1. Introduction
“When she leans back away from Da5id, his face has changed. He looks dazed and expressionless. Maybe Da5id really looks that way; maybe Snow Crash has messed up his avatar somehow so that it’s no longer tracking Da5id’s true facial expressions. But he’s staring straight ahead, eyes frozen in their sockets [
1].” Those exposed to unfathomable “Snow Crash” – a mysterious new drug and a linguistic/computer virus that has surfaced in both the virtual and the real world – in the metaverse experience their virtual avatars being “hacked” and rendered useless, which induces a state of catatonia in reality, making users susceptible to mind control and manipulation [
2]. Through the development of the metaverse concept from the Sumerian myth (5500 - 1800 BC) and mind-altering novel, “Snow Crash” in 1992, to today’s information age, human- and society-centred urban metaverse worlds – cybercommunities – are meant to mirror the fabric of urban life by providing virtually inhabitable cities with no harm to their residents. The metaverse, which aims to build high-fidelity virtual worlds with which to interact, can be engaged within the Smart City (SC) ecosystem with high immersive Quality of Experiences (QoE) leading to increased Quality of Life (QoL) [
3]. Urban metaverse worlds – an extension of residents and urban society, where the virtual and the physically real blend and are more organically integrated and where real-person resident avatars, government avatars, governmental entities, organisations, businesses, and avatars driven by Artificial Intelligence (i.e. AI bots or virtual users) can interact – would impact urban ways of living significantly on a global scale, with many practical implementations by democratising skills/assets within an urban ecosystem. The success of urban metaverse communities, augmented with wisdom, depends on the quality of data-driven SC Digital Twins (DTs), the seamless exchange of data between cyber and physical worlds (e.g. between residents and their counterpart “3D Avatars” – pseudo-physical presence) and the processing of the data effectively and efficiently with no vicious interventions and threats. An urban metaverse ecosystem framework – MetaOmniCity – was designed in [
3] to demonstrate a variety of insights and directions for policymakers, city planners and all other stakeholders about how to transform data-driven SCs with DTs into virtually inhabitable cities with a network of shared immersive urban experiences from a metaverse point of view. MetaOmniCity, allowing the metaversification of cities with granular virtual societies, i.e. MetaSocieties, aims to facilitate the building of community and citizen-tailored high-fidelity virtual urban metaverse cyberspaces for future sustainable smart urbanism in which the city productivity, wealth, and QoL can be increased – thus substantially benefiting every citizen, enabling innovation, and economic development within a city.
The potential risks and threats in this ecosystem that incorporates Web3 can be extremer than the ones in Web2, since we are immersed with multiple tightly coupled wearable sensor-rich devices perceiving the blend of the real and the virtual – with possible imminent negative experiences, if these platforms are not designed well to mitigate these potential hazards. The metaverse, with its enriched sets of capabilities, has the potential to affect its users dramatically beyond the digital environment in a variety of aspects where users would spend more time in urban metaverse cyberspaces as metaverse technologies improve and immersive cyberspaces, with a rich set of experiences, grow. Cybersecurity and privacy protection are the two crucial challenges in making secure and reliable urban cyberspaces thrive, as cybercrime activities are expected to be rampant in this ecosystem with trillion dollars of economic value in the years to come. Ensuring seamless connectivity, data accuracy, and user privacy are critical aspects that need further attention for the efficacy of urban metaverse cyberspaces, particularly, from technical, legislative, and ethical standpoints. The use of advanced infusion metaverse technologies (e.g. VR/AR headset, full haptic body suits, i.e. Motion Capture Suits (MoCaps)) increases the quality of resident experiences in the urban ecosystem. On one hand, the incorporation of these immersive devices into urban metaverse worlds involves technical, security, and privacy challenges. On the other hand, the abilities of these devices can be instrumented to improve privacy and security when combined with other technologies such as blockchain and AI. Our research question in this study can be summarised as: How can metaverse and urban ecosystems be moulded to generate safe and secure urban metaverse cyberspaces? Can the concepts of Web3, “you control your identity” and “you control your own data”’, work in this moulded ecosystem as intended in the metaverse concept to alleviate privacy concerns? What are the possible risks and cyberthreats in this cybercommunity, and how can these threats be addressed? In this direction, this paper, by analysing potential cyberthreats in the urban metaverse cyberspaces, proposes a blockchain-based authentication technique, which uses the metaverse immersive devices and can be instrumented effectively against identity impersonation and theft of credentials, identity, or avatars. Particular contributions in this paper can be outlined as follows.
The essential building blocks of the urban metaverse ecosystem – the so called MetaCyberCity – are surveyed concisely to visualise strengths in cybersecurity and shortcomings towards cyberthreats.
The possible cyberthreats for the urban metaverse cyberspaces are revealed, and how these threats can be addressed with a series of countermeasures is analysed.
A blockchain-based authentication approach, which uses the metaverse-immersive devices to generate Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning (PPML) models, is designed. This design, by avoiding single point failure and eliminating a trusted third party for the verification of the authenticity of models, can be instrumented effectively against identity impersonation and theft of credentials, identity, or avatars within urban metaverse cyberspaces – without renouncing targeted functional abilities of the immersive devices and the essential objectives of the urban metaverse cyberspaces.
The remainder of this paper is organised as follows. The related works are presented in
Section 2. The components of urban metaverse cyberspaces are summarised in
Section 3. Cyberthreats and basic countermeasures for urban cyberspaces is explained in
Section 4. The proposed methodology is introduced in
Section 5.
Section 6 discloses the essential challenges in revealing and addressing cyberthreats within urban metaverse worlds. The lessons learned are unfolded in
Section 7. Discussion along with open issues is provided in
Section 8. Finally,
Section 9 concludes the key findings and outlines potential future directions.
4. Cyberthreats and Basic Countermeasures for Urban Cyberspaces
Possible urban cyberrisks, cyberthreats, and privacy concerns are analysed in this section before exploring the proposed PPML authentication technique in
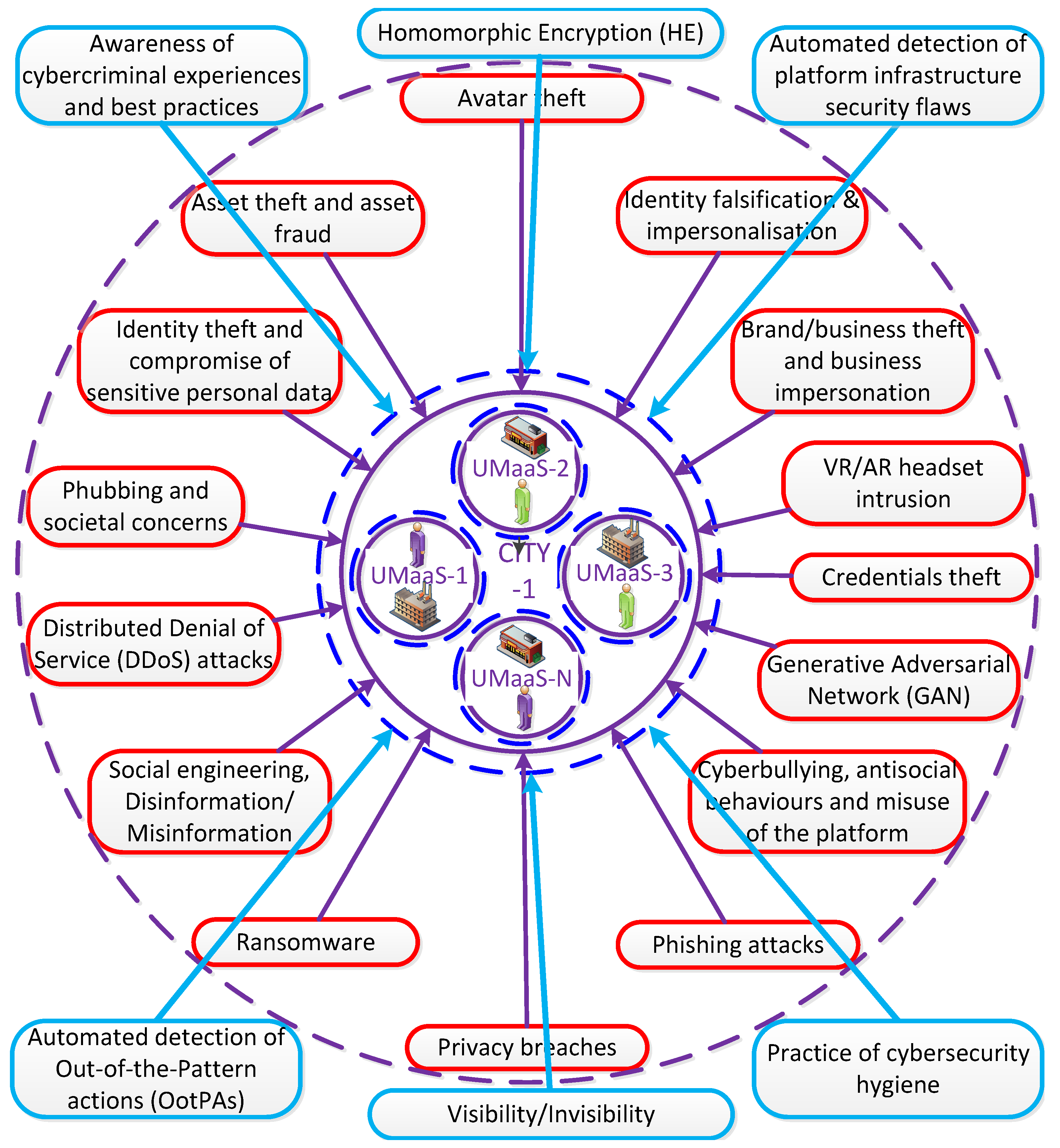
Section 5. Urban metaverse cyberspaces, using the 3D elevation of linear Internet, will inevitably be a target for cybercriminals due to their economic value with valuable assets, immersive nature, and large volumes of data, particularly, vision-based data, to be exploited in many aspects. The drivers behind cyberattacks can be for a variety of reasons such as money-driven, ego-satisfaction, curiosity, or joy-motive through privacy intrusion. Urban metaverse cyber worlds, on the new and more evolved decentralised 3D Web3, harbour new types of threats in addition to the current threats we are very much familiar with on web2 due to their immersive nature and new types of assets. Profiles of cybercriminals should be revealed to combat them in a more effective manner using appropriate tools developed for these specific profiles, which is not the scope of this paper. Vast amounts of data including movements, preferences, emotions and biometrics will be collected in the urban cybercommunities. This BD is subject to potential data breaches, unauthorized access, and misuse of sensitive information. We need to get ready to deal with these hazards while we are embracing many promising potentials within this new type of urban ecosystem. The main threats that can be launched in urban cybercommunities are demonstrated in
Figure 5 along with the basic countermeasures. These cyberthreats are intertwined with one another and it is difficult to differentiate them with distinctive borders. We explain these threats in the following subsections before revealing the proposed approach in this study in
Section 5. We would like to explain a couple of critical points before moving to the following subsections. Regarding the metaverse environment, quantum information technology is capable of enhancing the system’s security and privacy, improving the computational scales, optimizing the output, improving the communication, securing the network channels, providing absolute randomness for metaverse-based applications, and supporting ML implementations in the metaverse by integrating quantum ML [
66]. On one hand, promising Quantum Computing (QC) enables advanced immersive environments instilled with wisdom/insights that can be acquired from related BD, on the other hand, the encryption codes of blockchain, which can not be decrypted for tens or hundreds of years using the current computing power, can be decrypted in hours/days/weeks using the high power of QC. Therefore, cybersecurity in blockchain technologies should be improved in parallel with QC. Strictly speaking, blockchain platforms require significant improvement regarding crypto technologies, which is the most critical main building block. They may be replaced by other newly promising technologies integrated with 6G to mitigate these concerns where 6G networks are expected to emerge as Distributed Trust-Based Secure Networks (TBSN) where security, privacy and trust are the key pillars to meet these requirements [
38].
