Introduction
Numerous numerical models have been developed during the last two decades to simulate floods using the finite volume method to solve shallow water equations (SWEs) in two dimensions (2D) (Bradford and Sanders 2002; Begnudelli and Sanders 2007; Song, Zhou, Guo, et al. 2011; Hou et al. 2015). Shallow water modeling is computationally expensive, especially for computing large domains and mesh refinement to improve the numerical scheme's stability and accuracy (Lai and Khan 2017; Hu and Song 2018). Parallel computing using GPUs can be implemented to overcome this problem. Often, GPU codes can achieve a performance that cannot be obtained by standard CPU systems (Caplan et al. 2019). Generally, GPU programming models are CUDA (NVIDIA 2022), OpenCL (Group 2022), and OpenACC (OpenACC 2022). Since CUDA and OpenCL are low-level programming approaches, users are required to develop the code each time according to the GPU specifications (Xue and Roy 2021). Rewriting code may be quite challenging for developers in terms of programming time and knowledge of computer architecture systems (Caplan et al. 2019). OpenACC is a high-level programming approach, that works only by adding directives to the code. The compiler, such as the NVIDIA HPC SDK, will automatically thread the parallel regions to the GPUs (Norman 2022).
OpenACC has been successfully applied to many 2D hydrodynamic models. Herdman et al. (2012) CloverLeaf mini application accelerated with the OpenACC programming model, achieving a 4.91 speedup with the NVIDIA X2090 GPU over a 16-core CPU. Zhang et al. (2016) the flow field case was performed using an OpenACC parallel computing application, with a speedup of 18.6 achieved by employing the NVIDIA Quadro K2000 GPU compared to a 4-core CPU. Zhang et al. (2017) proposed a 2D parallel dam break model using OpenACC applications and obtained 20.7 speedups using the NVIDIA Tesla K20c GPU versus a 4-core CPU.
To obtain better computation performance, multiple GPUs may be needed. In this work, a hybrid MPI/OpenACC framework is developed with domain decomposition. CPUs are defined as hosts that manage control instructions and file I/O. GPUs are defined as devices that handle the most computationally intensive parts of the code.
In this paper, a parallel approach using hybrid MPI and OpenACC on multiple GPUs is developed to tackle the 2D shallow water problem using an explicit-time finite volume model on an unstructured triangular mesh. A domain decomposition is presented employing METIS (Karypis and Kumar 1997) and CUDA-aware MPI (Kraus 2013). In addition to second-order spatial accuracy, the scheme also implements second-order temporal accuracy to avoid extremely diffusive results. The parallel performance of the developed in-house code (Saleem and Mohammad 2020) examined by benchmark test cases.
The article is structured as follows: In Section 2, given the governing equations for SWEs. The SWEs are then discretized using an explicit-time Godunov-type finite volume technique on a triangular grid, as described in Section 3. In Sections 4 and 5, domain decomposition and parallel implementation are provided, respectively.
Shallow water equations
The 2D SWEs in its conservative version proposed by Song, Zhou, Guo, et al. (2011); Song, Zhou, Li, et al. (2011)
The variable vectors
,
,
, and
are given by
in which
indicates the water height;
and
are velocities in the
and
directions, respectively; the gravitational acceleration is defined by
; (
,
) and (
,
) denote the bed and friction sources in the
and
directions, respectively; here
represents the bed elevation.
where
is the coefficient of roughness.
Numerical scheme
Finite volume discretization on unstructured triangular grids for 2D SWEs
Equation (1) can be written in integral form as
Equation (4) can be rewritten by applying the divergence theorem as
where
,
, and
denote the domain, boundary, and outward normal vector as defined by
, respectively.
represent the flux vector normal to the boundary and is given by
herein
is the velocity perpendicular to the cell face. The line integral of the
over all faces of the triangular cell may be represented algebraically as
where
and
are the index and length of the face, respectively.
indicates Riemann states. The discretization of equation (5) in an arbitrary triangular cell
is
in which
and
denote the area and average variables of the cell
, respectively;
is the index of the cell.
