1. Introduction
Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) represent the two main phenotypes of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), which are characterized by chronic inflammation of the entire or of specific parts of gastrointestinal system. Both phenotypes share similar pathophysiologic mechanism and clinical presentation. The real etiopathogenesis is still incompletely understood [
1]. It is known that genetic predisposition, along with microbiologic intraluminal factors and environmental factors determine the onset, as well as the course of the disease [
2,
3]. This fine mechanism of regulation of chronic inflammation is, at least in part, controlled by intestinal dendritic cell (DC) [
4]. This cell controls, “feels“ and catches an intraluminal antigen, and transports it to the lymphatic tissue [
4]. Therefore, its role is balancing of the response to the luminal antigen [
4]. Disturbing this fine balance between the tolerability and the active immunologic response are is the crucial step in IBD pathogenesis [
5,
6]. DC is the main population of antigen-presenting cells in lamina propria [
7,
8,
9]. Besides lamina propria, these cells are present in lymphoid aggregates of small intestine [
10]. In specimens of colonic and rectal biopsies, an immature HLA-DR
+lin
- DC of CD11c+ subpopulation is identified, which, through maturation, obtains phenotype of CD83
+ mature DC [
11,
12].
At the present, widely accepted pathophysiologic model of DC role proposes that immature DC continuously enters the mucosal lamina propria, Peyer’s patches and lymphoid follicle’s of colon. It becomes more mature and positions itself in different parts of the colon, depending on expression of specific cytokines [
13,
14]. After transporting the antigen through epithelial cells, or uptaking apoptotic particles of epithelial cells, it travels to the mesenteric lymph nodes or intrafollicular regions in the form of activated, mature cell. This migration is associated with cytokine receptors for T zone of lymph node, such as CCR7. This ‘ready’ but still inert DC can stimulate a differentiation of a T cell into a regulatory T cell, which, in turn, mediates as tolerant observer after the encounter with antigen. Intestinal stromal cells can also create suppressive environment which stimulates DC to steer a differentiation of T lymphocytes into regulatory T lymphocytes. Contrary to this response to „innocent “antigen, mucosal pathogens initiate active local and systemic immunologic response. The initial contact of pathogen with epithelial cells, its cell components, adherent DC or macrophages include recognizing microbial pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) or pattern recognition receptor (PPR), such as TLR receptors [
15,
16,
17,
18]. TLR signalling from epithelial cells results in production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines such as IL-1, IL-8, IL-6, TNFα, CCL5 and CCL20 , which attract and activate neutrophils, macrophages and DC [
19]. Beside this intermediate pathway, DC can be activated directly by pathogens through TLR and other surface receptors. This causes a complete cell activation with high level of expression of MHC, costimulatory and adhesive molecules and cytokines. A phenotype of consequent T lymphocyte response is either directly or indirectly determined by the type of host-pathogen contact. Signals which DC receive directly from pathogens and tissue signals on the site of contact in lymph nodes during the first contact of „priming“ T lymphocytes will activate specific DC subpopulation (characterized by expression of specific PPR), which then determines the type of response to pathogen: either toleration or active defence response [
20,
21,
22,
23]. It is evident that the function of mucosal DC and its subpopulations is regulated by local microenvironment which includes immunologic cells as well as luminal bacteria [
24]. All these factors take part in maintaining intestinal homeostasis. However, certain functions of DC and its subpopulations still remain unknown, and further studies are warranted to obtain more information regarding factors which regulate the intestinal inflammation.
The aim of this study is to assess the impact of applied therapy, level of inflammation in biopsy specimen and phenotype of inflammatory bowel diseases on presence of mucosal mature CD83+ dendritic cell in colonic biopsy samples.
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
In this study, there were 219 subjects included, older than 18. They underwent colonoscopy during two-year period, from 2015 to 2017, at Gastroenterology clinic of „Polyclinic for internal medicine, gynaecology and psychiatry “J&J MEDICI “. The subjects were divided into three groups: 1) subjects with IBD diagnosis, currently without therapy; 2) subjects with IBD who take azathioprine or anti-TNF therapy for at least 6 months, but do not take corticosteroids for at least 6 weeks; 3) healthy subjects in control group. The diagnosis of UC was based on ECCO guidelines from year 2008, 2012 and 2018 [
25,
26,
27]. CD diagnosis was based on ECCO guidelines from year 2010, 2016 and 2018 [
27,
28,
29].
There were 100 subjects with UC. Among them, 68 were without therapy, 15 on azathioprine and 17 on anti-TNF. There were 44 subjects with CD. Among them, 43 were without therapy, 13 on azathioprine and 12 on anti-TNF. In control group, there were 75 healthy subjects.
2.2. Endoscopy
Colonoscopy was performed with the VP 3500HD endoscopic video processor with an XL 4450 light source and EC530 and EC600 endoscopes (Fuji, Japan). In UC subjects
Mayo endoscopic Subscore (MES) was used as index of endoscopic assessment of disease activity [
30,
31]. In CD subjects,
The simple endoscopic score for Crohn`s disease (SES-CD) was used as index of endoscopic assessment of disease activity [
31,
32,
33].
2.3. Fecal Calprotectin
Faecal calprotectin level was measured in stool sample once in each subject during ten-day period prior to his/her colonoscopy. Calprotectin concentration (µg/g) was assessed by immunoturbidimetric method (Buhlmann laboratories AG, Schonenbuch, Switzerland) on device Beckman-Coulter AU 168 (Beckman Coulter Inc, USA).
2.4. Colonic Biopsy Samples Analysis
Colonic biopsy samples of subjects with UC and CD were taken from sites of endoscopically visible disease. For UC, this was the descending colon, and for CD, it was the ascending colon. In the control group, biopsy samples were taken from the descending colon.
- a)
Histologic analysis
Bioptic samples of colonic mucosa were fixated in 4% buffered formaldehyde for 24 hours, then washed in 0.1 M phosphate buffer and, after dehydrating, embedded in paraffin at 56° C. They were cut in 4 micrometers wide slices and attached to positively charged slides (Superftost plus, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, SAD). For staining, standard hemalaun-eosinophilic (HE) was used in automatic staining device HE 600 (Ventana, Tucson, Arizona, USA). Stained samples were analysed using light microscope Olympus BX41. Histopathologic results were divided in three groups: acute inflammation, chronic inflammation and no inflammation.
