of cholinesterase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafadarnejad, F.; Karimpour-Razkenari, E.; Sameem, B.; Saeedi, M.; Firuzi, O.; Edraki, N.; Mahdavi, M.; Akbarzadeh, T. Novel N-benzylpyridinium moiety linked to arylisoxazole derivatives as selective butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors: synthesis, biological evaluation, and docking study. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 92, 103192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanari, M.-L.; Navarrete, F.; Ginsberg, S.D.; Manzanares, J.; Sáez-Valero, J. , García-Ayllón, M.-S. Increased expression of readthrough acetylcholinesterase variants in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients. J. Alzheimers Dis 2016, 53, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvesh, S.; Hopkins, D.A.; Geula, C. Neurobiology of butyrylcholinesterase. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, G.; Cash, A.D.; Smith, M.A. Alzheimer Disease and Oxidative Stress. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2002, 2, 2,120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolnay, M.; Probst, A. REVIEW: tau protein pathology in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1999, 25, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M. K.; Sharma, P.; Tripathi, A.; Tripathi, P.N.; Srivastava, P.; Seth, A.; Shrivastava, S. K. Computational exploration and experimental validation to identify a dual inhibitor of cholinesterase and amyloid-beta for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2020, 34, 983–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Srivastava, P.; Seth, A.; Tripathi, P. N.; Banerjee, A. G.; Shrivastava, S. K. Comprehensive review of mechanisms of pathogenesis involved in Alzheimer’s disease and potential therapeutic strategies. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 174, 53–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatta, P.; Drago, D.; Bolognin, S.; Sensi, S. L. Alzheimer’s disease, metal ions and metal homeostatic therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birks, J. Cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 25, CD005593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geula, C.; Darvesh, S. Butyrylcholinesterase, cholinergic neurotransmission and the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Drugs Today (Barc) 2004, 40, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M. M.; Gabr, M. T. Multitarget therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belluti, F.; Rampa, A.; Piazzi, L.; Bisi, A.; Gobbi, S.; Bartolini, M.; Andrisano, V.; Cavalli, A.; Recanatini, M.; Valenti, P. Cholinesterase inhibitors: xanthostigmine derivatives blocking the acetylcholinesterase-induced beta-amyloid aggregation. J. med. Chem. 2005, 48, 4444–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, S.; Cavalli, A.; Ceccarini, L.; Bartolini, M.; Belluti, F.; Bisi, A.; Andrisano, V.; Recanatini, M.; Rampa, A. Structure-activity relationships and binding mode in the human acetylcholinesterase active site of pseudo-irreversible inhibitors related to xanthostigmine. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozurkova, M. ; Hamulakova, S, Gazova Z, Paulikova H, Kristian P. Neuroactive Multifunctional Tacrine Congeners with Cholinesterase, Anti-Amyloid aggregation and neuroprotective properties. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). [CrossRef]
- Youdim, M.B. Multi target neuroprotective and neurorestorative anti-Parkinson and anti-Alzheimer drugs ladostigil and m30 derived from rasagiline. Exp Neurobiol. 2013, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 21. Amit, T; Avramovich-Tirosh, Y.; Youdim, M.B.; Mandel, S. Targeting multiple Alzheimer’s disease etiologies with multimodal neuroprotective and neurorestorative iron chelators. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 1296–1305. [CrossRef]
- Saadeh, H.A.; Sweidan, K.A.; Mubarak, M.S. Recent advances in the synthesis and biological activity of 8-hydroxyquinolines. Molecules 2020, 25, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadeh, H.A.; Sweidan, K.A.; Mubarak, M.S. Recent advances in the synthesis and biological activity of 8-hydroxyquinolines. Molecules 2020, 25, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, A.A.; Alanazi, F.K.; Raish, M. Design and synthesis of multi-functional smallmolecule based inhibitors of amyloid-β aggregation: Molecular modeling and in vitro evaluation. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, A.; Piccionello, A.P.; Sgarbossa, A.; Vilasi, S.; Ricci, C.; Ghetti, F, et al. Curcumin-like compounds designed to modify amyloid beta peptide aggregation patterns. RSC Advances 2017; 7:31714–31724. [CrossRef]
- Earl, C.; Bagneris, C.; Zeman, K.; Cole, A.; Barrett, T.; Savva, R. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 4286-4300. [CrossRef]
- Chalupova, K.; Korabecny, J.; Bartolini, M.; Monti, B.; Lamba, D.; Caliandro, R.; et al. Novel tacrine-tryptophan hybrids: Multi-target directed ligands as potential treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, W.Y.; Chen, T.T.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Xiong, B.; Xu, Y.C.; Shen, J. Virtual screening and structure-based discovery of indole acylguanidines as potent beta-secretase (BACE1) inhibitors. Molecules 2013, 18, 5706–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Aktulga, H.M.; Belfon, K.; Ben-Shalom, I.Y.; Berryman, J.T., Brozell, S.R., et al., Amber 2023, University of California, San Francisco.

