Introduction
Idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias are defined as rhythm disorders detected in individuals without structural heart disease or genetic ion channel defects,. Idiopathic premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are rhythm problems that are commonly encountered in clinical practice. While they often present asymptomatically, they can rarely lead to syncope or sudden cardiac death[
1]. Idiopathic PVCs are generally considered benign, but studies have shown that increasing PVC burden can lead to impairments in left ventricular function[
2,
3,
4,
5]. The PVC burden, QRS duration, short coupling interval duration, frequency of non-sustained ventricular tachycardia, and presence of PVCs with different morphologies have been reported to predict left ventricular dysfunction[
6,
7,
8]. It has been demonstrated in the literature that increasing PVC frequency can lead to ventricular dilatation and reduced ejection fraction (EF)[
4,
5]. In patients with preserved LVEF, data concerning the association between premature PVC burden and functional impairment in the left ventricle are limited. Recently, the use of speckle tracking echocardiography has been associated with the detection of subclinical ventricular dysfunction by assessing left ventricular global longitudinal strain (LVGLS) values. However, the cut-off values for PVC burden that cause impairment in left ventricular function have not yet been clearly defined[
8,
9,
10]. In our study, we aimed to investigate the effects of PVC burden on left ventricular function (LVGLS and Myocardial Performance Index, MPI) in patients with normal LVEF who have idiopathic PVCs. Additionally, we aimed to determine the cut-off values of PVC burden that predict impairment in LVGLS.
Material and Method
Study Population
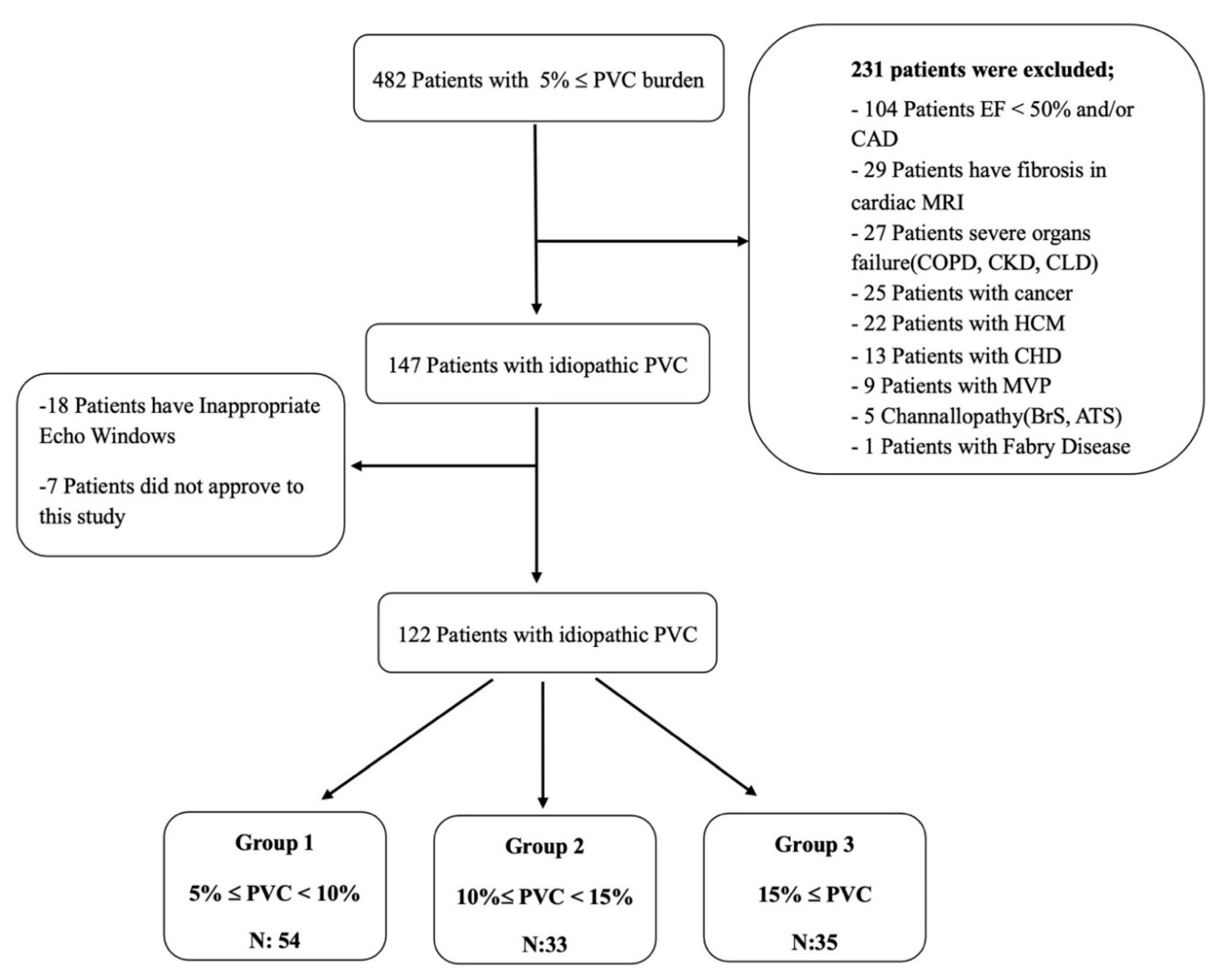
Our study included consecutive patients who presented to our arrhythmia clinic between 2019 and 2022 with a diagnosis of idiopathic frequent PVCs. The 24-hour rhythm Holter recordings of the patients were reviewed. A total of 147 patients with an idiopathic PVC burden of more than 5% were analyzed. Among them, 122 patients who met the inclusion criteria, had appropriate echocardiographic images and had no familial relationship with each other were selected and included in the study.
