1. Introduction
The 1064 nm laser possesses distinct attributes such as a lengthy wavelength, deep-reaching capability, and the capacity to be absorbed by melanin, oxyhemoglobin, and water within skin tissue. The 1064nm laser is mainly absorbed by the melanin group, but the melanin content in skin tissue is relatively small compared to water and hemoglobin; therefore, the 1064nm laser is able to enter the tissue more deeply, and has greater ablative capacity. The laser is similarly able to penetrate deeper into the skin when acting on skin tissue [
1,
2,
3]. This laser variant finds widespread employment in skin ailment therapy, with its impact on skin integrity forming a pivotal facet of laser-based biological investigations. The study of the interaction mechanism between 1064nm laser and skin tissue is a very complex and widely used basic research [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9], such as laser surgery, laser thermotherapy and laser imaging, which has become a difficult problem at the intersection of laser physics and biomedicine. As early as 1965, Polanyi et al. [
10] used a high-power continuous 1064 nm laser to irradiate human tissues, causing vaporization and evaporation of the irradiated tissues to achieve the effect of cutting the tissues, and at the same time using a low-power laser to irradiate the cutting site to coagulate the tissues in order to achieve the effect of hemostasis. Existing literature predominantly asserts that the curative and deleterious consequences of laser action on the skin predominantly hinge upon the photothermal effect induced by the laser [
11]. Dang et al. [
12] established that non-ablative treatment utilizing the 1064 nm laser can heighten skin suppleness and amplify collagen content within murine skin tissue, indicating that the photothermal effect fosters the production of type I collagen. Employing a 1064 nm laser, Kim et al. [
13] eliminated the epidermis and dermis of rats by means of photothermal decomposition to ablate benign skin anomalies. Their perspective posits this laser as a viable choice for managing benign skin disorders.
Given the rapid development of laser technology and the broad spectrum of laser application in biomedical, industrial, military and other fields [
14,
15,
16,
17], inadvertent laser-induced harm is a recurring occurrence [
18,
19], with skin impairment trailing only ocular injuries. 1064 nm infrared laser is not visible by the naked eye thus leading to easier accidental injury. Imprecise control of laser dosage during therapy can result in minor skin damage. Laser can be used as a debridement modality to reduce intraoperative bleeding for the removal of necrotic tissue from burns, but it may cause excessive damage to healthy tissue due to dosage control. Laser thermal damage may destroy basal cells and other related tissues that are closely associated with regeneration, resulting in delayed or even non-healing of the wound as well as severe scarring at a later stage [
20]. Concurrently, utilization of high-power lasers has the potential to inflict skin harm, especially when safety measures during laser production and development are lax or when operators lack sufficient awareness of protective protocols, leading to adverse consequences. Laser weapons may also cause irreversible damage to the skin of personnel when attacking a target, and similarly, laser radiation can cause serious damage to human skin tissue such as ablation, carbonization, vaporization, coagulation, and sputtering [
21]. The influence of elevated infrared doses is fundamentally linked to robust temperature escalation, and the extent of skin damage correlates closely with infrared dose magnitude [
22]. Rationally and effectively harnessing the thermal energy generated by the interplay between lasers and biological tissue to attain the sought-after thermal impact or damage extent is pivotal for laser-based diagnosis and disease management. However, forestalling inadvertent harm to neighboring normal tissues arising from excessive heat stands as the most pivotal facet of laser medicine necessitating safeguarding. Notably, the literature still presents a scarcity of investigations concerning the effects of laser-induced skin damage and the attendant repair traits. Hence, delving into the precise molecular mechanisms underpinning skin injury and repair assumes utmost significance.
In general, skin wound repair is a complex biological process governed by a multitude of factors [
23,
24], encompassing the release of diverse cytokines, chemokines, and inflammatory agents. Simultaneously, it relies on the synergy between distinct cells to cohesively regulate wound recuperation. Investigations reveal that growth factor levels, encompassing fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF), within tissues during acute skin injuries sustain their functional efficacy and partake in the healing trajectory [
25]. Nevertheless, as the duration of skin injury prolongs, inflammatory cells persistently infiltrate the wound site. This shift in the protein milieu culminates in the continuous degradation of growth factors, attenuating their capacity to foster healing, consequently inducing wound healing delay [
26,
27]. Other inquiries underscore the role of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in governing cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and glucose metabolism. Activation of this pathway expeditiously advances wound healing by enhancing cell proliferation and invasion [
28]. Notably, certain analyses assert the pivotal regulatory function of fibroblast proliferation, migration, activation, and apoptosis in skin wound repair, particularly underscoring the significance of fibroblast apoptosis during the later phases of healing. Noteworthy is the discovery that mice with a knockout of the apoptosis-related gene apolipoprotein (ApoE) exhibit escalated extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, reduced bcl-2 expression, persistent myofibroblast activation, decreased apoptosis, culminating ultimately in scar formation [
29]. Conversely, augmented fibroblast apoptosis during the later stages of injury repair contributes to the restoration of skin integrity [
30]. Currently, there is little research on the biological processes involved in the repair of laser-induced skin damage, and it is hypothesized that cell proliferation and apoptosis play an important role in this process, which is the focus of this study.
The journey of skin healing is concomitant with scab formation, engendering diverse degrees of scarring. While collagen synthesis and extracellular matrix accumulation represent pivotal facets of wound healing, excessive deposition can precipitate the development of skin scars [
31,
32,
33]. Investigations highlight the intrinsic link between the healing course of skin injuries and apoptosis, modulated by intracellular apoptotic regulatory proteins. The Bax and Caspase families wield a critical role in mitochondria-mediated apoptosis [
34,
35,
36]. Our prior research efforts have elucidated certain characteristics of skin injury and repair resultant from laser exposure [
37,
38]. The study of the quantity-effect relationship between lasers and skin tissues is an important part of the analysis of the mechanism of the biological action of lasers, and also is the basis for clinical application. To delve deeper into the mechanisms governing laser-induced skin injury and subsequent repair, this study examined changes in collagen architecture and the expression of apoptosis-associated proteins, namely Bax, caspase-3, and caspase-9, within porcine skin wounds during the ensuing wound healing post laser irradiation. This investigation imparts an experimental and theoretical foundation for comprehending the ramifications and mechanisms of cutaneous thermal injuries triggered by a 1064 nm infrared laser. Additionally, it furnishes an indispensable quantitative and qualitative research approach for the future exploration of laser-induced skin wound effects and the recovery process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
Five Guizhou miniature fragrant pigs, characterized by white hair and weighing 20~25 kg each, were procured from Beijing Liulihe Kexing Experimental Animal Breeding Center (Animal production license No. SCXK (Beijing) 2017-0003). These pigs were housed at the Beijing Institute of Radiation Medicine Experiment Animal Center. A standard feeding regimen was followed for 3 to 7 days before the experiment, with the stipulation that only pigs displaying no abnormalities could partake in the study. Preceding and following the experiment, individual pig accommodations were provided. Ethical clearance was obtained from the Beijing Institute of Radiation Medicine Experiment Animal Center in accordance with approved Animal Protocols (IACUC-DWZX-2019-502).
