Introduction
Visceral adipose tissue (VAT) is a complex and metabolically active tissue, which can produce different adipokines and hormones [
1]. Accumulation of VAT is a strong predictor of all cause, cardiovascular-specific and cancer-specific mortality [
2]. In addition, many studies provided evidence that VAT is closely related to increased risk of insulin resistance [
3,
4], atherosclerosis [
5], dyslipidemia [
6], hypertension [
7], hepatic steatosis [
8] , coronary heart disease [
1,
9] and different types of cancer [
1]. Participating in exercise intervention provided favorable effects on accumulated VAT [
10,
11]. While the majority of interventions focus on aerobic i.e. endurance exercise [
10], there is considerable evidence for significant effects of isolated resistance exercise training (RT) on VAT [
10,
12,
13] in persons with overweight and obesity. Reviewing the exercise protocols of the RT-exercise studies revealed that the majority of studies applied multiple-set protocols for three sessions per week [
12,
13]. Apart from the advanced training volume, most RT protocols [
12] prescribed moderate to high exercise intensity (60-85% 1Repetition Maximum 1RM) with set endpoints to fatigue or failure [
14]. However, considering the limited affinity of people be it with or without overweight and obesity, to join frequent and intensive exercise (RT) programs in conventional gyms, less elaborated training concepts might be an option. Whole-body electromyostimulation [
15], a time-effective, joint friendly and highly customizable training technology might be such a candidate. Preliminary evidence suggests similar positive effects of 1.5x 20 min of RT-type WB-EMS
1 compared to a high intensity RT protocol on fat and fat free mass in untrained, predominately overweight men [
16]. However, to our best knowledge the effects of WB-EMS on VAT has yet to be evaluated in cohorts with overweight or obesity. Thus, the aim of the present study was to determine the effect of WB-EMS on VAT in people with overweight or obesity. Correspondingly, our hypothesis was that WB-EMS significantly decreases VAT compared to control.
Material and methods
Study design
The randomized controlled WB-EMS trial (RCT) is part of the “electromyostimulation for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis (OA) (EMSOAT) study”. The study applied a balanced parallel group design (WB-EMS versus control group) and evaluated the effects of seven months of WB-EMS application on outcomes related to knee osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults with overweight and