1. Introduction
In ancient times, known as harvestmen in China, Nereid sandworms (nereids) were also known as sea worms, sea maggots, sea centipedes, sea worms, and sea locusts. There are more than 80 species and genera distributed in China. The common species include amber spiny sandworms (Neanthes succinae), swimmer sandworms (Nereis pelagica), medium-sized sandworms (Nereis zhongshaensis), Perinereis nuntia Savigny, Neanthes japonica lzuka and Perinereis aibuhitensis grube. As invertebrates, the larvae of sandworms feed on plankton, and when they mature, they mainly eat humus. As invertebrates, artificial aquacultured sandworms have high nutritional and economic value and are often used as bait for fishing. The double-toothed periwinkle sandworms, most frequently documented, predominantly inhabit regions such as the South China Sea, East China Sea, Yellow Sea, and Bohai Sea, where interstitial sediment is rich in organic matter [
1,
2]. In terms of biological classification, they belong to the Annelida phylum, within the Polychaeta class, Errantia order, and Nereidae family, specifically the genus Perinereis. The structure of Perinereis is segmented, excluding the stomach, and comprises a head, trunk, and tail. Each segment possesses paired parapodia, and the entire body exhibits bilateral symmetry with two distinct colorations: green and red. Internally, a true coelom and a closed circulatory system segregate the blood from interstitial spaces, facilitating efficient nutrient absorption and unimpeded elimination of metabolic wastes. Notably, there exists a pronounced morphological distinction between juvenile and adult B. bisporus. Post-sexual maturation, observable changes include a gradual reduction in the size of digestive tract cells and the disappearance of septa between body segments, among others [
3].
2. Medicinal Properties of the Sandworm and Modern Pharmacological Research
2.1. As Herbal Medicine
According to the “Compendium of Gleanings”, “tonifying the spleen and stomach, blood, diuresis, urination”, and “Materia Medica Seeking Origin” also have related records, “warming the stomach, tonifying the qi, less vinegar good”. The meridians are the spleen and stomach meridians.
Sandworms are rich in a variety of plant proteins, amino acids, unsaturated fatty acids and vitamins and minerals. The mineral content is high, and the plant is rich in trace elements. In addition to iron and calcium, zinc, phosphorus and other substances are also beneficial to the human body. These substances are absorbed and can improve the body’s hematopoietic function but also promote the development of bones, young children or elderly people, often anemia and osteoporosis. Joint diseases have very good preventive and mitigating effects. Trace elements and unsaturated fatty acids also have direct impacts on the human brain, accelerating brain development and slowing brain aging, preventing Alzheimer’s disease and improving memory.
Sandworm powder can improve the activity of human cells, replenish the central nervous system, alleviate physiological deficiencies, enhance the body’s physical fitness and improve the health of the human body. In daily life, this herb can cause rheumatism and blood circulation, and the treatment of human rheumatism, bone pain and arthritic swelling pain is among the commonly used traditional Chinese medicines. Many patients consume this drug after its therapeutic effect. In addition to these medicinal functions, sandworms can also activate blood stasis, swelling, and pain. In the treatment of these symptoms, the first step is to wash the sandworms for drying, and after the sandworms are directly dried and soaked in a certain concentration of white wine for a period of time, the resulting wine can be eaten orally or coated on the wound to relieve and reduce the patient’s symptoms of swelling and pain. In medicine, sandworms can also stop pain, and itching can also accelerate the body’s metabolism of toxins, which can also enhance the body’s ability to resist stress. In ordinary daily life, the sandworms are mashed directly on itchy skin or skin pain by redness and swelling and can quickly stop pain and itching so that the skin can quickly return to a normal state. Sandworms also contain a large amount of collagen and a variety of active ingredients. In addition to food consumption, they can nourish the skin to keep the skin tender and prevent skin diseases and improve skin elasticity; moreover, to reduce wrinkles, often eating can be aesthetically pleasing and anti-aging.
2.2. As a Western Drug
The active protease of Sarcophaga spp. has been shown to have a certain killing effect on lung cancer cells. According to the findings of G. Zhang et al. [
4], the active protease extracted from Sarcophaga spp. can inhibit the growth of SPC-A-1 and induce apoptosis. The mechanism of apoptosis involves the active protease regulating the expression of Bax and Bcl-2 as well as apoptosis-related genes, further regulating the release of Cyt-C, activating the Cystatin Caspase 9 and activating the apoptosis-executing protease Caspase 3. The mechanism of apoptosis involves the active protease regulating the protein expression of Bax and Bcl-2 and genes related to apoptosis, further regulating the release of Cyt-C, which activates cystatinase Caspase 9 and activates the apoptosis-executing protease Caspase 3. Then, PARP is cleaved by the protease Caspase 3 to activate apoptotic signals related to it, which ultimately leads to the apoptotic death of SPC-A-1 cells and plays an antitumor role. In addition to their effect on lung cancer, the proteins extracted from Sarcophaga spp. also have a significant killing effect on leukemia Jurkat cells. J. Zhang et al. [
5] reported that sandworm protein extracts also significantly inhibited proliferation, induced apoptosis, and killed leukemia cells. Their results showed that by increasing the duration of action and dose of the protein, the inhibitory effect of the protein on Jurkat cells became time-dose dependent.
In research related to the sandworm drug, a protease known as fibrinolytic enzyme (thrombolysin) has been identified. This protease, extracted from the sandworm’s body, has been demonstrated through numerous experiments to possess the capability of dissolving the robust aorta thrombus in rats.
Li [
6], through fibrin plate experiments, confirmed that not only can the protease quickly and efficiently dissolve fibrin in vitro but also that in vivo, the use of the protease can reduce the dissolution time of euglobulin and the content of fibrin and fibrinogen; moreover, the protease does not affect blood coagulation function, bleeding or other complications and is expected to lead to the development of a new generation of antithrombotic drugs. Bai et al. [
7]from China discovered that protease extracted from the sandworm could inhibit platelet coagulation in rats, triggered by arachidonic acid, ADP, and collagen. This inhibition effectively reduced the maximum coagulation rate of platelets. Utilizing a dextran polymer-induced rat model of stagnant anemia and hyperviscosity, it was observed that the sandworm’s fibrinolytic enzyme diminished whole blood viscosity in rats without impacting red blood cell pressure, plasma viscosity, or erythrocyte sedimentation rate. In (2007), Zhang [
8] successfully isolated and purified a novel marine fibrinolytic enzyme from the sandworm employing salting-out and other methods. This enzyme demonstrated significant thrombolytic and fibrinolytic activities, along with notable pH and thermal stability. Further, Li et al. [
8] extracted and purified a new metalloproteinase with fibrinolytic activity, termed NVMP, from the sandworm. This process involved varying concentrations of ammonium sulfate hydrochloratography and chromatographic column fractionation. The molecular weight of NVMP ranges between 28 and 32 kDa, with an optimal pH of 6.0 and a preferred reaction temperature of 40 °C. Certain metal ions, like Zn2⁺ and Cu2⁺, were found to inhibit its activity, whereas others enhanced its protein activity. The NVMP can directly degrade fibrin or indirectly degrade fibrin after the fibrinolytic enzyme zymogen is activated to fibrinolytic enzymes; thus, facilitating thrombolysis. Li et al. [
9] cloned the cDNA library of NVMPs through plasmid reconstruction, plasmid transformation, expression transformation and isolation and purification to ultimately obtain recombinant thrombolytic protein. This protein significantly activated fibrinolytic enzyme zymogen activity in vitro, was thermally stable, and had a pH range ranging from 6–9. These experimental data and findings provide theoretical and practical significance for the future development of thrombolytic and antithrombotic drugs in combination with sarcoplasmic fibrinolytic enzymes or fibrinolytic kinases in preclinical studies and for the treatment of myocardial infarction caused by ST-segment elevation.
