1. Introduction
Tracheal intubation is essential for providing adequate oxygenation and ventilation support to critically ill emergency patients with inadequate oxygenation or airway patency failure.
Prior to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the most common method for tracheal intubation was direct laryngoscopy. The literature indicates, however, that using a direct laryngoscope for intubation is extremely challenging, with an initial success rate of only 51–61% [
1,
2,
3]. For these reasons, emergency room tracheal intubation is the responsibility of trained and experienced medical personnel [
4]. Nevertheless, the COVID-19 pandemic altered emergency airway management in emergency rooms and influenced intubation instruction for novice practitioners.
Wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) can make rapid, safe, and effective intubation challenging, but during the COVID-19 pandemic, healthcare providers must perform tracheal intubation on critically ill patients while wearing PPE. However, intubation via direct laryngoscopy while wearing PPE is extremely challenging. Ultimately, emergency physicians have chosen video laryngoscopy over direct laryngoscopy [
5,
6,
7] as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and the use of PPE. Video laryngoscopy has been developed and implemented to enhance the intubation success rate. Nevertheless, a lack of understanding of the specialized characteristics of video laryngoscopes [9,10,11,12,13] and the different types and characteristics of video laryngoscopes can make intubation more difficult than direct laryngoscopy.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made it difficult to provide novice operators with sufficient intubation experience; therefore, airway management training for novices is essential in these circumstances.
In a previous study, we educated novices using the ALRYNGO, a channel-type video laryngoscope with an AI-based glottal guidance system developed in preparation for the pandemic; the Pentax Airwayscope (Pentax-AWS); the direct laryngoscope; and the McGrath video laryngoscope. This previous study demonstrated that a video laryngoscope of the channel type, which may be unfamiliar, can be utilized adequately.
It is risky to assume that the channel-type video laryngoscope's demonstrated educational effect in mannequin studies will be the same in clinical settings. Consequently, it is necessary to confirm these educational effects in the clinical setting.
Therefore, after applying the educational program of the previous study to senior residents in the Department of Emergency Medicine who were proficient with direct laryngoscopes in a clinical setting but had no experience with channel-type video laryngoscopes, we conducted a prospective randomized controlled clinical trial.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
In this prospective randomized controlled clinical trial, we aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of the A-LRYNGO channel-type video laryngoscope with an AI-based glottis guidance system in senior emergency medicine residents for endotracheal intubation at the Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital in March 2022. The Institutional Review Board of Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital approved this study in June 2020 (IRB No. HKS 2020-06-021). This clinical trial was registered with the identifier KCT0007433 at cris.nih.go.kr.
2.2. Equipment and Materials
All participants performed intubations using four laryngoscopes: a direct laryngoscope (Macintosh, Macintosh #4 blade), one nonchannel-type video laryngoscope and two channel-type video laryngoscopes.
An endotracheal tube with an inner diameter of 7.5 mm (Portex, St. Paul, MN, USA) was used in this study. A bag-valve mask (BVM; Ambu® Mark IV - Reusable Resuscitator, Ballerup, Denmark) was used in this study.
One of the channel-type video laryngoscopes used was the Pentax Airwayscope (AWS; PENTAX Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The other channel-type video laryngoscope was the ALRYNGO (A-LRYNGO; AIMD Corporation, Seoul, Republic of Korea).
2.3. Participants
Six senior emergency medicine residents skilled in direct laryngoscopy performed tracheal intubation with one of three randomly assigned airway devices for patients who required tracheal intubation and ventilator care in the emergency department among severely critically ill patients aged 18 or older. Patients with a difficult airway or a history of trauma were not included in the study, and safe intubation was ensured by using the right equipment for patients.
The sample size was calculated based on the results of a pilot study. The mean and standard deviation (SD) time from visualization of the glottis to completion of endotracheal tube insertion and removal of the laryngoscope was 5.83 ± 1.17 with direct laryngoscope, 12.05 ± 4.63 with Pentax AWS and 11.42 ± 2.17 with ALRYNGO in a pilot study. We enrolled twenty patients would be adequate for each device.