2.2. Laser Radiation Method
Prior to laser exposure, the miniature pigs were anesthetized using intramuscular injection of a 3% sodium pentobarbital solution at a dosage of 1 mL/kg. Subsequently, the intended injury site was shaved. A laser irradiation region measuring approximately 15 cm by 30 cm was marked out on the right side of the pig's spine, with a grid pattern of 5×10 arrays established. A 1064 nm continuous laser was emitted through fiber conduction from a self-developed laser system. The laser output power spanned from 12 W to 955 W and was notably stable, exhibiting a robust linear correlation with the current (linear correlation coefficient
R2=0.9999). The laser exposure time (t) was programmed to 0.5 seconds. Laser power (P) was gauged using a laser power meter (BGS6333-P400, Beijing Monochrome Optoelectronic Technology Co., Ltd.), and the irradiation spot's diameter (d) was standardized at 1 cm. The laser irradiation power density (H) was computed using the parameters above, utilizing the equation
. In the 5×10 grid arrays, each grid location represented an irradiation point, with identical laser dosage administered to the five grids within a column. The dosage spectrum spanned from 29.4 J/cm² to 708.2 J/cm², with laser power sequentially escalating from low to high. Prior investigations had indicated that doses below 126.4 J/cm² caused primarily reversible erythema reactions that vanished within seconds or minutes [
37]. Hence, for this study, low, medium, and high doses (126.4 J/cm², 320.3 J/cm², and 514.3 J/cm²) were selected based on the severity of the injury. A locating ring was utilized to ensure a consistent distance of 10 cm between the laser device tip and the skin surface. The optical path of laser-induced skin damage in miniature pigs is depicted in
Figure 1.
2.3. Method to Observe Damage Spots
Following 1064nm laser irradiation at 6 hours and 3, 7, 14, and 28 days, one pig was anesthetized for reexamination. The healing regions of skin wounds were examined and photographed for measurement. To avert potential harm to animals during handling and immobilization, which could lead to wound tearing, and considering the elevated risk of animal mortality from multiple anesthesia sessions, the experiment adopted a staggered approach for observing different animals at distinct time points. This avoided continuous observation of the same animal over the full 28-day span. One pig was humanely euthanized to obtain samples at a particular time point, yielding five samples at identical irradiation doses. These wound samples were fixed in 4% neutral formaldehyde solution, tissue sections were paraffin-embedded from the damaged areas, and Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) staining was conducted. The resulting pathological sections were examined under a light microscope to assess the morphological changes in cutaneous wounds.
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of Collagen in Skin Wounds
Paraffin sections of wound samples underwent Sirius Red staining. Using a polarized light microscope, the structure and appearance of type I and type III collagen were analyzed. Type I collagen appeared as mature, red or orange coarse fibers, while type III collagen manifested as immature, green slender fibers. After 1064nm laser irradiation at 6 hours and 3, 7, 14, and 28 days, five images with equal fields of view (FOV) were randomly captured from each sample under consistent sampling conditions. Comparable quantitative collagen analysis was performed on normal skin tissues extracted from each pig's back. The collagen's area density percentage was computed in the stained images using the following formula: (Positive area of type I collagen + Positive area of type III collagen) / Total image area × 100%. These areas were manually selected and quantified using ImagePro Plus 6.0 software (as depicted in
Figure 2), and the software was employed to calculate the average value.
2.5. Apoptosis Detection by TUNEL Staining
Paraffin sections were prepared from the affected tissue spots for TUNEL staining. This technique, an in-situ terminal transferase labeling method, accurately portrays the primary biochemical and morphological attributes of cellular apoptosis by staining apoptotic cell nuclei or apoptotic bodies. Components including Protease K (G1234), TUNEL kit (G1507), DAB chromogenic agent (G1212), and hematoxylin staining solution (G1076) were acquired from Wuhan Servicebio Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Post 1064nm laser irradiation at 6 hours and 3, 7, 14, and 28 days, apoptosis occurrences were visualized within the wound tissue under a light microscope. Apoptotic cells exhibited positive brown staining, with blue nuclei.
2.6. Immunohistochemical Detection
Subsequent to paraffin section preparation from damaged tissue spots, the expression levels of bax, caspase-3, and caspase-9 proteins were assessed through immunohistochemical (IHC) staining. Caspase-9, functioning downstream of mitochondria within the intrinsic pathway, and caspase-3, serving as an effector caspase during the final stages of apoptosis, were evaluated. Additionally, Bax, a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family pivotal in intrinsic apoptotic signaling regulation, was examined. Rabbit anti-mouse polyclonal antibodies for bax (bs-0127R), caspase-3 (bs-0081R), and caspase-9 (bs-20773R) were sourced from Beijing Boaosen Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Within wound tissue, brownish-yellow granules in the cytoplasm or nucleus were examined under a light microscope. Subsequent to 1064nm laser irradiation at 3, 7, 14, and 28 days, five images with consistent fields of view (FOV) were randomly captured from the wound region under identical sampling conditions. These images were analyzed using Image-Pro Plus 6.0 software, yielding the integrated optical density (IOD) of positive protein expression, as illustrated in
Figure 2. Based on the IOD value of the normal group, the relative positive protein expression value was determined by calculating the ratio of IOD in the irradiation group to that in the normal group. Subsequently, the average value was computed, and statistical analysis was performed using the software.
Figure 2.
Software-driven quantitative analysis of collagen and apoptosis-related protein in skin wounds.
Figure 2.
Software-driven quantitative analysis of collagen and apoptosis-related protein in skin wounds.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
The results were subjected to analysis using SPSS 13.0 software, presented as . Group comparisons were conducted through one-way ANOVA, with statistical significance set at P < 0.05.