4.1. Urban Metaverse Cyberthreats
4.1.1. Identity falsification & impersonation
Virtual human systems, i) by achieving both realistic virtual humans with face expression recognition and smooth and flexible dialogue engines with chatbots, and ii) by targeting to achieve emotional recognition and emotional empathy, typically consist of five main modules: character generation, voice generation, animation generation, audio and video synthesis display, and interaction using information technologies, such as computer graphics, motion capture, ML, high-precision rendering, and speech synthesis [
67]. Convincing, false representations of individuals – by exploiting the immersive nature of the metaverse – can be created, as fake avatars using high-level imitation technologies (e.g. GAN (
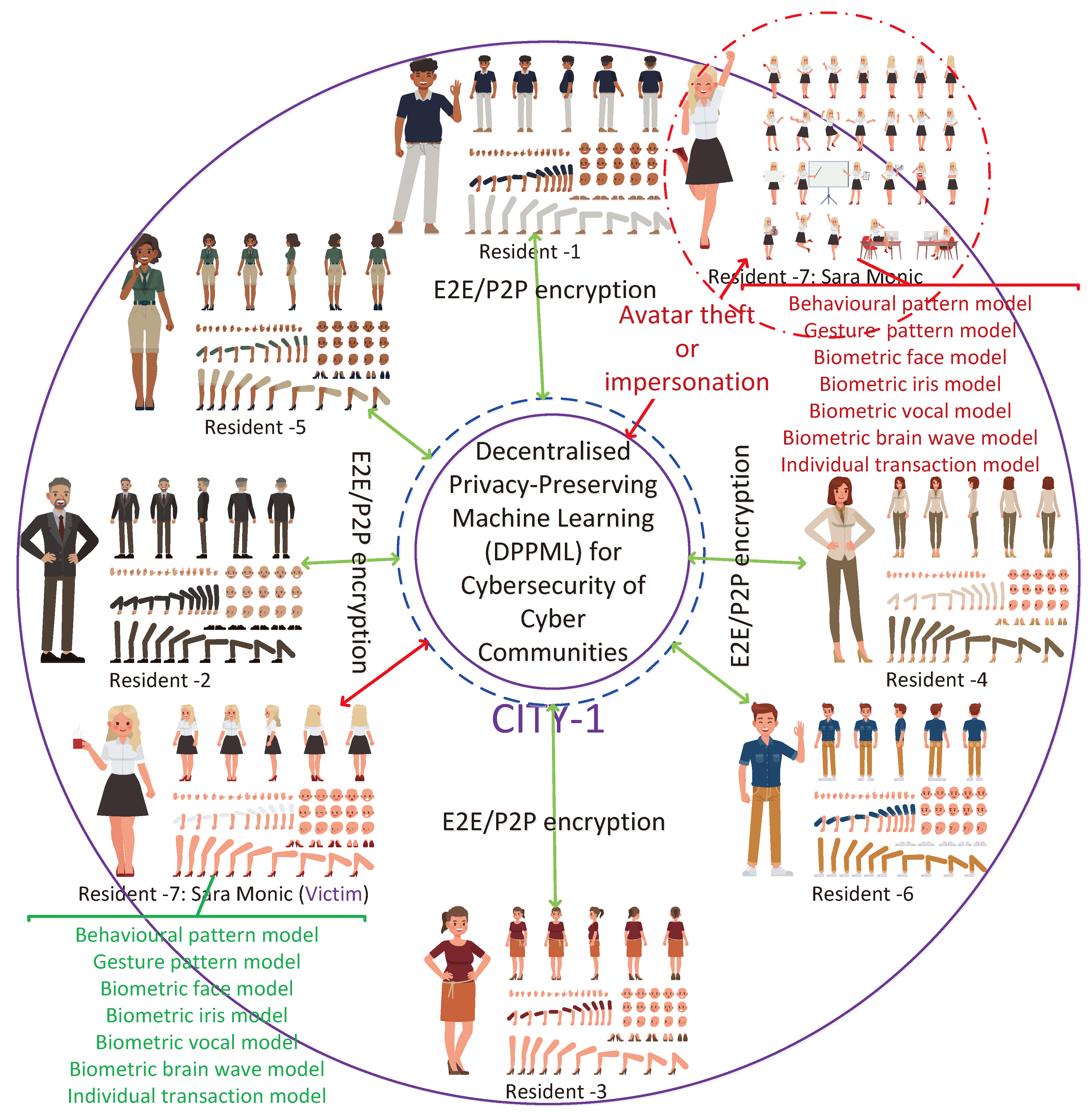
Section 4.1.15)) to impersonate friends, other users, trusted figures, well-known individuals, or influential figures such as famous people, leading to many different forms of harm – such as scamming, virtual harassment, phishing, etc. One way that this is achieved is through the DeepFake which utilises AI to combine real and AI-generated visual and auditory media to create a fabrication of reality – for example, given enough samples of an individual’s voice, a deep-learned model of that person’s unique voice can be created, which then could be made to say anything that someone likes or hates. Pretending to be another avatar (i.e. identity forgery, dual identity) using biometrics such as facial features, and voice will be easier as avatars become more realistic looking as technology progresses. In this way, the other impersonated users in the environment can be exploited to manipulate users into transferring valuable assets, revealing sensitive information or credentials, or engaging in hazardous activities. Registration of residents/avatars and businesses to the MetaCyberCity and UMaaSs using authentication tokens given by the government would mitigate these concerns, but this may not be an ideal option for residents concerning privacy regarding being tracked by the government.
4.1.2. Identity theft and compromise of sensitive personal data
High volumes of sensitive personal data about us are collected through high-level tracking technologies (e.g. VR/AR headsets). This data (e.g. biometrics, financial information, health-related information, sexual orientation, race, movement patterns, voice patterns, brain waves) can be compromised and aid in the execution of various malicious actions. The metaverse environments can be compromised by malicious software (i.e. Malware) that can stop us from reaching our environment, prevent us from transferring our personal data, or send our credentials to other sources by penetrating our information. Spear phishing tailored to particular subjects is the main concern in deceiving the subject with more believable tactics, after sensitive, personal information is compromised. This information can be stolen and exploited severely, particularly for financial gain, posing a high risk to users’ real-world identities. Stronger and more effective authentication approaches are being developed to protect users by avoiding any possible identity theft. Malicious software attacks can target vulnerabilities in metaverse platforms, leading to unauthorized access, data breaches, or disruption of services. Every now and then, our highly sensitive personal data gets leaked and becomes compromised due to the ineffective implementation of cybersecurity measures in the online services/social media that we use. Compromised identity data can be moulded to create fake avatars that can mimic their counterparts to manipulate other users (
Section 4.1.1).
4.1.3. Credentials Theft
Users` private data including their wallets, avatars, and assets are encrypted on the blockchain. First, users should follow the practice of cybersecurity hygiene strictly (
Section 4.2.2) and should not be sharing their private keys with others in cybercommunities to avoid every type of attack that is summarised in
Figure 5. The encryption approaches currently used in the blockchain seem safe to protect them against decryption approaches considering the current computing power. Nevertheless, it is noteworthy to emphasise that every encrypted code is vulnerable to decryption and we are witnessing the theft of huge amounts of assets (e.g. crypto money) in the metaverse worlds. Stolen credentials can be used to make unauthorized purchases and to launder money through stolen metaverse accounts.
4.1.4. Avatar theft
Avatars, with unique features, are the assets of their users and are supposed to function in urban metaverse cyberspaces to represent their counterparts. All the assets of a user are encrypted on the blockchain ledgers to fight against theft and other attacks. Attackers can use others` avatars in our environment to deceive us easily. Private data credentials in the metaverse could become compromised and an avatar of a user can be hijacked to take over the environment of the user and to deceive other users in the cybercommunity. The stolen avatar, i.e. virtual persona, can be controlled by cybercriminals in the name of the persona to be used for cyberattacks. Concretely speaking, a stolen avatar can be used to harass other users, spread misinformation, or engage in other harmful activities, tarnishing the reputation of the user’s real counterpart. Stolen avatars might be used for money laundering purposes with cryptocurrencies. Vladimirov et al. [
68] analyses the threats that a realistic digital clone (avatar) of a person can have in the wrong hands from the perspective of security and privacy. In his study, a network intrusion detection system, by protecting against cyberattacks, misuse, and negligence, and dynamic information flow tracking methods, by monitoring the flow of user login details, are proposed to detect unauthorised access to the metaverse platforms in an automated way to avoid avatar theft.
