Submitted:
29 January 2024
Posted:
30 January 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultivation
2.2. Preparation of the ZnCl2 Solution
2.3. Preparation of the Materials
2.4. Preparation of the Extracts
2.5. Metabolic Activity of hFOB 1.19 and Cytotoxicity of Zn2+ towards hFOB 1.19 after Long-Term Cultivation at Different Temperatures
2.6. Cytotoxicity of Zn2+ and Extracts towards hFOB 1.19 and L929 in Different Media
2.7. Zn2+ and Extracts Cytotoxicity towards hFOB 1.19 and L929 in Different Media
2.8. Evaluation of Metabolic Activity (Resazurin Assay)
2.9. ICP-MS Measurement
3. Results
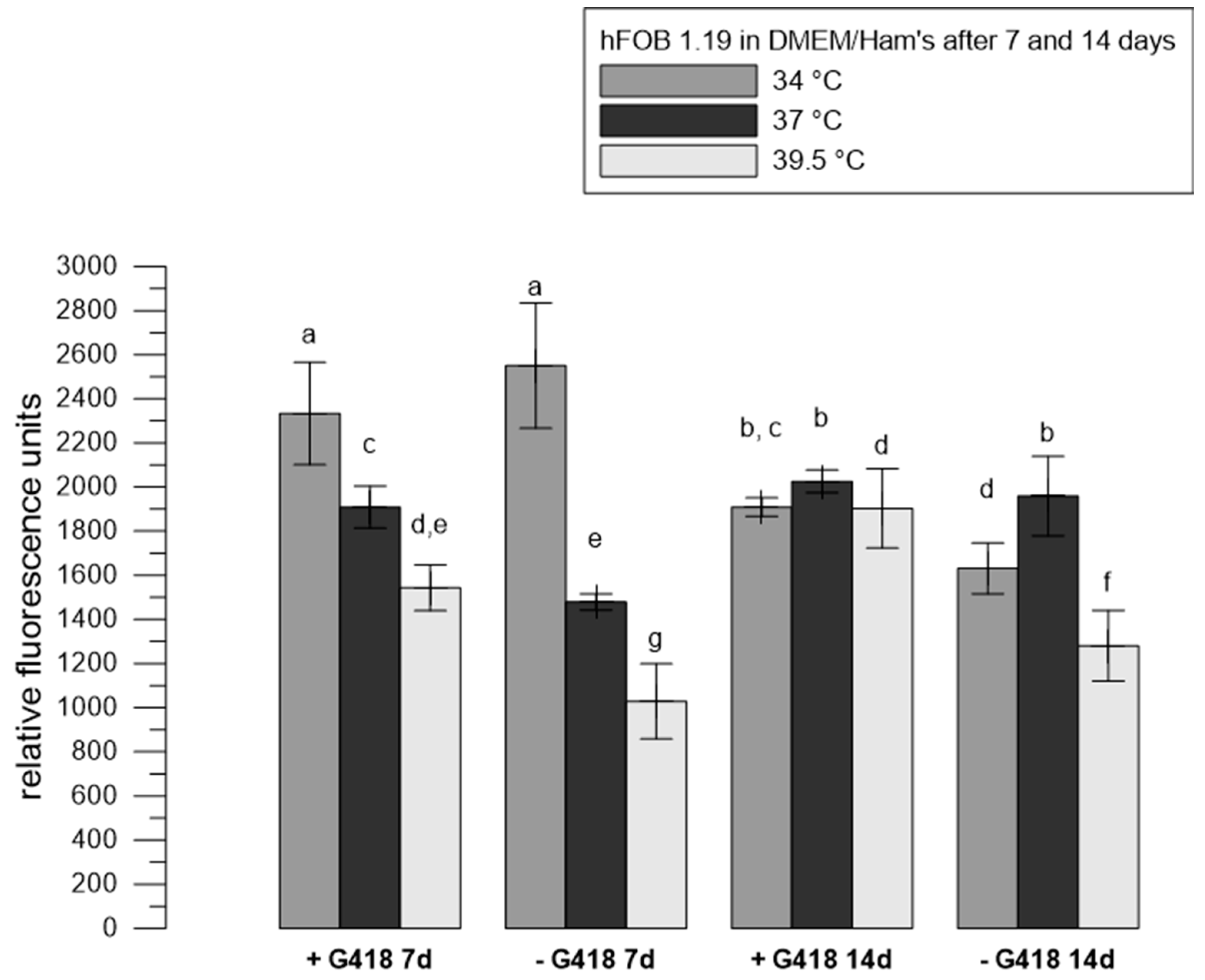
3.1. The Influence of Selection Reagent on the Metabolic Activity of hFOB 1.19
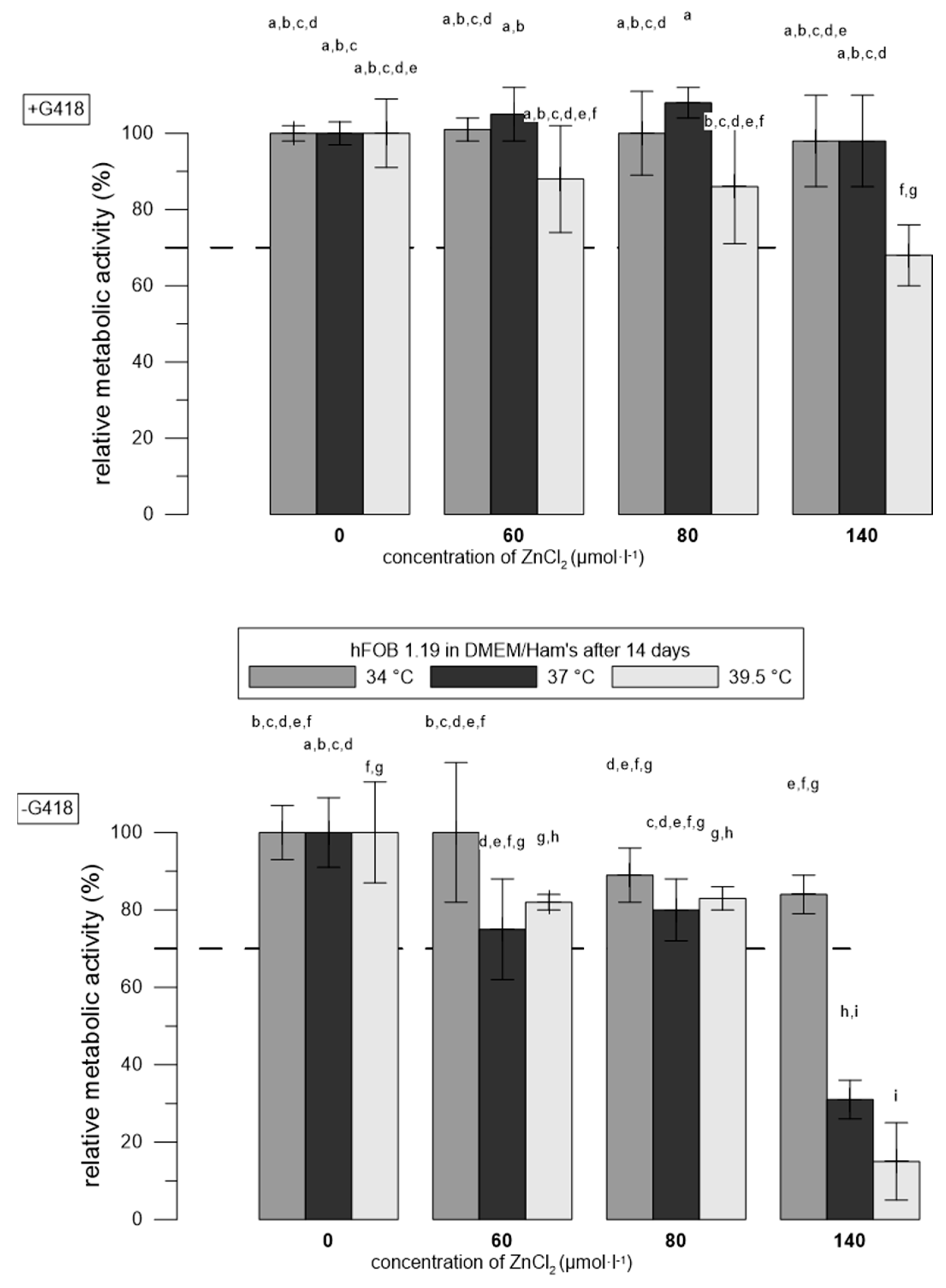