2.4. Interventions
Prior to the start of the study, a senior emergency medicine resident received a 1-hour lecture on the channel-type video laryngoscope, including its features and usage, as well as a 1-hour hands-on workshop.
To randomize the device in the clinical study, a sealed envelope containing a device-specific identification card was utilized. Before intubation, every intubator wore a personal protective equipment. When intubation began, the person who measured the intubation time divided the total intubation time into three time intervals, each of which was measured and recorded on the record sheet.
The first time interval began when the blade tip of each device passed the incisor and ended when the participant said, "I can see the glottis, C-L grade I IV" The second time interval began when the participant stated, "I can see the glottis" and ended when the endotracheal tube was inserted and the laryngoscope was removed. The third time interval occurred between the completion of endotracheal tube insertion and the participant's first BVM-assisted manual ventilation.
2.5. Outcomes
The primary outcome was the intubation time. The intubation time was divided into three intervals and recorded by a recorder. The recorder was informed about how to assess the intubation time and was blinded to all authors of this study. The first interval extended from the moment of the blade of each laryngoscope passing the incisor to visualization of the glottis (IVT). The second interval extended from visualization of the glottis to endotracheal tube insertion completion with removal of the blade (VFT). The last interval extended from endotracheal tube insertion to first manual ventilation (FVT). We defined intubation failure as follows: esophageal intubation or IVT +VFT for 90 seconds or more.
The secondary outcomes were the glottis view using the Cormack-Lehane grade (C-L grade) and the glottis guidance performance of A-LRYNGO’s artificial intelligence. A short questionnaire survey was conducted with residents who underwent intubation.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
All datasets were compiled using a standard spreadsheet application (Excel, Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA) and were analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) 26.0 KO for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). We generated descriptive statistics and presented them as frequencies and percentages for categorical data and medians with interquartile ranges (IQRs) for continuous data because the data were not normally distributed. To compare each time interval by type of laryngoscope, the Kruskal‒Wallis test was used for continuous variables. A x2 test was used to compare categorical variables, such as the intubation success rate. To compare each time interval by type of device before and after the hands-on workshop, the Wilcoxon signed rank test was used for continuous variables. For all data, P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. However, a post hoc analysis was conducted with the Mann‒Whitney test using a Bonferroni correction, and P < 0.017 was considered significant. Kaplan‒Meier analysis was performed to analyze the cumulative success rate in terms of the total intubation time.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics (Table 1)
This table compares the baseline characteristics of three groups of patients: DL, Pentax AWS, and ALRYNGO. Three features are compared: sex, age, and diagnosis. According to sex, the patients in all three groups had a similar ratio of males to females. According to age, the patients in the DL group were the oldest, and the patients in the ALRYNGO group were the youngest. According to the diagnosis, the patients in all three groups were diagnosed with COVID-19 pneumonia, cerebrovascular diseases, and cardiac arrest. Since the p value was greater than 0.05 for all features, we concluded that there was no significant difference between the three groups.
Table 1 shows that the baseline characteristics of the patients in the three groups were similar. This suggests that the patients in the three groups were comparable groups.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics.
| |
DL |
Pentax AWS |
ALRYNGO |
p value |
Sex,
Male: Female |
11:9 |
10:10 |
11:9 |
0.938 |
|
Age, Median (IQR) |
72.00 (17.75) |
71.00 (13.00) |
77.00 (10.75) |
0.123 |
Diagnosis,
COVID19 pneumonia : Cerebrovascular diseases : Cardiac arrest |
9:6:5 |
12:4:4 |
10:5:5 |
0.968 |
3.2. Comparison of Intubation Performance with Three Laryngoscopes (Table 2)
There were significant differences among the three laryngoscopes—direct laryngoscope, Pentax AWS, and ALRYNGO—in terms of IVT and VFT. However, there was also a significant difference in FVT.
