Submitted:
06 February 2024
Posted:
06 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Real-Time Augmentation Information Analyses
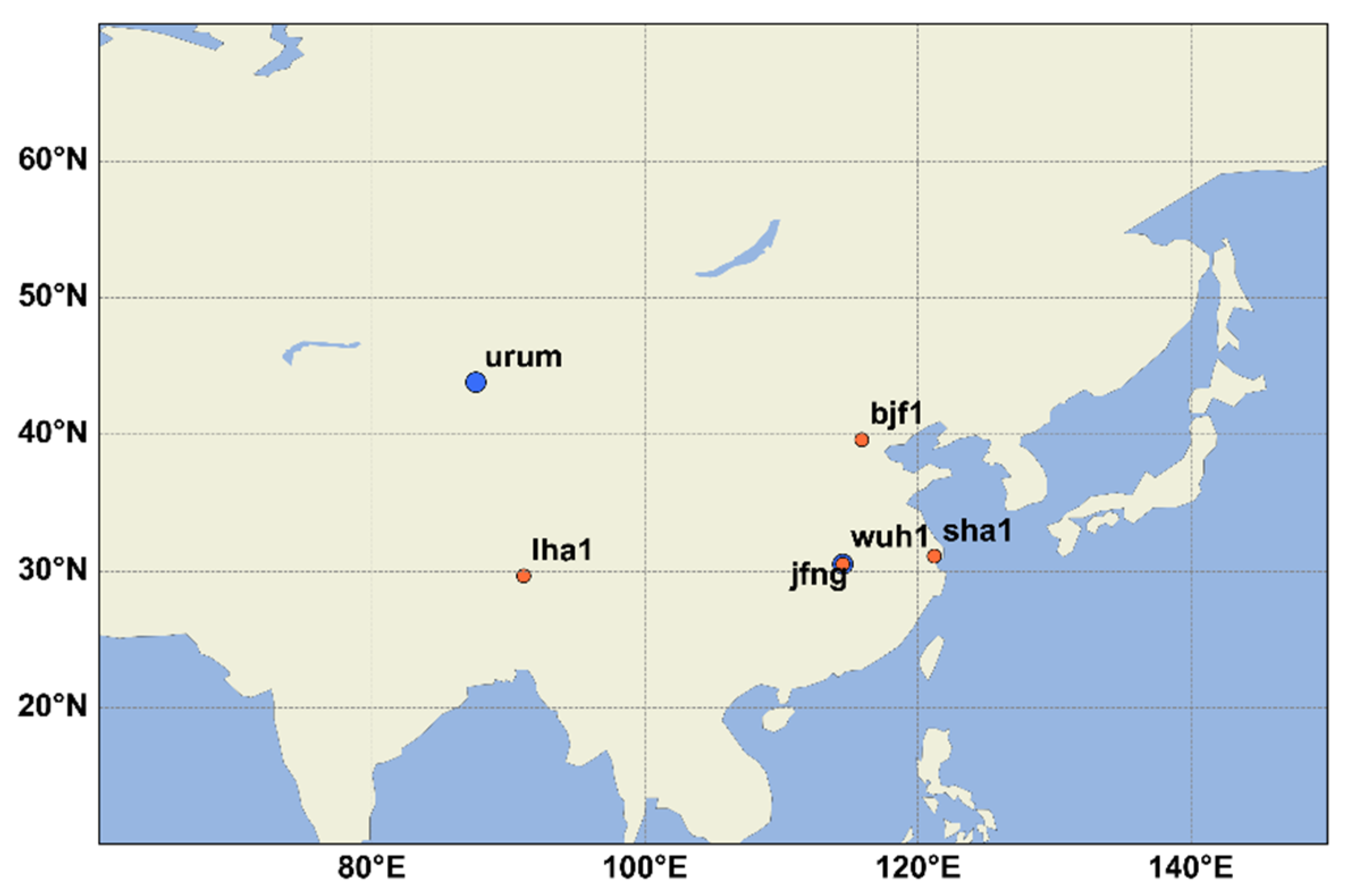
2.1. Real-Time Augmentation Information Acquisition
- (1)
- IGS real-time augmentation information.
- (2)
- PPP-B2b real-time augmentation information.
- (3)
- BDSBAS real-time augmentation information.
2.2. Real-Time Orbit and Clock Offset Recovery Method
2.2.1. Real-Time Orbit Recovery
- (1)
- IGS real-time orbit recovery
- (2)
- PPP-B2b real-time orbit recovery
- (3)
- BDSBAS real-time orbit recovery
2.2.2. Real-Time Clock Offset Recovery
- (1)