- b)
Immunohistology analysis
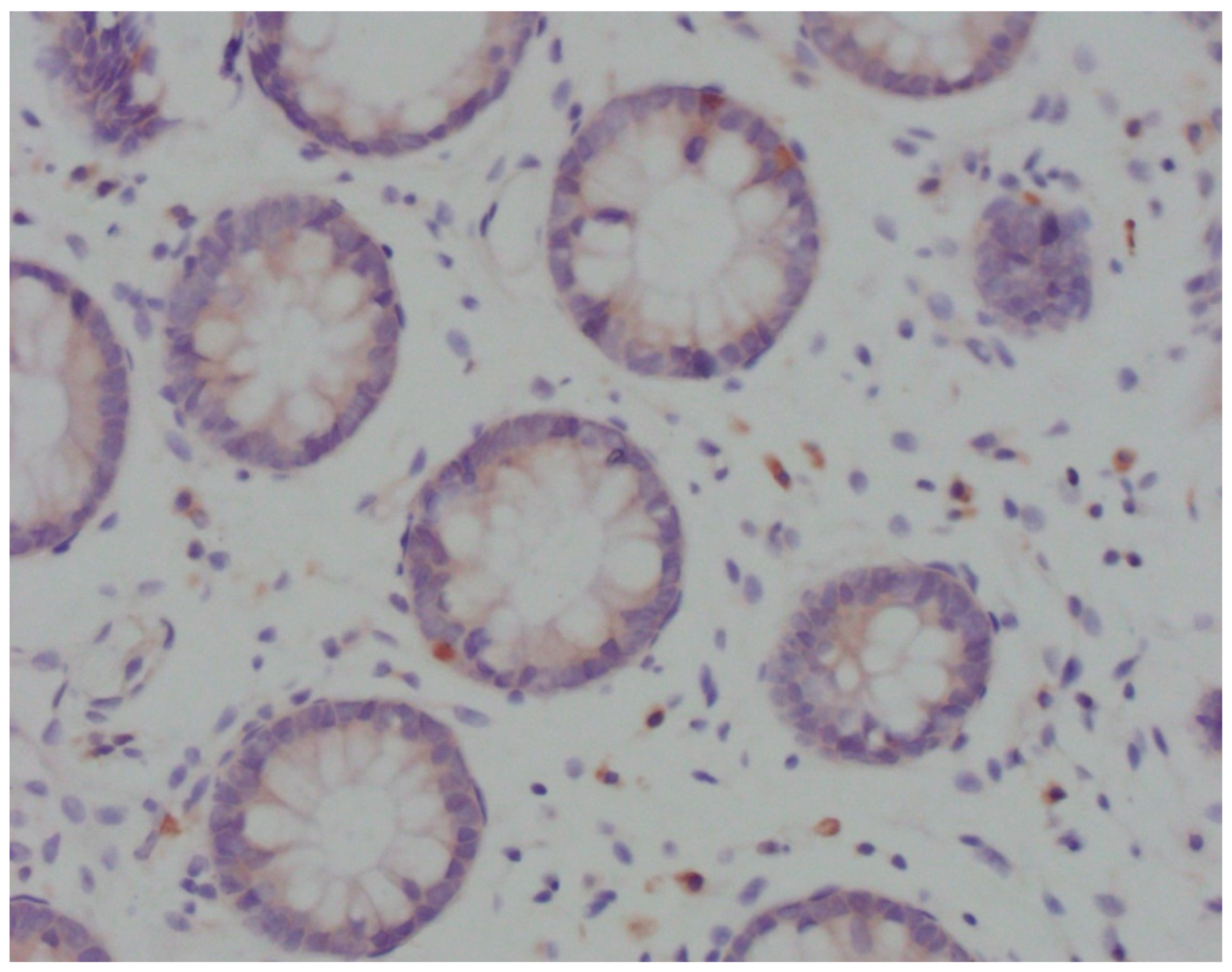
Immunohistochemical analysis was performed in device Bench Mark ULTRA IHC/ISH Staining Module (Ventana, Tucson, Arizona, USA) with positive control. After deparaffinization in xylol and rehydration through alcohol descending concentrations, the slices were cooked in EDTA pH 8.2 buffer for 10-30 minutes. Endogenous peroxidase was inactivated by incubation in H2O2. After that, the slices were washed out in phosphate buffer solution (PBS) and incubated in primary antibody Anti-CD83 ab205343 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) in moist atmosphere for 32 minutes. After washing out in PBS, the slices were incubated in system for secondary detection Ultraview Universal DAB DEtection Kit (Ventana, Tucson, Arizona, USA). Stained samples were analysed using light microscope Olympus BX41. In areas with the most intensive staining, intraepithelial mature CD83
+ DC were counted per 100 enterocytes (
Figure 1).
2.5. Statistic Analysis
All data analysis was performed with SPSS 20. As the Shapiro-Wilk test indicated statistically significant deviation from the normal distribution of all numeric variables, the median and interquartile ranges were used. Statistical significance of the differences in categorical demographic and clinical characteristics was calculated by the chi-square (χ2) test and Fisher’s exact test. Analysis of the statistical significance of differences in CD83+ DC number among the three study groups was performed with the Kruskal-Wallis’s test. Post hoc analysis was performed with the Mann-Whitney test. In our analysis, we also used binary logistic regression.
Statistical significance was set to p<0,05, and all confidence intervals were given at 95%.
3. Results
3.1. All Subjects
There were 219 subjects included in this study, all older than 18. Among them, 100 (46%) had UC, 44 (20%) had CD and 75 (34%) were in control group. There were 113 male (51%) and 106 (49%) female subjects. The age median was 40 years (Q1-Q3:31-55 y; min-max:15-80 y) (43.7±15.6 y).
Groups with a different presence CD83
+DC (0, ≥1) were adjusted according to age (p = 0.889) and sex (p = 0.419) (
Table 1).
The presence of mature CD83
+ DCs (0, ≥1) significantly differed among disease types (p=0.001). In CD83
+DC≥1 group number of UC subjects was 1.6 times lower and number of CD subjects was 4.7 times higher than in CD83
+DC=0 group. The odds for CD83
+DC presence are 4 times higher in CD group than in control group (OR:4; 95%CI:1.1-14.6; p=0.035). Analysing the number of subjects with UC and CD (without controls) in groups with different CD83
+DC presence (0, ≥1), we found also a significant difference (0, ≥1) (p<0.001). There were only 8% CD subjects without CD83
+DC. The odds for CD83
+DC presence were 7.8 times higher in CD group than in UC group (OR:7.8; 95% CI:2.2-27; p<0.001). (
Table 1).