3. Main Types of Sandworm Proteins and Their Functions
The proteins of the sandworm are encoded mainly by the sandworm protein-encoding gene family, and the genes encoding SP1, SP2, SP3, SP4, SP5, and SP6 are six different genes in the sandworm protein family. The different kinds of sandworm protein genes have different genetic characteristics, and the following are the genetic characteristics of the various proteins:
The SP1 gene: The SP1 gene is a member of the protein-encoding gene family of the sandworm and is located on chromosome 1 of the sandworm. The protein encoded by this gene has immunomodulatory and antioxidant functions. The SP1 gene plays an important role in the immune system of silkworms and can promote the activation and proliferation of immune cells in silkworms; thus, improving their immunity. The SP1 gene contains five exons and four introns, and the protein encoded by this gene consists of 286 amino acids.
The SP2 gene is located on chromosome 2 of Bombyx mori and encodes a protein with antibacterial, antiviral, and antitumor functions. The SP2 protein can recognize and bind to pathogens such as bacteria and viruses; thus, exerting antibacterial and antiviral effects. In addition, the SP2 protein can induce apoptosis in tumor cells and has antitumor effects. The SP2 gene contains five exons and four introns, and the encoded protein consists of 284 amino acids.
The SP3 gene is located on chromosome 3 of Bombyx mori and encodes a protein with immunomodulatory and antimicrobial functions that can promote the activation and proliferation of Bombyx mori immune cells; thus, improving the immune ability of Bombyx mori. Moreover, the SP3 protein can also recognize and bind to pathogens such as bacteria; thus, playing an antibacterial role. The SP3 gene contains four exons and three introns, and the encoded protein consists of 247 amino acids.
The SP4 gene is located on chromosome 4 of Bombyx mori and encodes a protein with antitumor and immunomodulatory functions; the SP4 protein can induce the apoptosis of tumor cells and has antitumor effects. Moreover, the SP4 protein can promote the activation and proliferation of immune cells in Bombyx mori to improve its immunity. The SP4 gene contains 5 exons and 4 introns, and the encoded protein consists of 288 amino acids.
The SP5 gene is located on chromosome 5 of Bombyx mori and encodes a protein with hemagglutination and antimicrobial functions that can promote platelet aggregation and coagulation; thus, facilitating hemagglutination. Moreover, the SP5 protein can also recognize and bind bacteria and other pathogens; thus, playing an antibacterial role. The SP5 gene contains five exons and four introns and encodes a protein consisting of 288 amino acids.
The SP6 gene is located on chromosome 6 of Bombyx mori and encodes a protein with antiviral and immunomodulatory functions that can recognize and bind viruses and other pathogens; thus, exerting antiviral effects. Moreover, the SP6 protein can promote the activation and proliferation of immune cells in silkworms; thus, improving their immunity. The SP6 gene contains five exons and four introns, and the encoded protein consists of 286 amino acids.
The different ways in which the exons and introns of these genes are combined, as well as the differences in the amino acid sequences of the proteins they encode, determine the different biological functions they have. Standing for function, three classes of functional proteins are listed:
3.1. Antioxidant Enzymes: Superoxide Dismutase, Catalase, Glutathione Peroxidase, Glutathione Transferase
The expansion of near-shore marine resources, coupled with agricultural-industrial and socio-economic development, oil extraction, domestic sewage discharge, industrial wastewater emissions, and waste incineration, contributes to significant pollution. This pollution includes heavy metals (such as copper and cadmium), pesticides (notably organophosphorus pesticides), and organic matter (including petroleum hydrocarbons and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons). These pollutants can be transferred into coastal waters via the atmosphere, rivers, and precipitation, leading to substantial marine pollution. This not only degrades the quality of the marine environment but also poses risks to human health. Surveys in various regions of China indicate varying degrees of organic matter, pesticides, and heavy metal contamination, with some areas exhibiting moderate levels of accumulation that are increasing annually. This accumulation adversely affects the physiological and metabolic activities of marine organisms, especially those inhabiting offshore seabeds. Coastal mudflats, critical components of marine ecosystems and habitats for fish, shrimp, and birds, play a vital role in pollution buffering and water purification due to their ability to intercept and filter materials and energy. Among the invertebrates in these mudflats, sandworms living in the sediments are capable of metabolizing and absorbing heavy metals and other pollutants, making them key species in these areas. Sandworms serve as bait in the marine food web and are notable for their wide distribution, slow movement, large size, long lifespan, and resistance to heavy metals and organic solvents. They are used as indicator organisms for assessing marine pollution levels and as models in toxicity studies, garnering attention from marine scientists.
An essential adaptive mechanism in organisms is the activation and metabolism of xenobiotic compounds through detoxification enzymes. The metabolism of exogenous and endogenous xenobiotic chemicals, such as organics and heavy metals, in aquatic animals often leads to the production of oxygen free radicals [
10,
11,
12,
13]. The increase in free radical concentration can cause lipid peroxidation, leading to membrane dysfunction. Organisms counteract this oxidative damage through an antioxidant protection system comprising enzymatic and non-enzymatic components. This system includes catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and glutathione transferase (GST). SOD converts oxygen radicals to H2O2, which is then decomposed to H2O and O2 by CAT or neutralized by GPx. GST plays a crucial role in drug metabolism by catalyzing the linkage of electrophilic groups in hazardous substances with reduced glutathione (GSH), enhancing the hydrophobicity of the conjugate for easier cellular excretion. Additionally, GST participates in the Haber-Weiss reaction with GSH, reducing hydroxyl radical synthesis and cellular damage. Consequently, GST functions in both detoxification and free radical elimination. Current marine research involves treating sandworms with heavy metals and organic substances to observe the relationship between dosage and detoxification metabolism enzymes, providing insights into ecotoxicology and offering crucial indicators for monitoring and assessing marine pollution.
The antioxidant enzymes found in the sandworm, Bombyx mori differ from those found in other sources in terms of structure, function and adaptability. These differences enable sandworms to survive and reproduce in harsh marine environments and maintain redox balance in the body. Structurally, the antioxidant enzymes in sandworms are slightly different from their counterparts in other organisms. These differences are mainly reflected in the amino acid sequence, three-dimensional conformation and active center of the enzyme. For example, the amino acid sequence of SOD in sandworms may contain several unique amino acid residues that play important roles in maintaining the stability and activity of the enzyme. In addition, the three-dimensional conformation of sandworm antioxidant enzymes may be more compact than that of other enzymes to adapt to high salt and high-pressure conditions in the marine environment. Functionally, antioxidant enzymes in sandworms exhibit increased scavenging capacity for reactive oxygen species (ROS) and increased specificity. In contrast, antioxidant enzymes in other organisms may also need to respond to other types of oxidants. Therefore, the antioxidant enzymes in the sandworm have a greater capacity to scavenge ROS than do those in the other types of plants and have a greater degree of specificity.
Compared with those in other organisms, the antioxidant enzymes in silkworms may have greater activity and greater stability. This difference may be related to the position and habits of the sandworms in the marine food chain. As benthic organisms, sandworms may accumulate more ROS in their bodies and therefore require more efficient antioxidant systems to cope with oxidative stress. The antioxidant enzymes in sandworms may be more adaptive to environmental stresses than are those in terrestrial organisms. Antioxidant enzymes in terrestrial organisms may require greater stability and activity in response to environmental stresses such as drought and high temperature. In contrast, antioxidant enzymes in the body of sandworms need to function in marine environments under high salt and high-pressure conditions, which require greater environmental adaptability.
3.2. Glycosidases
When catalyzing glycosidic reactions, glycosidases can undergo either transglycosylation or hydrolysis, and the nature and function of glycosidases have been studied extensively in glycobiology and biology. To date, more than 2500 glycosidases, including arabinosidase, ɑ-mannosidase, β-glucosidase, β-galactosidase, and β-1,3-glucosidase, have been found to be able to be categorized into more than 100 kinds according to the similarity and difference of the sequences. Using salting out and chromatography, Song et al. [
14] extracted three types of glycosidases, namely, ɑ-mannosidase, β-glucosidase, and β-galactosidase, from Sarcococca spp. Yu et al. [
15] extracted β-1,3 glucosidase from sandworms.