4. Discussion
For a considerable duration, the focus of laser injury has predominantly been on ocular injury. Nevertheless, there exist limited literary reports on the process of laser-induced skin injury and subsequent healing in animals. Being the outermost organ of the human body, the skin is more prone to thermal damage when compared to other tissues. When subjected to laser hyperthermia, the skin's surface temperature experiences an instantaneous elevation to a specific level, consequently predisposing it to skin burns and the initiation of skin collagen denaturation. Alterations in the configuration of proteins and organelles within biological tissues can give rise to cell demise or even tissue necrosis. In this investigation, miniature pigs, exhibiting akin skin structures to humans, were employed as the experimental subjects, owing to their resemblant skin physiological structures, epidermal morphology, renewal cycles, and wound mending patterns. The epidermal composition of miniature pigs encompasses the basal layer, spinous layer, granular layer, transparent layer, and stratum corneum, while the dermal layer comprises the papillary and reticular layers, coupled with subcutaneous tissue and skin appendages. Moreover, the body fluids and metabolic processes subsequent to skin burns manifest striking similarities. Thus, miniature pigs present a more exemplary animal model for investigating laser burns [
39,
40]. In this experimentation, the light source employed was the 1064 nm laser, which illuminated the experimental pigs at varying doses. The alterations in collagen structure and apoptotic cells within skin wounds were meticulously observed, alongside the quantitative analysis of collagen content and the expression of apoptosis-related proteins within skin lesions.
Skin injury and wound healing represent intricate biological processes, typically encompassing hemostasis, inflammation, tissue regeneration, remodeling, and maturation stages [
41,
42]. Earlier investigations have revealed a lack of discernible hemostasis or exudation phases in the recuperative trajectory of mouse skin trauma induced by lasers. This distinguishes it from conventional skin trauma or burns, constituting a crucial distinction [
37]. Some studies have similarly concluded differences in skin damage and wound healing between laser irradiation and thermal burns. Zhang et al. [
43] have similarly concluded some difference between laser irradiation and thermal burn in terms of skin damage and wound healing. Findings from this study illustrated the dry nature of pig skin wound surfaces, with no signs of inflammatory exudates or bleeding three days following laser exposure. The wound healing journey of pig skin injuries also lacked conspicuous hemostasis or exudation periods. Laser-triggered skin injuries predominantly manifested as instances of acute coagulation necrosis, characterized by white spots and scorched areas. Remarkably, throughout the healing course, all wounds remained uninfected and non-suppurative, potentially differing from responses seen in skin trauma or burns. Within this study, the size and depth of skin injuries following laser treatment exhibited a positive correlation with the administered irradiation dose. Specifically, injuries within the low-dose group were primarily confined to the epidermal and superficial dermal layers, while the medium- and high-dose groups displayed injuries that extended to the subcutaneous tissue layer. After a span of 28 days post-irradiation, the white spot injuries induced by low-dose lasers exhibited near-complete macroscopic recovery, closely resembling the normal group. Conversely, burn injuries inflicted by medium- and high-dose lasers still prominently featured scabs on the wound surfaces. The recuperation of skin wounds beneath these scabs lagged behind that of the normal group. Notably, even the skin surface of the high-dose group had not achieved complete closure.
Collagen creation following skin trauma emerges as a pivotal factor influencing the recuperation of skin injuries. The skin's collagen primarily comprises type I and type III collagen. Type I collagen contributes to the structural integrity of the skin [
44]. Type III collagen's production surges in the initial phases of wound healing, significantly contributing to collagen reconstruction and repair. In the early stage post laser irradiation (3 days), collagen within each irradiation group exhibited degradation and necrosis, inducing substantial impairment to the collagen's structural integrity, consequently leading to a marked decline in collagen content. In the intermediate stage post laser irradiation (7-14 days), collagen structure began to regenerate, characterized mainly by slender type III collagen fibers, and collagen content exhibited gradual augmentation. In the later stage post laser irradiation (28 days), coarse type I collagen escalated across each irradiation group, yielding an uneven and lax collagen structure. Despite the increase, collagen content remained significantly inferior to that of the normal group. Within the recovery process of laser-induced skin injuries by means of medium- and high-dose exposures, the synthesis of skin tissue collagen encountered pronounced inhibition. Consequently, the collagen structure and content within wounds resulting from these exposures struggled to fully revert to normal levels. Hence, it is postulated that the scarcity of collagen during the intermediate and later stages of laser irradiation constitutes a pivotal determinant behind the sluggish wound healing observed within medium- and high-dose groups. Furthermore, select investigations have disclosed elevated collagen content in skin burns or trauma compared to normal skin tissue during the late phases of recovery, particularly during scar formation. However, this experimentation revealed lower collagen content in laser-induced skin injuries than the standard levels. This disparity could stem from the comparatively tardy recovery of laser-induced skin injuries in contrast to non-laser-induced skin burns or trauma. Specifically, even 28 days after laser irradiation, noticeable late-stage granulation tissue persisted within the skin wounds of medium- and high-dose groups, marked by the vigorous proliferation of fibroblasts and inadequate collagen fiber synthesis. This serves as an indication that wound healing had yet to fully reach maturation and remodeling stages. The outcomes stated above necessitate further research and validation. The conjecture remains that insufficient collagen synthesis stands as a fundamental mechanism contributing to delayed wound healing following medium- and high-dose laser irradiation.
The progression of wound healing is influenced by numerous factors, including radiation, which can disrupt the normal function of fibroblasts within skin tissue. Earlier explorations into the mechanics of wound healing in the context of radiation-induced wounds unveiled the involvement of apoptosis across the entirety of the wound healing process. Notably, the distinctive features included an earlier onset and a prolonged subsistence of apoptosis. Moreover, excessive apoptosis was deemed a primary contributor to delayed wound healing [
45]. Further investigations highlighted the crucial roles of the pro-apoptotic protein bax and the anti-apoptotic protein bcl-2 in regulating apoptosis within skin wounds and the subsequent healing processes [
46]. Presently, the multifaceted regulatory mechanism of the apoptosis pathway is still under study. However, the caspase-dependent pathway has been distinctly recognized, with the bcl-2 and caspase families emerging as two pivotal protein families deeply involved in this process. Functioning as a cluster of cysteine proteases with a specific affinity for aspartic acid cleavage, the caspase family constitutes a protease system that directly precipitates the disintegration of apoptotic cells, thereby assuming a central role in transmitting apoptotic signals. The apoptotic pathways are primarily classified into endogenous and exogenous pathways. Within this framework, Caspase-9 assumes the role of an essential catalyst within the endogenous apoptotic pathway. Once activated, it proceeds to engage downstream effectors, such as Caspase-3, which in turn targets key cellular structures and regulatory proteins to facilitate apoptotic cell demise [
46,
47]. In contrast, the exogenous apoptosis pathway hinges upon death receptors located on the cellular membrane. Activation of this pathway necessitates the involvement of caspase-8, culminating in the activation of caspase-3 and consequent initiation of cellular apoptosis [
48].