| No. | Binding Energy Kcalmol-1 | Inhibition constant (Ki nmol) | Experimental inhibition % |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AChE | hBChE | AChE | hBChE | AChE | BChE | |
| 15 | -14.83 | -12.36 | 0.013 | 0.87 | 64.9 | 75.69 |
| 16 | -15.32 | -10.92 | 0.006 | 9.89 | 71.3 | 65.88 |
| 17 | -14.37 | -12.36 | 0.03 | 0. 87 | 58.2 | 91.53 |
| 18 | -15.63 | -12.97 | 0.004 | 0.31 | 79.9 | 94.47 |
| 19 | -14.85 | -12.64 | 0.013 | 0.54 | 64.1 | 86.65 |
| 20 | -15.16 | -11.82 | 0.008 | 2.17 | 68.5 | 74.35 |
| 21 | -10.42 | -11.61 | 23.1 | 3.07 | 50.8 | 72.7 |
| 22 | -11.9 | -11.03 | 1.89 | 8.22 | 81.3 | 84.06 |
| 23 | -11.98 | -10.91 | 1.66 | 10.03 | 69.6 | 54.58 |
| 24 | -14.42 | -11.88 | 0.027 | 1.96 | 74.4 | 80.77 |
| 25 | -11.24 | -13.79 | 5.78 | 0.08 | 74.4 | 78.73 |
| 26 | -11.4 | -12.23 | 4.38 | 1.09 | 47.8 | 74.95 |
| 27 | -9.92 | -11.78 | 53.13 | 2.34 | 60.8 | 79.18 |
| 28 | -10.97 | -12.75 | 9.07 | 0.45 | 33.8 | 67.57 |
| Xray | -14.22 | -11.38 | 0.038 | 4.55 | -------------- | ------------- |
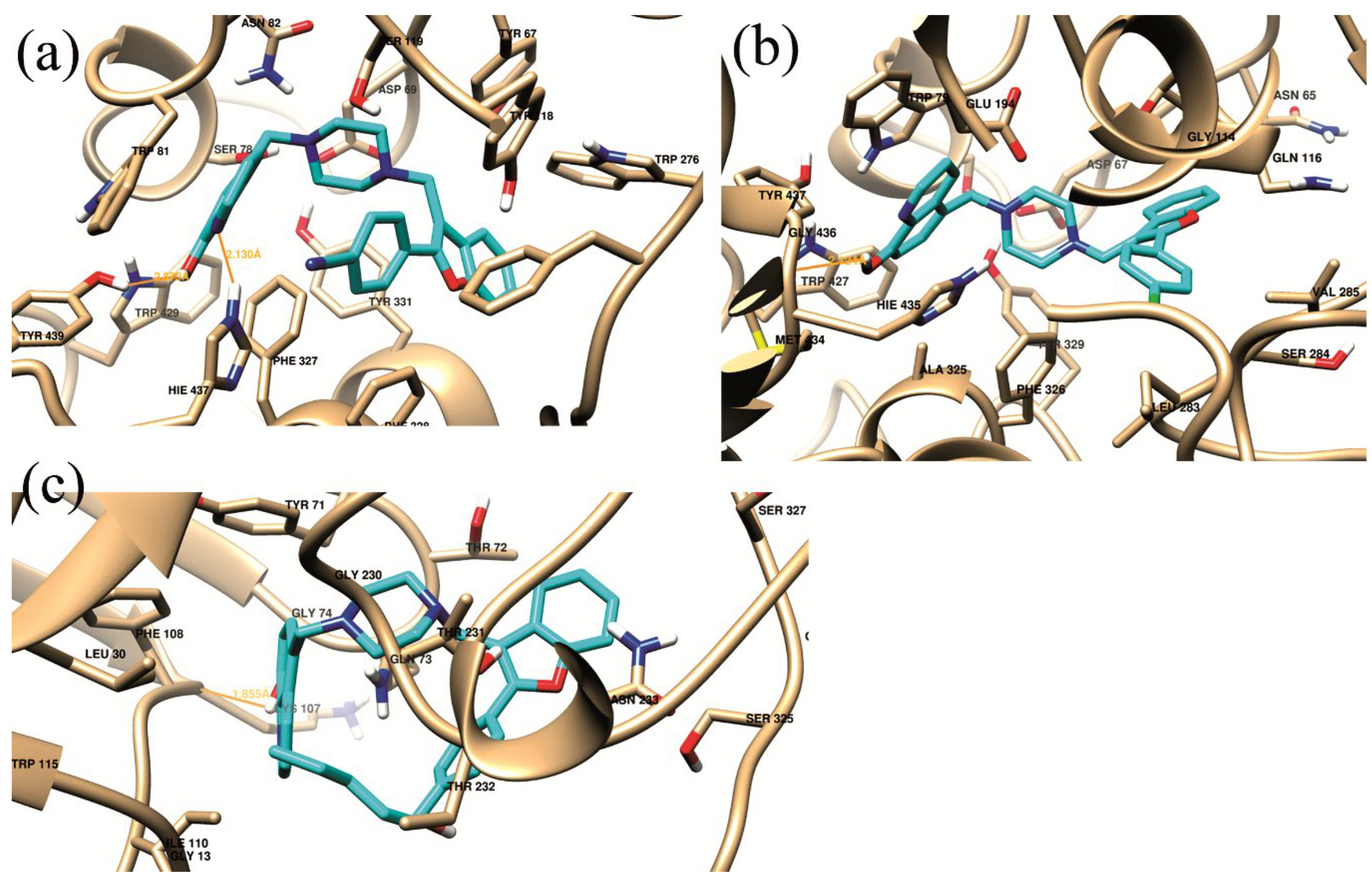
