Submitted:
05 February 2024
Posted:
06 February 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
0. Introduction
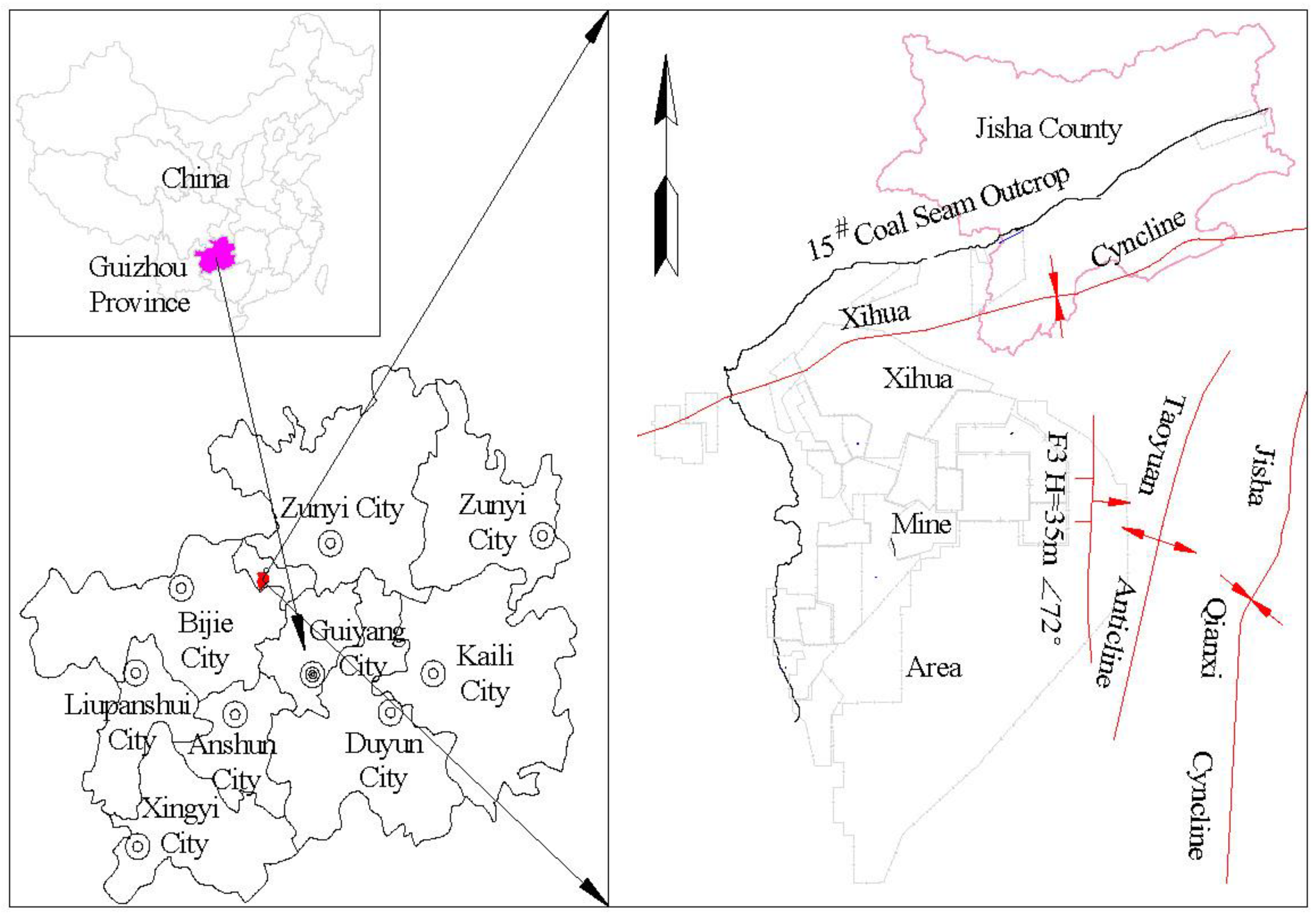
1. Overview of Mining Area
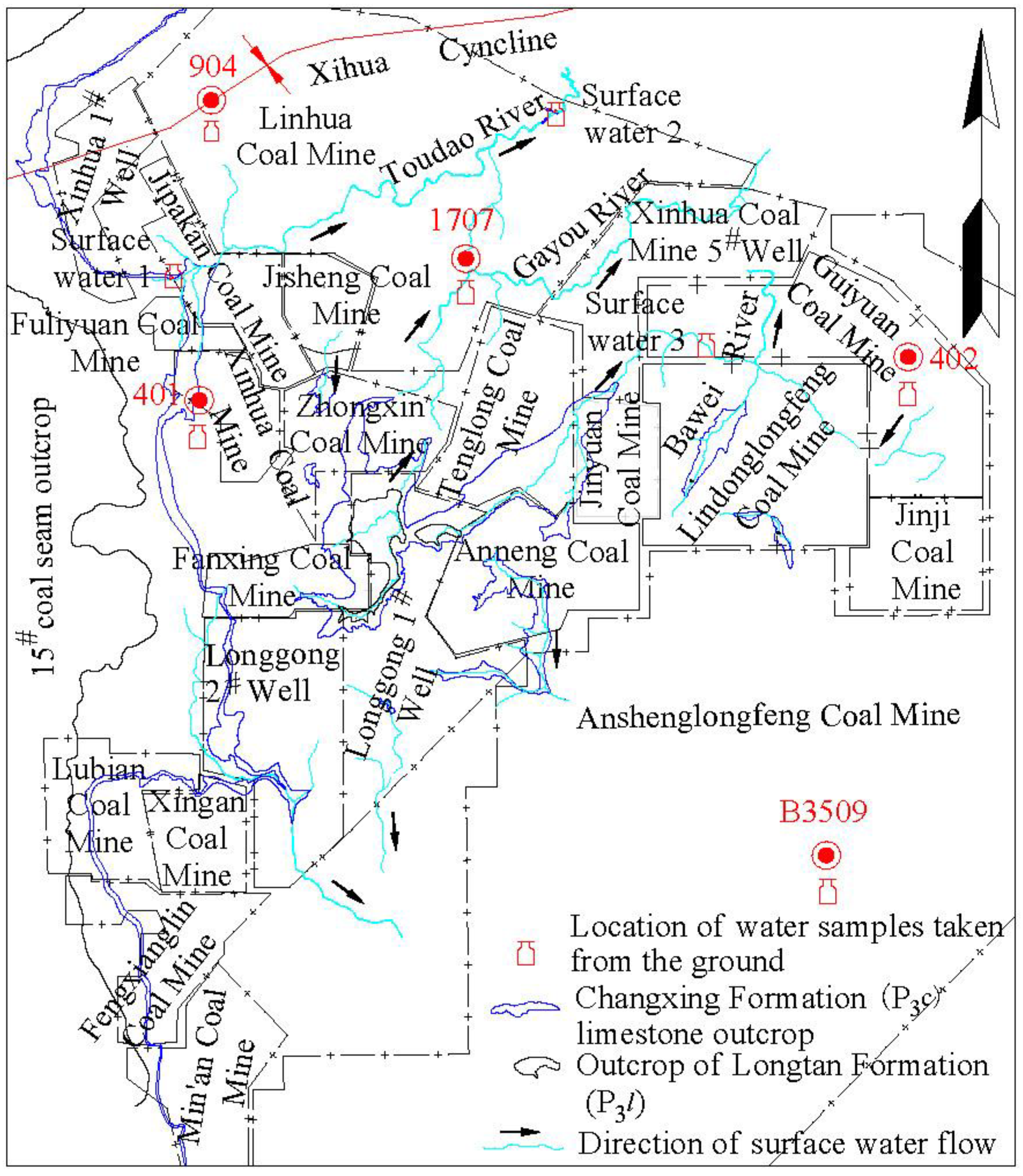
1.1. Basic Information of the Mining Area
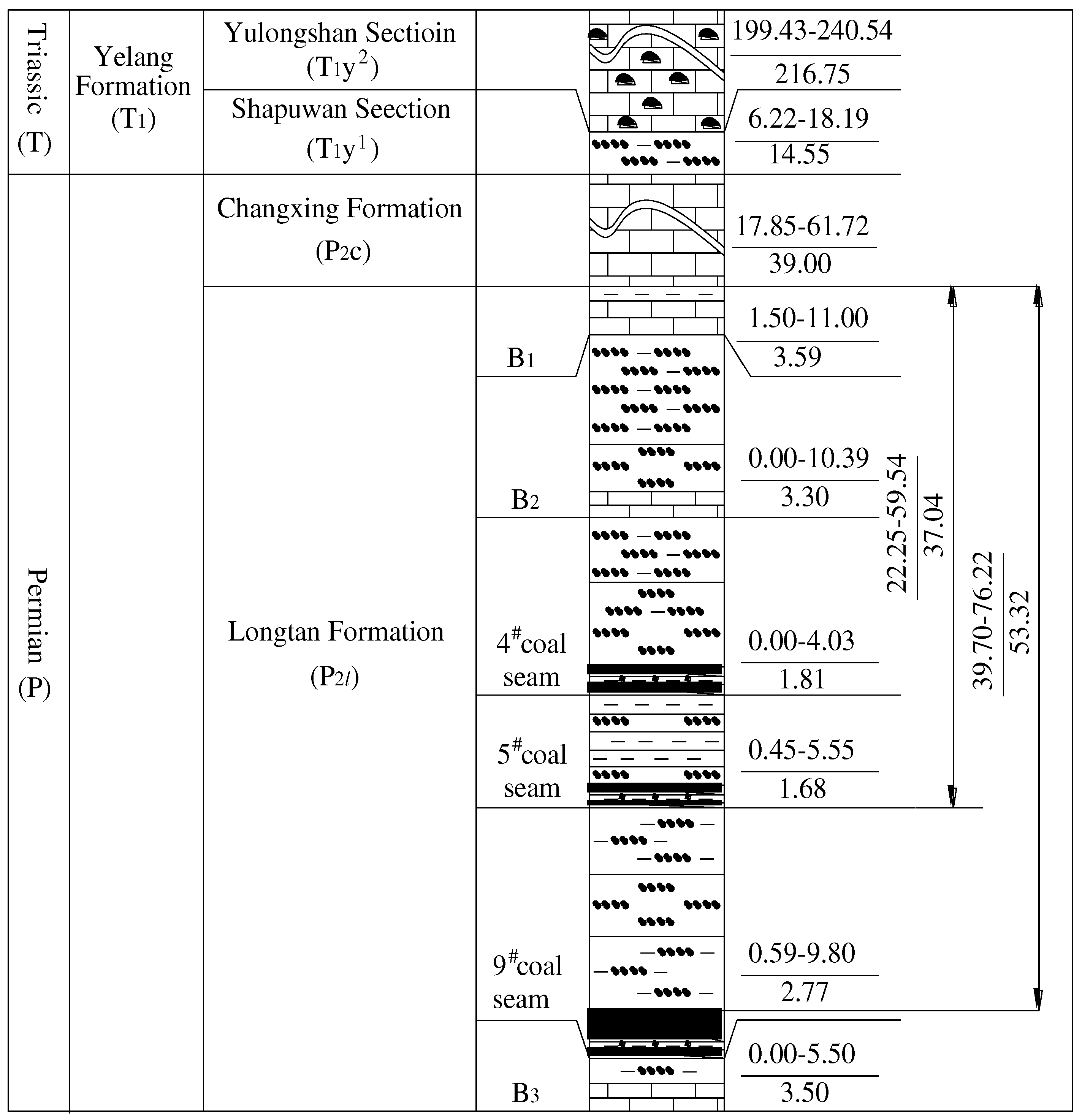
1.2. Introduction to Geology and Hydrogeology of Mining Areas
1.3. Water Inrush Situation in Coal Mines in the Mining Area
2. Hydrogeological Characteristics of Limestone in Changxing Formation
3. Research on Water-Inrush Sources
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Water Inrush Working Face
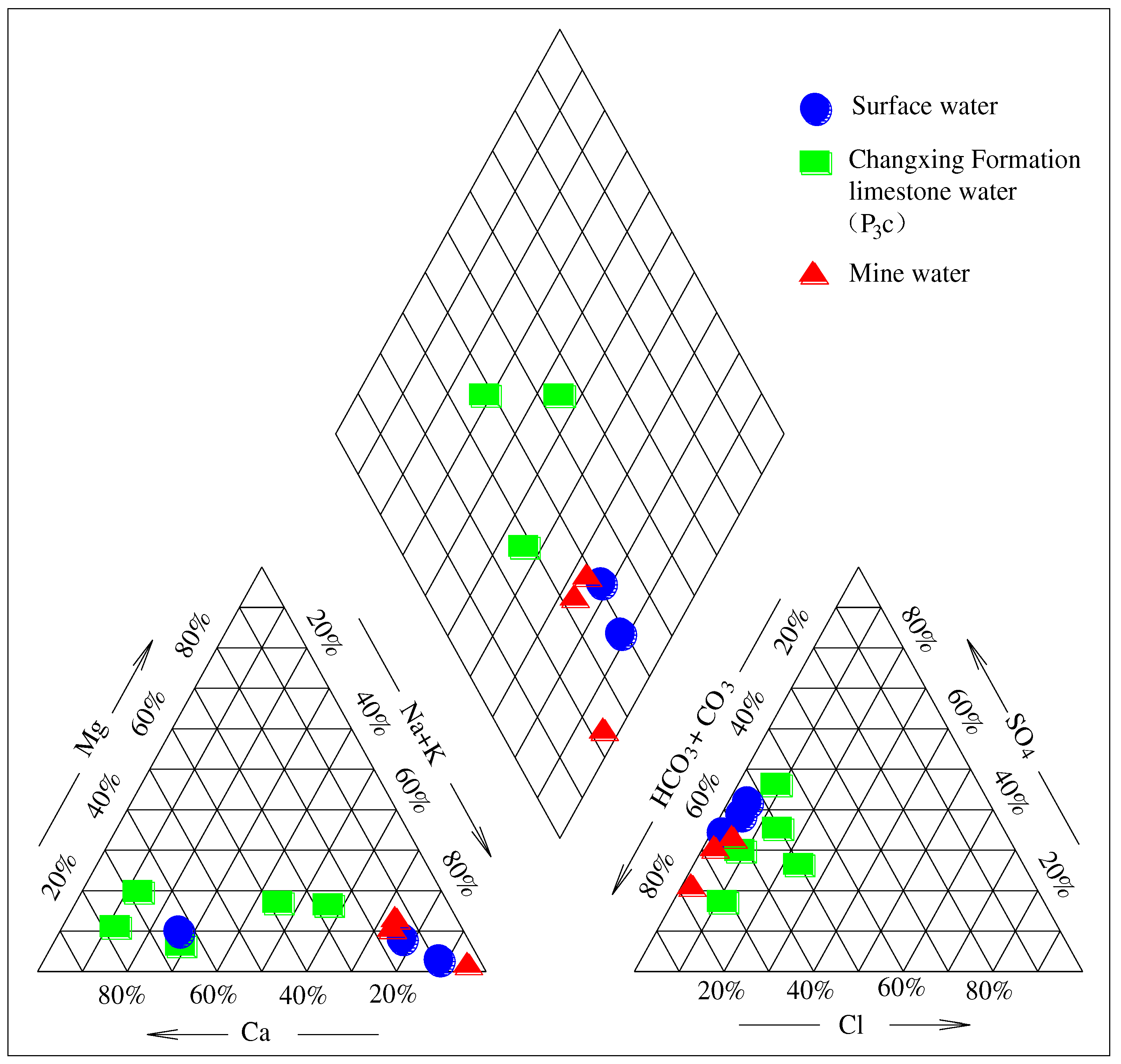
3.2. Chemical Analysis of Water Inflow in the Working Face
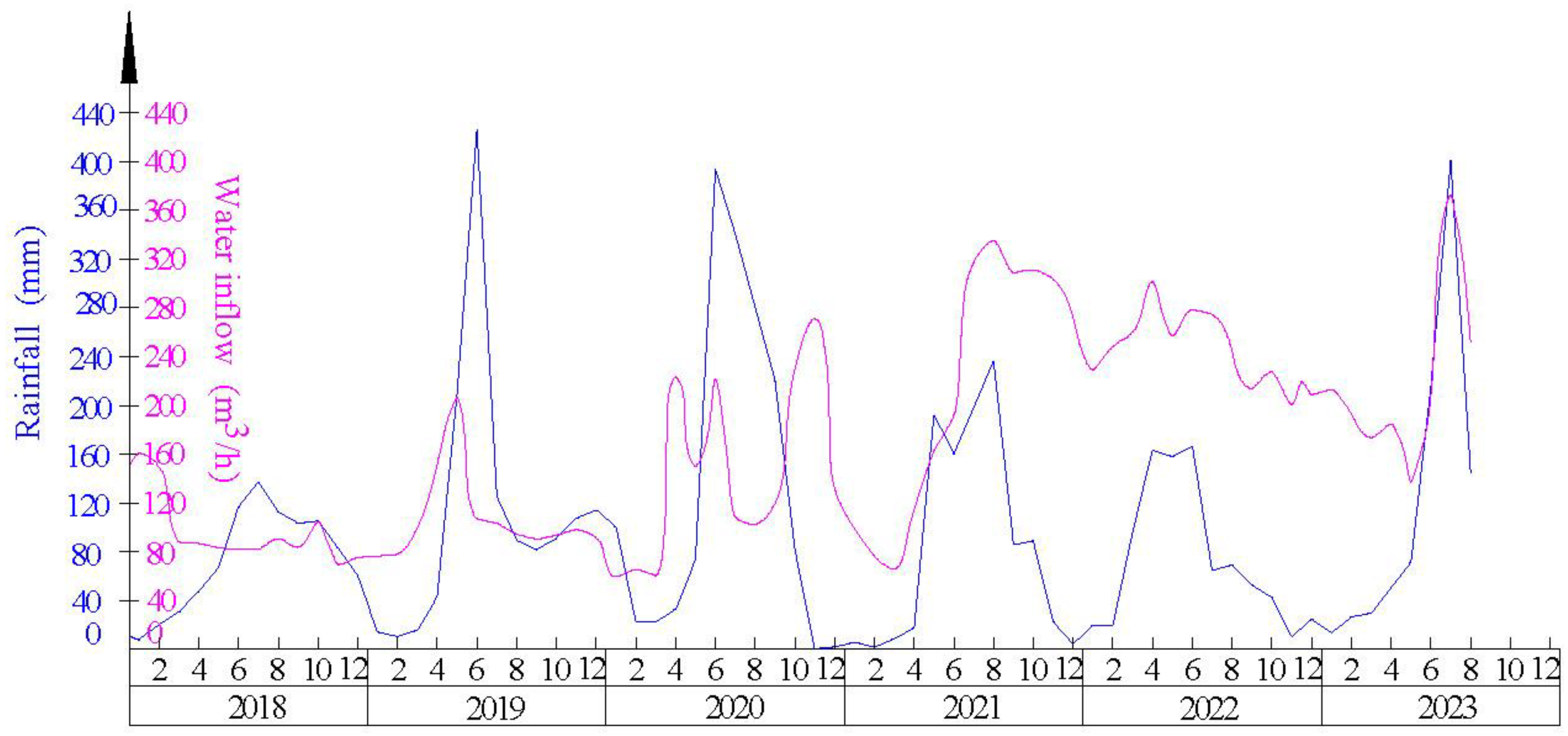
3.3. Analysis of the Correlation between Mine Water Inflow and Atmospheric Precipitation
4. Mechanism of Atmospheric Precipitation Replenishment Underground Stope
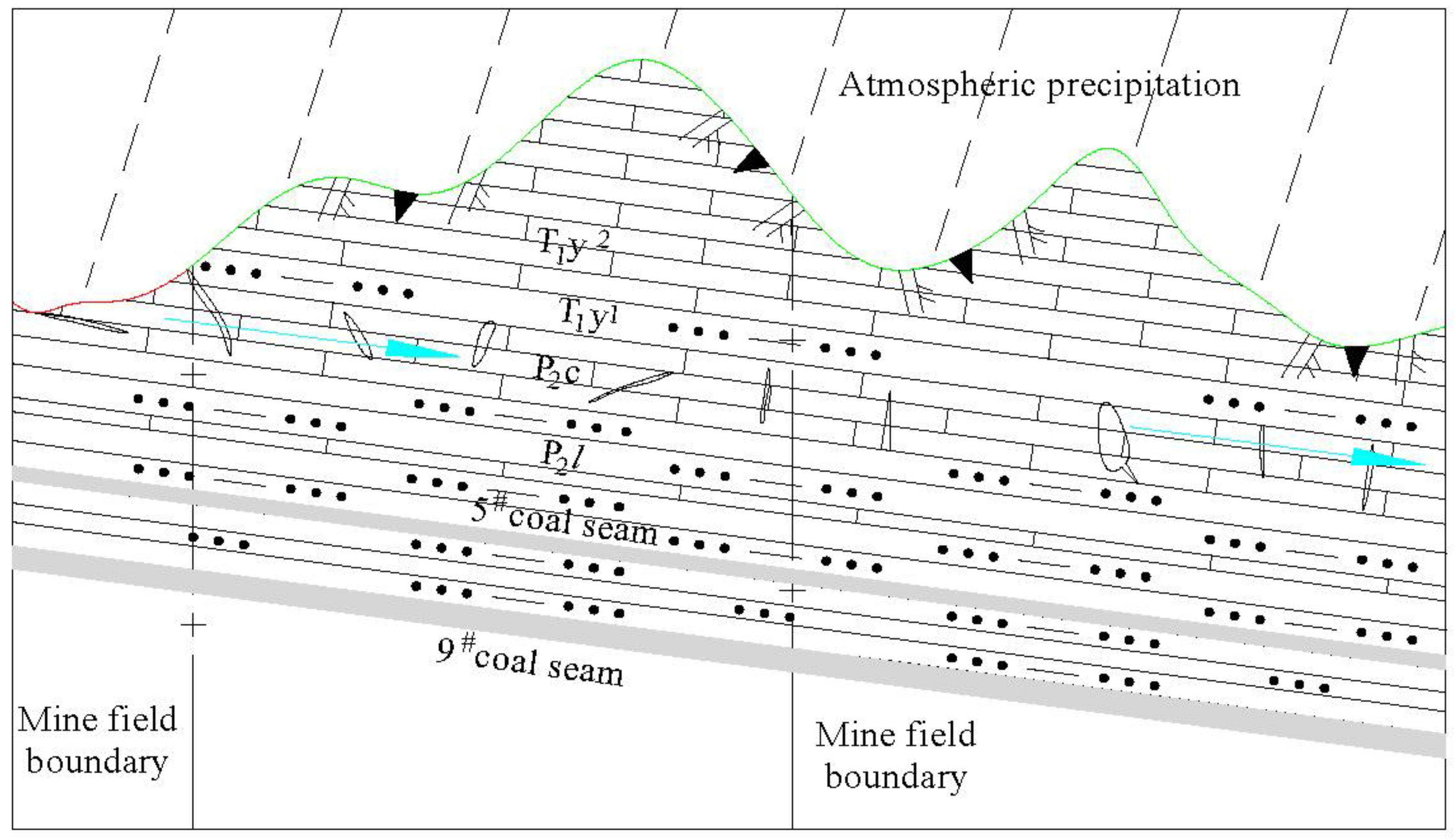
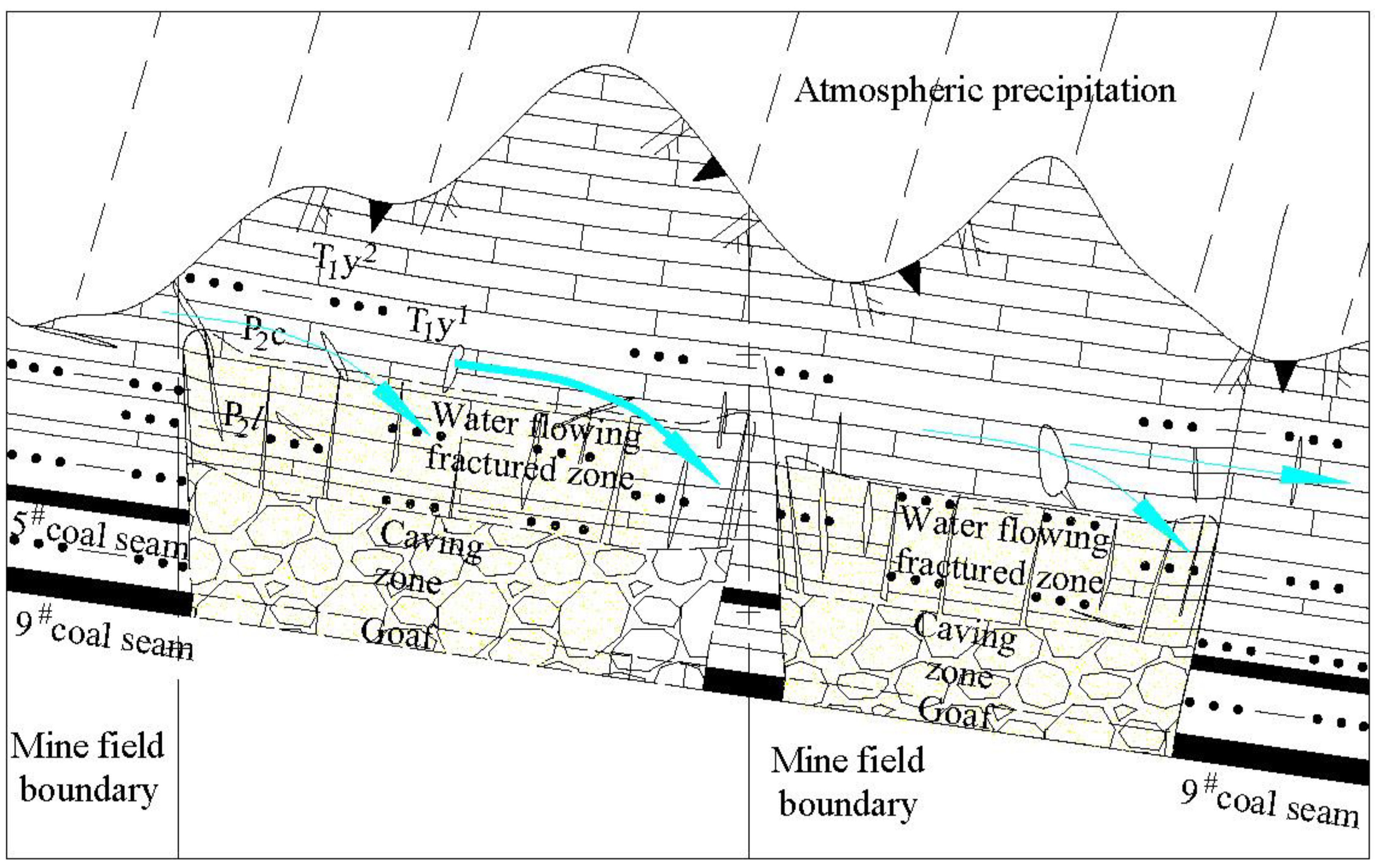
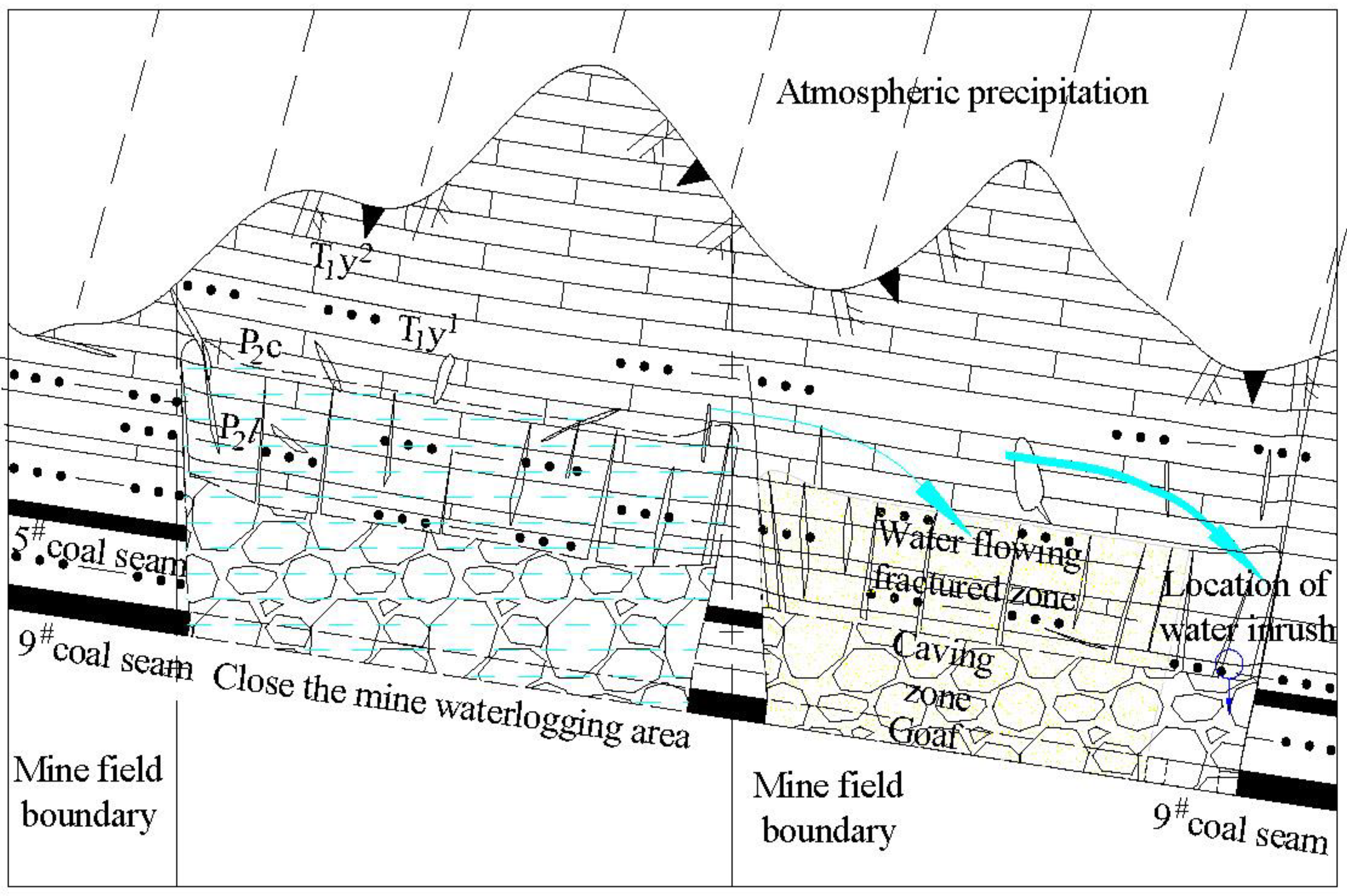
5. Conclusions
References
- Song, Z. The Impact and Prediction Analysis of Atmospheric Precipitation on Coal Mine Water Inflow in Southwest Mountain Areas - Taking Xiaotun Mine as an Example. China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, J.; Qin, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Z. Disastrous Mechanism of Water Burst by Karst Roof Channel in Rocky Desertification Mining Area in Southwest China. Geofluids 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, S.; Xu, F. Evolution and modeling of mine water inflow and hazard characteristics in southern coalfields of China: A case of Meitanba Mine. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology 2020, 32, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Prediction of Water Inflow in Huoshaopu Coal Mine in Panxian Basin, Guizhou Province. China Coal Geology 2019, 31, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, W. Characteristics of an underground stope channel supplied by atmospheric precipitation and its water disaster prevention in the karst mining areas of Guizhou. Scientifc Reports,2023( 13):15892. [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Prediction of Mine Pit Water Inflow in Qinglong Coal Mine, Qianxi, Guizhou. Coal Technology 2015, 34, 228–230. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, L.; Fan, J.; Zhang, G.; et al. Study on inorganic and organic hydrochemical characteristics and water source discrimination in Xiaotun coal mine. Energy and Environmental Protection 2019, 41, 94–99,104. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Yan, K. Evaluation of drilling effect for water exploration on the roof of the working face. Energy Technology and Management 2007, 80–81. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S. Research on the distribution characteristics of confined water and safe mining techniques in the Qianbei mining area. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), Beijing, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, S.; Du, F.; et al. Research on the development law of karst caves on water conducting fractures under the influence of mining in Southwest Karst Mining Areas. Coal Science and Technology 2023, 51, 106–117. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Luo, X.; Su, D.; et al. Research on the mechanism of water inrush in the thick limestone lower roof of Qianbei Coalfield. Coal Technology 2021, 40, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.; Yao, X.; Zhang, W.; et al. Research on the Formation Mechanism and Comprehensive Prevention and Control Technology of Separation Water in Changxing Formation of Qianbei Coalfield. Coal Technology 2023, 42, 128–132. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wei, T.; Liu, Z. Construction of evaluation index system for water abundance of karst aquifers and risk assessment of water inrush on coal seam roof in Southwest China. Journal of China Coal Society 2022, 47, 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, W.; et al. Study on the occurrence characteristics of karst groundwater in coal measures Roof. Coal Eng. 2017, 49, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, G.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, X. Research on the characteristics of water barrier damage and surface water infiltration under coal mining conditions in karst mountainous areas. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology 2012, 39, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Deng, K.