1. Introduction
Strawberry (
Fragaria ananassa), a perennial herbaceous plant belonging to the genus Fragaria in the Rosaceae family, is renowned for its short cultivation cycle and high economic yield. This fruit is prominent among consumers because of its exceptional taste and significant nutritional value. Strawberries are an important economic crop in globally and China[
1]. According to data from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, as of 2020, China boasted a strawberry cultivation area of over 127,000 hm
2, with a production surpassing 3.336 million tons, ranking it as the world's leading producer[
2].The predominant method of cultivation in China is greenhouse cultivation, which involves enclosed spaces, elevated temperatures, and high humidity.The continuous cultivation practices have led to the accumulation of pathogens, resulting in frequent outbreaks of strawberry diseases and economic losses, which hinder the sustainable development of the strawberry industry[
3].One of the major diseases affecting strawberry is root rot, particularly in continuously cultivated strawberry fields[
4]. The complex array of pathogens contributing to strawberry root rot includes
Neopestalotiopsis clavispora,
Phytophthora fragariae,
Fusarium solani,
Fusarium oxysporum,
Rhizoctonia solani, Colletotrichum acutatum, and
Armillaria mellea[
5,
6].The primary method of controlling strawberry root rot is the use chemicals in current production practices, due to the diversity of pathogens and the lack of strawberry varieties with high resistance of root rot[
7,
8]. However, the use of fungicides for the edible strawberry fruits posed a potential risk to human health. Hence, it is urgent to explore novel control strategies for strawberry root rot. Biological control measures are particularly effective to reduce soil-borne pathogens. The screening and application of biocontrol microorganisms to control root rot is very important for the sustainable development of the strawberry industry.
Trichoderma species have been tried as BCA (Biological Control Agents) and used as an alternative to synthetic fungicides to control a variety of plant diseases[
9,
10]. The biocontrol mechanisms of Trichoderma are based on the activation of multiple mechanisms, either indirectly, by competing for space and nutrients, promoting plant growth and plant defensive mechanisms, and antibiosis, or directly, by mycoparasitism[
11,
12]. Studies indicate that
Trichoderma spp. could increase the resistance of strawberry roots pathogens. Zhang et al. [
13] found that
T. harzianum M10-3-2 could significantly inhibit
F. solani, which was the agent of strawberry root rot.
T. asperellum D7-3 had remarkable growth-promoting effects on strawberries, and
T. koningiopsis M0-3-3 enhances the biocontrol efficacy of other strains against strawberry root rot. They also proved that the combination of the three Trichoderma strains( M10-3-2, D7-3 and M 0-3-3) was more effective than the individual treatments. Mercado et al. [
14] discovered that
T. harzianum could effectively control strawberry root rot caused by
C. acutatum. Rees et al. [
15] found that
T. atrobrunneum significantly reduced the incidence of strawberry root rot caused by
A. mellea. Mirzaeipour et al. [
16] obtained three Trichoderma strains with control effective for strawberry root rot caused by
R. solani. Despite substantial research on the use of Trichoderma strains to control strawberry root rot, the focus had mainly been on the control the pathongens including
R. solani,
C. acutatum,
F. solani, and
A. mellea. Studies on the screening of Trichoderma strains is still relatively lack against strawberry root rot caused by
N. clavispora.
In this study, the potential role of T. asperellum CMT10 isolated from healthy strawberry rhizosphere soil was investigated as biological control agents of strawberry root rot caused by N. clavispora. To achieve this goal, plate culture, microscopy observation and root drenching methods were employed to investigate the biocontrol mechanism and control efficacy of T. asperellum CMT10 on strawberry root rot, as well as its growth-promoting effect on strawberry seedlings. The purpose of this study was to elucidate control efficacy against strawberry root rot caused by N. clavispora and growth-promoting effects of T. asperellum CMT10, and to provide effective biocontrol microorganisms and application techniques for environmentally friendly control of strawberry root rot.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Pathogen and Plant Materials
Neopestalotiopsis clavispora strain CMGF3 was isolated from strawberry with symptoms of root rot (our preliminary work), and the fungus was cultured on potato dextrose agar (PDA; 20% potato, 2% dextrose, 1.5% agar) for 7 d at 28 °C. One-year-old strawberry seedlings of a commercial cultivar “Hongyan” were provided by “Shilixiang” strawberry seedling cultivation facility.
2.2. Isolation and Screen of Trichoderma strains
Soil samples were collected from healthy strawberries rhizosphere soil of ”Shilixiang” strawberry planting field (112°57’1451”E, 34°79’4223”N) in Luoyang, Henan Province. One gram of soil was taken in a Falcon tube (50 mL) containing sterile distilled water (SDW) and shaken (180 rpm) for 1 h. The samples were diluted five times, and 100 µL was spread onto potato dextrose agar (PDA) plates [
17]. The Trichoderma colonies were transferred to a new PDA medium 7 d after incubation at 28°C for purification culture.
A total of 10 Trichoderma strains were screened for antagonistic activity against mycelial growths of
N. clavispora CMGF3, using a dual culture plate assay as the procedure developed by Pimentel et al.[
18]. One mycelial disc (4 mm diameter) each of a
Trichoderma sp. and
N. clavispora was excised from the growing edges of 7-day-old cultures and placed 2 cm apart on opposite sides of PDA plates (90 mm). The plates were incubated for 7 days at 28°C. A control of
N. clavispora alone on PDA plates was used.The experimental design was completely randomized with 20 treatments and 3 replications.The growth rate of
N. clavispora was determined by measuring the colony diameter.The percent inhibition was calculated as follows: percent inhibition (%)=[(pathogen colony diameter in the control treatment-pathogen colony diameter in the challenge treatment)/pathogen colony diameter in the control treatment]x 100.
2.3. Morphological and Molecular identification of Trichoderma CMT10
The purified Trichoderma CMT10 was inoculated on a PDA plate medium and cultured in the dark for 7 days at 28°C. Its macroscopic morphology was observed like color and texture of the colony surface verse and reverse, presence or absence of pigmentation, and pattern of growth and sporulation, and images of the colonies were obtained. Microscopic morphologies such as conidia and conidiophore were observed using an optical microscope (ZEISS Axio Scope5, Oberkochen, Germany). Morphological identification relied on the descriptions found in previous research [
19,
20].
Trichoderma CMT10 was cultured on PDA medium at 28°C for 7 days. Mycelia were harvested from the cultures, and genomic DNA (gDNA) was extracted using a DNA extraction kit (TIANGEN Biotech, Beijing, China).Then, the extracted DNA were used as a template to amplify the ITS (internal transcribed spacer) region and
tef1-α (translation elongation factor-1α) region; the primers were designed with reference to previous studies[
21,
22]. All amplified loci, primers, and PCR conditions are listed in
Table 1.The PCR was carried out using the TIANGEN Golden Easy PCR kit (TIANGEN Biotech,Beijing,China).The PCR products were subjected to direct automated sequencing using fluorescent terminators using an ABI 377 Prism Sequencer (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China).The sequences were confirmed with a BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) search of the NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) database (
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), and a phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining (NJ) method, with 1,000 bootstrap replications in the MEGA 10.0 package. Phylogenetic analysis with ITS-
tef-1α gene sequences was carried out to illustrate the position of Trichoderma CMT10. After identification, the sequences were submitted to Genbank. The strains utilized in this study and their corresponding GenBank accession numbers are listed in
Table 2.
2.4. Biocontrol Mechanism of Trichoderma CMT10 against N. clavispora
2.4.1. Inhibitory effects of volatile compounds from Trichoderma CMT10 on N. clavispora
To determine the effect of the volatile compounds secreted by Trichoderma CMT10 against the growth of
N. clavispora CMGF3 , exposure of Trichoderma volatile compounds was performed using the confrontation culture method [
23].Mycelial discs of Trichoderma were cut using a sterile cork borer (5 mm diameter) and placed at the center of a freshly prepared PDA plate, and were cultured for 3 days at 28°C in the dark. A mycelial disc (5 mm diameter) of the fungal pathogen
N. clavispora CMGF3 was placed onto another freshly prepared PDA plate in the same manner. PDA plates inoculated with
N. clavispora mycelial plugs were placed on top of the PDA plates inoculated with Trichoderma CMT10 and the plates were then sealed with parafilm.A control without Trichoderma inoculation was used.The inhibition of mycelial growth of
N. clavispora was observed at 28°C for 7 d.The experiment was performed twice in triplicates.
2.4.2. Inhibitory effects of Non-volatile compounds from Trichoderma CMT10 on N. clavispora
The effect of non-volatile compounds of Trichoderma CMT10 against the growth of the fungal pathogen N. clavispora CMGF3 under in vitro conditions was determined as follows. Trichoderma CMT10 was diluted with sterile water to obtain a conidial suspension containing 1×108 spores/mL, and 100 µL conidial suspension were inoculated into 100 mL of potato dextrose broth (PDB) medium at 28°C for 4 d under shaking conditions (180 rpm). The fermented liquid was centrifuged at 8 000 rpm for 2 min, and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter to obtain sterile filtrate. Therefore, the sterile filtrate was spread onto PDA plates at a ratio of 1:9, and a 7-day-old cultured N. clavispora CMGF3 mycelium plug was placed onto a PDA plate. A mixture of sterile water medium was used as the control. After 7 days of incubation at 28°C, the diameter of the pathogen was measured, and the inhibition rate was calculated. The experiment was performed twice in triplicates.