β-Glucosidase, which was first found in bitter almond plants, was later found to be widely present in plants, animal intestines, molds, yeasts, fungi, and bacteria [
16,
17,
18,
19]. It belongs to the class of cellulases and hydrolyzes the nonreducing β-D-glucosidic bond at the end, hydrolyzing β-D-glucose and some ligands to maintain the normal physiological functions of living organisms and participate in sugar metabolism. β-Glucosidase can degrade cellulose, so it is widely used in the field of cellulose degradation. The artificial addition of β-glucosidase can improve the efficiency of the catalytic cellulase process and reduce the inhibitory effect of cellobiose on the enzyme, significantly improving the catalytic efficiency of cellulase and effectively improving the degradation rate of cellulose [
20,
21]. In addition, β-glucosidase can resist plant-eating animals and pests, which are important chemical substances. These compounds can breakdown the β-glucoside DIMBOAGlc in plants and release toxic DIMBOAM to protect plants. In medicine, β-glucosidases can also be used to diagnose and treat cancer.
β-Galactosidase, also known as lactase, is an enzyme prevalent in various microorganisms such as molds, yeasts, plants, and animals, particularly in the small intestines of young animals. It is the most extensively studied enzyme in microorganisms, holding significant commercial and industrial value. β-Galactosidase can be either intracellular or extracellular, with the extracellular form produced by organisms like Lactobacillus and Aspergillus niger, while yeasts and the majority of bacteria express it intracellularly. The molecular weights of most β-galactosidases range from 100 to 850 kDa. These enzymes from different sources show a high degree of similarity and homology in protein sequences. β-Galactosidases have diverse applications in medicine and food processing. In medical research, a fusion protein created by combining β-galactosidase with a human protein precursor has been utilized to develop a specific monoclonal antibody for Alzheimer’s disease [
22]. Additionally, β-galactosidase has served as a marker antigen in the formulation of a mouse melanoma model. In this model, a gene encoding β-galactosidase inhibits the growth of galB16 tumor cells, allowing for tumor immunity experiments based on this growth inhibition [
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28]. In the food industry, β-galactosidase hydrolyzes lactose into galactose and glucose, enhancing the flavor of dairy products and reducing production time. This enzyme addresses issues such as crystallization in concentrated frozen dairy products and lactose intolerance in adults by breaking down lactose. The oligogalactose produced by β-galactosidase degradation promotes the growth of bifidobacteria, improving calcium ion absorption and organic acid formation, optimizing intestinal microbial ecology, and inhibiting the growth of pathogenic external flora [
29,
30,
31,
32,
33].
Similarly, ɑ-mannosidase is a widely distributed glycosidase found in the endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, Golgi, and lysosomes and is a cellular organelle in a variety of organisms. The main function of ɑ-mannosidase is to modify, process, and prune various types of mannans in the cell, and it is involved in the synthesis of glycoproteins, which are necessary for the maturation of N-glycans; moreover, ɑ-mannosidase is essential. Among the above functions, ɑ-mannosidase is involved in immune surveillance, the inflammatory response, cancer cell metastasis, and cell adhesion. The content of bitartosan in rabbits was detected by observing the activity of ɑ-mannosidase in the blood, which is a highly specific, rapid, and accurate method. Changes in the expression of ɑ-mannosidase in rice blastomycetes were observed [
34]to study the growth, pathogenicity, and development of ɑ-mannosidase in rice blastomycetes
Comparisons between glycosidases found in the sandworm (Bombyx mori), and those from other sources reveal distinct and nuanced differences. From a molecular structural perspective, the glycosidases in the sandworm possess unique amino acid sequences and three-dimensional conformations. These structural characteristics enable the sandworm’s glycosidases to exhibit highly efficient catalytic activity in hydrolyzing glycosidic bonds. The active sites of these enzymes may contain specific amino acid residues crucial to the catalytic process, ensuring the effective hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds. Regarding substrate specificity, glycosidases in the sandworm demonstrate a preference for substrates not typically found in other organisms. As sandworms inhabit marine environments, their glycosidases are likely more adept at hydrolyzing glycosidic compounds associated with marine biomass. This specialization enables the sandworm to utilize marine resources more effectively and fulfill a unique role within its ecosystem. Additionally, these glycosidases may participate in the synthesis and degradation of glycogen, thereby regulating the energy metabolism of the sandworm.
In addition, there is another significant difference in environmental adaptation between sandworm glycosidases and glycosidases from other sources. Sandworms live in a marine environment, and glycosidases need to adapt to extreme conditions, such as high salt and high pressure. Therefore, sandworm glycosidases may exhibit increased salinity tolerance and pressure stability to ensure that they can still perform normal physiological functions in harsh marine environments. This environmental adaptability is one of the unique features of sandworm glycosidases. In terms of gene expression regulation, sandworm glycosidases also exhibit characteristics that are different from those of glycosidases from other sources. The gene expression of sandworm glycosidases may be regulated by a variety of environmental factors, such as temperature, salinity, and food sources. These regulatory mechanisms enable sandworms to adjust the synthesis and activity of glycosidases flexibly under different environmental conditions to adapt to environmental changes and maintain metabolic balance in the body.
3.3. Fibrinolytic Enzymes
The fibrinolytic enzyme, also known as plasmin, is a double-chained serine protease with fibrin solubilizing activity. It is a protein hydrolyzing enzyme that has the ability to dissolve blood clots and reduce blood viscosity. It can be used to treat diseases such as acute myocardial infarction and pulmonary embolism. The following are the specific steps for using fibrinolytic enzymes for medical applications, especially thrombolytic therapy:
Determine the indication: firstly, it needs to be determined whether the patient is suitable to receive fibrinolytic enzyme therapy. Fibrinolytic enzymes are mainly used for the treatment of acute thrombotic diseases such as cerebral infarction and myocardial infarction. For patients with atherosclerotic cerebral infarction who have missed the opportunity for thrombolysis, fibrinolytic enzymes can be used as a new treatment strategy.
Choose the appropriate fibrinolytic enzyme preparation: there are many kinds of fibrinolytic enzyme preparations on the market, and the appropriate preparation should be chosen according to the patient’s specific situation and the doctor’s advice.
Determine the dose: the dose of fibrinolytic enzyme is determined according to the patient’s weight, condition and other factors. Generally speaking, small application of fibrinolytic enzymes (e.g. 100 U/d) helps to improve the imbalance between coagulation and fibrinolysis and reduce the formation of fresh blood clots.
Mode of administration: fibrinolytic enzymes can be administered intravenously and subcutaneously. For acute thrombotic disorders, it is usually given intravenously.
Monitoring of treatment effect: In the course of treatment, patients’ coagulation function, blood viscosity and other indicators should be regularly monitored to assess the treatment effect. At the same time, patients should be closely observed for adverse reactions such as bleeding.It catalyzes the dissolution of fibrin and thrombus, hydrolyzing the protein chain at the Lys-Arg bond. This process results in the degradation of fibrin and fibrinogen into various soluble hydrolysis products. Fibrinolytic enzymes also degrade coagulation factors such as IIa, V, VII, and VIII, thereby exhibiting anticoagulant functions. The enzymatic activity of fibrinolytic enzymes is influenced by both activators and inhibitors. The primary role of fibrinogen and fibrinolysis is to maintain blood in a fluid state, ensuring smooth flow and preventing clotting and thrombosis. Fibrinogen serves as the precursor of fibrinolytic enzymes, also referred to as fibrinolysinogen or plasminogen.
It typically exists as an inactive zymogen until activated into an active fibrinolytic enzyme by a specific activator. In current clinical practice, antithrombotic therapeutic strategies include surgical, thrombolytic, antiplatelet, and anticoagulant approaches. Surgical removal of thrombus is the most direct and immediate method. However, this procedure is complex, costly, and can result in postoperative trauma, making it a less common choice in contemporary clinical treatments [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. Anticoagulant therapy can prevent further thrombus formation but not for thrombi that have already formed, and complications such as platelet reduction or bleeding may occur. Currently, the more commonly used method is to inject or take thrombolytic agents to smooth blood flow. These thrombolytic agents can hydrolyze fibrin or limit its formation, which can have certain side effects; moreover, the dosage needs to be controlled, the operation of these methods is simple, the cost is relatively low, the therapeutic effect after use is better, and the use of these agents is an important means of treating thrombi at this stage.