The inclusion criteria of our study were defined as being older than 18 years of age, having a PVC burden of over 5% and providing informed voluntary consent. Exclusion criteria for our study were patients with a diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD), cardiomyopathy, moderate to severe valvular heart disease (VHD), congenital heart disease (CHD), diagnosed arrhythmic genetic syndromes, ion channel defects, left ventricular hypertrophy, mitral valve prolapse (MVP), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <50%, presence of fibrosis on cardiac MRI, severe organ failure (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, chronic liver disease) , cancer diagnosis. These patients were excluded from the study. The definition of idiopathic frequent PVC was determined as to be PVCs outside the exclusion criteria stated above. Informed consent was obtained from each patient and the study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki 1975, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa (E-69291215-900-16420 and 2 March 2021). The 122 patients included in the study were divided into three groups based on the PVC burden. A flow chart of this study is given in
Figure 1. The demographic characteristics of the patients were obtained by reviewing the hospital automation system notes, calling patients for follow-up visits and conducting face-to-face interviews, as well as scanning patient medical records.
Electrocardiography (ECG) and Rhythm Holter Analysis
The baseline heart rates, QTc intervals, and presence or absence of PVCs were evaluated in the available 12-lead ECG recordings of the patients. The QTc intervals were calculated using the Bazett formula (QTc = QT / √R-R).
In the Holter recordings of the patients reviewed and included in the study, along with PVC burden, the average heart rate, minimum heart rate, maximum heart rate, presence of non-sustained ventricular tachycardia (NSVT), and its morphology were noted. The PVC burden of the patients was obtained by dividing the number of PVCs detected in the 24-hour Holter recordings by the total QRS count calculated within 24 hours and it was recorded in the patient files.
The included patients were divided into three groups based on their PVC burden for evaluation. The groups were defined as follows based on PVC burden: Group 1 for patients with 5%≤ PVC <10%, Group 2 for patients with 10%≤ PVC <15%, and Group 3 for patients with PVC burden ≥15%.
