Submitted:
04 February 2024
Posted:
05 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
- -
-
Max. Tolerated Dose (Human) (log mg/kg/day):Daidzin: 0.488log mg/kg/dayLuteolin: 0.499 log mg/kg/daySilibinin: 0.65 log mg/kg/dayFisetin: 0.579log mg/kg/day
- -
-
Oral Rat Acute Toxicity (LD50) (mol/kg):Daidzin: 2.738 mol/kgLuteolin: 2.455 mol/kgSilibinin: 2.559 mol/kgFisetin: 2.465 mol/kg
- -
-
Oral Rat Chronic Toxicity (LOAEL) (log mg/kg_bw/day):Daidzin: 4.717log mg/kg_bw/dayLuteolin: 2.409 log mg/kg_bw/daySilibinin: 3.494 log mg/kg_bw/dayFisetin: 1.921 log mg/kg_bw/day
- -
-
Minnow Toxicity (LC50) (log mM):Daidzin: 3.902log mMLuteolin: 3.169log mMSilibinin:2.543 log mMFisetin: 2.273 log mM
| Ligand | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|
| Daidzin | -10.9 |
| luteolin | -9.7 |
| silibinin | -10.1 |
| Fisetin | -9.5 |
| Crystal ligand E92 * | -11 |
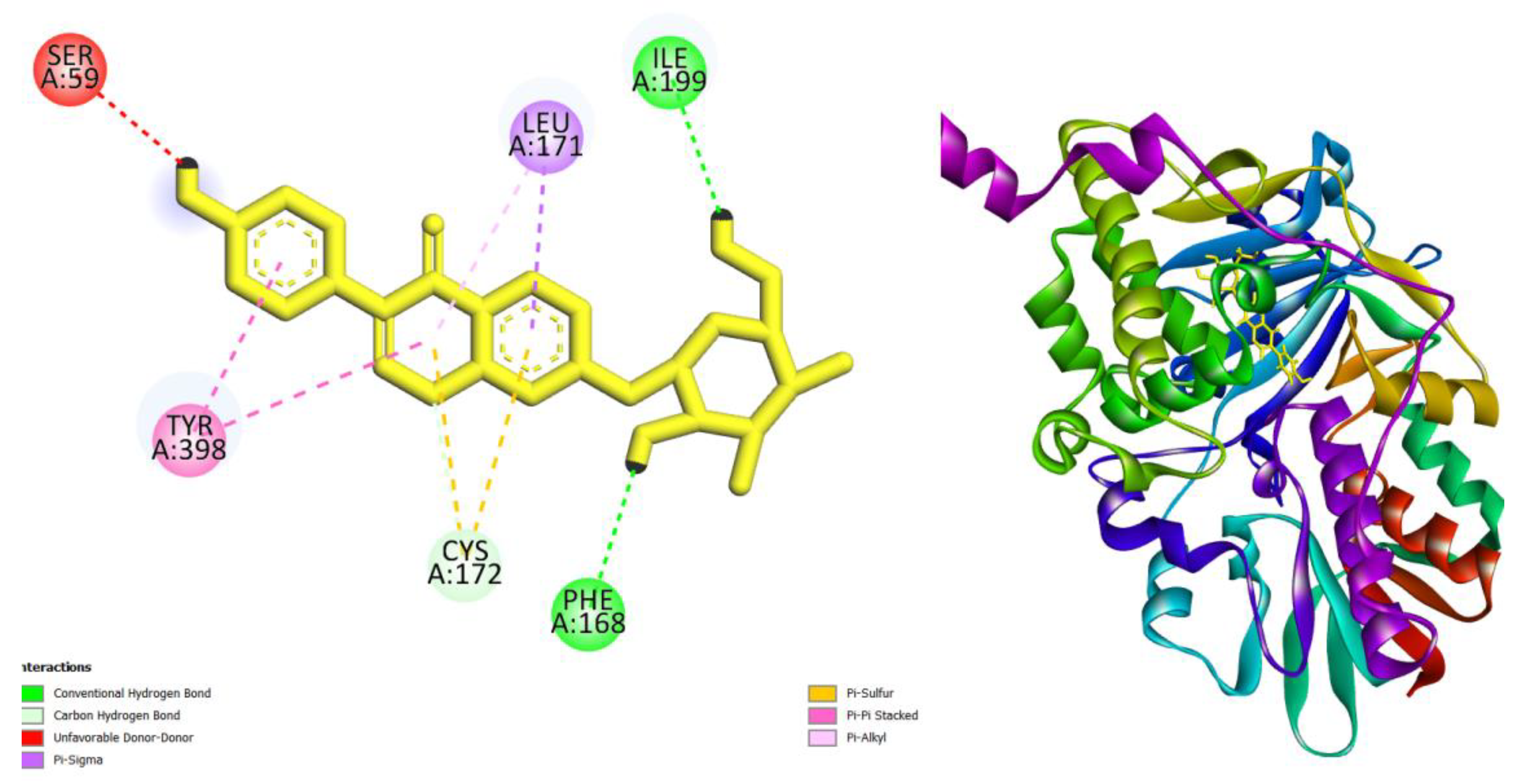
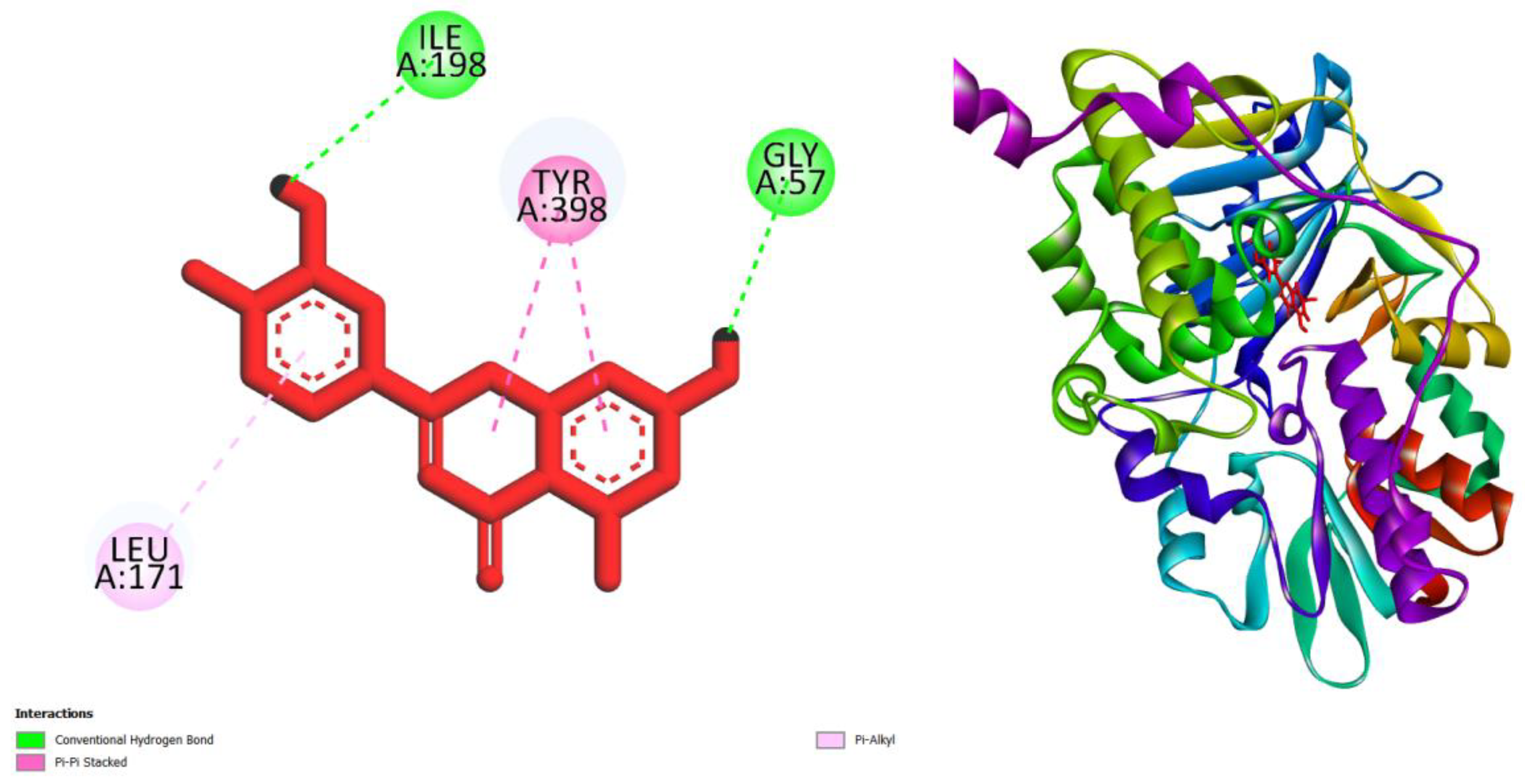
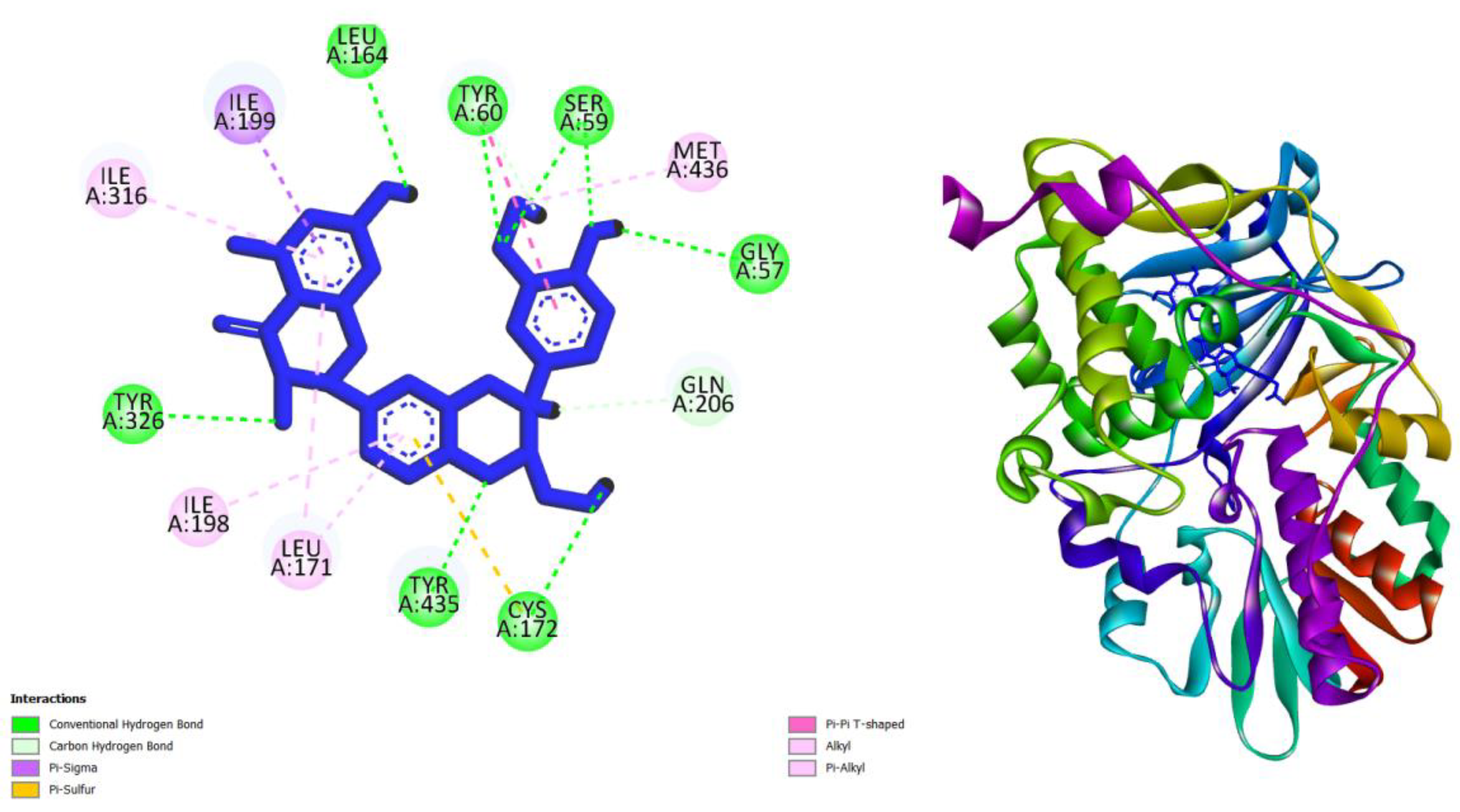
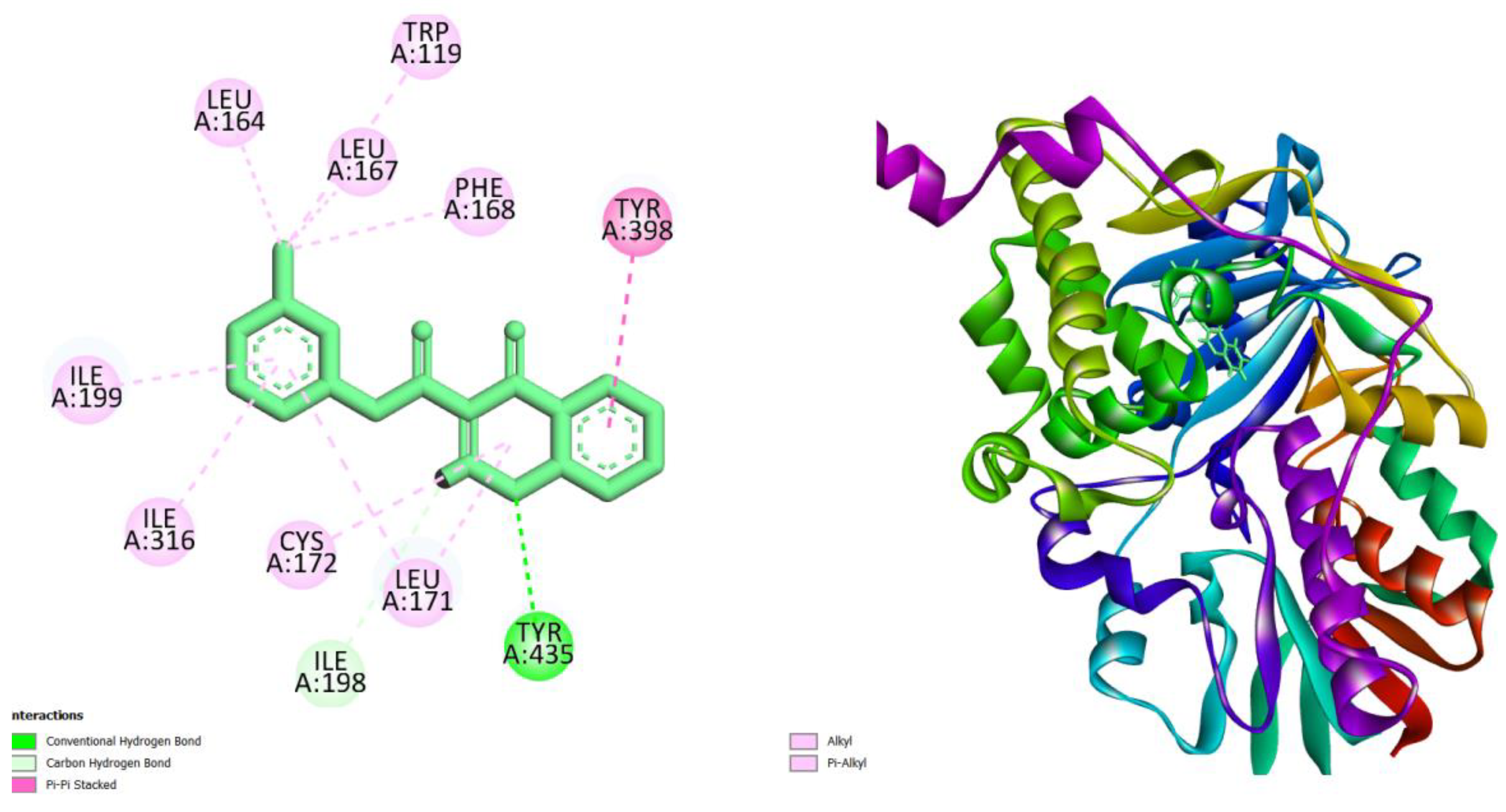
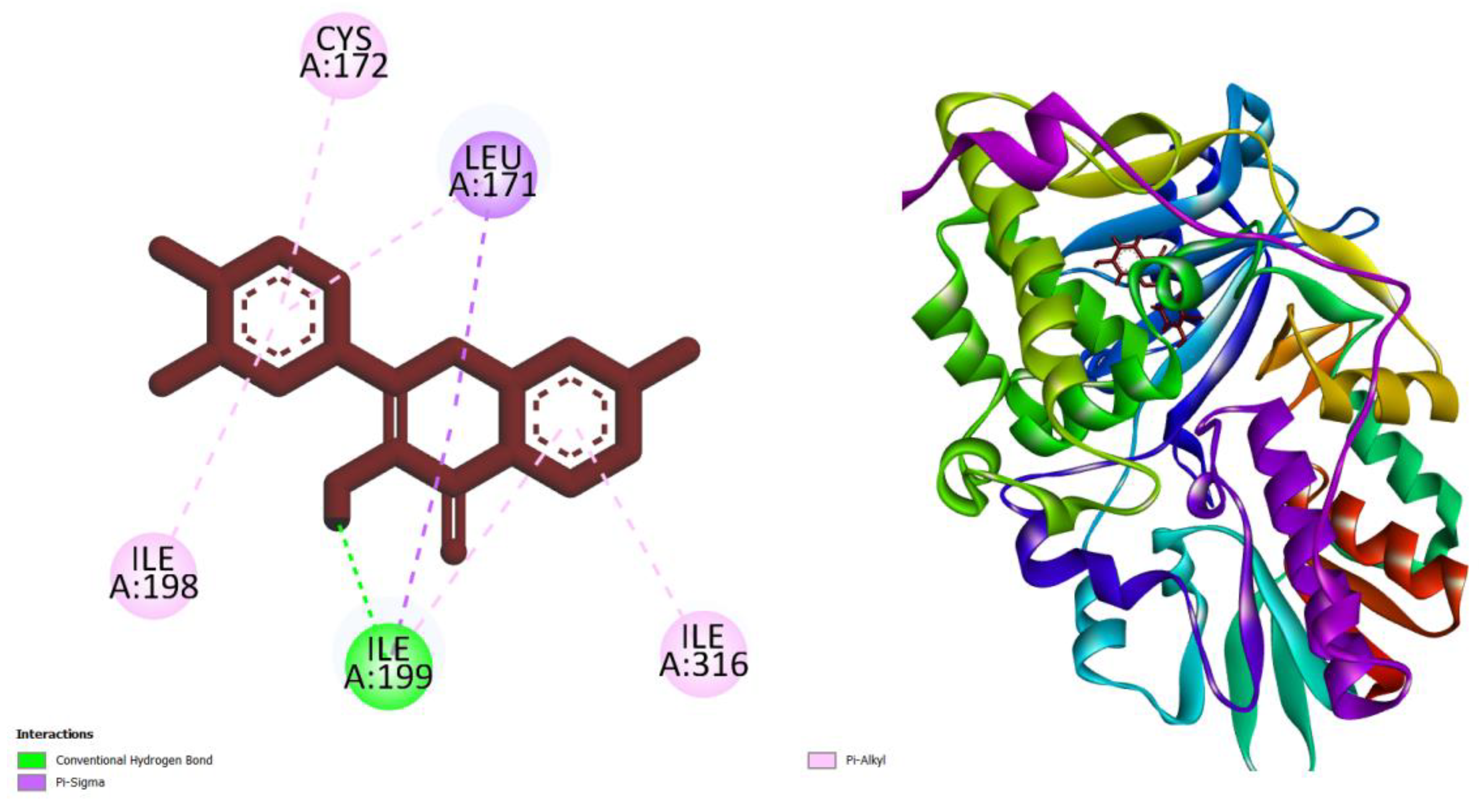
| Compounds | AMES toxicity | Max. tolerated dose (human) (log mg/kg/day) |
Oral Rat Acute Toxicity (LD50) (mol/kg) | Oral Rat Chronic Toxicity (LOAEL) (log mg/kg_bw/day) | Hepatotoxicity | Skin Sensitisation |
T. Pyriformis toxicity (log ug/L) |
Minnow toxicity (log mM) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daidzin | No | 0.488 | 2.738 | 4.717 | no | no | 0.285 | 3.902 | |||
| Luteolin | No | 0.499 | 2.455 | 2.409 | no | no | 0.326 | 3.169 | |||
| Silibinin | No | 0.65 | 2.559 | 3.494 | no | no | 0.285 | 2.543 | |||
| Fisetin | No | 0.579 | 2.465 | 1.921 | yes | no | 0.376 | 2.273 | |||
4. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mathew, B., Ravichandran, V., Raghuraman, S., Rangarajan, T. M., Abdelgawad, M. A., Ahmad, I., ... & Kim, H. (2023). Two dimensional-QSAR and molecular dynamics studies of a selected class of aldoxime-and hydroxy-functionalized chalcones as monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 41(19), 9256-9266. [CrossRef]
- Melfi, F., Carradori, S., Angeli, A., & D’Agostino, I. (2023). Nature as a source and inspiration for human monoamine oxidase B (Hmao-B) inhibition: A review of the recent advances in chemical modification of natural compounds. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery, (just-accepted).
- Zhang, C., Zhang, Y., Lv, Y., Guo, J., Gao, B., Lu, Y., ... & Xie, Y. (2023). Chromone-based monoamine oxidase B inhibitor with potential iron-chelating activity for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 38(1), 100-117. [CrossRef]
- Reis J, Manzella N, Cagide F, Mialet-Perez J, Uriarte E, Parini A, Borges F, Binda C. Tight-Binding Inhibition of Human Monoamine Oxidase B by Chromone Analogs: A Kinetic, Crystallographic, and Biological Analysis. J Med Chem. 2018 May 10;61(9):4203-4212. [CrossRef]
- Oh, J. M., Kumar, S., Sudevan, S. T., Hendawy, O. M., Abdelgawad, M. A., Musa, A., ... & Mathew, B. (2023). Halogenated class of oximes as a new class of monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: Synthesis, Biochemistry, and Molecular dynamics study. Computational Biology and Chemistry, 107899. [CrossRef]
- Chew, Z. X., Lim, C. L., Ng, K. Y., Chye, S. M., Ling, A. P., & Koh, R. Y. (2023). The Role of Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease-An Update. CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders), 22(3), 329-352. [CrossRef]