obesity. The present study focused on WB-EMS effects on visceral adipose tissue volume. Briefly, EMSOAT was planned, initiated and conducted by the Institute of Radiology, University Hospital Nürnberg, Germany. The University Ethics Committee of the FAU approved the trial (Nr. 352_20 B) that fully complies with the Helsinki Declaration “Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects“[
17]. After receiving detailed information, all study participants gave their written informed consent. The project was fully registered under ClinicalTrials.gov: (NCT05672264).
Participants
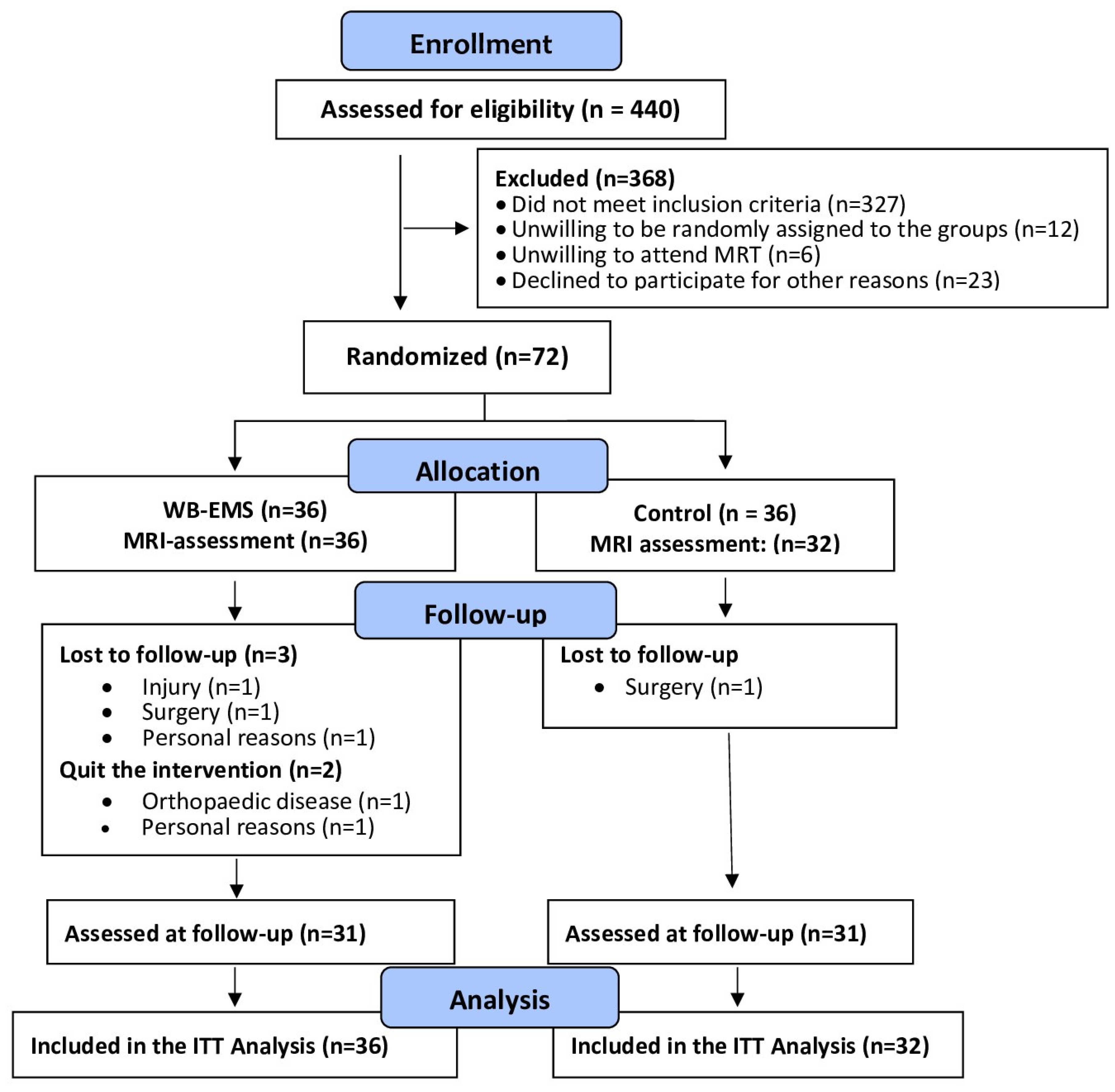
Briefly, between March 2022 and June 2022 local newspapers, social media and selected physicians disseminated our study call that included the core eligibility criteria. A total of 440 women and men responded by email or telephone and were provided with more detailed written study information. Potential participants that confirmed their preliminary eligibility were further checked by detailed standardized phone calls conducted by carefully briefed research assistants. Inclusion criteria applied were (a) age 40-70 years old; (b) overweight or obesity (BMI>25 kg/m
2); (c) fulfilling clinical ACR criteria for knee OA [
18]; (d) osteoarthritic knee pain on at least 50% of the days during the last 3 months with an average pain intensity of >2.5 on a 0-10 numerical rating scale [
19]. Exclusion criteria applied were: (a) any WB-EMS application or regular resistance exercise (≥60 min per week) during the last 12 months; (b) glucocorticoid or opioid pain therapy; (c) trauma of the knee joint within the last 12 weeks; (d) intra-articular injections in the knee joint in the last 12 weeks; (e) conditions, diseases and corresponding therapy with relevant impact on our study outcomes (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia); (f) contraindications for WB-EMS [
20] or MRI-application and (g) ≥4 weeks of absence during the 29-week conditioning and intervention phase. Lastly, the study physician verified final eligibility. Twelve of the 84 eligible participants refused to participate predominately due to the random allocation to the study groups (WB-EMS or control). Thus, finally 72 participants were eligible and willing to participate in the present study. However, mainly due to time constraints four participants (all CG) were unable to join the MRI assessments (i.e. baseline and 29 week control), thus in summary 68 participants with MRI data were included in the present analysis on WB-EMS effects on visceral adipose tissue changes (
Figure 1).
