1. Introduction
The extreme-mass-ratio inspirals (EMRIs) are sources of gravitational waves (GWs), where stellar-mass compact objects (COs) are captured and spiral into massive black holes (MBHs) in the centers of galaxies [
1,
2,
3]. The emission of GWs gradually causes the eccentric orbit to shrink and become more circular. During the last year of inspirals before plunge, it is estimated that over 10
5 cycles can be observed by space based GW observatories [
4], such as Taiji [
5,
6], Tianqin [
7] and LISA [
8]. This rich phase evolution information can be used to constrain gravity theories beyond general relativity [
9,
10,
11], test the no-hair theorem [
12] and study the astrophysics of galaxies [
13,
14] with a high precision. Therefore, EMRI data analysis becomes a crucial task.
Time-frequency methods provide a straightforward solution for detecting high SNR signals without the need for waveform models. Once the signal tracks in the time-frequency plane are well fitted, the waveform models can be used to estimate a subset of source parameters [
15,
16]. The advantage of this approach is that it is computationally cheap. However, the disadvantage is that it requires a lot of tuning for the threshold fitting in the time-frequency plane, and it is difficult to detect signals with low SNR. Recently, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based methods have been developed, where different inputs such as time domain data [
17], frequency domain data [
18], and time-frequency planes by Q-transform [
19,
20] are fed to the neural network. These methods provide an alternative computationally efficient solution for EMRI data analysis, but they are still limited to high SNR signals.
Template-based matched filtering is the best option for a deeper search in SNR, although it is computationally expensive. In EMRI data analysis, accurate EMRI waveforms are quite complicated and computationally expensive when considering the self-force of the COs [
21]. As a result, phenomenological waveforms from the kluge family are widely used at present in the development of EMRI data analysis methods. The analytical kluge (AK) waveform [27] is used in the Mock LISA Data Challenges (MLDCs) [
22,
23,
24,
25] and the latest LISA Data Challenge (LDC) [
26], while the augmented analytical kluge (AAK) waveform [28] is used in the Taiji data challenge [29]. The AK waveform includes 14 parameters, with the spin of the COs usually being ignored. Six of these parameters contribute to the phase evolution of the waveform and need to be estimated with high precision, thus contributing a prominent 6-dimensional sharp peak to the signal location in the parameter space of the fitness function. The AK waveform consists of superposition of multiple harmonics, resulting in multiple secondary peaks surrounding the primary one in the parameter space [30]. The primary peak indicates a good match of all the harmonics, while the secondary peaks indicate that a subset of harmonics is matched well, especially the dominant ones. Therefore, it is difficult for a global optimizer to locate a complete signal in such a high-dimensional and multimodal parameter space.
It is well known that longer duration signals contribute more sensitivity and less flexibility to coherent matched filtering [31], and the sharp peak can only be located within a reasonable range width [32]. As a result, hierarchical search methods are effective in overcoming the methodological difficulties in EMRI data analysis. It can be implemented by either using shorter duration signal and gradually turning to longer signal with the constrained information utilized in the next search [31,35] or by initially searching for fixed duration signal within a wide range and later focusing on narrower ranges extracted from the previous searches [32] in matched filtering. It is also beneficial to develop mixed versions by combining these two approaches together.
Given the fitness function usually defined by the log-likelihood ratio (LLR), Bayesian [34] or Fisherian methods [33] are the most commonly used ones for estimating the posterior probability density function or the global best-fit fitness value and location, which are then used for signal detection and parameter estimation. In EMRI data analysis, modified Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods, such as constrained Metropolis–Hastings Monte Carlo (MHMC) [35], Evolutionary Monte Carlo (EMC) [36] and parallel tempered Markov Chain Monte Carlo (PTMCMC) [37,38], have been used in previous works. The global optimizer, Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) [39,40,41,42,43], has been used in our previous work for a 10-dimensional EMRI search problem [44] and proven effective in the LIGO data analysis of inspiral signals [45,46,47,48] and transient signals [49,50,51], the pulsar timing array data analysis of supermassive black holes [52,53,54,55,56,57], and the LISA data analysis of Galactic binaries [58,59,60,61,62]. In this paper, we extend the application of PSO to an EMRI search problem with two different dimensions: an 8-dimensional search and a 7-dimensional search, respectively. Our results demonstrate that the PSO-based search algorithm is able to accurately estimate the simulated signals with SNR value of 50 and duration of 0.5 years by using these reduced dimensionality LLR. Notably, it should be emphasized that the current search ranges employed are substantially broader than those utilized in our previous work, resulting in an significant increase in the parameter space volume, approximately ∼50-fold for the 8-dimensional search and ∼100-fold for the 7-dimensional search.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2, we describe the consistent TDI combinations, noise model, and the signal model as LDCs used in the paper. In
Section 3, we present how the reduced dimensionality likelihoods are defined. The Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm used for matched filtering are illustrated in
Section 4. Finally, in
Section 5 we report the results and give the corresponding discussions in
Section 6.
2. Data description
First, we describe the application of time-delay interferometry (TDI) [63] in this paper, which is employed by space-based GWs detectors to mitigate the dominant laser frequency noise. Subsequently, we present the theoretical model of power spectral densities (PSDs) utilized by LDCs. Lastly, we provide a description of the current standard waveform model employed for EMRI data analysis.
2.1. TDI combinations
Throughout the paper, we adhere to the coordinate and TDI conventions defined in [64]. Given the definitions of the polarization tensors
and LISA orbit, we can derive the corresponding geometrical quantities
and
from the orbit. Here,
represents the unit vector along the arm
l, and
denotes the position vector of the
k-th satellite. The sky location,
and
, can be used to define the unit vector
which indicates the direction of GW propagation. The antenna patterns
of the single arm
l are given by
where
is the polarization angle and the quantities
are defined by
The symbol : denotes the contraction operation on arbitrary tensors
U and
V, namely
, and ⊗ represents
for arbitrary vectors
a and
b.
By mapping the antenna patterns
to the polarization waveforms
, we can express the corresponding strain response of the arm
l as
,
The expression for the single arm response of the laser along the arm
l can then be given as follows:
where the labels
s and
r represent the laser sender and receiver of the satellite, respectively, and
l denotes the arm link between the two involved satellites. The sign of
l is positive when the label
follows a cyclic permutation of indices
labelling the three satellites; otherwise, it is negative. By following the well-designed optical path of the TDI combinations
X,
Y and
Z of the first generation, the laser frequency noise can be cancelled under the approximation of constant arm length. This cancellation is achieved by linearly combining the artificially delayed single arm responses
, as shown below:
where the
are linked to the single arm responses
through
. The first generation TDI combination
X (same for
Y or
Z) is calculated as the difference between two Michelson-type responses. Each Michelson-type response consists of an optical path with 4 single arm responses. Each single arm response introduces a delay corresponding to it’s arm length along the optical path. Consequently, there are 0, 1, 2, and 3 accumulated indices for the delays
L in the
of Eq.
