Submitted:
07 February 2024
Posted:
07 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Performance assessment of presurgical tests
2.3. Multiple binary logistic model
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
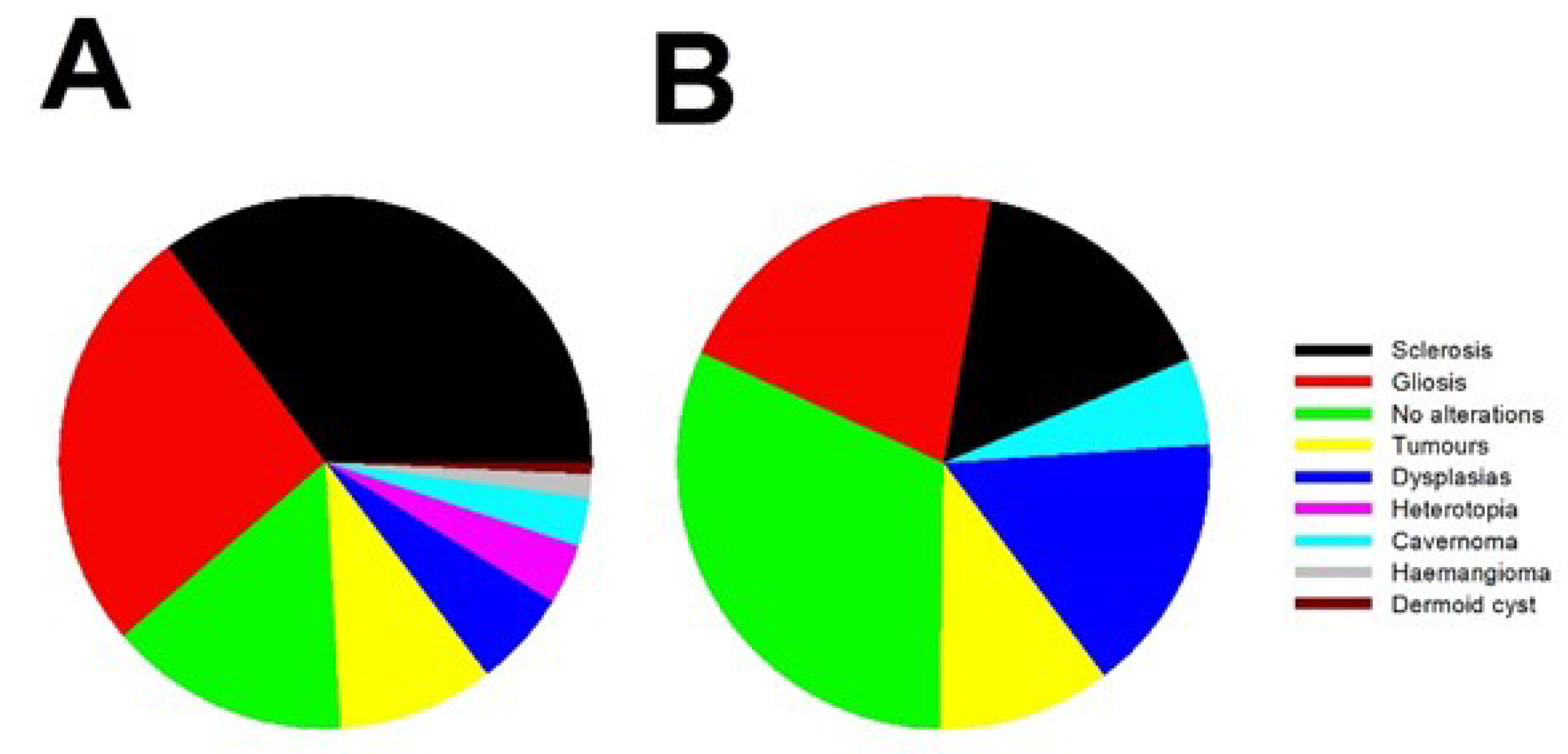
3.1. Clinical results
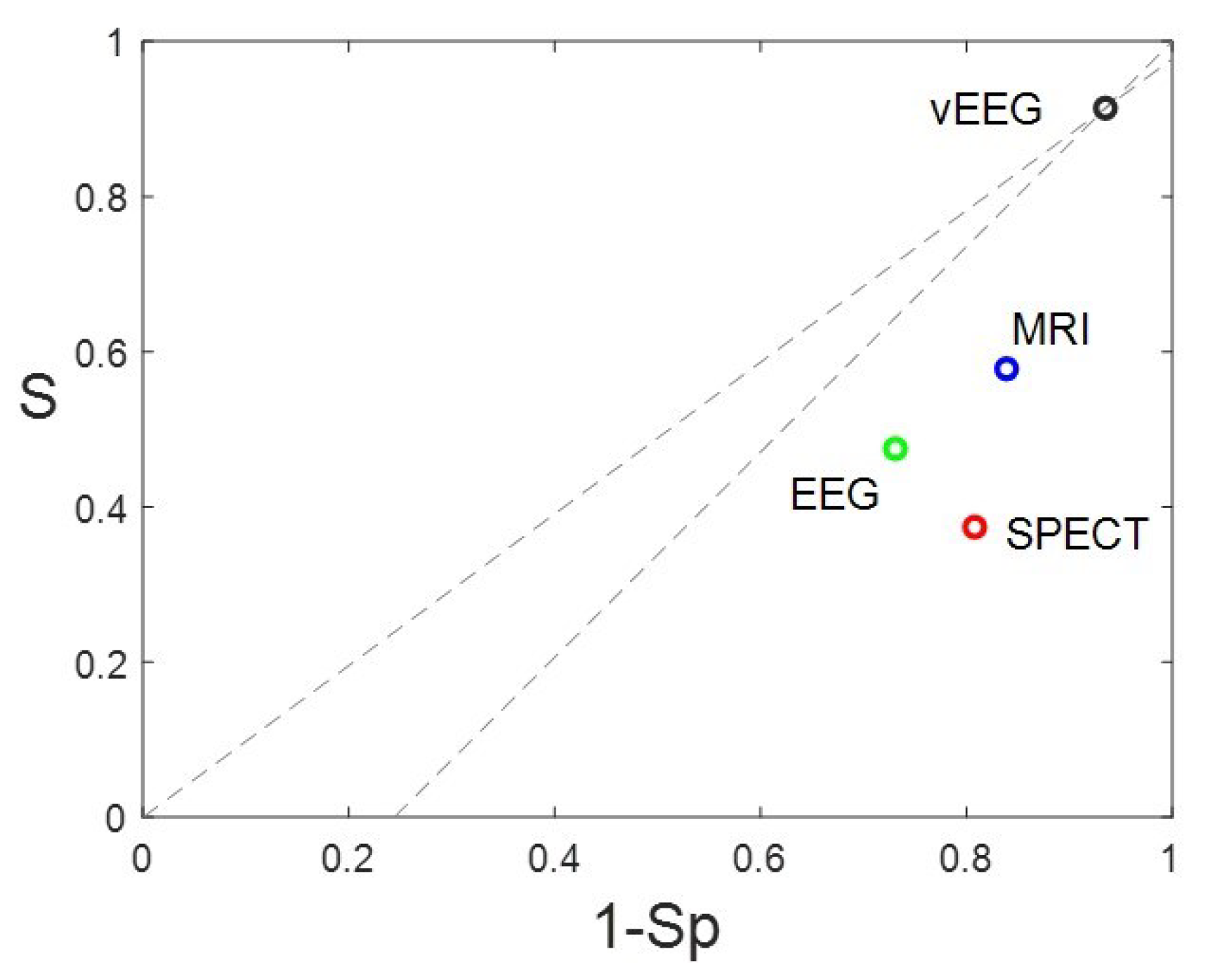
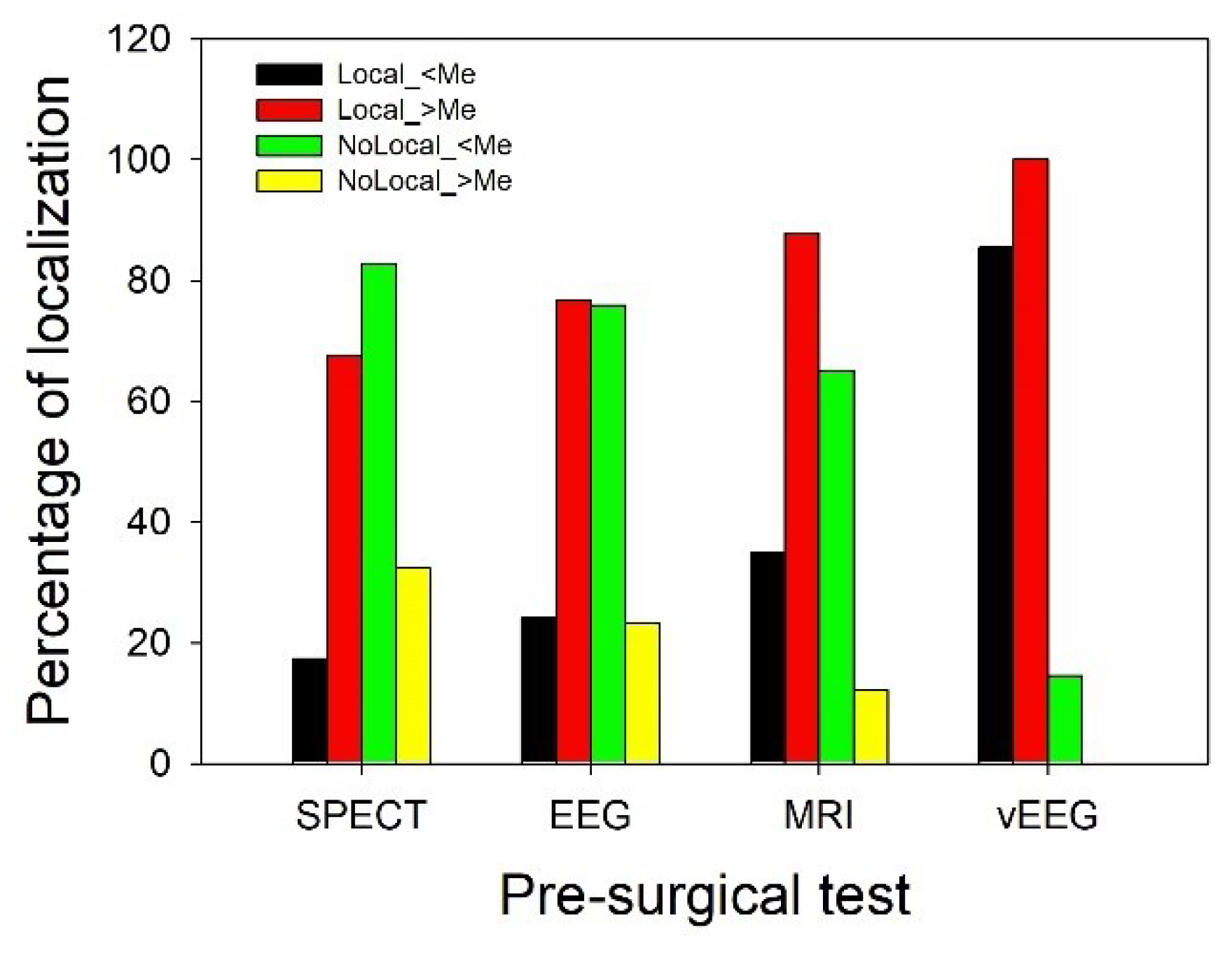
3.2. Evaluation of presurgical accuracy in localization of the EZ.
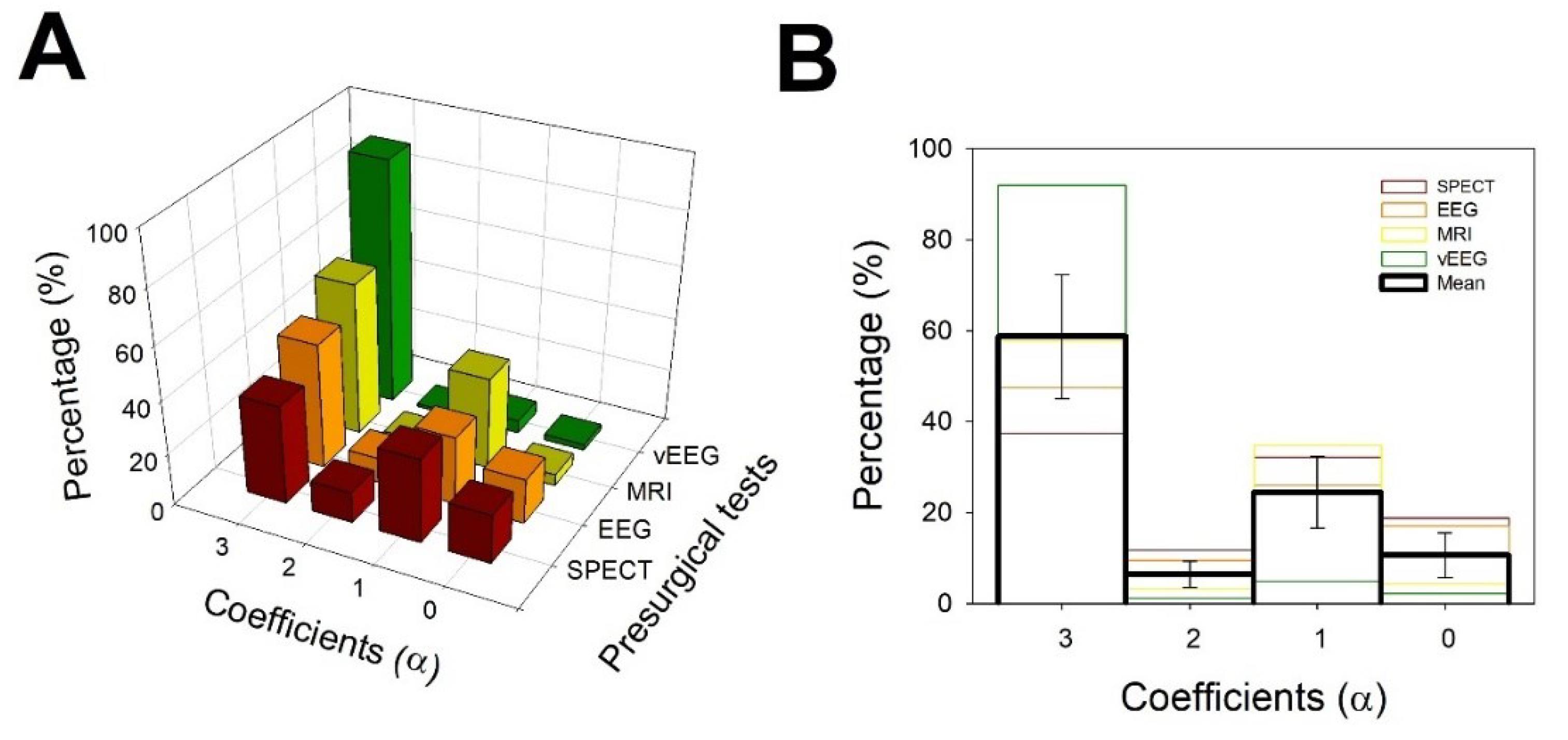
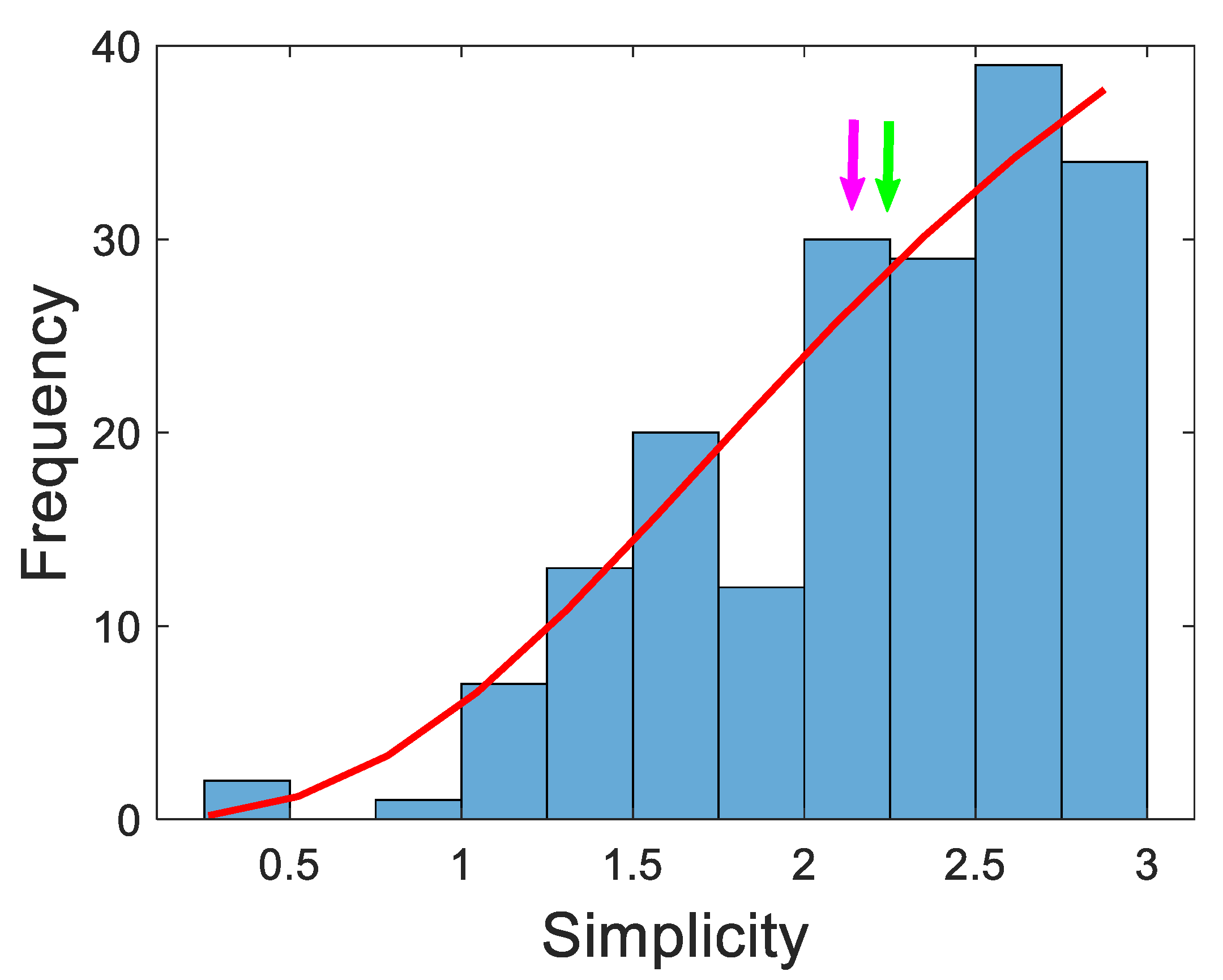
3.3. Evaluation of simplicity of diagnosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Initially, we computed the “null model” (L0) and obtained the null deviance (d0). Then, we computed a simple binary regression model for every preSurg, obtaining the deviances for everyone, i.e., dSPECT, dEEG, dMRI and dVEEG. Obviously, each of these parameters was smaller than d0. Then, we computed following Equation 12 and identified the highest. Let us suppose
- We evaluated the significance of the LR by means of . If was greater than 3.84 (95 percentile for one d.o.f.), then the variable k was incorporated into the model.
- We computed two-variable models, obtaining , where i = preSurg-{k}. Obviously, we had three possibilities. We identified the lowest one, named . We evaluated , and if it was greater than 3.84, we incorporated the variable l into the model.