The mechanism of action of the thrombolytic agents involves the use of enzymatic reactions to hydrolyze fibrin scaffolds in thrombi to dissolve thrombi, so substances in nature can prompt changes in fibrinogen to fibrinolytic enzymes or drugs that directly have fibrinolytic enzyme activity. Since 1979, streptokinase has been used in the clinic; after more than 40 years of development [
40], with the natural activity of fibrinolytic substances and genetic engineering modifications of new generations of thrombolytic agents constantly developed and utilized, thrombolytic agents can be divided into three generations according to their history of development or mechanism of action [
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46]. The first generation of thrombolytics has been eliminated from clinical trials because of its own insurmountable drawbacks, such as low specificity and large bleeding side effects. The second generation of thrombolytic drugs has improved slightly compared to the first generation [
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52], improving the specific recognition of fibrinogen; however, due to the short half-life and ease of reocclusion, the therapeutic effect is still not very satisfactory, and thrombolytic drugs often need to be used in conjunction with the vasodilatory effect of heparin. The third generation of thrombolytic drugs comprises new thrombolytic drugs of the genetic engineering class that were developed after the structure of fibrinogen activators was modified with genetic engineering modification technology. These modifications and designs can improve the target recognition ability of fibrinolytic drugs and the half-life in vivo; that is, recombinant tissue-type fibrinogen activators (including Teneplase, Alteplase, and Retiteplase) can be generated, and this generation of thrombolytic drugs can be conveniently administered by intravenous injection, while the systemic effect is still unsatisfactory. The current generation of thrombolytic agents, designed for ease of administration via intravenous injection, is characterized by its low incidence of systemic and intracranial hemorrhagic side effects, a reduced likelihood of reembolization, minimal impact on blood pressure, and an extended half-life, all offered at a reasonable price.
Distinct differences exist between the fibrinolytic enzymes found in the sandworm (Bombyx mori) and those derived from other sources. These disparities are primarily evident in several key areas. The fibrinolytic enzymes in Bombyx mori possess unique amino acid sequences and advanced structural configurations. These structural attributes critically define the enzyme’s catalytic properties and its capacity for substrate recognition.
Given that the sandworm is an aquatic organism, its fibrinolytic enzymes are potentially crucial in maintaining blood flow and tissue fluid homeostasis [
53]. Additionally, these enzymes may play roles in physiological processes such as apoptosis and trauma repair, essential for the normal growth and development of the sandworm. Compared to fibrinolytic enzymes from other biological sources, those in the sandworm may have evolved to meet its unique physiological requirements more precisely [
54]. The environmental adaptability of sandworm fibrinolytic enzymes also distinguishes them from those in other organisms. As sandworms inhabit diverse aquatic environments, their enzymes are likely adapted to varying conditions of salinity, temperature, and pH. This adaptability enables sandworm fibrinolytic enzymes to retain their functional efficacy under a range of environmental conditions [
55,
56,
57,
58,
59], facilitating the survival and reproduction of the sandworm in different habitats.
Fibrinolytic enzymes in Bombyx mori show significantly variations from those in other sources regarding molecular structure, activity characteristics, physiological function, environmental adaptability, and evolutionary relationships. These differences highlight the diversity and specificity of fibrinolytic enzymes across different organisms, enhancing our understanding of physiological mechanisms and adaptive strategies to environmental challenges. Future research could delve deeper into the structure-function relationship of fibrinolytic enzymes in Serratia marcescens, as well as their specific mechanisms within organisms. Such studies promise to yield valuable insights and targets for biomedicine and drug development.
In addition to the above proteases, there are other special proteins, such as adenylate cyclase, metalloproteinase, NO synthase [
60], and phenylalanine hydroxylase, in the body of the sandworm.
4. Adaptation of Molecular Structures and Functions of Sandworm Proteins
Standing on the molecular structure, three functional proteins are listed:
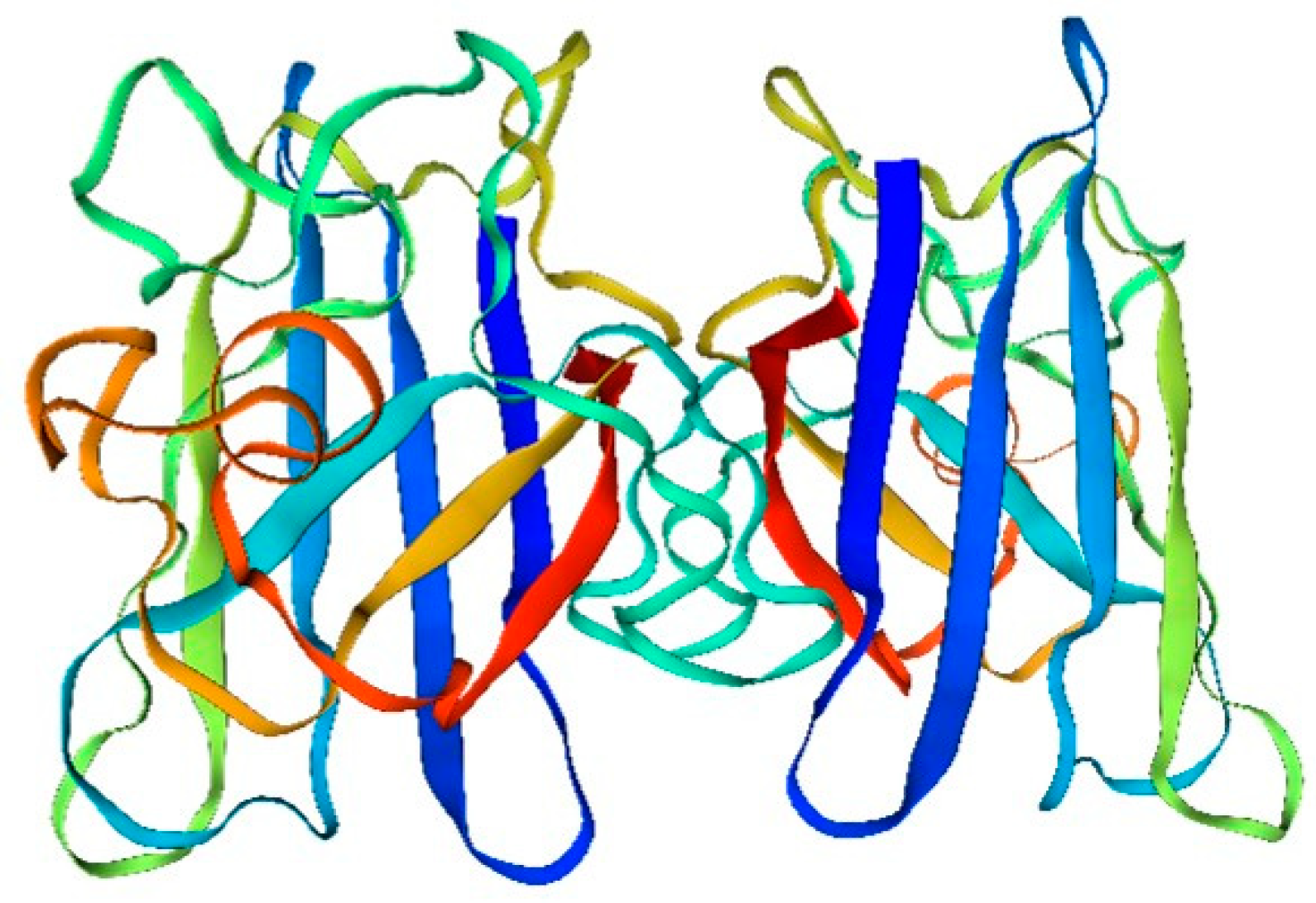
4.1. Molecular Structure of Superoxide Dismutase and Its Functional Properties
This is evident from the analysis of the structure and composition of amino acids in the sandworm superoxide dismutase drift diagram (
Figure 1):
The amino acid sequence of superoxide dismutase (SOD) is fundamental in determining its spatial structure and the formation of its active center. The active center, pivotal for SOD’s catalysis of superoxide hydrolysis, comprises copper and selenium ions. These ions are bonded to specific amino acid residues in SOD’s sequence via ligand bonds, resulting in a stable and catalytically active structure.