Randomization and blinding
Participants allocated themselves to the WB-EMS or control group by drawing lots. Lots were placed in small opaque capsules (“kinder egg”, Ferrero, Italy) and drawn from a bowl. A researcher not involved in the present project prepared the lots to realize allocation concealment. After the randomization procedure, the primary investigator (SK) enrolled participants and instructed them in detail about their study status and corresponding dos and don´ts. Research assistants, testers and outcome assessors were kept unaware of the participants’ group status (WB-EMS or CG) and were not allowed to ask, either.
Study procedures
The WB-EMS training group (WB-EMS) conducted seven months of WB-EMS application as described below, while the control group (CG) was provided with a “usual care” intervention” (physiotherapy – see below). Further, the WB-EMS and CG completed a self-management education program for knee OA.
WB-EMS Intervention
We applied a standard WB-EMS session [
21,
22] 1.5x 20 min per week (e.g. every Monday every second Thursday) for 29 weeks including 4 weeks of familiarization and conditioning with the miha bodytec type II device (Gersthofen, Germany). Briefly, thighs and upper arms, gluteals, abdomen, chest, lower back, latissimus and upper back were stimulated simultaneously but with dedicated impulse intensity. Using bipolar current, the WB-EMS scheduled an impulse low frequency of 85Hz, an impulse-width of 350 µs and a direct impulse boost with 6 s of EMS stimulation intermitted by 4 s of impulse break. Based on the close interaction between the licensed trainer and a maximum of two trainees, impulse intensity as prescribed by the rate of perceived exertion (RPE) was carefully increased to “6-7” (i.e. “hard+ to very hard”) on the Borg CR10 Scale [
23]. During the session, impulse intensity for all electrodes was carefully adapted every 3 min in order to ensure a constant impulse intensity [
24]. Video guided low intensity exercises were conducted during the 6 s impulse phase in a standing position.
Control intervention (Physiotherapy)
As per usual care practice in Germany, the control group was provided with six standardized physiotherapy sessions of 20 min each. The session included applications and exercises for pain reduction, muscle tissue detonization, mobility of the knee joint and lower extremity muscle strength.
Self management
A self-management program of osteoarthritis [
25] with 6 sessions of 60 min each was applied for both groups. Briefly, the program aimed to provide education, information and counselling to prevent the progression of OA, reduce fear, avoidance attitudes and thus improve quality of life and mobility of the participants.
Study outcomes
As stated, the EMSOAT study predominately focuses on outcomes related to knee osteoarthritis. The present contribution addressed abdominal fat changes considered as secondary outcomes of the EMSOAT project.