4.1.5. Asset theft and asset fraud
A virtual economy, containing valuable assets, within an urban cybercommunity has the potential to thrive significantly. These assets like digital currencies, NFTs, virtual items, and real estate purchases by users will be the primary targets of money-driven cybercriminals for the purposes of theft and fraud. Residents can lose their possessions if cybercriminals gain access to their digital credentials (
Section 4.1.3) and wallets. Moreover, the falsification of digital assets (i.e. virtual forgery) for fraudulent transactions will be another path that will be followed by cybercriminals. The genuine-like virtual forgery assets can be readily created using high-level imitation technologies – e.g. GAN with the generative and discriminator models (
Section 4.1.15). The securing of digital wallets for the protection of virtual assets and cybersecurity measures against virtual forgery will be the main subject within the metaverse cybercommunities. Fake digital assets such as non-existent properties, services, and fraudulent cryptocurrencies can be traded with legitimate currency with promises of unrealistic returns.
4.1.6. Brand/business theft and business impersonation
Businesses and users will create digital replicas of their real physical assets (e.g. real-world stores) in urban metaverse worlds. Virtual businesses can be hijacked for the purpose of ransom. Hijacked businesses/stores can be used to obtain user financial gains and credentials. Furthermore, the false version of shops can be created either to damage the brand`s reputation or to exploit the reputation from a financial perspective. Moreover, impersonated businesses/stores that mimic legitimate companies can be used to compromise user accounts/credentials along with financial damages. For instance, criminals can create a fake store that looks identical to the real one to sell counterfeit products and the users may believe that they are buying real goods within these fake metaverse businesses. These digital businesses can be copied by cybercriminals to scam other businesses and organisations including governmental entities as well.
4.1.7. Cyberbullying, antisocial behaviours and misuse of the platform
An urban metaverse ecosystem, with immersive abilities, would be an ideal space for antisocial behaviours such as cyberbullying, sexual assault, and fraud. In a virtual reality game, VRChat, a violating incident occurs about once every seven minutes [
69]. Criminal actions are expected to increase as the metaverse expands with multiple application areas. These crimes will impact the victim’s emotional and mental health, much like the way these crimes affect victims in the physical world [
33]. These crimes, impacting emotional and mental health, can be committed by avatars with fake identities and may not be traceable regarding data sovereignty. Avatars can be registered with tokens to the MetaCyberCity and UMaaSs to mitigate these concerns, enabling the tracing of bad behaviour within the metaverse ecosystem, and leading to holding users accountable for their inappropriate actions such as cancelling their tokens. Furthermore, physical rules of avatars can be enforced using the metaverse software. For instance, Meta launched “Personal Boundary” for Horizon Worlds that will give people more control over their VR experience; the roughly 4-foot distance between an avatar and others will remain on by default for non-friends, and now an avatar can adjust his/her personal boundary from the settings menu in Horizon Worlds [
70]. Moreover, the users can be exposed to racism. The interaction of children with strangers in metaverse worlds needs to be analysed before allowing children to immerse within uncontrolled virtual worlds concerning the misuse of these networks. Detection of abnormal content (e.g. inappropriate images, videos, text) in real-time using automated content profiling equipped with advanced AI tools is paramount to avoid imminent consequences of these attacks.
4.1.8. Phubbing and societal concerns
Phubbing is the act of rejecting or ignoring the company of a person in favour of a mobile phone. There is a high probability with the urban metaverse ecosystem that the level of phubbing increases within our real social environments due to its immersive virtual nature. From a cyber-dystopia point of view, the reduction of real, urban physical social interactions – intimate, real close relationships – replaced by virtual experiences using avatars within urban metaverse worlds may cause unforeseen negative effects and new types of psychological problems (e.g. the feeling of loneliness, social segregation, social exclusion) for humans, since metaverse worlds cannot be sufficient to meet the real closeness despite their immersive services, which should be analysed by related disciplines and the ways for addressing these societal concerns need to be revealed [
3]. Moreover, it is well known that physical inactivity increases the risk of serious health conditions coronary heart disease, stroke, hypertension, and osteoporosis [
71]. The massive use of metaverse environments may cause physical inactivity and physical activities should be incentivised within urban metaverse worlds to avoid aforementioned health problems [
3].
4.1.9. Phishing attacks
In addition to the aforementioned phishing attacks mentioned in other subsections (
Section 4.1.1,
Section 4.1.2), cybercriminals might create fake metaverse platforms (e.g. UMaaSs) that mimic both popular metaverse cyberspaces and avatars using AI-generated bots and then use phishing techniques to trick residents into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details while they are thinking that they are interacting with legitimate metaverse communities.
4.1.10. Social engineering & Disinformation/Misinformation
Residents can be manipulated based on the contents either created by themselves or in which they are interested. Trustworthiness and reliability of the content on social platforms have been in question all the time. The Matrix trilogy explores the interconnection between the body, the brain, and the mind, especially how that connection changes when the world turns out to be an illusion [
72]. Virtual products (as a part of an advertisement) or AI-driven avatars, with their seemingly authentic stories, can be injected into the urban metaverse cyberspace as they are a part of the real environment to influence us one way or the other. Residents might be targeted for money laundering purposes. Social engineering attacks can be more convincing compared to web2, as cyber attackers can deceive users in a variety of effective approaches, particularly, using identity falsification and impersonation scams (
Section 4.1.1) such as the creation of realistic avatars (
Section 4.1.1 and
Section 4.1.2) and businesses/stores (
Section 4.1.6) by exploiting the trust of others. Residents can be manipulated into taking malicious actions based on their interests, their sensitive information (single/married, sexual orientation, race) and their way of thinking. They can be drawn into fake romantic relationships and may end with huge financial losses based on the financial information revealed through well-established trusted relationships or end with physical and mental damages with real-world meetings. It might be difficult to distinguish between truth and disinformation/misinformation as the urban metaverse spaces look like a realistic environment. Some checks and balances are required to validate the genuineness of actions and associated contents to be protected thoroughly.
4.1.11. Ransomware
Avatars, businesses, and assets or even urban metaverse worlds can be hijacked for ransomware purposes. Due to the information required for participation in the metaverse, malicious actors have more potential areas of information available to them to ransom. The strategy for a ransomer is to gain access to a system holding important information, insert their software which takes control of the system, and demand payment in exchange for not deleting the information. The metaverse, by the nature of its suffix, is interconnected, requiring communication between many different moving parts – meaning that the value of a single set of information has the potential to be exploited exponentially. Instant ransomware attacks to live events (e.g. live concerts), while experiences are happening, are expected to increase in this ecosystem to exploit the situation by putting severe pressure.
4.1.12. Privacy breaches
Sharing experiences within metaverse cyberspaces means sharing your whole life including yourself, your emotions, and your reactions to events with the outside world. The immersive nature of the metaverse cybercommunities reveals more of us regarding the generated information using multiple sensors, which may violate our privacy out of our control. Our body signature (i.e. digital footprint) based on the body-based data (e.g. facial and eye biometrics, vocal pitches, posture, gestures, location) along with our reactions to developing events is being inevitably exposed as we engage in urban metaverse cyberspaces using highly immersive technologies, particularly, with VR/AR/XR headsets. Privacy protection or even information on privacy policies was found to be scarce in an analysis of 25 SCs with key concerns [
73]. Owners of data are concerned with the risks of unauthorized usage of their sensitive data by various entities, including service providers [
74] on the cloud platforms, particularly on the private cloud platform. We learned from the court cases and compensations that the technology giants governing social media had sold their user data to third parties without the consent of their users, which is a breach of privacy and security and these types of actions reduce trust in these companies. How to prevent sensitive data from unauthorised reading becomes an imperative issue in the development of cybercommunities regarding the collection of data from a highly distributed diverse computing environment and immense integration of DTs with the domains within SC, and with national and global domains [
44]. Within this context, urban metaverse cyberspaces should be transparent with users about how they process the sensitive data of their users (
Figure 6). Data sharing should be implemented using a consent-based approach where no personal data can be shared with third parties. Empowering users in the metaverse requires granular privacy controls and the ability to control what data is shared. Residents should be able to withdraw their pre-given consents and their collected data must be deleted urgently if demanded by them. Users must be informed of the policies of the platform about what types of data can be deleted if requested by the user concerning transparency. Residents should be able to leave the platforms as they wish without giving a reason.
The more the avatar resembles the user with advancing technologies, the more personal data such as physiological and behavioural signatures as well as the environmental space can be compromised with the sensory data transformation using immersive devices (e.g. VR/AR headset, MoCaps, haptics gloves, Hand Tracking Toolkit (HTT), different types of Wearable Sensors (WSs)). Invasions of data privacy is one of the concerns. Privacy is supposed to be protected on Web3 where the owned data or assets are encrypted using distributed blockchain data structures and they can be shared with the other parties via smart contracts by the authorisation of the owner using private keys (i.e. cryptographic password or personal digital signature) securely within this token economy. Unauthorized access to user behaviour tracking that leads to emotion recognition for specific types of inputs could lead to serious privacy violations. For instance, users can be targeted by advertisements and they can be tracked with individual trajectory content management techniques, which can harm them mentally and financially. The invasion of physical privacy is the other concern. An avatar can be attacked by other avatars in the virtual environment, which may cause psychological harm to the user of the avatar in the context that “the avatar is physically me”. Personal boundaries with close friends and others should be defined in the settings of immersive urban platforms as elaborated in
Section 4.1.7.