- IGS real-time clock offset recovery
- (2)
- PPP-B2b real-time clock offset recovery
- (3)
- BDSBAS real-time clock offset recovery
2.3. Real-Time Product Quality Analysis
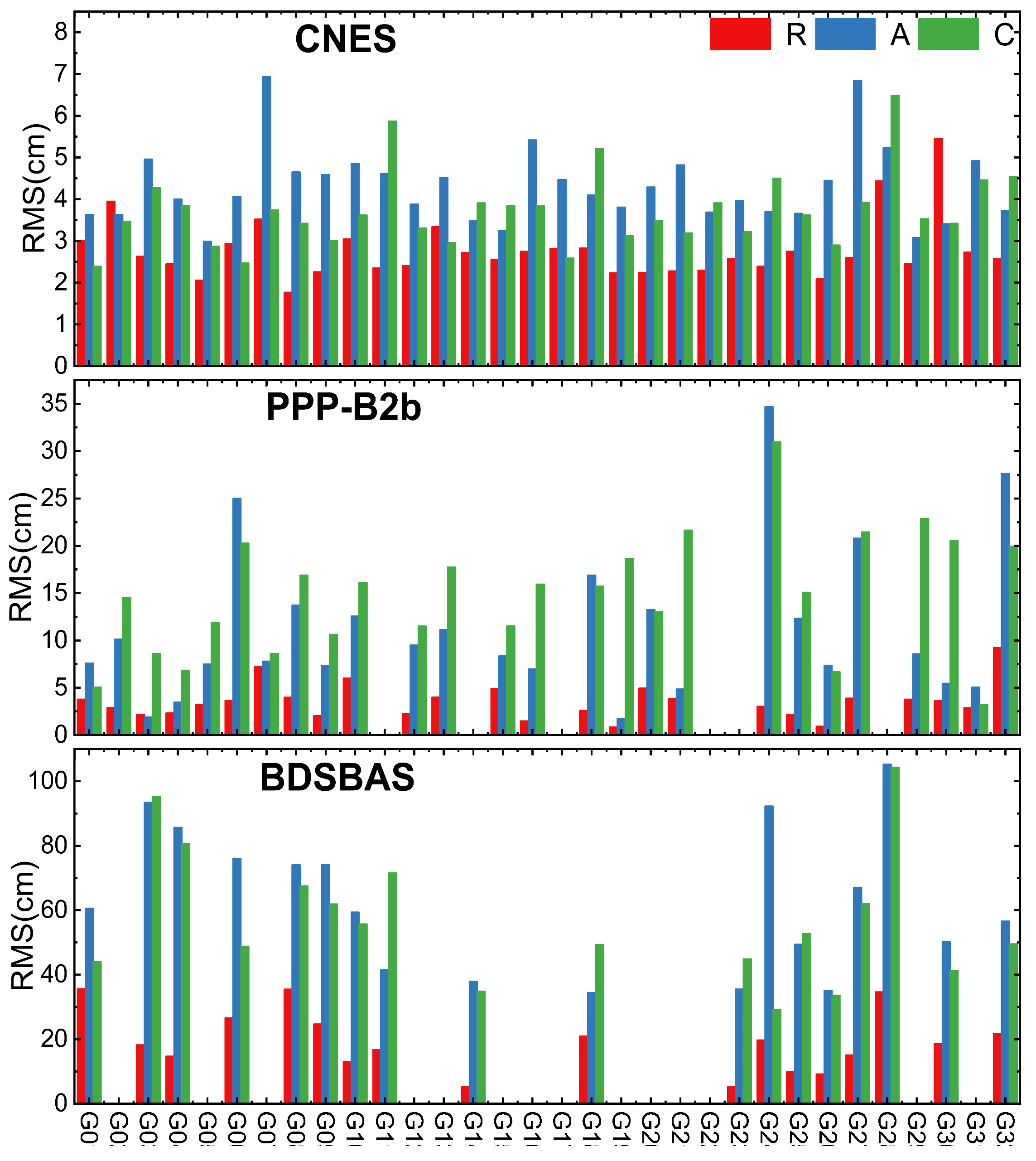
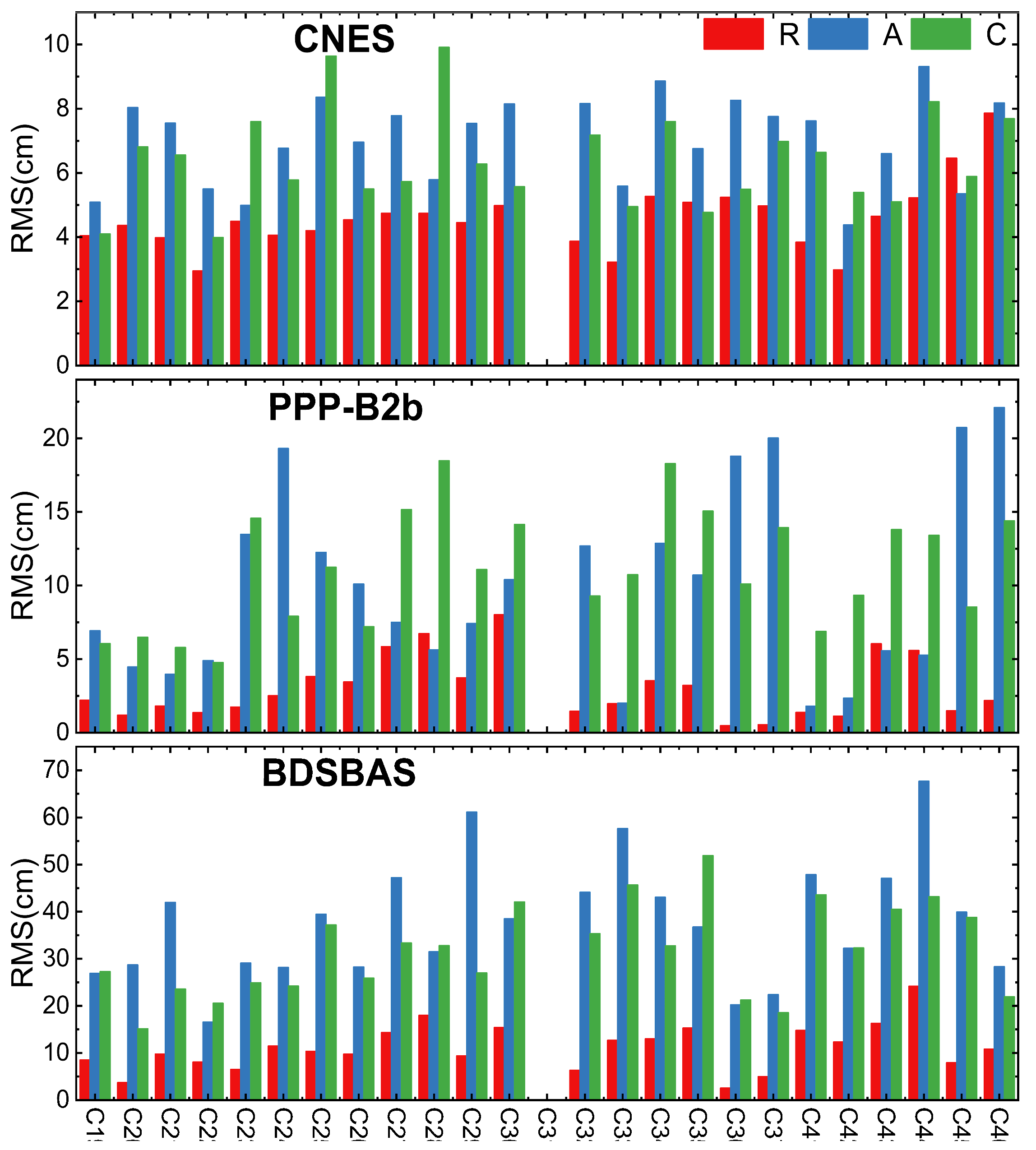
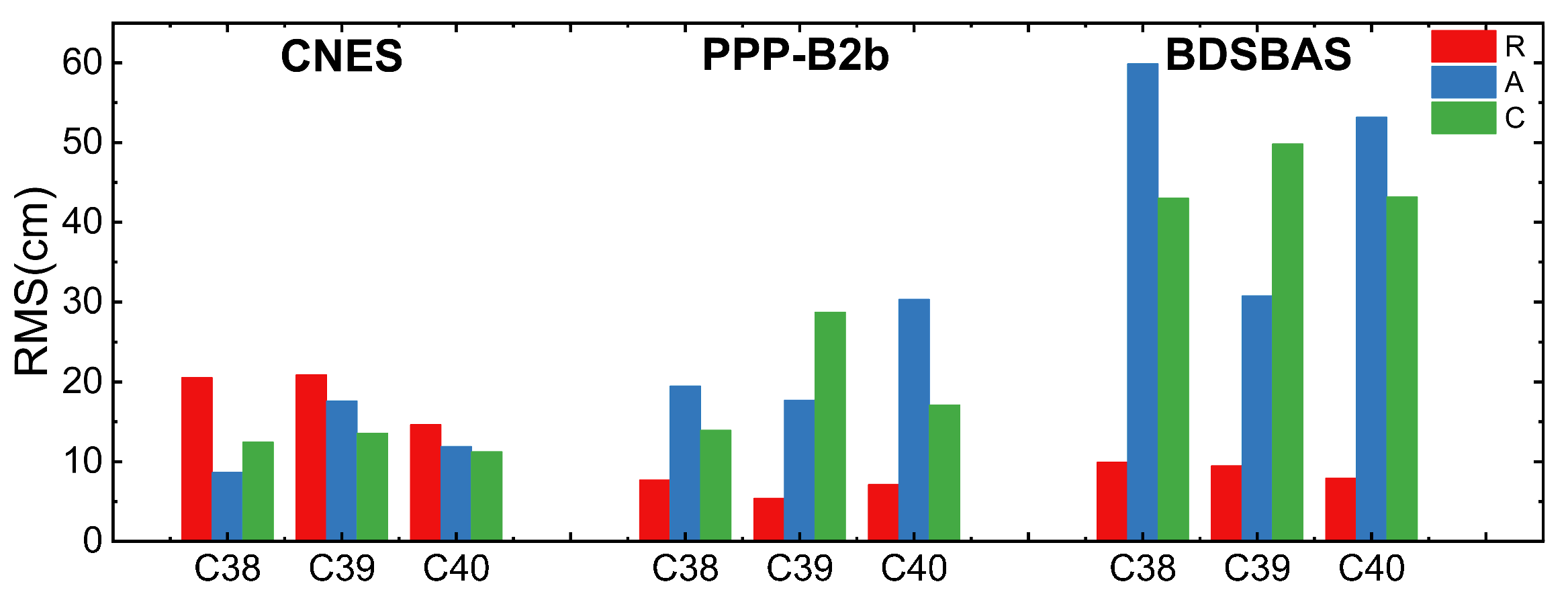
2.3.1. Real-Time Orbit Accuracy Analysis
- (1)
- GPS orbit accuracy
- (2)
- BDS-3 orbit accuracy
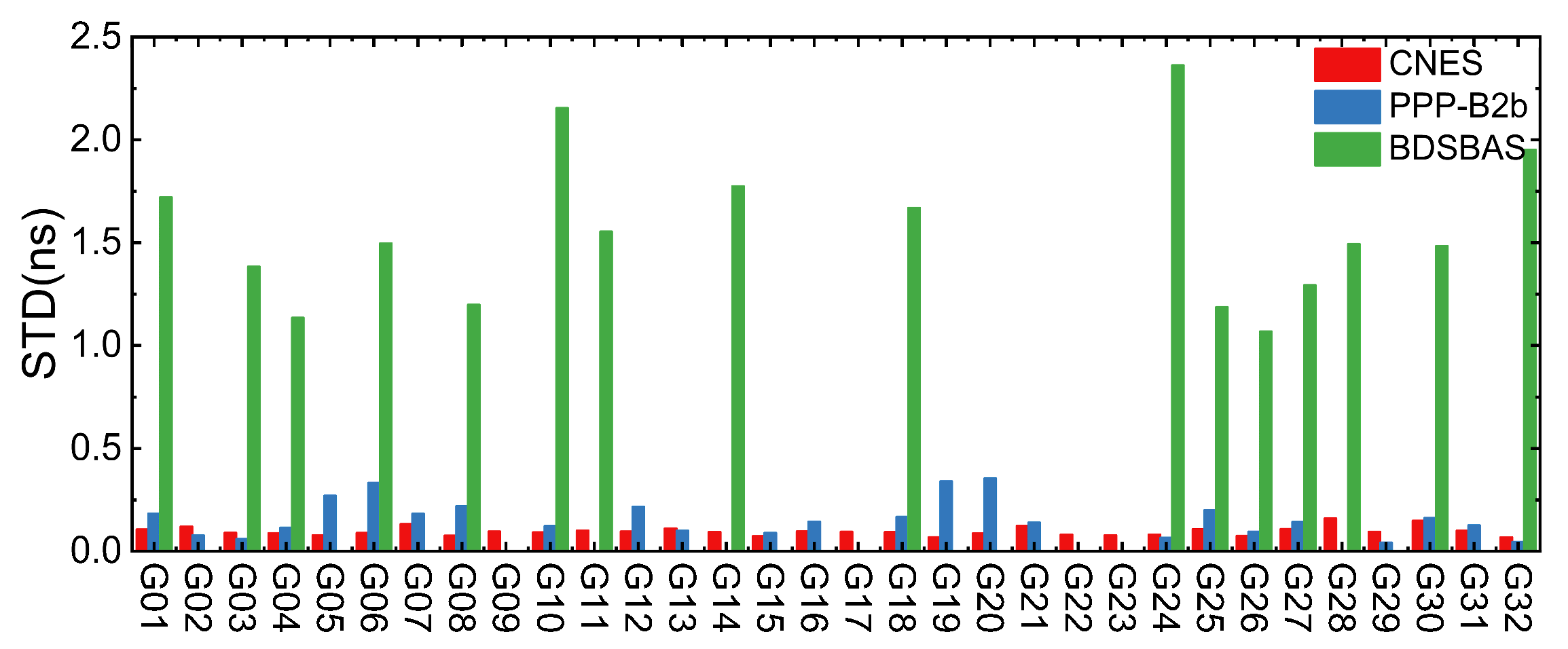
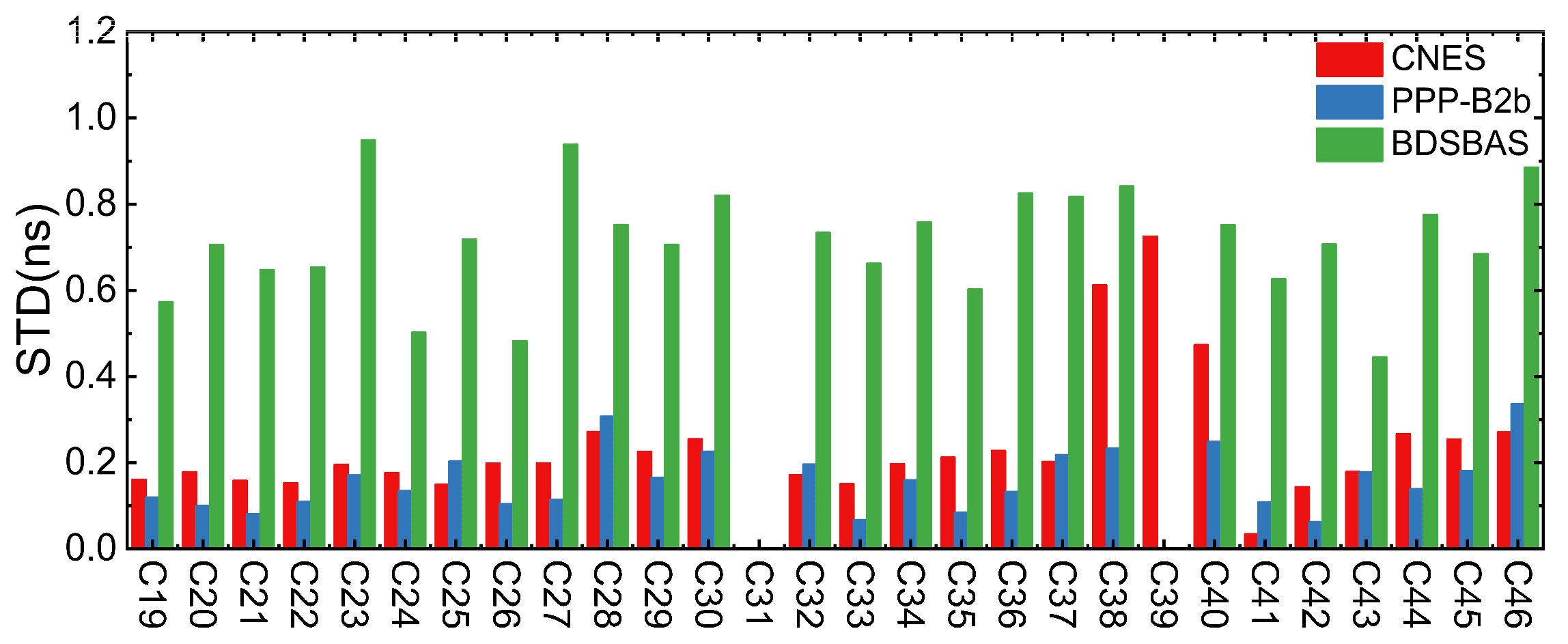
2.3.2. Real-Time Clock Offset Accuracy Analysis
- (1)
- GPS clock offset accuracy
- (2)
- BDS-3 clock offset accuracy
3. Real-Time PPP Performance Evaluation
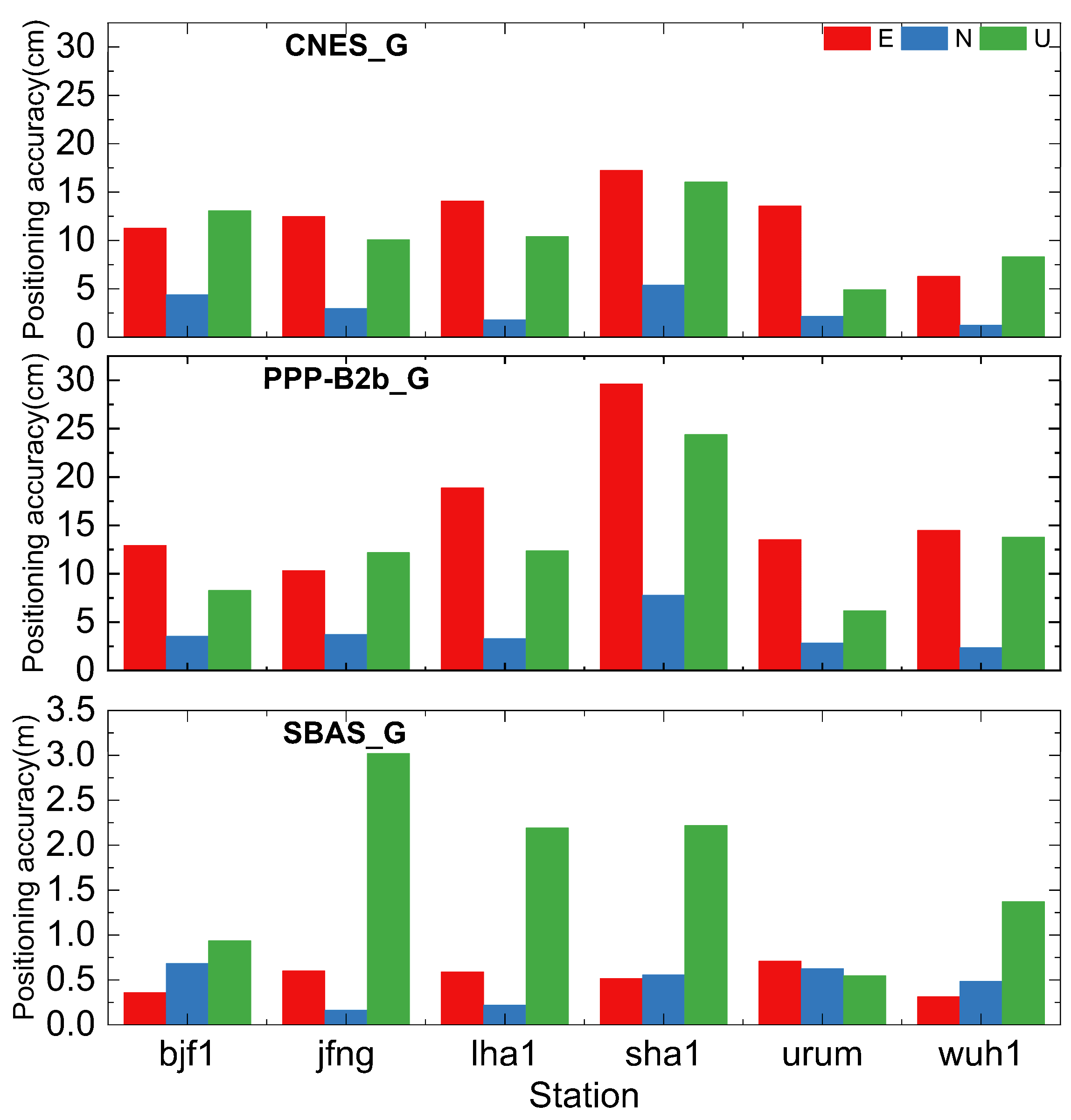