3.2. Zn2+ Were More Toxic to hFOB 1.19 Cells at Restrictive Temperatures than at Permissive Temperatures
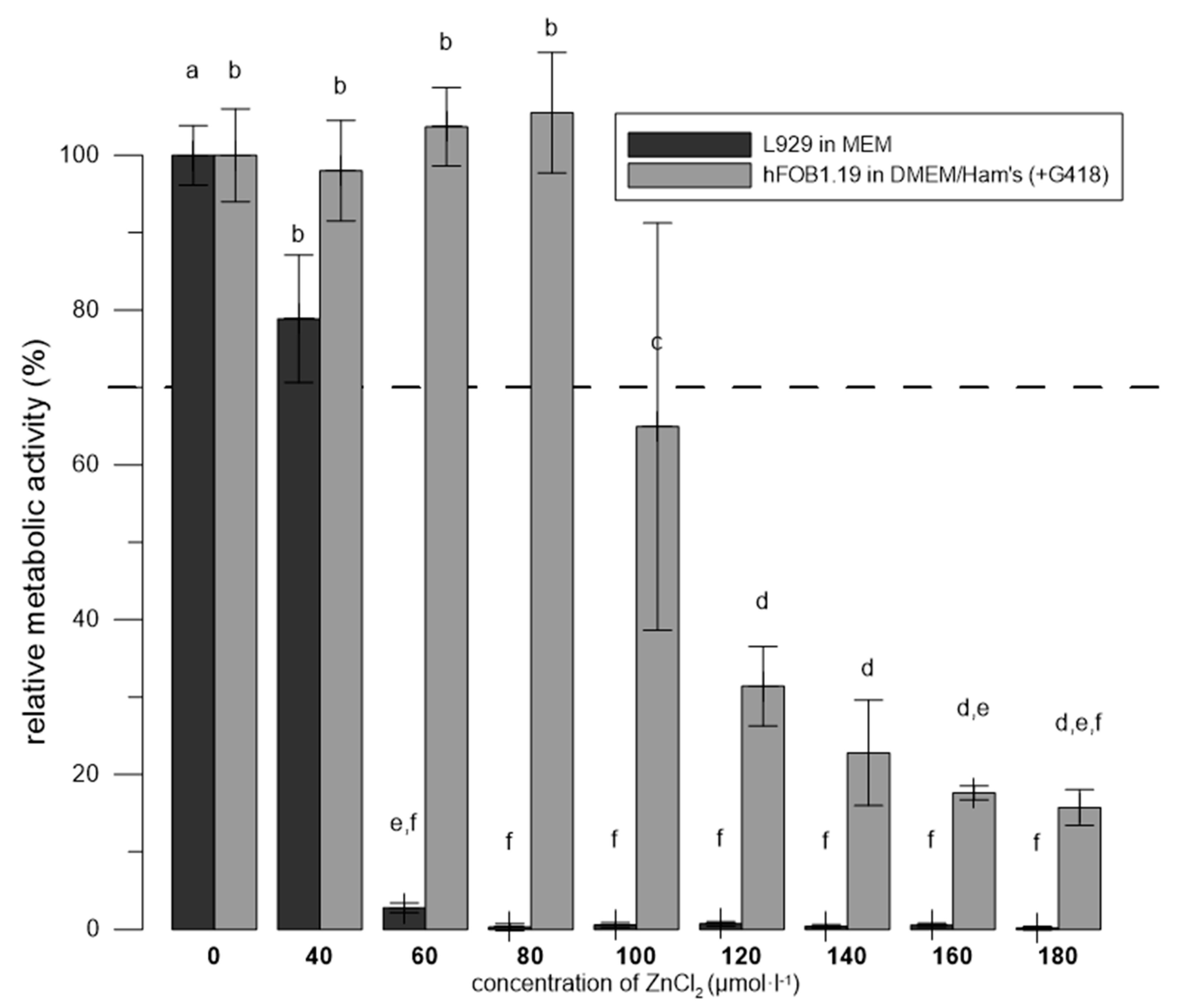
3.3. Zn2+ Were More Toxic to L929 than to hFOB 1.19 in the Media Recommended for Each Cell Line
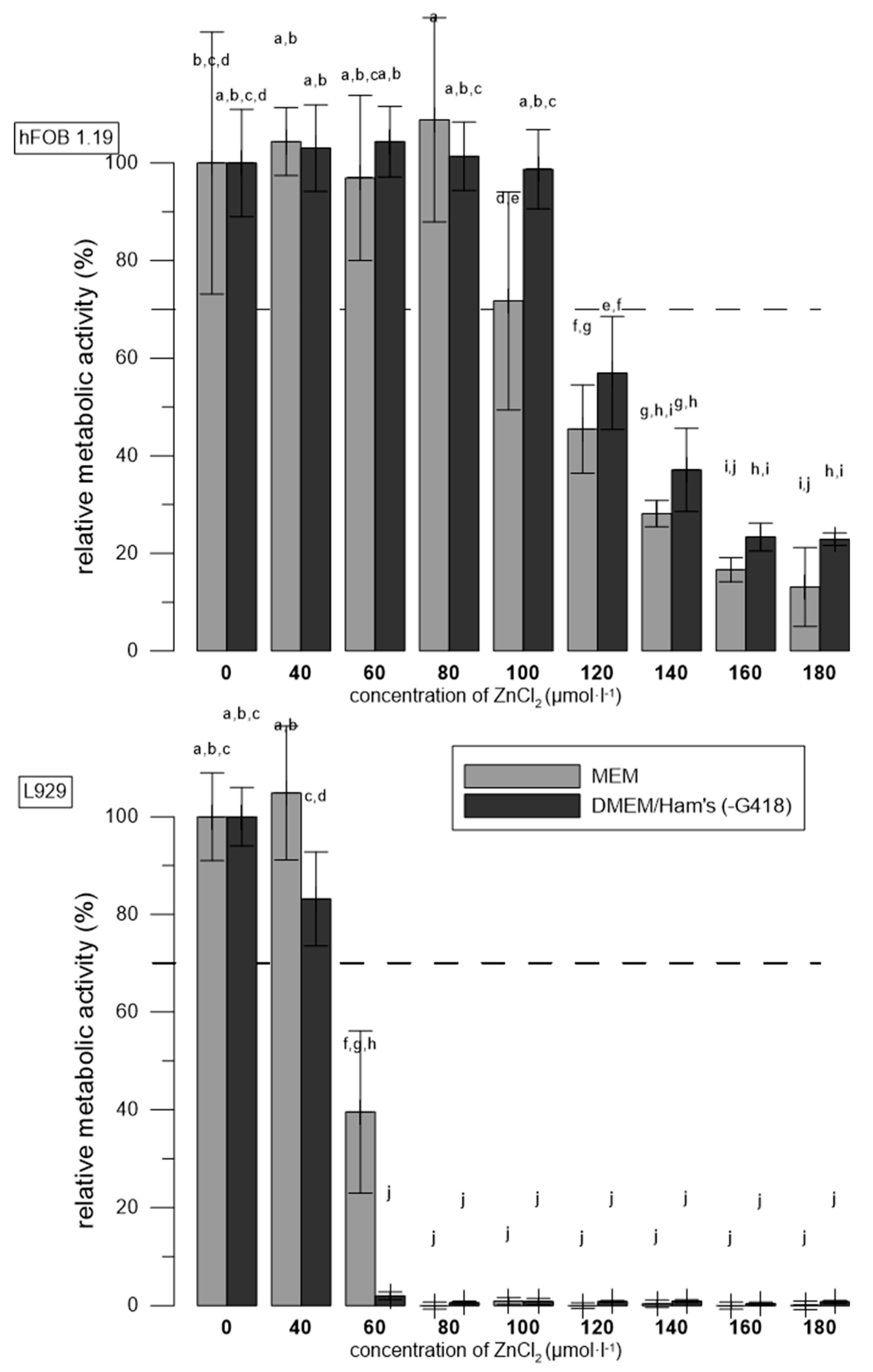
3.4. The Effect of Media Used
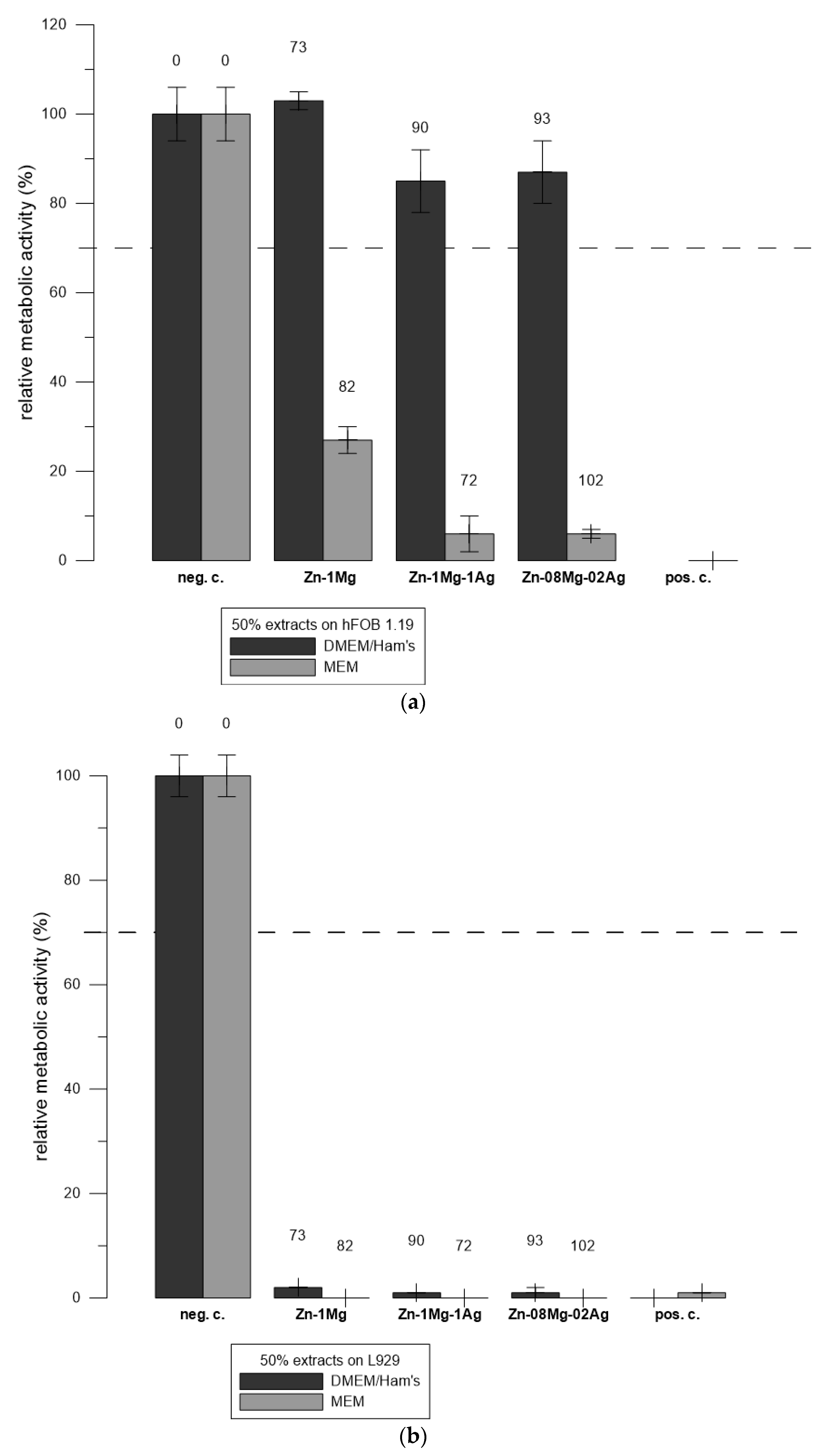
3.5. Comparison of the Cytotoxicity of Extracts of Alloys in Different Media towards hFOB 1.19 and L929
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Y.F. Zheng, X.N. Gu, F. Witte, Biodegradable metals, Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports 77 (2014) 1-34. [CrossRef]
- D. Vojtěch, J. Kubásek, J. Šerák, P. Novák, Mechanical and corrosion properties of newly developed biodegradable Zn-based alloys for bone fixation, Acta Biomater. 7(9) (2011) 3515-3522. [CrossRef]