4.1.13. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Metaverse urban cyberspaces are composed of distributed devices and services using wireless communication technologies and this wireless communication can be interrupted easily using jammer-type devices. Implementing advanced multiverse realms with smart wearables is analysed in [
37]. Wearable hardware, which is one of the most important components of the metaverse, can also create new threats. With the increase in the use of VR headsets which may serve as suitable access points for hackers or AR devices in which the biometric data of residents are stored, they may become ideal targets for attacks. GPS services on which immersive devices rely can be easily spoofed or jammed and GPS signals can be lost promptly due to DoS attacks with a jammer with a reaction time in the order of a couple of microseconds, which causes severe prolonged signal outages. Due to the expected massive number of connected devices and network tenants, the 6G ecosystem would tend to be highly prone to DDoS attacks [
38]. DoS attacks, theft of avatars and privacy breaches, in particular, for wearable metaverse devices, are the three main cybersecurity concerns in urban cybercommunities. Prevention of privacy intrusions without reducing overall QoE along with real socialising needs to be ensured. Blockchain technology has been introduced to mitigate these concerns in urban use cases. A framework that uses blockchain technologies was proposed in [
40] for DTs to ensure the security of transactions during the data streaming between virtual entities and physical entities. Similar security frameworks are expected to be developed in parallel with the increasing number of metaverse use cases in the years to come. Moreover, immersive services can be disrupted due to a lack of standardized metaverse security measures concerning the vulnerabilities and inconsistencies between a variety of interconnected devices and applications, which can impact users` experiences negatively.
4.1.14. VR/AR headset intrusion
Malicious actors can track every move of a resident through VR/AR headsets and user profiles can be built on this intrusion to be exploited. The experiences of residents can be manipulated, which can harm the users physically, mentally and financially. Facial, eye, ear, and body motion (e.g. gait motion, posture) features are transferred from VR/AR headsets to the counterpart avatars either to authenticate the user or to mimic user expressions and this is recorded on distributed or centralised ledgers on the blockchain operating systems for a variety of purposes. Furthermore, the personal surrounding is also recorded most of the time through a VR/AR headset to either determine the space to move for the avatar or to show i) where the user is going and looking, ii) whom the user is with, and iii) what the user is doing. Recording of these unique identifiers with biometric data creates serious data and identity protection risks along with privacy risks with our surroundings. Facial and eye expressions, emotions, and brain waves indicate how the user reacts to specific events or objects and they can be highly valuable data to be exploited for a variety of purposes (e.g. targeted product advertisement, DeepFake creations, identity theft (
Section 4.1.4). Furthermore, vital signs (e.g. heart and respiratory rates) can be detected through smart devices and AR/VR sets. Cyberattackers are inclined to exploit the vulnerabilities in VR/AR devices to steal the aforementioned sensitive personal information or to partially take control of these devices with several intrusion activities such as content placement. How we are responding to the placed items in the virtual environment can make us the target of advertisements. The privacy of users will be violated substantially when a hacker gains access to a user’s VR/AR headset, sharing your life with you and seeing every part of your life. Users of VR headsets immersed in the virtual environment are in a vulnerable position, and they can be physically harmed by the manipulation of their perception and they can be directed in the wrong direction, leading to physical damage or life-threatening actions. Moreover, they, particularly children, can be mentally harmed by inappropriate content out of the context placed in virtual environments through wearable immersive devices.
4.1.15. Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)
Several security weaknesses can threaten the safety of the CDL training process within the metaverse ecosystem, which might result in fatal attacks to either the pre-trained large model or the local sensitive data sets possessed by an individual entity [
22]. The GAN attack has shown that poorly protected local data is vulnerable to being learned by adversaries [
24]. In CDL, malicious participants in the urban metaverse cybercommunity can upload deceptive parameters to degenerate the model performance, or they can abuse the downloaded parameters to construct a GAN to acquire the private information of others illegally [
22]. GAN, using generative AI approaches, may cause the generation of unhealthy, highly realistic synthetic trained models, which can disrupt/interrupt automated metaverse services and infiltrate behind/through services to gain access to the environment to exploit sensitive, private data (e.g. identity falsification & impersonation, asset fraud). Moreover, assets can be forged easily using GAN attacks. Efficient adversary detection-deactivation approaches are needed to disable the GAN attacks for a secure urban ecosystem.
4.2. Basic Countermeasures for Urban Cyberspaces
4.2.1. Agreed-upon standards, policies and ethics
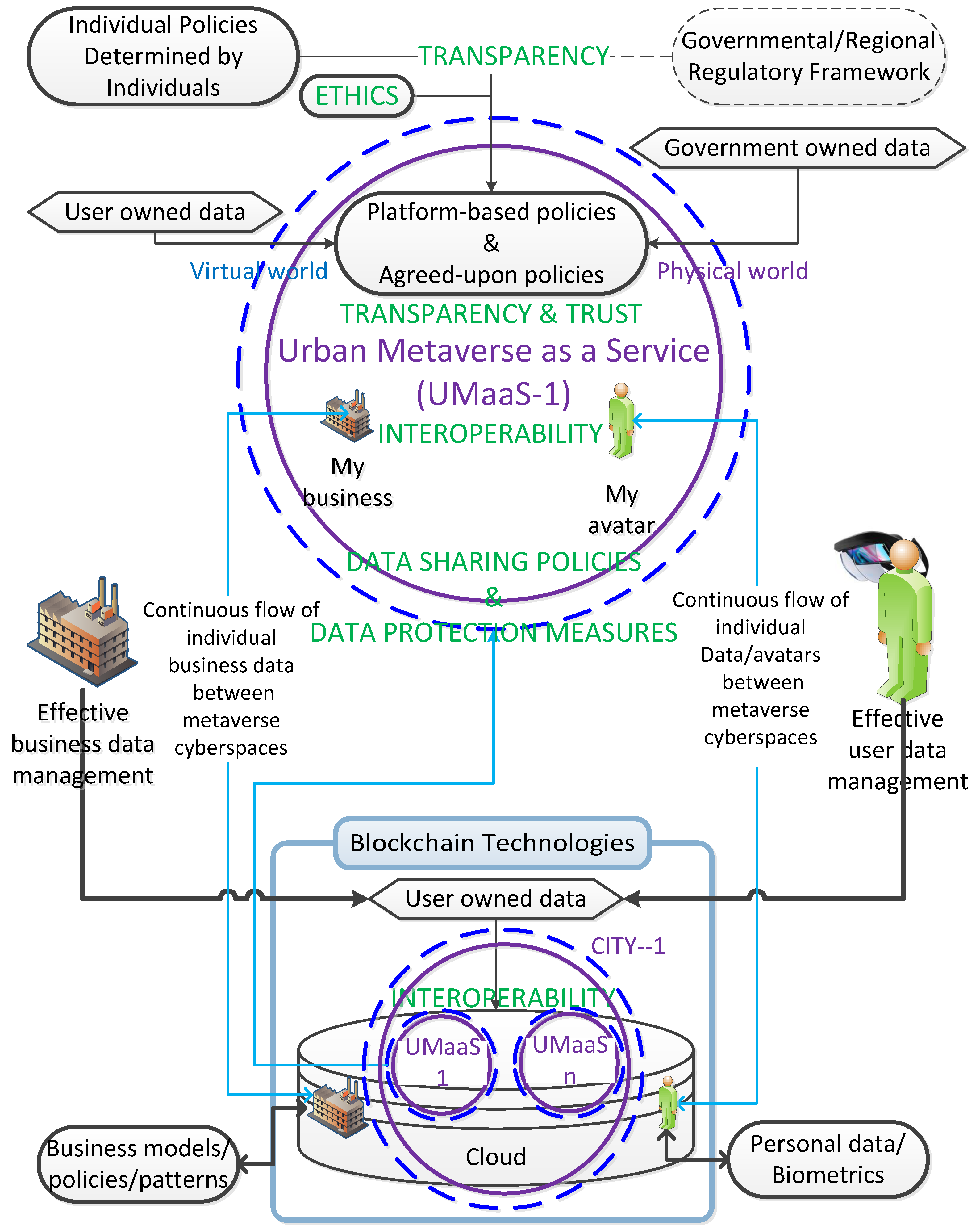
As shown in
Figure 6, the platform-based policies per specific cybercommunity, by considering its intended objectives and basic requirements, are moulded using i) individual policies determined by the users and businesses of cybercommunities regarding the rights of data sovereignty and ii) governmental or regional regulatory framework (e.g. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)). The policies are determined and agreed upon by all stakeholders through a transparent, trustable, and ethical scheme. Individual sensitive data is not retained in cybercommunities if there is no necessity considering the regulatory framework and it is deleted instantly when the necessity is not a case any longer. Data protection measures within cybercommunities should be sufficiently assuring, and the sharing of data with third parties by cybercommunities should be consent-based - no data sharing without the ratification of data owners. Avatars and cyber businesses, along with their assets, should be teleoperating from one cybercommunity to the other within the urban metaverse ecosystem considering the interoperable ability of the metaverse. By keeping these essential metrics of the metaverse ecosystem in mind, which are instilled in the MetaCyberCity.
4.2.2. Practice of cybersecurity hygiene
A chain is only as strong as its weakest link. Lack of metaverse awareness, regarding the understanding of the underlying cyber risks, should be mitigated. In this direction, everybody has to prepare themselves for the advantages and disadvantages of the technology by equipping themselves with some level of understanding about metaverse immersive experiences regarding the use of this developing technology before engaging in this ecosystem. The human factor is the main concern in the cybersecurity measures. Therefore, first and foremost, all users of any urban metaverse platform have to be trained using the tools instilled into the platform about how to practice cybersecurity hygiene to avoid everyday cyberattacks (
Section 4.1) such as malware exposures or social engineering specific. Even the best systems can not be protected without practising cybersecurity hygiene properly.