For IVT, the direct laryngoscope required a median time of 11.17 (IQR: 7.11), whereas Pentax AWS and ALRYNGO took 17.61 (IQR: 8.78) and 22.07 (IQR: 8.40), respectively, showing significant differences (p < 0.05). The VFT was the fastest with the direct laryngoscope, taking a median time of 5.41 (IQR: 0.60). Pentax AWS and ALRYNGO required longer times, with median times of 11.36 (IQR: 2.56) and 11.80 (IQR: 1.75), respectively (p < 0.05). Regarding FVT, the direct laryngoscope took the least time (median: 5.18, IQR: 0.82), while Pentax AWS and ALRYNGO required more time, with median times of 11.38 (IQR: 3.17) and 11.22 (IQR: 2.29), respectively; the differences were significant (p < 0.05).
However, the intubation success rate was 100% for all three laryngoscopes.
Among the three, the ALRYNGO and Pentax AWS had the highest frequency of C-L grade I (easiest intubation) at 80%, and the direct laryngoscope had the lowest frequency of 10%.
In post hoc analysis, significant differences were found between the direct laryngoscope and the other two laryngoscopes in terms of IVT, VFT, and FVT (direct laryngoscope vs. Pentax AWS: p = 0.01 for VFT, p < 0.01 for VFT and IVT; direct laryngoscope vs. ALRYNGO: p < 0.001 for all). And significant difference was found between the Pentax AWS and ALRYNGO in term of IVT (p=0.004). However, in the VFT and FVT, no significant differences were found between Pentax AWS and ALRYNGO (p = 1.00).
Table 2.
Comparison of intubation performance with three laryngoscopes.
Table 2.
Comparison of intubation performance with three laryngoscopes.
| Devices |
IVT |
VFT |
FVT |
Success Rate, % |
C-L Grade, n (%) |
| I |
II |
III |
IV |
| Direct Laryngoscope |
11.17 (7.11) |
5.41 (0.60) |
5.18 (0.82) |
100 |
2 (10%) |
10 (50%) |
8 (40%) |
0 (0%) |
| Pentax-AWS |
17.61 (8.78) |
11.36 (2.56) |
11.38 (3.17) |
100 |
16 (80%) |
4 (20%) |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
| ALRYNGO |
22.07 (8.40) |
11.80 (1.75) |
11.22 (2.29) |
100 |
16 (80%) |
4 (20%) |
0 (0%) |
0 (0%) |
|
p value |
< 0.05 |
< 0.05 |
< 0.05 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Post hoc Analysis |
p value a)
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Direct Laryngoscope |
vs. |
Pentax-AWS |
0.01 |
< 0.01 |
< 0.01 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Direct Laryngoscope |
vs. |
ALRYNGO |
< 0.01 |
< 0.01 |
< 0.01 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Pentax-AWS |
vs. |
ALRYNGO |
0.004 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
3.3. Cumulative Success Rate with the Three Laryngoscopes (Figure 1)
For the cumulative success rate in terms of total intubation time among the three laryngoscopes—direct laryngoscope, Pentax AWS, and ALRYNGO—a statistically significant difference was observed. The direct laryngoscope demonstrated the highest cumulative success rate, followed by the Pentax AWS and ALRYNGO. This difference was statistically significant, with a p value of less than 0.001.
Figure 1.
Cumulative success rate with the three laryngoscopes in total intubation time.
Figure 1.
Cumulative success rate with the three laryngoscopes in total intubation time.