Explanatory outcomes
Changes of physical activity and exercise between baseline and 29-week FU
Changes of dietary intake between baseline and 29-week FU
Changes in medication use between baseline and 29-week FU
Assessments
MRI data acquisition and examination
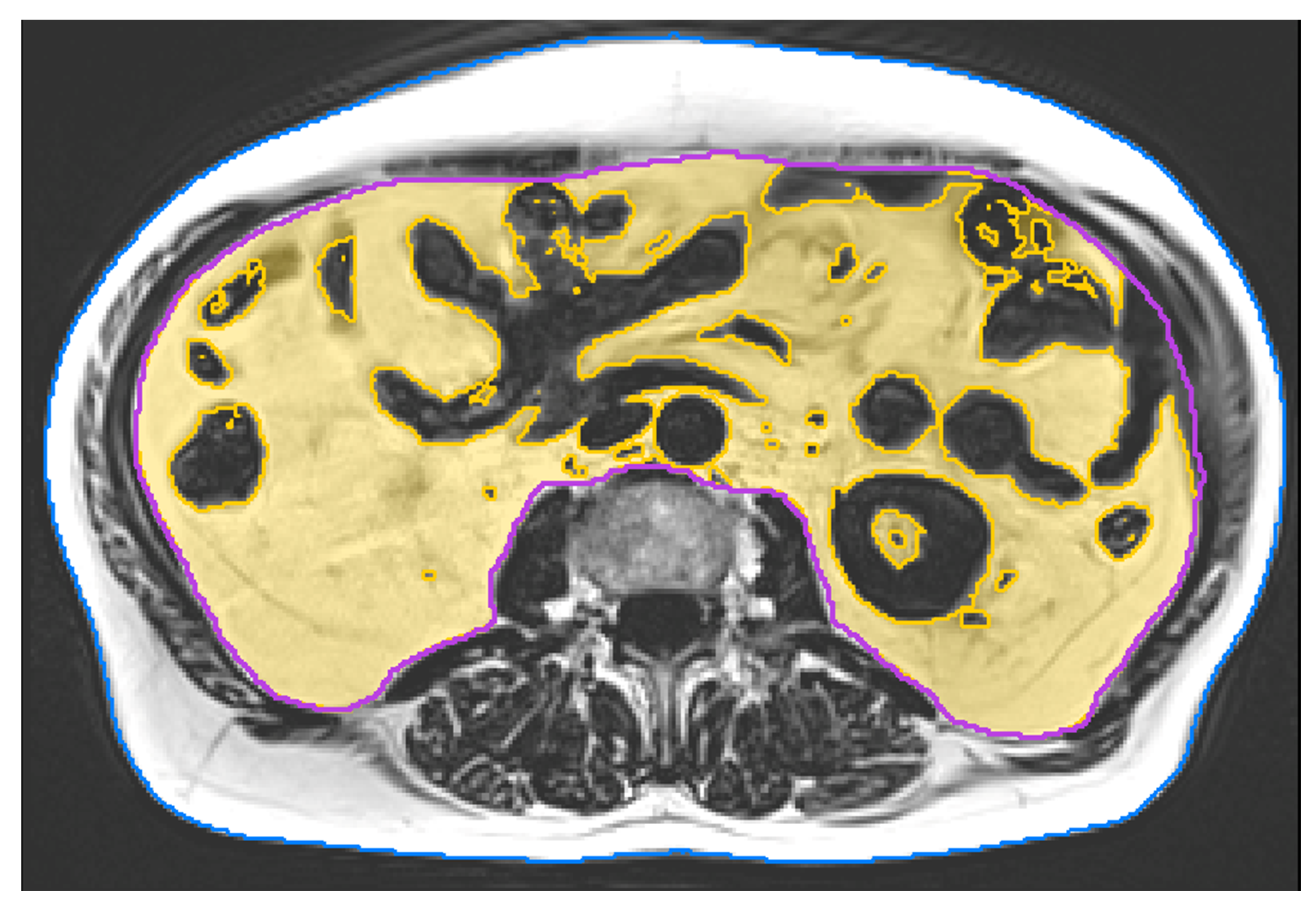
MRI scans were acquired at baseline and after 29 weeks of intervention. All scans were consistently acquired on a 3 Tesla scanner (PRISMA, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany). We applied a non-contrast enhanced 2-point Dixon Gradient Echo Volumetric Interpolated Breath-hold Examination (VIBE) sequence (TE: 1.29 ms; TR: 3.97 ms; matrix size: 320x260; voxel size: 1.2×1.2x3.5 mm
3; slice gap: 0.7 mm). Twelve slices covered a total length of approximately 5 cm from mid L2 to mid L3. Image analysis was performed using MIAF (Medical Image Analysis Framework, Friedrich-Alexander-University of Erlangen-Nürnberg) as described in detail in a previous publication [
26]. The first and last slice were left out due to intensity inhomogeneity. In the remaining ten slices, the outer contour of the body was determined automatically. The contour of the abdominal cavity was manually segmented by a supervised and trained research assistant. This was performed slice by slice using open source software Fiji [
27]. Between both measurements of a participant, the position of the scanned volumes was evaluated and non-overlapping slices were cut off if necessary. In order to separate VAT inside the abdominal cavity from inner organs such as kidneys or intestines, and blood vessels, we used a threshold calculated by the Otsu Method [
28] (
Figure 2).