Transthoracic Echocardiographic (TTE) Evaluation
The echocardiographic measurements and evaluations were performed by two experienced cardiologists who were blinded to patient characteristics. Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) recordings of the patients were obtained using the Philips Epiq 7 (Philips Medical Systems, MA, USA) device. In TTE, each patient's parasternal long-axis and short-axis views, as well as apical two-chamber, apical three-chamber, and apical four-chamber views, were obtained under ECG guidance. LVEF was calculated by evaluating three consecutive beats without PVC and using the a modified Simpson's method. Images were obtained using the techniques recommended by the European Association of Echocardiography (EAE)/American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) guidelines[
11]. Apical two-chamber, apical three-chamber, and apical four-chamber recordings were analyzed for LV-GLS. LV-GLS values were calculated and recorded using the QLAB-CMQ Autostrain computer program. For the calculation of the MPI, measurements of the mitral valve inflow velocities were obtained using a pulse wave Doppler cursor positioned below the plane of the aortic valve in the apical five-chamber view. All measurements were recorded as the average of measurements obtained over three consecutive cardiac cycles.
The isovolumetric relaxation time (IVRT) was measured as the time interval from aortic valve closure to mitral valve opening. The isovolumetric contraction time (IVCT) was measured as the time interval from mitral valve closure to aortic valve opening. The ejection time (ET) was measured as the duration from the opening to the closure of the aortic valve in the left ventricular outflow velocity profile. The Myocardial Performance Index (MPI) was calculated by dividing the sum of IVRT and IVCT by ET. The obtained MPI values and GLS values were recorded in the patient files.
The study protocol was approved by the local ethics committee. Informed consent was obtained from each patient regarding our study.
Statistical Analysis
The data obtained in the study were analyzed using SPSS21 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois). A normal distribution analysis of the data was performed using the Shapiro-Wilk (W) test. Continuous variables that showed a normal distribution were presented as mean ± standard deviation, while abnormally distributed variables were reported as median (minimum-maximum) values. Categorical variables were presented in tables as frequencies and percentages. The normally distributed continuous variables among the three groups in our study were evaluated using the One-Way ANOVA test, while the abnormally distributed data were evaluated using the Kruskal-Wallis H test.
Categorical data were compared using the chi-square test. The relationship between the number of PVCs, PVC burden, LV-GLS, and MPI index parameters in our study was evaluated using correlation analysis. Since three of these parameters did not follow a normal distribution, correlation coefficients, and statistical significance were calculated using the Spearman test. In our study, different cut-off values for PVC count and PVC burden predicting deterioration in GLS were examined using Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) curve analysis. Specificity and sensitivity calculations were performed in the presence of a significant threshold value. A multiple linear regression model was constructed to identify the parameters predicting the decrease in LV-GLS; with this model, the determination of independent variables affecting the dependent variable was achieved. A total of 20 patients were randomly selected for intra- and interobserver variability analysis for GLS values, according to this; the Bland–Altman analysis was performed (
Figure S1). Statistical significance was considered at p <0.05 in all analyses.
Results
Clinical and Demographical Features and Laboratory Parameters:
Approximately 56.6% of the patients included in our study were female, and the mean age of the entire population was 45.71 ± 12.7 years. Furthermore, 69.7% of the included patients had palpitation complaints, and the average PVC count in the 24-hour rhythm holter recordings was determined as 12321 ± 8353. The evaluation of the groups in terms of baseline clinical and demographic parameters is presented in
Table 1. A significant difference in BMI was observed among the groups, with the difference originating from the higher body mass index(BMI) in Group 2 (25.4 ± 2.7, 26.6 ± 3.5, 24.7 ± 2.7; p: 0.029, respectively). In the study, it was observed that the average duration of symptoms in patients was 15 months; however, no significant difference was observed among the groups (15.57 ± 8.2; 14.94 ± 6.8; 18.54 ± 9.7; p: 0.123, respectively). Approximately 62% of the patients included in the study were evaluated for the presence of structural heart diseases and cardiac fibrosis using cardiac MRI, and none of the patients exhibited these findings. No significant differences were found among the groups regarding other clinical and demographic parameters. No significant differences were observed among the groups in terms of laboratory parameters (
Table S1).