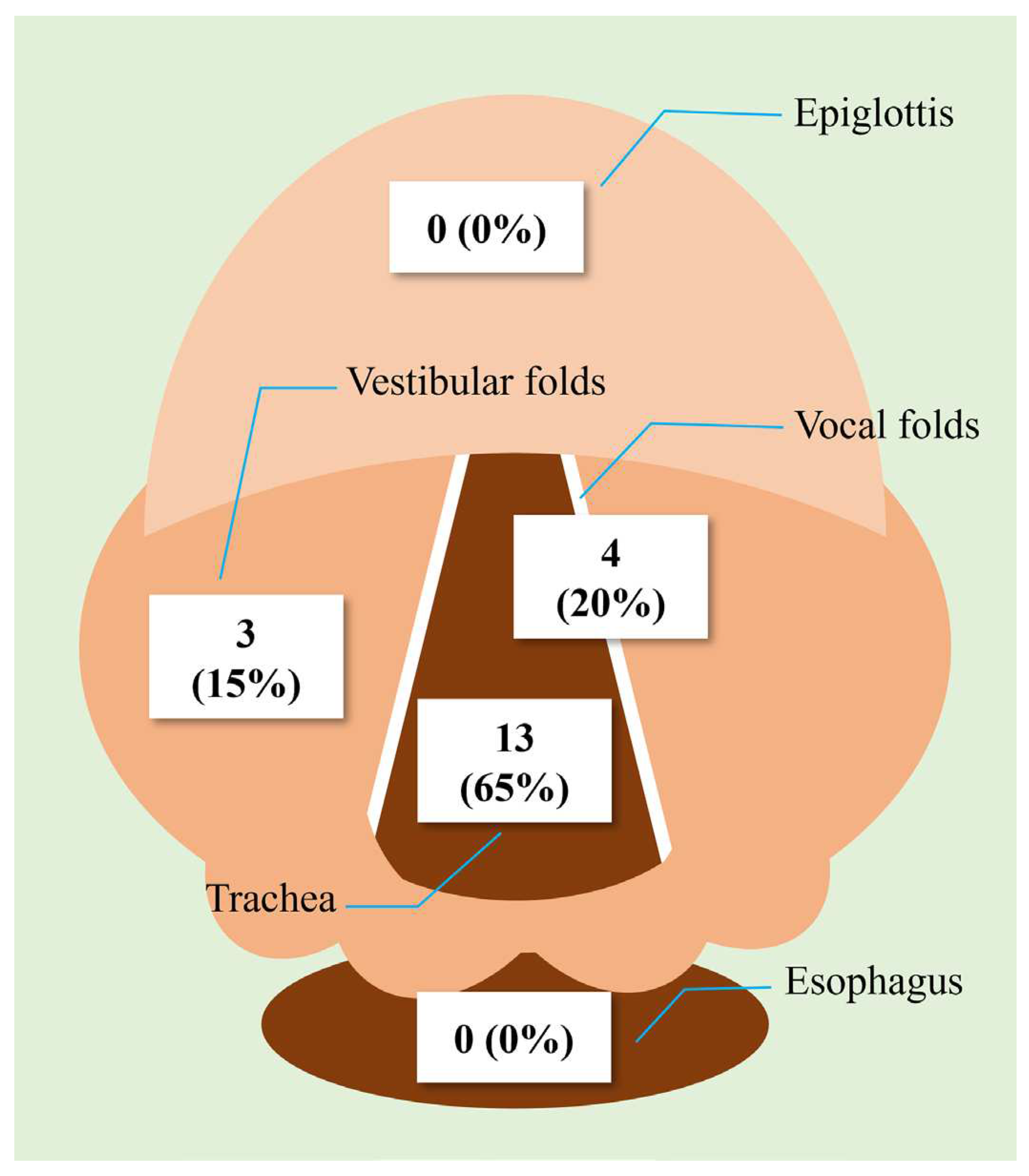
3.4. Artificial Intelligence-Based Glottis Guidance with ALRYNGO (Figure 2)
In terms of the performance of ALRYNGO's artificial intelligence-based glottis guidance, out of a total of 10 trials, 60% provided accurate guidance through the trachea, and 20% identified the vocal fold position; thus, 80% provided appropriate guidance through the glottis. It was found that 20% were guided by the vestibular folds. There were no other cases of guidance through the esophagus or epiglottis.
Figure 2.
Performance of ALRYNGO's artificial intelligence-based glottis guidance.
Figure 2.
Performance of ALRYNGO's artificial intelligence-based glottis guidance.
3.5. Results of the Short Questionnaire for All Participants (Table 3)
Six senior residents who participated in intubation were investigated in this study. After practicing on a mannequin, all participants reported that the channel-type video laryngoscope was intuitive and simple to operate. In contrast, all residents reported that it was difficult to enter the oral cavity from the mouth when using the channel-type video laryngoscope on actual patients, in stark contrast to their experience with mannequins. In addition, they reported that it took longer to find the vocal cords and that they were unfamiliar with inserting the endotracheal tube and separating it from the device.
Table 3.
Results of the short questionnaire for all participants.
Table 3.
