Submitted:
05 February 2024
Posted:
06 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
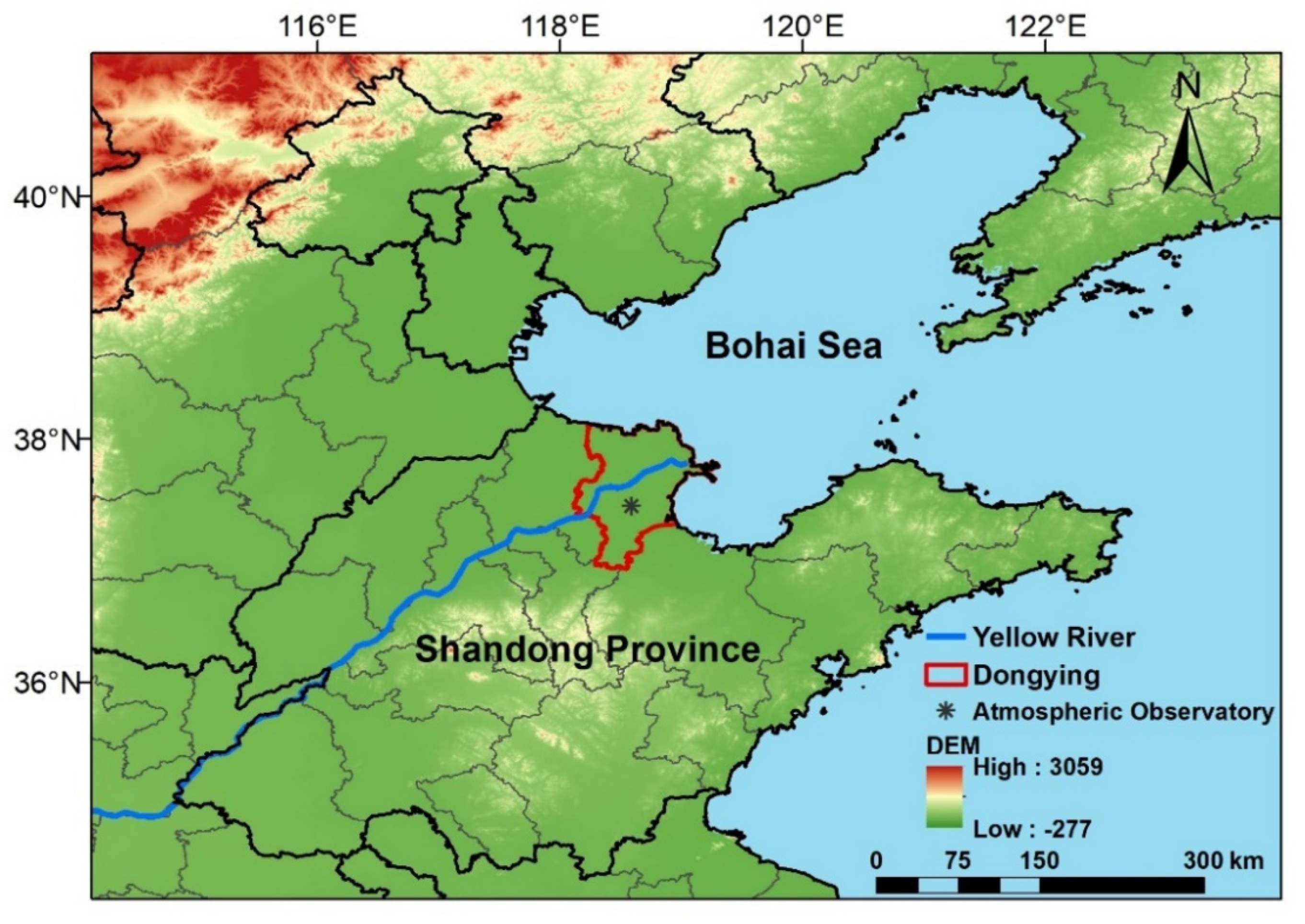
2.1. Observation Period and Location
2.2. Relevant Definitions
2.3. Data Processing
2.3.1. Transformation Rate of Nitrates and Sulfates
2.3.2. Calculation of Secondary Organic Carbon
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Nocturnal Ozone Concentration in Dongying
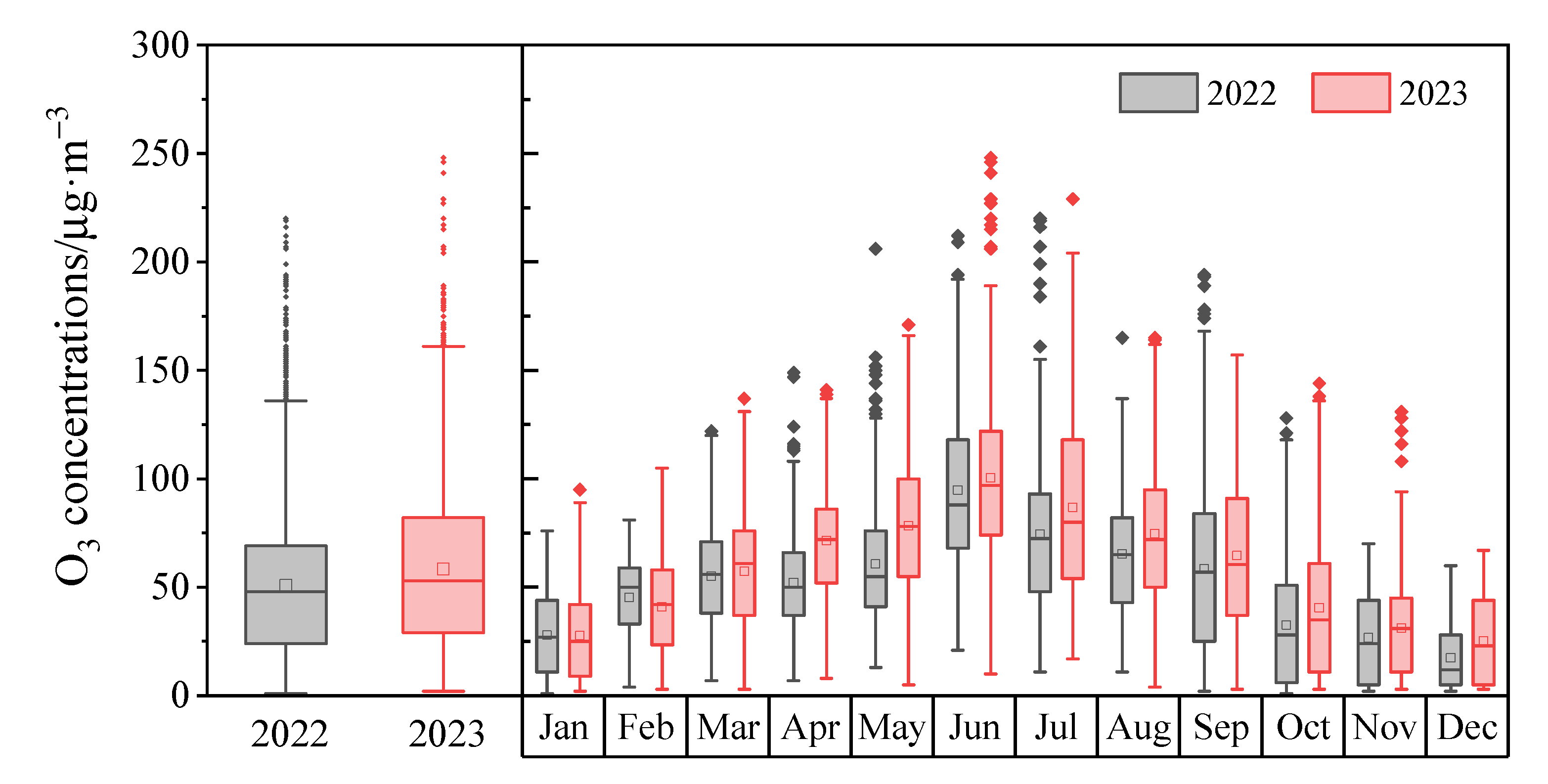
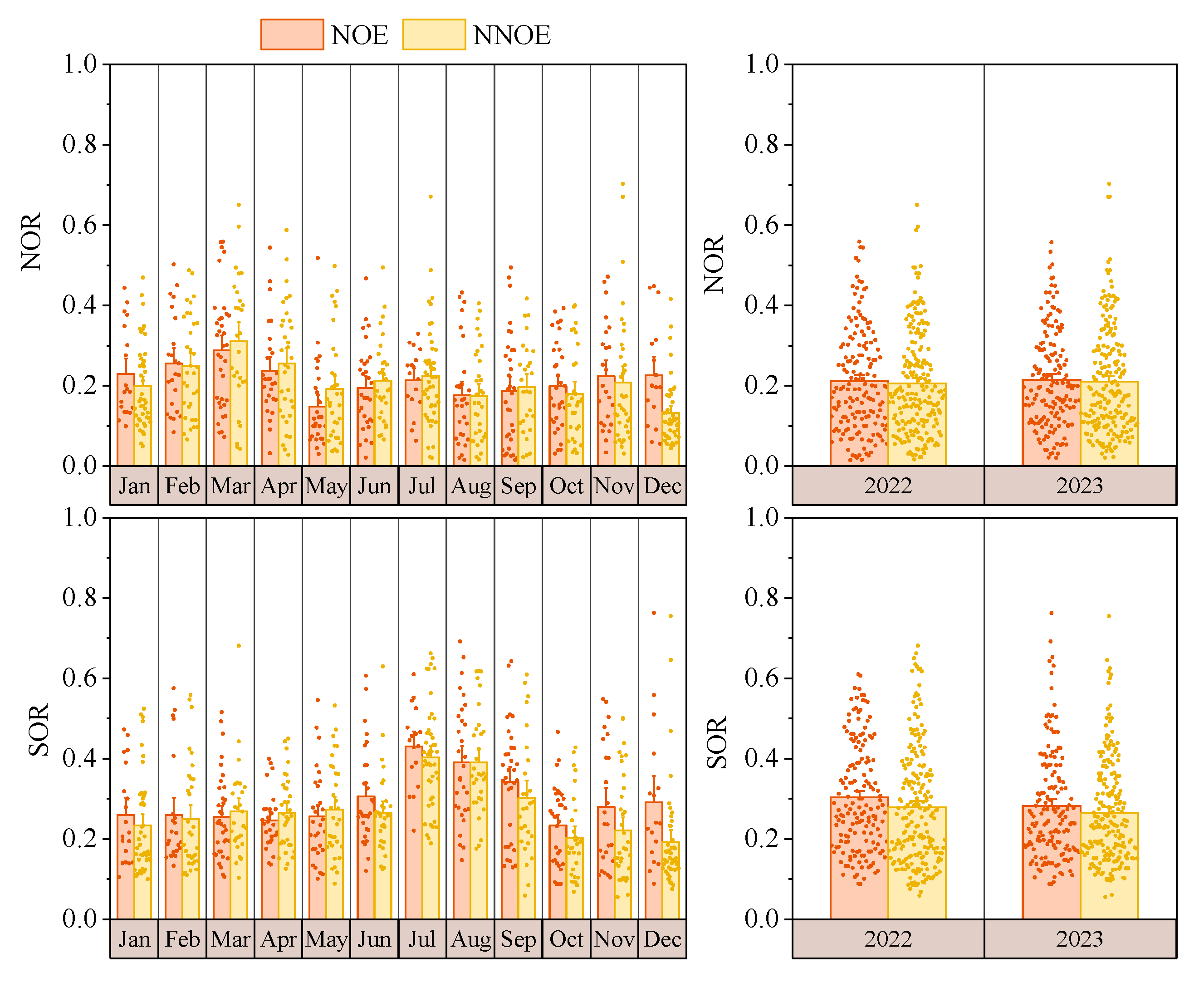
3.1.1. Inter-Annual and Inter-Monthly Variations
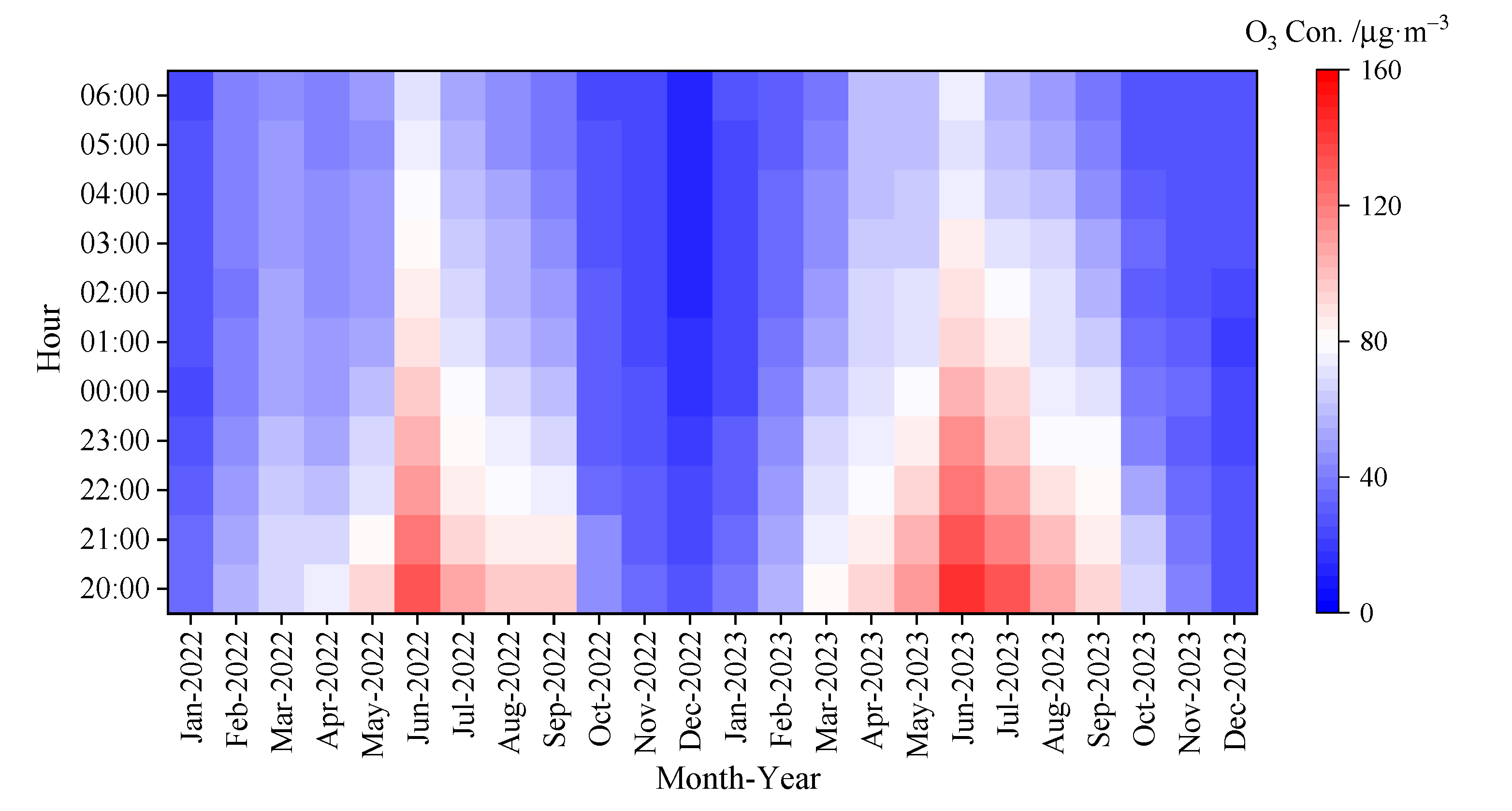
3.1.2. Diurnal Variation
3.2. Characteristics of Nocturnal Ozone Enhancement Events in Dongying
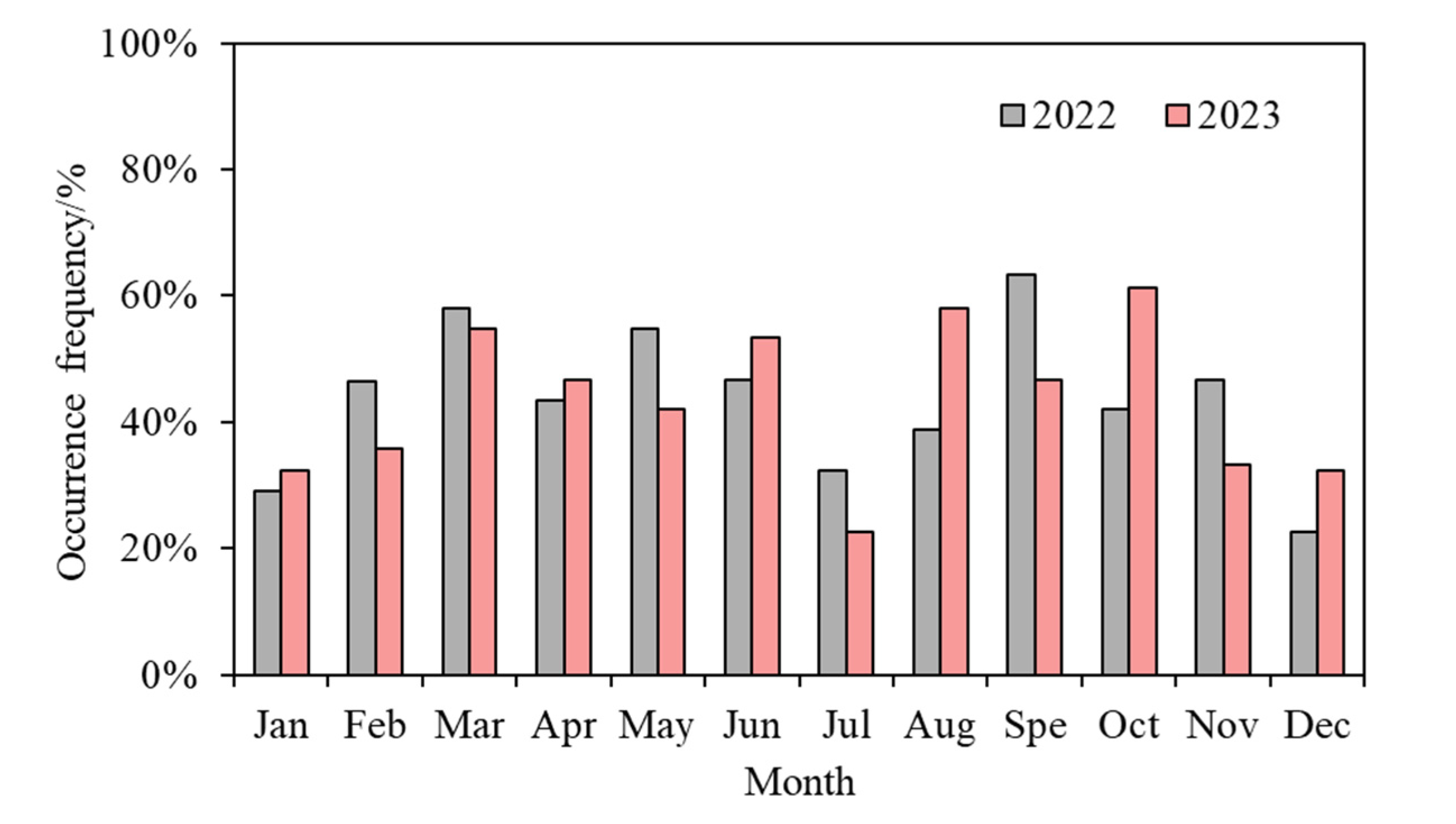
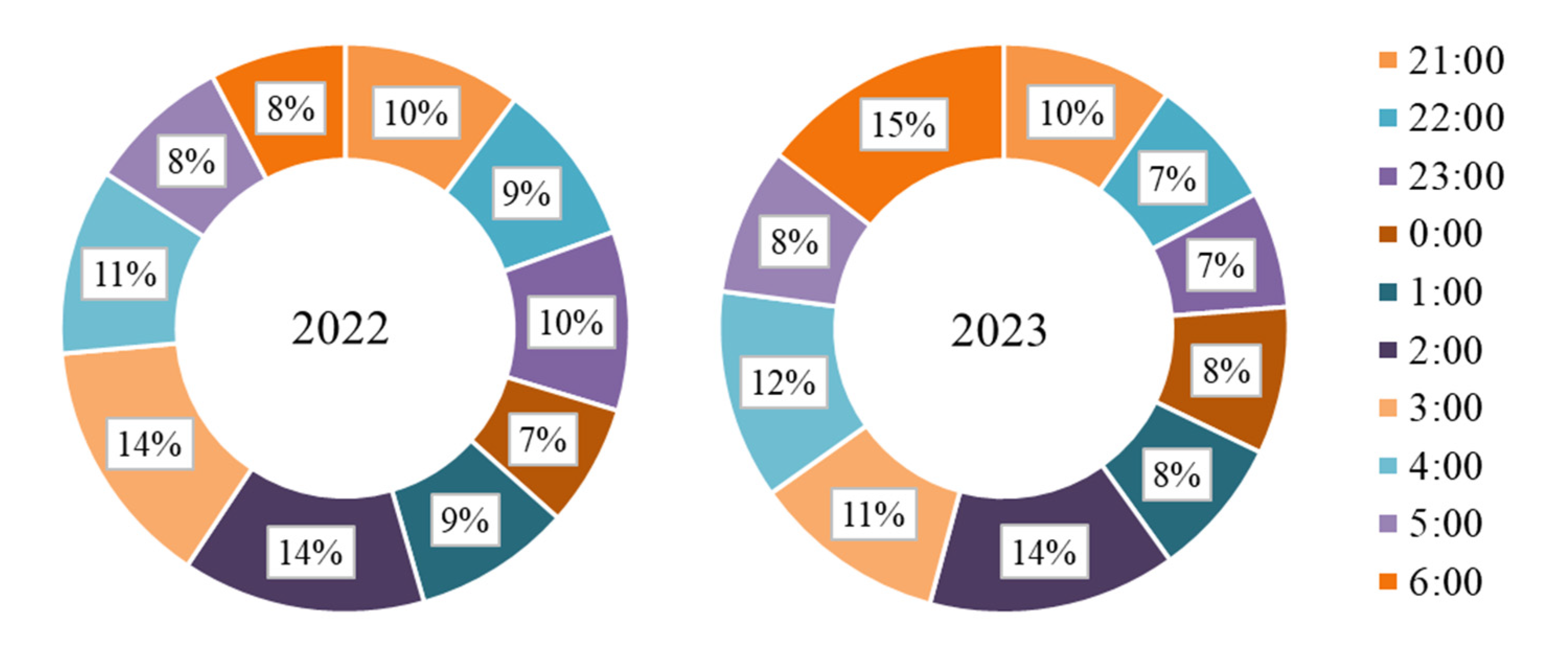
3.2.1. Frequency Characteristics
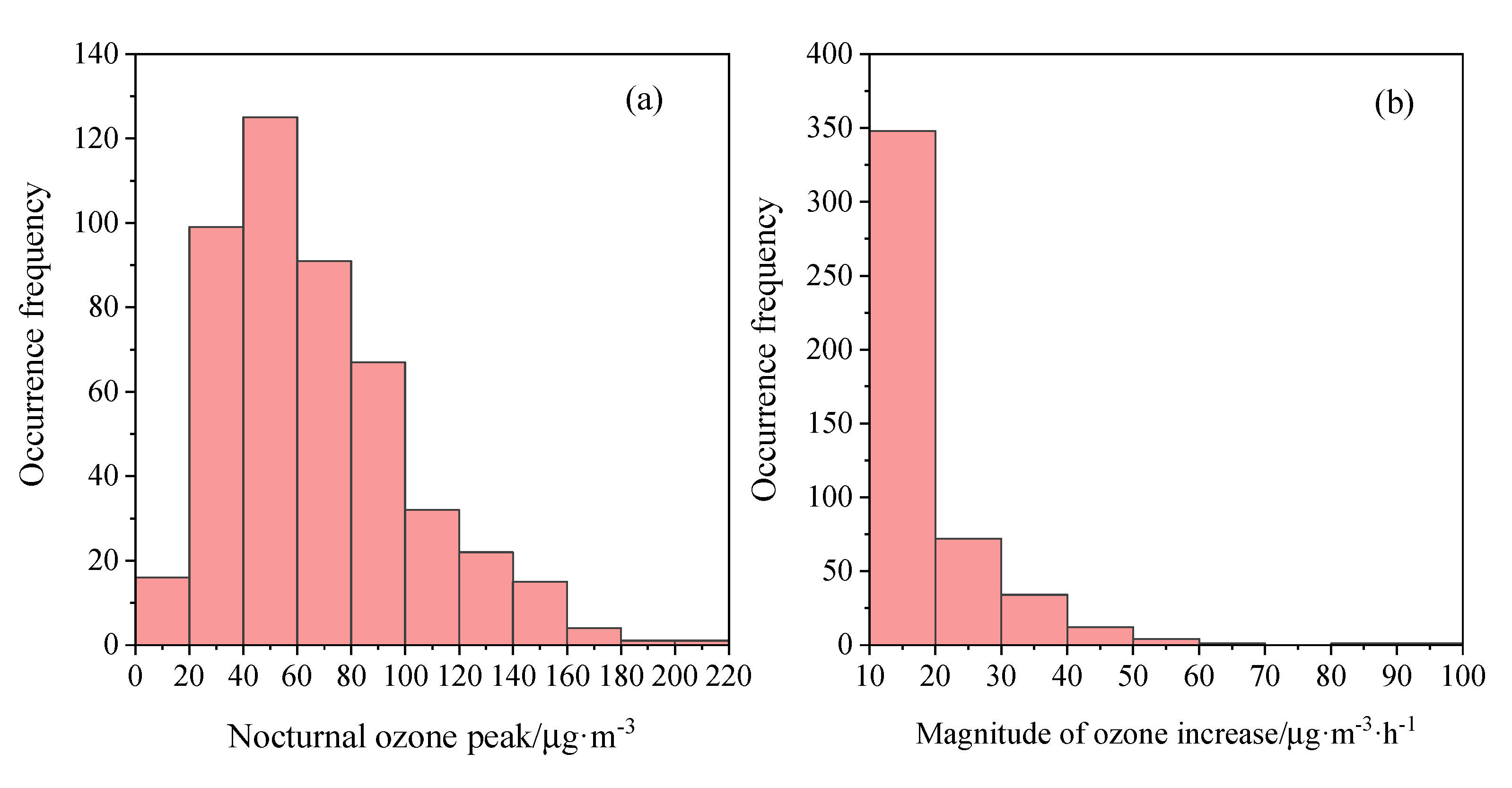
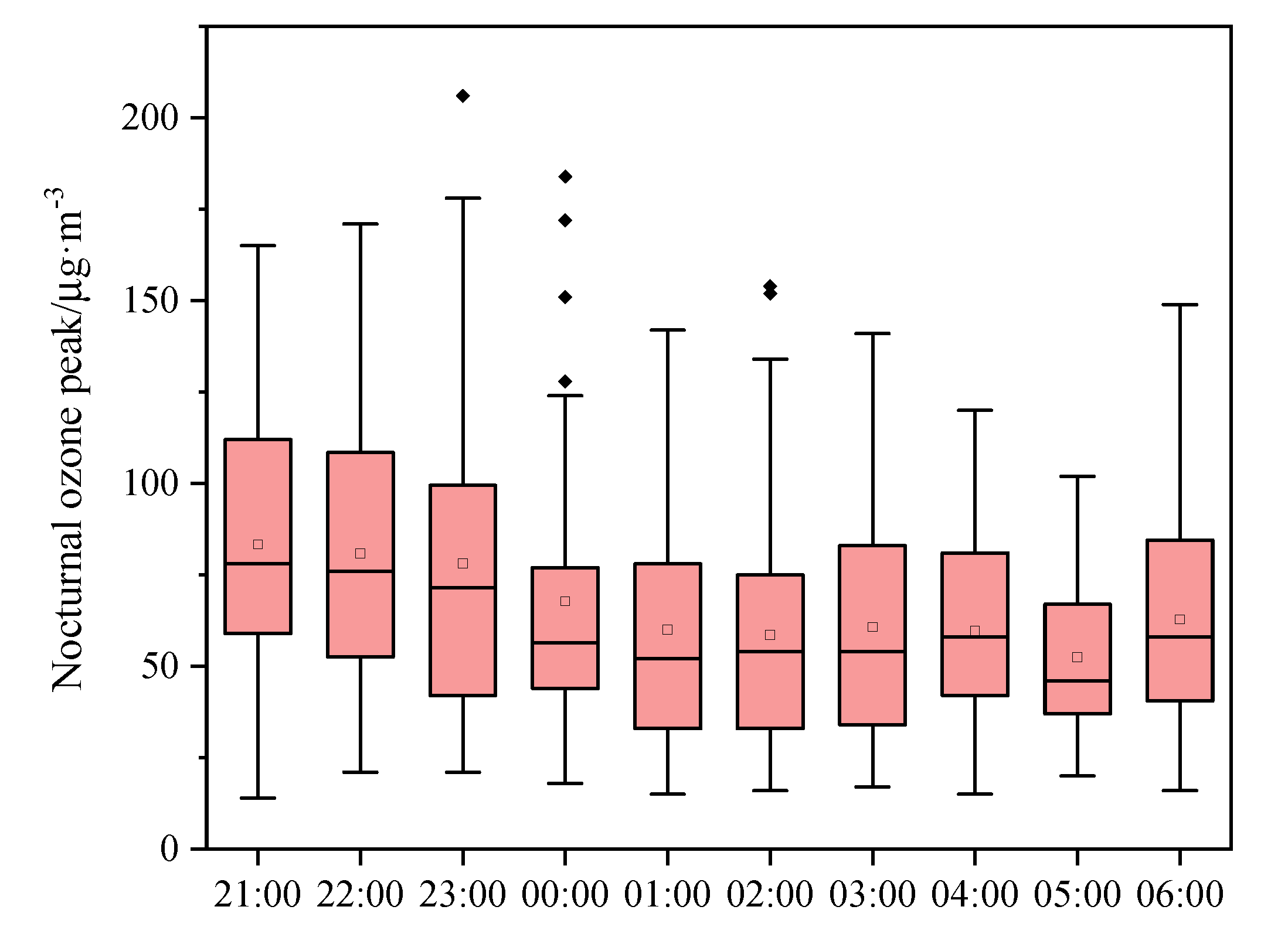
3.2.2. Characteristics of Nocturnal Ozone Peak and Ozone Increase Magnitude
3.3. Effects of Nocturnal Ozone Enhancement Events on Ozone and PM2.5 Concentrations in Dongying
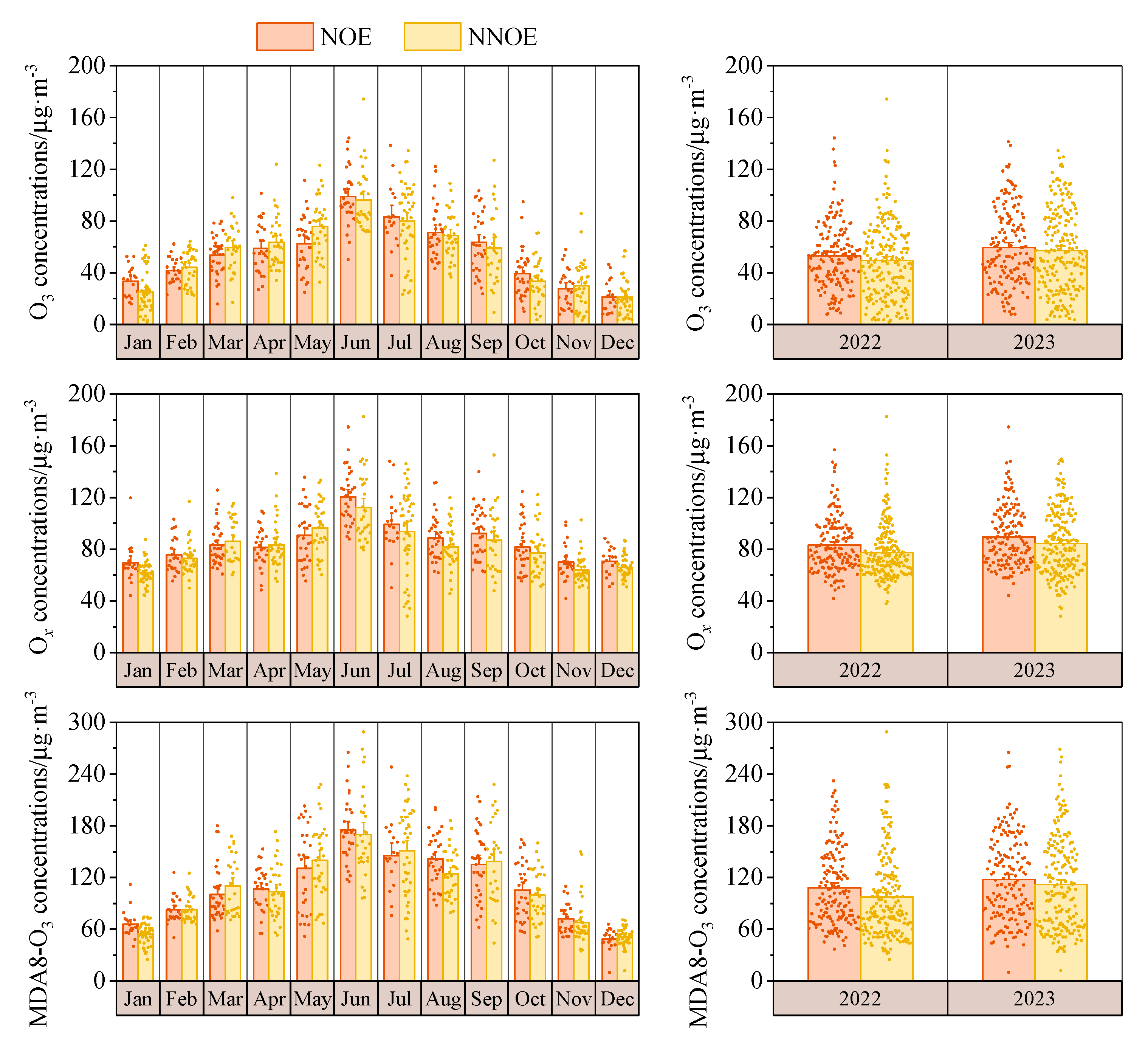
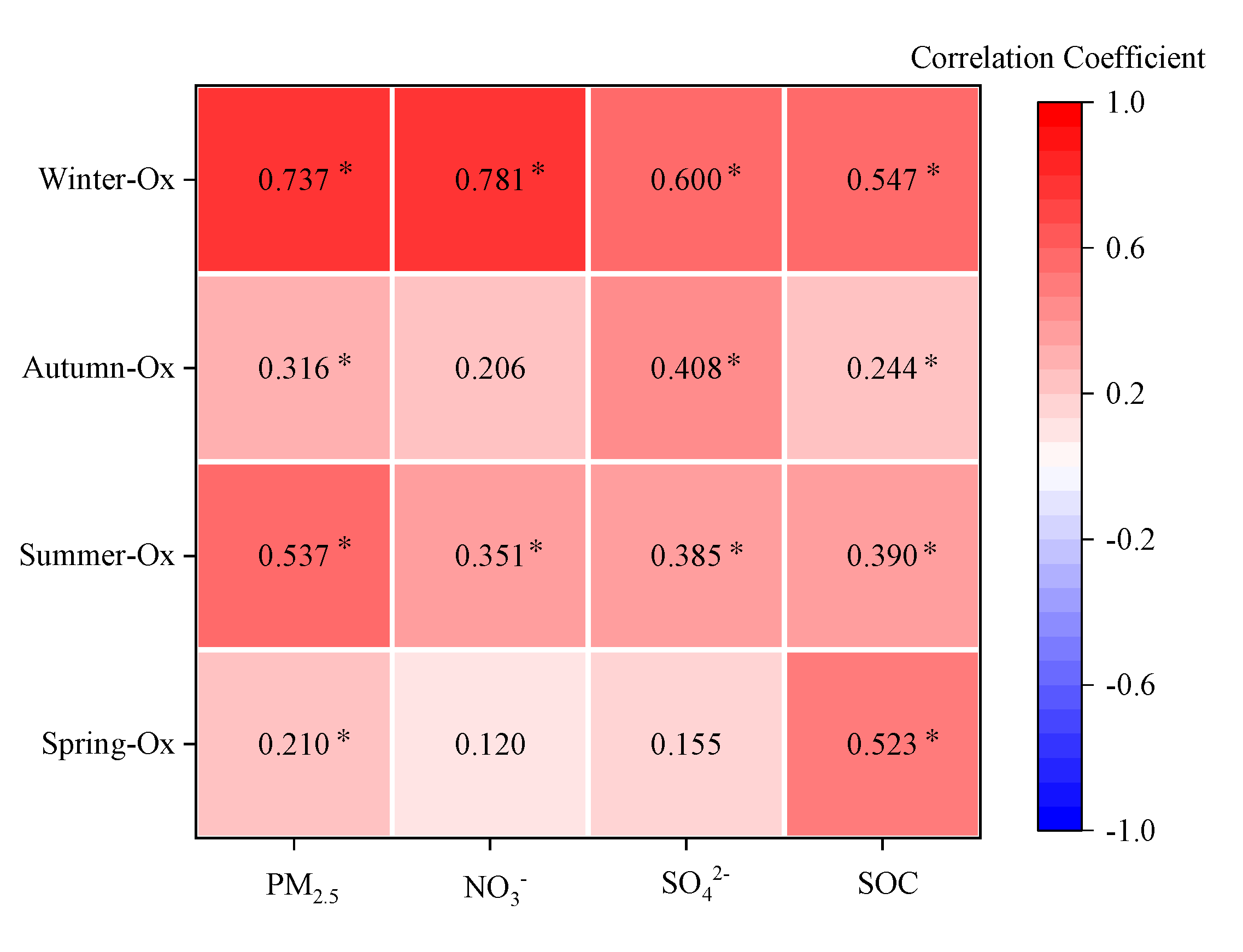
3.3.1. Effects on Ozone and Atmospheric Oxidation at Night and the Next Day
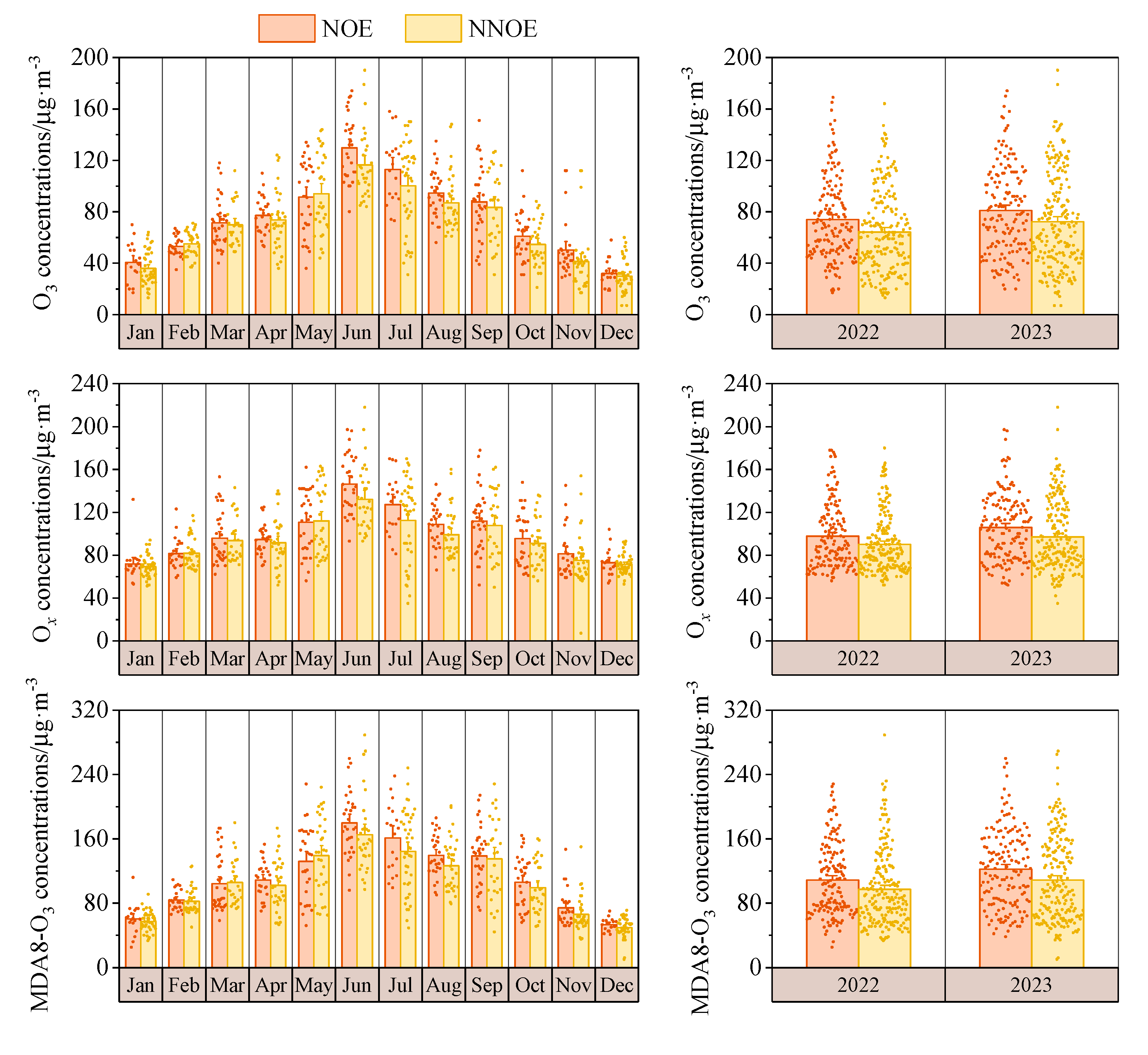
3.3.2. Effects on PM2.5 Concentration and Secondary Components at Night and the Next Day
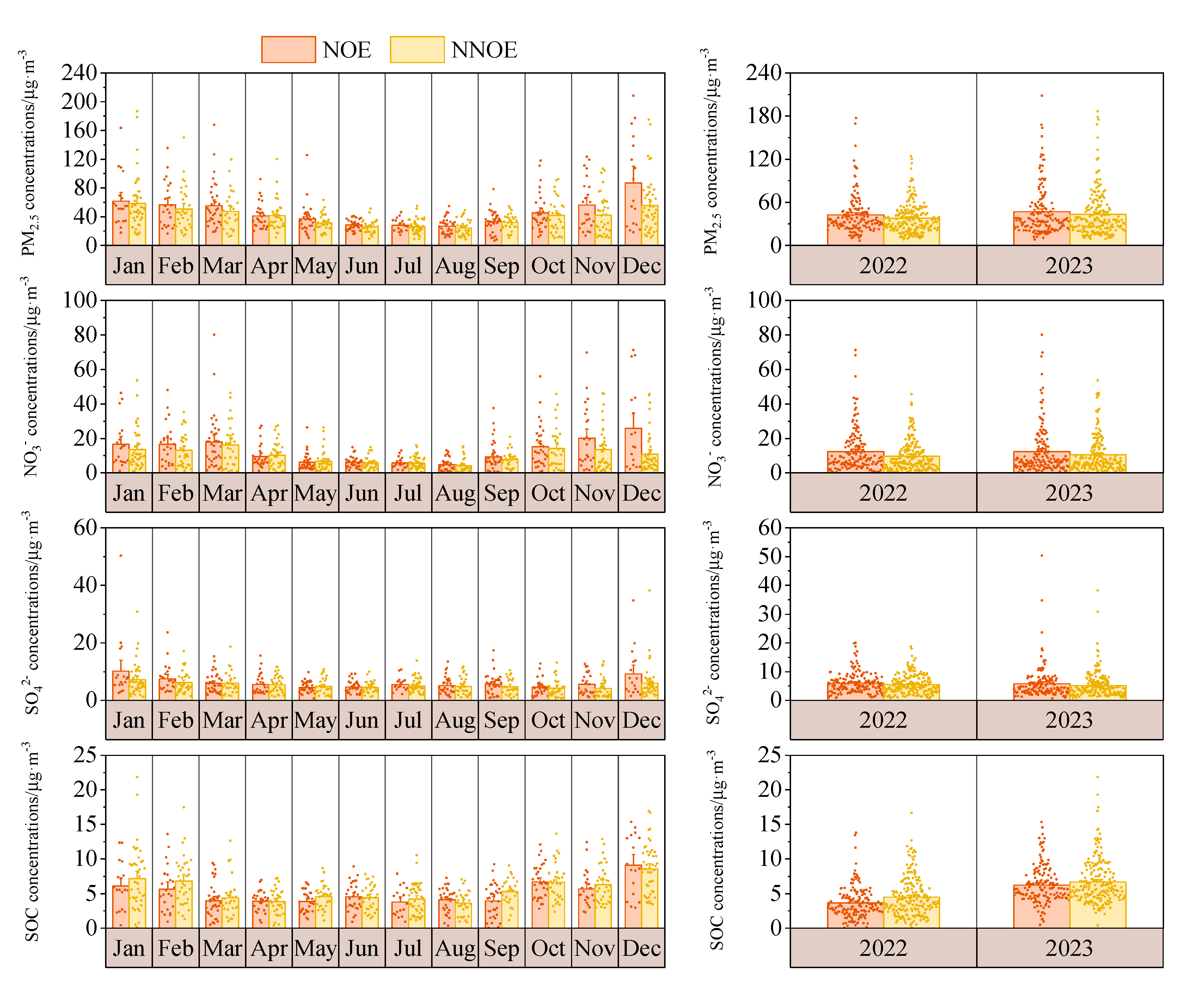
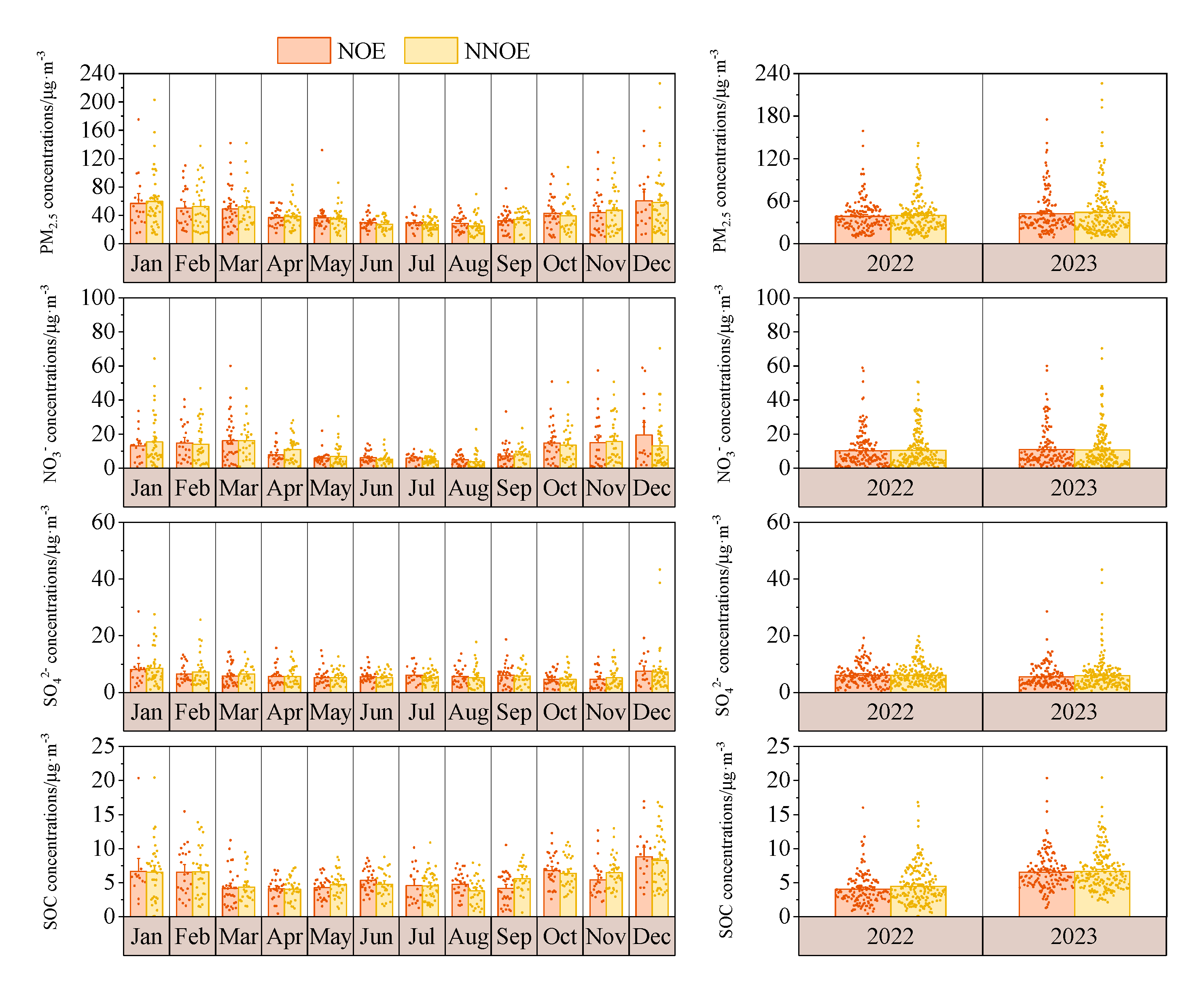