The evaluation of the groups in terms of electrocardiographic (ECG) and echocardiographic (Echo) parameters in our study is presented in
Table 2. The presence of PVCs in the baseline ECG recordings were more frequently observed in Group 2 and Group 3 patients with a PVC burden of 10% or higher (22.2%, 42.4%, 51.4%; p=0.013). Similarly, on the 24-hour ambulatory rhythm holter recordings, NSVT episodes were more frequently observed in Group 2 and Group 3 patients, showing statistically significant differences (14.8%, 39.4%, 42.9%; p=0.006). There were no significant differences among the groups in terms of the rate of polymorphic PVCs in the Holter recordings, QTc values in the baseline ECG recordings, and other ECG and Holter parameters. The right ventricular end-diastolic diameters (RVd) were found to be significantly lower in Group 2 patients compared to the other groups (22.33 ± 1.9, 23.48 ± 1.9, 22.57 ± 2.0; p=0.044, respectively). Although the myocardial performance index (MPI) did not reach statistical significance, numerically lower values were observed in Group 3 patients with PVC burden >15% (0.50 ± 0.06, 0.48 ± 0.08, 0.47 ± 0.06; p=0.143, respectively). When comparing LV-GLS values among the groups, a statistically significant difference was observed (-18.89 ± 1.4, -17.55 ± 2.1, -16.26 ± 1.3, p<0.001, respectively). No significant differences were found among the groups in terms of other Echo parameters.
Correlation and Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
The correlation analyses between PVC burden, PVC count, LV-GLS and MPI values are presented in
Table 3. An increase in PVC count and PVC burden showed a positive, moderate-level, and significant correlation with deterioration in GLS values (r: 0.555; p<0.001, r: 0.536; p<0.001, respectively). Similarly, an increase in PVC count and PVC burden showed a negative, weak-level, and significant correlation with MPI values (r: 0.220; p: 0.015, r: 0.219; p: 0.015, respectively). In addition, a correlation analysis was conducted to assess the relationship between the duration of symptoms in patients and LV-GLS values. Despite being weak, a positive correlation was identified between symptom duration and LV-GLS (r: 0.195; p: 0.032).
According to the multiple linear regression modeling, ten parameters (PVC(%), hemoglobin, ECG QTc, left atrium, left ventricular diastolic diameter, MPI, body mass index, age, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion, RVd) were assessed for their ability to predict the decrease in LV-GLS. It was determined that the percentage(%) of PVC independently predicted the decrease in LV-GLS(β: 0.525, p
<0,001; adjusted R
2:0,340) (
Table 4). Other parameters were not found to be statistically significant in this modeling.