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, C. Effects of mining speed on the developmental features of mining-induced ground fissures. Bull Eng Geol Environ, 2019, (78): 6297-6309. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ji, D.; Han, P.; Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; He, F. Study of water-conducting fractured zone development law and assessment method in longwall mining of shallow coal seam. Scientifc Reports, 2022,(12):7994. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, J.; Liang, B. Research on the dynamic evolution law of fssures in shallow-buried and short-distance coal seam mining in Lijiahao Coal Mine. Scientifc Reports, 2023, 5625. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Cui, D.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Similar simulation of mining-induced fissure development law and cave destruction character when mining in karst area. Journal of Underground Space and Engineering 2019, 15, 93–100, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, H. A study on the development height of water conducting fracture zones during mining under thick limestone in the northern Guizhou coalfield. Inner Mongolia Coal Economy 2021, (24), 234–236. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Zeng, C.; Gong, X.; et al. Hydrological and hydrochemical regime of a typical subterraneous river in a deep canyon karst area: A case study in the Santang underground river, Guizhou. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology 2022, 49, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Gao, J.; Du, K.; et al. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanismin coal mine underground reservoir. Coal Science and Technology 2020, 48, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Z.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.; Du, J. Quality Assessment and Hydrogeochemistry of Surface Water in the Liujiang Basin, Hebei Province. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry 2019, 38, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cai, Y. Analysis of dynamic influencing factors of mine water inflow - Taking a coal mine in Guizhou as an example. Water Conservancy Science and Technology and Economy 2021, 27, 61–65,76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Research progress of precipitation infiltration supplement in karst aquifer system. Joural of China Hydrology 2014, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
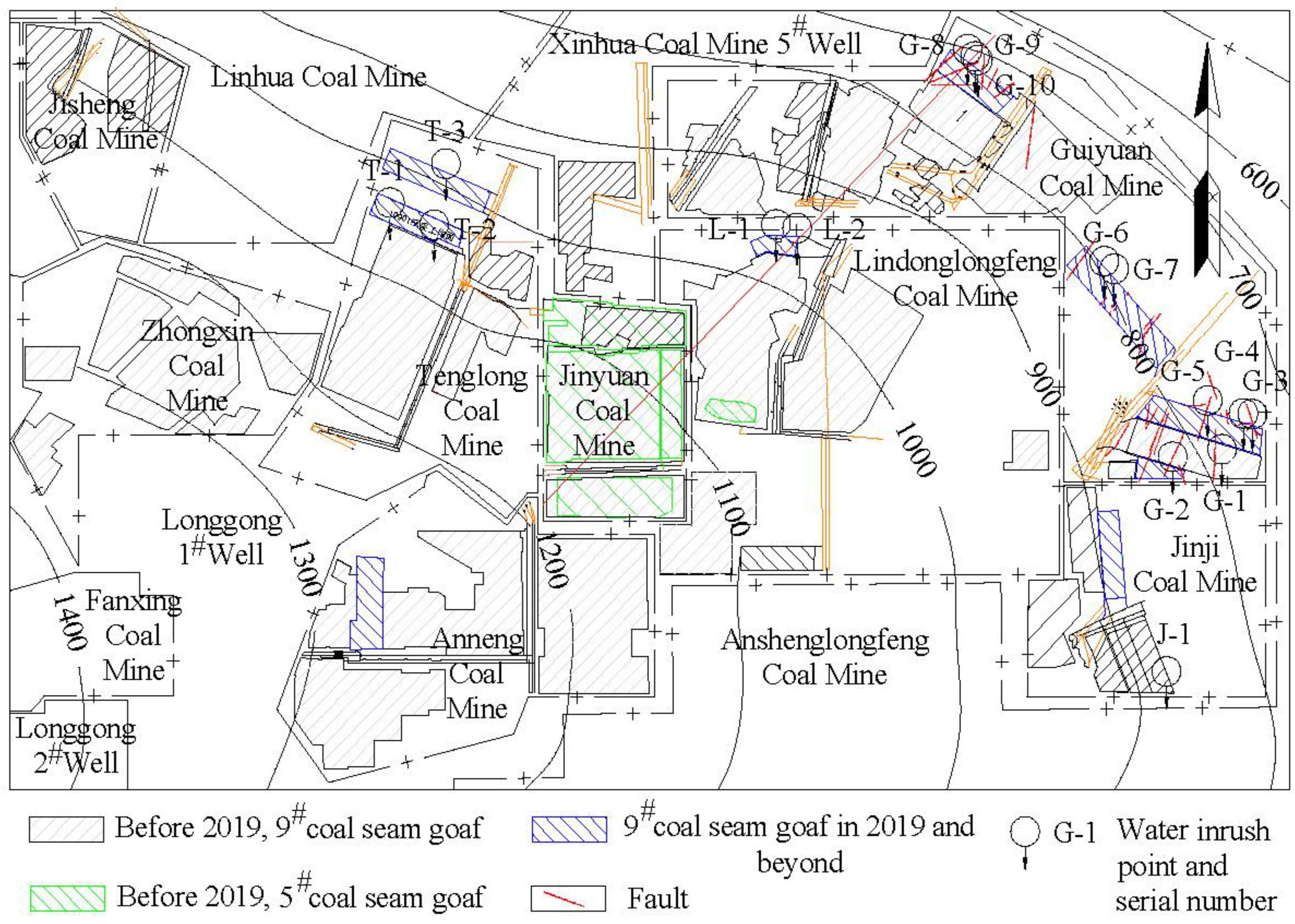
| Coal mine |
Water inrush working face | Location of water inrush | Structure of water inrush site and working face situation | Water inrush time (year, month, day) | Sudden water volume (m3/h) | Elevation of water inrush point (burial depth) (m) | Water inrush point number |
| Guiyuan Coal Mine |
10903 | 276m has been mined, in the middle of the working face | Near the fault | 2016.6.16 | 280 | 783(367) | G-1 |
| 10901 | 80m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Between two faults | 2019.2.30 | 160 | 833(415) | G-2 | |