- Chopade, P., Chopade, N., Zhao, Z., Mitragotri, S., Liao, R., & Chandran Suja, V. (2023). Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease therapies in the clinic. Bioengineering & Translational Medicine, 8(1), e10367. [CrossRef]
- Funayama, M., Nishioka, K., Li, Y., & Hattori, N. (2023). Molecular genetics of Parkinson’s disease: Contributions and global trends. Journal of Human Genetics, 68(3), 125-130. [CrossRef]
- Cherian, A., Divya, K. P., & Vijayaraghavan, A. (2023). Parkinson’s disease–genetic cause. Current Opinion in Neurology, 36(4), 292-301.
- Kulkarni, A., Preeti, K., Tryphena, K. P., Srivastava, S., Singh, S. B., & Khatri, D. K. (2023). Proteostasis in Parkinson’s disease: Recent development and possible implication in diagnosis and therapeutics. Ageing Research Reviews, 84, 101816. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., & Meng, Y. (2023). Application value of peripheral blood IgG and IgM combined with ultrasonic echo parameters of substantia nigra in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering Reviews, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Ding, J., Tang, S., Mei, Z., Wang, L., Huang, Q., Hu, H., ... & Wu, J. (2023). Vina-GPU 2.0: Further Accelerating AutoDock Vina and Its Derivatives with Graphics Processing Units. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 63(7), 1982-1998. [CrossRef]
- Azzam, K. A. (2023). SwissADME and pkCSM webservers predictors: An integrated online platform for accurate and comprehensive predictions for in silico ADME/T properties of artemisinin and its derivatives. Kompleksnoe Ispolzovanie Mineralnogo Syra= Complex use of mineral resources, 325(2), 14-21. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