ROC Analysis
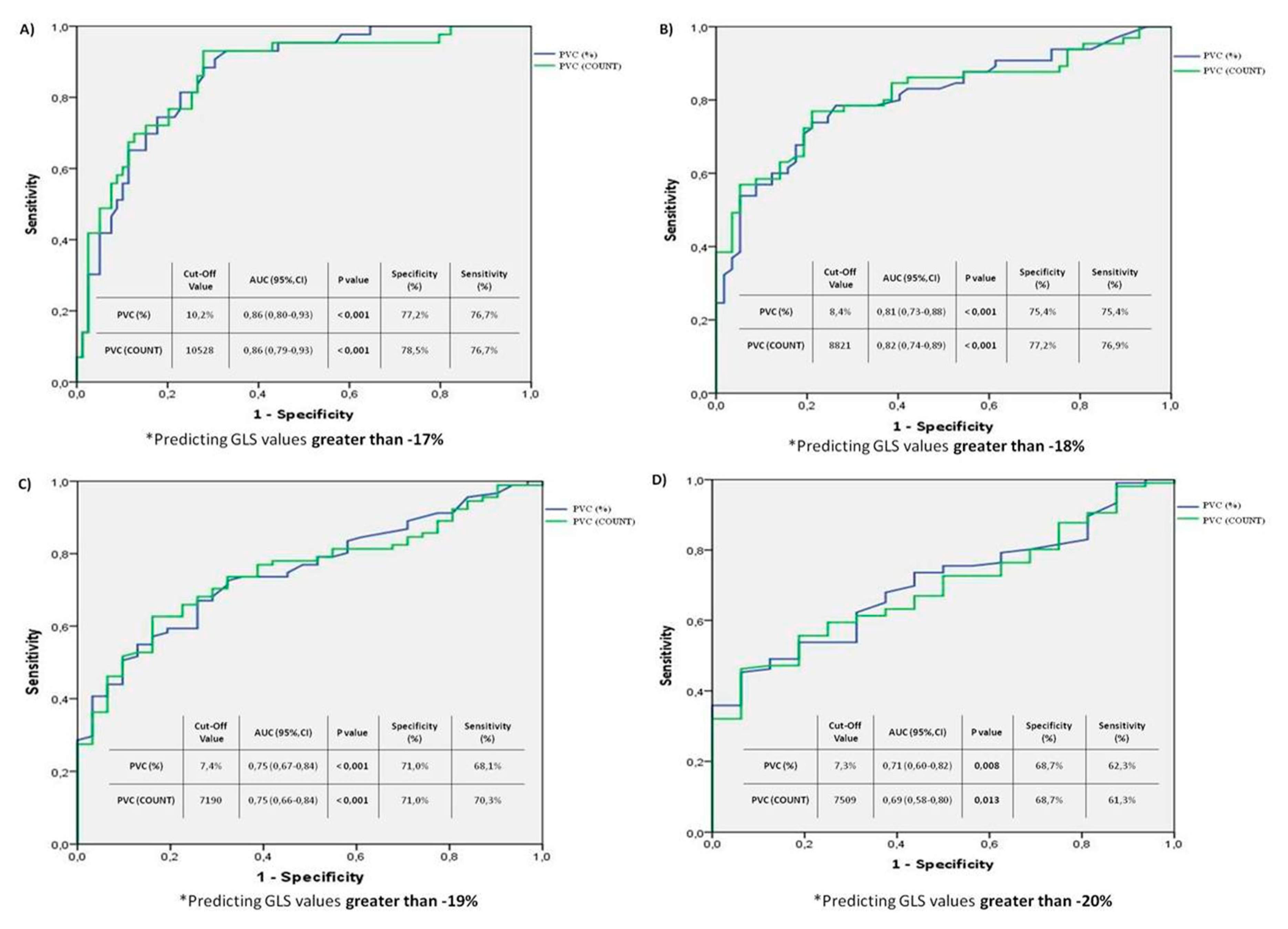
The results of the ROC curve analysis modeling examples conducted to determine the cut-off values of PVC burden and PVC count predicting deterioration in LV-GLS, based on different LV-GLS values (-17, -18, -19, -20), are shown in
Figure 2. In the first analysis (
Figure 2A), a PVC burden cut-off value of 10.2% was found to be associated with a LV-GLS deterioration greater than -17, with a specificity of 77.2% and a sensitivity of 77.6% (PVC 10.2% cut-off value, AUC: 0.86 [0.80-0.93] 95% CI; p<0.001). In the second analysis (
Figure 2B), a PVC burden cut-off value of 8.4% was associated with a LV-GLS deterioration greater than -18, with a specificity of 75.4% and a sensitivity of 75.4% (PVC 8.4% cut-off value, AUC: 0.81 [0.73-0.88] 95% CI; p<0.001). In the third analysis (
Figure 2C), a PVC burden cut-off value of 7.4% was associated with a LV-GLS deterioration greater than -19, with a specificity of 71% and a sensitivity of 68.1% (PVC 7.4% cut-off value, AUC: 0.75 [0.67-0.84] 95% CI; p<0.001). Finally, in the fourth analysis (
Figure 2D), a PVC burden cut-off value of 7.3% predicted a GLS deterioration greater than -20, with a specificity of 68.7% and sensitivity of 62.3% (PVC 7.3% cut-off value, AUC: 0.71 [0.60-0.82] 95% CI; p<0.008).