Results of the short questionnaire for all participants.
| Question |
5-point Likert Scale, n (%) |
| |
Strongly disagree |
Disagree |
Neutral |
Agree |
Strongly agree |
| - Effective lecture and hands-on workshop? |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
2 (33.3) |
4 (66.7) |
| - The channel-type video laryngoscopes were used differently in patients and manikins? |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
6 (100) |
| - Agree that a channel-type video laryngoscope is more comfortable and easier than a direct laryngoscope? |
5 (83.3) |
1 (16.7) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
| - Agree that channel type is superior to direct laryngoscope in glottis view. |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
2 (33.3) |
4 (66.7) |
| Open question & answer |
| Describe your channel-type video laryngoscope difficulties. |
- Unlike the direct laryngoscope, the large blade made it hard to insert the suction catheter for oral and pharyngeal secretions. |
| - Inserting the blade into the patient's mouth was difficult. In addition, after securing the glottis view, the tube's tip kept getting caught in the posterior cartilage, making it hard to adjust the direction. |
| - After inserting the tube into the airway, separating it from the channel was much different in the mannequin. Tooth damage and airway tube loss seemed too risky. |
| - Suctioning was difficult and different in mannequins. I worried that if the tube did not enter, friction would damage the balloon. |
4. Discussion
The COVID-19 pandemic is fading, but the potential for dangerous outcomes from COVID-19 infection remains significant. There is also a perpetual possibility of repeating pandemic situations. Therefore, the importance of healthcare workers being proficient in airway management for critically ill patients while wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) cannot be overstated. In this situation, many countries worldwide have begun to recommend the use of video laryngoscopes over direct laryngoscopy to prevent infection among healthcare workers and improve intubation success.
According to a mannequin simulation study reported by Micheal Aziz et al. in 2009, the use of a Macintosh video laryngoscope resulted in higher intubation success rates than a Macintosh direct laryngoscope. Muhammad A. Malik et al. reported a comparative study among medical students using a direct laryngoscope, Glidescope, and Pentax AWS. They suggested that the Pentax AWS is an easier device for novice practitioners to learn and use.
In 2011, Hayashi K et al. from Japan compared the channel-type video laryngoscope, Pentax AWS, and Airtraq with the direct laryngoscope. They suggested that using the Pentax AWS allowed novice practitioners to secure a better laryngeal view and perform safer intubation with minimal training. Moreover, Yamada K et al. in 2012 compared Glidescope, Pentax AWS, and a direct laryngoscope among novice practitioners. They reported that the Glidescope and Pentax AWS provided better laryngeal visibility and ease of device operation.
In 2020, Kyong Yi et al. conducted a comparative study among nurses without intubation experience, comparing the McGrath, Pentax AWS, and direct laryngoscope. They suggested that the McGrath and Pentax AWS are suitable devices for novice practitioners. In 2021, Yuryo Murakami et al. also stated that the McGrath and Pentax AWS were better devices for novice practitioners than the direct laryngoscope in terms of laryngeal view and intubation success. Although none of these studies involved PPE, they all proposed that video laryngoscopes provide safer and faster laryngeal views and are suitable devices for beginners.
Most recently, in 2022, Choi et al. compared the educational effects of a direct laryngoscope, McGrath, and channel-type video laryngoscope (Pentax AWS and ALRYNGO) among novice practitioners wearing PPE. They suggested that the channel-type video laryngoscope was easier to learn, more convenient to use, and offered better laryngeal view, intubation success, and intubation time for novice practitioners, even when wearing PPE.
Other studies conducted with PPE involved not novice training but seasoned emergency medicine physicians. Thus, these studies reported that the influence of PPE was minimal. However, all these studies were not conducted with actual patients but were simulation studies using mannequins. Meanwhile, in 2018, a study compared a direct laryngoscope and Pentax AWS in actual patients. In this study, Kyu Nam Kim et al. suggested that the Pentax AWS should be included in future intubation training because it provided a better laryngeal view more quickly and easily to novice practitioners and shortened the intubation time. However, this study was conducted with interns who did not wear PPE and were novices in using all airway devices, including direct laryngoscopes. The patients in this study had already completed all evaluations for the airway and were prepared for elective surgery, allowing for safe intubation after fasting for sufficient time.