- Pospíšilová, D. Vojtěch, Zinc alloys for biodegradable medical implants, Mater. Sci. Forum, Trans Tech Publ, 2014, pp. 457-460. [CrossRef]
- J. Venezuela, M.S. Dargusch, The influence of alloying and fabrication techniques on the mechanical properties, biodegradability and biocompatibility of zinc: A comprehensive review, Acta Biomaterialia 87 (2019) 1-40. [CrossRef]
- H. Yang, B. Jia, Z. Zhang, X. Qu, G. Li, W. Lin, D. Zhu, K. Dai, Y. Zheng, Alloying design of biodegradable zinc as promising bone implants for load-bearing applications, Nature Communications 11(1) (2020) 401. [CrossRef]
- G. Katarivas Levy, J. Goldman, E. Aghion, The Prospects of Zinc as a Structural Material for Biodegradable Implants—A Review Paper, Metals 7(10) (2017). [CrossRef]
- Antoniac, R. Adam, A. Biță, M. Miculescu, O. Trante, I.M. Petrescu, M. Pogărășteanu, Comparative Assessment of In Vitro and In Vivo Biodegradation of Mg-1Ca Magnesium Alloys for Orthopedic Applications, Materials (Basel) 14(1) (2020). [CrossRef]
- S. Janardhanan, M.O. Wang, J.P. Fisher, Coculture strategies in bone tissue engineering: The impact of culture conditions on pluripotent stem cell populations, Tissue Engineering–Part B: Reviews 18(4) (2012) 312-321. [CrossRef]
- G. Hulsart-Billström, J.I. Dawson, S. Hofmann, R. Müller, M.J. Stoddart, M. Alini, R. Redl, A. El Haj, R. Brown, V. Salih, J. Hilborn, S. Larsson, R.O.C. Oreffo, A surprisingly poor correlation between in vitro and in vivo testing of biomaterials for bone regeneration: results of a multicentre analysis, European Cells and Materials 31 (2016) 312-322. [CrossRef]
- G. Rijal, W. Li, Native-mimicking in vitro microenvironment: An elusive and seductive future for tumor modeling and tissue engineering, J. Biol. Eng. 12(1) (2018). [CrossRef]
- J.M. Anderson, Future challenges in the in vitro and in vivo evaluation of biomaterial biocompatibility, Regenerative Biomaterials 3(2) (2016) 73-77. [CrossRef]
- S. Ray, M.E. Anderson, G. Loeber, D. McVey, P. Tegtmeyer, Functional characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40 large T antigen, J Virol 66(11) (1992) 6509-6516. [CrossRef]
- Reynisdóttir, D. O’Reilly, L. Miller, C.J.J.o.v. Prives, Thermally inactivated simian virus 40 tsA58 mutant T antigen cannot initiate viral DNA replication in vitro, 64(12) (1990) 6234-6245. [CrossRef]
- ISO, Biological evaluation of medical devices, Part 5:Tests for in vitro cytotoxicity, 2009, p. 34.