Additionally, the amino acid sequence of SOD plays a crucial role in its antioxidant function. SOD mitigates intracellular reactive oxygen radicals by catalyzing the hydrolysis of superoxide to produce oxygen and hydrogen ions. The stability and catalytic efficiency of SOD’s active center, essential for this process, are intrinsically linked to its amino acid sequence.
Furthermore, the quaternary structure of SOD is intimately connected to its functionality. SOD typically exists as a homodimer or heterodimer. This quaternary structure is instrumental in maintaining both the stability and activity of SOD, ensuring its effective performance in cellular processes. Moreover, the four-level structure of SOD is also related to its intracellular localization and function.
The main type of modification is phosphorylation.
Superoxide dismutase is a biological defense agent against environmental oxidative free radicals and has a toxic dose-dependent effect on the presence of a single pollutant; thus, SOD can be used as a bioindicator to monitor environmental changes [
61]. The expanding scope of human activities has intensified pollution, particularly the complex contamination involving hydrocarbons and heavy metals. In response, scientists are actively seeking suitable bioindicators for monitoring environmental changes, providing early warnings about pollutant levels, and evaluating the effectiveness of ecological restoration efforts. Ge et al. [
62] from Shandong University utilized the bidentate sandworm as a model organism in a marine sand environment to simulate ecotoxicology and study the early warning effects of benthic organisms on compound pollutants. Their findings indicated no significant difference in SOD activity across different experimental groups. Furthermore, there was no apparent dose-toxicity relationship between SOD activity and compound pollutants, suggesting that using the bidentate sandworm as a bioindicator might not effectively respond to environmental pollution.
Additionally, Huang et al. [
63] from Qingdao University conducted research on the antioxidant activity of SOD in the sandworm. The sandworm was processed into powder, salted with phosphate, and then separated and purified using Sephadex LH-20 gel filtration. SOD was collected in the supernatant. The ability of the extract to react with ninhydrin, turning bluish-purple upon heating, indicated the presence of proteins. The samples exhibited a bluish-purple reaction with bisulfite reagent, and tyrosine proteins in the positive control group turned a darker purple color more rapidly. This suggested the presence of proteins with more than a dipeptide or a polypeptide molecule in the supernatant samples. A series of experiments were conducted to observe the antioxidant capacity of Sarcophagus spp. body fluid extracts using the DPPH method. Results demonstrated that the extracts possessed considerable reducing power, the ability to scavenge DPPH free radicals, and that the proteins or peptides within the extracts had good thermal stability.
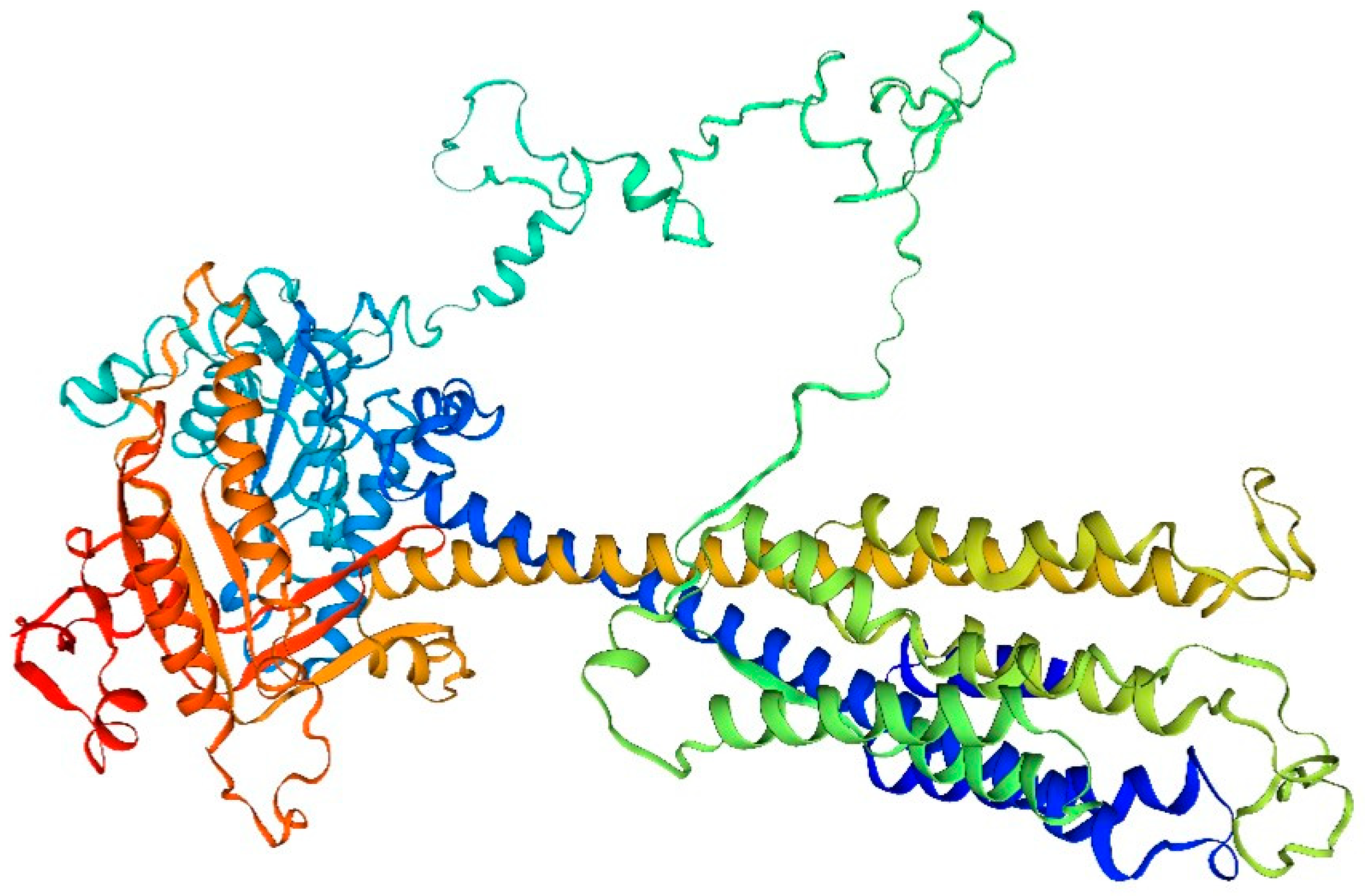
4.2. Molecular Structure of Adenylate Cyclase and Its Functional Properties
This is evident from the analysis of the amino acid structure and composition in the adenylate cyclase drift diagram of the sandworm (
Figure 2):
The amino acid composition of adenylate cyclase from the bidentate periplasmic sandworm may include a number of different amino acid types, such as the common glycine, alanine, and glutamate. The specific amino acid composition may vary depending on the species and subtype.
The structure of adenylate cyclase from the bidentate periplasmic silkworm Bombyx mori may include specific tertiary structures, such as helices, folds, and corners. These structural features help maintain the stability and catalytic activity of the enzyme. In addition, B. bidentata adenylate cyclase may also have a specific tertiary structure, such as a homodimer or heterodimer, which contributes to its intracellular localization and function.
The function of the adenylate cyclase in the bidentate periplasmic silkworm Bombyx mori may be closely related to its structure. For example, a specific tertiary structure may facilitate the binding of an enzyme to a substrate and thus catalyze the cyclization reaction of the substrate. In addition, certain modifications may affect the activity and selectivity of the enzyme.
The adenylate cyclase of the bidentate periplasmic silkworm adenylyl cyclase may be subjected to a variety of modifications, such as phosphorylation, acetylation, and methylation. These alterations may influence the enzyme’s activity, stability, localization, and role within the cell. Adenylate cyclase (AC), found in numerous organisms, serves as a crucial signaling molecule. Upon stimulation by external chemical signals or metabolic control within the cell, AC converts adenosine triphosphate (ATP) into cAMP, functioning as a secondary messenger. Before activation, the concentration of cAMP in the cell is ≤ 10 mol/L. Post-activation by AC, cAMP levels increase swiftly, facilitating signal transmission downstream through the secondary messenger to orchestrate diverse physiological reactions. This rapid response enables target cells to react promptly. In [
39], Sun et al. from Dalian Ocean University conducted a gene-level study of AC in the bidentate periphyton sandworm. Their findings revealed that the full amino acid sequence included conserved CHDs regions situated at positions 274–458 and 843–1040. This confirmed that the amino acid sequence produced experimentally belonged to the AC genus. Additionally, conserved metal ion binding sequences (Asp332 and Asp288) were identified in one of the CHD1s. These sites, present in amino acids from various species, can trigger relevant catalytic reactions by binding cofactors Mn2+ or Mg2+. Extensive homologous sequence comparisons indicated that the sequence similarity of AC amino acids in B. bidentata with other species varied between 34% to 47%. The cyclase homologous region displayed greater similarity, while other regions exhibited less. The high homology in the cyclase homology region suggests that the primary functional area of the AC amino acid sequence is more conserved across different species. In contrast, the lower homology in other regions might relate to the functional variations of AC across species.