6, respectively, and the corresponding signs follow the same rule as the links
l. Additionally, we can obtain the mutually independent noise TDI combinations
A,
E and
T by linearly combining the TDI combinations
X,
Y and
Z as follows:
In this paper, we focus on the data analysis method for individual EMRI source. As a result, the corresponding data model of each combination
I is described by
where
represents the TDI combination
I, with
,
denotes the single EMRI signal, and
represents the purely instrumental noise for simplicity. We have chosen to concentrate solely on the TDI combinations
A and
E because the TDI combination
T is less sensitive to GWs, which aligns with the treatment employed by numerous other studies.
2.2. Noise model and signal to noise ratio
We utilize the identical PSD model of TDI combinations
A and
E, as provided in [64],
where
f is the Fourier frequency,
is the corresponding angular frequency, and
L is the arm length which is constant in first generation TDI. The acceleration noise
and the Instrumental Optical Metrology System noise
under the noise model ’SciRDv1’ are defined in [65] as follows:
Having acquired the analytical expressions of the PSD, the inner product between two signals
and
is defined by
where
denotes the DFT of a time series
,
and
,
, with
being the sampling frequency. In terms of the inner product, the SNR of a signal can be defined as follows:
It is also convenient to define the combined overlap between two signals
and
(
) as following:
which is commonly used to assess the quality of the match between injected and estimated signals in mock data analysis [22]. The overlap of the individual combination, either
A or
E, can be obtained by setting the other combination to zero.
2.3. Signal model: EMRI waveform
The AK waveform [27] includes 14 parameters, namely, , M, , , , , , , , , , , and D. The first six parameters represent the mass of the COs, the mass of the MBH, the inclination angle between the orbital angular momentum of the COs and the spin direction of the MBH, the spin magnitude of the MBH, the initial orbital eccentricity, and the initial orbital frequency. These parameters contribute to the orbital dynamics of EMRI sources. The angles and denote the ecliptic colatitude and longitude of the source’s sky location in the Solar System Barycenter (SSB) frame, while and represent the polar and azimuthal angles of the spin direction of the MBH in the SSB frame. Additionally, , , and correspond to the initial angles of orbital motion, pericenter precession, and Lense-Thirring precession, respectively. Finally, D represents the distance between the source and the SSB center. The polarization angle is a constant in the static frame, as discussed in [35], and depends on , , and .
The orbital dynamics in AK waveform are described by the following set of ordinary differential equations (ODEs). These ODEs involve the five quantities:
,
,
,
e, and
, where the
and
e are the orbital frequency and the orbital eccentricity, respectively, and
,
, and
are the phases describing orbital motion, pericenter precession, and Lense-Thirring precession, respectively.
It is computationally expensive to solve the ODEs using a time interval of 15 seconds, which corresponds to the observational cadence of LISA. However, the slow evolution of the orbital parameters predicted for most of EMRI sources allows us to use a larger cadence of 15360 seconds when solving the ODEs. As suggested in [64], the fifth-order Cash-Karp Runge-Kutta ODEs solver [66] is used at the larger cadence, and the solutions are then interpolated to the desired cadence of 15 seconds.
With the ODEs solutions at our disposal, we can now proceed to the calculation of the polarization waveforms. For each harmonic labeled as
, the following quantities in it’s polarization waveforms are time independent: (1) the amplitude factor
such as
, (2) the initial phase
, and (3) the time independent amplitude
. The exact forms of
are provided in [64], and the superscript
c indicates the quantity is an unknown constant. Therefore, the polarization waveforms can be expressed as follows:
where the parameter set
contains 14 parameters,
denotes the 13 parameters excluding
D,
represents the 8 parameters excluding
D,
,
,
,
, and
, and the parameter set
includes the 6 ODEs-related parameters,
,
M,
,
,
, and
. Thus we have
Based on the number of parameters that they depend on,
and
denote the 14 and 13-dimensional polarization waveforms, respectively, while the time varying components correspond to the term
, where the power distributions among harmonics depend on the index
n. In the case of the AK model, the range of values for
m is from
to 2, resulting in a total of 5 harmonics for each
n. Here, we adopt the same choice as our previous work [44] to select the loudest 10 harmonics by analyzing the
. Therefore, the choice is to pick up two values for
n from the values 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 used in LDC. It is worth mentioning that additional harmonics could be considered once computational limitations, such as accessing sufficient cores or utilizing a Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) code, are overcome. However, for the current study, we will focus on the loudest 10 harmonics based on the cluster resources available to us. As shown in
Table 1, the power distributions among harmonics indicate that the harmonics with
are considerably weaker compared to other harmonics with different values of
n. Furthermore, as
n increases (with
), the strength of the harmonics diminishes. This trend holds true for moderate eccentric sources, such as those with
.
Table 1 follows the same conventions as Table 1 in our previous paper [44], with two exceptions: (1) the harmonics indices turn to
n varying from 1 to 5, and (2) the power fraction is used instead of the SNR fraction, as their summation equals unity. Therefore, for moderate eccentric sources, the optimal choice for the loudest 10 harmonics would be those with
. It requires more attention to select the dominant harmonics for high eccentric sources, e.g.,
, where the power distributions across harmonics exhibit greater fluctuations.
3. Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test
3.1. 13-dimensional LLR
In the context of stationary Gaussian noise, the log-likelihood ratio (LLR) of given data
containing an assumed EMRI signal
is defined as follows:
The
is usually called
template in matched filtering to distinguish it from the unknown and true signal encoded in the noisy data. In the Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test [33], the global maximum of the LLR,
and the corresponding location
are used for signal detection and parameter estimation, respectively. Analytically maximizing over
by
leads to
with the maximizer being
We call
the 13-dimensional LLR [35]. Creating further nested levels in the maximization of
that separate out the time-independent parts provide reduced dimensionality LLRs, namely 8-dimensional and 7-dimensional ones, as discussed below.
3.2. 8-dimensional LLR
By incorporating the polarization waveforms of the
i-th harmonic in Eq.
21 with the antenna patterns of arm
l in Eq.
1, we can obtain the corresponding strain response as follows:
Here the map for harmonics indices from
to
i are
and
where
i ranges from 1 to 25 in LDC.
The linearity from strain responses to TDI responses for combination
I leads to the same linear combination,
because only the time varying terms
are projected to the TDI delays and the time independent coefficients
, which absorb the parameters
,
,
,
, and
, remain unchanged.
To apply this linear decomposition in Eq.
30 to the inner products in the 13-dimensional LLR in Eq. 27, we can express the inner products as follows:
In our previous work [44], we introduced an approach in which the three initial angles
,
, and
are separated from the remaining 10 parameters in Eq. 27. This allows us to apply local maximization [67] over the three initial angles for a given point in the 10-dimensional parameter space and perform the search over the 10 parameters using PSO. In this paper, we extend the approach by employing local maximization [67] over the five parameters:
,
,
,
and
, and using PSO for the remaining 8-dimensional search. The following quantities,
and
, can be pre-calculated for each specific
. This enables computationally efficient local maximization over the coefficients
, namely over
,
,
,
and
.