3.1. Time integration
The two-stage explicit Runge-Kutta scheme (Liang and Marche 2009; Liang 2010; Song, Zhou, Guo, et al. 2011; Song, Zhou, Li, et al. 2011; Hou et al. 2013; Hou et al. 2015) is employed to achieve second-order temporal accuracy, and the new time step of equation (8) is obtained by
where
And
is given by
3.2. Stability criteria
The stability of the explicit scheme on a triangular grid is handled by selecting an appropriate time step using the Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy (CFL) proposed by Delis, Nikolos, and Kazolea (2011); Delis and Nikolos (2013). If
is the minimum distance from the
ith triangle’s centroid to its faces, the CFL condition is expressed as
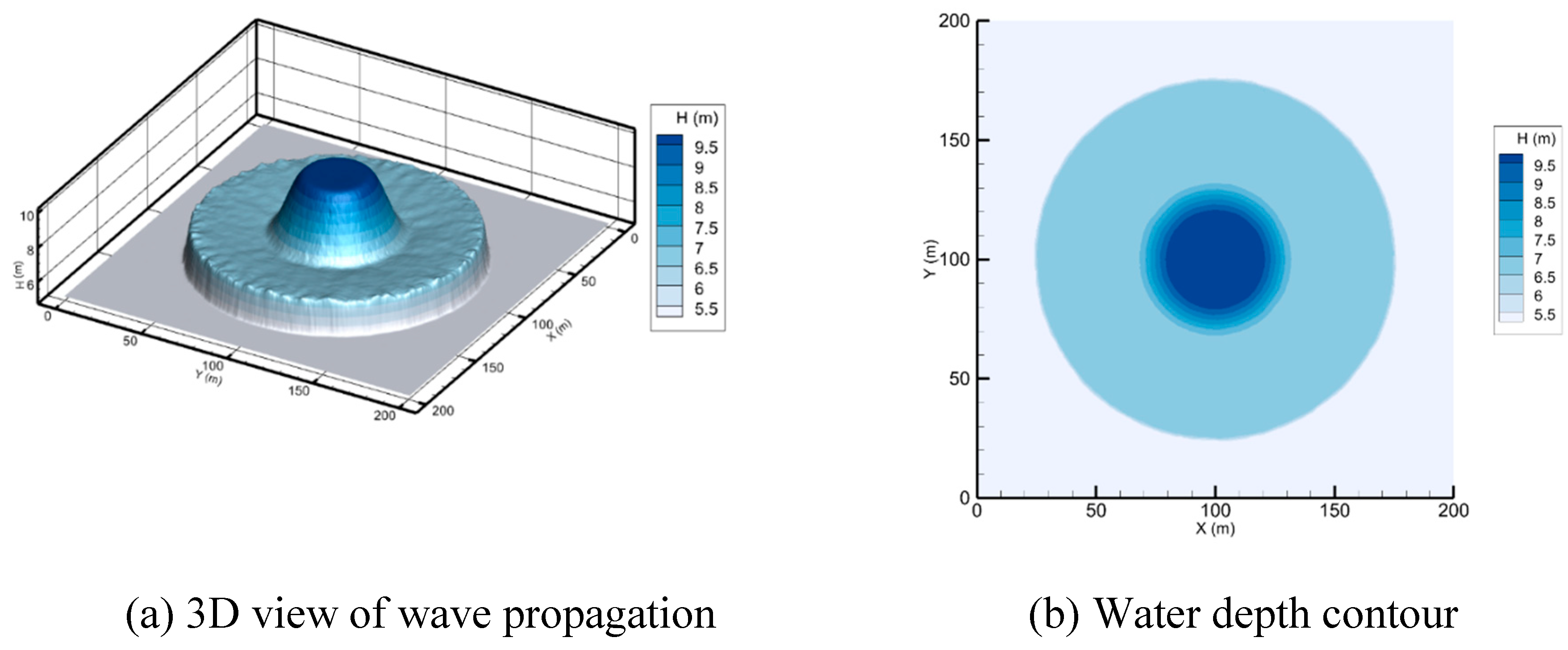
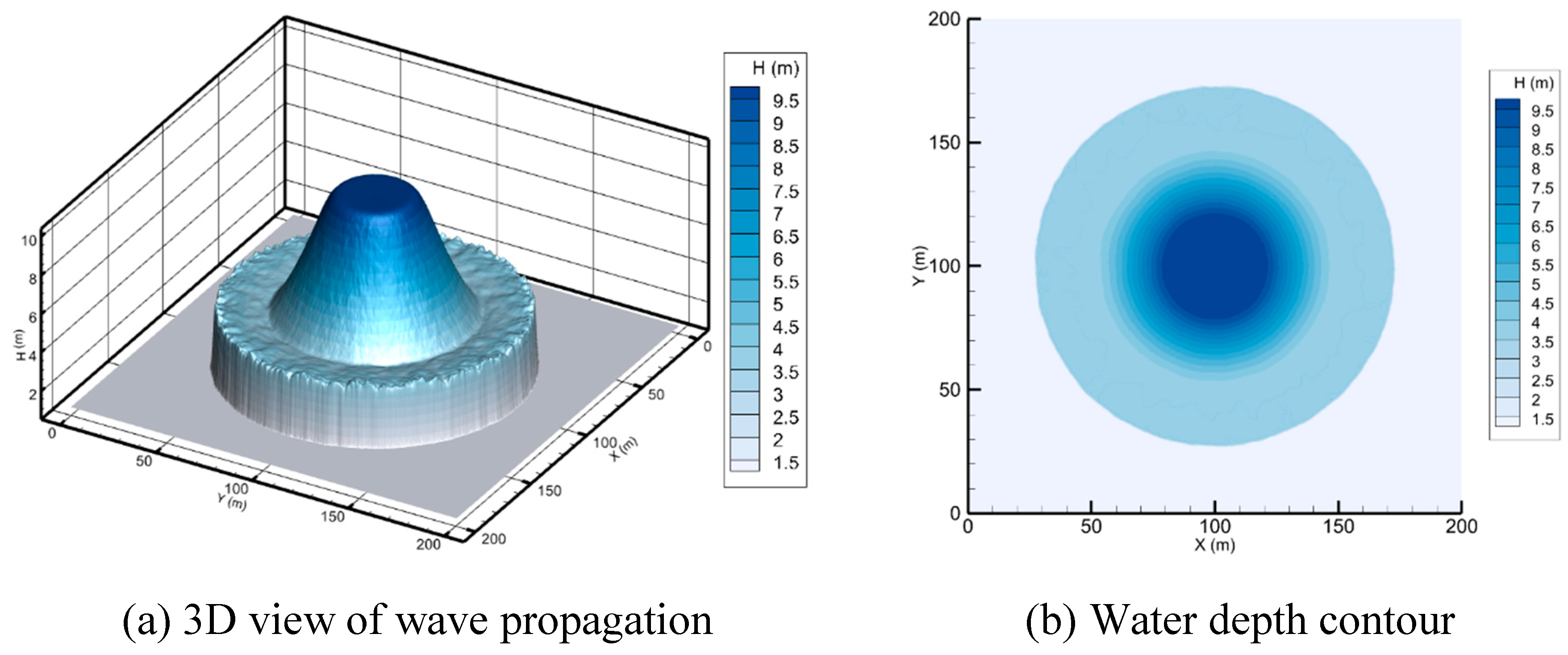