However, there has been a lack of conclusive reports on cellular apoptosis and its associated regulatory proteins within the course of laser-induced skin injuries and subsequent repair. This experiment uniquely examined alterations in cellular apoptosis throughout the process of laser-induced skin injuries and healing in miniature pigs, providing preliminary insights into the functions of select apoptosis-related proteins. The findings indicated that in the initial stage (3 days) following laser exposure, the skin wound tissue exhibited minimal cell apoptosis due to acute tissue necrosis. Transitioning to the intermediate stage (7 and 14 days) after irradiation, apoptotic cells surfaced within the newly forming epidermis of the skin wounds, exemplified by occurrences in the low-dose group of 126.4 J/cm² on the 7th day. Simultaneously, a significant rise in apoptotic cells was observed within the emerging dermis of the skin wounds, particularly involving fibroblasts and vascular endothelial cells. This phenomenon was evident in the medium-dose group of 320.3 J/cm² and the high-dose groups of 514.3 J/cm² on the 14th day. As the irradiation progressed to the late stage (28 days), corresponding with the phase of skin wound remodeling, the new epithelial layer largely enveloped the wound, leading to a decline in apoptotic cell count. Although the apoptosis level in the low-dose group closely resembled that of the normal group, the medium- and high-dose groups maintained significantly elevated apoptosis rates compared to the normal group. During the phases of skin wound healing, the expression of proapoptotic proteins—namely, bax, caspase-3, and caspase-9—experienced substantial upregulation, with synchronous alterations among the three proteins. Hence, it is hypothesized that at distinct stages of wound healing, when cell numbers within newly forming skin tissue necessitate augmentation or reduction, apoptotic signaling molecules stimulate the expression of bax, caspase-3, and caspase-9 proteins through both intracellular and extracellular signal transduction pathways. Caspase-3 regulation is influenced by both endogenous and exogenous apoptotic signaling molecules. Consequently, this experimentation discerned more pronounced shifts in caspase-3 expression, suggesting its potential role in directly facilitating cellular apoptosis. During the intermediate and later phases (14 and 28 days) of wound healing, the heightened expression of bax, caspase-3, and caspase-9 proteins in the nascent tissues of the medium- and high-dose groups culminated in excessive cellular apoptosis, potentially hindering the progress of skin wound healing. Thus, the conjecture emerges that excessive cellular apoptosis constitutes an additional fundamental mechanism contributing to the delayed wound healing observed in the wake of medium- and high-dose laser irradiation.
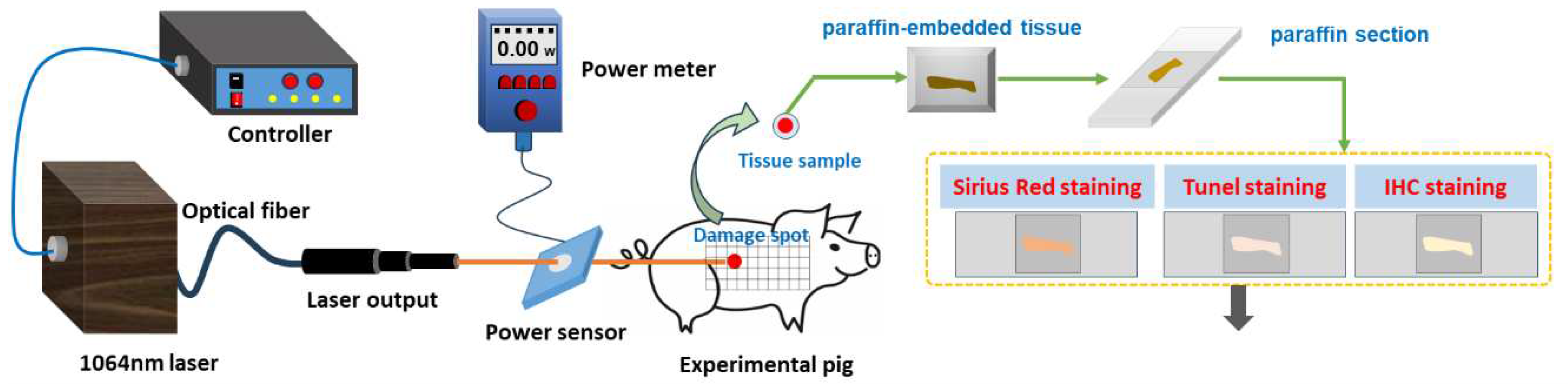
Figure 1.
Laser radiation and detection methods of laser-induced skin damage in miniature pigs.
Figure 1.
Laser radiation and detection methods of laser-induced skin damage in miniature pigs.
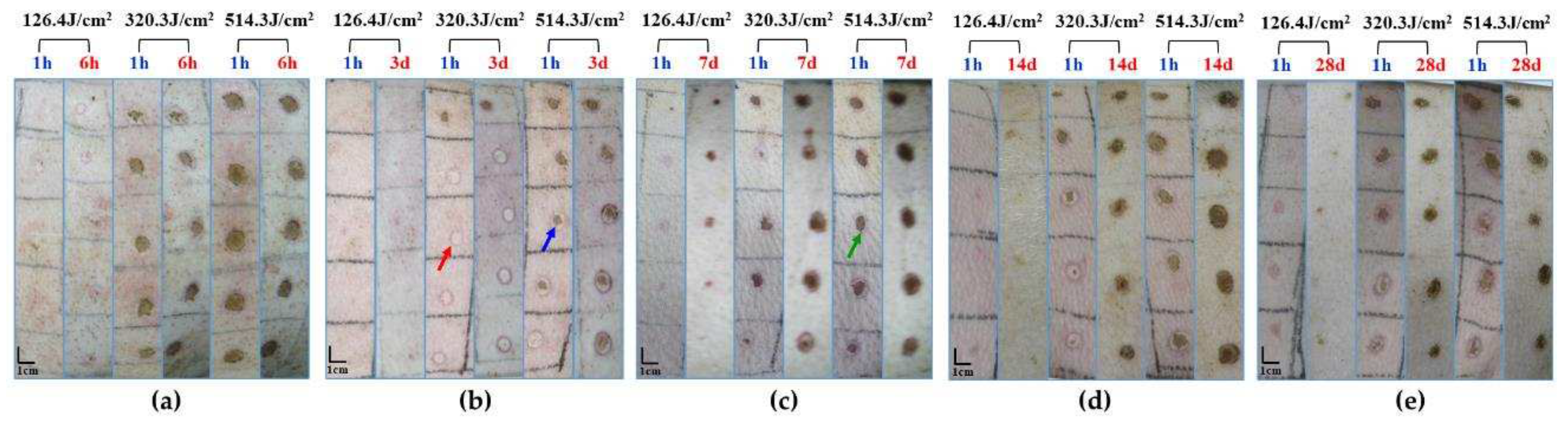
Figure 3.