The nature of the fitness function over the 5-dimensional subspace, consisting of
,
,
,
and
, is illustrated in
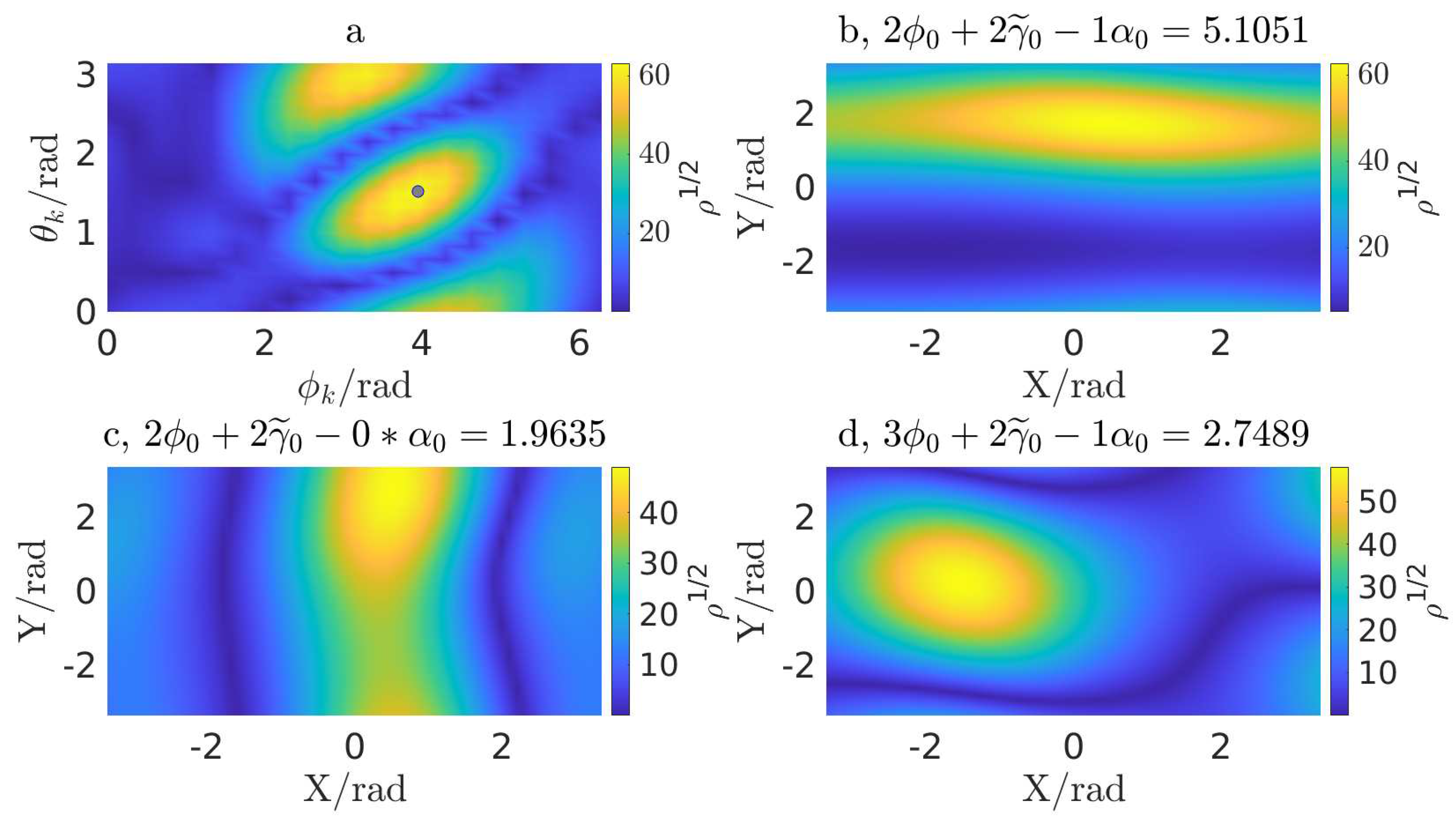
Figure 1. The figure showcases the LLR (square root) landscape of a 2-dimensional slice of
and
(
Figure 1, a), as well as three randomly selected planes (
Figure 1, b,c,d) in the 3-dimensional subspace composed of
,
and
. This representation is valid for the specific location, although similar patterns have been observed from the other locations as well. Given the presence of a fairly small number of local maxima with comparable or equal values, local maximization approach is well-suited for handling this 5-dimensional subspace.
To ensure that the global maximum is caught, we employed a total of 243 independent runs of a local maximizer starting from initial points distributed over a grid, with each angle in the 5-dimensional subspace enumerated from the 1-dimensional grid , which are uniform spacing from 0 to . The best-fit 5-dimensional location is determined from the run that returns the highest value.
3.3. 7-dimensional LLR
The initial orbital frequency, namely
, corresponds to the moment
at which the EMRI signal is captured by the detector, thus it’s varying results in a uniform shift of time label to all the harmonics of the signal. As discussed in [36], the corresponding shift of the time label can be numerically maximized in two ways for arbitrary harmonic, denoted as
here. The first is phase rotation in frequency domain,
where
n denotes the number of the shift and
represents the observational cadence. The inverse Fast Fourier Transform of the term
, which rotate the
by the same amount of
at each
, returns the delayed term
. For the same shift, the second is straightforward lag sliding in time domain as follows:
where the zero paddings at the end of the shifted signal cover
n zeros.
The detector noise in low frequency region is usually large, as a result, a fiducial
, e.g., 1mHz, can be determined through a pre-analysis of the detector’s features, which indicates that the detector has reached a level of sensitivity to detect the GWs of EMRI signals starting from the chosen fiducial
. Therefore, the 8-dimensional TDI responses
in Eq.
30 could be calculated by running forward ODEs using
with it’s initial
specified as the selected fiducial value, and the initial
being one of the parameters for matched filtering. We can then systematically shift the
lag-by-lag starting from the lag of the fiducial
until the 8-dimensional LLR maximum is achieved, the corresponding lag provides the best-fit estimation of
and
. Here, we set the number of shifts to 11 for computational limitations.