2.4.3. Hyperparasitism of Trichoderma CMT10 on N. clavispora
The hyperparasitism of Trichoderma CMT10 on
N. clavispora CMGF3 was observed using a dual culture method[
24].Under sterile conditions, 1 mL of melted PDA medium was pipetted onto a sterilized glass slide to make a PDA membrane. After solidification of the medium, Trichoderma CMT10 and
N. clavispora CMGF3 mycelial discs were separately inoculated onto the membrane (with a 6 cm distance between them) at 28°C for incubation 24-72 h. The growth was recorded at 12 h intervals. After successful fungal superparasitism on the pathogen, the dual culture areas were observed using an optical microscope (ZEISS Axio Scope5, Oberkochen, Germany).
2.5. Growth Promotion Properties of Trichoderma CMT10
The precipitated Ca
3(PO
4)
2 on Pikovskaya's agar media (glucose, 10 g; (NH
4)
2SO
4, 0.5 g; NaCl 0.3 g; MgSO
4 0.3 g; MnSO
4 0.03 g; K
2SO
4, 0.3 g; FeSO
4 0.03 g; Ca
3(PO
4)
2 5.0 g; agar 15.0 g; pH 7.0-7.5) was used for the qualitative detection of the phosphate -solubilizing of Trichoderma CMT10[
25]. Siderophore production was done by chrome azure S (CAS) agar media (CAS 0.06 g; HDTMA 0.07 g; FeCl
3•6H
2O 0.003 g; NaH
2PO
4•2H
2O 0.30 g; Na
2HPO
4•12H
2O 1.21g; NH
4Cl 0.125 g; KH
2PO4 0.038 g; NaCl 0.06 g; agar 9.0 g; pH 6.7-6.9)[
26]. Nitrogen fixation was determined by nitrogenfree agar medium (KH
2PO
4 0.20 g; MgSO
4 0.20 g; NaCl 0.20 g; CaCO
3 5.0 g; mannitol 10.0 g; agar 15.0 g; pH 6.9-7.91)[
27]. The qualitative detection method of growth promotion properties of Trichoderma CMT10 relied on the descriptions found in previous research [
28], and Trichoderma CMT10 was quantitatively tested to biosynthesis IAA according to Brick et al. [
29].
2.6. Control Effects of Trichoderma CMT10 on Strawberry Root Rot
Mycelial discs of Trichoderma CMT10 and
N. clavispora CMGF3 were inoculated at the center of PDA plates at 28°C for 7 d.The conidial suspensions ( 1×10
8 spores/mL) of Trichoderma and pathogen were prepared using sterile water, then stored at 4°C for later use. One-year-old strawberry seedlings of a commercial cultivar “Hongyan” were used. The seedlings were carefully selected from the nursery with one plant per pot. Each plant was transplanted into a plastic pot (diameter, 28 cm; bottom diameter, 20 cm; height, 30 cm). Plants were grown in soil in a growth chamber at 22°C and 75% humidity with a 16-h-light/8-h-dark photoperiod. After acclimation for 15 d, plants were used for pathogen infection and to assess the control efficacy of Trichoderma CMT10 on strawberry root rot. The potting root irrigation method was used for inoculation.The experiment included four treatments: 1) inoculation with
N. clavispora CMGF3 only; 2) inoculation with Trichoderma CMT10 only; 3) inoculation with
N. clavispora CMGF3 after 3 d followed by Trichoderma CMT10 ; 4) water inoculation as a control. Each treatment consisted of 5 pots, with 3 replicates. Plants were inoculated with 5 mL of conidial suspension of CMGF3 and CMT10 through the soil around each plant. All the treatments were followed by 60 days of incubation at 28°C and 80% relative humidity. The disease severity of the seedlings was assessed using a scoring system of 0-5 modified from the report of Vestberg et al. [
30]. Level 0 signifies an entire plant in a healthy state; Level 1 indicates a root disease incidence of ≤30%, with normal leaves; Level 2 is characterized by a root disease incidence greater than 30% and equal to or less than 60%, with normal leaves; Level 3 represents a root disease incidence greater than 60% and equal to or smaller than 80%, accompanied by yellowing leaves; Level 4 indicates a root disease incidence exceeding 80%, leading to leaf wilting; and Level 5 signifies complete plant mortality. The disease index and control efficacy were calculated based on the grading results. Disease Index = ∑ (Disease Level × Number of Plants at That Level) / (Total Number of Plants × Highest Disease Level) × 100; Control Efficacy (%) = (Control Disease Index − treatment disease index) / control disease index × 100.
2.7. Growth-Promoting Effects of Trichoderma CMT10 on Strawberry Seedlings
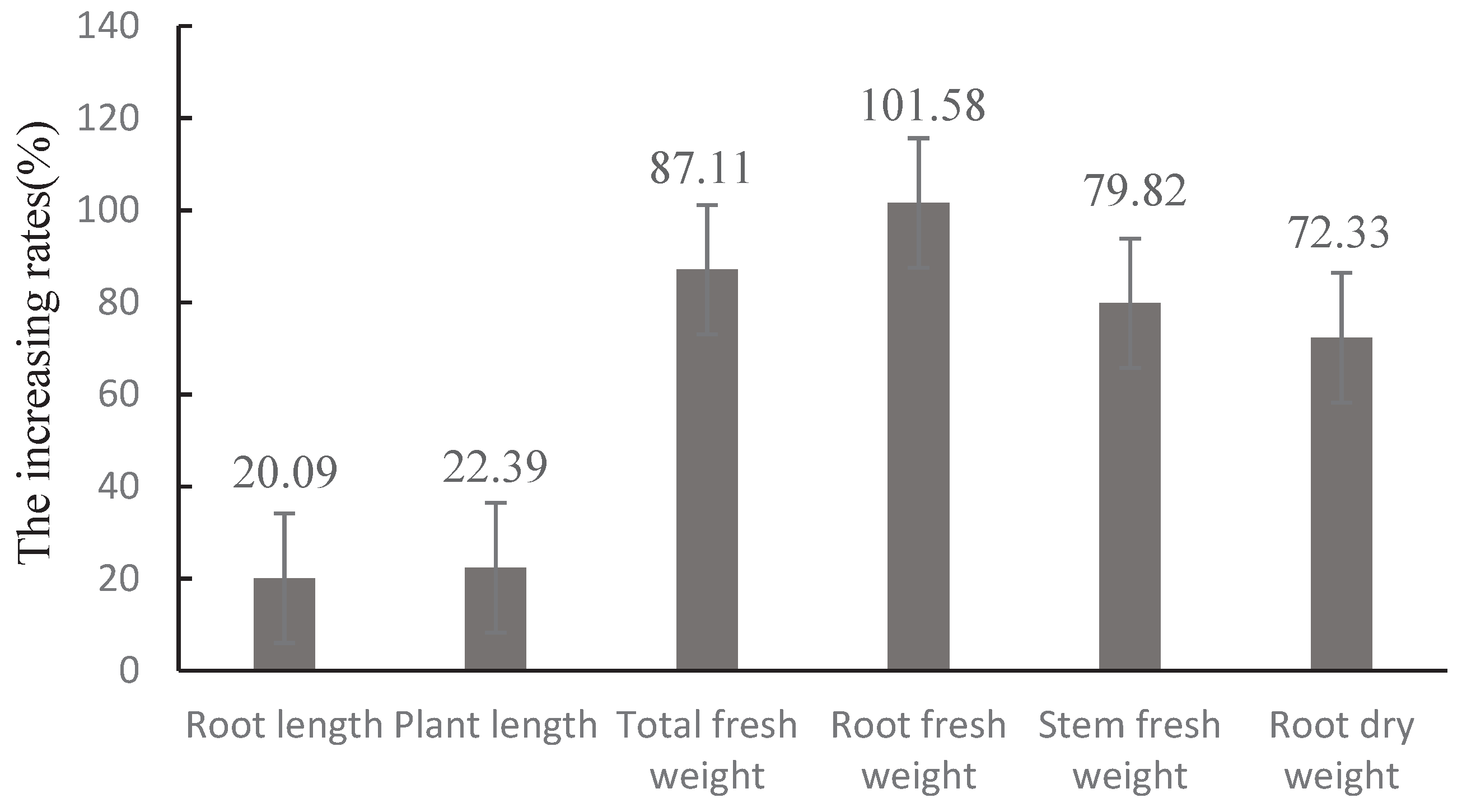
The same method used in section 2.6 was used in the experiment, which consisted of two treatments: 1)inoculation with Trichoderma CMT10; 2) water inoculation as a control. Each treatment consisted of 5 pots, with 3 replicates. Plants were inoculated with 5 mL of conidial suspension(1×108 spores/mL) of CMT10 through the soil around each plant, and the plants were incubated for 60 days at 28°C. Afterward, the strawberry seedlings were carefully excavated, and their height, root length, and fresh weight (stem and leaf fresh weight, root fresh weight, and total fresh weight) were measured. The roots were dried at 45°C in an oven, and dry weight was measured. The growth-promoting rate was calculated as follows:Growth promotion Rate (%) = (treatment biomass − Control Biomass) / control biomass × 100.