| 10905 | 74m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Near the fault | 2020.3.10 | 229 | 747(421) | G-3 | |
| 143m has been mined, and the lower part of the working fac | Near the fault | 2020.5.12 | 150 | 751(436) | G-4 | ||
| 425m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Near the fault | 2020.11.8 | 290 | 776(433) | G-5 | ||
| 10908 | 247m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Normal stratigraphic blocks (slow advancement of the working face) | 2021.10.13 | 210 | 808(394) | G-6 | |
| 341m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Normal stratigraphic blocks (slow advancement of the working face) | 2022.2.14 | 80 | 807(439) | G-7 | ||
| 2093 | 161m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Near the fault | 2019.7.15 | 150 | 728.5(431.5) | G-8 | |
| 237m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Near the fault | 2019.11.23 | 470 | 729.8(432.6) | G-9 | ||
| 270m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Near the fault | 2019.12.10 | 350 | 730.9(439.4) | G-10 | ||
| Jinji Coal Mine | 1905 | 71m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Normal stratigraphic blocks, near the near starting cut of the working face | 2018.12.20 | 200 | 877.5(366.1) | J-1 |
| Lindong- longfeng Coal Mine |
5914 | 202m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Expose the fault location | 2019.7.22 | 160 | 979.3(146.2) | L-1 |
| 365m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Normal stratigraphic block, stop mining position | 2020.3.24 | 210 | 977.8(127.4) | L-2 | ||