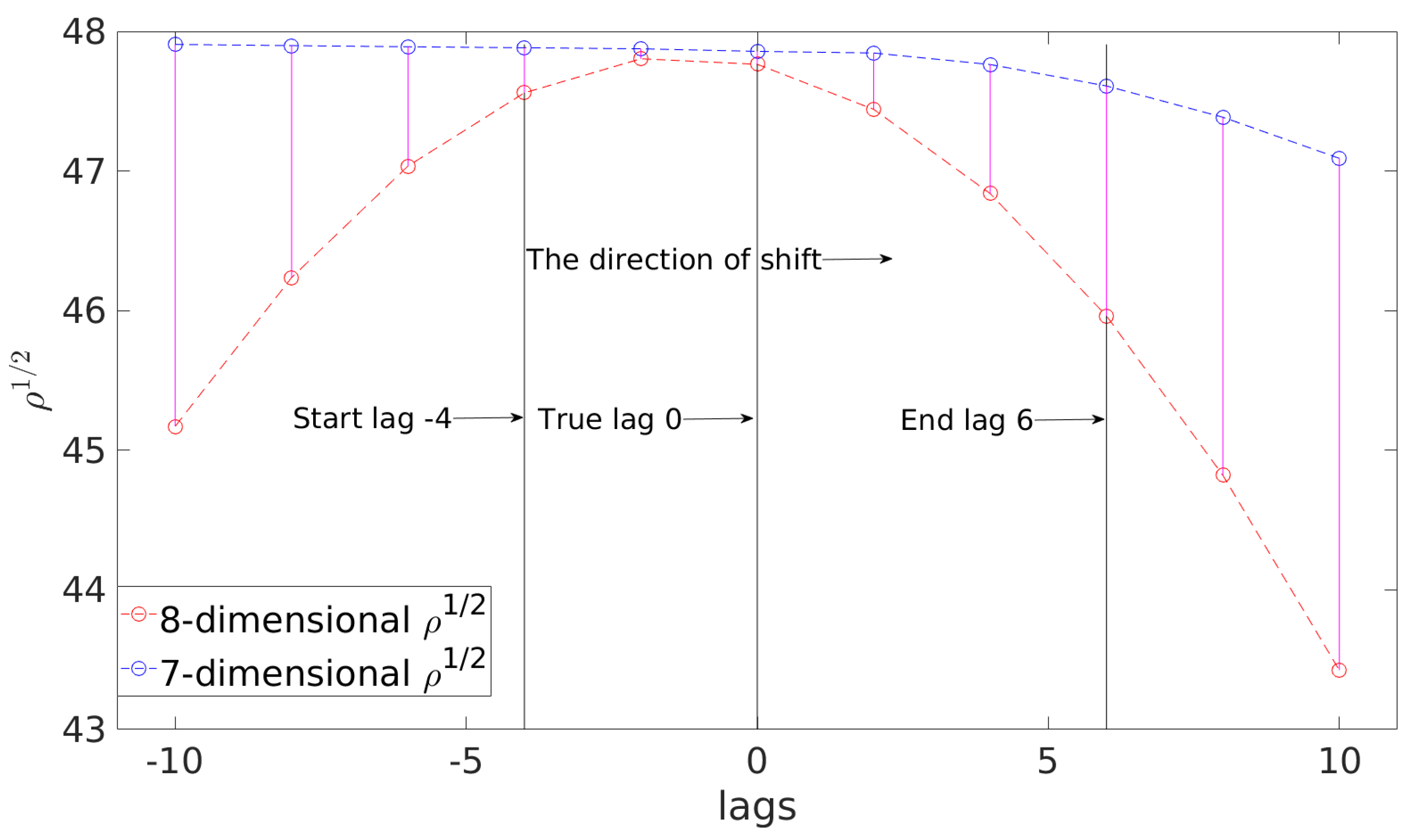
Figure 2 illustrates the 8-dimensional and the 7-dimensional LLRs as functions of the lag. The lag varies from
to 10 where the zero lag corresponds to the true lag of LDC
,
Hz. It can be observed that the 8-dimensional LLRs using the negative lags can be successfully mapped to the 7-dimensional LLRs with a well fitted
by properly shifting the corresponding
. This is possible because the total 11 shifts can cover the zero lag anyway, whereas the positive lags fail to locate the zero lag due to the rightward shift of
.
In this paper, the lag of the fiducial
is determined by considering 4 lags ahead of the LDC true lag, thus the corresponding value is
Hz. In order to accurately capture unknown EMRI signals, it would generally be necessary to fit more lags. However, due to the computational expense of the shifting operations for
and the evaluations of the 8-dimensional LLRs by using the current code, only 11 lag-by-lag shifts are utilized, enumerating lags from
to 6 as illustrated in
Figure 2. This setting ensures the scanning of the true lag, and is used to demonstrate the functionality of the 7-dimensional LLR. In future works, we plan to address these computational challenges by implementing a GPU-accelerated code, which will allow for the exploration of additional lags.
4. Particle Swarm Optimization
As discussed earlier, the search using reduced dimensional likelihoods involves the following steps. First, the distance
D in the 14-dimensional LLR in Eq.
23 is analytically maximized. Next, the local maximization over the five angles
,
,
,
, and
are carried out using the Simplex algorithm of Nelder and Mead [67]. Finally the remaining parameters in the set
(8-dimensional search), or
excluding
(7-dimensional search), are numerically maximized by PSO. In this chapter, we briefly describe the PSO algorithm [39,40,41].
Given the fitness function
where
is defined in
, the optimization problem can be stated as follows:
The best location,
, refers to the point in the search space
that yields the highest fitness value, represented as
,
M is the dimension of the parameter space for
. Locating the primary peak of a multimodal fitness function can be challenging. The PSO algorithm, which is utilized in this paper as a global maximizer, is a suitable approach for addressing such challenges. Successful applications of PSO in handling similar issues are discussed in
Section 1. It should be noted that in our case, the fitness functions are the 8-dimensional LLR discussed in
Section 3.2 and the 7-dimensional LLR discussed in
Section 3.3.
PSO consists of multiple agents, known as particles. Each particle updates it’s position by considering the information from both itself and it’s neighbouring particles at each iteration. The algorithm aims to converge towards the global maximum, which corresponds to the primary peak of the fitness function within the search space, by utilizing a balance between global exploration and local exploitation. Such balance typically results in good performance of PSO search. However, finding the right balance requires tuning the related parameters, which is problem-specific. One of the key advantages of PSO algorithm is that it requires only a few tunable parameters, namely the number of iterations
and the number of independent runs
of PSO. If the probability that an individual PSO fails to locate the primary peak of the fitness function is denoted as
p, then the probability that at least one search from
independent PSO searches, using different random seeds, succeeds in locating the primary peak is given by
. This probability approaches unity exponentially fast with
. Therefore, multiple independent runs are a quick and easy way to significantly enhance the performance of a PSO-based search. It is recommended to start with
in the range of
, and
set to 2000, as discussed in [41]. These values can be adjusted based on the specific fitness function being used. The actual values used in this paper are described in
Section 5. For more detailed information on an objective strategy for tuning PSO, refer to [45].
The PSO dynamics of the
i-th particle in the swarm is described by two equations as follows:
where
t represent an iteration,
and
denote the respective positions before and after the update.
represents the amount of position increment, referred to as velocity, while
is the corresponding projection component for
j-th parameter. The quantity
and
represent the current location and
personal best (
pbest) location of the
j-th parameter, while
represents the
global best (
gbest) location among all particles of the
j-th parameter. The Eq. 37 provides the key feature of PSO update. The first term represents the influence of the momentum of the
i-th particle with
being the inertia weight. The second and third terms represent the acceleration effects, where the former considers the influence of the particle itself and the latter represents the influence from neighboring particles, with
and
being the acceleration coefficients. The randomness of PSO algorithm arises from the utilization of random variables
and
, which are drawn from a uniform distribution between 0 and 1. The location of
pbest and
gbest are updated following the rules as below:
The typical settings for PSO are as follows: (1) , (2) linearly decreasing inertia weight over iterations, (3) constraining the velocity by a given parameter, referred to as the maximum velocity, , such that for all iterations and particles, (4) randomly generating initial positions and velocities for all particles, and (5) setting the number of particles in the swarm to . The "let-them-fly" boundary condition is used, where the position and velocity of a particle remain unchanged, and a fitness value of is assigned once the particle leaves the search space. As a result, the actual number of fitness function (likelihood) evaluations for individual PSO search would be smaller than the value of .