| Complex | Hb-residue (Frac %) | ΔGvdw | ΔGelec | ΔGpolara | ΔGSurf b | ΔGMM/GBSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | HIE_437@HE2(16.25%) SER_197@HG (11.5%) |
-67.9357 | -18.8145 | 36.9524 | -7.2966 | -57.0944 |
| (b) | HIE_435@O (42.25%) | -60.6058 | -8.3630 | 23.8192 | -6.6235 | -51.7731 |
| (c) | THR_231@HB (10.25%) THR_232@H (9.5%) LYS_107@O (33.75%) |
-49.274 | -6.0429 | 18.5027 | -6.0780 | -42.8924 |
| Complex | Residue Number Residue interaction energy kcalmol-1 |
|||||||||
| (a) | Asp69 -2.425 |
Ser78 -2.294 |
Trp81 -3.357 |
Asn82 -1.732 |
Tyr118 -2.301 |
Phe327 -2.227 |
Phe328 -2.342 |
Tyr331 -3.312 |
Hie437 -4.539 |
Tyr439 -1.749 |
| (b) | Asp67 -1.703 |
Trp79 -3.81 |
Gln116 -2.185 |
Thr117 -1.58 |
Glu194 -1.538 |
Ala325 -1.947 |
Phe326 -1.613 |
Tyr329 -1.768 |
Met434 -1.21 |
Hie435 -2.594 |
| (c) | Gln12 -1.046 |
Tyr71 -3.218 |
Thr72 -1.382 |
Gln73 -5.179 |
Lys107 -1.412 |
Phe108 -2.287 |
Ile110 -0.864 |
Gly230 -1.344 |
Thr231 -2.098 |
Thr232 -1.408 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