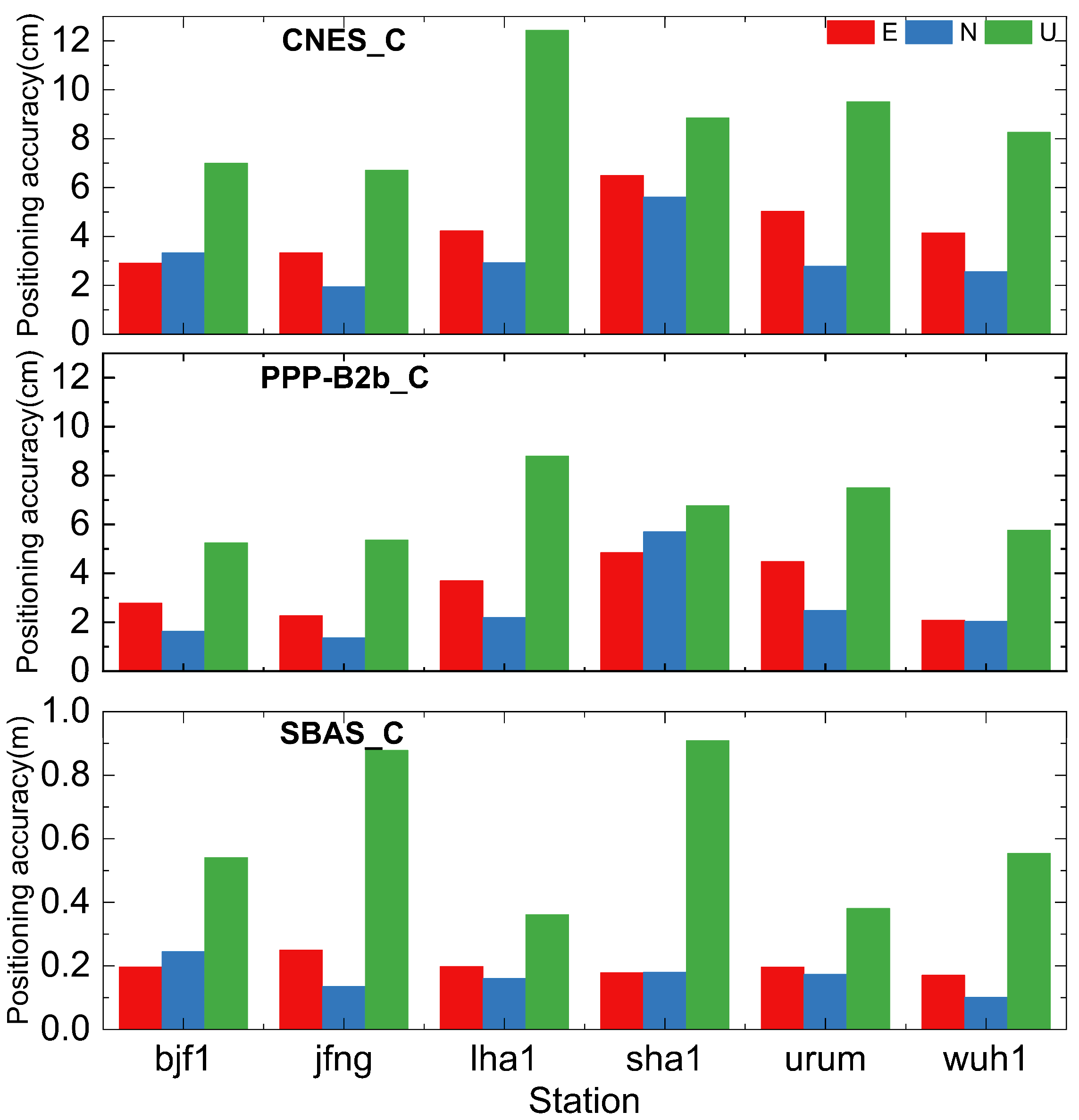
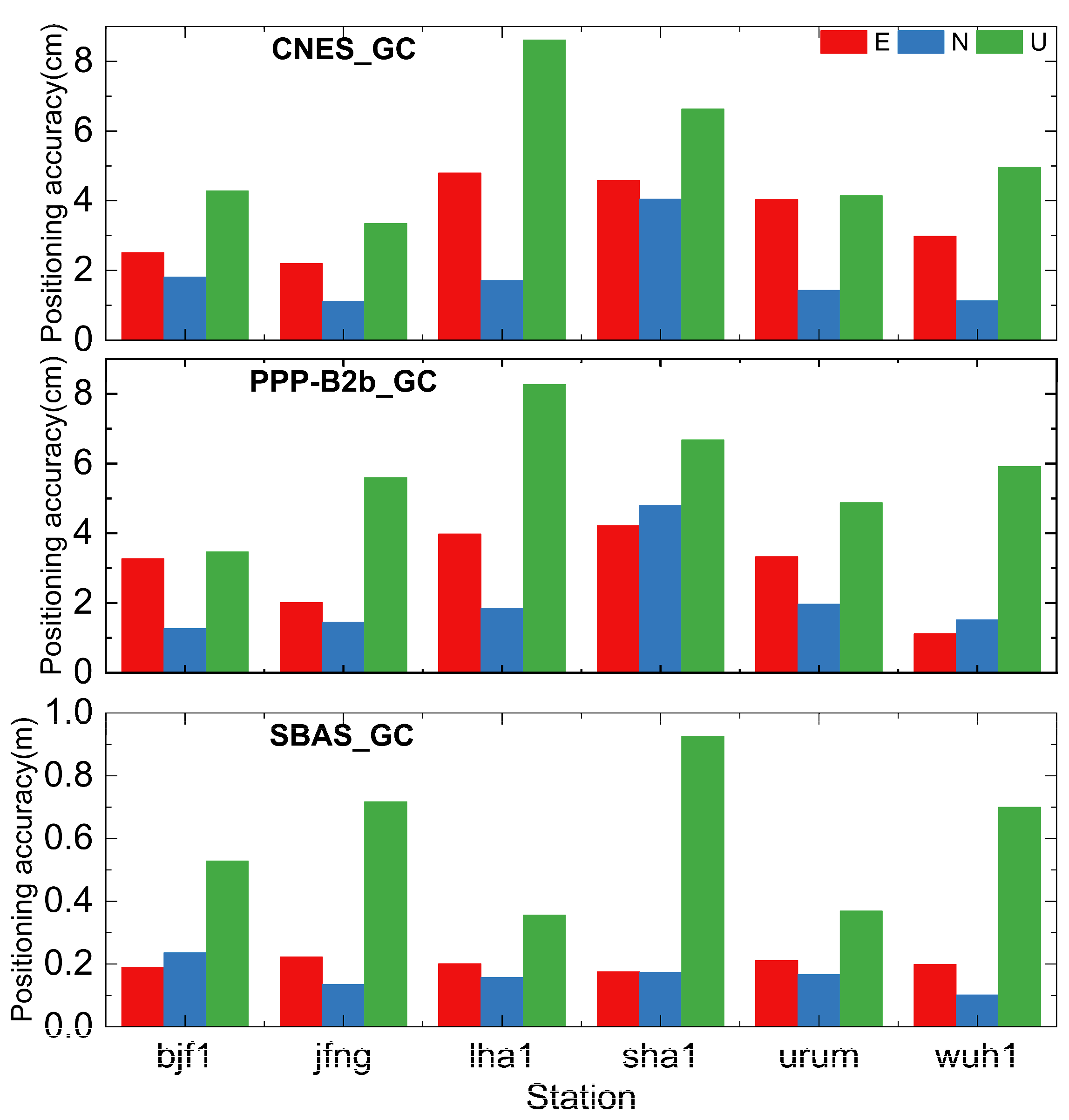
3.1. PPP Accuracy Analysis Based on Real-Time Augmentation Information
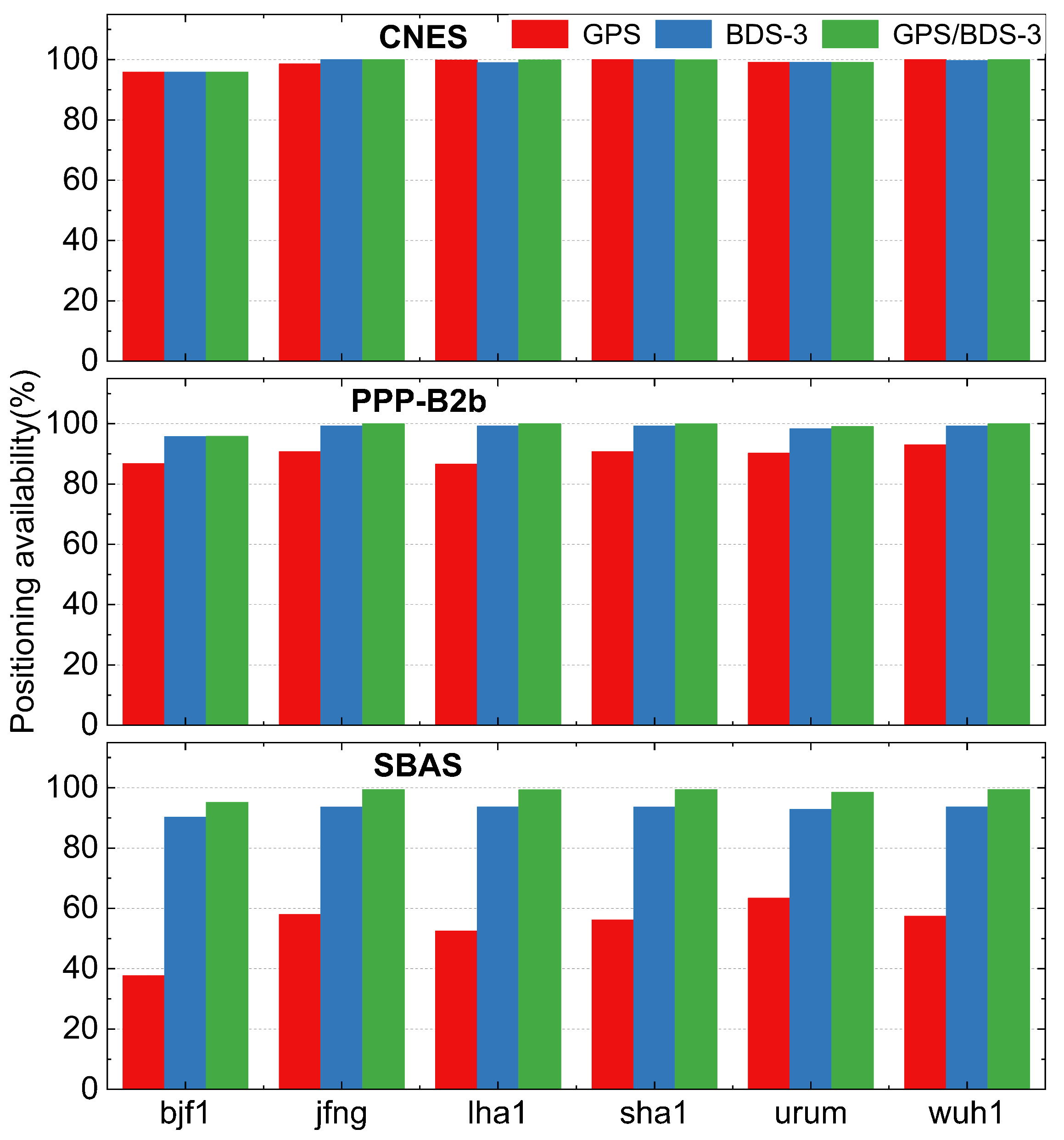
3.2. Positioning Availability Analysis Based on Real-Time Augmentation Information
4. Application Field Analysis
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- PPP-B2b and CNES RT orbit accuracy is consistent in radial direction, PPP-B2b GPS RT orbit accuracy is marginally poorer than CNES, BDS-3 orbit accuracy is slightly better than CNES, but within 5 cm. PPP-B2b RT orbit accuracy is worse than CNES in A and C