Discussion
In our study, a significant difference was found in LV-GLS values between the three groups formed according to PVC burden. The correlation analyses revealed a moderate-level significant correlation between PVC burden and the deterioration of LV-GLS values. In the ROC analysis models conducted to determine the cut-off values of PVC burden predicting the deterioration of LV-GLS values, we found that PVC burden above 8.4% particularly predicted a decrease of more than -18 in LV-GLS values with a specificity and sensitivity rate of 75.4%. Furthermore, we determined that PVC load exceeding 10.2% were associated with a deterioration of more than -17 in LV-GLS values with a specificity of 77.2% and sensitivity of 77.6%. Similarly, in correlation analyses, we observed a weak-level significant negative correlation between PVC burden and the MPI values. In our multiple linear regression model, we identified that the PVC burden as an independent predictor for the reduction in LV-GLS.
Upon reviewing the literature ,Ling Y. et al.'s study compared 38 patients with a mean PVC burden of 22.8%±9 and 39 healthy control subjects with normal LV-EF values, revealing a significant decrease in strain values compared to the control group. In the subgroup analysis of the same study, they compared 17 individuals with a PVC burden above 20% to 21 individuals with a PVC burden below 20% and found no significant differences in left ventricular dimensions, LVEF values, and left ventricular strain values [
12]. In the study conducted by Ban JE. et al., analyzed 127 patients without structural heart disease who had a daily PVC burden of more than 10%. They reported LVEF < 50% in 22% of the patients and stated that a PVC burden above 26% predicted impaired LV function with 71% specificity and 79% sensitivity[
13]. A similar study was conducted by Baman TS et al., where they included 174 patients and reported a mean LVEF of 37%±10. They indicated that 33% of the study population consisted of patients with reduced LVEF and a PVC burden above 24%, which predicted impaired left ventricular function with 78% specificity and 79% sensitivity. Furthermore, in this study, they reported that the lowest PVC burden leading to reversible cardiomyopathy was above 10% [
14]. In a study conducted by Lie ØH et al., involving 52 patients with outflow tract PVCs, they reported that a PVC burden above 8% could be associated with impaired LV-GLS. They considered an LV-GLS value greater than -18 as indicative of impaired left ventricular function and conducted their analyses accordingly[
15]. Additionally, Shanmugam N. et al. demonstrated in their published cases that even a PVC burden above 4% could lead to impairments in left ventricular function[
16].
There are studies in the literature investigating the effects of PVC burden on left ventricular function. However, studies on LV-GLS and MPI values, which allow us to evaluate LV function in patients with preserved LV-EF values, are limited. Recently, strain echocardiography, which enables the detection of subclinical impairments without a decline in LV-EF, has become widely used. Although some studies have provided cut-off values for LV-GLS values[
15], there is no specific LV-GLS cut-off value indicating impairment for our patient group as it has not been studied.
The association between the PVC burden and the decrease in LV-GLS has been emphasized in numerous studies [
10,
12,
14,
15]. Upon examining parameters predicting this decrease, clinical parameters such as age and BMI, as well as various parameters like electrocardiogram and laboratory findings, were found to be non-significant. In accordance with our conducted multiple linear regression modeling, we identified that the only parameter independently predicting the decrease in LV-GLS is the PVC burden.