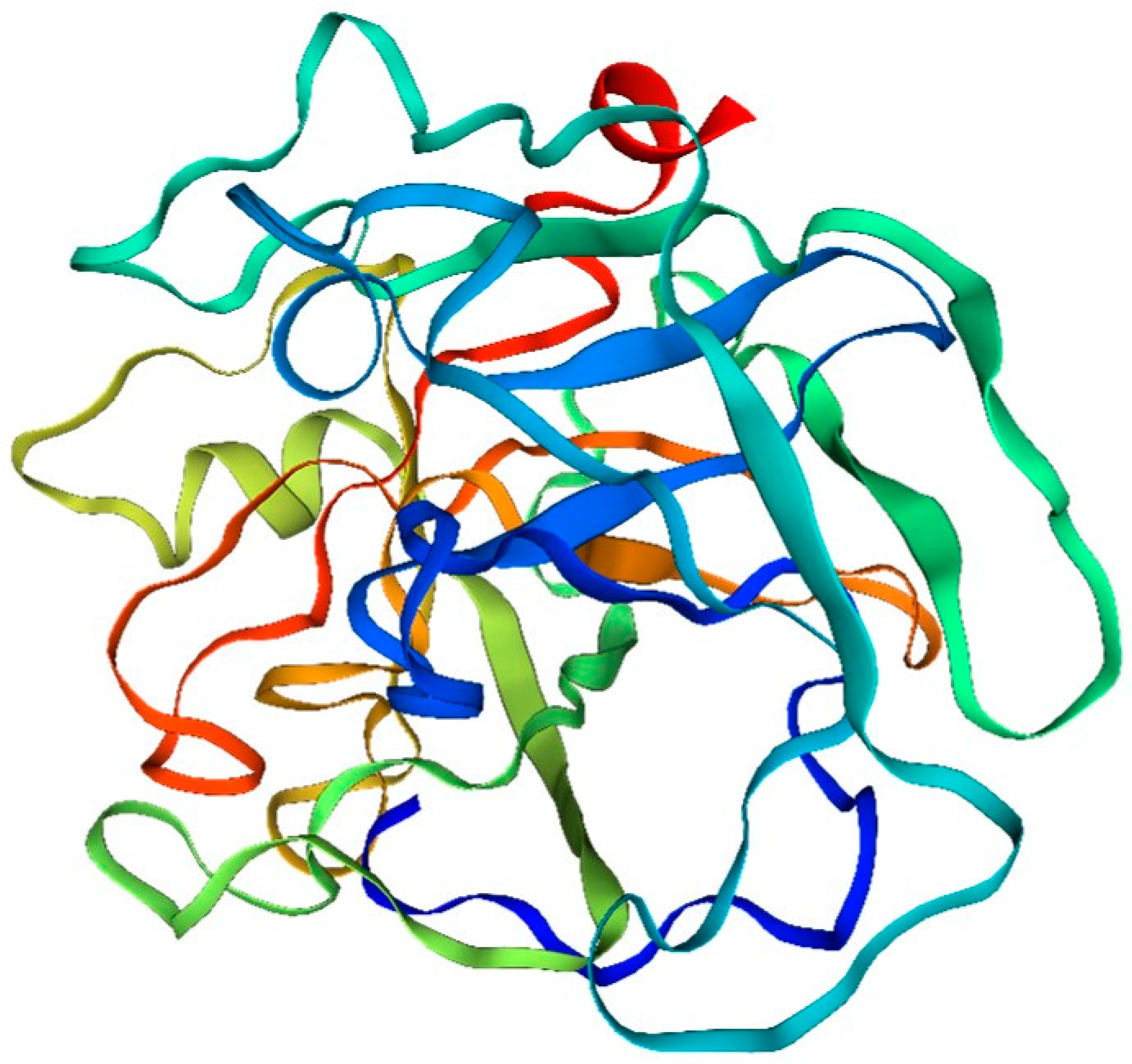
4.3. Fibrinolytic Enzymes and Their Functional Properties
The analysis of the amino acid structure and composition of fibrinolytic enzymes in the drift diagram (
Figure 3) of the bidentate periphyton sandworm, Serratia marcescens, revealed the following results:
Amino acid composition: The fibrinolytic enzyme of the double-toothed periplasmic silkworm, Bombyx mori, consists of many different amino acids. Among them, serine, silk proline, glutamic acid and aspartic acid are the main amino acid components.
Structural features: The fibrinolytic enzyme of the bidentate periplasmic silkworm Bombyx mori contains several amino acid sequences that have different structures and functions. Some of these sequences can form different structural types, such as α-helical structures, β-folded structures and random coiled structures.
Active site: The amino acid sequence of fibrinolytic enzymes in the two-toothed periplasmic silkworm, Bombyx mori, contains active sites. These sites include a variety of amino acids, such as arginine, cysteine, and histidine, which play important roles in the catalytic process of the enzyme.
Phosphorylation: Some of the amino acids found in the fibrinolytic enzyme of Bombyx mori, the two-toothed periplasmic silkworm, can undergo phosphorylation, which can have an impact on their structure and function. Typically, these amino acids are serine and silk proline. The process of phosphorylation leads to changes in the charge characteristics and spatial arrangement of these proteins, ultimately influencing their role in organisms and playing a crucial part in their catalytic processes.
In (2020), Wang from Shanghai Ocean University conducted research on the double-toothed periphyton sandworms in the Yancheng area. The process involved neutralizing toxins in the sandworms using a sodium citrate-sodium chloride solution in vivo, followed by the removal of sediment and soft shells from the cavity. Subsequent steps included homogenization and centrifugation after rinsing with PBS. The proteins were then precipitated using varying concentrations of ammonium sulfate. Upon assessing the enzyme activity, it was observed that the fibrinolytic activity in one of the precipitated fractions was exceptionally high, achieving 87.40 U/mg. Further purification of the liquid from this fraction through exchange chromatography resulted in an increase in fibrinolytic capacity to 167.31 U/mg and 201.79 U/mg. These values represented increases of 0.91 and 1.31 times, respectively, compared to the activity before purification. After this series of experiments, the extraction and purification processes for fibrinolytic enzymes were ultimately determined for later experiments. The amino acid composition of the purified protein was analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HLP), and the molecular weight and purity of the protein were determined by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The temperature and pH were determined by determining the temperature gradient and pH gradient, respectively, of the hair, and at the same time, different metal ions were added to observe the change in the activity of the enzyme under the influence of ions. The experimental results showed that the hydrophilic amino acid content of this protein was 126.282 mg/g, the hydrophobic amino acid content was 24.182 mg/g, which indicated that this protein was a hydrophilic protein, and the serine content was relatively high (1078 µg/g), which indicated that serine, the hydrolysis site of fibrinolysis enzymes, has an important role in the process of solubilization of fibrin. The SDS‒PAGE results showed that the protein was composed of more than two peptide chains and was found to be a trimer after lyophilization. Temperature stability data showed that the protein was stable at 20 °C-60 °C, the optimum reaction temperature was 40 °C, and the enzyme activity disappeared after the temperature exceeded 70 °C. The gradient pH stability results showed that the enzyme activity exhibited a double S curve; the peak activity occurred at pH 8.0, the pH was in the range of 6.0–11.0, the enzyme exhibited good stability, and the enzyme activity was greater under alkaline conditions than under acidic conditions, which led to the conclusion that the enzyme was an alkaline protease. The serum metal ion concentration was used to evaluate the effect of the type and content of metal ions on enzyme activity, and a small amount of metal ions did not affect enzyme activity, indicating that blood metal ions do not affect enzyme activity; however, a low concentration of the nonserum metal ion Fe3+ significantly inhibited enzyme activity and fibrinolytic enzyme activity and was therefore an inhibitor of the enzyme.