direction, both are at decimeter-level. For CNES, except IGSO satellites, the orbit accuracy of other satellites is about centimeter level. BDSBAS real-time orbit accuracy is worse than CNES and PPP-B2b, which reached the decimeter-level.
- (2)
- The performance of CNES and PPP-B2b RT clock offset are consistent, CNES GPS RT clock offset accuracy is marginally higher than that of PPP-B2b, BDS-3 real-time clock offset accuracy is marginally inferior to that of PPP-B2b, especially for IGSO satellite. The BDSBAS RT clock offset accuracy is considerably inferior to that of CNES and PPP-B2b, but it has reached the sub-nanosecond level.
- (3)
- The RT PPP performance of BDS-3-only based on PPP-B2b service is marginally greater than CNES service, and that of GPS-only and GPS/BDS-3 dual systems is marginally worse than CNES, but it still reaches centimeter-level. The RT PPP performance of BDSBAS service is in decimeter level, except for the U component of GPS-only, which may be caused by the limited quantity of GPS satellites that can be corrected.
- (4)
- The RT PPP positioning accuracy and availability of GPS/BDS-3 and BDS-3-only are on par with CNES and PPP-B2b services. The acquisition of RT augmentation information is where the two services’ applications diverge most. CNES RT service rely on unobstructed network environment, while PPP-B2b only serves China and surrounding areas. For BDSBAS RT services, its positioning integrity and continuity have significant advantages, mainly applied in aviation and maritime fields.
References
- Wang, L.; Yue, F.; Miao, C. GPS/GLONASS /GALILEO Real-time service (RTS) product performance evaluation analysis. Navigation Positioning and Timing 2020, 7, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Li, Z.S.; Wang, L.; et al. Assessment of Multiple GNSS Real-Time SSR Products from Different Analysis Centers. International Journal of Geo-Information 2018, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Precise Point Positioning Service Signal PPP-B2b (Version 1.0). http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/202008/P020230516574071340728.pdf. (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- China Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Satellite Based Augmentation System Service Signal BDSBAS-B1C (Version 1.0). http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/202008/ P020200803362065480963.pdf. (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- IWG. SBAS L5 DFMC Interface Control Document (SBAS L5 DFMC ICD) (version 3). http://www.esa.int.