Another parameter reflecting the left ventricular function is the MPI value. Studies on heart failure, acute coronary syndrome, hypertension, and diabetic patients have reported that a decrease in MPI values is associated with the severity of coronary artery disease, mortality, and morbidity [
17,
18,
19]. The effects of PVC burden on MPI in patients with preserved LV-EF have not been extensively studied. In our study, no significant difference was found among groups in terms of MPI. However, correlation analyses revealed a weak but significant correlation between PVC burden, frequency, and MPI values, indicating impairment.
The duration of symptoms related to PVCs can influence LV-GLS values, as much as the frequency of PVCs. In a previous study, a symptom duration of 60 months or more was identified as a predictor for PVC-induced cardiomyopathy in patients with idiopathic PVCs [
20]. In our study, we also detected a weak but discernible correlation between the duration of symptoms related to PVCs and LV-GLS values.
The limitations of our study were its single-center nature, recording holter data from only 3 leads for a 24-hour period, and the PVC origin not being clearly determined due to the PVC detection rate on ECG being less than 35%, moreover the majority of enrolled patients declined to undergo electrophysiological study(EPS), thereby preventing the invasive identification of PVC origins. In addition, despite the availability of symptom duration data for patients, other limitations include the lack of long-term follow-up and the impact of LV-GLS values on major cardiovascular endpoints.
Conclusion
In our study, we observed significant impairment in LV-GLS values in groups with a high PVC burden. Increased PVC burden and frequency were moderately correlated with impaired LV-GLS values, additionally, an increase in PVC burden was identified as an independent predictor of deterioration in LVGLS.
Furthermore, contrary to most of the literature, it was found that even lower levels of PVC burden could be associated with impairments in left ventricular function in individuals with preserved LVEF and structurally normal hearts. This suggests that in this group of patients, early consideration of permanent treatments such as ablation may be warranted, and their follow-up should include strain echocardiography in addition to standard echocardiography. These findings could have implications for clinical outcomes, particularly in terms of treatment prioritization, and therefore, more comprehensive follow-up studies are needed.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1, Figure S1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation: Arslan Sukru, Arabacı H. Ozan; Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review & Editing: Arslan Sukru, Arabacı H. Ozan, Oktay Veysel; Resources and Data Curation: Deniz Furkan, Gokce M. Emin; Formal Analysis and Sotfware: Arslan Seyma; Supervision,Validation; Oktay Veysel, Yıldız Mustafa, Uzunhasan Isıl. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research received no external funding.
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-assisted technologies in the writing process
None.
Authors’ Note
All authors made important contributions to the design of the study, the collection and analysis of the data, and the drafting. All authors confirmed the final article before publication.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa (E-69291215-900-16420 and 2 March 2021)
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
References
- Kennedy HL, Whitlock JA, Sprague MK, Kennedy LJ, Buckingham TA, Goldberg RJ. Long-term follow-up of asymptomatic healthy subjects with frequent and complex ventricular ectopy. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 24;312(4):193-197. [CrossRef]
- Chugh SS, Shen WK, Luria DM, Smith HC. First evidence of premature ventricular complex-induced cardiomyopathy: a potentially reversible cause of heart failure. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2000 Mar;11(3):328-329. [CrossRef]
- Redfearn DP, Hill JD, Keal R, Toff WD, Stafford PJ. Left ventricular dysfunction resulting from frequent unifocal ventricular ectopics with resolution following radiofrequency ablation. Europace. 2003 Jul;5(3):247-250. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal V, Vittinghoff E, Whitman IR, Dewland TA, Dukes JW, Marcus GM. Relation Between Ventricular Premature Complexes and Incident Heart Failure. Am J Cardiol. 1: 2017 Apr 15;119(8), 2017. [CrossRef]
- Niwano S, Wakisaka Y, Niwano H, Fukaya H, Kurokawa S, Kiryu M, et al. Prognostic significance of frequent premature ventricular contractions originating from the ventricular outflow tract in patients with normal left ventricular function. Heart. 2009 Aug;95(15):1230-7. [CrossRef]
- Del Carpio Munoz F, Syed FF, Noheria A, Cha YM, Friedman PA, Hammill SC, et al. Characteristics of premature ventricular complexes as correlates of reduced left ventricular systolic function: study of the burden, duration, coupling interval, morphology and site of origin of PVCs. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2011 Jul;22(7):791-798.