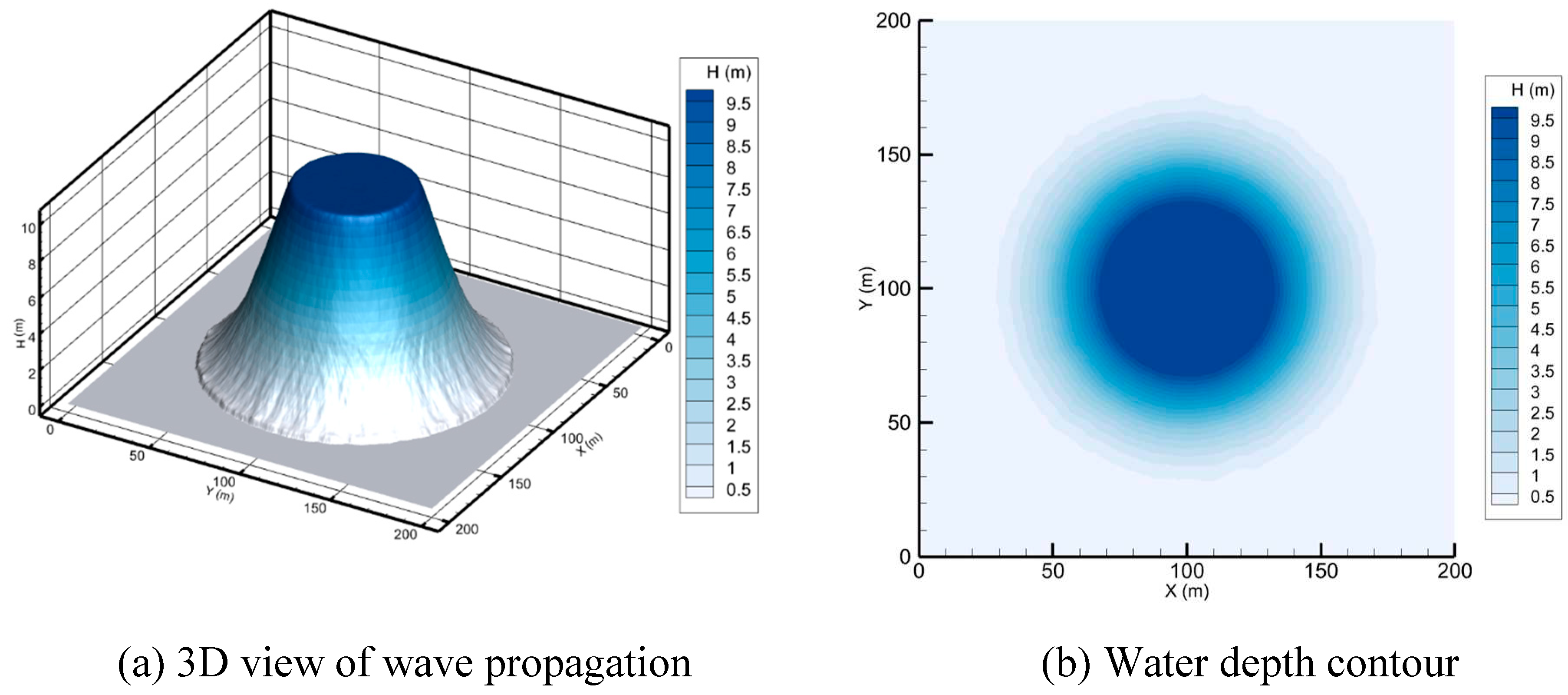
In this paper, the numerical scheme is based on an explicit-time, finite volume Godunov-type cell-centered approach on an unstructured triangular mesh. The Harten-Lax-Van-Leer-Contact (HLLC) approximate Riemann solver (Toro 2001; Liang and Borthwick 2009; Song, Zhou, Guo, et al. 2011; Hou et al. 2013) is utilized to calculate the cell interface fluxes. The current numerical method similar to Song, Zhou, Guo, et al. (2011) incorporates the sloping bottom model as well as volume-free surface relationships (VFRs) (Begnudelli and Sanders 2006) to give an efficient and robust scheme for tracking stationary or moving wet/dry fronts. A water depth reconstruction technique (Begnudelli and Sanders 2007; Song, Zhou, Guo, et al. 2011) is adopted, to tackle the trapping of small water volumes on sloping beds. Second-order accuracy in spatial is obtained by employing the MUSCL method (Van Leer 1979; Hubbard 1999). The adaptive method proposed by Hou et al. (2013) is applied to relieve unphysically high velocities produced by the MUSCL reconstruction near the wet/dry interfaces. Source terms are separated into bed slope and friction components, as expressed in equation (2). The bed slope terms are precisely discretized depending on the water level at the cell centroid, and the well-balanced feature is maintained, as explained by Song, Zhou, Guo, et al. (2011). The sources of friction are resolved via a semi-implicit method (Song, Zhou, Guo, et al. 2011; Bi et al. 2015).