- We repeated this procedure until the four preSurg were incorporated or after a new incorporation did not result in significant results.
| Variable | Coefficient (± SEM) | Wald statistic | Odds Ratio | Confidence interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | -4.425 ± 1.385 | 10.207 | 0.012 | 0.001-0.181 |
| VEEG | 3.106 ± 1.224 | 6.440 | 22.329 | 2.028-245.859 |
| MRI | 2.558 ± 1.364 | 3.516 | 12.914 | 0.891-187.250 |
| EEG | 1.905 ±1.419 | 1.803 | 6.718 | 0.417-108.335 |
References
- de Tisi, J.; Bell, G.S.; Peacock, J.L.; McEvoy, A.W.; Harkness, W.F.; Sander, J.W.; Duncan, J.S. The long-term outcome of adult epilepsy surgery, patterns of seizure remission, and relapse: a cohort study. Lancet 2011, 378, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenow, F.; Luders, H. Presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Brain 2001, 124, 1683–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jehi, L.; Jette, N.; Kwon, C.S.; Josephson, C.B.; Burneo, J.G.; Cendes, F.; Sperling, M.R.; Baxendale, S.; Busch, R.M.; Triki, C.C.; Cross, J.H.; Ekstein, D.; Englot, D.J.; Luan, G.; Palmini, A.; Rios, L.; Wang, X.; Roessler, K.; Rydenhag, B.; Ramantani, G.; Schuele, S.; Wilmshurst, J.M.; Wilson, S.; Wiebe, S. Timing of referral