To enhance the exploitation capability of PSO, particularly for multimodal fitness functions, a variation called
local best (
lbest) PSO [42] has been proposed as an improvement over the
gbest PSO. In the
lbest PSO, for each particle
i, a smaller swarm is utilized to determine the
lbest position denoted as
and the corresponding fitness value
. These values are then used to replace the
gbest position
,
in Eq. 37 and the corresponding fitness value
in Eq. 39. The typical configuration for the smaller swarm surrounding the
i-th particle is a ring structure consisting of three particles, whose indices are given by
, with the first and last particle connected in a circular manner. It is worth noting that the
lbest PSO reduces to the
gbest PSO when the ring includes all the particles. The selection of the fitness value for the
lbest of the
i-th particle follows the criteria, as shown below,
Here, a more comprehensive exploitation is achieved by slower convergence in the
lbest PSO, thus making it more computationally expensive than
gbest PSO.
5. Results
In this paper, we have utilized 0.5 years data containing a single EMRI signal with the same source parameters as LDC-1.2 [64] except for a shorter distance
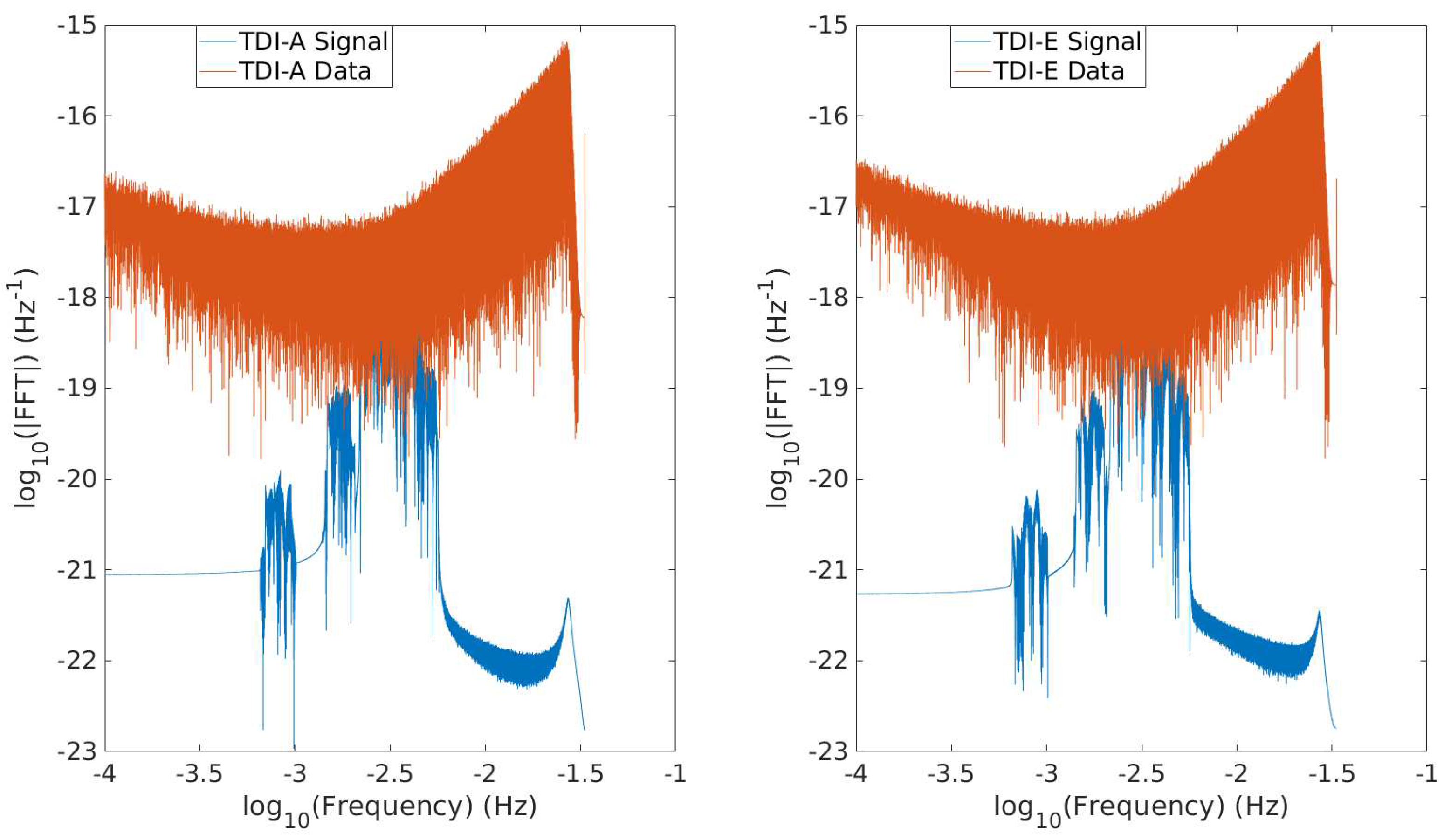
D of 1.535300 Gpc, resulting in an SNR value of 50 for the injected signal. This SNR value has been widely used as a benchmark for 0.5 years signals in recent studies [19,20,32]. While our search method is not inherently restricted to a shorter data length, constraints on computational resources and a pending GPU-acceleration of our code sets the above limit on the data length. The noise realization used in our analysis is obtained by subtracting the signal from the data, with both provided in LDC-1.2 [64], ensuring that our simulated data shares the same characteristics as the LDC data but with a scaling of shorter duration and higher SNR. In
Figure 3, the spectra of the injected signal and the simulated data for TDI combinations
A and
E are displayed, revealing the relatively weak nature of the injected signal compared to the simulated data.
The values of the source parameters and the width of the search ranges used for the 8-dimensional and the 7-dimensional searches are presented in
Table 2. The FIM
represents the estimation error of the CRLB for each parameter at SNR of 50, evaluated at the injected source parameters. The injected signal parameters are also called the true ones in the following.
We set the tunable hyperparameters for PSO as follows: is set to 6, and is set to 15000 for the 8-dimensional searches, 20000 for the first two 7-dimensional searches, and 25000 for the remaining four 7-dimensional searches. Due to limited computational resources, the independent 6 searches have to be carried out serially. Due to the presence of noise in the data, both PSO and local maximization are expected to find best-fit fitness values that are higher than that at the true location, which are called successful search. In order to further reduce computational costs, the searches are terminated once a successful search occurred. Consequently, the actual is 4 for the 8-dimensional searches and 6 for the 7-dimensional searches.
The results obtained from the 8-dimensional and the 7-dimensional searches are summarized in
Table 3 and
Table 4, respectively. We report the square roots of the best-fit fitness values from each PSO search, which provide the estimated SNRs. Additional details regarding
Table 3 and
Table 4 are provided below.
For the 8-dimensional PSO outputs shown in
Table 3, it can be observed that the errors in the parameters
,
M,
,
are
, while the error in the parameter
D is
. The errors in the sky location are within ≈0.1 radians. However, the errors in the parameters
and
vary significantly among different PSO outputs where the successful PSO output returns a minimum error of approximately
with an overlap of
, and the other PSO outputs yield larger errors up to
with smaller overlap values. Those discrepancies are reasonable because
and
are the initial values of the ODEs in Eq.