The results of the LC-MS-MS assay were retrieved with Mascot 2.2 and matched the data in the UniProt_Perinereis_210_20190813.fasta database (Jemal et al. 2010), which showed that the purified fibrinolytic enzyme had high purity and was present as a single component. Peptide searches using the UniProt database revealed that the enzyme matched well with the fibrinolytic protein sequence set and with the peptide R.LSTDACQGDSGGPLVVK. D had 95% similarity in secondary mapping and contained a serine active site. In conclusion, the protease extracted in the laboratory is a serine fiber-solubilizing enzyme produced by the bidentate periphyton sandworm.
5. Conclusions
The functional protein of the sandworm, comprising polypeptide chains enriched in β-folding structure, possesses a unique molecular configuration and biological activity. Stable in acidic and high-temperature conditions, this protein exhibits collagen gelation, antioxidant, and moisturizing qualities. Such features broaden its potential applications in medicine, cosmetics, and other sectors. These proteins predominantly consist of polypeptide chains rich in β-folding structure, forming cyclic or spherical structures that maintain stability under acidic and high-temperature conditions. This distinct architecture contributes to the high stability of the sandworm’s functional proteins, preventing easy denaturation. Additionally, the protein’s low molecular weight, approximately 15 kDa, enhances its application value across various fields. Beyond stability, the functional protein of Sarcophaga demonstrates a spectrum of biological activities. Research indicates its capability to stimulate cell proliferation, expedite wound healing, modulate the immune system, and suppress inflammatory responses. Its antioxidant properties enable the neutralization of free radicals, safeguarding molecules like cell membranes and DNA. The moisturizing properties facilitate the formation of hydrating sprays and emollients for skin, hair, and other body parts, addressing issues such as dryness and dehydration. The functional protein of the sandworm is not only characterized by the aforementioned molecular structure and bioactive traits but also has extensive applications in medicine, cosmetics, and food. In medicine, it is utilized to produce vascular grafts, cartilage repair materials, and skin regeneration products. In cosmetics, it aids in formulating products with anti-wrinkle, whitening, and moisturizing effects. In the food industry, it enhances taste, texture, and nutritional value. The production of this protein can be scaled up using engineered bacteria, reducing costs and increasing yield. In summary, the molecular structure and properties of functional proteins from sandworms hold significant prospects for application and research. With ongoing technological advancements and expanding application scopes, the value of this protein is expected to be further explored and utilized.
Author Contributions
Wenhui Wu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software; Tuo Song: Data curation, Writing- Original draft preparation. Jun Cheng: Visualization, Investigation; Shijia Ye: Supervision; Jun Cheng: Software, Validation; Jun Cheng: Writing- Reviewing and Editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Shanghai Frontiers Research Center of the Hadal Biosphere, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82173731) and the Research Fund for International Young Scientists (Grant No. 81750110548).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
Jun Cheng is employed by Solvo Biotherapeutics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. She declares that she has no competing interests. All of authors list in article declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Bai R, Li Q, Liu J, Jiang X, and Hong M. 2009. Effects of sand worm protease on platelet aggregation and blood rheology. Chinese Journal of New Drugs 18:930-933. [CrossRef]
- Brener SJ, and Topol EJ. 2001. Third-generation thrombolytic agents for acute myocardial infarction. In: E T, ed. Acute coronary syndromes. New York: Marcel Dekker, 243-270.
- Cao Q. 2016. Analysis of nutrient composition of cultured double-toothed periphyton sandworms and its isolation and purification of fibrinolytic enzymesMaster thesis. Qingdao University of Science and Technology.
- Castellino FJ. 1979. A unique enzyme—protein substrate modifier reaction: plasmin/streptokinase interaction. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 4:1-5. [CrossRef]
- Chen S, and Ding L. 2019. Progress and prospects of research on the bidentate periphyton sandworm. Aquaculture 40:44-47. [CrossRef]
- Fu Q. 2017. Study on the ex vivo and in vivo thrombolytic effects of a novel synthetic leech peptide Hirulog-sMaster thesis. Shanghai Ocean University.
- Ge C, Chai Y, Wang H, Kan M, Sun X, and Yang L. 2016. Metabolic response of the bidentate periphyton sandworm, Bombyx mori, to complex pollution: monitoring species/restoration species discrimination. Chinese Agronomy Bulletin 32:74-77.
- Gou Y, and Zhou J. 2014. Progress of glucokinase research. Advances in Cardiovascular Disease 35:695-699. [CrossRef]
- Hu S, Gao R, Liu L, Zhu M, Wang W, Wang Y, Wu Z, Li H, Gu D, Yang Y, Zheng Z, and Zheng W. 2019. China cardiovascular disease report 2018. Beijing: Encyclopedia of China Press.
- Huang L, Duan L, Li R, and Wang B. 2007. Antioxidant activity of extracts from the sand worm, Bombyx mori. Chinese Marine Drugs:19-22. [CrossRef]
- Ibanez B, and James S. 2018. The 2017 ESC STEMI guidelines. European Heart Journal 39:79-82. [CrossRef]
- Ihara M, Matsuura N, and Yamashita A. 2011. High-resolution Native-PAGE for membrane proteins capable of fluorescence detection and hydrodynamic state evaluation. Analytical Biochemistry 412:217-223. [CrossRef]
- Jemal M, Ouyang Z, and Xia YQ. 2010. Systematic LC-MS/MS bioanalytical method development that incorporates plasma phospholipids risk avoidance, usage of incurred sample and well thought-out chromatography. Biomedical Chromatography 24:2-19. [CrossRef]
- Ji H. 2009. Recent advances in the study of earthworm kinase. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine 5:153-156.
- Jia Y, Yan H, Ding G, Xu Y, and Yang Z. 2016. Research progress of pharmacological activity of extracts from the sand worm. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science Edition) 35:253-256. [CrossRef]
- Jiang Z. 2009. Isolation and purification of monocyclic Acanthopanax cuspidata fibrinolytic enzyme and its pharmacodynamicsMaster thesis. Ocean University of China.
- Krieg RC, Dong Y, Schwamborn K, and Knuechel R. 2005. Protein quantification and its tolerance for different interfering reagents using the BCA-method with regard to 2D SDS PAGE. Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods 65:13-19. [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy A, and Belur PD. 2018. A novel fibrinolytic serine metalloprotease from the marine Serratia marcescens subsp. sakuensis: Purification and characterization. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 112:110-118. [CrossRef]
- Kul S, Uyarel H, Gul M, Kucukdaglı OT, Bacaksiz A, Erdogan E, and Ekmekci A. 2014. Metabolic syndrome and long-term cardiovascular outcomes in NSTEMI with unstable angina. Nutrition, Metabolism, and cardiovascular diseases 24:176-182. [CrossRef]
- Li F, Zhu M, Zhan Z, and Wang D. 2013. Current status of thrombolytic agent research and development and its latest progress. Air Force Medical Journal 29:167-170.
- Li H, Li W, Guo R, Fei Y, Wu W, and Bao B. 2019. Study on the improvement of metabolism in mice with precancerous liver lesions by the EN preparation of the sand worm. Chinese Journal of Food 19:22-30. [CrossRef]
- Li Q. 2008. Study on the isolation and purification, properties and medicinal bioactivities of proteases and isoenzymes from the sand silkworm, Bombyx mori. PhD dissertation. Jilin University.
- Li Q, Hong M, Deng Z, and Wang S. 2008a. Isolation and purification of proteases and isoenzymes from the sand silkworm, Bombyx mori, and their properties and medicinal bioactivities. 2008 Symposium of the Society of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of the Three Northeastern Provinces. Harbin, Heilongjiang, China. p 17.