Baseline characteristics and confounding factors
Body height was assessed by a Holtain stadiometer (Crymych Dyfed., UK). Direct-segmental, multi-frequency Bio-Impedance-Analysis (DSM-BIA, InBody 770, Seoul, Korea) was used to determine body mass and body composition. Overweight (25.0-29.9 kg/m2) and (≥30.0 kg/m2) obesity were classified according to Body Mass Index (BMI).
At baseline, a detailed standardized questionnaire asked for (a) demographic parameters, (b) physical limitations, diseases, operations, pharmacologic therapy, dietary supplements and (c) lifestyle, including physical activity, exercise and diet. After 29 weeks of intervention, all the participants completed the FU questionnaire that aimed to determine changes of conditions/diseases, pharmacologic and physical therapy, physical activity, exercise and diet, i.e. factors with potential impact on the present outcomes. The questionnaires were carefully checked for consistency, completeness and accuracy by the primary investigator (SK) together with the participants.
Sample size calculation
The sample size calculation was based on a parameter not addressed in the present contribution. Briefly 36 participants per group were needed to determine effects on the primary outcome “pain of the knee joint” as determined by the KOOS (Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score) questionnaire, applying a statistical power of 80% and an α-level of 5% and a two-tailed T-test approach.
Statistical analysis
As recommended for RCTs, we applied the Intention to treat (ITT) principle that included all participants randomly assigned to the study arms (WB-EMS vs. CG) regardless of their loss to follow-up. However as reported, due to the lack of MRI baseline
and FU data, four participants of the CG could not be included in the analysis. We applied R statistics software (R Development Core Team Vienna, Austria) in combination with Amelia II [
29] for multiple imputation (ITT). The full data set was used for multiple imputation, with imputation repeated 100 times. Normal distribution was checked graphically (gg-plots, residual plots). Using the t-test, within-group changes were analyzed. ANCOVA adjusted for baseline differences of the corresponding outcome was applied to determine between group differences (i.e. “effects”) after 29 weeks. Differences in distribution of categorical variables were analyzed by Pearson chi-square tests (Tab.1). All tests were 2-tailed, significance was accepted at p <0.05.
Results
Table 1 displays baseline results of the study cohort. In summary, no significant differences were observed between the WB-EMS and the CG at baseline.
Drop-out and loss to follow-up is displayed in
Figure 1. Briefly, four participants (WB-EMS: n=3 vs. CG: n=1) were unable to attend the 29-week FU assessment. A further two participants of the WB-EMS group quit the study due to reasons not related to the intervention. Attendance rate averaged 88±10% in the WB-EMS group. Predominately due to diseases, four participants (WB-EMS) exercised on average less than once a week. Attendance in the physiotherapy sessions (CG) was >90%. No adverse effects or injuries were observed during the WB-EMS sessions, and (apart from occasional delayed onset muscular soreness) no participant reported any WB-EMS-related relevant discomfort during or after WB-EMS application.
Study outcome
Table 2 shows results for VAT at baseline and corresponding changes after 29 weeks of intervention. In summary, no significant WB-EMS-induced effects (p=.097), i.e. group differences for absolute changes between WB-EMS vs. CG, on visceral adipose tissue volume were observed. In detail, VAT volume increased non-significantly in the CG (p=.261) and decreased non-significantly in the WB-EMS group (p=.160).