2.8. Data Statistics and Analysis
Data obtained from the experiments were processed using Excel 2010 and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed using DPS 7.05 statistical software. Duncan's new multiple range test was used to assess significant differences, and the significance level was set at p=0.05.
Results
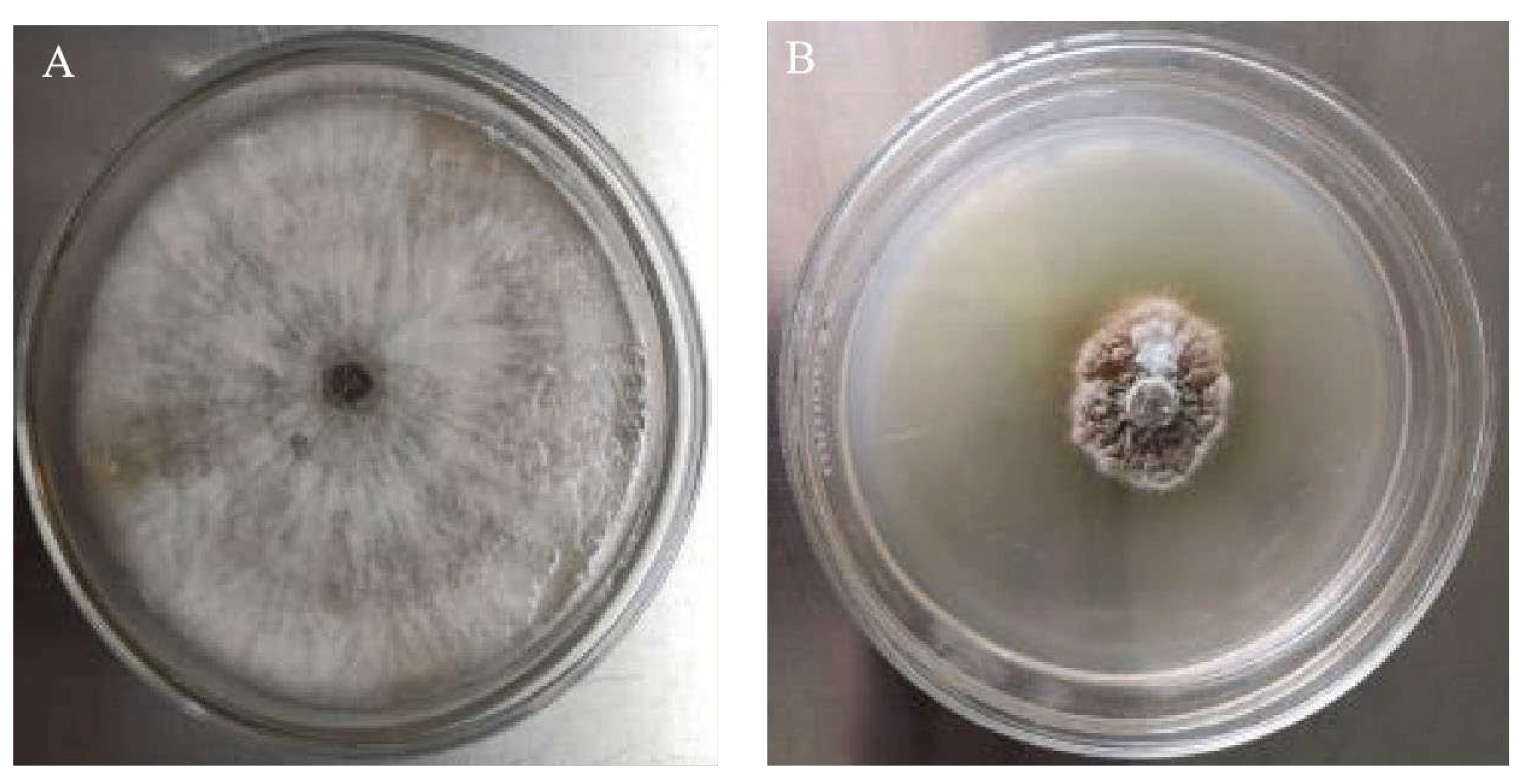
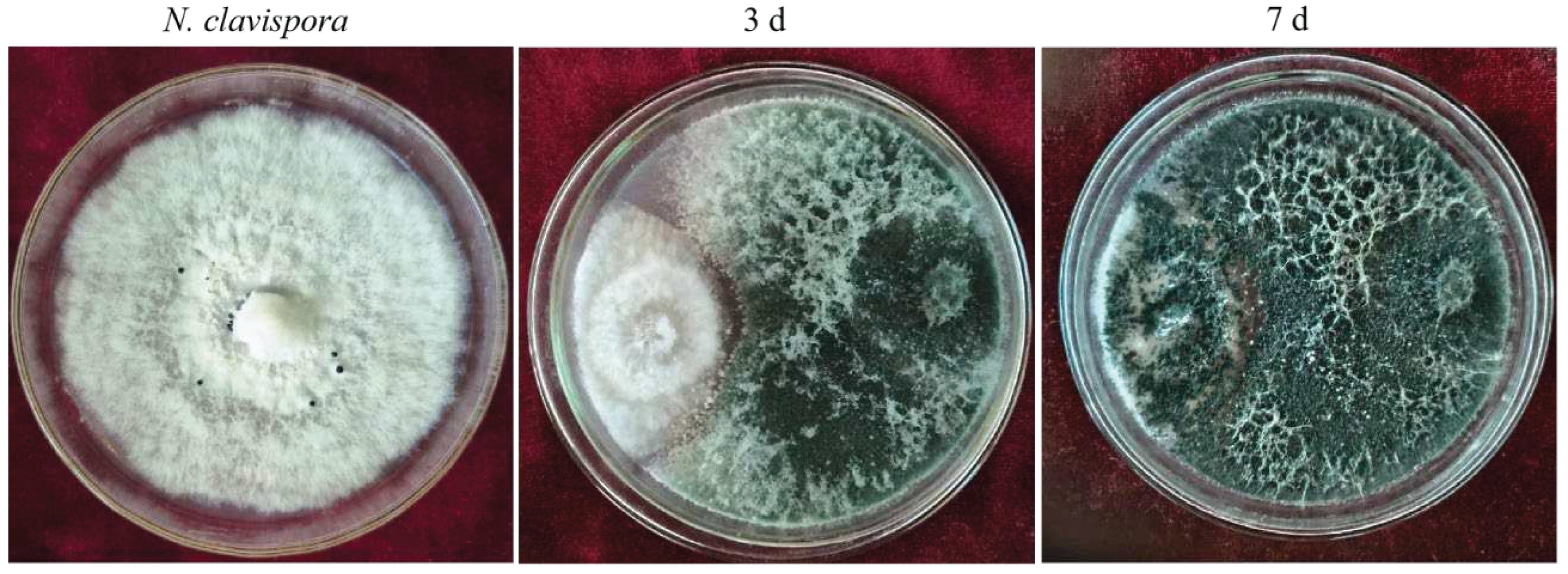
3.1. Screening of Trichoderma Strains with Inhibitory Effects on N. clavispora
Ten Trichoderma strains were isolated by the dilution culture method. The two Trichoderma isolates, CMT10 and CMT4 were found to inhibit the mycelial growths of
N. clavispora CMGF3,with inhibitory rates of 65.49% and 51.37%, respectively. CMT10 displayed significant inhibition activity against
N. clavispora (Table 3). Further observations indicated that the mycelial growth of CMT10 was faster than that of CMGF3 and could thus quickly occupy the nutrient space. After 3 d of the dual culture, the mycelia of pathogen CMGF3 only reached one-third of the culture dish, and an inhibition zone appeared between the CMT10 and CMGF3. Moreover, the mycelia of CMGF3 near the inhibition zone were sparse, indicating weakened growth. By day 7 of the dual culture, the mycelia of CMT10 completely covered CMGF3 colony and completely inhibiting the growth and reproduction of CMGF3 (
Figure 1). The results indicate that Trichoderma CMT10 could strongly inhibit mycelial growth and reproduction of CMGF3, demonstrating a robust competitive advantage against the strawberry root rot pathogen.