20 which describe the orbital dynamics of the EMRI source (the other three initial angles don’t determine the morphology of the ODES solution, only contributing a constant shift). Therefore, the phase match are more sensitive to these parameters, thus requiring longer iterations to converge.
For the 7-dimensional PSO outputs presented in
Table 4, no successful search is found where the best-fit fitness value exceeds that at the true location. However, the 4th PSO output returns errors of approximately
for the parameters
,
M,
,
,
and
,
for the distance
D, and
radians for the sky location, with an overlap of
. This indicates that the signal is indeed captured, making it a successful search. The 3th and 5th PSO outputs exhibit similar features to the first three PSO outputs in the 8-dimensional searches where the larger errors in
result in the smaller fitness values. The errors in
are same for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 5th PSO outputs, which may be attributed to the small range of 11 lags used to shift the 8-dimensional
A and
E template starting from the lag of the fiducial
. It should be noted that the fitting of
should cover more lags to obtain a more accurate estimation over
.
The successful PSO searches (the 4th PSO for both dimension) demonstrate smaller errors in the parameters , M, , , and for the 7-dimensional search () compared to those for the 8-dimensional search (). This suggests that the utilization of reduced dimensional LLR and increased iterations effectively reduce estimation errors, particularly for parameters that related with GWs phase. The fact that all PSO runs found fitness values close to each other but at various offsets for estimated errors, ranging from to , illustrates the presence of large number of secondary peaks in the fitness function.
6. Discussion
We have extended the previous work on a 10-dimensional LLR [44] search to an 8-dimensional and a 7-dimensional LLR search, in which progressively more parameters are locally maximized while the remaining are globally maximized using PSO. In the 8-dimensional search, we performed a 5-dimensional local maximization over the three initial angles , and , and the angles and describing the spin direction of the MBH. In the 7-dimensional search, we used a fiducial value of and applied lag-by-lag shift to the 8-dimensional TDI responses to fit the true .
The low estimated errors and the corresponding high overlap between the estimated and injected signals indicate that both the 8-dimensional and the 7-dimensional search work well within a wider search range. Our approach used the same search range widths for
and
M as the low mass-ratio sources prescribed in MLDC 1.3.4 and 1.3.5, and half the width of the MLDC value for the parameter
[
23]. This serves as a guide for future hierarchical searches, as demonstrated in [32] using certain clustering techniques, in how much they need to narrow down the search ranges for parameters such as
,
and
.
The larger errors observed for
and
, compared to the smaller errors for other parameters in
Table 3 and
Table 4, indicate that matched filtering is more sensitive to these two parameters, thus it becomes more difficult to accurately determine them. This insight inspires us to explore more advanced optimization algorithms, such as the Cooperative Coevolution Particle Swarm Optimization (CCPSO) [43>], where only a subset of parameters are updated at each iteration to improve the optimization process. We expect that this approach will help PSO particles in escaping from secondary peaks and converging faster towards the primary peak in the parameter space of the fitness function. The additional computational cost can be mitigated by implementing a faster code using GPU acceleration.
In systems with higher eccentricity (), the power distributions over harmonics become more erratic, which depend on the harmonics index n only for the 8-dimensional waveform. Consequently, the loudest 10 harmonics, with fixed values n belonging to the set , might not be the optimal choice any longer. Hence, we need to develop methods to select the dominant harmonics on the fly in such systems.
The existence of multiple secondary peaks can hinder the PSO update process, making it difficult for particles to converge towards the primary peak. As a result, larger estimation errors of the signal parameters may occur. To effectively tackle this issue, one possible approach is to employ the reduced dimensional LLR and increase the number of iterations for PSO searches. Nevertheless, the increased computational requirements necessitate the utilization of additional cores or GPUs in the code.
In our paper, we only search for the injected signal with SNR of 50 and duration of 0.5 years, due to limited computational resources. This SNR value is higher compared to the SNR of the LDC-1.2 data with the same duration. In future work, it is important to explore lower SNR values to assess the robustness of our method. We also plan to conduct additional tests, such as random placement of the true location, wider search ranges, and longer data duration, to further validate our approach.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.D.M. and X.-B.Z.; software X.-B.Z. and S.D.M. (for PSO); validation X.-B.Z., S.D.M., H.-G.L., and Y.-X.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.-B.Z.; writing—review and editing, S.D.M., H.-G.L., and Y.-X.L.; supervision, S.D.M. and H.-G.L.; project administration, Y.-X.L.; funding acquisition H.-G.L., Y.-X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work of X-B.Z., H-G.L., and Y-X.L. was supported by the following grants. (1)National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant No. 2021YFC2203003); (2) The National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2022YFA1402704); (3) The National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 11834005 and No. 12247101).
Data Availability Statement
The LDC data used in this study is publicly available from
https://lisa-ldc.lal.in2p3.fr. The PSO code used in this study is based on one provided in the GitHub repository RAAPTR available at
https://github.com/yanwang2012/RAAPTR. The rest of the code simply implements the mathematical formalism for GLRT and MLE described in this paper, with all necessary details provided to aid reproducibility.
Acknowledgments
The computations were performed on the high-performance computers of the State Key Laboratory of Scientific and Engineering Computing, Chinese Academy of Sciences. We express our gratitude to RunQiu Liu for granting us access to the cluster and providing invaluable suggestions for our research. We also extend our appreciation to the administrator, Yin Qian, for assisting us in utilizing the cluster effectively. Furthermore, we would like to acknowledge the insightful discussions we had with Xian Chen, Wen-biao Han, Peng Xu, Wen-lin Tang, Qun-ying Xie, Xue-hao Zhang, Shao-dong Zhao, Yi-yang Guo, Han-zhi Wang, Shu-zhu Jin, Qian-yun Yun, and Hou-qiang Teng.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AK |
Analytical Kludge |
| CO |
Compact Object |
| CRLB |