Macroscopic depiction of cutaneous wound healing in miniature pigs exposed to a 1064 nm laser. (a) Experiment pig 1, observed 1 hour and 6 hours post-irradiation prior to euthanasia. (b) Experiment pig 2, observed 1 hour and 3 days post-irradiation prior to euthanasia. (c) Experiment pig 3, observed 1 hour and 7 days post-irradiation prior to euthanasia. (d) Experiment pig 4, observed 1 hour and 14 days post-irradiation prior to euthanasia. (e) Experiment pig 5, observed 1 hour and 28 days post-irradiation prior to euthanasia. Red arrows denote white spots, blue arrows denote small burnt spots at the center of white spots, and green arrows denote burnt spots.
Figure 3.
Macroscopic depiction of cutaneous wound healing in miniature pigs exposed to a 1064 nm laser. (a) Experiment pig 1, observed 1 hour and 6 hours post-irradiation prior to euthanasia. (b) Experiment pig 2, observed 1 hour and 3 days post-irradiation prior to euthanasia. (c) Experiment pig 3, observed 1 hour and 7 days post-irradiation prior to euthanasia. (d) Experiment pig 4, observed 1 hour and 14 days post-irradiation prior to euthanasia. (e) Experiment pig 5, observed 1 hour and 28 days post-irradiation prior to euthanasia. Red arrows denote white spots, blue arrows denote small burnt spots at the center of white spots, and green arrows denote burnt spots.
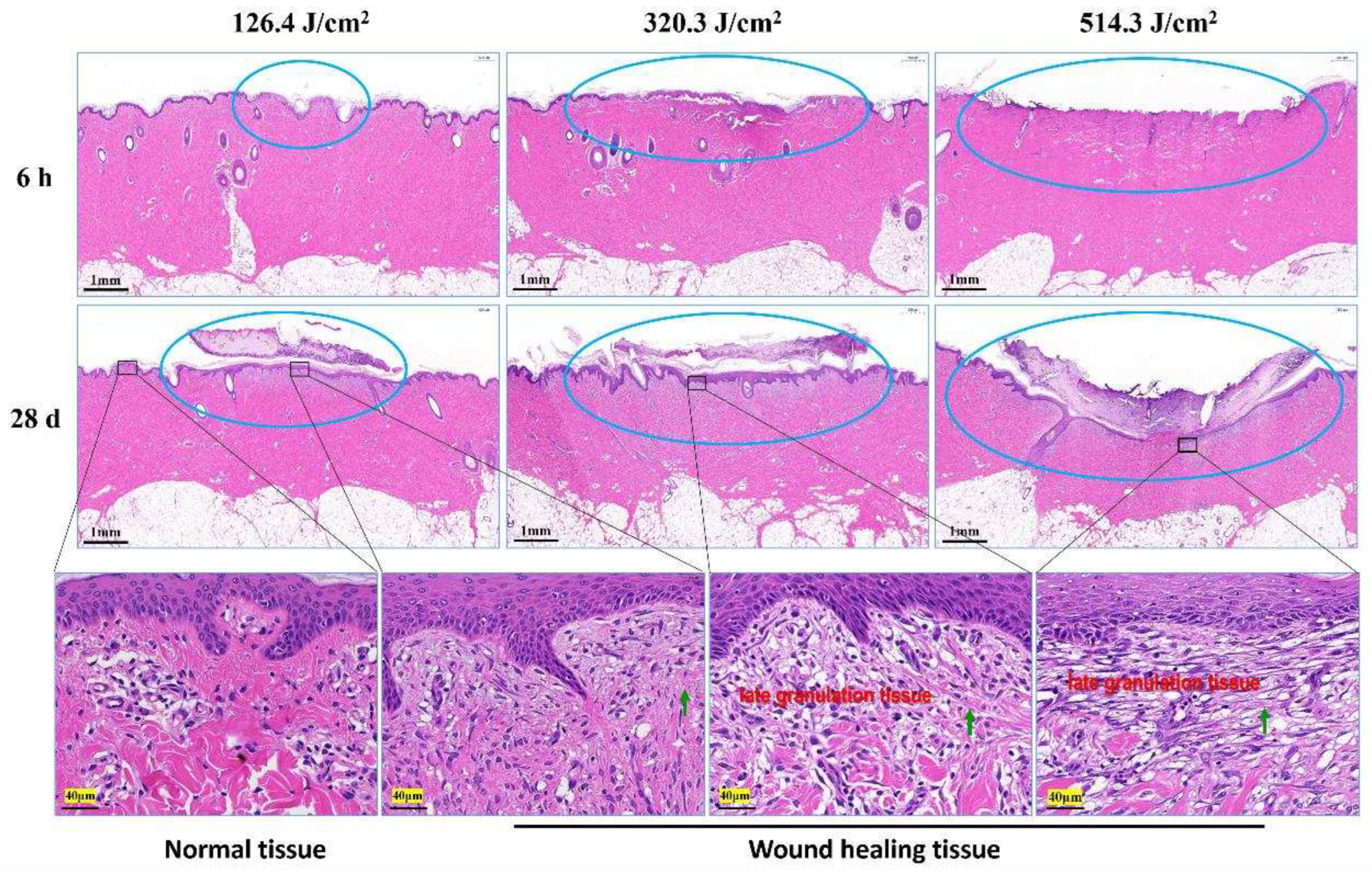
Figure 4.
Pathological observation of skin wound healing in miniature pigs exposed to a 1064 nm laser. Blue circles denote skin wound sites. The images in the third row correspond to magnified views marked by boxes in the second row. Green arrows indicate newly synthesized collagen fibers.
Figure 4.
Pathological observation of skin wound healing in miniature pigs exposed to a 1064 nm laser. Blue circles denote skin wound sites. The images in the third row correspond to magnified views marked by boxes in the second row. Green arrows indicate newly synthesized collagen fibers.