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Ma, X.; Lu, K.; Jiang, M.; Zou, Q.; Wang, H.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Y. Direct evidence of local photochemical production driven ozone episode in Beijing: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 148868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeren, Y.Z.; Zhou, B.N.; Zheng, Y.H.; Jiang, F.; Lyu, X.; Xue, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Guo, H. Does ozone pollution share the same formation mechanisms in the bay areas of China? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14326–14337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Geng, G.; Cheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, L.; Shi, Q.; Tong, D.; He, K.; Zhang, Q. Drivers of increasing ozone during the two phases of Clean Air Actions in China 2013-2020. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8954–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Hong, J.y.; Zhang, L.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Severe surface ozone pollution in China: a global perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strode, S.A.; Ziemke, J.R.; Oman, L.D.; Lamsal, L.N.; Olsen, M.A.; Liu, J. Global changes in the diurnal cycle of surface ozone. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, C.; Wang, Y.; Estes, M.; Lei, R.; Jia, B.; Wang, S.C.; Sun, J. Clustering surface ozone diurnal cycles to understand the impact of circulation patterns in Houston, TX. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 2019, 124, 13457–13474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Youn, D.; Liang, X.; Wuebbles, D. Global model simulation of summertime U.S. ozone diurnal cycle and its sensitivity to PBL mixing, spatial resolution, and emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8470–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Du, E.; Guo, Z.; de Vries, W. The diurnal cycle of summer tropospheric ozone concentrations across Chinese cities: Spatial patterns and main drivers. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.W.; Huang, X.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.Y.; Ding, A. Understanding ozone pollution in the Yangtze River Delta of eastern China from the perspective of diurnal cycles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, R. Diurnal characteristics of surface level O3 and other important trace gases in New England. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.w.; Ma, Z.q.; Li, Z.m.; Wu, J.; Guo, H.; Yin, X.; Ma, X.; Qiao, L. Impacts of meteorological conditions on nocturnal surface ozone enhancement during the summertime in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, S. Meteorology and topographic influences on nocturnal ozone increase during the summertime over Shaoguan, China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Lu, X.; Wang, H.l.