Cramer-Rao Lower Bound |
| DFT |
Discrete Fourier Transform |
| EMRI |
Extreme Mass Ratio Inspiral |
| FIM |
Fisher Information Matrix |
| GWs |
Gravitational Waves |
| GLRT |
Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test |
| GPUs |
Graphics Processing Units |
| LDC |
LISA Data Challenge |
| LLR |
Log-Likelihood Ratio |
| LISA |
Laser Interferometer Space Antenna |
| MCMC |
Markov Chain Monte Carlo |
| MLDC |
Mock LISA Data Challenge |
| MBH |
Massive Black Hole |
| ODEs |
Ordinary Differential Equations |
| PSD |
Power Spectral Density |
| PSO |
Particle Swarm Optimization |
| SNR |
Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| SSB |
Solar System Barycenter |
| TDI |
Time Delay Interferometry |
References
- Amaro-Seoane, “The gravitational capture of compact objects by massive black holes,”. [arXiv:2011.03059 [gr-qc]]. [CrossRef]
- S. Babak, J. S. Babak, J. Gair, A. Sesana, E. Barausse, C. F. Sopuerta, C. P. L. Berry, E. Berti, P. Amaro-Seoane, A. Petiteau and A. Klein, “Science with the space-based interferometer LISA. V: Extreme mass-ratio inspirals,” Phys. Rev. D 95, no.10, 103012 (2017). [CrossRef]
- H. M. Fan, Y. M. Hu, E. Barausse, A. Sesana, J. d. Zhang, X. Zhang, T. G. Zi and J. Mei, “Science with the TianQin observatory: Preliminary result on extreme-mass-ratio inspirals,” Phys. Rev. D 102, no.6, 063016 (2020). [CrossRef]
- J. R. Gair, L. Barack, T. Creighton, C. Cutler, S. L. Larson, E. S. Phinney and M. Vallisneri, “Event rate estimates for LISA extreme mass ratio capture sources,” Class. Quant. Grav. 21, S1595-S1606 (2004). [CrossRef]
- W. R. Hu and Y. L. Wu, “The Taiji Program in Space for gravitational wave physics and the nature of gravity,” Natl. Sci. Rev. 4, no.5, 685-686 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Z. Luo, Z. Guo, G. Jin, Y. Wu and W. Hu, “A brief analysis to Taiji: Science and technology,” Results Phys. 16, 102918 (2020). [CrossRef]
- J. Luo et al. [TianQin], “TianQin: a space-borne gravitational wave detector,” Class. Quant. Grav. 33, no.3, 035010 (2016). [CrossRef]
- P. Amaro-Seoane et al. [LISA], “Laser Interferometer Space Antenna,” [arXiv:1702.00786 [astro-ph.IM]]. [CrossRef]
- A. J. K. Chua, S. Hee, W. J. Handley, E. Higson, C. J. Moore, J. R. Gair, M. P. Hobson and A. N. Lasenby, “Towards a framework for testing general relativity with extreme-mass-ratio-inspiral observations,” Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 478, no.1, 28-40 (2018). [CrossRef]
- S. Yang, S. Xin, C. Zhang and W. Han, “Testing Gravity Theory With Extreme Mass-Ratio Inspirals: Recent Progress,” MDPI Proc. 17, no.1, 11 (2019). [CrossRef]
- P. Shen, W. B. Han, C. Zhang, S. C. Yang, X. Y. Zhong, Y. Jiang and Q. Cui, “Influence of mass-ratio corrections in extreme-mass-ratio inspirals for testing general relativity,” Phys. Rev. D 108, no.6, 064015 (2023). [CrossRef]
- T. G. Zi, J. D. Zhang, H. M. Fan, X. T. Zhang, Y. M. Hu, C. Shi and J. Mei, “Science with the TianQin Observatory: Preliminary results on testing the no-hair theorem with extreme mass ratio inspirals,” Phys. Rev. D 104, no.6, 064008 (2021). [CrossRef]
- C. P. L. Berry, S. A. Hughes, C. F. Sopuerta, A. J. K. Chua, A. Heffernan, K. Holley-Bockelmann, D. P. Mihaylov, M. C. Miller and A. Sesana, “The unique potential of extreme mass-ratio inspirals for gravitational-wave astronomy,” [arXiv:1903.03686 [astro-ph.HE]]. [CrossRef]
- P. Amaro-Seoane, J. R. Gair, M. Freitag, M. Coleman Miller, I. Mandel, C. J. Cutler and S. Babak, “Astrophysics, detection and science applications of intermediate- and extreme mass-ratio inspirals,” Class. Quant. Grav. 24, R113-R169 (2007). [CrossRef]
- J. R. Gair, I. Mandel and L. Wen, “Time-frequency analysis of extreme-mass-ratio inspiral signals in mock LISA data,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 122, 012037 (2008). [CrossRef]
- J. R. Gair, I. Mandel and L. Wen, “Improved time-frequency analysis of extreme-mass-ratio inspiral signals in mock LISA data,” Class. Quant. Grav. 25, 184031 (2008). [CrossRef]
- X. T. Zhang, C. Messenger, N. Korsakova, M. L. Chan, Y. M. Hu and J. d. Zhang, “Detecting gravitational waves from extreme mass ratio inspirals using convolutional neural networks,” Phys. Rev. D 105, no.12, 123027 (2022). [CrossRef]
- T. Zhao, Y. Zhou, R. Shi, Z. Cao and Z. Ren, “DECODE: DilatEd COnvolutional neural network for Detecting Extreme-mass-ratio inspirals,” [arXiv:2308.16422 [astro-ph.IM]]. [CrossRef]
- Q. Yun, W. B. Han, Y. Y. Guo, H. Wang and M. Du, “Detecting extreme-mass-ratio inspirals for space-borne detectors with deep learning,” [arXiv:2309.06694 [gr-qc]]. [CrossRef]
- Q. Yun, W. B. Han, Y. Y. Guo, H. Wang and M. Du, “The detection, extraction and parameter estimation of extreme-mass-ratio inspirals with deep learning,” [arXiv:2311.18640 [gr-qc]]. [CrossRef]
- L. Barack and A. Pound, “Self-force and radiation reaction in general relativity,” Rept. Prog. Phys. 82, no.1, 016904 (2019). [CrossRef]
- S. Babak, J. G. Baker, M. J. Benacquista, N. J. Cornish, J. Crowder, S. L. Larson, E. Plagnol, E. K. Porter, M. Vallisneri and A. Vecchio, et al. “The Mock LISA Data Challenges: From Challenge 1B to Challenge 3,” Class. Quant. Grav. 25, 184026 (2008). [CrossRef]
- K. A. Arnaud, S. Babak, J. G. Baker, M. J. Benacquista, N. J. Cornish, C. Cutler, L. S. Finn, S. L. Larson, T. Littenberg and E. K. Porter, et al. “An Overview of the second round of the Mock LISA Data Challenges,” Class. Quant. Grav. 24, S551-S564 (2007). [CrossRef]
- S. Babak et al. [Mock LISA Data Challenge Task Force], “The Mock LISA Data Challenges: From Challenge 3 to Challenge 4,” Class. Quant. Grav. 27, 084009 (2010). [CrossRef]
- E. K. Porter, “An Overview of LISA Data Analysis Algorithms,” [arXiv:0910.0373 [gr-qc]]. [CrossRef]
- Q. Baghi [LDC Working Group], “The LISA Data Challenges,” [arXiv:2204.12142 [gr-qc]].
- L. Barack and C. Cutler, “LISA capture sources: Approximate waveform, signal-to-noise ratios, and parameter estimation accuracy,” Phys. Rev. D 69, 082005 (2004). [CrossRef]
- M. L. Katz, A. J. K. Chua, L. Speri, N. Warburton and S. A. Hughes, “Fast extreme-mass-ratio-inspiral waveforms: New tools for millihertz gravitational-wave data analysis,” Phys. Rev. D 104, no.6, 064047 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Z. Ren, T. Zhao, Z. Cao, Z. K. Guo, W. B. Han, H. B. Jin and Y. L. Wu, “Taiji data challenge for exploring gravitational wave universe,” Front. Phys. (Beijing) 18, no.6, 64302 (2023). [CrossRef]
- A. J. K. Chua and C. J. Cutler, “Nonlocal parameter degeneracy in the intrinsic space of gravitational-wave signals from extreme-mass-ratio inspirals,” Phys. Rev. D 106, no.12, 124046 (2022). [CrossRef]
- D. Bandopadhyay and C. J. Moore, “LISA stellar-mass black hole searches with semicoherent and particle-swarm methods,” Phys. Rev. D 108, no.8, 084014 (2023). [CrossRef]
- C. Q. Ye, H. M. Fan, A. Torres-Orjuela, J. d. Zhang and Y. M. Hu, “Identification of Gravitational-waves from Extreme Mass Ratio Inspirals,” [arXiv:2310.03520 [gr-qc]]. [CrossRef]
- S. M. Kay, Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing, (Prentice Hall, 1993), Vol. 1&2.