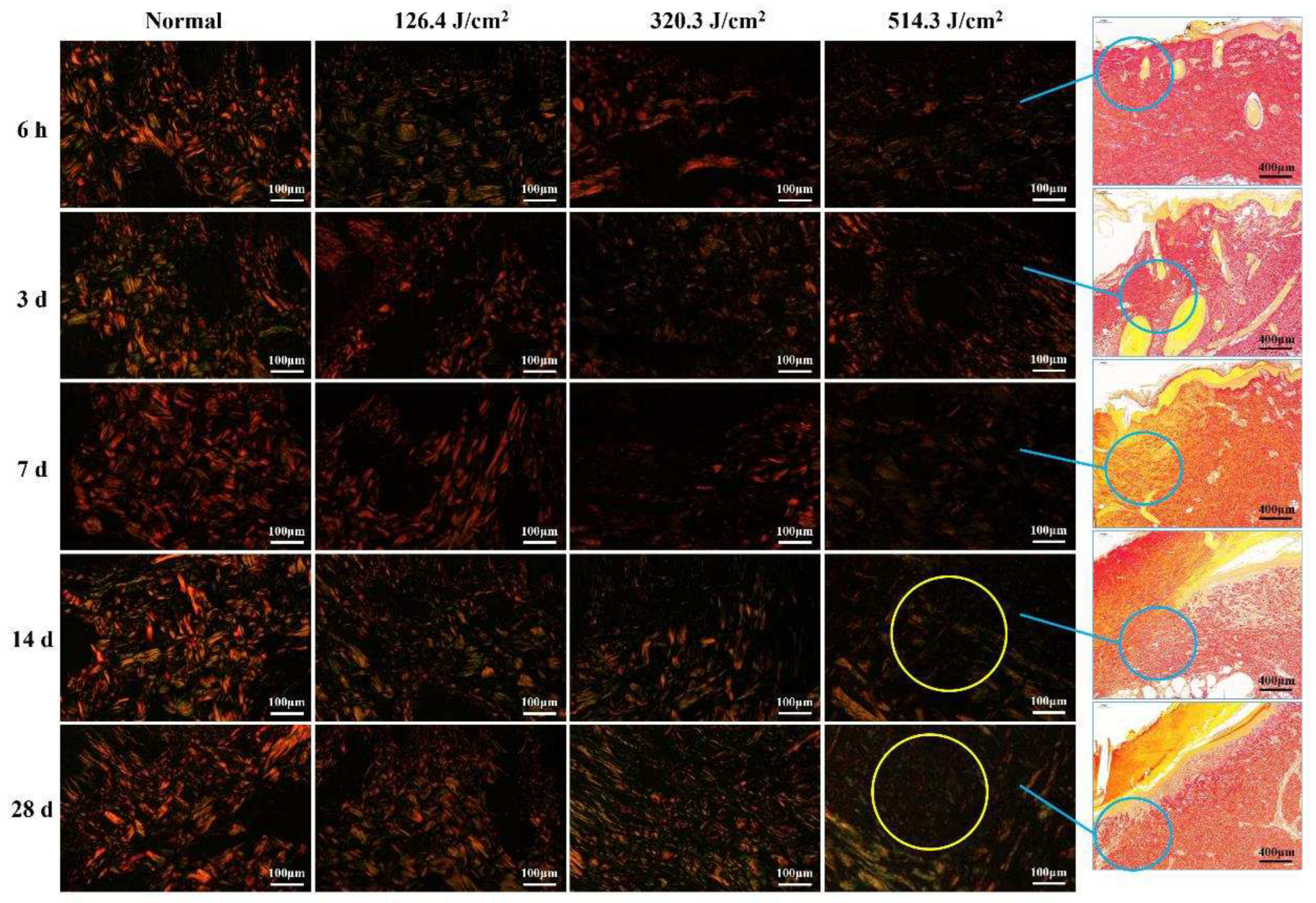
Figure 5.
Evolution of collagen structure in skin wounds of miniature pigs post-laser irradiation (Sirius Red staining). Columns 1 through 4 represent images under a polarized light microscope, while column 5 presents images under a light microscope with varying scales. Blue circles approximate the position of collagen structures in the wounds, while yellow circles highlight the "collagen cavity" within the wound region.
Figure 5.
Evolution of collagen structure in skin wounds of miniature pigs post-laser irradiation (Sirius Red staining). Columns 1 through 4 represent images under a polarized light microscope, while column 5 presents images under a light microscope with varying scales. Blue circles approximate the position of collagen structures in the wounds, while yellow circles highlight the "collagen cavity" within the wound region.
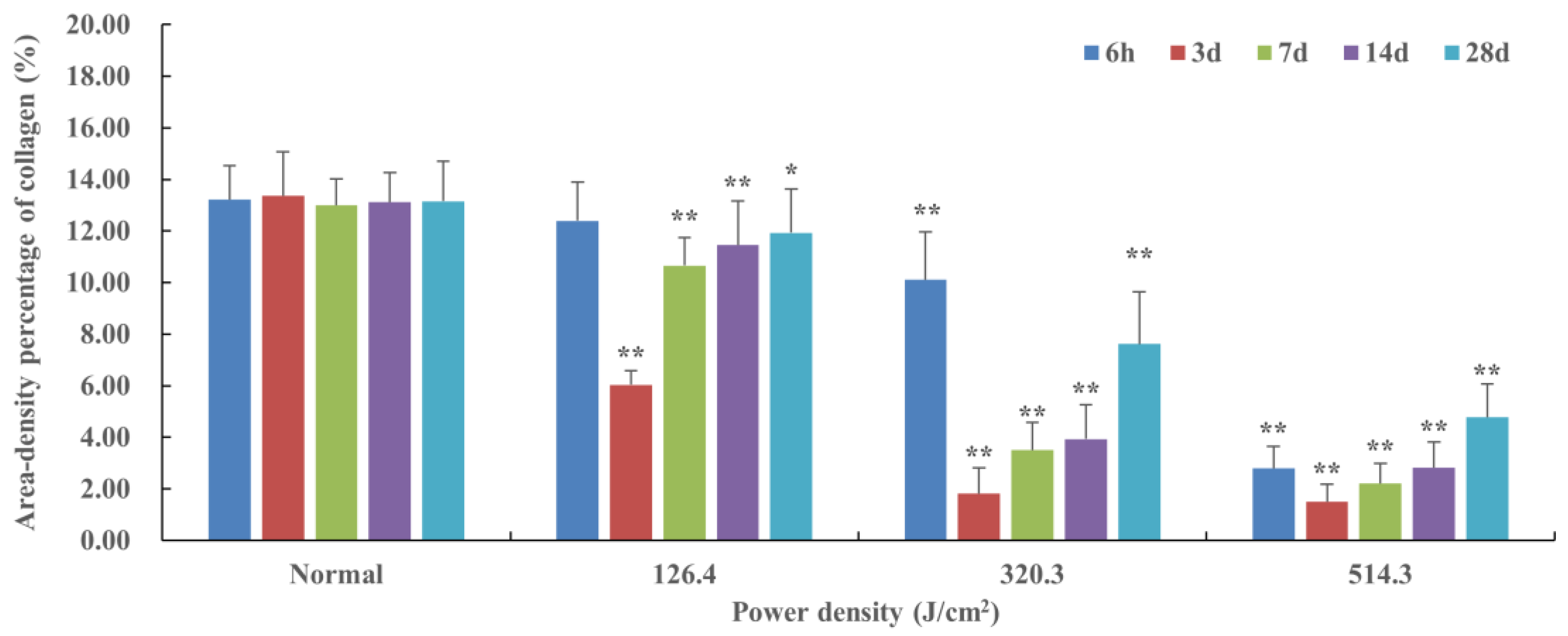
Figure 6.