Domain decomposition and halo cells
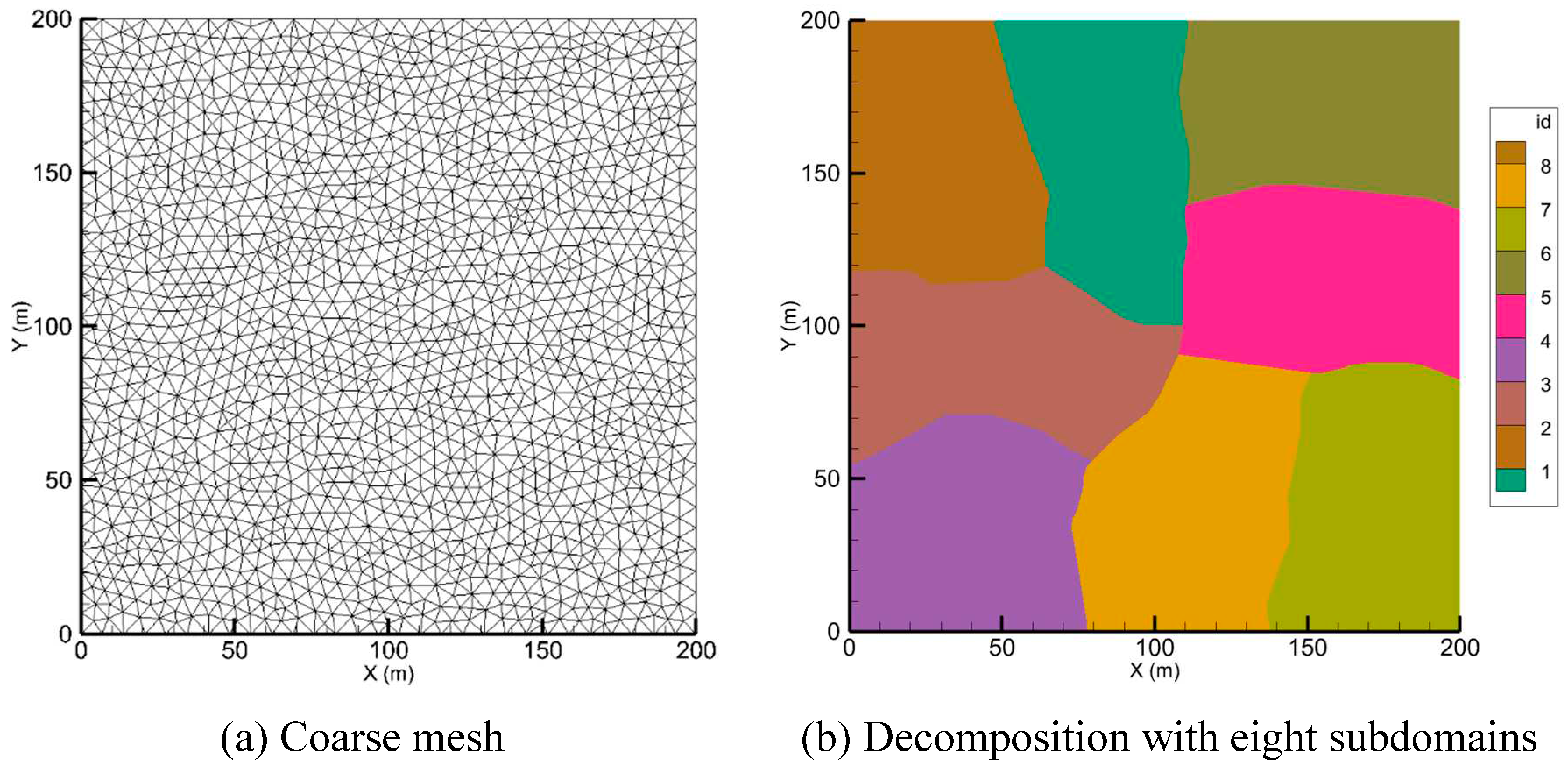
The preprocessing step generates the 2D unstructured triangular mesh for the whole domain, similar to Saleem and Mohammad (2020). The whole domain mesh is decomposed into subdomains by applying the mesh’s graph’s partitioning tools from the METIS library (Karypis and Kumar 1997). The goal is to minimize the contact surfaces between subdomains to reduce processor communication costs (Lai and Khan 2017). To perform data exchange between subdomains using the MPI library, each subdomain is typically given one layer of halo cells or ghost cells. The halo cells in this paper are generated as follows: (i) For each subdomain, the boundary edges are identified. (ii) The nodes of boundary edges are compared with the nodes of other subdomains’ boundary edges, and a list of shared nodes are created. (iii) The cells of each subdomain are investigated against the shared nodes list; the cells that have two consecutive nodes in the shared list are the sent cells for the compared subdomain and the received cells, or halo cells, for the neighbor subdomain.
After finding send and receive cells for each subdomain, the subdomain cells are renumbered as follows: the interior cells will be sent or received first, followed by the cells that will be sent to adjacent subdomains, and the halo cells or received cells from the neighboring subdomains at the end.