| Tenglong Coal Mine | 1091 | 163m has been mined, and the upper part of the working face | 40m Normal stratigraphic block segment, 40m away from the shorting cut of the nearby working face | 2020.4.19 | 80 | 1047.3(342.7) | T-1 |
| 536m has been mined, and the upper part of the working face | Normal geological blocks, slow mining in the working face | 2020.11.11 | 800 | 1047.4(350.1) | T-2 | ||
| 10903 | 465m has been mined, and the lower part of the working face | Near the fault | 2022.6.19 | Collapse water and gangue | 993.4(274.1) | T-3 |
| Water sample location | Surface water(mg/L) | Changxing Formation (P3c)Limestone Water(mg/L) | Mine water(mg/L) | |||||||||
| Cation | Ca2+ | 23.55 | 45.89 | 112.04 | 65.38 | 17.01 | 60.17 | 47.62 | 52.75 | 4.80 | 21.15 | 15.66 |
| Mg2+ | 4.20 | 14.73 | 10.20 | 8.60 | 6.15 | 3.40 | 8.19 | 14.14 | 1.46 | 8.07 | 8.55 | |
| Na+ | 257.83 | 280.60 | 54.79 | 15.54 | 38.90 | 30.05 | 10.60 | 72.93 | 344.00 | 115.00 | 96.50 | |
| K+ | 1.85 | 2.86 | 1.33 | 1.74 | 7.10 | 1.30 | 1.50 | |||||
| NH4+ | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | 1.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 0.52 | |
| Anion | HCO3+ | 469.61 | 558.68 | 288.85 | 142.54 | 137.53 | 163.66 | 106.90 | 192.09 | 642.17 | 249.27 | 227.40 |
| CO32+ | 7.24 | 4.34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 45.57 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| SO42+ | 196.54 | 305.41 | 175.34 | 58.45 | 25.31 | 60.81 | 58.45 | 153.12 | 150.00 | 104.00 | 80.00 | |