- Jun S. Liu, Monte Carlo Strategies in Scientific Computing, (Springer Verlag, 2008). [CrossRef]
- S. Babak, J. R. Gair and E. K. Porter, “An Algorithm for detection of extreme mass ratio inspirals in LISA data,” Class. Quant. Grav. 26, 135004 (2009). [CrossRef]
- N. J. Cornish, “Detection Strategies for Extreme Mass Ratio Inspirals,” Class. Quant. Grav. 28, 094016 (2011). [CrossRef]
- A. Ali, thesis 2011, “Bayesian Inference on EMRI Signals in LISA Data”. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2292/7123.
- A. Ali, N. Christensen, R. Meyer and C. Rover, “Bayesian inference on EMRI signals using low frequency approximations,” Class. Quant. Grav. 29, 145014 (2012). [CrossRef]
- J. Kennedy and R. C. Eberhart, Particle swarm optimization, in Proceedings International Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE, Perth, 1995), pp. 1942–1948. [CrossRef]
- D. Bratton and J. Kennedy, "Defining a Standard for Particle Swarm Optimization," 2007 IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2007, pp. 120-127. [CrossRef]
- S. D. Mohanty, "Swarm Intelligence Methods for Statistical Regression", CRC Press, December 2018. 20 December. [CrossRef]
- D. Bratton and J. Kennedy, "Defining a Standard for Particle Swarm Optimization," 2007 IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2007, pp. 120-127. [CrossRef]
- X. Li and X. Yao, "Cooperatively Coevolving Particle Swarms for Large Scale Optimization," in IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 210-224, April 2012. [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Mohanty, S.D.; Luo, H.; Liu, Y. Swarm intelligence methods for Extreme Mass Ratio Inspiral search: First application of Particle Swarm Optimization. Preprints 2024, 2024011586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang and S. D. Mohanty, “Particle Swarm Optimization and gravitational wave data analysis: Performance on a binary inspiral testbed,” Phys. Rev. D 81, 063002 (2010). [CrossRef]
- T. S. Weerathunga and S. D. Mohanty, “Performance of Particle Swarm Optimization on the fully-coherent all-sky search for gravitational waves from compact binary coalescences,” Phys. Rev. D 95, no.12, 124030 (2017). [CrossRef]
- M. E. Normandin, S. D. Mohanty and T. S. Weerathunga, “Particle Swarm Optimization based search for gravitational waves from compact binary coalescences: performance improvements,” Phys. Rev. D 98, no.4, 044029 (2018). [CrossRef]
- M. E. Normandin and S. D. Mohanty, “Towards a real-time fully-coherent all-sky search for gravitational waves from compact binary coalescences using particle swarm optimization,” Phys. Rev. D 101, no.8, 082001 (2020). [CrossRef]
- S. D. Mohanty, “Spline Based Search Method For Unmodeled Transient Gravitational Wave Chirps,” Phys. Rev. D 96, no.10, 102008 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.D., Fahnestock, E. “Adaptive spline fitting with particle swarm optimization,” Comput Stat 36, 155–191 (2021). [CrossRef]
- S. D. Mohanty and M. A. T. Chowdhury, “Glitch subtraction from gravitational wave data using adaptive spline fitting,” Class. Quant. Grav. 40, no.12, 125001 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang, S. D. Mohanty and F. A. Jenet, “A coherent method for the detection and estimation of continuous gravitational wave signals using a pulsar timing array,” Astrophys. J. 795, no.1, 96 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang, S. D. Mohanty and F. A. Jenet, “Coherent network analysis for continuous gravitational wave signals in a pulsar timing array: Pulsar phases as extrinsic parameters,” Astrophys. J. 815, no.2, 125 (2015). [CrossRef]
- X. Zhu, L. Wen, J. Xiong, Y. Xu, Y. Wang, S. D. Mohanty, G. Hobbs and R. N. Manchester, “Detection and localization of continuous gravitational waves with pulsar timing arrays: the role of pulsar terms,” Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 461, no.2, 1317-1327 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang and S. D. Mohanty, “Pulsar Timing Array Based Search for Supermassive Black Hole Binaries in the Square Kilometer Array Era,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, no.15, 151104 (2017) [erratum: Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, no.16, 169901 (2020)]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang, S. D. Mohanty and Y. Q. Qian, “Continuous gravitational wave searches with pulsar timing arrays: Maximization versus marginalization over pulsar phase parameters,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 840, no.1, 012058 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Y. Q. Qian, S. D. Mohanty and Y. Wang, “Iterative time-domain method for resolving multiple gravitational wave sources in pulsar timing array data,” Phys. Rev. D 106, no.2, 023016 (2022). [CrossRef]
- X. Zhang, S. D. Mohanty, X. Zou and Y. Liu, “Resolving Galactic binaries in LISA data using particle swarm optimization and cross-validation,” Phys. Rev. D 104, 024023 (2021). [CrossRef]
- X. H. Zhang, S. D. Zhao, S. D. Mohanty and Y. X. Liu, “Resolving Galactic binaries using a network of space-borne gravitational wave detectors,” Phys. Rev. D 106, no.10, 102004 (2022). [CrossRef]
- P. Gao, X. L. Fan, Z. J. Cao and X. H. Zhang, “Fast resolution of Galactic binaries in LISA data,” Phys. Rev. D 107, no.12, 123029 (2023). [CrossRef]
- P. Gao, X. Fan and Z. Cao, “Simultaneously search for multi-target Galactic binary gravitational waves in reduced parameter space with LMPSO-CV,” [arXiv:2401.09300 [gr-qc]]. [CrossRef]
- Y. Lu, E. K. Li, Y. M. Hu, J. d. Zhang and J. Mei, “An Implementation of Galactic White Dwarf Binary Data Analysis for MLDC-3.1,” Res. Astron. Astrophys. 23, no.1, 015022 (2023). [CrossRef]
- M. Tinto and S. V. Dhurandhar, “TIME DELAY,” Living Rev. Rel. 8, 4 (2005). [CrossRef]
- LISA Data Challenge, code and maunal. Available online: https://lisa-ldc.lal.in2p3.fr/code and https://lisa-ldc.lal.in2p3.fr/static/data/pdf/LDC-manual-002.pdf.
- S. Babak, A. Petiteau and M. Hewitson, “LISA Sensitivity and SNR Calculations,” [arXiv:2108.01167 [astro-ph.IM]]. [CrossRef]
- William H. Press, Saul A. Teukolsky, William T. Vetterling, Brian P. Flannery, “Numerical Recipes in Fortran 90: The Art of Parallel Scientific Computing, 2nd ed. (Fortran Numerical Recipes 2)“,Cambridge University Press, Year: 1996. [CrossRef]
- The gsl library. Available online: https://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/doc/html/multimin.html.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).