The presence of mature CD83
+ DCs (0, ≥1) significantly differed among subjects with specific histologic inflammation type (p=0.049). There were 1.7 times less subjects with acute inflammation in CD83
+DC≥1 group and 1.7 times more subjects with acute inflammation in CD83
+DC=0 group. The odds for CD83
+DC presence (CD83
+DC≥1) in subjects without inflammation were 2.1 times higher than in those with acute inflammation (OR=5.9;95%CI:1.1-4.3; p=0.030). There was no significant difference between the number of subjects with acute and chronic inflammation (p=0.086). But the odds for CD83
+DC presence were 2.2 times higher in subjects without or with chronic inflammation than in those with acute inflammation (OR=2.2; 95%CI:1.2-4.1; p=0.015) (
Table 1).
The presence of mature CD83
+ DCs (0, ≥1) significantly differed among subjects according to applied therapy (p=0,001). There were 3,6 times more subjects with CD83
+DS≥1 than those with CD83
+DS=0 in the group with therapy. The odds for CD83
+DC presence were 4.8 times higher in subjects who had been on therapy than in those who hadn’t (OR=4.8;95%CI:1.8-12.7; p=0.002) (
Table 1).
A multiple logistic regression was then performed, with CD83
+DC (0, ≥1) as dependent variable and subjects' groups (combined controls and UC; CD), histopathology (combined chronic and no inflammation; acute inflammation) and therapy (no; yes) as independent variables. All three variables have shown statistically significant correlation with CD83
+DC (0, ≥1) in multivariate logistic regression. The odds for CD83
+DC presence were 5.2 times higher in CD group than in combined control/UC group. The odds for CD83
+DC presence were 2.6 times higher in subjects without inflammation or with chronic inflammation than in those with acute inflammation. It was also 3.7 times higher in subjects without therapy than in those on therapy (
Table 2).
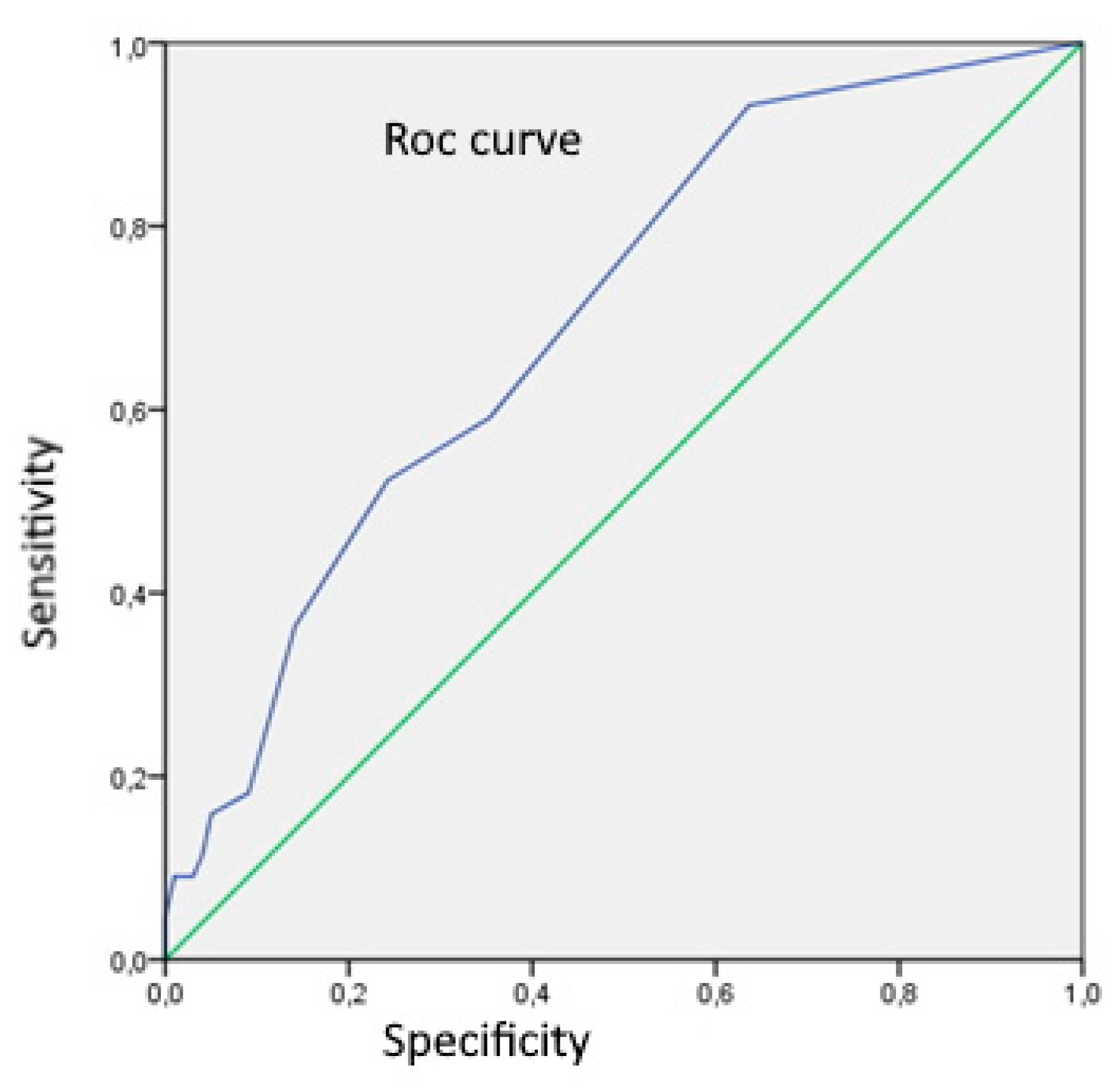
Using Rock analysis for assessment of CD83
+DC number as a differentiation marker between UC and CD, we got a cut-off value of 0.5, with sensitivity and specificity of 93,2% and 36,4% respectively (
Figure 2).
Analysing the number of CD83
+DC according to the type of disease shows that only 7% subjects with CD had n CD83
+DS/ 100 e ≤0,5 (
Table 3).
3.2. Ulcerative Colitis Subjects
The presence of mature CD83
+ DCs (0, ≥1) was also analysed separately in UC group (
Table 4).