Table 3.
Antagonism test of of Trichoderma strains against N. clavispora on PDA plates.
Table 3.
Antagonism test of of Trichoderma strains against N. clavispora on PDA plates.
| Treatments |
Colony diameter |
Inhibition rate |
| CMT10 |
2.93±0.153 |
65.49 a |
| CMT4 |
4.13±0.058 |
51.37 b |
| CMGF3 |
8.50±0.000 |
- |
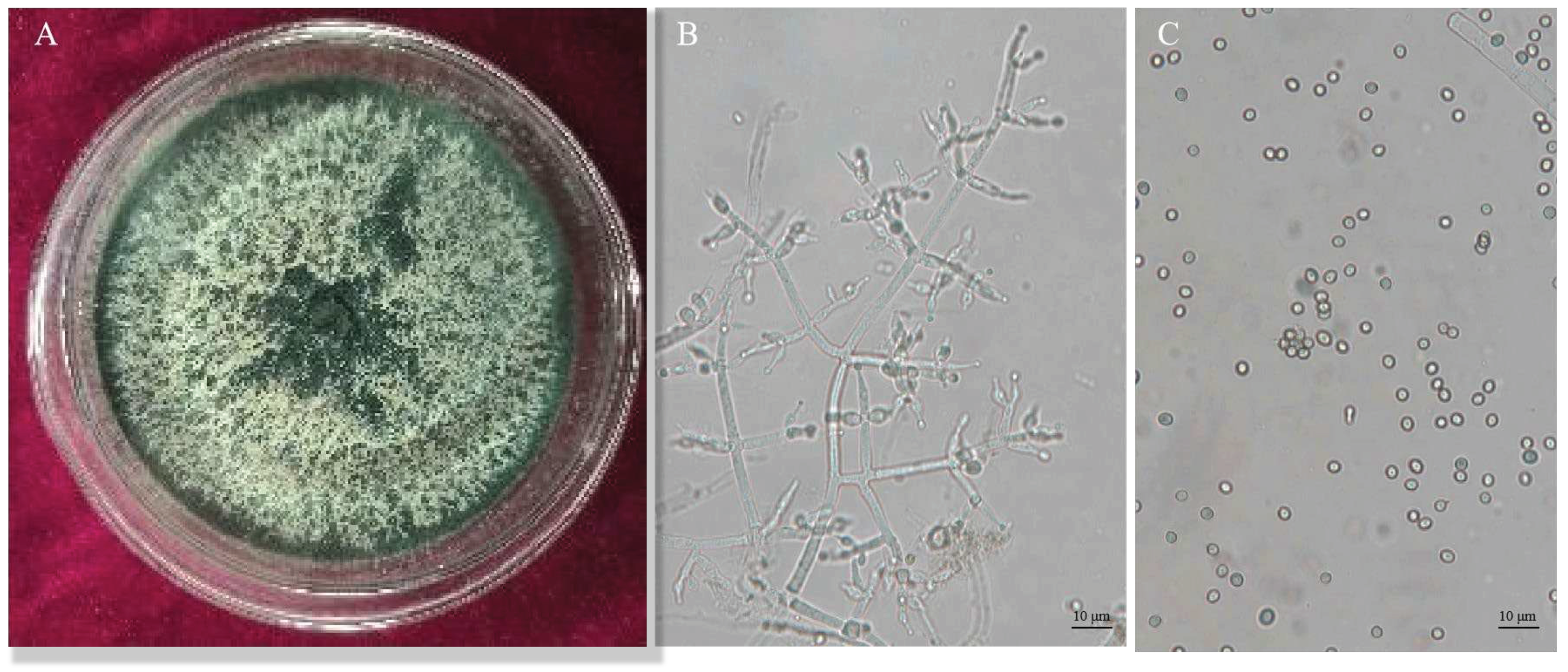
3.2. Identification of Trichoderma CMT10
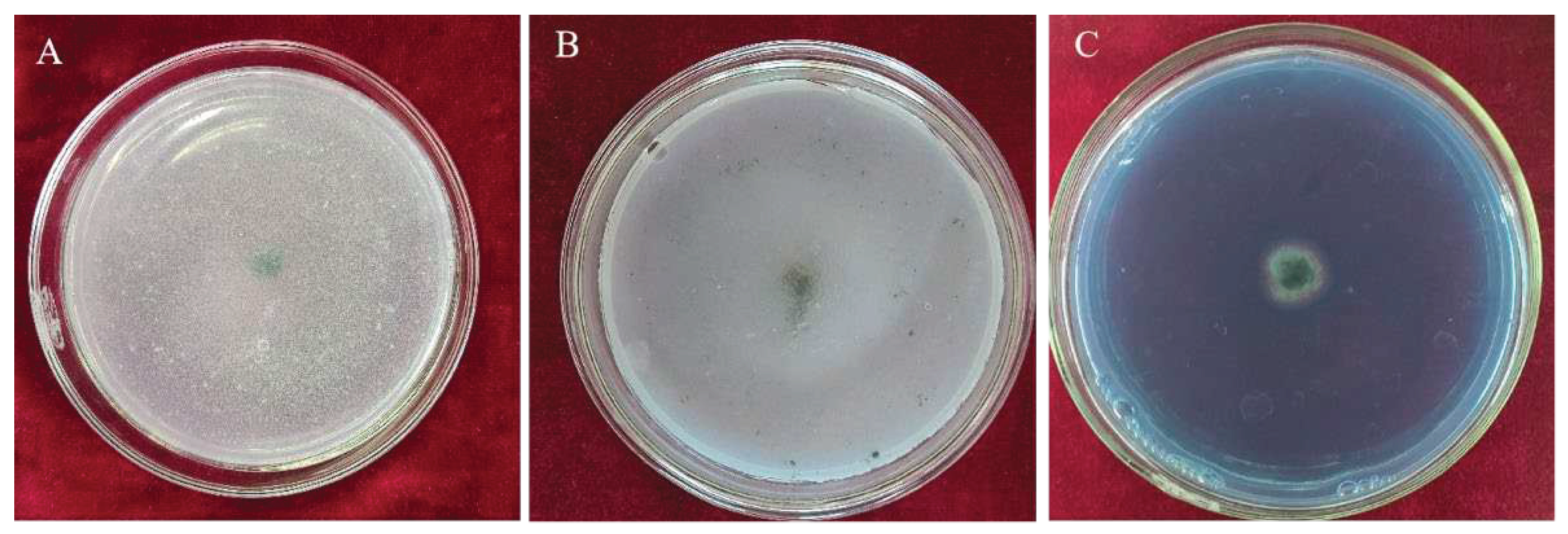
Trichoderma CMT10 displayed a fast growth on PDA medium, with aerial mycelia completely covering the entire culture dish within 3 days. Initially, the colony appeared white, but it changed to yellow-green and green later. The green conidia were produced and completely covered the plate after 5 days (
Figure 2A). Microscopically, it was observed the branches were pyramidal in type with verticillate, frequently pared lateral branches that arose from main axis with 2-5 phialides clustered at the top. The angle with the main axis was 90°, and the lateral branches re-branched. The phialides were ampulliform, somewhat thicker in the middle ,and terminated with conidia(
Figure 2B). The conidia were spherical to ellipsoidal, 2(–3.7)×3.2(–4.5) μm, single-celled and light green (
Figure 2C). Based on these cultural and morphological characteristics, the strain CMT10 was identified as