Parallel implementation
Simulating shallow water flows using a finite volume scheme is computationally intensive. Since the explicit time-stepping procedure is adopted, and within a single time step the numerical mesh calculation is uncorrelated. Therefore, the loop computation on each grid can be performed in parallel (Zhang et al. 2017). In this study, the hybrid MPI/OpenACC is applied to leverage multiple GPUs on a single node. MPI is a parallel programming approach (Forum 2021) that allows data to be shared between processors through messages (Xue, Jackson, and Roy 2021). OpenACC is a high-level programming model (OpenACC 2022) that utilizes directives and clauses to automatically parallelize loops (Hu and Song 2018). The OpenACC parallel loop directive with the level of parallelism gang, worker, vector, and seq clauses are adopted in the code to offload loops to the GPU automatically (OpenACC 2022). For tightly nested loops, OpenACC loop collapsing is employed to combine many loops into one loop, which significantly improves on-node parallelization efficiency (Zhang et al. 2019). The OpenACC routine directive is utilized to call functions or subroutines inside the parallel loops (OpenACC 2022). The async directive, which decreases kernel launch overhead, is another key OpenACC directive used in the code (Wright et al. 2021), and the OpenACC wait statement is adopted to control OpenACC queuing (Norman 2022). The reduction clause is used to manage race conditions in the code when multiple parallel threads access the same memory location in a way that may lead to incorrect results (Norman 2022).
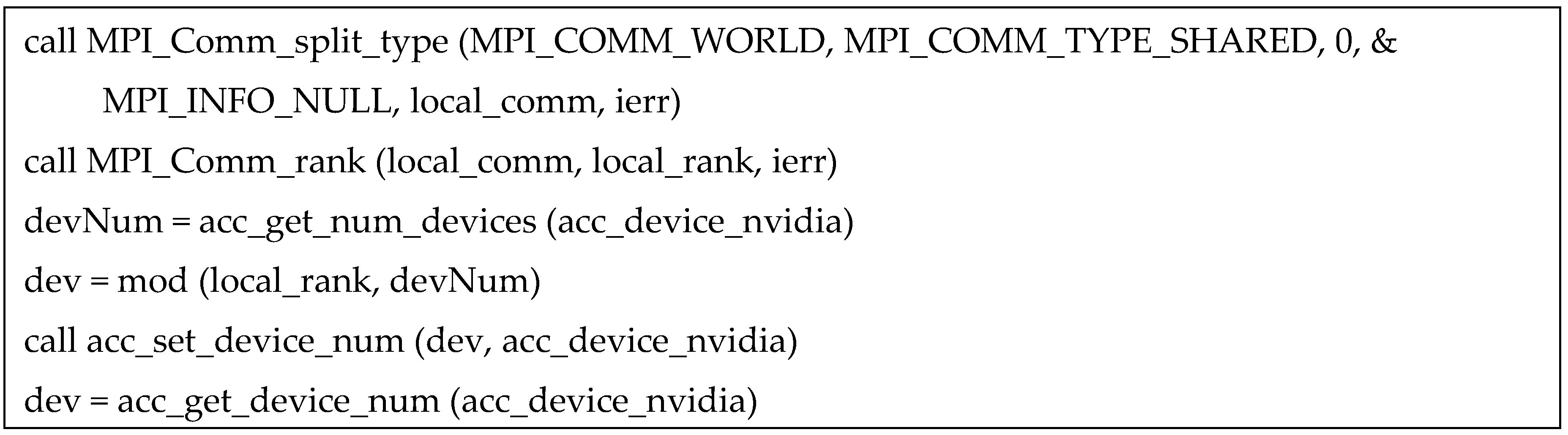
As shown in
Figure 1, boilerplate code (Colgrove 2021) is implemented to assign each MPI rank to a specified GPU. The OpenACC
set device_num () function is utilized to set the desired GPU. Once the GPU number is set, all upcoming OpenACC directives will be sent to the selected GPU until another GPU is specified with the same function (OpenACC 2022). In this study, non-blocking communication is adopted using
MPI_Isend and
MPI_Irecv to exchange halo cells between subdomains, and blocking
MPI_Waitall is called to check the completeness of the communication. The CUDA-aware MPI (Kraus 2013) library with GPUDirect for peer-to-peer (P2P) transfer is used to directly buffers between the memories of two GPUs on the same node. In OpenACC, the
host_data use_device () is utilized before MPI calls to avoid CPU and GPU data transfer. To improve the performance, computation and MPI communication are overlapped. As proposed in Kraus (2022), for each subdomain, the computation of cells close to the boundary is performed, then the halo cells are exchanged between the subdomains concurrently while computing the internal cells.