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; He, G.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. The unexpected high frequency of nocturnal surface ozone enhancement events over China: characteristics and mechanisms. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 15243–15261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, J.Y.; Huang, R.J.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Qiao, X.R.; Cheng, Y.L.; Zhao, B.; Yin, D.J.; Gao, D.; et al. The aggravation of summertime nocturnal ozone pollution in China and its potential impact on the trend of nitrate aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL103242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, I.; Thorsson, S.; Andersson-Sköld, Y. Summer nocturnal ozone maxima in Göteborg, Sweden. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2615–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmond, J.A.; McKendry, I.G. Secondary ozone maxima in a very stable nocturnal boundary layer: observations from the Lower Fraser Valley, BC. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5771–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathokleous, E.; Feng, Z.; Sicard, P. Surge in nocturnal ozone pollution. Science 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduwais, A.K.; Dasari, H.P.; Karumuri, R.K.; Gandham, H.; Alharbi, B.H.; Ashok, K.; Hoteit, I. Transport mechanisms of nocturnal surface ozone over Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Ge, B.; Lin, W.; Ji, D.; Pan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. Increase in daytime ozone exposure due to nighttime accumulation in a typical city in eastern China during 2014–2020. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Lu, K.; Zhang, L.; Tham, Y.J.; Shi, Z.; Aikin, K.; Fan, S.; Brown, S.S.; et al. Increased night-time oxidation over China despite widespread decrease across the globe. Nat. Geosci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, K.L.; Davis, D.D.; Marini, R.P.; Decoteau, D.R. Effects of nighttime ozone treatment at ambient concentrations on sensitive and resistant snap bean genotypes. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. 2018, 143, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathokleous, E.; Feng, Z.; Oksanen, E.; Sicard, P.; Wang, Q.; Saitanis, C.J.; Araminiene, V.; Blande, J.D.; Hayes, F.; Calatayud, V.; et al. Ozone affects plant, insect, and soil microbial communities: A threat to terrestrial ecosystems and biodiversity. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, W.; You, Y.; Xie, Q.; Jia, S.; Wang, X. Quantitative impacts of vertical transport on the long-term trend of nocturnal ozone increase over the Pearl River Delta region during 2006–2019. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Pang, Y.; Ma, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Anomalous surface O3 changes in North China Plain during the northwestward movement of a landing typhoon. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, S.; Deng, T.; Liu, R.; Chen, J.; He, G.; Leung, J.C.-H.; Wang, N.; Liu, S.C. Impact of a subtropical high and a typhoon on a severe ozone pollution episode in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 10751–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.D.; Xin, J.Y.; Wang, W.F.; Jia, D.J.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Tong, L.; Ma, Y.; et al. Effects of the sea-land breeze on coastal ozone pollution in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, W. A Stratospheric intrusion-influenced ozone pollution episode associated with an intense horizontal-trough event. Atmosphere 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.-Z.; Luo, K.; Gao, X.; Gao, Y.; Fan, J.-R.; Fu, J.S.; Chen, C.-H. Exploring the stratospheric source of ozone pollution over China during the 2016 Group of Twenty summit. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; He, C.; Wang, H.; Miao, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Cao, T.; Deng, T.; Wu, D.; et al. Nocturnal ground-level ozone enhancement over the Pearl River Estuary: Two case studies based on vertical observations. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2023, 43, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; He, G.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, N.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Fan, S. Characteristics of nocturnal ozone enhancement events and a case study of horizontal transport in Guangzhou during warm season. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2023, 43, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Shen, H.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Sun, Z.; Ji, Y.; Xue, L.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Shang, F. Characteristics and sensitivity analysis of ozone in the representative city of the Yellow River Delta in summer. Res. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhang, L.; Liang, H. Variation characteristics and correlation analysis of air quality index and acid rain in Dongying City. J. environ. eng. technol. 2021, 11, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; An, C.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Yan, X.; Gao, X.; Chu, W.; Zhong, X.; Shang, F.; Li, J.; et al. Causes investigation of PM2.5 and O3 complex pollution in a typical coastal city in the Bohai Bay Region of China in autumn: based on one-month continuous intensive observation and model simulation. Atmosphere 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Ji, Y.; Chu, W.; Yan, X.; Bi, F.; Gao, Y.; Xue, L.; Shang, F.; Li, J.; Li, H. Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of ground-level-ozone and its relationship with meteorological conditions in a representative city in the Bohai Rim from 2017 to 2022. Environ. Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Huang, Y.; Bao, S. A new exploration on the strategic functions of central cities from the perspective of the rise of the Yellow River Delta. Truth Seeking. 2013, S2, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; He, C.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Pei, C.; Qiu, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; et al. Nighttime ozone in the lower boundary layer and its influences on surface ozone: insights from 3-year tower-based measurements in South China and regional air quality modeling. EGUsphere 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y. Observational study of surface ozone at an urban site in East China. Atmos. Res. 2008, 89, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, C.; Hu, Y.; Chan, P.-W.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Effects of horizontal transport and vertical mixing on nocturnal ozone pollution in the Pearl River Delta. Atmosphere 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, M.F.; Latif, M.T.; Juneng, L.; Khan, M.F.; Ahamad, F.; Chung, J.X.; Mohtar, A.A.A. Spatio-temporal assessment of nocturnal surface ozone in Malaysia. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 207, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
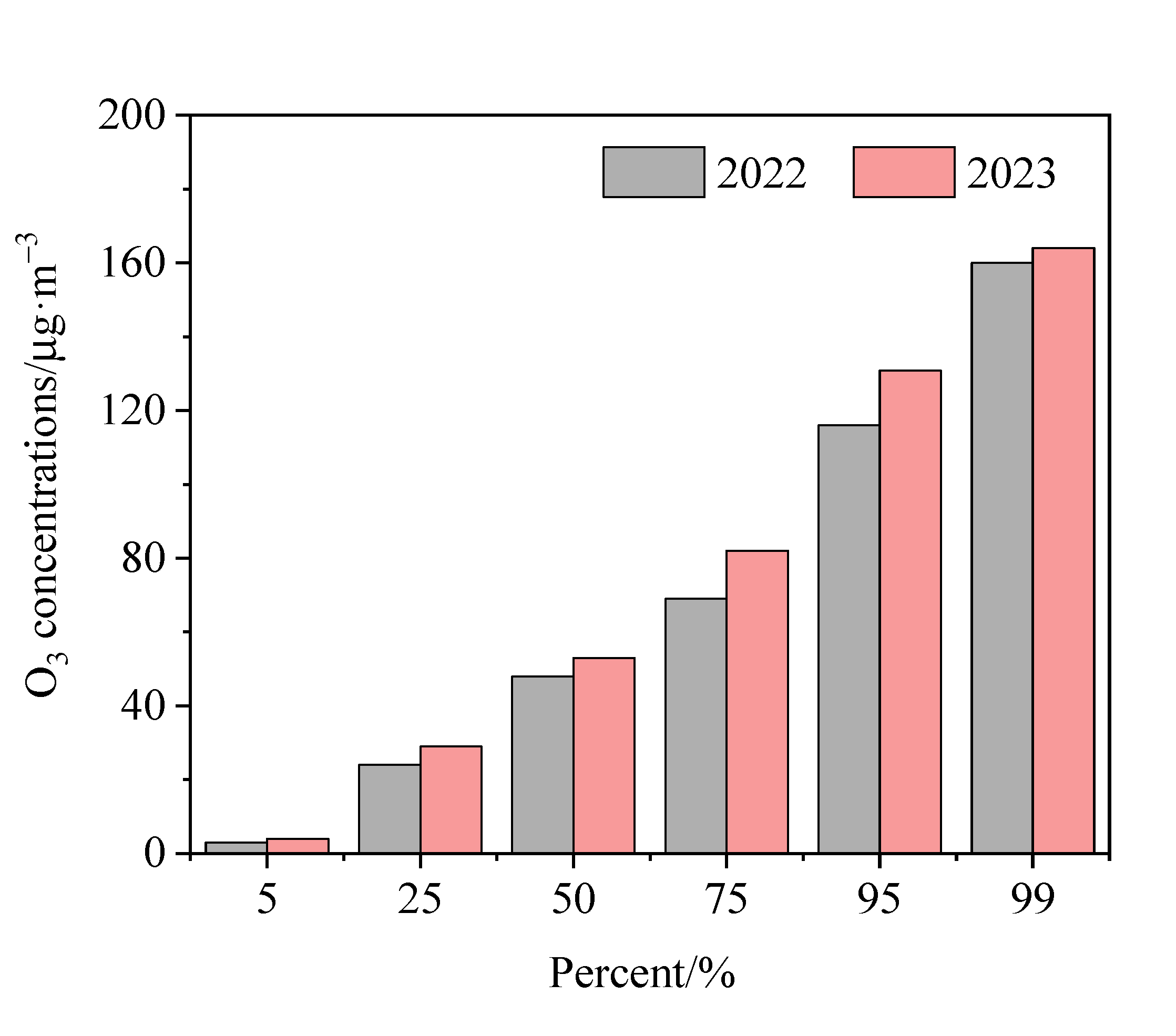
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