The presence of mature CD83
+DCs (0, ≥1) significantly differed among different endoscopy scores (MES) (p=0,002). The odds for DC presence (CD83
+DC≥1) were 4,7 times higher in subjects with MES 0 or MES 1 than in subjects with MES 2 or MES 3 (OR: 4,7;95%CI=1,8-12,2; p=0,002). The presence of mature CD83
+ DCs (0, ≥1) also significantly differed among those with acute inflammation and those with chronic or no inflammation (p=0,046). The odds for CD83
+DC presence was 2.6 higher in chronic or no inflammation group than in acute inflammation group (OR:2,6; 95%CI=1,1-6; p=0,013). There was no significant correlation between presence of CD83
+DC (0, ≥1) and calprotectin level (p=0,555). The presence of mature CD83
+ DCs (0, ≥1) significantly differed according to whether therapy is applied or not (p=0,007). We found 3 times more subjects with CD83
+DC≥1 who had been on therapy (azathioprine, antiTNF) than those who hadn’t. The odds for DC presence were 4.5 times higher in subjects on therapy in comparison to those without therapy (OR: 4,5;95%CI=1,6-13; p=0,006). Subjects’ groups with different CD83
+DC presence didn’t differ according to gender (p=0.532) or age (p=0.530) (
Table 4).
A multivariate logistic regression confirmed the combined effect of MES and histopathologic results on CD83
+DC presence. The odds for CD83
+DC presence were 5 times higher in group with MES 0,1 and with no/chronic inflammation than in group with MES 2,3 and with acute inflammation (OR:5;95%CI 1,4-17,5; p=0,012), adjusted for therapy (
Table 5).
The presence of mature CD83
+DCs (0, ≥1) significantly differed among subjects' groups on different therapy (p<0,004). There was a statistically equal number of subjects without (46%) and with (54%) CD83
+DC among UC subjects who were not on therapy. Number of subjects without CD83
+DC in group with no therapy was 2 times higher than in control group, 3.5 times higher than in group on azathioprine, and 2.6 times higher than in group on anti- TNF. (
Table 6).
3.3. Crohn's Disease Subjects
Crohn's disease group has only 3 subjects without CD83
+DS, 15 subjects with one CD83
+DS and 26 subjects with CD83
+DS = 2 – 10. Therefore, we divided them in two groups: CD83
+DS ≤ 1 (n=18) and CD83
+DS > 1 (n=26), and analysed according to different features (
Table 7).
The presence of mature CD83
+DCs (≤1, >1) significantly differed between different endoscopy scores SES-CD (p=0,006). The odds for CD83
+DC>1 were 7,9 times higher in SES-CD≤5,9 group than in SES>5,9 group (OR=7,9; p=0,006). The presence of mature CD83
+DCs (≤1, >1) also significantly differed regarding calprotectin level. There were 3 times more subjects with CD83
+DC>1 than CD83
+DC<1 in group calprotectin value ≤449 µg/g (p=0,006). The odds for CD83
+DC>1 were 7,9 times higher in subjects with calprotectin level ≤449 µg/g than in those with calprotectin level >449 µg/g (OR=7,9; p=0,006). In addition, the presence of mature CD83
+DCs (≤1, >1) significantly differed between the group with acute inflammation and the groups with no inflammation and chronic inflammation. (p=0,004). The odds for CD83
+DC>1 were 8.4 times higher in subjects’ group without or with chronic inflammation than in group with acute inflammation (OR=8,4; p=0,003). Most of the subjects with CD83
+DC>1 was on therapy. Subjects’ groups with different CD83
+DC presence didn’t differ according to gender (p=0.176) or age (p=0.879) (
Table 7).
There was significant difference in CD83
+DC presence (≤1;>1) between healthy subjects and CD subjects on any type of therapy (χ
2=22.4; p<0.001; Cramer`s V=0.434). All the subjects on anti-TNF had CD83
+DC > 1. The number of subjects with CD83
+DC> 1 was 3.7 times higher in those on azathioprine than in those without therapy, and it was 1.6 times higher than in healthy subjects (
Table 8).
4. Discussion
In this study we have analysed the presence of CD83
+DC in colonic biopsy specimens of CD and UC patients, and we found that the presence was higher in CD than in UC subjects. There were few previous studies which analysed mature DC presence in different IBD types. Middel and Baumgart have also proved an increased number of CD83
+ DC in tissue of patients with CD and UC. Thise study showed the increased number of cells which expressed costimulatory molecules such as CD40, CD80, CD83 and CD86 in mucous tissue of CD, but also in those of UC patients [
34,
35,
36]. Radwan and al. had primarily compared both IBD types with control group of healthy subjects, assessing the number of mucosal mature DC grown in cell culture; a significantly higher presence of mature DC was observed in both IBD groups compared with that of controls. [
37]. On the other hand, the Radwan-Kwiatek's studies of DC in blood had shown a significantly decreased number of immature cells, which was explained as the result of cells migration into the inflamed intestinal tissue. This cells’ presence decrease correlates well with severity and extent of inflammation process [
38]. Baumgart and al. have reported that in IBD patients a low expressing of costimulating molecule CD86 in DC in peripheral blood had been found, and CD83 expressing was had been absent [
36]. Velde and al. reported similar results, as well as Middel and al., while Bell and al. in their study did not prove statistically significant difference in CD83
+DC, regardless of existing difference in DC number median [
11,
12,
34].
When we had analysed subjects according to the presence of CD83
+DC in specific histologic inflammation type, we found that this presence was higher in subjects with chronic inflammation or no inflammation than in those with acute inflammation. Besides, there was significantly lower presence of CD83
+DC in subjects’ group with histopathological signs of acute inflammation than in healthy controls. Until now, only Bates and al. reported results from mice colitis model study, in which CD83
+DC role had been studied in different levels of inflammation. Their results showed that loss of CD83 in DC would lead to the worsening and acutisation of inflammation level in colitis model [
39]. Middel and al., comparing CD 83
+DC number in areas of active vs. non-active inflammation of the same patient, found a higher number of CD83
+DC in samples with active inflammation [
34]. In the study conducted by Bell and al. a difference in DC number median had been found between different histopathologic levels of inflammation; however, it wasn't statistically significant [
11].
Assessing the number of CD83+DC as a differentiation marker between UC and CD in our study, we got a cut-off value of 0.5 CD83+DC, with sensitivity and specificity of 93,2% and 36,4% respectively. We showed that only 7% of subjects with CD had n CD83+DS≤0,5. There are no earlier studies which assessed a DC number as a differentiation marker between UC and CD.
We had also analysed a relationship between CD83
+DC presence and applied therapy in study subjects and found a significantly higher presence in those who were on therapy. In the study of Silva and al. the influence of different therapy on CD83
+DC number in patients with CD had been analysed; the DC number was decreased significantly only in patients treated with systemic corticosteroids [
40].