Conclusion
A shallow water flow model using MPI and OpenACC has been developed to solve the 2D shallow water equations using the Godunov-type finite volume approach. The scheme is second-order accurate in both space and time.
The unstructured 2D triangular grid was used to implement the multi-GPU explicit-time-step finite volume model. Domain decomposition was performed by the METIS library, and to minimize the MPI message latency time, the sent and received cell numbering was especially considered for each subdomain.
Finally, the single-GPU and multi-GPU models' performances were compared to the multi-CPU model. The maximum speedup ratios obtained with 1 GPU, 4 GPUs, and 8 GPUs are 56.18, 182.33, and 331.51, respectively, versus a 6-core CPU with the largest grid resolution. It was concluded that as the resolution of mesh cells increases, so does the speedup ratio.
References
- Alcrudo, Francisco, and Pilar Garcia-Navarro. 1993. 'A high-resolution Godunov-type scheme in finite volumes for the 2D shallow-water equations', International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 16: 489-505.
- AWS. 2022. 'Linux Accelerated Computing', Accessed 8 November. https://www.amazonaws.cn/en/ec2/instance-types/.
- Begnudelli, Lorenzo, and Brett F Sanders. 2006. 'Unstructured grid finite-volume algorithm for shallow-water flow and scalar transport with wetting and drying', Journal of hydraulic engineering, 132: 371-84.
- ———. 2007. 'Conservative wetting and drying methodology for quadrilateral grid finite-volume models', Journal of hydraulic engineering, 133: 312-22.
- Bi, Sheng, Lixiang Song, Jianzhong Zhou, Linghang Xing, Guobing Huang, Minghai Huang, and Suncana Kursan. 2015. 'Two-dimensional shallow water flow modeling based on an improved unstructured finite volume algorithm', Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 7: 1687814015598181.
- Bradford, Scott F, and Brett F Sanders. 2002. 'Finite-volume model for shallow-water flooding of arbitrary topography', Journal of hydraulic engineering, 128: 289-98.
- Caplan, Ronald M, Jon A Linker, Zoran Mikić, Cooper Downs, Tibor Török, and VS Titov. 2019. "GPU Acceleration of an Established Solar MHD Code using OpenACC." In Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 012012. IOP Publishing.
- Colgrove, Mathew. 2021. 'Boiler plate code', Accessed 20 August. https://forums.developer.nvidia.com/t/failure-when-using-openacc-after-mpi-init/176124/2.
- Delis, AI, and IK Nikolos. 2013. 'A novel multidimensional solution reconstruction and edge-based limiting procedure for unstructured cell-centered finite volumes with application to shallow water dynamics', International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 71: 584-633.
- Delis, Anargiros I, IK Nikolos, and M Kazolea. 2011. 'Performance and comparison of cell-centered and node-centered unstructured finite volume discretizations for shallow water free surface flows', Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 18: 57-118.
- Forum, MPI. 2021. "MPI: A Message-Passing Interface Standard Version 4.0." In.
- Group, Khronos. 2022. 'Khronos OpenCL Working Group, The OpenCL Specification', Accessed 10 July. https://registry.khronos.org/OpenCL/specs/3.0-unified/html/OpenCL_API.html.
- Herdman, JA, WP Gaudin, Simon McIntosh-Smith, Michael Boulton, David A Beckingsale, AC Mallinson, and Stephen A Jarvis. 2012. "Accelerating hydrocodes with OpenACC, OpenCL and CUDA." In 2012 SC Companion: High Performance Computing, Networking Storage and Analysis, 465-71. IEEE.
- Hou, Jingming, Qiuhua Liang, Hongbin Zhang, and Reinhard Hinkelmann. 2015. 'An efficient unstructured MUSCL scheme for solving the 2D shallow water equations', Environmental Modelling & Software, 66: 131-52.
- Hou, Jingming, Franz Simons, Mohamed Mahgoub, and Reinhard Hinkelmann. 2013. 'A robust well-balanced model on unstructured grids for shallow water flows with wetting and drying over complex topography', Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering, 257: 126-49.
- Hu, Xiaozhang, and Lixiang Song. 2018. 'Hydrodynamic modeling of flash flood in mountain watersheds based on high-performance GPU computing', Natural hazards, 91: 567-86.