| Cl+ | 27.76 | 9.75 | 15.07 | 39.36 | 12.87 | 13.51 | 18.19 | 22.12 | 17.29 | 13.59 | 6.31 | |
| NO3+ | 3.09 | 7.56 | 0.20 | 0 | 0.20 | 5.22 | 1.77 | 0.04 | 0.50 | 1.98 | 2.11 | |
| NO2+ | 0.03 | 0.62 | 0 | 0 | <0. 12 | 0.06 | <0.12 | 0.24 | 0.272 | <0.10 | 0.006 | |
| Total hardness (mg/L) | 77.06 | 175.24 | 321.82 | 200.27 | 102.72 | 164.21 | 152.65 | 189.98 | 86.05 | 86.05 | 74.31 | |
| Total dissolved solidsTDS (mg/L) | 716.00 | 907.50 | 510.50 | 250.53 | 144.00 | 279.50 | 168.00 | 430 | 892.59 | 393.58 | 327.76 | |
| PH | 8.9 | 8.6 | 7.17 | 7.5 | 7.82 | 8.4 | 8.55 | 6.1 | 8.18 | 8.18 | 8.11 | |
| Water quality type | HCO3 ·SO4 - Na |
HCO3·SO4 -Na |
HCO3·SO4-Ca·Na | HCO3 ·SO4 -Ca |
HCO3 · - Na· Ca |
HCO3 ·SO4 -Ca· Na |
HCO3· SO4 -Ca. ·Na |
HCO3.SO4- Na·Ca | HCO3- Na |
HCO3 ·SO4 -Na |
HCO3 ·SO4 -Na |
|
| Elevation (burial depth)(m) | 1171.2 | 1327.5 | 1072.8 | 829.70 (305.86) |
1364.46 (21.27) | 1038.00 (332.45) |
794.70 (322.12) |
979.3 (231.5) |
945 (450) |
776 (419) |
985 (172) |
|
| Notes | Surface water 1 | Surface water2 | Surface water 3 | 1707 Borehole in Linhua Coal Mine | 401 Borehole in Fuliyuan Coal Mine (near the outcrop) | 904 Borehole in Linhua Coal Mine | 402 Borehole in Guiyuan Coal Mine | B3509-2 Borehole in Anshenglongfeng Coal Mine | 10908 working face of Guiyuan Coal Mine | 10905 working face of Guiyuan Coal Mine | Water outlet point of Changxing Formation limestone in the main shaft of Guiyuan Coal Mine | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