4.1. Ulcerative Colitis Subjects
According to our results, subjects with acute inflammation had significantly lower presence of CD83
+DC compared to those with chronic or no inflammations. In previously mentioned study of Bates and al., a role of CD83 molecule in regulation of immunologic homeostasis was proposed: a loss of CD83 in DC had worsened the inflammation in colitis model [
39]. Their results were based on mice colitis model [
39].
It was also proved that DC isolated from lamina propria in mice had significantly decreased expression of maturation marker CD83 [
39].
This mice colitis model could give us an explanation of how DC, in immunologic reservoir such as intestinal lamina propria, prevents an excessive inflammation. An overexpressed CD83 on mucosal surface “protects” from colitis, while loss of expression on CD83 in DC worsens the colitis. This was the first time that CD83
+DC role in immunologic homeostasis was proved [
39]. In study of Kawashima and al. on surgical specimens from UC patients, an increased CD83
+DC number was isolated by immunofluorescent method from cell culture, primarily from lymphoid aggregates in specimens with histopathologically active disease [
41]. An increased number of CD83
+DC was found also by Baumgart and al.; this time by isolation from blood by immunocytochemical method [
42].
In our study most of subjects in group with endoscopic index of disease activity MES 2 and 3 had histologically acute inflammation, accompanied with higher faecal calprotectin levels. Similar results were reported in study of Roseth and al., who had analysed a histological inflammation activity in tissue specimens of UC patients, with the purpose of defining calprotectin cut-off level in mucosal healing [
43]. Results from studies of Viera and al., D'Inca and al., Kaiser and al. were also similar to our results; the highest level of faecal calprotectin was in subjects with acute inflammation [
44,
45,
46]. Bodelier and al. reported similar results regarding MES grade and faecal calprotectin levels, as well as D’ Haens and al [
47,
48]. Recent meta- analysis published by Moslia and al. showed similar results, with overall sensitivity and specificity of faecal calprotectin level in precising endoscopically active disease 88 and 79% respectively [
49].
According to our results, the CD83
+DC presence was significantly higher in subjects’ groups with MES 0 and 1 than in MES 2 and 3. Duchmann and al. concluded, by indirectly assessing the infiltration of lamina propria with T lymphocytes in endoscopically actively inflamed parts of intestinal mucosa, that present mature DC were activators of T lymphocytes [
50].
A combined influence of MES endoscopic index and histopathologic results on CD83+DC presence was showed in our results. CD83+DC presence was the highest in group MES 0,1/ no inflammation/chronic inflammation. There are no earlier studies which compared both endoscopic and histopathologic UC activity with presence of mature CD83+DC.
Analysing the presence of CD83
+DC in UC patients’ group with different therapy, we found significantly lower presence of CD83
+DC in patients without therapy than in those on specific therapy (azathioprine or anti-TNF). When we had additionally compared each of these UC patients’ groups (with specific therapy or without therapy) with control group, we found the lowest CD83
+DC presence again in UC patient group without therapy. Bhandaru and al. in their study proved
in vitro the influence of azathioprine on migration of DC and releasing of TNF-L [
51]. On the other hand, Hart and al., who were also assessing the effect of azathioprine on DC through TLR expression, didn't find significant correlation between the number of DC and azathioprine therapy. [
52].
4.2. Crohn's Disease Subjects
While conducting the study, we observed that the presence of CD83
+DC was significantly lower in group with acute inflammation compared to those with chronic or no inflammations. Similar results were reported by Silva and al., after they had compared colonic tissue specimens of CD patients with inflammation with those without inflammation [
53]. In their study on cell culture, Bell and al. observed that immediately after bioptic sampling there was no significant difference in CD83
+ DC number among groups with different histologic inflammation activity, although there was difference in median values of CD83
+DC in these groups. Middel and al. in their study on CD patients found an increased CD83
+ DC number in specimens with histologically active inflammation, compared with those without inflammation [
34].
Assessing the endoscopic index SES-CD we found a significantly higher median of SES-CD in patients with histologically acute inflammation than in those with other inflammation levels. This was accompanied by higher levels of faecal calprotectin levels in these patients. Similar results were reported by Bodelier and al., as well as by D’ Haens and.al [
47,
48]. An overall meta-analysis of Mosli and al., showed similar results, with overall sensitivity and specificity of faecal calprotectin levels for predicting endoscopically active disease 87 and 67% respectively [
49]. According to our results, the CD83
+DC presence was significantly higher in subjects’ groups with higher SES-CD calprotectin level. There are no earlier studies which compared endoscopic SES-CD score and calprotectin with presence of mature CD83
+DC.
When we had compared the CD83
+DC presence of subjects on therapy (azathioprine or anti- TNF) with that of control group, we found that it was significantly higher in subjects on therapy. The median of CD83
+DC number was 3 times higher in azathioprine group or anti-TNF group than in control group. In the group of CD patients who were on anti-TNF, all subjects had number of CD83
+DC >1. Hart and al. had also assessed the effect of anti-TNF drugs on DC through expression of CD40, and they found significant decrease of CD40 expression in DC after application of anti-TNF therapy to the bioptic specimens [
52]. Silva and al. compared corticosteroid effects with those of other drugs. They proved significant decrease of CD83
+DC in bioptic specimens of subjects on corticosteroid therapy, while this change was not found in subjects’ group on azathioprin [
53].