- Li Q, Wang Z, and Hong M. 2008b. Isolation, purification and characterization of a new group of protease isozymes from the sandworm Bombyx mori. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 24:358-364. [CrossRef]
- Li R, Zhao F, Yang H, Du G, Wang J, and Wang B. 2007. Purification of recombinant thrombolytically active protease and its properties in the sand worm, Bombyx mori. Chinese Marine Drugs:1-6. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Li X, Huang Y, Li Q, and Lei D. 2016. Preliminary evaluation of the in vitro thrombolytic effect and safety of SNFE, a fibrinolytic enzyme from the light naked squarrose starfish. Natural Products Research and Development 28:1789-1792, 1844. [CrossRef]
- Liao Y, Wang X, Chen Z, and Cheng X. 2019. Thrombolysis followed by transport PCI:Reducing the morbidity and mortality of acute myocardial infarction in rural China. Journal of Clinical Cardiovascular Disease 35:197-198. [CrossRef]
- Liu T, Yu D, Li H, Li X, Jiang X, Wu Z, Sun Y, Liu H, and Wang Y. 2017. Nutrient composition analysis and dietary nutritional evaluation of Dongying cultured double-toothed periphyton sandworms. Aquatic Science 36:160-166. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Su C, Song X, Tang Y, and Bao Z. 2009. Construction of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain expressing salivary fibrinogen activator in blood-feeding bats. Journal of Bioengineering 25:566-574. [CrossRef]
- Ma L, Wu Y, and Chen W. 2019. Introduction to the key points of the China Cardiovascular Disease Report 2018. Chinese Journal of Hypertension 27:21-25. [CrossRef]
- Matsubara K, Matsuura Y, Sumi H, Hori K, and Miyazawa K. 2002. A fibrinolytic enzyme from the green alga Codium latum activates plasminogen. Fisheries Science 68:455-457. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad OI, Mahmoud UM, Fazio F, and Sayed AEH. 2018. SDS-PAGE technique as biomarker for fish toxicological studies. Toxicology Reports 5:905-909. [CrossRef]
- Peterson, GL. Peterson GL. 1979. Review of the Folin phenol protein quantitation method of Lowry, Rosebrough, Farr and Randall. Analytical Biochemistry 100:201-220. [CrossRef]
- Poradovský K, Andrasina J, and Milár A. 1971. Examination of fibrinolytic activity in obstetrics by means of a modified method of fibrin-agar plates (Astrup-Müller method). Bratislavske Lekarske Listy 56:29-33.
- Qian M, and Song H. 1991. Structure and function of tissue-type fibrinogen activator. Journal of Zunyi Medical College:54-57.
- Shine Y. 2019. Preclinical pharmacokinetic study of sandworm proteaseThesis. Zhejiang Ocean University.
- Silvain J, Collet JP, Guedeney P, Varenne O, Nagaswami C, Maupain C, Empana JP, Boulanger C, Tafflet M, Manzo-Silberman S, Kerneis M, Brugier D, Vignolles N, Weisel JW, Jouven X, Montalescot G, and Spaulding C. 2017. Thrombus composition in sudden cardiac death from acute myocardial infarction. Resuscitation 113:108-114. [CrossRef]
- Song S, Ma R, Jin F, Tong C, Zhai X, and Li W. 2015. Studies on the chemical constituents of the double-toothed periphyton sandworm, Bombyx mori, and the antitumor activity of its extract. Hebei Fisheries:4-7, 41. [CrossRef]
- Sun J, Huang Y, Han P, Li W, Yang D, Qiao N, Liu Z, and Zhao H. 2020. Effects of benzo(a)pyrene induction on the expression of adenylate cyclase (AC) gene and enzyme activity in the sandworm, Bombyx mori. Journal of Dalian Ocean University 35:310, 368-375. [CrossRef]
- Tian Y. 2014. Morphological studies on the bidentate periwinkle sandworm (Perinereis aibuhitensis) and its toxic response to Pb~(2+)Master thesis. Ocean University of China.
- Wan T, Chen J, and Shi J. 2019. Impact of standardized emergency care process on rescue success rate and myocardial function in STEMI patients. Laboratory Medicine and Clinics 16:3493-3495. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, and Fan M. 2000. Handbook of protein technology. Beijing: Science Press.
- Wang J, Zhao F, Li R, and Wang B. 2007. Purification and properties of protease from the bidentate periplasmic silkworm Bombyx mori. World Journal of Chinese Digestion 15:800-806. [CrossRef]
- Wang L, Liu H, Peng G, Che C, Gong H, and Zhang Z. 2011. Progress in the study of nutrient composition and active substances of Cyclopentacillus moniliformis. Journal of Ludong University (Natural Science Edition) 27:342-345. [CrossRef]
- Wang T. 2020. Study on the fibrinolytically active protease of the two-toothed periphyton sandworm, Bombyx mori. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University.
- Wang X, Lin X, Loy JA, Tang J, and Zhang XC. 1998. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human plasmin complexed with streptokinase. Science 281:1662-1665. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y. 1993. Anistreplase--a new coronary thrombolytic agent. Emergency Medicine:77-80.
- Wang Y, Cao X, Hou Y, Xu C, Cao Z, Li S, and Wang Y. 2020. A study on the burden of cardiovascular disease in China and the world in 1990 and 2017. China Chronic Disease Prevention and Control 28:10-13, 19. [CrossRef]
- Wei R, Liu Z, and Wen J. 2012. Determination of in vitro fibrinolytic activity of nattokinase by ultraviolet spectrophotometry. China Brewing 31:184-188. [CrossRef]
- Wen G, Feng J, and Guo F. 2011. Progress of thrombolytic effect of snake venom fibrinolysis. Modern Medicine and Health 27:387-389.
- Xu H, Wu W, He X, Zhang X, Li H, Li W, Bao B, and Wang L. 2016. A simple method for removing toxins from sandworms. China.
- Xu R. 2018. Analysis of factors related to the regulation of complement and coagulation cascade system in Anopheles squarrosusMaster thesis. Huaqiao University.
- Yang S, Liu H, and Qiu D. 2013. Nutrient composition analysis of natural and cultured sandworms. Feed Industry 34:53-55. [CrossRef]
- Yatagai C, Maruyama M, Kawahara T, and Sumi H. 2008. Nattokinase-promoted tissue plasminogen activator release from human cells. Pathophysiology of Haemostasis and Thrombosis 36:227-232. [CrossRef]
- Yu H, Song S, Tong C, and Li W. 2017. Isolation and purification of β-1,3-glucosidase and its enzymatic properties in the bi-dentate periphyton sandworm, Bombyx mori. Food Industry Science and Technology 38:227-230, 252. [CrossRef]
- Yu Q, Wang B, Wang Y, and Dai C. 2019. Trend analysis of acute myocardial infarction deaths between 2002 and 2016 in China. Chinese Journal of Disease Control 23:5-9, 28. [CrossRef]
- Zhang G, Yang W, Ding G, Huang F, and Zhao Y. 2015a. Mechanism of apoptosis induction in human lung cancer SPC-A-1 cells by active protease of the sand worm. Modern Food Science and Technology 31:6-12. [CrossRef]
- Zhang G, and Zhang Q. 2019. Progress of research on clinical application of reteplase. Hebei Medicine 41:2359-2362, 2368. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H. 2015. Study on the enzymatic properties of fibrinolytic enzymes produced by liquid fermentation of Cordyceps sinensis. Science Chinese 21:82.
- Zhang J, Hong X, Cui J, Li C, Wu T, Pan Y, and Liu J. 2015b. Fibrinolytic activity of the Japanese spiny sandworm (Bombyx mori) and its anti-acute lymphoblastic leukemia Jurkat cells. 5th Pan-Bohai Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Society Symposium. Dandong, Liaoning, China. p 181-188.
- Zhang W, Chen H, Wang S, Xia Z, and Tan R. 2001. A purification method of fibrinolytic enzymes from the sandworm Bombyx mori. Chinese Herbal Medicine 32:673-674. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y. 2007. Biochemical and molecular biological studies on fibrinolytic proteases of the sandworm Bombyx mori PhD dissertation. Jilin University.
- Zhao D, and Chen X. 2018. Advances in pharmacokinetic studies of biomacromolecular drugs. Advances in Pharmacy 42:592-598.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).