Quantitative analysis of area-density percentage of collagen in skin wounds 6h to 28d after laser irradiation. In comparison to the normal group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
Figure 6.
Quantitative analysis of area-density percentage of collagen in skin wounds 6h to 28d after laser irradiation. In comparison to the normal group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
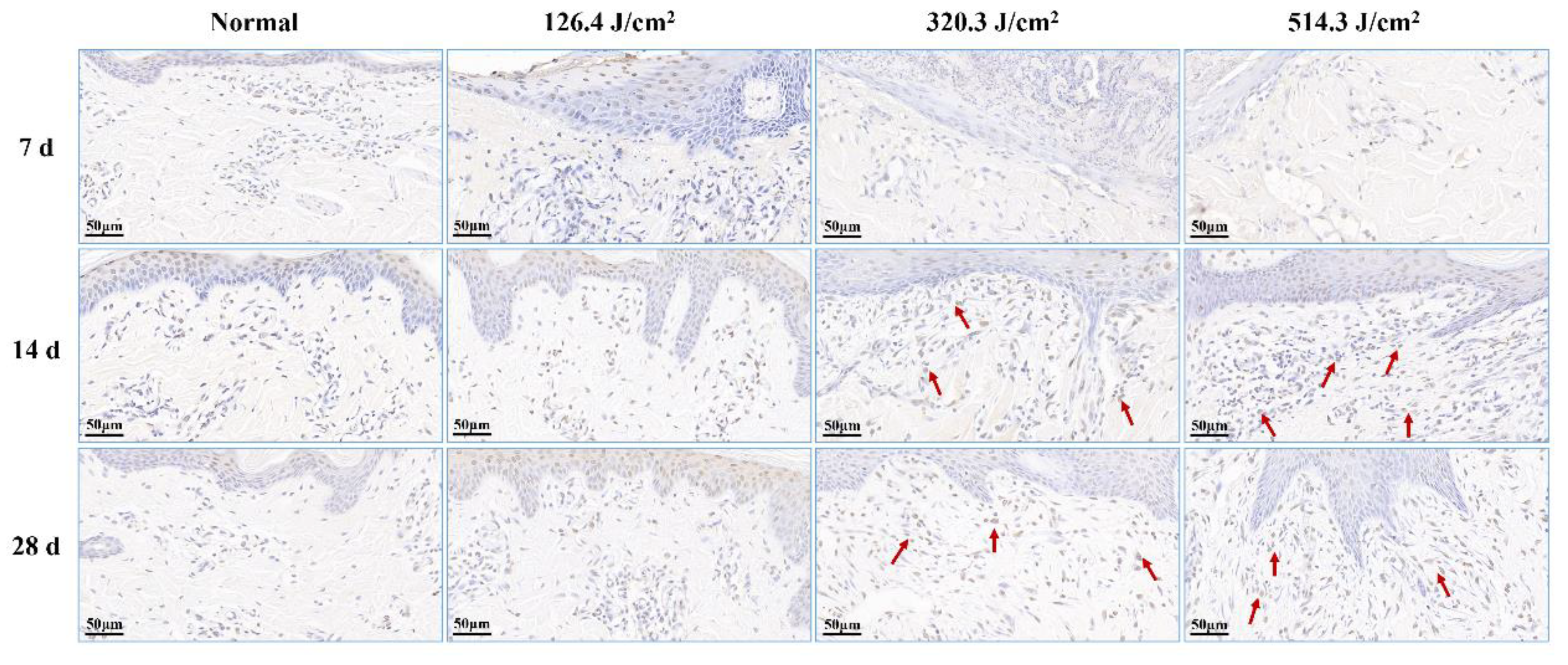
Figure 7.
Alterations in apoptotic cells within pig skin wounds at various intervals following diverse doses of laser irradiation (TUNEL staining). Apoptotic cells in newly formed tissue are denoted by red arrows.
Figure 7.
Alterations in apoptotic cells within pig skin wounds at various intervals following diverse doses of laser irradiation (TUNEL staining). Apoptotic cells in newly formed tissue are denoted by red arrows.
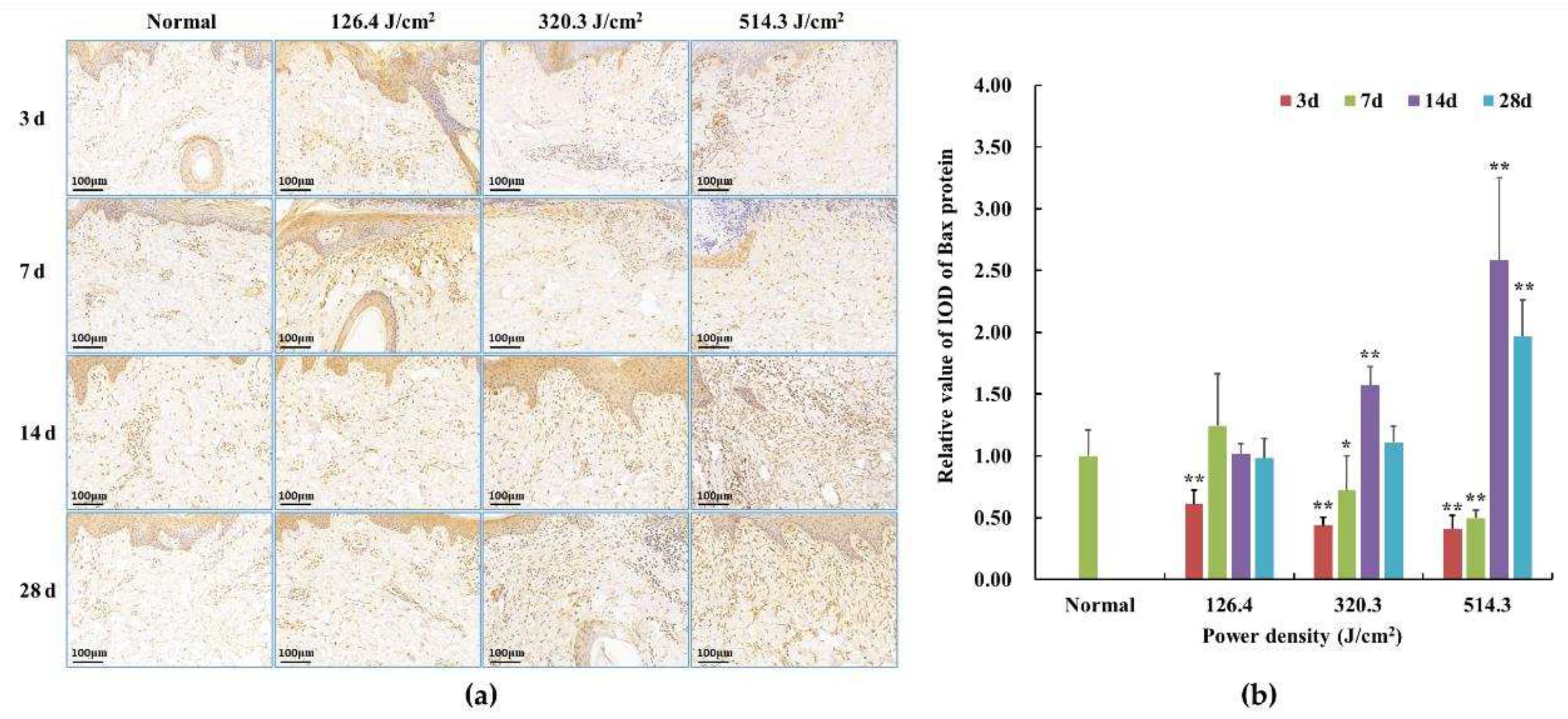
Figure 8.