T. asperellum.
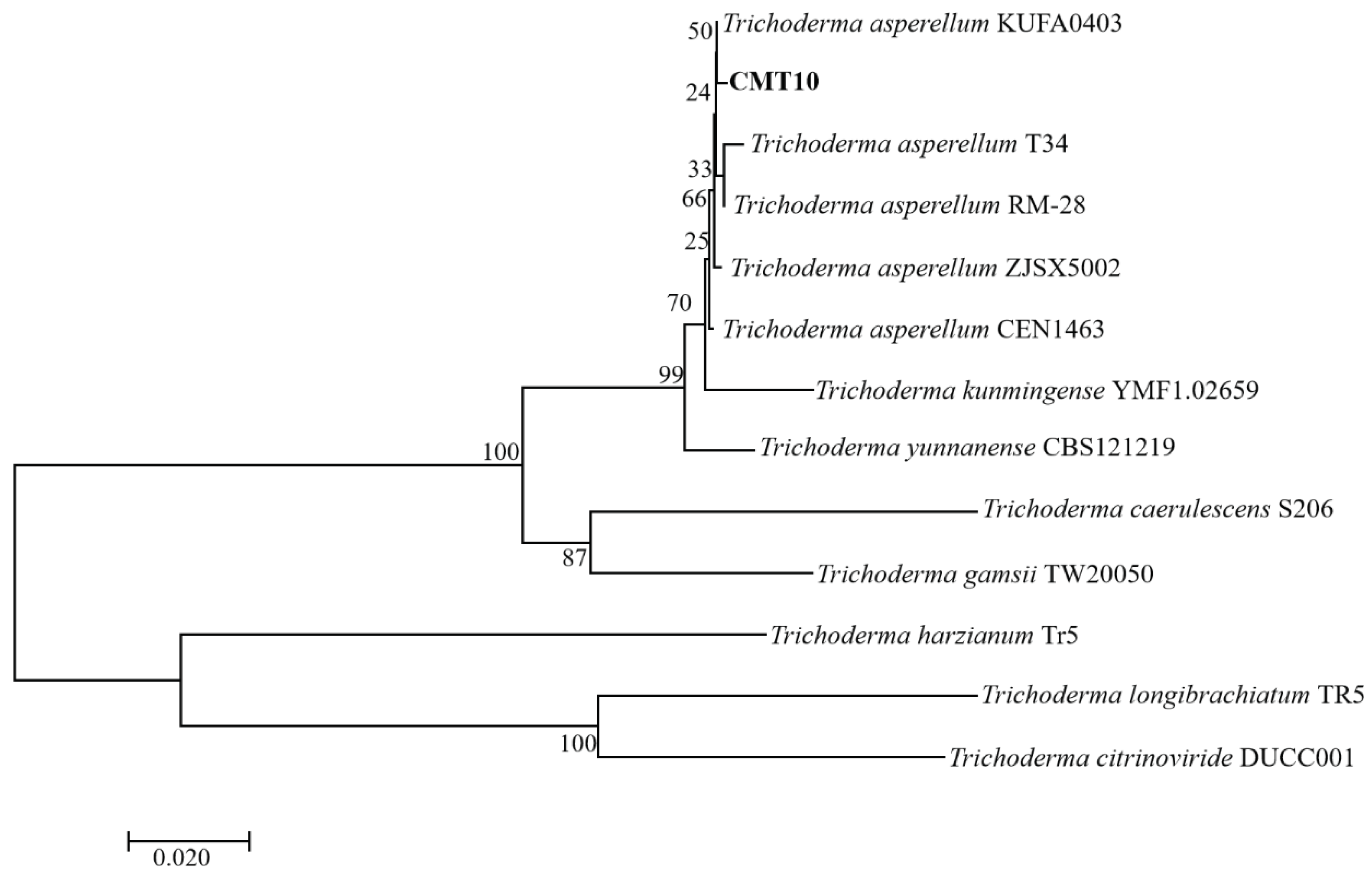
The ITS regions and
tef1-α regions of of Trichoderma CMT10 were amplified and sequenced. The GenBank accession numbers were PP126513 and PP171486, respectively. The phylogenetic tree based on ITS-
tef1-α gene sequences showed that Trichoderma CMT10 was closely related to
T. asperellum strains CEN1463, T34, ZJSX5002, KUFA0403, and RM-28 (
Figure 3). The details of the strain names, origins, and accession numbers are listed in
Table 2. Therefore, the CMT10 strain was identified as
T. asperellum according to the morphological characterization and molecular analysis.
3.3. Biocontrol Mechanism of Trichoderma CMT10 against N. clavispora
3.3.1. Inhibition Rates of Volatile Metabolites from Trichoderma CMT10 on N. clavispora
The effect of volatile metabolites emitted by
T. asperellum CMT10 was tested against the growth of
N. clavispora using the confrontation culture method.The mycelia of pathogenic CMGF3 was inhibited significantly by the volatile metabolites of CMT10, compared to the control. The inhibition rate was 69.84% at 7d after confrontation culture (
Figure 4). On the tenth day, the mycelia of the pathogenic CMGF3 had ceased to grow, while the mycelia of
T. asperellum CMT10 continued to spread and encroach upon the colony of the pathogenic CMGF3.
3.3.2. Inhibition Rates of Non-volatile Metabolites from Trichoderma CMT10 on N. clavispora
The antibacterial activity of non-volatile metabolites produced by
T. asperellum CMT10 was assessed against the fungal pathogen CMGF3. The results demonstrated that non-volatile metabolites of CMT10 had a strong inhibitory effect to the growth of the fungal pathogen CMGF3 on PDA plates. After 7 d of incubation at 28°C, the colony diameter of the CMT10-treated fungal growth was reduced significantly, compared to the untreated control (
Figure 5).The inhibition rate of non-volatile metabolites produced by
T. asperellum CMT10 was 79.67% against CMGF3.
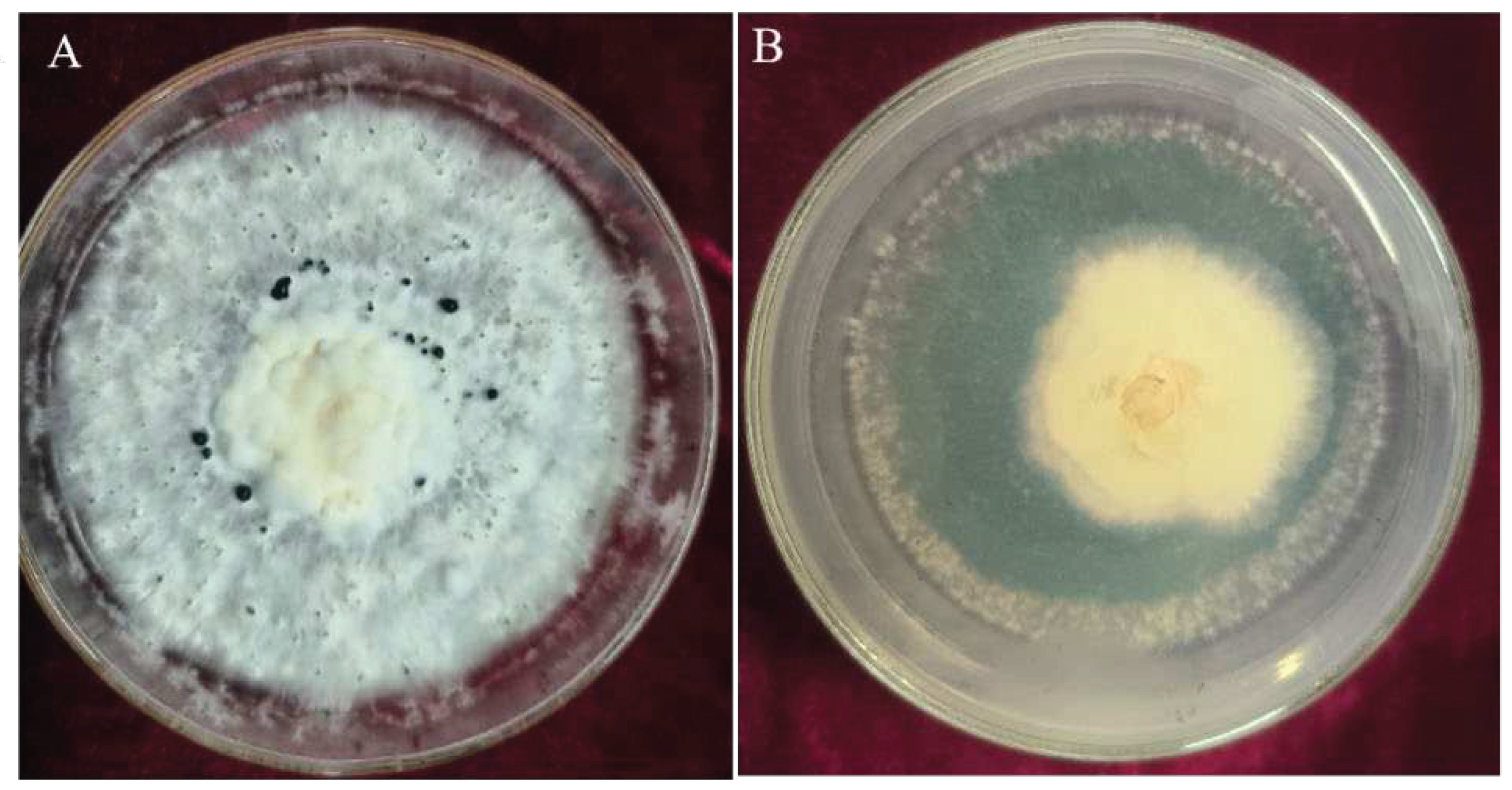
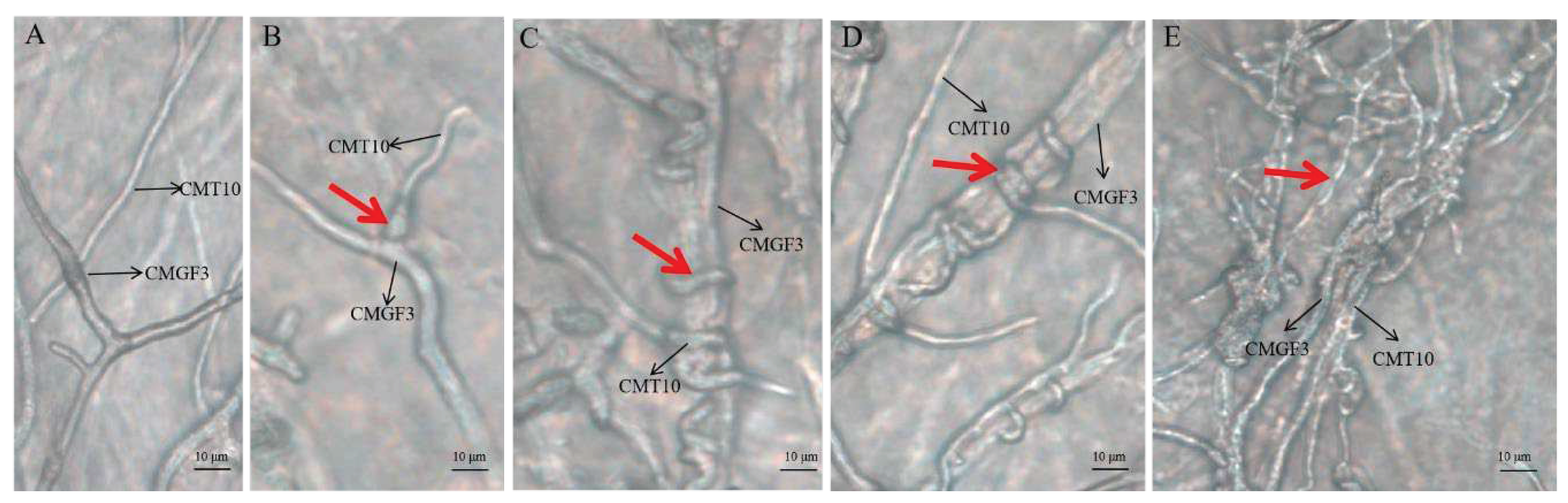
3.3.3. Hyperparasitism of Trichoderma CMT10 on N. clavispora
Microscopic observation the hyphal interaction between
T. asperellum CMT10 and the pathogen CMGF3 revealed that the mycelia of both strains began to contact each other, but the antagonistic effect between them was not evident after 48 h (
Figure 6A). CMT10 mycelia were attached to CMGF3 after 72 h(
Figure 6B). After 96 h, CMT10 mycelia grew along and entwined with CMGF3 mycelia, causing contraction of CMGF3 mycelia (
Figure 6 C, D). Moreover, CMGF3 mycelia were observed being penetrated and were embedded by CMT10 mycelia (