Urban metaverse cyberspaces look like our real environment, a kind of DT of it. First, we should be thinking of incorporating similar cybersecurity measures that are implemented in our real environment along with the ones in Web2 into this real and virtual blended ecosystem and, accordingly, urban metaverse cyberspaces should be protected in a similar way by their main managing bodies (i.e. city governors) with policies in place (
Figure 6) and advanced automated AI tools to detect instant attacks. For instance, strong metaverse credentials, with multiple-factor authentication (MFA), should be performed to protect ourselves from the most severe cyberattacks. Furthermore, we should keep in mind that this is not our real environment and further measures using novel cybersecurity techniques are required to protect ourselves from further possible cyberthreats (
Figure 5) augmented in this environment as elaborated in
Section 4.1. Technically speaking, the cybersecurity approaches should be specifically developed to the features and objectives of metaverse cybercommunities regarding the advantages and shortcomings of Web3. Every third-party individual entity (e.g. user, business) within the cybercommunity is untrusted, considering semi-honest parties or honest but curious parties. In this sense, the main urban entity (i.e. MetaCyberCity) and its cybercommunity entities (i.e. UMaaSs) (
Figure 4) should be addressing the concerns of its residents appropriately, privacy concerns in particular, to provide proper cybersecurity hygiene such as: Are transactions safe? Is my data protected? Is my privacy protected in the metaverse urban spaces? Am I protected against the bad behaviours of other avatars? Etc. Having said this, it is worth emphasising that the human factor will remain the weakest point of defence, despite immense awareness efforts, meaning that the only other option is to strengthen other areas with effective AI approaches, such as the ability to monitor other AI-based attacks, as explored throughout this paper, where the platform-based generated data is in the hands of the good to be processed by advanced AI tools in order to serve noble ends.
4.2.3. Automated detection of platform infrastructure security flaws
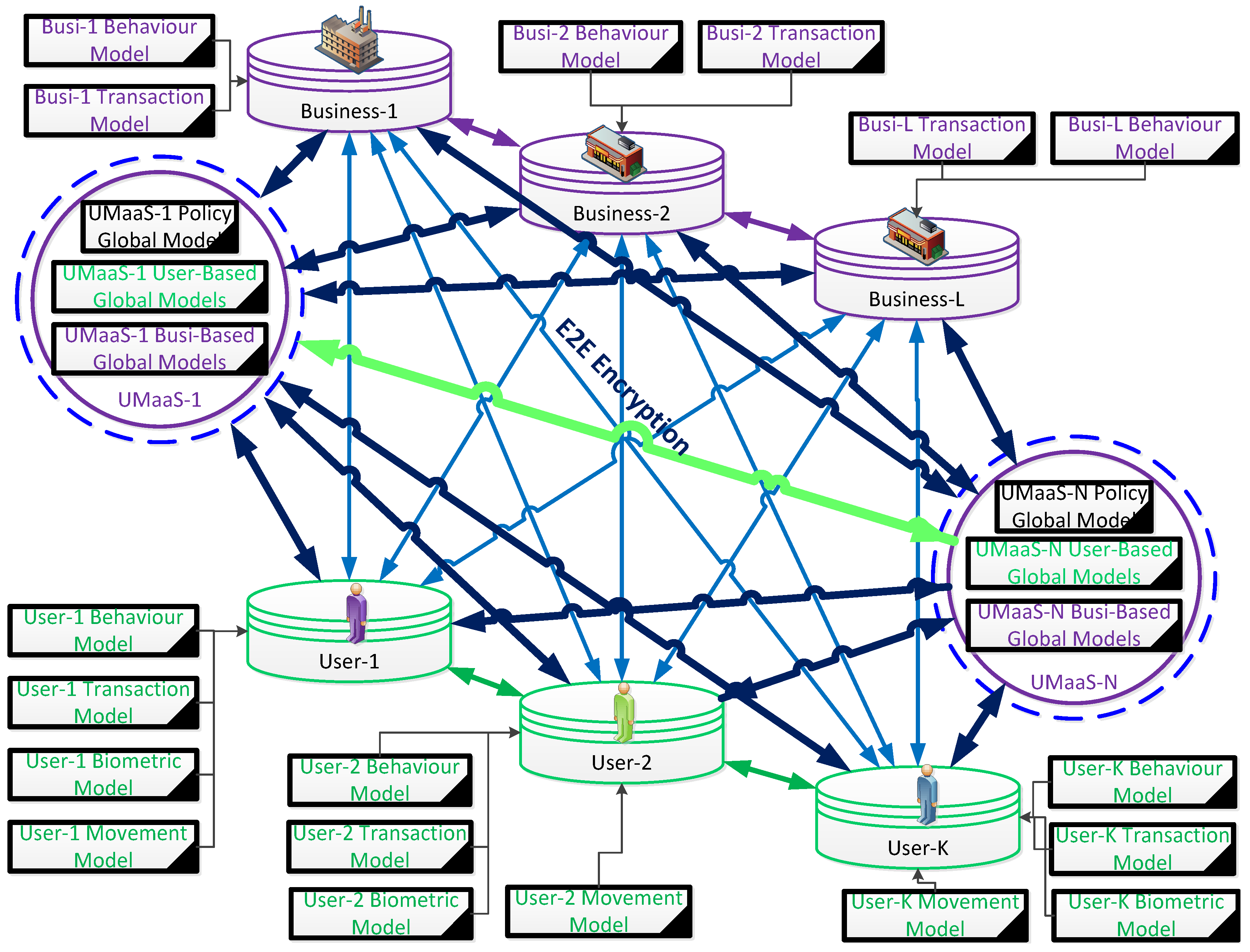
Every resident user, every business and every granular UMaaS is accepted as a private entity and all entities can communicate with each other within this design (
Figure 7). The main communication scheme between entities is managed by the particular architecture of a UMaaS in which immersive experiences are taking place regarding the agreed-upon policies (
Figure 6). Urban Metaverse cyber platforms, UMaaSs, should have effective governance and moderation policies to identify and mitigate malicious activities. Platform system attacks or insufficient resources can stop the functioning of the platform, leading to interruptions of experiences (e.g. interruption of an event such as a concert) within the platform. Finding the weak points of the system to defend better against cyberattacks is crucial in the metaverse. What cybersecurity level, that the MetaCyberCity and UMaaSs has, shall be measured regarding the resilience to the potential metaverse cyberthreats (
Section 4.1) before embarking on the MetaCyberCity or UMaaS. From a system engineering standpoint, a system shall adapt itself to the developing circumstances outside that surround and interact with the system to reduce risks and evolve. Urban metaverse cyberspaces should be able to detect and fix security flaws within the system in an automated manner and notify the affected data subjects where there are data breaches or other damages. Detection of flaws (e.g. abnormal resource usage) comes with protection solutions as well. The data, belonging to the particular platform, such as network trafficking, and resource usage are analysed in real time using the platform-based trained system models to improve the platform performance and to find out the abnormal activities taking place within the platform (cyberphobic attacks to avatars, malware attacks, spreading misinformation and disinformation, AI-generated bot attacks, GAN attacks, stealing and/or manipulation of system-owned data (system data breaches)). AIOps are already in place to manage the infrastructure of the metaverse worlds, particularly in managing structured and unstructured data and storing and disseminating it. More explicitly, AIOps provides event correlation capabilities by analysing real-time data and can determine deviations from typical patterns that might point to system anomalies. AI can be used effectively to predict attacks in the metaverse urban cyberspaces. ML-based trained models can help detect attacks directly to the infrastructure of the platform and defend the system from these attacks by improving its defence mechanisms with real-time effective solutions in an automated manner. Platform-based activities, interactions and experiences can be monitored using automated decentralised privacy-preserving CL models, by considering the privacy of residents, to avoid any interruptions in real time.
4.2.4. Automated detection of Out-of-the-Pattern actions (OotPAs)
P2P/E2E interactions between entities are illustrated in
Figure 7 within the distributed urban ecosystem. In addition to the interactions with other residents, users interact with urban businesses (e.g. via AI-driven avatars) within immersive urban metaverse cyberspaces to carry out commercial actions, such as the purchase of goods and their maintenance with smart metaverse contracts. Automated detection of outliers with inconsistencies that don’t fit the real-world decent life norms or automated detection of behaviours that don’t match the trusted individual’s or business’s actions using advanced AI tools is paramount to provide residents and businesses with a secure environment with high QoE. Besides, residents with their avatars, businesses, virtual stores, AI-generated avatars/bots can be classified with a scale of categorisation (e.g. ranging from very bad to very good) for various criteria (e.g. trust, use of language, behaviours) based on their pre-observed, pre-noted actions and the feedback obtained from the other residents and businesses in the same metaverse cyberspace. Each entity can upgrade the other entity’s credibility. Entities can hide their previous adverse actions in the real world from others but not in the urban metaverse environment where the previous actions are noted and not forgotten, considering the agreed-upon policies of the particular metaverse cyberspace (
Figure 6). Any user should face punishment if acting against the policies of the platform virtually or legally based on the severity of the actions. They, based on their actions, can be categorised as “red”, “orange”, “yellow”, or “green” regarding their risk profiles based on the aforementioned criteria, but always by prioritising privacy and respecting data sovereignty. Entities, with repeated, extreme adverse actions, can be tagged with colours on a red gradient to make other virtual businesses and residents vigilant against these entities. Entities can be banned from entering cybercommunities where their actions are getting severe. However, all these approaches, which are dependent on human responsible actions, are not sufficient to provide residents with completely instant, automated, and secure protection within this newly developing urban metaverse ecosystem, considering the large number of transactions and actions, which need to be authenticated and verified immediately.