- C. Pautke, M. Schieker, T. Tischer, A. Kolk, P. Neth, W. Mutschler, S. Milz, Characterization of osteosarcoma cell lines MG-63, Saos-2 and U-2 OS in comparison to human osteoblasts, Anticancer Res. 24(6) (2004) 3743-8.
- E.M. Czekanska, M.J. Stoddart, J.R. Ralphs, R.G. Richards, J.S. Hayes, A phenotypic comparison of osteoblast cell lines versus human primary osteoblasts for biomaterials testing, J Biomed Mater Res A (2013). [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu, T. Du, A. Qiao, Y. Mu, H. Yang, Zinc-Based Biodegradable Materials for Orthopaedic Internal Fixation, Journal of functional biomaterials 13(4) (2022). [CrossRef]
- W. Yuan, D. Xia, S. Wu, Y. Zheng, Z. Guan, J.V. Rau, A review on current research status of the surface modification of Zn-based biodegradable metals, Bioactive Materials 7 (2022) 192-216. [CrossRef]
- E. Jablonska, J. Kubasek, D. Vojtech, T. Ruml, J. Lipov, Test conditions can significantly affect the results of in vitro cytotoxicity testing of degradable metallic biomaterials, Sci. Rep. 11(1) (2021) 6628. [CrossRef]
- S.A. Harris, R.J. Enger, L.B. Riggs, T.C. Spelsberg, Development and characterization of a conditionally immortalized human fetal osteoblastic cell line, Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 10(2) (1995) 178-186. [CrossRef]
- M. Subramaniam, S.M. Jalal, D.J. Rickard, S.A. Harris, M.E. Bolander, T.C. Spelsberg, Further characterization of human fetal osteoblastic hFOB 1.19 and hFOB/ER alpha cells: bone formation in vivo and karyotype analysis using multicolor fluorescent in situ hybridization, J. Cell. Biochem. 87(1) (2002) 9-15. [CrossRef]
- M.-L. Yen, C.-C. Chien, I.-M. Chiu, H.-I. Huang, Y.-C. Chen, H.-I. Hu, B. Yen, Multilineage Differentiation and Characterization of the Human Fetal Osteoblastic 1.19 Cell Line: A Possible In Vitro Model of Human Mesenchymal Progenitors, Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio) 25 (2007) 125-31. [CrossRef]
- S. Marozin, B. Simon-Nobbe, S. Irausek, L.W.K. Chung, G. Lepperdinger, Kinship of conditionally immortalized cells derived from fetal bone to human bone-derived mesenchymal stroma cells, Sci. Rep. 11(1) (2021) 10933. [CrossRef]
- M. Cieslik, A. Mertas, A. Morawska-Chochół, D. Sabat, R. Orlicki, A. Owczarek, W. Król, T. Cieślik, The Evaluation of the Possibilities of Using PLGA Co-Polymer and Its Composites with Carbon Fibers or Hydroxyapatite in the Bone Tissue Regeneration Process–in Vitro and in Vivo Examinations, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 10 (2009) 3224-34. [CrossRef]
- K. Steckiewicz, E. Barcinska, A. Malankowska, A. Zauszkiewicz-Pawlak, G. Nowaczyk, A. Zaleska-Medynska, I. Inkielewicz-Stepniak, Impact of gold nanoparticles shape on their cytotoxicity against human osteoblast and osteosarcoma in in vitro model. Evaluation of the safety of use and anti-cancer potential, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 30 (2019). [CrossRef]
- M. Pallavi, J. Waterman, Y. Koo, J. Sankar, Y. Yun, In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Possible Corrosion Products from Mg-Based Biodegradable Metals: Magnesium Oxide and Magnesium Hydroxide Nanoparticles, Applied Sciences 9 (2019) 4304. [CrossRef]
- P.V. Gnaneshwar, S.V. Sudakaran, S. Abisegapriyan, J. Sherine, S. Ramakrishna, M.H.A. Rahim, M.M. Yusoff, R. Jose, J.R. Venugopal, Ramification of zinc oxide doped hydroxyapatite biocomposites for the mineralization of osteoblasts, Materials Science and Engineering: C 96 (2019) 337-346. [CrossRef]
- H.J. Donahue, Z. Li, Z. Zhou, C.E. Yellowley, Differentiation of human fetal osteoblastic cells and gap junctional intercellular communication, Am J Physiol-Cell Ph 278(2) (2000) C315-C322. [CrossRef]
- Oki, B. Parveen, S. Hossain, S. Adeniji, H. Donahue, Preparation and in vitro bioactivity of zinc containing sol-gel–derived bioglass materials, Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 69A(2) (2004) 216-221. [CrossRef]