Figure 6E). The results showed that
T. asperellum CMT10 indicates a strong hyperparasitic effect against the strawberry root rot pathogen
N. clavispora CMGF3.
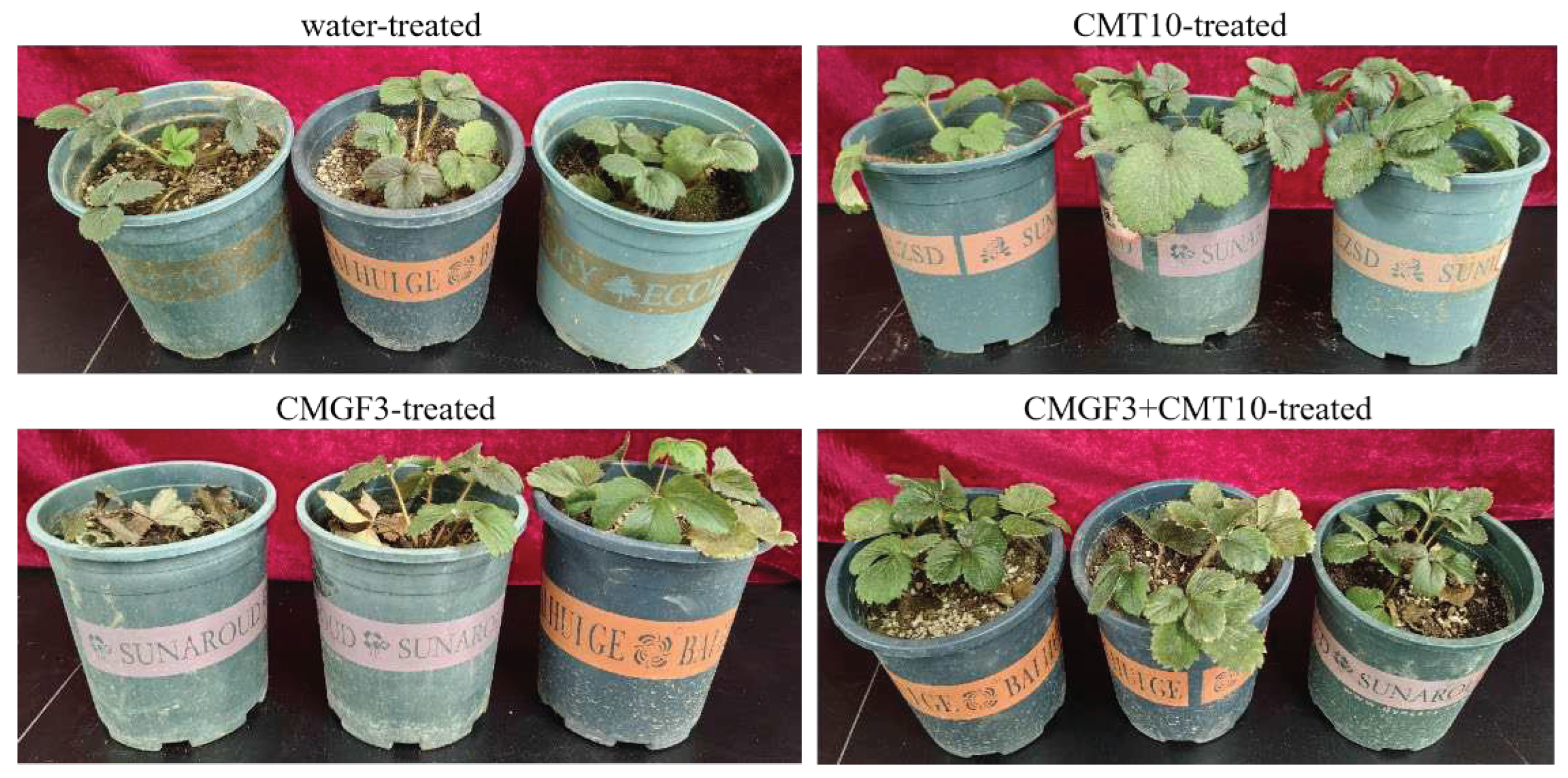
2.5. Biocontrol Efficacy of T. asperellum CMT10 against Strawberry Root Rot
The incidence of strawberry root rot of each treatment was investigated after inoculation for 60 days (Table 3,
Figure 8). The results revealed that the treatment with inoculation of
T. asperellum CMT10 and the water control did not exhibit disease symptoms in strawberry. Treatment with the inoculation of
N. clavispora CMGF3 showed the most severe disease symptoms, with a disease index of 84.00, which was significantly higher than that of the other treatments (P≤0.05). The disease index for treatment with
N. clavispora CMGF3 +
T. asperellum CMT10 was 31.00, and its biocontrol efficacy against strawberry root rot reached 63.00%, indicating that
T. asperellum CMT10 effectively controlled the occurrence of potted strawberry root rot.
Table 3.
The control effects of T. asperellum CMT10 against strawberry root rot.
Table 3.
The control effects of T. asperellum CMT10 against strawberry root rot.
| Treatments |
Disease index |
Control efficiency (%) |
| CMGF3 |
84.00±0.04a |
- |
| CMT10 |
0.00±0.00c |
- |
| CMGF3+CMT10 |
31.00±0.61b |
63.00±0.07a |
| CK |
0.00±0.00c |
- |
4. Discussion
4.1. Significance of Exploring Biocontrol Resources for Strawberry Root Rot
The prevention of strawberry root rot is complicated due to its diverse composition of pathogens, making it difficult to control. In particular, this disease causes substantial economic losses to the strawberry industry in greenhouse cultivation[
31].
Trichoderma spp., recognized as crucial biocontrol resource, have been widely utilized in disease control of various crops[
32].