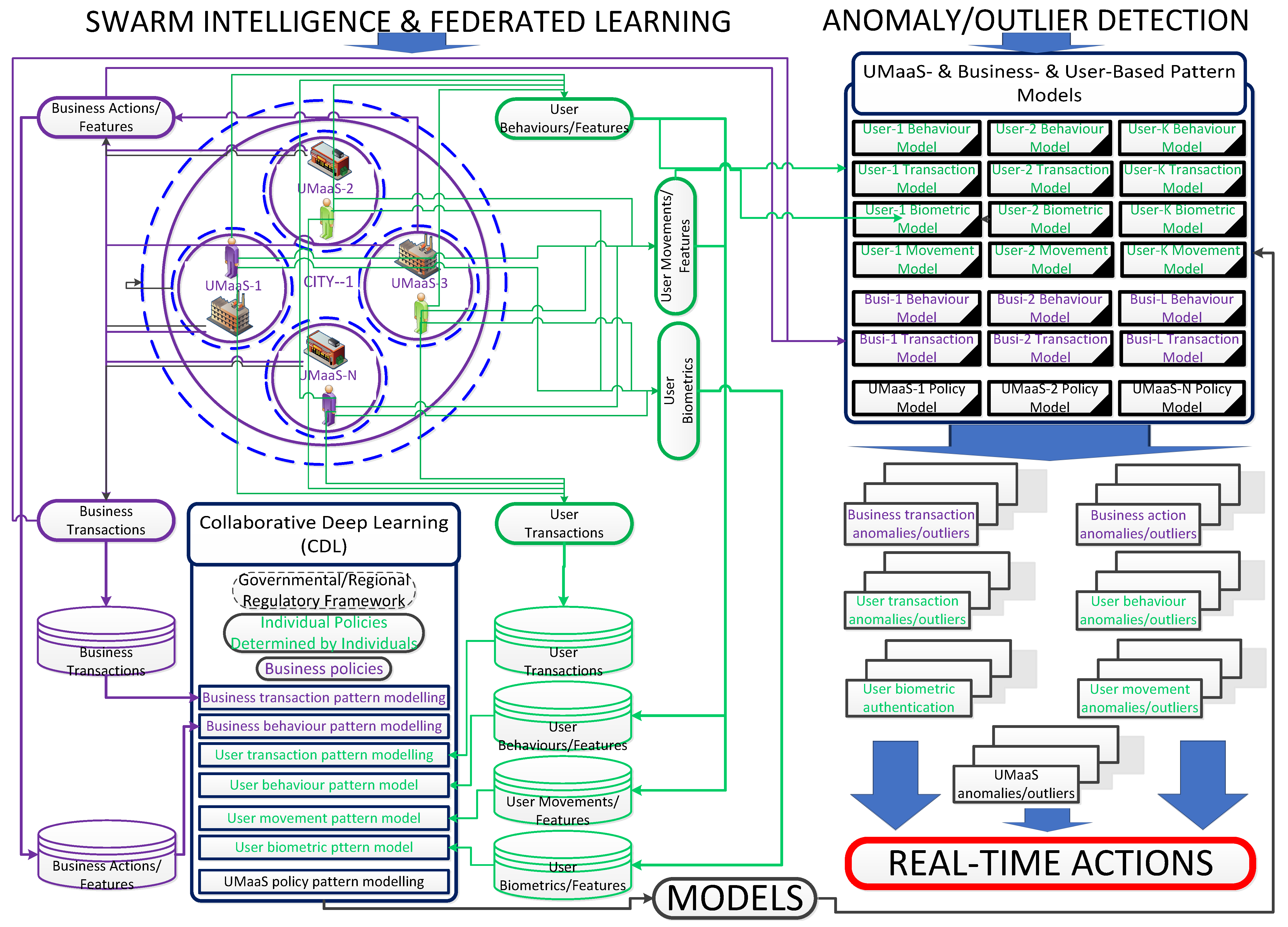
CDL/FL, as elaborated in
Section 2.3, can help detect OotPAs to alleviate cyberthreats. As shown in
Figure 8, automated platform-, user- and/or business-focused cybersecurity ML models can be generated by utilising SAI, primarily CDL to both detect OotPAs leading to the detection of cyberattacks and address those attacks in real time using the automated cybersecurity measures (
Figure 5). A decentralised privacy-preserving CDL architecture, where every resident user, every business, and every granular UMaaS is accepted as a private entity and all entities can communicate with one another whenever needed to run local, automated, and allowed queries on local models and to contribute to the construction of targeted global models of UMaaSs within this design, is conceptualised in
Figure 7. Nevertheless, these approaches have their shortcomings in providing the required level of privacy, authentication and verification mechanisms as explained in
Section 2.3. It is worth explaining that in addition to profit-driven companies within the urban community, we extend the concept of “business entity” within this paper by including all other value-adding community organisations and institutions within an urban environment: governmental organisations and institutions (e.g. educational units, hospitals), and Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs) (e.g. British Heart Foundation and private universities) .
4.2.5. Awareness of cybercriminal experiences and best practices
A sense of urgency to gain something (e.g. crypto money, assets, tickets, membership, promotions) may pressure urban metaverse users into hasty decisions, leading to harmful consequences. Most of the cyberthreats and risks can be avoided by staying vigilant with a high level of cybersecurity hygiene (
Section 4.2.2) within the urban metaverse cybercommunity. The MetaCyberCity and its granular functions/organisations – UMaaSs – should have cybersecurity awareness platforms and encountered vicious events (e.g. scams, impersonation, suspicious activities, etc.) should be reported via these platforms to raise awareness to help prevent these adverse actions. Furthermore, advanced automated cybersecurity mechanisms, which mitigate the encountered experienced cyberthreats, should be incorporated into the MetaCyberCity swiftly.
4.2.6. Visibility verses invisibility & Anonymity
Invisibility, feeling the immersive nature of the cybercommunities without being seen, situations where an individual’s identity is unknown to other users using an anonymous avatar during the immersive interaction, are two sensitive subjects, which should be investigated in detail with respect to the objectives and requirements of specific cybercommunities and the rights of other users within the same cybercommunity. It is noteworthy to emphasise that specific transactions and immersive communications may require the authentication of the individual’s identity to avoid any potential fraudulent attacks. Technically speaking, users can make other people invisible to themselves and themselves invisible to other users. Privacy can be provided via an invisibility option that can be defined in the settings of urban cybercommunities without violating the rights of other users who join the platform actively. For instance, a person can join a metaverse meeting or a concert without being noticed by other users. Anonymity can be authenticated by the platform that knows the true identity of the user even though the individual identity is still unknown to other users for privacy and security reasons. It is noteworthy to highlight that these rights – having an invisible or anonymous avatar – can effectively be exploited by cybercriminals as well. The fact that you can make multiple avatars, which are not NFTs, and act with different levels of anonymity makes it easier for cybercriminals to get away with their crimes, making it hard to hold people or businesses responsible for their adverse behaviours. Therefore, this subject is an open issue that needs to be discussed by the research community comprehensively.
4.2.7. Homomorphic Encryption (HE)
HE enables multiple entities to perform complex queries and computations on encrypted data without compromising the privacy of data and its encryption. The processed result still may remain in encrypted form for the owner of the data to decrypt it using the private key for visualisation. Concretely speaking, sensitive data can be shared and computed without the need to decrypt, but with a large computational overhead. The ciphertext operation’s computational complexity is much higher than that of the plaintext operation’s, both in terms of memory consumption and processing time [
75]. There are three types of HE, namely: partially HE, somewhat HE, and fully HE. Fully HE produces the largest computational overhead compared to the other two HEs, while having infinite addition and multiplication operations on ciphertexts. Fully HE is being employed by many giant companies such as Microsoft to compute sensitive data in the public domain despite its computational overhead and complexity. Most importantly, it allows to training of homomorphic-based encryption structures to build larger learning models, namely CDL models, using SAI. HE’s goal is to prevent recovery of the original data in order to protect the data from unauthorised access and user’s privacy. ML-as-a-Service (MLaaS) techniques using the processing of encrypted data with HE-like approaches will be focused on in the future, particularly, for applications which need a high level of privacy-preserving requirements on data that is stored in public domains and needs to be computed by multiple entities. Another privacy preservation technique, which has captured a wide range of attention, is differential privacy that was developed in [
76], by which noise is added to the data to secure the data from attacks. However, the more noise added to the data to provide further security and privacy, the less the model accuracy is obtained. This technique is out of the scope of this paper.
5. Blockchain-Based Decentralised Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning (DPPML) Authentication and Verification Approach
Large numbers of daily transactions and actions, taking place in a short period of time, require an efficient way of authentication, while the complexity of transactions and, more importantly, the complexity of cyberattacks is significantly increasing with newly developed metaverse technologies, particularly with wearable immersive metaverse devices. No third-party entity, including a centralised server/government, is trusted – considering semi-honest parties or honest but curious parties on the encryption-based and fully decentralised blockchain architecture in which data is supposed to be owned by its producers and is not managed by a centralised authority – which makes this ecosystem an ideal target for cybercriminals to exploit maliciously. Adverse events need to be detected in real-time to avoid dire circumstances such as losing individual data, NFTs, virtual real estate, cryptocurrency, or a breach of privacy on the blockchain in which traceability of transactions and actions is difficult to follow, due to the nature of the blockchain ecosystem with high level of data sovereignty and privacy. It needs to be assured that effective AI-based cybersecurity solutions are in place to defend residents from attacks without renouncing this nature. AI approaches can learn patterns with ML models that indicate a normal or abnormal transaction/action or cyberthreats. The modelling with ML and its real-time counteraction abilities in the urban metaverse ecosystem is conceptualised in a broader perspective in
Figure 8. Automated solutions with privacy-preserving mechanisms can mitigate the cyberthreats (
Section 4.1) effectively within the urban metaverse ecosystem. SAI, merged with blockchain, can play a prominent role in securing transactions and all other actions with a high level of privacy.