to evaluate for epilepsy surgery: Expert Consensus Recommendations from the Surgical Therapies Commission of the International League Against Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 2491–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, J.S.; Winston, G.P.; Koepp, M.J.; Ourselin, S. Brain imaging in the assessment for epilepsy surgery. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sola, R.G.; Hernando-Requejo, V.; Pastor, J.; García-Navarrete, E.; DeFelipe, J.; Alijarde, M.T.; Sánchez, A.; Domínguez-Gadea, L.; Martín-Plasencia, P.; Maestú, F.; DeFelipe-Oroquieta, J.; Ramón-Cajal, S.; Pulido-Rivas, P. Epilepsia farmacorresistente del lóbulo temporal. Exploración con electrodos del foramen oval y resultados quirúrgicos [Pharmacoresistant temporal-lobe epilepsy. Exploration with foramen ovale electrodes and surgical outcomes]. Rev Neurol. 2005, 41, 4–16. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pastor, J.; Hernando-Requejo, V.; Domínguez-Gadea, L.; de Llano, I.; Meilán-Paz, M.L.; Martínez-Chacón, J.L.; Sola, R.G. Impacto de la experiencia sobre los resultados quirúrgicos en la epilepsia del lóbulo temporal [Impact of experience on improving the surgical outcome in temporal lobe epilepsy]. Rev Neurol. 2005, 41, 709–716. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernasconi, A.; Cendes, F.; Theodore, W.H.; Gill, R.S.; Koepp, M.J.; Hogan, R.E.; Jackson, G.D.; Federico, P.; Labate, A.; Vaudano, A.E.; Blümcke, I.; Ryvlin, P.; Bernasconi, N. Recommendations for the use of structural magnetic resonance imaging in the care of patients with epilepsy: A consensus report from the International League Against Epilepsy Neuroimaging Task Force. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 1054–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherpour, J.; Jaber, M.; Voges, B.; Apostolova, I.; Sauvigny, T.; House, P.M.; Lanz, M.; Lindenau, M.; Klutmann, S.; Martens, T.; Stodieck, S.; Buchert, R. Predicting the Outcome of Epilepsy Surgery by Covariance Pattern Analysis of Ictal Perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med. 2022, 63, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, S.; Blume, W.T.; Girvin, J.P.; Eliasziw, M. Effectiveness and Efficiency of Surgery for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Study Group. A randomized, controlled trial of surgery for temporal-lobe epilepsy. N Engl J Med. 2001, 345, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J., Jr. The current place of epilepsy surgery. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, C.; Cossu, M.; Guerrini, R.; Di Gennaro, G.; Villani, F.; De Palma, L.; Grisotto, L.; Consales, A.; Battaglia, D.; Zamponi, N.; d’Orio, P.; Revay, M.; Rizzi, M.; Casciato, S.; Esposito, V.; Quarato, P.P.; Di Giacomo, R.; Didato, G.; Pastori, C.; Pavia, G.C.; Pellacani, S.; Matta, G.; Pacetti, M.; Tamburrini, G.; Cesaroni, E.; Colicchio, G.; Vatti, G.; Asioli, S.; Caulo, M.; TLE Study Group; Marras, C. E.; Tassi, L. Temporal lobe epilepsy surgery in children and adults: A multicenter study. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, P.; Lin, Q.; Zhou, D.; An, D. Postoperative seizure and memory outcome of temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis: A systematic review. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 2845–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jehi, L. The Epileptogenic Zone: Concept and Definition. Epilepsy Curr. 2018, 18, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomei, F.; Wendling, F.; Bellanger, J.J.; Regis, J.; Chauvel, P. Neural networks involving the medial temporal structures in temporal lobe epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 1746–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, S.S. Neural networks in human epilepsy: evidence of and implications for treatment. Epilepsia 2002, 43, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, K.M.; Tabesh, A.; Sainju, R.K.; DeSantis, S.M.; Naselaris, T.; Joseph, J.E.; Ahlman, M.A.; Spicer, K.M.; Glazier, S.S.; Edwards, J.C.; Bonilha, L. Perfusion network shift during seizures in medial temporal lobe epilepsy. PLoS One 2013, 8, e53204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor, J.; Sola, R.G.; Vega-Zelaya, L.; Garnés, O.; Ortega, J. New network and synchronization approaches in focal research epilepsy and treatment. Health 2013, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.; Vega-Zelaya, L. Redes neurales en epilepsia. In Contribución Iberoamericana a la Epilepsia; Velasco, A.L., Ed.; Editorial Alfil, Mexico: ISBN, 2018; pp. 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Franco Nicolás, M.; Vivo Molina, J.M. Análisis de curvas ROC. Principios básicos y aplicaciones. La Muralla SA, Madrid. 2007; ISBN 978-84-7133-772-6. [Google Scholar]
- Silva Ayçaguer, L.C.; Barroso Utra, I.M. Regresión Logística. La Muralla SA; Madrid. 2004; ISBN 84-7133-738-X. [Google Scholar]
- Hosmer, D.E.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied logistic regressions, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA. [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, M.R.; Schiller, J.J.; Srinivasan, R.A. Probability and statistics; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA; ISBN 978-0-07-177751-3.