Trichoderma spp. had played a pivotal role in the prevention and control of strawberry root rot. However, due to the diverse composition of root rot pathogens, most studies have focused on Trichoderma against
Fusarium spp. and
Rhizoctonia solani [
33,
34]. Studies focusing on
N. clavispora, a pathogen associated with strawberry root rot, were scarce. In this study,
N. clavispora, an important pathogen causing strawberry root rot, was specifically selected as targete pathogenic fungi, and obtained a strain of
T. asperellum CMT10 with significant inhibition activity against
N. clavispora. This study highlighted the remarkable effectiveness of
T. asperellum against strawberry root rot and its ability to promote growth in strawberry seedlings. These findings contributed to the development of biocontrol resources for managing strawberry root rot and broadened the potential applications of
T. asperellum.
4.2. Biocontrol Mechanism of T. asperellum CMT10
Most studies had demonstrated that Trichoderma strains could inhibit pathogenic fungi through nutrient and spatial competition, hyperparasitism and the production of antibiotic secondary metabolites, while they could also promot plant growth and enhance plant stress resistance [
35]. Ecological niche competition was a crucial mechanism of biocontrol microorganisms for preventing disease in biocontrol. Trichoderma, a biocontrol agent, was able to rapidly occupy ecological niches in environments with low concentrations of nutrients, which can cause pathogenic fungi to lose their ability to thrive and survive [
36]. Risoli et al. [
37] found that the growth rate of Trichoderma was 2.0-4.2 times that of
Botrytis cinerea, indicating a significantly faster growth of Trichoderma compared to the pathogen, impeding the growth and reproduction of the pathogen. The results of this study indicated that
T. asperellum CMT10 could significantly inhibit the growth and reproduction of
N. clavispora. In the initial phase, CMT10 exhibited rapid growth and strong competitiveness,and it quickly occupied nutritional and ecological spatial sites and produced an inhibition zone. In the later stages of cultivation,
N. clavispora colony completely disappeared and was replaced by dark green conidia of
T. asperellum.
Trichoderma employed the mechanism of antibiosis in its biological control. Metabolites produced by Trichoderma, both volatile and non-volatile, have been reported to restrict the growth of various pathogenic fungi[
38]. The metabolites included triohodexrmin, gliotoxin, viridin, and peptide antibiotics[
39]. Naglot et al.[
40] found that metabolites of Trichoderma significantly inhibited
F. oxysporum with an inhibition rate of up to 54.81%. Manganiello et al.[
41] discovered that volatile secondary metabolites secreted by
T. viride TG050609 caused irregular growth, fragmentation, and even dissolution of
Phytophthora nicotianae. By determining the inhibitory effects of non-volatile and volatile metabolites of
T. asperellum CMT10 on
N. clavispora causing strawberry root rot, it was found that after 7 days of cultivation on CMT10 fermented metabolite plates, the inhibition rate reached 79.67%, and the inhibition rate of volatile metabolites against
N. clavispora reached 69.84%. This suggests that CMT10 metabolites have a strong inhibitory effect on
N. clavispora that causes strawberry root rot. However, the metabolites responsible for this effect remain unclear and require further investigation.
Hyperparasitism was a vital mechanism employed by Trichoderma for its biological control.Trichoderma recognized lectins on the mycelia of a pathogenic fungi and engages in processes such as identification, contact, wrapping, penetration, parasitism, and dissolution of the fungi[
42]. Hewedy et al.[
43] found that
T. harzianum Th6 could adhere to, invade and disrupting the mycelia of
F. graminearum. Larran et al.[
44] observed that
T. harzianum could form adhesive structures on the mycelia of
F. sudanense, leading to curling, wrinkling, and dissolution the mycelia of
F. sudanense. The present study also found that
T. asperellum CMT10 exhibited hyperparasitism against
N. clavispora. It could recognize, contact, wrap, and parasitize the mycelia of pathogen. However, the mycelium dissolution, protoplasm leakage, or cell disintegration were not observed, which may be related to the observation time during cultivation. It is believed that cell wall hydrolytic enzymes secreted by Trichoderma played a crucial role in its hyperparasitic activity, such as chitinases, glucanases, and proteases, which can dissolve the cell walls of pathogenic fungi, allowing Trichoderma to parasitize, absorb nutrients, and ultimately cause death of the pathogenic fungi[
45]. Whether
T. asperellum CMT10 can secrete enzymes with lytic effects remains unclear, and is a direction for future research.
4.3. Practical Application of Trichoderma asperellum CMT10
Currently, the production of Trichoderma generally involves the simultaneous or sequential action of several disease prevention mechanisms. Trichoderma can utilize different antagonistic mechanisms at different stages to biocontrol effects[
46]. This study demonstrated that
T. asperellum CMT10 exerted competitive, antibiosis, and hyperparasitic effects against the pathogenic fungi causing strawberry root rot.
T. asperellum CMT10 could effectively controll the occurrence of strawberry root rot. However, the biocontrol mechanisms at different stages of interaction between Trichoderma and the pathogenic fungi in plants still need further exploration, which may provide a theoretical foundation for the practical application of T. asperellum CMT10 in strawberry production. Therefore, future research should focus on field disease control effect and the interactive relationships among T. asperellum CMT10, the pathogenic fungi causing root rot, and the host plant. In addition, this study specifically evaluated the growth-promoting effects of T. asperellum CMT10 on strawberry seedlings by measuring parameters such as plant height, root length, total fresh weight, root fresh weight, stem fresh weight, and root dry weight. It is essential to conduct more field experiments to fully understand the growth-promoting effects of CMT10 on strawberry plants, as well as investigate the impact of T. asperellum CMT10 on strawberry fruit size, yield, and quality.
5. Conclusions
In summary, Trichoderma asperellum CMT10 was obtained among 10 Trichoderma strains as a potent biocontrol agent against N. clavispora, the pathogenic fungi caused strawberry root rot. The results of the pot experiment demonstrated that T. asperellum CMT10 effectively inhibited root rot and significantly enhanced the growth of strawberry seedlings. These findings indicate that T. asperellum CMT10 has great potential as a biocontrol resource for preventing and controlling strawberry root rot, making it a promising candidate for future development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.Y.; methodology, P.L., Z.W., W.R., and R.Y.; software, D.W.,Y.M., W.Y., and W.R.; formal analysis, P.L., W.R., and R.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, R.Y.; visualization, D.W.,Y.M., and W.R.; project administration, R.Y. and W.Y.; funding acquisition, W.Y. and R.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Program of Henan province of China (232102320111), the Science and Technology Planning Major Project of Fujian province of China (2022N0010), and the Natural Resources Science and Technology Innovation Project of Fujian province of China (KY-090000-04-2022-016).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets that support the findings of the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Basu, A.; Nguyen, A.; Betts, N.M.; Lyons, T. J. Strawberry as a functional food:An evidence-based review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 790–806.
- Ji, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, Q.H.; Geng, C.; Duan, K. Colletotrichum species pathogenic to strawberry: discovery history, global diversity, prevalence in China, and the host range of top two species. Phytopathol Res. 2022, 4, 42. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Du,Y.Q.; Cai,W.W.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhu, J.Q. Effect of complex antagonistic bacteria on controlling strawberry root rot. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 100-110.
- Lazcano, C.; Boyd, E.; Holmes, G.; Hewavitharana, S.; Pasulka, A.; Ivors, K. The rhizosphere microbiome plays a role in the resistance to soil-borne pathogens and nutrient uptake of strawberry cultivars under field conditions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3188. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Jamshaid, M.; Zahid, M.A.; Andreasson, E.; Vetukuri, R.A.; Stenberg, J.A. Biological control of strawberry crown rot, root rot and grey mould by the beneficial fungus Aureobasidium pullulans. Bio-Control. 2021, 66, 535-545.
- Baggio, J.S.; Cordova, L.G.; Peres, N.A. Sources of inoculum and survival of 22 Macrophomina phaseolina in Florida strawberry fields. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2417-2424. [CrossRef]
- Feliziani, E.; Romanazzi, G. Postharvest decay of strawberry fruit: etiology, epidemiology, and disease management. J. Berry Res. 2016, 6, 47–63. [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Kim, T.Y.; Won, S.J.; Moon, J.H.; Ajuna, H.B.; Kim, K. .; Ahn, Y.S. Control of fungal diseases and fruit yield improvement of strawberry using Bacillus velezensis CE100. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 365. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.J.; Yang, H.M.; Jin, J.; Yan, H.H.; Wang, J.P.; Zhang, R.Q. Synergistic activity of antagonistic Trichoderma spp. and Rhizoctonia solani increases disease severity on strawberry petioles. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2022,164, 375–389. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-lateif, K.S. Trichoderma as biological control weapon against soil borne plant pathogens. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 2299–2306.
- Benítez, T.; Rincón, A.M.; Limón, M.C.; Codón, A.C. Biocontrol mechanisms of Trichoderma strains. Int. Microbiol. 2004, 7, 249-260.
- Ferreira, F.V.; Musumeci, M.A. Trichoderma as biological control agent: scope and prospects to improve efficacy. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 90. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Du, G.D.; Song, Y.N.; Lu, X.F.; Ying, N. Screening, identification and the effect validation of Trichoderma against the root rot of strawberry. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University 2015, 46, 654-660.