- Altıntaş B, Özkalaycı F, Çinier G, Kaya İ, Aktan A, Küp A, et al. The effect of idiopathic premature ventricular complexes on left ventricular ejection fraction. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2020 Mar;25(2):e12702. [CrossRef]
- Panizo JG, Barra S, Mellor G, Heck P, Agarwal S. Premature Ventricular Complex-induced Cardiomyopathy. Arrhythm Electrophysiol Rev. 2018 Jun;7(2):128-134.
- Luebbert J, Auberson D, Marchlinski F. Premature Ventricular Complexes in Apparently Normal Hearts. Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2016 Sep;8(3):503-514. [CrossRef]
- Verdonschot JAJ, Henkens MTHM, Wang P, Schummers G, Raafs AG, Krapels IPC, et al. A global longitudinal strain cut-off value to predict adverse outcomes in individuals with a normal ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail. 2021 Oct;8(5):4343-4345. [CrossRef]
- Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015 Jan;28(1):1-39.e14. [CrossRef]
- Ling Y, Wan Q, Chen Q, Zhu W. Assessment of subtle cardiac dysfunction in patients with frequent premature ventricular complexes by real-time three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography. Clin Cardiol. 2017 Aug;40(8):554-558. [CrossRef]
- Ban JE, Park HC, Park JS, Nagamoto Y, Choi JI, Lim HE, et al. Electrocardiographic and electrophysiological characteristics of premature ventricular complexes associated with left ventricular dysfunction in patients without structural heart disease. Europace. 2013 May;15(5):735-741. [CrossRef]
- Baman TS, Lange DC, Ilg KJ, Gupta SK, Liu TY, Alguire C, et al. Relationship between burden of premature ventricular complexes and left ventricular function. Heart Rhythm. 2010 Jul;7(7):865-869. [CrossRef]
- Lie ØH, Saberniak J, Dejgaard LA, Stokke MK, Hegbom F, Anfinsen OG, et al. Lower than expected burden of premature ventricular contractions impairs myocardial function. ESC Heart Fail. 2017 Nov;4(4):585-594. [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam N, Chua TP, Ward D. 'Frequent' ventricular bigeminy a reversible cause of dilated cardiomyopathy. How frequent is 'frequent'? Eur J Heart Fail. 2006 Dec;8(8):869-873.
- Sheel, B. K. , Badiuzzaman, M., Haque, T., Rahman, H., Biswas, A. K., & Khan, S. R. "Association between Myocardial Performance Index (Tei-Index) and Severity of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Non-ST Segment Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome." Bangladesh Heart Journal 37.1 (2022): 16-26. [CrossRef]
- Carluccio E, Biagioli P, Alunni G, Murrone A, Zuchi C, Biscottini E, et al. Improvement of myocardial performance (Tei) index closely reflects intrinsic improvement of cardiac function: assessment in revascularized hibernating myocardium. Echocardiography. 2012 Mar;29(3):298-306. [CrossRef]
- Abaci O, Kocas C, Oktay V, Arslan S, Turkmen Y, Bostan C, et al. Relationship between myocardial performance index and severity of coronary artery disease in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2017 Jan/Feb;28(1):4-7. [CrossRef]
- Yokokawa M, Kim HM, Good E, Chugh A, Pelosi F Jr, Alguire C, et al. Relation of symptoms and symptom duration to premature ventricular complex-induced cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm. 2012 Jan;9(1):92-95. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).