Authentication of residents and verifying their true identities without a third party or a central authority is imperative in developing private and secure urban metaverse cybercommunities. Regular identity checks are crucial to both address fake avatars or avatars that have been stolen via unauthorised access to user credentials and avoid their imminent adverse consequences – such as breach of privacy and loss of assets. Individual data that can be used for authentication is composed of i) biographic identification data such as name, surname, date of birth, and ii) biometric identification data as biological characteristics (DNA, facial features, height, fingerprints, iris features, vein features, and palm features) and behavioural/gesture patterns (facial expressions, movement patterns (gait), lip motion, emotion expression or reactions to interactions using physiological responses, voice pitch patterns/prints, and speech patterns). Automated Emotion Recognition (AER) and Automated Behaviour Recognition (ABR) technologies can detect humans’ emotional/behavioural states in real-time using facial expressions, voice attributes, text, body movements, and neurological signals and have a broad range of applications across many sectors [
77]. Using these features to train networks and models raises privacy and ethical concerns in various aspects. Privacy and ethical concerns in applying AI for learning expressions and patterns using the aforementioned individual features, which is out of the scope of this research, are explored in [
78] for interested readers. The way of building DL gesture models should consider these privacy and ethical concerns as well as the regulatory framework (
Figure 6). Human beings, with their body and behavioural/gesture signatures, are drastically different from each other in many ways, and they can be identified based on their biological or behavioural/gesture characteristics with a high level of identification assurance. It is worth mentioning that physics-based character skills of individuals can be gained through reinforcement learning, which can improve the realism of individuals in regard to avatars [
79] as well. Every action or transaction during the immersive interaction of individuals can be copied into the metaverse ecosystem. These consecutive actions or transactions generate particular patterns, in other words, a cyber identity of individuals, that differentiates them from other users. Within this context, metaverse immersive devices can help residents protect the boundaries of their privacy despite the security and privacy challenges that come with these devices, particularly VR/AR headsets, which are elaborated in
Section 4.1.14. The capabilities of these devices can be instrumented to improve privacy and security when combined with other technologies such as blockchain and SAI as explained earlier in
Section 1. The actions of residents can be profiled through their bodies, coupled with advanced multiple sensory technologies that are based on a variety of body signatures, while interacting with the metaverse ecosystem, particularly by using VR headsets and full haptic body suits, i.e. MoCaps, equipped with multi-sensory abilities enabling tactile sensation. Users immerse themselves with full-body haptic suits including finger and full-body tracking sets, by which every motion can be replicated in virtual worlds and the real world with a bidirectional haptic interaction (e.g. touch, and handshake in a virtual environment). A sequence of these motions can build our unique body features by extracting the patterns from users’ gesture cues, which leads to patterns distinguishing us from the rest of the world. These patterns, as well as the aforementioned distinctive individual signatures, can be utilised effectively for authentication purposes via a diverse range of metaverse technologies (e.g. VR/AR headset, MoCaps, haptics gloves, and HTT), different types of many other Wearable Sensors (WSs)), which are improving with larger sets of options and a diverse range of attributes. For instance, Wearable Resistive Sensors (WRSs) that could directly characterise joint movements are one of the most promising technologies for hand gesture recognition due to their easy integration, low cost, and simple signal acquisition [
80].
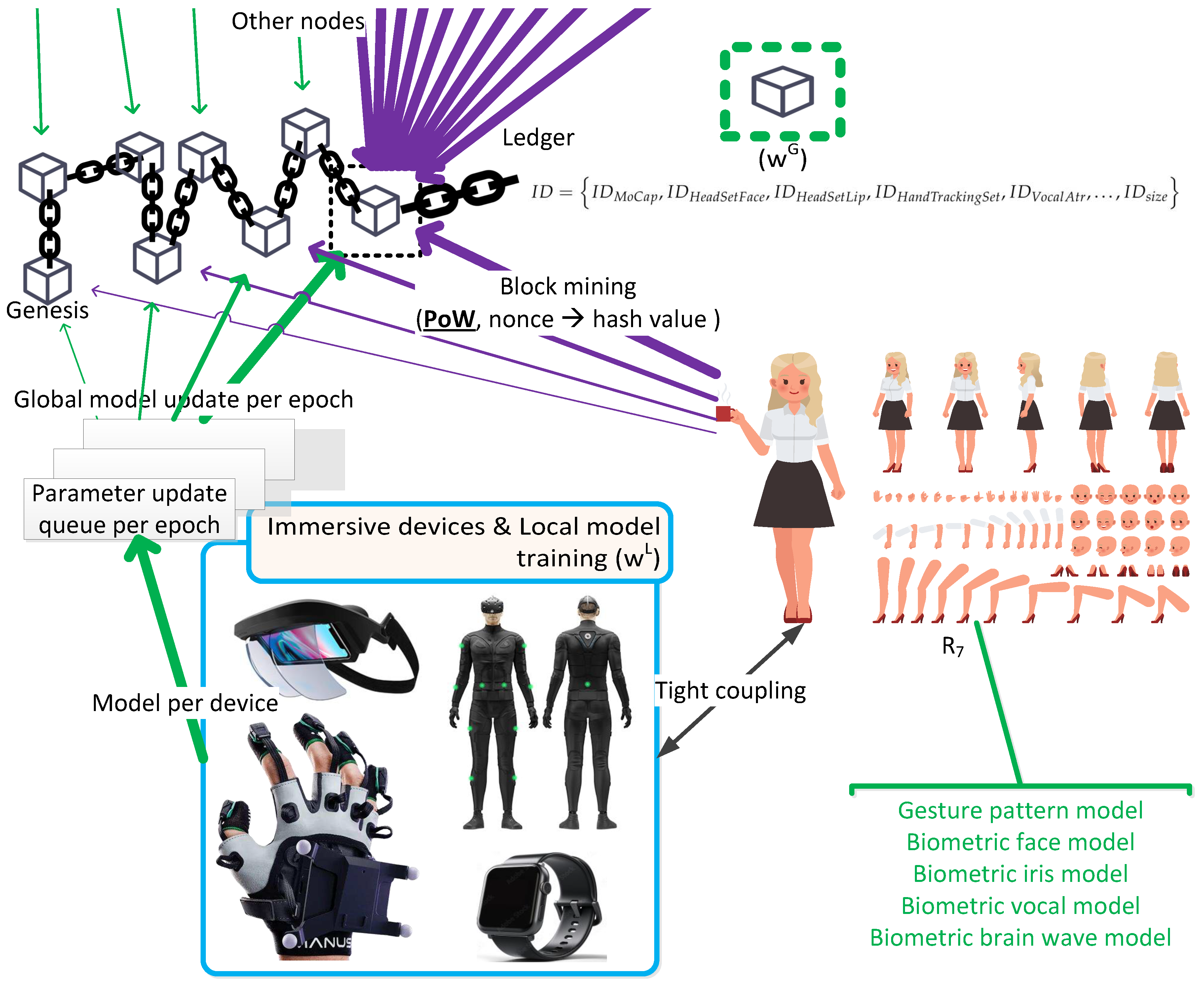
The urban metaverse cyberspaces and associated entities are distributed on the decentralised public and private ledgers (
Figure 7). AI models are required to be trained at the edges locally and encrypted update gradients need to be transferred to construct larger or global models regarding the principles of CL/FL as expressed earlier in
Section 2.3. In order to improve collaboration in learning, the privacy concerns of each data subject should be addressed by extending the concept of privacy protection to the original learning entity. In this vein, a DPPML scheme, based on transparency and personal consent (
Figure 6), is developed using the cyber gesture signature with wearable immersive devices to protect users’ privacy while verifying the authenticity of the subject, where the data subjects in more control with further security measures. Cyber signatures, which make the subject different from other subjects, can be built through their body language using tightly coupled immersive wearable metaverse devices as visualised in
Figure 9. The pseudo codes of model training with a MoCap device are presented on blockchain in Algorithms 1 and 2. More specifically, Algorithm 1 shows the local training of the model with epochs fed by the particular online instant features acquired from the device, which is worn by one of the active nodes on the blockchain whereas Algorithm 2 displays the global model update with the blockchain operations for verification of the update gradients acquired from all the active nodes on the blockchain through blockchain mining. Algorithm 1 is run by each node individually at the edges locally whereas Algorithm 2 is run on blockchain by all the active nodes where current nodes can leave and new nodes can join at any time. From a more technical standpoint, the gesture feature set for particular attributes,
, of resident entities,
, need to be trained per individual with an epoch sample size,
. Local weights (
) and global weights (
) are synchronously updated after every epoch iteration to generate particular vocal or gesture models,
, per immersive device,
, as displayed in Eq. 1.
Residents,
R, perform the PoW operations with a block generation rate of
and whoever is successful in reaching a hash key, by finding a nonce that is smaller than the target value based on the difficulty of PoW, places the candidate block with their locally trained, updated model gradient parameters along with the other emerging models updated successfully by other nodes similarly with the previous PoW operations. Then, they continue mining with the agreed-upon PoW and update their model parameters likewise obtained from the next local epoch operations until their models converge to a solution that satisfies a targeted accuracy rate,
, (i.e.
where
is a very small value). The last blocks during the training process with block mining, which stores each resident’s individual aggregated local model updates, are added to the blockchain with their block headers and block bodies as a distributed ledger (
Figure 9), and downloaded by other residents,
R, as nodes in the blockchain to carry on the next PoW operations with a newly generated candidate block. The body of the block has the last generated hash key corresponding to the individual resident model. In other words, all the updated particular models are transferred to the last block with the hash keys that are used to update the gradients for those models. All the other residents/miners quit the current PoW operations when they receive the new block that is added to the blockchain to download this block and start the PoW operations from scratch, with the most recent updates using their candidate blocks with their updates, which are distributed to all other nodes. During this process, every resident, who performs the PoW for his/her model update parameter with a successful hashing, verifies all the previous model updates with the previous PoW operations as well, which are updated by other residents for their model training. The residents whose models have converged to a solution either stop the PoW operations and leave the mining as a node or continue as is to verify other residents’ model updates with their current, successful updates, without providing further input updates – considering that the mining reward is still applicable even though data reward is no longer offered. The creation of blocks in chronological order, through the PoW consensus mechanism per
, stops when no resident remains as an active node, where all the models of residents – per
– that are expected to be completed as new nodes get added to the blockchain to build their models. Local model updates for all residents as nodes are aggregated at the last block separately, leading to final global models that correspond to individual residents. In other words, the blockchain expands further when new residents join the MetaCyberCity or UMaaSs. Users are not allowed to be successful for two consecutive PoW hashing in order not to verify their own model updates, which aims to include multiple verifications with distributed ledgers with timestamps. The final block is composed of the final aggregated individual models of residents per
as in Eq. 2 for
, MoCap, until new nodes join.