- Mercado, J.A.; Barceló, M.; Pliego, C.; Rey, M.; Caballero, J.L.; Muñoz-Blanco, J.; Ruano-Rosa, D.; López-Herrera, C.; de Los Santos, B.; Romero-Muñoz, F.; Pliego-Alfaro, F. Expression of the β-1,3-glucanase gene bgn13.1 from Trichoderma harzianum in strawberry increases tolerance to crown rot diseases but interferes with plant growth. Transgenic Res. 2015, 24, 979-989. [CrossRef]
- Rees, H.J.; Drakulic, J.; Cromey, M.G.; Bailey, A.M.; Foster, G.D. Endophytic Trichoderma spp. can protect strawberry and privet plants from infection by the fungus Armillaria mellea. PLoS ONE 2022,17, e0271622. [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeipour, Z.; Bazgir, E.; Zafari, D.; Darvishnia, M. Selection and biocontrol efficiency of Trichoderma isolates against Rhizoctonia root rot and their growth promotion effects on strawberry plants. J. Plant Pathol. 2023, 105, 1563–1579. [CrossRef]
- Debbi, A.; Boureghda, H.; Monte, E.; Hermosa, R. Distribution and genetic variability of Fusarium oxysporum associated with tomato diseases in Algeria and a biocontrol strategy with indigenous Trichoderma spp. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 282. [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.F.; Arnão, E.; Warner, A.J.; Subedi, A.; Rocha, L.F.; Srour, A.; Bond, J.P.; Fakhoury, A.M. Trichoderma isolates inhibit Fusarium virguliforme growth, reduce root rot, and induce defense-related genes on soybean seedlings. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1949-1959. [CrossRef]
- Shaigan, S.; Seraji, A.; Moghaddam, S.A. Identification and investigation on antagonistic effect of Trichoderma spp. on tea seedlings white foot and root rot (Sclerotium rolfsii Sacc.) in vitro condition. Pak J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 11,2346-2350.
- Yang H. Classification and identification of Trichoderma. China Land Press:Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 14–20.
- White, T. J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics,” in PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications. Academic Press: San Diego, America; 1990; pp. 315–322.
- O’donnell, k.; Kistler, H.C.; Cigelnik, E.; Ploetz, R.Mul-tiple evolutionary origins of the fungus causing Panama disease of banana: concordant evidence from nuclear and mitochondrial gene genealogies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.1998, 95, 2044-2049. [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, T.; Rajan, S.; Muthukumar, M.; Ram, G.; Yadav, K.; Kumar, S.; Ahmad, I.; Nidhi, K.; Mishra, V.K.; Vinay,K.; Jha Sunil, K. Biological management of banana Fusarium wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense tropical race 4 using antagonistic fungal isolate CSR-T-3 (Trichoderma reesei). Front. Microbiol. 2020,11, 595845.
- G, K.A.; L, X.G.; L, Y.G.; Z,T.B.; W, S.L. Potential of Trichoderma harzianum and T. atroviride to Control Botryosphaeria berengeriana f. sp. piricola, the cause of apple ring rot. J. Phytopathology 2002, 150, 271–276.
- Nautiyal, C.S. An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 265–270. [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Lim, Y.; Lee, S.E.; Yang, N.W.; Rhee, J.H. CAS agar diffusion assay for the measurement of siderophores in biological fluids. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 44, 89–95. [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, F.; Eltem, R. Identification and characterization of endophytic bacteria isolated from in vitro cultures of peach and pear rootstocks. 3 Biotech. 2016, 6,120. [CrossRef]
- 28. Yao; C.X.; Li X.j.; Li Q.; Xing, G.Z.; Fang, W.Y.; Li, C.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yao, C.X.; Xu, M.; Li, F.F.; Song, R.F.; Zhang, W.M.; Li, S.J.; Shen, X.; Zhang, D.F. Screening and identification of antagonistic bacteria against tobacco Fusarium root rot and evaluation of their effects on growth promoting and disease control. Chinese Journal of Biological Control 2021, 37,1066-1072.
- Brick, J.M.; Bostock, R.M.; Silversone, S.E. Rapid in situ assay for indole acetic acid production by bacteria immobilized on nitrocellulose membrane. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 535–538. [CrossRef]
- Vestberg, M.; Kukkonen, S.; Saari, K; Parikka, P.; Huttunen, J.; Tainio, L.; Devos, N.; Weekers, F.; Kevers, C.; Thonart, P.; Lemoine, M.C.; Cordier, C.; Alabouvette, C.; Gianinazzi, S. Microbial inoculation for improving the growth and health of micropropagated strawberry. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2004, 27, 243-258.
- Zhang, M.; Kong, Z.; Fu, H.; Shu, X.; Xue, Q.; Lai, H.; Guo, Q. Rhizosphere microbial ecological characteristics of strawberry root rot. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1286740. [CrossRef]
- Elad, Y.; Chet, I.; Henis, Y. Biological control of Rhizoctonia solani in strawberry fields by Trichoderma harzianum. Plant Soil 1981, 60, 245–254. [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Muñiz, P.; Borrero, C.; Ordóñez-Martín, J.; Pastrana, A.M.; Avilés, M. Optimization of the use of industrial wastes in Anaerobic soil disinfestation for the control of Fusarium wilt in strawberry. Plants (Basel) 2023, 12, 3185. [CrossRef]
- Tyśkiewicz, R.; Nowak, A.; Ozimek, E.; Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J. Trichoderma: the current status of its application in agriculture for the biocontrol of fungal phytopathogens and stimulation of plant growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2329. [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, M.; Ruan, J.; Chen, J. Trichoderma and its role in biological control of plant fungal and nematode disease. Front Microbiol. 2023, 14,1160551. [CrossRef]
- Mohiddin, F.A.; Padder, S.A.; Bhat, A.H.; Ahanger, M.A.; Shikari, A.B.; Wani, S.H., Bhat, F.A.; Nabi, S.U.; Hamid, A.; Bhat, N.A.; Sofi, N.R.; Waza, S.A.; Hamid, B.; Parveen, S.; Hussain, A.; Bhat, A.N.; Ali, O.M.; Dar, M.S.; Abdel Latef, A.A.H. Phylogeny and optimization of Trichoderma harzianum for Chitinase production: evaluation of their antifungal behaviour against the prominent soil borne phyto-pathogens of temperate India. Microorganisms 2021, 9,1962.
- Risoli, S.; Cotrozzi, L.; Sarrocco, S.; Nuzzaci, M.; Pellegrini, E.; Vitti, A. Trichoderma-induced resistance to Botrytis cinerea in Solanum species: a meta-analysis. Plan. Theory 2022, 11,180. [CrossRef]
- Kottb, M.; Gigolashvili, T.; Großkinsky, D.K.; Piechulla, B. Trichoderma volatiles effecting Arabidopsis: from inhibition to protection against phytopathogenic fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 995. [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, C.R.; Bilesky-José, N.; de Lima, R.; Fraceto, L.F. Encapsulation of Trichoderma harzianum preserves enzymatic activity and enhances the potential for biological control. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 225. [CrossRef]
- Naglot, A.; Goswami, S.; Rahman, I.; Shrimali, D.D.; Yadav, K.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Veer, V. Antagonistic potential of native Trichoderma viride strain against potent tea fungal pathogens in north east India. Plant Pathol. J. 2015, 31, 278–289. [CrossRef]
- Manganiello, G.; Sacco, A.; Ercolano, M.R.; Vinale, F.; Lanzuise, S.; Pascale, A.; Napolitano, M.; Lombardi, N.; Lorito, M.; Woo, S.L. Modulation of tomato response to Rhizoctonia solani by Trichoderma harzianum and its secondary metabolite harzianic acid. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9,1966. [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.; Le Cocq, K.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Moore, K.; Winsbury, R.; de Torres Zabala, M.; Studholme, D.J.; Salmon, D.; Thornton,C.R.; Grant,M.R. Transcriptional reprogramming underpins enhanced plant growth promotion by the biocontrol fungus Trichoderma hamatum GD12 during antagonistic interactions with Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in soil. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17,1425–1441. [CrossRef]
- Hewedy, O.A.; Abdel Lateif, K.S.; Seleiman, M.F.; Shami, A.; Albarakaty, F.M.; M El-Meihy, R. Phylogenetic diversity of Trichoderma strains and their antagonistic potential against soil-borne pathogens under stress conditions. Biology (Basel) 2020, 9,189. [CrossRef]
- Larran, S.; Santamarina Siurana, M.P.; Roselló Caselles, J.; Simón, M.R.; Perelló, A. In vitro antagonistic activity of Trichoderma harzianum against Fusarium sudanense causing seedling blight and seed rot on wheat. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 23276-23283. [CrossRef]
- Sood, M.; Kapoor, D.; Kumar, V.; Sheteiwy, M.S.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Landi, M.; Araniti, F.; Sharma, A. Trichoderma: The secrets of a multitalented biocontrol agent. Plants 2020, 9, 762. [CrossRef]
- Jogaiah, S.; Abdelrahman, M.; Tran, L.P.; Ito, S.I. (). Different mechanisms of Trichoderma virens-mediated resistance in tomato against Fusarium wilt involve the jasmonic and salicylic acid pathways. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 870–882.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).