- China Satellite Navigation Office. Interface specification for signal in space of BeiDou satellite-based augmentation system -Dual-frequency augmentation service signal BDSBAS-B2a. http://www.beidou.gov.cn/yw/xwzx/202212/W020221231 599398885146.pdf. (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Zhao, S.; Yang, Li.; Gao, Y. Analysis of GPS real-time precision single-point positioning performance based on SSR information. Geodesy and Geodynamics 2019, 39, 952–955. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, H.Z.; Gao, Y.; et al. Evaluation and Analysis of Real-time Precise Orbits and Clocks Products from Different IGS Analysis Centers. Advances in Space Research 2018, 61, 2942–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, B.C.; Yuan, Y.B.; et al. Real-Time Precise Point Positioning (RTPPP) with Raw Observations and Its Application in Real-time Regional Ionospheric VTEC Modeling. Journal of Geodesy 2018, 92, 1267–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Yuan, H. Assessment of Multiple GNSS Real-Time SSR Products from Different Analysis Centers. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf 2018, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, G.; Wang, L.; Xie, W. BDS/GPS/Galileo Precise Point Positioning Performance Analysis of Android Smartphones Based on Real-Time Stream Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.C.; Chen, L.; Nan, S.; et al. Decoding PPP Corrections from BDS B2b Signals Using a Software-defined Receiver: An Initial Performance Evaluation. Sensors Journal 2021, 21, 7871–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.W.; Meng, X.W. Accuracy Analysis of Precise Point Positioning Using BDS-3 PPP-B2b Signals. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics 2021, 41, 516–519. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.W.; Zhao, X.K.; Lou, Y.D.; et al. Performance Evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b Service. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 2023, 48, 408–415. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; et al. Initial Assessment of the BDS-3 PPP-B2b RTS Compared with the CNES RTS. GPS Solutions 2021, 25, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Gong, H.; Peng, J.; et al. Performance Assessment of Real-Time Precise Point Positioning Using BDS PPP-B2b Service Signal. Advances in Space Research 2021, 68, 3242–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Du, J. Initial Assessment of BDS PPP-B2b Service: Precision of Orbit and Clock Corrections, and PPP Performance. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhou, C.; Wu, Z.H. BDS-3 PPP-B2b signal accuracy and precision single-point positioning performance evaluation. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science Technology (Natural Science Edition) 2022, 14, 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.Z.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, G.; et al. Beidou-3 system PPP-B2b space signal performance evaluation. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting 2023, 43, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y. , Yang, Y. Li, J. Performance evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b precise point positioning service. GPS Solut 2021, 25, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Lyu, D.; Zeng, F.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, R. Comprehensive Analysis of PPP-B2b Service and Its Impact on BDS-3/GPS Real-Time PPP Time Transfer. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C., Hu, X., Chen, J. et al. Orbit determination, clock estimation and performance evaluation of BDS-3 PPP-B2b service. J Geod 2022, 96, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, M. Comprehensive Analyses of PPP-B2b Performance in China and Surrounding Areas. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T. Li, Z.Q.; et al. Real-time Ocean precise point positioning with BDS-3 service signal PPP-B2b. Measurement 2022, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Yang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Q.; Lv, J.; Gao, Z. Evaluation of BDS-3 B1C/B2b Single/Dual-Frequency PPP Using PPP-B2b and RTS SSR Products in Both Static and Dynamic Applications. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.R. Accuracy evaluation of BeiDou-3 PPP-B2b signal. GNSS World of China 2023, 48, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F. Theory and Technique on GNSS Integrity Augment. D.E. Thesis, PLA Information Engineering university, Zhengzhou, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.L.; Meng, Y.N.; Geng, C.J.; et al. BDS-3 performance assessment: PNT, SBAS, PPP, SMC and SAR. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica 2021, 50, 427–435. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.P.; Hu, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.Z.; et al. Preliminary evaluation of performance improvement of Beidou satellite-based augmentation system. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science) 2017, 45, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, B. Regional Single Frequency Service Availability Evaluation of BDSBAS. Navigation Positioning and Timing 2021, 8, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.; Chen, Q.; Guo, R.; et al. Basic navigation message parameters comparison between BDS-2 and BDS-3. Science of Surveying and Mapping 2020, 45, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xin, J.; Zhao, L.; Tian, Q.; Zhou, S.; Wu, B. Development Status and Service Performance Preliminary Analysis for BDSBAS. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Ding, Q.; Gao, W.G.; et al. Principle and performance of BDSBAS and PPP-B2b of BDS-3. Satell Navig 2022, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. 10 Application Scenarios of BDS in Africa. http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/202008/ P020211105587887134672.pdf. (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Yao, Y.; He, Y.; Yi, W.; et al. Method for evaluating real-time GNSS satellite clock products. GPS Solutions 2017, 21, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, F. Research on GPS/BDS-3 Precise Point Positioning Technology Based on Real-time Enhanced Information. M.E. Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.J.; Zhang, Z.T.; He, X.F.; et al. Stability Analysis of BDS-3 Satellite Differential Code Bias and Its Impacts on Single Point Positioning. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 2023, 48, 425–432. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Sun, F.P.; et al. Performance Analysis of Multi-GNSS Precise Point Positioning. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology 2016, 33, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.X; Ge, M.R. Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J Geod 2015, 89, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| IOD Type | Message Type |
| IODSSR | 1, 2, 3, and 4 |
| IODP | 1 and 4 |
| IODCorr | 2 and 4 |
| IODN | 2 and broadcast ephemeris |
| Project | Processing strategies |
| Solution type | Dual-frequency static PPP (GPS (L1+L2)/BDS-3 (B1I+B3I)) |
| estimator | Kalman filter |
| Observations | Carrier phase and code observation |
| Sample | 30s |
| Cut-off angle | 10o |
| stochastic model | elevation angle weighting model |
| ionospheric delay | Ionospheric-free combination |
| Tropospheric delay | dry component: SAAS+GMF model [36] |
| Wet component: random walk estimation | |
| relativistic effect | model correction [36] |
| Receiver antenna phase center | igs20.atx file correction (BDS-3 replaced by PCO of GPS) |
| phase windup | model correction [36] |
| Satellite orbit/clock offset | CNES, PPP-B2b and BDSBAS products |
| Augmentation Information Source | Broadcast Method | Service Area | Tracking Station Network | Spatial-temporal Reference |
| CNES RTS | Internet | Global | Global | WGS84/GPST |
| PPP-B2b | GEO satellites | China and surrounding regions | Regional + inter-satellite links | BDCS/BDT |
| BDSBAS | GEO satellites | China and surrounding regions | Regional | WGS84/BDT |
| Category | Application | Accuracy (RMS) | Coverage Area | Availability |
| Environmental Protection | Environmental Monitoring, Inspection | 0.5-2m | Protected Areas | 95% |
| Agriculture | Agricultural Machinery Autonomous Driving | 0.1m | Cultivated Areas | 99% |
| Railways | Vehicle Control, Automatic Maintenance Inspection | 0.1m | Railway Lines | 99.5% |
| Highways | Maintenance Inspection, Vehicle Management | 0.1m | Highways | 99.5% |
| Emergency Rescue | Emergency Communication | 0.1m | Production Areas | 98% |
| Municipal | Bus Dispatch and Management | 0.5m | Urban Areas | 98% |
| Tourism | Tourist Guidance | 1.0m | Scenic Areas | 95% |
| Surveying and Mapping | Surveying, Engineering Measurement | 0.02m | Entire Area | 98% |
| Aviation | Aircraft Landing Guidance, Route Planning | 4m | Airport Areas | 99% |
| Maritime | Ship Entry and Exit Guidance, Route Planning | 10m | Port Areas | 99% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