- Hubbard, ME. Hubbard, ME. 1999. 'Multidimensional slope limiters for MUSCL-type finite volume schemes on unstructured grids', Journal of computational Physics, 155: 54-74.
- Karypis, George, and Vipin Kumar. 1997. 'METIS: A software package for partitioning unstructured graphs, partitioning meshes, and computing fill-reducing orderings of sparse matrices'.
- Kraus, Jiri. 2013. 'An Introduction to CUDA-Aware MPI', Accessed 17 August. https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/introduction-cuda-aware-mpi/.
- ———. 2022. 'Multi-GPU Programming with MPI', Accessed 20 August. https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtcspring22-s41018/.
- Lai, Wencong, and Abdul A Khan. 2017. 'A parallel two-dimensional discontinuous galerkin method for shallow-water flows using high-resolution unstructured meshes', Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 31: 04016073.
- Liang, Qiuhua. 2010. 'Flood simulation using a well-balanced shallow flow model', Journal of hydraulic engineering, 136: 669-75.
- Liang, Qiuhua, and Alistair GL Borthwick. 2009. 'Adaptive quadtree simulation of shallow flows with wet–dry fronts over complex topography', Computers & Fluids, 38: 221-34.
- Liang, Qiuhua, and Fabien Marche. 2009. 'Numerical resolution of well-balanced shallow water equations with complex source terms', Advances in Water Resources, 32: 873-84.
- Norman, Matthew R. 2022. 'Introduction to OpenACC directives', Accessed 5 August. https://github.com/mrnorman/miniWeather/blob/main/documentation/intro_to_openacc.pdf.
- NVIDIA. 2022. 'CUDA C++ Programming Guide', Accessed 10 July. https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/pdf/CUDA_C_Programming_Guide.pdf.
- OpenACC. 2022. 'OpenACC Programming and best practices guide', Accessed 10 July. https://www.openacc.org/sites/default/files/inline-files/openacc-guide.pdf.
- Saleem, Ayhan H, and Jowhar R Mohammad. 2020. 'Simulation of Mosul Dam Break Using Finite Volume Method', Polytechnic Journal, 10: 10-20.
- Song, Lixiang, Jianzhong Zhou, Jun Guo, Qiang Zou, and Yi Liu. 2011. 'A robust well-balanced finite volume model for shallow water flows with wetting and drying over irregular terrain', Advances in Water Resources, 34: 915-32.
- Song, Lixiang, Jianzhong Zhou, Qingqing Li, Xiaoling Yang, and Yongchuan Zhang. 2011. 'An unstructured finite volume model for dam-break floods with wet/dry fronts over complex topography', International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 67: 960-80.
- Toro, Eleuterio F. 2001. Shock-capturing methods for free-surface shallow flows (Wiley-Blackwell).
- Van Leer, Bram. 1979. 'Towards the ultimate conservative difference scheme. V. A second-order sequel to Godunov's method', Journal of computational Physics, 32: 101-36.
- Wright, Eric, Damien Przybylski, Matthias Rempel, Cena Miller, Supreeth Suresh, Shiquan Su, Richard Loft, and Sunita Chandrasekaran. 2021. "Refactoring the MPS/University of Chicago Radiative MHD (MURaM) model for GPU/CPU performance portability using OpenACC directives." In Proceedings of the Platform for Advanced Scientific Computing Conference, 1-12.
- Xue, Weicheng, Charles W Jackson, and Christoper J Roy. 2021. 'An improved framework of GPU computing for CFD applications on structured grids using OpenACC', Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 156: 64-85.
- Xue, Weicheng, and Christoper J Roy. 2021. 'Multi-GPU performance optimization of a computational fluid dynamics code using OpenACC', Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 33: e6036.
- Zhang, HW, J Zhu, ZW Ma, GY Kan, X Wang, and W Zhang. 2019. 'Acceleration of three-dimensional Tokamak magnetohydrodynamical code with graphics processing unit and OpenACC heterogeneous parallel programming', International Journal of Computational Fluid Dynamics, 33: 393-406.
- Zhang, Shanghong, Rui Yuan, Yu Wu, and Yujun Yi. 2016. 'Implementation and efficiency analysis of parallel computation using OpenACC: a case study using flow field simulations', International Journal of Computational Fluid Dynamics, 30: 79-88.
- ———. 2017. 'Parallel computation of a dam-break flow model using OpenACC applications', Journal of hydraulic engineering, 143: 04016070.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).