Confounding factors
After the intervention period, no significant changes within the groups or between group differences of physical activity (p=.124), exercise participation ≥60min/w (p=.607) or exercise volume (p=.976) were reported by the participants. Five participants of the CG and four participants of the WB-EMS group (p=.794) reported changes in dietary habits, consistent with reductions of carbohydrates/sugar and/or lower energy intake during the study period. Finally, no relevant changes of medication (e.g. glucocorticoids), conditions (e.g. eating disorders) or diseases (e.g. thyroid function) with potential impact on abdominal adipose tissue parameters were reported.
Discussion
In this trial that compare WB-EMS to a control group of standard of care (physiotherapy), we could not find significant effects on VAT after 7 months of 1.5x 20 min/week WB-EMS in overweight to obese adults. Reviewing the mechanisms of WB-EMS effects on body fat changes induced by increments of energy expenditure, largely comparable to conventional RT-exercise, at least three effects can be identified. (a) Firstly, the acute energy expenditure during WB-EMS [
30], which is limited by the low training volume. (b) The post-exercise effect induced by energy restoration, repair and adaptive processes post-exercise (EPOC) that is particularly pronounced after WB-EMS application [
31]. (c) Changes in resting metabolic rate due to hypertrophic effects after WB-EMS [
22]. Although the aforementioned meta-analyses [
10,
12,
13] reported significant (low to moderate) effect sizes, in detail single RCTs in the area of isolated RT interventions and VAT rarely revealed significant effects, thus our results of positive, albeit non-significant findings on VAT is not exceptional. Some characteristics of our study might have additionally contributed to this result. Firstly, we included more women than men in our study. is considerable evidence that VAT response to RT in women is less pronounced compared to men [
10]. In parallel, although a recent meta-analysis [
12] did not report differences in VAT reductions between RT applicants with overweight vs. obesity, in a recent network meta-analysis [
10] RT was ineffective in reducing VAT in people with body fat rates ≥40%. Considering that one quarter of our cohort featured such an advanced body fat rate may have contributed to our non-significant results. Further, from a sport-specific point of view, one may argue that the low training volume of our WB-EMS protocol (1.5x 20/week) might have prevented more beneficial results. As reported, most RT trials with a positive impact on VAT applied three and more sessions per week. The WB-EMS pilot study of Park et al. [
32] reported favorable effects on intra-abdominal fat in older obese women applying 3x 40 min/week of WB-EMS superimposed on aerobic dance. This approach is in diametral contrast to our, most scientific, and largely all commercial protocols, however, which focus on isolated and time-efficient WB-EMS application. Nevertheless, applying the identical MRT protocol for VAT, a recent low-volume (2x 40 min/w.), high-intensity RT-trial with 43 older men reported significant effects on VAT [
33].
Apart from cohort and exercise characteristics, one may argue that changes in dietary intake might have confounded results on VAT. While only a few participants listed changes in dietary habits during the 29-week study period, the reported alterations should rather decrease than increase caloric intake in both, the CG and WB-EMS. Still, we have to admit that more detailed monitoring of dietary intake by frequent dietary records would have provided more insight into this issue.
Some other limitations and particularities of the present trial VAT should be addressed. (a) First of all, VAT was not considered as the primary study outcome, correspondingly the sample size analysis did not focus on VAT. However, the sample size of 72 participants included in the ITT-analysis exceeds the sample size of most RT studies with significant positive effects on VAT [
10,
12]. (b) The study included adults with moderate to advanced knee osteoarthritis with overweight and obesity. Overweight and obesity is a strong predictor of knee OA [
34] not only due to the higher mechanical load, but also to the pro-inflammatory effects particularly triggered by the VAT fraction [
35]. Although WB-EMS might not be the most promising exercise for VAT reduction, the rationale for WB-EMS application in this cohort with OA was the opportunity of a joint-friendly protocol with low amplitude, low intensity movements/exercises. (c) Finally, another methodological weakness could be the lack of participant blinding. Optionally, the CG could have received the same intervention, but with a pulse intensity below the motor threshold. We decided against this alternative since (a) even low stimulus intensity (e.g. low intensity TENS) might trigger favourable effects on (knee) pain intensity (as the primary study outcome) and (b) we considered it more adequate to provide a real-world comparison with an established therapy approach on knee OA.