The participants in this study who performed the intubation were very familiar with direct laryngoscopy and had ample experience with intubation through direct laryngoscopy; they also had an abundance of experience using direct laryngoscopy while wearing PPE during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, they had no experience with channel-type video laryngoscopes, so they took a lecture and hands-on workshop just as in the previous study to ensure that the performance of Pentax AWS and ALRYNGO improved on the mannequin. Then, they proceeded with real patients who needed intubation in the emergency room.
Contrary to our expectations, when using Pentax AWS and ALRYNGO, all intubations were successful, but the intubation time was longer than with the direct laryngoscope. All the residents who participated in intubation reported that unlike in the mannequin, it was not easy to enter the oral cavity, it took longer to locate the larynx than with the direct laryngoscope even though the final laryngeal view was good, and the process of pushing the tube into the airway was not easy. This was clearly reflected in the intubation time.
Intubators familiar with direct laryngoscopy are used to visually confirming oral and hypopharyngeal structures as they insert the blade through the patient's mouth. However, these intubators were not familiar with seeing the structures through the screen and securing the laryngeal view after the blade entered the oral cavity when using equipment such as a channel-type video laryngoscope, which guides with a channel and fills the oral cavity with the blade, making it impossible to visually confirm oral and hypopharyngeal structures. This also suggests important differences between the structure of a mannequin and the actual oral and hypopharyngeal structures and situations of a human. A prime example is that in situations where oral or hypopharyngeal secretion needs to be suctioned, it took longer and was more difficult with channel-type video laryngoscopy than with direct laryngoscopy. As a result, in most cases, the initial placement of the blade tip was either too deep or too shallow, so adjusting the depth of the blade tip and securing the laryngeal view took time.
After securing the laryngeal view, during the process of pushing the endotracheal tube into the airway, the tube tip often becomes stuck on the posterior cartilage. The process of adjusting this and proceeding with the insertion inevitably took longer compared to using a direct laryngoscope.
Last, the process of removing the device from inside the mouth after the insertion was completed took a lot of time, as separating the tube from the blade was different from doing so on a mannequin. In the case of humans, it was difficult to separate quickly, as in a mannequin, because care must be taken to avoid damaging the teeth, and if the separation was not done properly, there was a risk of the tube slipping out of the airway. Therefore, it had to be carefully separated, and this was reflected in the time taken.
Through this study, the authors posed the question of whether, for intubators who are very familiar with direct laryngoscopy, adapting to the channel type video laryngoscope might be more challenging. In fact, intubation using direct laryngoscopy is a difficult procedure, and even at the expert level, using direct laryngoscopy in the emergency room is not easy. Therefore, it could be interpreted that the results of using the channel-type video laryngoscope were different when compared with a novice practitioner with no experience in airway management with direct laryngoscopy. However, there has been no research on a novice practitioner using a channel-type video laryngoscope on actual patients, so such an interpretation is difficult to accept as established. Nevertheless, we can infer from this study that the use of the channel-type video laryngoscope might not be easy if one has not used a channel-type device before.
This study has several limitations. First, the sample size was small. However, it was conducted by calculating the sample size based on the results of the pilot study comparing the three groups. Additionally, considering the small sample size, the comparison was made using the Kruskal‒Wallis test, a nonparametric method. If further research involving intubators with varying levels of proficiency with direct laryngoscopy is conducted with a larger sample size, more meaningful results can be obtained. Second, all difficult airways were excluded from the study. This decision was made for the safety of the patients and because it was deemed impossible to directly compare intubation time and success rate with direct laryngoscopy if difficult airways were included. If future research is conducted solely on difficult airways, the performance of the channel-type video laryngoscope in laryngeal view could be significantly better. Authors should discuss the results and how they can be interpreted from the perspective of previous studies and of the working hypotheses. The findings and their implications should be discussed in the broadest context possible. Future research directions may also be highlighted.