- L. Saidykhan, M.Z. Abu Bakar, Y. Rukayadi, A. Kura, S. Latifah, Development of nanoantibiotic delivery system using cockle shell-derived aragonite nanoparticles for treatment of osteomyelitis, International journal of nanomedicine 2016 (2016) 661–673. [CrossRef]
- V. Balla, A. Bhat, S. Bose, A. Bandyopadhyay, Laser Processed TiN Reinforced Ti6Al4V Composite Coatings, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 6 (2012) 9-20. [CrossRef]
- B. Setzer, M. Bächle, M.C. Metzger, R.J. Kohal, The gene-expression and phenotypic response of hFOB 1.19 osteoblasts to surface-modified titanium and zirconia, Biomaterials 30(6) (2009) 979-990. [CrossRef]
- G. Eugen, M. Claus, S. Anna-Maria, D. Niklas, S. Philipp, E. Andrea, M.-L. Andrea, V. Elke, Degradation of 3D-printed magnesium phosphate ceramics in vitro and a prognosis on their bone regeneration potential, Bioactive Materials 19 (2023) 376-391. [CrossRef]
- D. Predoi, S.L. Iconaru, M.V. Predoi, Fabrication of Silver- and Zinc-Doped Hydroxyapatite Coatings for Enhancing Antimicrobial Effect, Coatings 10(9) (2020) 905. [CrossRef]
- Donnadio, M. Bini, C. Centracchio, M. Mattarelli, S. Caponi, V. Ambrogi, D. Pietrella, A. Di Michele, R. Vivani, M. Nocchetti, Bioinspired Reactive Interfaces Based on Layered Double Hydroxides-Zn Rich Hydroxyapatite with Antibacterial Activity, ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 7(4) (2021) 1361-1373. [CrossRef]
- Laskus-Zakrzewska, P. Kazimierczak, J. Kolmas, Porous Composite Granules with Potential Function of Bone Substitute and Simvastatin Releasing System: A Preliminary Study, Materials 14(17) (2021) 5068. [CrossRef]
- Chirica, A.-M. Enciu, T. Teddy, M. Dudau, L. Albulescu, S.L. Iconaru, D. Predoi, I. Pasuk, M. Enculescu, C. Radu, C. Mihalcea, A.-C. Popa, N. Rusu, S. Niţă, C. Tănase, G. Stan, The Physico-Chemical Properties and Exploratory Real-Time Cell Analysis of Hydroxyapatite Nanopowders Substituted with Ce, Mg, Sr, and Zn (0.5–5 at.%), Materials 14 (2021) 3808. [CrossRef]
- J. Higuchi, K. Klimek, J. Wojnarowicz, A. Opalińska, A. Chodara, U. Szałaj, S. Dąbrowska, D. Fudala, G. Ginalska, Electrospun Membrane Surface Modification by Sonocoating with HA and ZnO:Ag Nanoparticles—Characterization and Evaluation of Osteoblasts and Bacterial Cell Behavior In Vitro, Cells 11(9) (2022) 1582. [CrossRef]
- P. Kazimierczak, J. Golus, J. Kolmas, M. Wojcik, D. Kolodynska, A. Przekora, Noncytotoxic zinc-doped nanohydroxyapatite-based bone scaffolds with strong bactericidal, bacteriostatic, and antibiofilm activity, Biomaterials Advances 139 (2022) 213011. [CrossRef]
- J. Kubasek, D. Vojtech, E. Jablonska, I. Pospisilova, J. Lipov, T. Ruml, Structure, mechanical characteristics and in vitro degradation, cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and mutagenicity of novel biodegradable Zn-Mg alloys, Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 58 (2016) 24-35. [CrossRef]
- J. Kubásek, J. Pinc, K. Hosová, M. Straková, O. Molnárová, J. Duchoň, D. Nečas, M. Čavojský, M. Knapek, M. Godec, I. Paulin, D. Vojtěch, J. Čapek, The evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of Zn-0.8Mg-0.2Sr alloy prepared by casting and extrusion, J. Alloy. Compd. 906 (2022). [CrossRef]
- D. Nečas, J. Kubásek, J. Pinc, I. Marek, Č. Donik, I. Paulin, D. Vojtěch, Ultrafine-Grained Zn–Mg–Sr Alloy Synthesized by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering, Materials 15(23) (2022) 8379. [CrossRef]
- D. Nečas, I. Marek, J. Pinc, D. Vojtěch, J. Kubásek, Advanced Zinc-Magnesium Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering, Materials 15(15) (2022) 5272. [CrossRef]
- T.L. Riss, R.A. Moravec, A.L. Niles, S. Duellman, H.A. Benink, T.J. Worzella, L. Minor, Cell Viability Assays, in: G.S. Sittampalam, N.P. Coussens, B. K. (Eds.), Assay Guidance Manual2016.