Conclusion
Although some participant characteristics might have contributed to our results, we conclude that largely due the low application volume, the present WB-EMS protocols as applied most in scientific and commercial settings might not be the perfect tool for decreasing VAT in overweight to obese adults.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Funding
We would like to thank the Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung for providing funding for the present study.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support from the non-profit organizations Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung and Netzwerk Knochengesundheit Erlangen e.V., Germany. The work was performed in (partial) fulfillment of the requirements for Benazir Burkhardt obtaining the degree Dr. med. dent.
Conflicts of Interest
Benazir Burkhardt, Oliver Chaudry, Stephanie Kast, Simon von Stengel, Klaus Engelke, Michael Uder and Wolfgang Kemmler declare that they have no conflict of interest. Frank Roemer is consultant to Grünenthal GmbH and is shareholder of Boston Imaging Core Lab (BICL) LLC.
References
- Silveira, E.A. , Kliemann N., Noll M., Sarrafzadegan N., de Oliveira C. Visceral obesity and incident cancer and cardiovascular disease: An integrative review of the epidemiological evidence. Obes Rev. 2021, 22, e13088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C. , Harhay M.O., Harhay M.N. Visceral adipose tissue dysfunction and mortality among a population-based sample of males and females. Diabetes Metab. 2016, 42, 382-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. , Kim K. CT-based measurement of visceral adipose tissue volume as a reliable tool for assessing metabolic risk factors in prediabetes across subtypes. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 17902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. , Hu T., Zhang S., Zhou L. Associations of Different Adipose Tissue Depots with Insulin Resistance: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Observational Studies. Sci Rep. 2015, 5, 18495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohman, M.K. , Wright A.P., Wickenheiser K.J., Luo W., Eitzman D.T. Visceral adipose tissue and atherosclerosis. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2009, 7, 169-79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Kruchten, R. , Lorbeer R., Muller-Peltzer K., et al. Association between Adipose Tissue Depots and Dyslipidemia: The KORA-MRI Population-Based Study. Nutrients. 2022, 14, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.E. , do Carmo J.M., da Silva A.A., Wang Z., Hall M.E. Obesity-induced hypertension: interaction of neurohumoral and renal mechanisms. Circ Res. 2015, 116, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J. , Kim Y.J., Kim D.H., et al. Visceral adipose tissue area is an independent risk factor for hepatic steatosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008, 23, 900-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q. , Wu Y., Gao Y., Zhang Z., Shi T., Yan B. Effect of visceral adipose tissue mass on coronary artery disease and heart failure: A Mendelian randomization study. Int J Obes (Lond). 2022, 46, 2102–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X. , He H., Xie K., Zhang L., Cao C. Effects of various exercise types on visceral adipose tissue in individuals with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of 84 randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. 2023, e13666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S. , Lee J. Effects of exercise interventions on weight, body mass index, lean body mass and accumulated visceral fat in overweight and obese individuals: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2021, 18, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafi, M. , Malandish A., Rosenkranz S.K., Ravasi A.A. Effect of resistance training with and without caloric restriction on visceral fat: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Obesity Reviews. 2021, 22, e13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, P. , Taaffe D.R., Galvão D.A., et al. Resistance training effectiveness on body composition and body weight outcomes in individuals with overweight and obesity across the lifespan: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity Reviews. 2022, 23, e13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, J. , Fisher J., Giessing J., Gentil P. Clarity in Reporting Terminology and Definitions of Set End Points in Resistance Training. Muscle Nerve. 2017, 10, 368-74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmler, W. , Kleinoder H., Fröhlich M. Editorial: Whole-Body Electromyostimulation: A Training Technology to Improve Health and Performance in Humans? Front Physiol. 