5. Conclusions
Even if healthcare professionals without experience with the channel-type video laryngoscope improve their performance on airway mannequins after training, their intubation performance may differ when applied to actual patients. For the intubation performance to improve in actual patients, an accurate understanding of the characteristics of the channel-type video laryngoscope as well as sufficient experience and education are necessary.
Author Contributions
Y Lee was involved in the study design, management, data collection, result interpretation and cowriting of the manuscript. TH Lime, HY Choi, JG Kim, YS Jang, and W Kim were involved in interpretation of the data and critical revision of the paper for important intellectual content. As corresponding author, GH Kang was involved in this study concept and design, critical revision of the paper, and final approval of the version to be published.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number: HI17C2410).
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nouruzi-Sedeh, P.; Schumann, M.; Groeben, H. Laryngoscopy via Macintosh blade versus GlideScope: success rate and time for endotracheal intubation in untrained medical personnel. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermann, A.; Russo, S.G.; Crozier, T.A.; et al. Novices ventilate and intubate quicker and safer via intubating laryngeal mask than by conventional bag-mask ventilation and laryngoscopy. Anesthesiology 2007, 107, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohlrieder, M.; Brimacombe, J.; von Goedecke, A.; et al. Guided insertion of the ProSeal laryngeal mask airway is superior to conventional tracheal intubation by first-month anesthesia residents after brief manikin-only training. Anesth Analg 2006, 103, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Je, S.; Cho, Y.; Choi, H.J.; Kang, B.; Lim, T.; Kang, H. An application of the learning curve-cumulative summation test to evaluate training for endotracheal intubation in emergency medicine. Emerg Med J. 2015, 32, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.; Sowers, N.; Campbell, S.; French, J.; Atkinson, P. Just the Facts: Airway management during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Canadian Journal of Emergency Medicine 2020, 22, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, T.M.; El-Boghdadly, K.; McGuire, B.; McNarry, A.F.; Patel, A.; Higgs, A. Consensus guidelines for managing the airway in patients with COVID-19. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazopoulos, K. Kolonia, E.Laou, M.Mermiri, V.Tsolaki, A.Koutsovasilis, G.Zakynthinos, K.Gourgoulianis, E.Arnaoutoglou, A.Chalkias. Video Laryngoscopy Improves Intubation Times with Level C Personal Protective Equipment in Novice Physicians: A Randomized Cross-Over manikin Study. The Journal of Emergency Medicine. [CrossRef]
- Je, S.; Cho, Y.; Choi, H.J.; Kang, B.; Lim, T.; Kang, H. An application of the learning curve-cumulative summation test to evaluate training for endotracheal intubation in emergency medicine. Emergency Medicine Journal 2015, 32, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, J.; Aoyama, T.; Kusano, Y.; et al. Description and first clinical application of AirWay Scope for tracheal intubation. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 2006, 18, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, Y.; Asai, T.; Arai, T.; et al. Pentax-AWS, a new videolaryngoscope, is more effective than the Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation in patients with restricted neck movements: a randomized comparative study. Br J Anaesth 2008, 100, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik MA, O'Donoghue C, Carney J, et al. Comparison of the Glidescope, the Pentax AWS, and the Truview EVO2 with the Macintosh laryngoscope in experienced anaesthetists: a manikin study. Br J Anaesth 2009, 102, 128–134. [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Hassett, P.; Carney, J.; et al. A comparison of the Glidescope, Pentax AWS, and Macintosh laryngoscopes when used by novice personnel: a manikin study. Can J Anaesth 2009, 56, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.K.; Huang, C.C.; Lee, Y.; et al. Comparison of 3 video laryngoscopes with the Macintosh in a manikin with easy and difficult simulated airways. Am J Emerg Med 2013, 31, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafael Ortega, M.D. , Mauricio Gonzalez, M.D., Ala Nozari, M.D., Ph.D., and Robert Canelli, M.D. Personal Protective Equipment and Covid-19. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 382, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Summary of probable SARS cases with onset of illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003. Emergencies Preparedness, Response 2004.