Residents upload their local true gradient updates (
) to form their model truthfully, with the required timestamp history where models, generated using false parameters, cannot result in authenticating the model owners during the use of the particular immersive device. Every entity feeds the DL model training process with the model-specific encrypted parameters until the model converges to a desired solution within a UMaaS or MetaCyberCity. The original user data is retained with the data owner and not shared with third parties and all the communicated packets are delivered between the entities using P2P/E2E ciphertexts (
Figure 7) to avoid any possible data leakage, which aims to preserve both the data’s sovereignty – and privacy, to a certain extent. Updated gradients may reveal individual private or actual information when associated with data attributes and structures. Therefore, encryption mechanisms provide further privacy protection even though the updated gradients or communicated packets have been anonymised. The above operations are repeated for all
using different blockchain forms.
|
Algorithm 1: Individual authentication modelling per immersive device: Local training (ID =. |
 |
Global gesture models, which are verified by other residents in the MetaCyberCity or UMaaSs and employ a PoW consensus mechanism, are employed to be used for authentication mechanisms as proof, which has been implemented in Algorithm 3, regularly during the metaverse immersive actions/activities, when requested by any active user in UMaaSs, or when required under particular circumstances such as before completing asset transactions to ensure the identity of the other party. In our approach, the use of the model to authenticate a resident with the blockchain-based model can be allowed by the resident using the private key and the last hash key that is associated with the particular user-/device-based model in the body of the block. Here, the blockchain is employed to provide trust among entities in modelling gestures using every online training phase automated by
, i.e. epoch, by avoiding single point failure regarding the training in a central server and not requiring a trusted third party for the verification of the authenticity of the model and data from which the model is generated. From a more technical standpoint, the gesture feature set for particular attributes from the particular immersive device,
, of the resident entity,
, need to be run with the model using a couple of sample size,
. The model results in either providing the authentication proof with a successful outcome where one of the feature sets is recognised or rejecting the authentication with an unsuccessful outcome with no recognition for any of the attribute sets in the sample array. Each entity knows nothing about the trained data and its providers` identity while using the global ML models in an automated manner with the entity parameters to get a targeted classified outcome needed. The global model construction and use of this model should ensure that there is no adversarial entity collaborating with the process, which can be avoided using effective E2E/P2P encryption mechanisms (
Figure 10). These gesture models, aiming at authenticating the other party through the use of immersive devices, can be instrumented effectively against the theft of credentials, identity, or avatars. Regular biometric checks can be implemented with the proposed approach to ensure that the avatar in action represents the intended correct person.
|
Algorithm 2: Individual authentication and verification modelling per immersive device: Global update with blockchain. |
 |
|
Algorithm 3: Proof of identity using blockchain-based DPPML pre-trained models with immersive devices where . |
 |
8. Discussion
Today, and every day, worldwide, one million more people are born-into or move-into a city [
85]. The global population is expected to double by 2050 [
86] and more than 68% of the population will be living in an urban environment by 2050 [
87] with a population of 5 billion [
88]. Metaverse worlds, enabling rich communication channels, have already become a part of our daily routine and an increasing number of people are embracing the growing number of metaverse worlds with immersive metaverse devices. Recent advances in metaverse technologies are providing many opportunities and urging city governments and all other stakeholders within an urban life to change the way of managing cities and doing business more intelligently in location and time-independent, high-fidelity virtual worlds [
3] to alleviate the problems of rapid urbanisation with limited urban resources, such as increasing population, pollution, traffic, noise, real-estate/office prices, and mobility difficulties. Urban life has already embraced many urban metaverse use cases with future objectives (as elaborated in [
3]) to increase the QoL by overcoming temporal and spatial restrictions, and the trend indicates that this would expedite exponentially in the years to come. Cybercommunities instilled with metaverse technologies should provide their residents with functional, safe, secure, and private worlds with high QoE to readily evolve and mitigate the problems of urbanisation. The near future will embrace more metaverse applications fuelled by advancing immersive metaverse technologies, leading to a change in the way of doing business in the urban ecosystem [
3]. Urban metaverse cyberspaces, as the main communication/interaction channel, will be connecting urban places and residents not only to one another within a city but also to the rest of the world. We visualise that residents will be spending most of their daily life in urban metaverse cyberspaces compared to real life for governmental interactions, socialising, or doing business in the years to come. Cities and their residents, who have abilities/skills/assets, can socialise, be creative and monetise their assets and time through this channel. These cyber worlds will be a target for cybercriminals to exploit as the economic value of these cyber worlds increases with their assets, and as the urge to reveal privacy via immersive devices is becoming a reality for residents, while controlling the boundaries of privacy is getting difficult with these devices. Municipalities are building their future with the concept of the metaverse and future urban cyber worlds are expected to evolve to be more immersive with advanced, real-time, data-driven, virtual/augmented platforms, devices, and hyper-realistic MetaHumans [
3]. Our research question was if we can turn the abilities of these immersive metaverse devices into the residents’ advantage in providing their security and avoiding a breach of privacy. In a broader perspective, if it is possible to build a trustworthy, urban metaverse cybercommunity, without requiring a centralised government to protect our privacy or a third party to mediate between entities, e.g. for a transaction. Regular identity authentication during interactions or before executing transactions in the urban metaverse worlds is crucial to address identity impersonation and theft of credentials, identity, or avatars and avoid their imminent adverse consequences. In this treatise, while the urban metaverse ecosystem is flourishing, this research analyses cyberthreats and basic cybersecurity measures against those cyberthreats comprehensively within the urban metaverse ecosystem. It reveals the cybersecurity gaps within these environments in the literature and real-world implementations. Additionally, it designs a novel blockchain-based DPPML authentication and verification approach to fill these gaps, based on physics-based characters of individuals (i.e. body cyber footprint/identity – e.g. facial expressions, movement patterns (gait), lip motion, emotional expression or reactions to experiences using physiological responses, voice pitch patterns/prints, and speech patterns) obtained from immersive metaverse wearable devices (e.g. VR/AR headset, MoCaps, haptics gloves, HTT). In this way, cyber signature models, with a diverse range of attributes, are built step by step, verified by other residents and placed in blockchain ledgers to be employed whenever needed to verify the authenticity of the residents/avatars even if all the credentials are in the hands of cybercriminals.
PPML/PPDL schemes in the literature have been introduced in
Section 2.3. As explained in the literature, standard FL/CL model generation tools based on wearable devices can be provided by the main urban city, or the developers of the metaverse devices, to users to train their models in a standard way, through which messages can be communicated between the entities in an automated manner using advanced AI techniques. However, updated gradients may reveal individual private or actual information when associated with data attributes and structures. Therefore, encryption mechanisms provide further privacy protection. Secure queries on sensitive private data through the aforementioned models without revealing their contents are possible using an agreed-upon, encrypted subset of the feature vector. The content of the query or input for trained models can be verified, allowing for computation and then the result is returned based on an authentication mechanism, e.g. HE (
Section 4.2.7). However, in addition to the inefficiency of homomorphic-based encryption, the authenticity of local or global models cannot be guaranteed without the authentication of a trusted third party. But, every third party within the urban metaverse ecosystem is untrusted, concerning privacy in particular, considering semi-honest parties or honest but curious parties. Moreover, the locally or globally pre-trained gesture models can be replaced by cybercriminals with their recently trained models instantly, particularly when the credentials of a user are hijacked. Therefore, a blockchain-based approach, which is elaborated in the following subsection, is proposed in this research. In this sense, the main urban entity (i.e. MetaCyberCity) and its cybercommunity entities (i.e. UMaaSs) (
Figure 4) should be addressing the concerns of its residents appropriately, privacy concerns in particular, without requiring the authentication of a third party, while immersing themselves with urban experiences and executing their transactions. The proposed blockchain-based DPPML authentication and verification approach in this research addresses those aforementioned concerns effectively and efficiently.
Considering the management of the identity definitions of an avatar/user, a balance should be established between privacy and security without compromising privacy. Centralised systems (controlled by either a single organisation or a couple of organisations – i.e. federated), which control all the identity definitions of an avatar’s single authentication token, have the obvious drawback of having a single target for malicious actors to focus their efforts on when compared to the management of SSI that is owned and controlled by the user in metaverse worlds. Although SSI is the targeted objective that gives all types of freedom and resilience to the user and the user is supposed to be privileged to fully control user-defined information and to have all the data related to this identity, trust in SSI within multiple metaverse cyberspaces along with the interoperability is the major challenge considering the generation of safe and interconnected metaverse worlds where audit trails are highly difficult to perform, if not impossible. Authentication of SSI by trusted cross-platforms and the interoperability of SSI through diverse metaverse cyberspaces will be the key research questions to be answered in the years to come in metaverse environments to realise the primary objectives of the metaverse. Will a single authentication avatar token allow the user to access to multiple metaverse virtual, urban worlds by enabling the user to travel between different metaverse cities? We do not have the red pill from “Snow Crash” to gain the ability to distinguish the illusion the Matrix creates from reality while engaging in cyber worlds. It is worth emphasising that it will be more difficult to differentiate what is real and what is not, where the real and the synthetic blend and are not readily distinguishable, due to the fact of experiencing events in metaverse environments with multiple of our sensors interacting with the events, leading to an increased susceptibility to manipulation. Therefore, users should be properly and appropriately trained based on their objectives in this ecosystem to be vigilant, particularly against frauds and to cope with the predicaments, particularly bullying and harassment. Then, the striking question comes forward: do we want to use the red pill to distinguish the real from the imaginary or the blue pill to remain ignorant so as to make ourselves more immersed in the environment?