5. Conclusions
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, as the two principal phenotypes of IBD, still have an incompletely comprehended pathophysiological mechanism of development. According to different pathophysiologic models, these two diseases have much in common, but there are also many differences between them. Since the discovery of DC, which is an antigen- presenting cell, there have been attempts to understand its position in the development of IBD. At the present, we know for certain that DC is present in the areas of contact between the human organism and the environment, continuously surveilling, catching and processing antigens. A complete function of DC is still unknown; it seems that its function depends on location and the role it takes. This study has tried to present the diversity of the role of intestinal mature CD83+DC in different types of IBD. The study also included an assessment of effect of different elements, such as demographic parameters, inflammation level and therapeutic procedures, on presence of mature CD83+DC in IBD. Finally, we anticipate a possible role of mature CD83+DC as valuable diagnostic parameter in distinction between UC and CD, as well as a good predictor of inflammation and treatment outcome in these diseases.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, investigation and writing – original draft preparation, B.R.D.; investigation, project administration M.B.; writing – review & editing, A.B.; supervision, A.T.; formal analysis, Ž.A.; methodology, K.V.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the University Hospital Split Ethics Committee (Approval Class. 500-03/18-01/73; Approval NO 2181-147-01/06/m.S.-19-3; 28.02.2019.).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
We disclose no restrictions on the availability of data, materials and associated protocols.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Jasminka Božiković and Jelena Joka Gašpić from “J&J MEDICI”, Polyclinic for Internal Medicine, Split, Croatia, and to Prof. Snježana Tomić, MPH, PhD, Department of Pathology, University Hospital Split, Split, Croatia, for obtaining the specimens for our study. We would also like to thank nurses from “J&J MEDICI”, Polyclinic for Internal Medicine, Split, Croatia: Vinka Stojanac, Milorada Poljak and Nina Romac, in addition to Ružica Ujaković, Department of Gastroenterology, University Hospital Split, Split, Croatia, for their assistance in endoscopic procedures. We offer special thanks to Vesna Čapkun for her assistance in the whole process.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- De Preter V. Metabolomics in the Clinical Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig Dis. 2015; 33: 2-10.
- Dupaul-Chicoine J, Dagenais M, Saleh M. Crosstalk between the intestinal microbiota and the innate immune system in intestinal homeostasis and inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19: 2227-37.
- Strober W, Fuss I, Mannon P. The fundamental basis of inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Invest. 2007; 117: 514-21.
- Niess JH. Role of mucosal dendritic cells in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14: 5138-48.
- Levine A, Griffiths A, Markowitz J, et al. Pediatric modification of the Montreal classification for inflammatory bowel disease: the Paris classification. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011; 17: 1314-21.
- Kaser A, Zeissig S, Blumberg RS. Inflammatory bowel disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 2010; 28: 573-621.
- Pavli P, Woodhams CE, Doe WF, et al. Isolation and characterization of antigen-presenting dendritic cells from the mouse intestinal lamina propria. Immunology. 1990; 70: 40-7.
- Liu LM, MacPherson GG. Rat intestinal dendritic cells: immunostimulatory potency and phenotypic characterization. Immunology. 1995; 85: 88-93.
- Pavli P, Hume DA, Van De Pol E, et al. Dendritic cells, the major antigen-presenting cells of the human colonic lamina propria. Immunology 1993; 78: 132-41.
- Moghaddami M, Cummins A, Mayrhofer G. Lymphocyte-filled villi: comparison with other lymphoid aggregations in the mucosa of the human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1998; 115: 1414-25.
- Bell SJ, Rigby R, English N, et al. Migration and maturation of human colonic dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2001; 166: 4958-67.
- Te Velde AA, Van Kooyk Y, Braat H, et al. Increased expression of DC-SIGN+IL-12+IL-18+ and CD83+IL-12-IL-18- dendritic cell populations in the colonic mucosa of patients with Crohn's disease. Eur J Immunol. 2003; 33: 143-51.
- Dieu MC, Vanbervliet B, Vicari A, et al. Selective recruitment of immature and mature dendritic cells by distinct chemokines expressed in different anatomic sites. J Exp Med. 1998; 188: 373-86.
- Zhao X, Sato A, Dela Cruz CS, et al. CCL9 is secreted by the follicle-associated epithelium and recruits dome region Peyer's patch CD11b+ dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2003; 171: 2797-803.
- Kaisho T, Akira S. Regulation of dendritic cell function through toll-like receptors. Curr Mol Med. 2003; 3: 759-71.
- Didierlaurent A, Sirard JC, Kraehenbuhl JP, et al. How the gut senses its content. Cell Microbiol. 2002; 4: 61-72.
- Barton GM, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors and their ligands. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002; 270: 81-92.
- Gewirtz AT. Intestinal epithelial toll-like receptors: to protect. And serve? Curr Pharm Des. 2003; 9: 1-5.
- Kagnoff MF, Eckmann L. Epithelial cells as sensors for microbial infection. J Clin Invest. 1997; 100: 6-10.
- Kapsenberg ML. Dendritic-cell control of pathogen-driven T-cell polarization. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003; 3: 984-93.
- Reis e Sousa C, Diebold SD, Edwards AD, et al. Regulation of dendritic cell function by microbial stimuli. Pathol Biol. 2003; 51: 67-8.
- Shortman K, Liu YJ. Mouse and human dendritic cell subtypes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002; 2: 151-61.
- Mazzoni A, Segal DM. Controlling the Toll road to dendritic cell polarization. J Leukoc Biol. 2004; 75: 721-30.
- Rescigno M, Di Sabatino A. Dendritic cells in intestinal homeostasis and disease. J Clin Invest. 2009; 119: 2441-50.
- Sange EF, Travis SPL, Vermeire S, et al. European evidence-based Consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis: Definitions and diagnosis. J Crohns Colitis. 2008; 2: 1–23.
- Dignass A, Eliakim R, Magro F, et al. Second European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis part 1: definitions and diagnosis. J Crohns Colitis. 2012; 6: 965-90.
- Maaser C, Sturm A, Vavricka SR, et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detections of complications. J Crohns and Colitis. 2018; 5: 1-34.
- Van Assche G, Dignass A, Panes J, et al. European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn's disease: Definitions and diagnosis. J Crohns and Colitis. 2010; 4: 7–27.
- Gomollón F, Dignass A, Annese V, et al. 3rd European Evidence-based Consensus on the Diagnosis and Management of Crohn's Disease 2016: Part 1: Diagnosis and Medical Management. J Crohns Colitis, 2017; 11: 3-25.
- Schroeder KW, Tremaine WJ, Ilstrup DM. Coated oral 5-aminosalicylic acid therapy for mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis. A randomized study. N Engl J Med 1987; 317: 1625–9.
- Annese V, Daperno M, Rutter MD, et al. European evidence based consensus for endoscopy in inflammatory bowel disease. Journal of Crohnʹs and Colitis. 2013; 7: 982–1018.
- Daperno M, D'Haens G, Van Assche G, et al. Development and validation of a new, simplified endoscopic activity score for Crohn's disease: the SES-CD. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 60: 505-12.
- Sipponen T, Nuutinen H, Turunen U, et al. Endoscopic evaluation of Crohn's disease activity: comparison of the CDEIS and the SES-CD. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010; 16: 2131-6.
- Middel P, Raddatz D, Gunawan B, et al. Increased number of mature dendritic cells in Crohn's disease: evidence for a chemokine mediated retention mechanism. Gut. 2006; 55: 220-7.
- Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. Inflammatory bowel disease: clinical aspects and established and evolving therapies. Lancet. 2007; 369: 1641-57.
- Baumgart DC, Metzke D, Schmitz J,et al. Patients with active inflammatory bowel disease lack immature peripheral blood plasmacytoid and myeloid dendritic cells. Gut. 2005; 54: 228-36.
- Radwan-Kwiatek K, Tabarkiewicz J, Radwan P, et al. CD1c+/CD19- and CD303+/CD123+ dendritic cells in the peripheral blood in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Pol J Environ Studies. 2007; 16: 526-529.
- Radwan-Kwiatek K, Radwan P, Tatarkiewicz J, et al. Circulating dendritic cells as a novel disease activity marker in inflammatory bowel disease? Gut 2009; 58: A258.
- Bates JM, Flanagan K, Mo L, et al. Dendritic cell CD83 homotypic interactions regulate inflammation and promote mucosal homeostasis. Mucosal Immunol. 2015; 8: 414-28.
- Silva MA, López CB, Riverin F, et al. Characterization and distribution of colonic dendritic cells in Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2004; 10: 504-12.
- Kawashima D, Oshitani N, Jinno Y, et al. Augmented expression of secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine and EBI1 ligand chemokine in Crohn's disease. J Clin Pathol. 2005; 58: 1057-63.
- Baumgart DC, Thomas S, Przesdzing I, et al. Exaggerated inflammatory response of primary human myeloid dendritic cells to lipopolysaccharide in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009; 157: 423–436.
- Røseth AG, Aadland E, Grzyb K. Normalization of faecal calprotectin: a predictor of mucosal healing in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2004; 39: 1017-20.
- Vieira A, Fang CB, Rolim EG, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease activity assessed by fecal calprotectin and lactoferrin: correlation with laboratory parameters, clinical, endoscopic and histological indexes. BMC Res Notes. 2009; 2: 221.
- D’Incà R, Dal Pont E, Di Leo V, et al. Calprotectin and lactoferrin in the assessment of intestinal inflammation and organic disease. Int J Colorectal Dis 2007; 22: 429 437.
- Kaiser T, Langhorst J, Wittkowski H, et al. Faecal S100A12 as a non invasive marker distinguishing inflammatory bowel disease from irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2007; 56: 1706 1713.
- Bodelier AG, Jonkers D, van den Heuvel T, et al. High percentage of IBD patients with indefinite fecal calprotectin levels: Additional value of a combination score. Dig Dis Sci. 2017; 62: 465-472.
- D'Haens G, Ferrante M, Vermeire S, et al. Fecal calprotectin is a surrogate marker for endoscopic lesions in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012; 18: 2218-24.
- Mosli MH, Zou G, Garg SK, et al. C-reactive protein, fecal calprotectin, and stool lactoferrin for detection of endoscopic activity in symptomatic inflammatory bowel disease patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015; 110: 802-19.
- Duchmann R, Kaiser I, Hermann E, et al. Tolerance exists towards resident intestinal flora but is broken in active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Clin Exp Immunol. 1995; 102: 448–455.
- Bhandaru M, Pasham V, Yang W, et al. Effect of azathioprine on Na(+)/H(+) exchanger activity in dendritic cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012; 29: 533-42.
- Hart AL, Hassi HO, Rigby RJ, et al. Characteristics of intestinal dendritic cells in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2005; 129: 50-65.
- Silva MA, Quera R, Valenzuela J, et al. Dendritic cells and toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in the ileum of Crohn's disease patients. Dig Dis Sci. 2008; 53: 1917-28.
Figure 1.
Light microscopy of CD83+ DCs (Olympus BX41; magnification ×40). Cytoplasmically brown-stained, irregularly shaped, CD83+ cells in close contact with the crypt epithelium.
Figure 1.
Light microscopy of CD83+ DCs (Olympus BX41; magnification ×40). Cytoplasmically brown-stained, irregularly shaped, CD83+ cells in close contact with the crypt epithelium.
Figure 2.
Rock analysis curve for assessment number of CD83+DC as a differentiation marker between UC and CD (area = 0,699; SE 0,046; p<0,001;95%CI:0,609-0,788).
Figure 2.
Rock analysis curve for assessment number of CD83+DC as a differentiation marker between UC and CD (area = 0,699; SE 0,046; p<0,001;95%CI:0,609-0,788).
Table 1.
Correlation between CD83+DC presence (0; ≥1) and age, sex, type of disease, histopathology inflammation pattern and therapy; univariate logistic regression.
Table 1.
Correlation between CD83+DC presence (0; ≥1) and age, sex, type of disease, histopathology inflammation pattern and therapy; univariate logistic regression.
| |
CD83+DC presence |
|
|
| |
0 |
≥1 |
p |
OR (95%CI) |
p c
|
Age (years)
|
39,5
(30-59; 15-79) |
40
(31-54;18-80) |
0,889 a
|
|
|
| Sex |
|
|
|
|
|
| Male |
32 (57) |
81 (50) |
0,419 b
|
|
|
| Female |
24 (43) |
82 (50) |
|
|
|
| Group of disease |
|
|
0.001 b
|
|
|
| Control† |
17 (30.4) |
58 (35.6) |
|
|
0,002 |
| UC |
36 (64.3) |
64 (39.3) |
|
0.513 (0.26-1.0) |
0,059 |
| CD |
3 (5.4) |
41 (25.3) |
|
4 (1.1-14.6) |
0,035 |
| |
|
|
<0.001 b
|
|
|
| UC† |
36 (92) |
64 (61) |
|
7.8 (2.2-27) |
0,001 |
| CD |
3 (8) |
41 (39) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
0.003 b
|
|
|
| Histopathology inflammation pattern |
|
|
0.049 b
|
|
|
| Acute† |
25 (44.6) |
44 (27) |
|
|
0.052 |
| No infl. |
21 (37.5) |
79 (48.5) |
|
2.1(1.1-4.3) |
0.030 |
| Chronic |
10 (17.9) |
40 (24.5) |
|
2.3 (0.97-5.3) |
0.058 |
| |
|
|
0.086 b
|
|
|
| Acute† |
25(71) |
44 (52) |
|
|
|
| Chronic |
10 (29) |
40 (48) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
0,022 b
|
|
|
| No infl. Chronic |
31 (55) |
119 (73) |
|
2.2 (1.2-4.1) |
0,015 |
| Acute† |
25 (45) |
44 (27) |
|
|
|
| Therapy |
|
|
0.001 b
|
|
|
| No† |
51 (91) |
111 (68) |
|
4.8 (1.8-12.7) |
0,002 |
| Yes |
5 (9) |
52 (32) |
|
|
|
Table 2.