- Tran, K.; Cimon, K.; Severn, M.; et al. Aerosol generating procedures and risk of transmission of acute respiratory infections to healthcare workers: A systematic review. PLoS One 2012, 7, e35797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. El-Boghdadly, D.J.N. K. El-Boghdadly, D.J.N.Wong, R. Owen, M.D. Neuman, S. Pocok, J.B. Carlisle, C. Johnstone, P. Andruszkiewicz, P.A. Baker, B.M. Biccard, G.L. Bryson, M.T.V.Chan, M.H. Cheng, K.J. Chin, M. Coburn, M.J. Fagerlund, S.N. Myatra, P.S. Myles, E.O’Sullivan, L.Pasin, F.Shamim, W.A. van Klei, I. Ahmad. Risks to healthcare workers following tracheal intubation of patients with COVID-19: a prospective international multicentre cohort study. Anaesthesia 2020 Jun 9. [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.; Dillman, D.; Kirsch, J.R.; Brambrink, A.; Aziz, M.; Dillman, D.; Kirsch, J.R.; Brambrink, A. Video Laryngoscopy with the Macintosh Video Laryngoscope in Simulated Prehospital Scenarios by Paramedic Students. Prehospital Emerg. Care 2009, 13, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, M.A.; Hassett, P.; Carney, J.; Higgins, B.D.; Harte, B.H.; Laffey, J.G. A comparison of the Glidescope®, Pentax-AWS®, and Macintosh laryngoscopes when used by novice personnel: a manikin study. Can. J. Anaesth. 2009, 56, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Suzuki, A.; Sugawara, A.; Kurosawa, A.; Takahata, O.; Iwasaki, H. Intubation training survey using four types of laryngoscopes among medical students: a comparison of the Macintosh laryngoscope, Miller laryngoscope, Airtraq and Pentax-AWS Airwayscope. Japanese Journal of Anesthesiology 2011, 60, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Fukuda, T.; Yamashita, S.; Takahashi, H.; Tanaka, M. Glidescope performance in tracheal intubation by novice laryngoscopists: a manikin study. Japanese Journal of Anesthesiology 2012, 61, 1386–1390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.N.; Jeong, M.A.; Na Oh, Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y. Efficacy of Pentax airway scope versus Macintosh laryngoscope when used by novice personnel: A prospective randomized controlled study. J Int Med Res. 2018, 46, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, I.K.; Kwak, H.J.; Lee, K.C.; Lee, J.H.; Min, S.K.; Kim, J.Y. Comparison of McGrath, Pentax, and Macintosh laryngoscope in normal and cervical immobilized manikin by novices: a randomized crossover trial. Eur J Med Res 2020, 25, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Ueki, R.; Niki, M.; Hirose, M.; Shimode, N. Three-day tracheal intubation manikin training for novice doctors using Macintosh laryngoscope, McGrath MAC videolaryngoscope and Pentax AirwayScope. Medicine 2021, 100, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, K.B.; Tsui, D.; Goodyear, P.; Irwin, M.G. Personal protection equipment for biological hazards: does it affect tracheal intubation performance? Resuscitation 2007, 74, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberle, S.J.; Sandefur, B.J.; Sunga, K.L.; Campbell, R.L.; Lohse, C.M.; Alecastro Puls, H.; Laudon, S.; Sztajnkrycer, M.D. Intubation Efficiency and Perceived Ease of Use of Video Laryngoscopy vs Direct Laryngoscopy While Wearing HazMat PPE: A Preliminary High-fidelity Mannequin Study. Prehospital & Disaster Medicine. 2015, 30, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Chung-Cheng; Chaou, Chung-Hsien; Tseng, Chiung-Yao; Lin, Chih-Chuan. The effect of personal protective equipment on emergency airway management by emergency physicians: a mannequin study. European Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2016, 23, 124–129. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott Taylor, R.; Pitzer, M.; Goldman, G.; Czysz, A.; Simunich, T.; Ashurst, J. Comparison of intubation devices in level C personal protective equipment: A cadaveric study. American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2018, 36, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Lee, Y.; Kang, G.H.; Jang, Y.S.; Kim, W.; Choi, H.Y.; Kim, J.G. Educational suitability of new channel-type video-laryngoscope with AI-based glottis guidance system for novices wearing personal-protective-equipment. Medicine (Baltimore) 2022, 101, e28890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).