Alterations in Bax protein expression within pig skin wounds at different intervals following diverse doses of laser irradiation (IHC staining). In comparison to the normal group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (a) Positive protein expression observed through immunohistochemical staining; (b) Quantitative analysis of Bax protein expression within skin wound tissue.
Figure 8.
Alterations in Bax protein expression within pig skin wounds at different intervals following diverse doses of laser irradiation (IHC staining). In comparison to the normal group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (a) Positive protein expression observed through immunohistochemical staining; (b) Quantitative analysis of Bax protein expression within skin wound tissue.
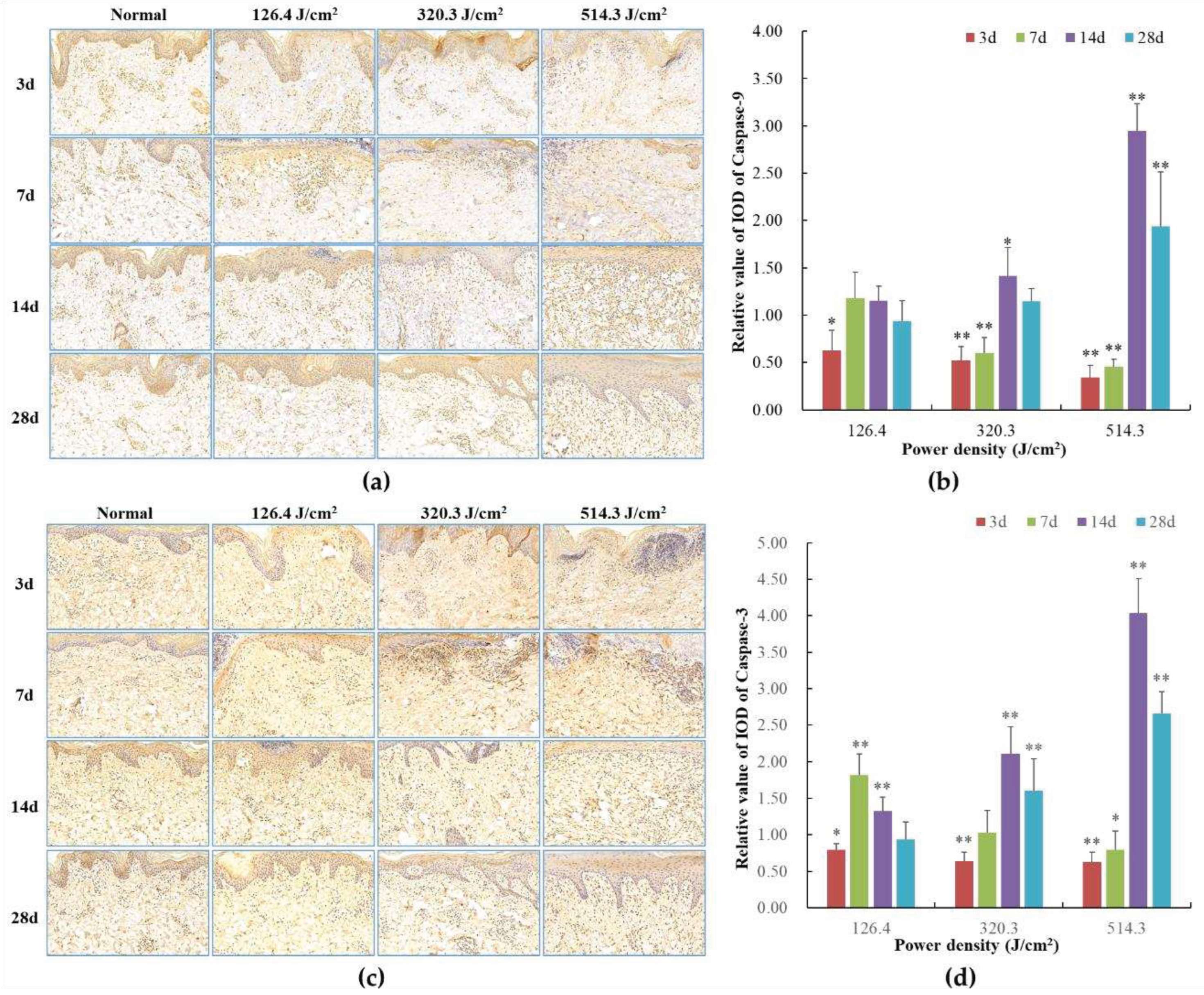
Figure 9.
Modifications in caspase protein expression within pig skin wounds across distinct intervals following varied doses of laser irradiation (IHC staining). In comparison to the normal group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (A) Positive caspase-9 protein expression through IHC staining; (B) Quantitative analysis of caspase-9 protein expression; (C) Positive caspase-3 protein expression through IHC staining; (D) Quantitative analysis of caspase-3 protein expression.
Figure 9.
Modifications in caspase protein expression within pig skin wounds across distinct intervals following varied doses of laser irradiation (IHC staining). In comparison to the normal group, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (A) Positive caspase-9 protein expression through IHC staining; (B) Quantitative analysis of caspase-9 protein expression; (C) Positive caspase-3 protein expression through IHC staining; (D) Quantitative analysis of caspase-3 protein expression.