2020, 11, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmler, W. , Teschler M., Weissenfels A., et al. Effects of Whole-Body Electromyostimulation versus High-Intensity Resistance Exercise on Body Composition and Strength: A Randomized Controlled Study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016, 2016, 9236809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World_Medical_Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA. 2013, 310, 2191-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, R. , Alarcon G., Appelrouth D., et al. The American College of Rheumatology criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis of the hip. Arthritis Rheum. 1991, 34, 505-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennell, K.L. , Nelligan R.K., Kimp A.J., et al. What type of exercise is most effective for people with knee osteoarthritis and co-morbid obesity?: The TARGET randomized controlled trial. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020, 28, 755-65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmler, W. , Weissenfels A., Willert S., et al. Recommended Contraindications for the Use of Non-Medical WB-Electromyostimulation. Dtsch Z Sportmed. 2019, 70, 278-81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, M. , Schoene D., Kohl M., von Stengel S., Uder M., Kemmler W. Non-athletic cohorts addressed by longitudinal whole-body electromyostimulation trials - An evidence map. Sensors (Basel). 2024. submitted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmler, W. , Shojaa M., Steele J., et al. Efficacy of Whole-Body Electromyostimulation (WB-EMS) on body composition and muscle strength in non-athletic adults. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Physiol. 2021, 12, 640657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg G., Borg E. (2010) The Borg CR Scales® Folder. Hasselby, Sweden.
- Kemmler, W. , Fröhlich M., Ludwig O., et al. Position statement and updated international guideline for safe and effective whole-body electromyostimulation training-the need for common sense in WB-EMS application. Front Physiol. 2023, 14, 1174103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.E. , Allen K.D., Golightly Y.M., Goode A.P., Jordan J.M. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: The chronic osteoarthritis management initiative of the U.S. bone and joint initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 43, 701-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudry, O. , Grimm A., Friedberger A., et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis to Assess Visceral and Abdominal Adipose Tissue. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2020, 28, 277-83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J. , Arganda-Carreras I., Frise E., et al. Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods. 2012, 9, 676-82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE transactions on systems, man, and cybernetics. 1979, 9, 62-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honaker, J. , King G. , Blackwell M. Amelia II: A program for missing data JSS. 2011, 45, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmler, W. , Von Stengel S., Schwarz J., Mayhew J.L. Effect of whole-body electromyostimulation on energy expenditure during exercise. J Strength Cond Res. 2012, 26, 240-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschler, M. , Wassermann A., Weissenfels A., et al. Short time effect of a single session of intense whole-body electromyostimulation on energy expenditure. A contribution to fat reduction? Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018, 43, 528-30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S. , Park J., Ham J.A., Jee Y. Effects of aerobic dance with electrical stimulant on body composition and radiological circumference of obese elderly women. Gazzetta Medica Italiana Archivio per le Scienze Mediche. 2021, 180, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, K. , Chaudry O., Uder M., et al. Effects of High-Intensity Resistance Training on Visceral Adipose Tissue and Abdominal Aortic Calcifications in Older Men with Osteosarcopenia - Results from the FrOST Study. Clin Interv Aging. 2023, 18, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, L.K. , March L., Anandacoomarasamy A. Obesity & osteoarthritis. Indian J Med Res. 2013, 138, 185-93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T. , Autieri M.V., Scalia R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375-C91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 1 |
Considering that WB-EMS is more a vehicle rather than a training method, the specification of the training protocol is of crucial importance for the effects on a given outcome. To date, the vast majority and nearly all commercial concepts apply protocols with moderate to high impulse intensity, low training volume (20-40 min/week), and intermitted impulse-impulse break setting, i.e. a resistance type protocol. |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).