- Biggerstaff, B.J. Comparing diagnostic test: a simple graphic using likelihood ratios. Statist. Med. 2000, 19, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeiser, B.; Zentner, J.; Steinhoff, B.J.; Brandt, A.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Kogias, E.; Hammen, T. The role of presurgical EEG parameters and of reoperation for seizure outcome in temporal lobe epilepsy. Seizure 2017, 51, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, C.; Koren, J.P.; Britto-Arias, M.; Zoche, L.; Pirker, S. Presurgical epilepsy evaluation and epilepsy surgery. F1000Res 2019, 8, F1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immonen, A.; Jutila, L.; Kälviäinen, R.; Mervaala, E.; Partanen, K.; Partanen, J.; Vanninen, R.; Ylinen, A.; Alafuzoff, I.; Paljärvi, L.; Hurskainen, H.; Rinne, J.; Puranen, M.; Vapalahti, M. Preoperative clinical evaluation, outline of surgical technique and outcome in temporal lobe epilepsy. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2004, 29, 87–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, A.; Demirciler, A.K.; Solmaz, S.; Ozgural, O.; Eroglu, U.; Wambe, A.; Tekneci, O. Surgical Treatment of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Micro-Neuroanatomical Details of the Medial Temporal Region. Turk Neurosurg. 2021, 31, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita-Sherman, M.; Li, M.; Joseph, B.; Yasuda, C.; Vegh, D.; De Campos, B.M.; Alvim, M.K.M.; Louis, S.; Bingaman, W.; Najm, I.; Jones, S.; Wang, X.; Blümcke, I.; Brinkmann, B.H.; Worrell, G.; Cendes, F.; Jehi, L. Incorporation of quantitative MRI in a model to predict temporal lobe epilepsy surgery outcome. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieshmann, U.C.; Larkin, D.; Varma, T.; Eldridge, P. Predictors of outcome after temporal lobectomy for refractory temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 2008, 118, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutila, L.; Immonen, A.; Mervaala, E.; Partanen, J.; Partanen, K.; Puranen, M.; Kälviäinen, R.; Alafuzoff, I.; Hurskainen, H.; Vapalahti, M.; Ylinen, A. Long term outcome of temporal lobe epilepsy surgery: analyses of 140 consecutive patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002, 73, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvim, M.K.M.; Morita, M.E.; Yasuda, C.L.; Damasceno, B.P.; Lopes, T.M.; Coan, A.C.; Ghizoni, E.; Tedeschi, H.; Cendes, F. Is inpatient ictal video-electroencephalographic monitoring mandatory in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with unilateral hippocampal sclerosis? A prospective study. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuba, R.; Tyrlíková, I.; Chrastina, J.; Slaná, B.; Pažourková, M.; Hemza, J.; Brázdil, M.; Novák, Z.; Hermanová, M.; Rektor, I. “MRI-negative PET-positive” temporal lobe epilepsy: invasive EEG findings, histopathology, and postoperative outcomes. Epilepsy Behav. 2011, 22, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Conceição, P.O.; Nascimento, P.P.; Mazetto, L.; Alonso, N.B.; Yacubian, E.M.; de Araujo Filho, G.M. Are psychiatric disorders exclusion criteria for video-EEG monitoring and epilepsy surgery in patients with mesial temporal sclerosis? Epilepsy Behav. 2013, 27, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnerat, B.Z.; Velasco, T.R.; Assirati, J.A., Jr.; Carlotti, C.G., Jr.; Sakamoto, A.C. On the prognostic value of ictal EEG patterns in temporal lobe epilepsy surgery: a cohort study. Seizure 2013, 22, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, N.M.; Eldridge, P.; Varma, T.; Wieshmann, U.C. The duration of temporal lobe epilepsy and seizure outcome after epilepsy surgery. Seizure 2010, 19, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebel, J.M.; Heerwig, C.; Möller, H.; Sauvigny, T.; Martens, T.; Dührsen, L.; Stodieck, S.R.G.; Brückner, K.; Lanz, M. Resective epilepsy surgery in patients aged 50 years and older–A retrospective study regarding seizure outcome, memory performance, and psychopathology. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 118, 107933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meguins, L.C.; Adry, R.A.; Silva-Junior, S.C.; Araújo Filho, G.M.; Marques, L.H. Shorter epilepsy duration is associated with better seizure outcome in temporal lobe epilepsy surgery. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2015, 73, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, C.; Giometto, S.; Lucenteforte, E.; Pellacani, S.; Matta, G.; Bettiol, A.; Minghetti, S.; Falorni, L.; Melani, F.; Di Giacomo, G.; Giordano, F.; De Masi, S.; Guerrini, R. Seizure Outcome of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Surgery in Adults and Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosurgery 2022. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.P.; Sani, S.; Kanner, A.M.; Stoub, T.; Morrin, M.; Palac, S.; Bergen, D.C.; Balabonov, A.; Smith, M.; Whisler, W.W.; Byrne, R.W. Medically intractable temporal lobe epilepsy in patients with normal MRI: surgical outcome in twenty-one consecutive patients. Seizure 2011, 20, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor, J.; Wix, R.; Meilán, M.L.; Martínez-Chacón, J.L.; De Dios, E.; Domínguez-Gadea, L.; HerreraPeco, I.; Sola, R.G. Etomidate accurately localizes the epileptic area in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor, J.; Domínguez-Gadea, L.; Sola, R.G.; Hernando, V.; Meilán, M.L.; De Dios, E.; Martínez-Chacón, J.L.; Martínez, M. First true initial ictal SPECT in partial epilepsy verified by electroencephalography. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2008, 4, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Cholinergic Signaling, Neural Excitability, and Epilepsy. Molecules 2021, 26, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyuz, E.; Polat, A.K.; Eroglu, E.; Kullu, I.; Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N. Revisiting the role of neurotransmitters in epilepsy: An updated review. Life Sci. 2021, 265, 118826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Central histaminergic signalling, neural excitability and epilepsy. Br J Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Outcome | Result of preSurg | α | True/False classification | Example from EEG* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EI | Indicates a lobe that coincides with the EZ | 3 | TP | Left temporal sharp waves |
| Indicates the hemisphere where EZ is located | 2 | FN | Left fronto-temporal sharp waves | |
| Indicates a non-informative result | 1 | FN | Physiological or generalized spike-wave | |
| Indicates the contralateral hemisphere | 0 | FN | Right sharp waves | |
| nEI | Indicates the same OpZ | 0 | FP | Left temporal sharp waves |
| Indicates a region different from OpZ | 1 | TN | Left frontal sharp waves |
| Variable | Men | Women | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 112 | 106 | |
| Age (years) | 37.0 ± 1.1 | 39.7 ± 1.1 | 0.077* |
| Start epilepsy (years) | 13.9 ± 1.1 | 14.1 ± 1.0 | 0.521** |
| Time of epilepsy (years) | 23.1 ± 1.2 | 25.6 ± 1.2 | 0.159* |
| AED | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 2.8 ± 0.1 | 0.055** |
| One | 3.6 | 3.6 | < 0.001*** |
| Two | 10.7 | 32.1 | |
| Three | 57.1 | 50.0 | |
| Four | 25.0 | 14.3 | |
| Five | 3.6 | 0.0 | |
| Frequency | |||
| Daily | 16.8 | 18.5 | 0.500*** |
| Weekly | 51.3 | 54.6 | |
| Monthly | 31.9 | 26.9 |
| Pre-surgical test | Outcome | Localization | Not localization | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EI | 0.386* (0.379-0.393) | 0.614 | 171 | |
| SPECT | nEI | 0.808 | 0.192** (0.179-0.206) | 26 |
| Total | 85 | 112 | 197 | |
| EI | 0.475* (0.467-0.482) | 0.525 | 158 | |
| EEG | nEI | 0.731 | 0.269** (0.253-0.285) | 26 |
| Total | 94 | 90 | 184 | |
| EI | 0.578* (0.571-0.584) | 0.422 | 187 | |
| MRI | nEI | 0.839 | 0.161** (0.150-0.173) | 31 |
| Total | 134 | 84 | 218 | |
| EI | 0.914* (0.911-0.918) | 0.086 | 187 | |
| VEEG | nEI | 0.935 | 0.065** (0.057-0.072) | 31 |
| Total | 200 | 18 | 218 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