Multivariate logistic regression for DC presence.
Table 2.
Multivariate logistic regression for DC presence.
| Independent variables |
|
OR (95%CI) |
p a
|
| Subjects’ groups |
Control and UC† |
5.2 (1.4-18.6) |
0.011 |
| |
CD |
|
|
| Histopathology |
No inflammation and chronic |
2.6 (1.3-5.2) |
0.005 |
| |
Acute† |
|
|
| Therapy |
No† |
3.7 (1.3-10.2) |
0.012 |
| |
Yea |
|
|
Table 3.
Number of CD83+DC according to the type of disease.
Table 3.
Number of CD83+DC according to the type of disease.
| |
UC
(n=100) |
CD
(n=44) |
p |
| CD83+DS > 0,5 |
64 (64)
|
41 (93) |
0,001a
|
| CD83+DS ≤ 0,5 |
36 (36) |
3 (7) |
|
Table 4.
Correlation between CD83+DC presence (0; ≥1) and age, sex, MES, histopathology, calprotectin and therapy in UC subjects; univariate logistic regression.
Table 4.
Correlation between CD83+DC presence (0; ≥1) and age, sex, MES, histopathology, calprotectin and therapy in UC subjects; univariate logistic regression.
| CD83+DC presence |
|---|
| |
0 |
≥1 |
p |
OR (95%CI) |
p c
|
Age (years)
|
44
(31-61.5;15-79) |
40
(32-55;19-75) |
0.530 a
|
|
|
| Sex |
|
|
|
|
|
| Male |
20 (55) |
30 (47) |
0.532 b
|
|
|
| Female |
16 (44) |
34 (54) |
|
|
|
| MES |
|
|
|
|
|
| Inactive disease and mild activityMES 0,1 |
7 (19.4) |
34 (53) |
0.002 b
|
4.7 (1.8-12.2) |
0.002 |
| Moderate activity and severe activityMES 2,3† |
29 (81) |
30 (47) |
|
|
|
| Histopathology |
|
|
|
|
|
| No inflammation† |
3 (8.3) |
12 (18.8) |
0.079 b
|
|
|
| Chronic |
9 (25) |
24 (37.5) |
|
|
|
| Acute |
24 (66.7) |
28 (43.8) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| No inflammation/ chronic inflammation |
12(33) |
28(44) |
0.046 b
|
2.6 (1.1-6) |
0.030 |
| Acute† |
24(67) |
36(50) |
|
|
|
| Calprotectin |
|
|
|
|
|
| 12-146 |
6 (16.7) |
19 (29.7) |
0.555 b
|
|
|
| 147-550 |
10 (27.8) |
15 (23.4) |
|
|
|
| 551-1799 |
6 (16.7) |
9 (14.1) |
|
|
|
| 1800 |
14 (38.9) |
21 (32.8) |
|
|
|
| Therapy |
|
|
|
|
|
| No† |
31 (86) |
37 (58) |
0.007 b
|
4.5 (1.6-13) |
0.006 |
| Yes |
5 (14) |
27 (42) |
|
|
|
Table 5.
CD83+DC presence in UC subjects; multivariate logistic regression.
Table 5.
CD83+DC presence in UC subjects; multivariate logistic regression.
| Independent variables |
|
OR (95%CI) |
p a
|
| MES- PHD |
0† |
5 (1,4-17,5) |
0,012 |
| |
1 |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| Therapy |
No† |
2,2 (0,61-8,5) |
0,229 |
| |
Yes |
|
|
Table 6.
Analysis of UC subjects with different therapy.
Table 6.
Analysis of UC subjects with different therapy.
| |
Healthy subjects |
Therapy |
|
| |
No therapy |
Azathioprine |
Anti TNF |
|
| CD83+DC |
|
|
|
|
0.004a
|
| 0 |
17(23) |
31(46) |
2(13) |
3(18) |
|
| ≥1 |
58(77) |
36(54) |
13(87) |
14(82) |
|
Table 7.
Correlation between CD83+DC presence (≤1, >1) and age, sex, SES-CD, histopathology, calprotectin and therapy in CD subjects; univariate logistic regression.
Table 7.
Correlation between CD83+DC presence (≤1, >1) and age, sex, SES-CD, histopathology, calprotectin and therapy in CD subjects; univariate logistic regression.
| CD83+DC presence |
|---|
| |
≤1 |
>1 |
p |
OR (95%CI) |
p c
|
Age (years)
|
36.5
(29-42;15-79) |
38.6
(27-52;18-64) |
0.879 a
|
|
|
| Sex |
|
|
|
|
|
| Male |
7 (39) |
13 (50) |
0.176 b
|
|
|
| Female |
11 (61) |
13 (50) |
|
|
|
| SES-CD |
|
|
|
|
|
| ≤5,9 |
4 (22) |
18 (69) |
0.006 b
|
7.9 (2-31) |
0.004 |
| >5,9† |
14 (78) |
8 (31) |
|
|
|
| Histopathology |
|
|
|
|
|
| No inflammation† |
1 (5.6) |
9 (34.6) |
0.004 b
|
|
|
| Chronic |
5 (27.8) |
12 (46.2) |
|
|
|
| Acute |
12 (66.7) |
5 (19.2) |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
| No inflammation/ chronic inflammation |
6 (33) |
21 (81) |
0.004 b
|
8.4 (2.1-33) |
0.003 |
| Acute† |
12 (67) |
5 (9) |
|
|
|
| Calprotectin |
|
|
|
|
|
| ≤449 |
4 (22) |
18 (69) |
0.006 b
|
7.9 (2-31) |
0.004 |
| >449† |
14 (78) |
8 (31) |
|
|
|
| Therapy |
|
|
|
|
|
| No |
15 (83) |
4 (15) |
|
|
|
| Yes |
3 (17) |
22 (85) |
|
|
|
Table 8.
Analysis of CD subjects with different therapy.
Table 8.
Analysis of CD subjects with different therapy.
| |
Healthy subjects |
Therapy |
|
| |
No therapy |
Azathioprine |
Anti TNF |
|
| CD83+DC |
|
|
|
|
<0.001a
|
| ≤1 |
40(53) |
15(79) |
3(23) |
0(0) |
|
| >1 |
35(47) |
4(21) |
10(77) |
12(100) |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).