- W. Liu, Y. Xiong, M. Gossen, Stability and homogeneity of transgene expression in isogenic cells, J. Mol. Med. 84(1) (2006) 57-64. [CrossRef]
- Ničová, Quantitative analysis of hFOB1.19 cell line proteome, The University of Chemistry and Technology, Prague, 2021.
- E. Jablonská, J. Kubásek, D. Vojtěch, T. Ruml, J. Lipov, Test conditions can significantly affect the results of in vitro cytotoxicity testing of degradable metallic biomaterials, Sci. Rep. 11(1) (2021). [CrossRef]
- T. Yao, Y. T. Yao, Y. Asayama, Animal-cell culture media: History, characteristics, and current issues, Reprod. Med. Biol. 16(2) (2017) 99-117. [CrossRef]
- Sigma-Aldrich, Riboflavin in Cell Culture. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/CZ/en/technical-documents/technical-article/cell-culture-and-cell-culture-analysis/mammalian-cell-culture/riboflavin (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- G. Chandra, A. Pandey, Biodegradable bone implants in orthopedic applications: a review, Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering 40(2) (2020) 596--610. [CrossRef]
- Z. Cui, M. Luo, Y. Zhang, D. Gong, W. Wang, J. Wang, Fabrication of high strength and plasticity of Zn-Mg composites with core–shell structure by spark plasma sintering, Materials Letters 279 (2020). [CrossRef]
- P. Sotoudeh Bagha, S. Khaleghpanah, S. Sheibani, M. Khakbiz, A. Zakeri, Characterization of nanostructured biodegradable Zn-Mn alloy synthesized by mechanical alloying, J. Alloy. Compd. 735 (2018) 1319-1327. [CrossRef]
- X. Xiao, E. X. Xiao, E. Liu, J. Shao, S. Ge, Advances on biodegradable zinc-silver-based alloys for biomedical applications, Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials 19 (2021) 22808000211062407. [CrossRef]
- A.B. Lansdown, Silver in health care: antimicrobial effects and safety in use, Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 33 (2006) 17-34. [CrossRef]
| Material | G418 | Temperatures | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| sol-gel–prepared glass materials with ZnO | not mentioned | 37 °C as permissive39.5 °C as restrictive | [29] |
| Zn-doped HA coatings | not mentioned | 37 °C | [34] |
| Reactive interfaces based on hydroxides-Zn rich HA | present | 37 °C | [35] |
| 3D porous granules based on Zn-containing CaPs | present | 34 °C | [36] |
| Zn- doped HA nanopowders | not mentioned | 34 °C | [37]. |
| HA and bimetallic nanocomposite of ZnO–Ag | present | 34 °C | [38] |
| Zn-doped nanoHA-based bone scaffolds | present | 34 °C | [39] |
| Designation (composition in wt. %) | Synthesis | Processing conditions (temperature and extrusion ratio) |
|---|---|---|
| Zn-1Mg | Powder metallurgy | Extrusion of powder billets at 200 °C and extrusion ratio 25 |
| Zn-1Mg-1Ag | Powder metallurgy | Extrusion of powder billets at 200 °C and extrusion ratio 25 |
| Zn-0.8Mg-0.2Ag | Conventional casting and extrusion | Extrusion of casted ingot at 200 °C and extrusion ratio 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





