Submitted:
26 January 2024
Posted:
29 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. MLIP expression in cancer
Expression of MLIP in different types of cancer
3. Molecular relationship of MLIP with pro-survival/oncogenic pathways and tumor suppressors
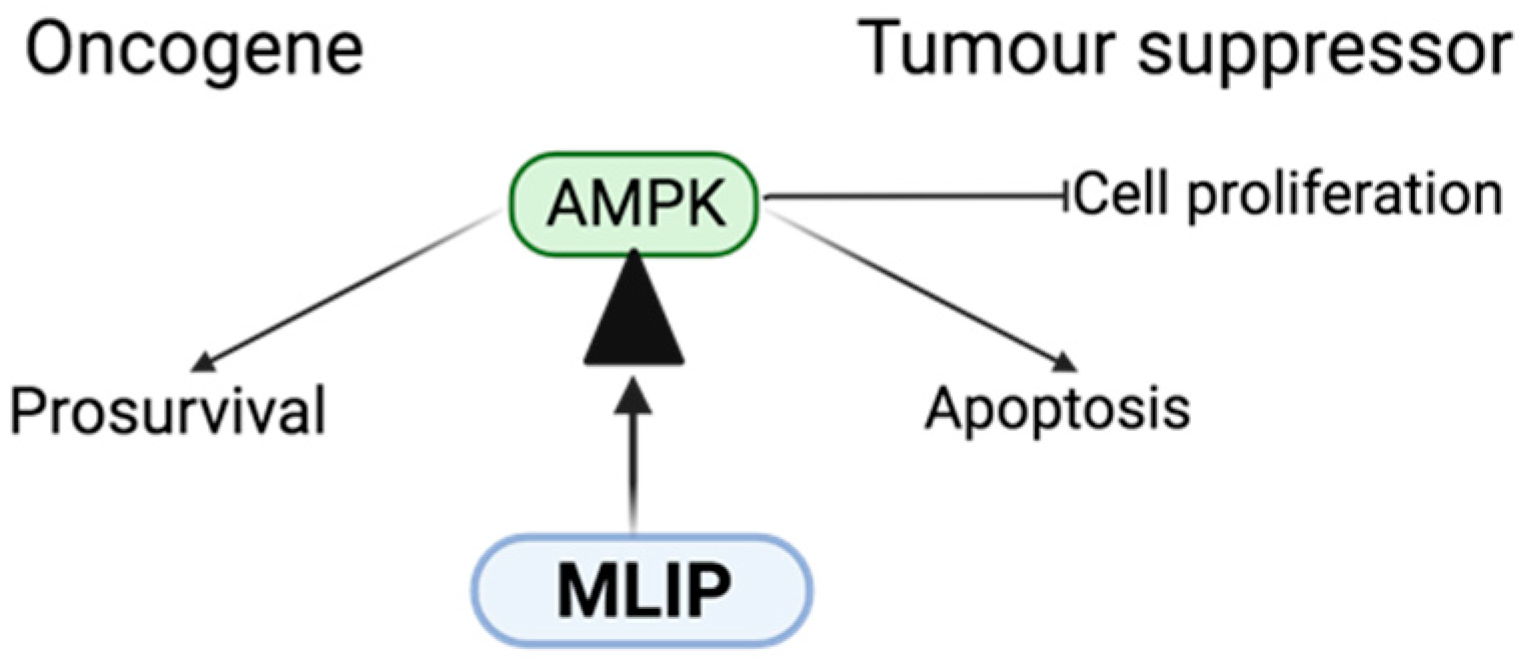
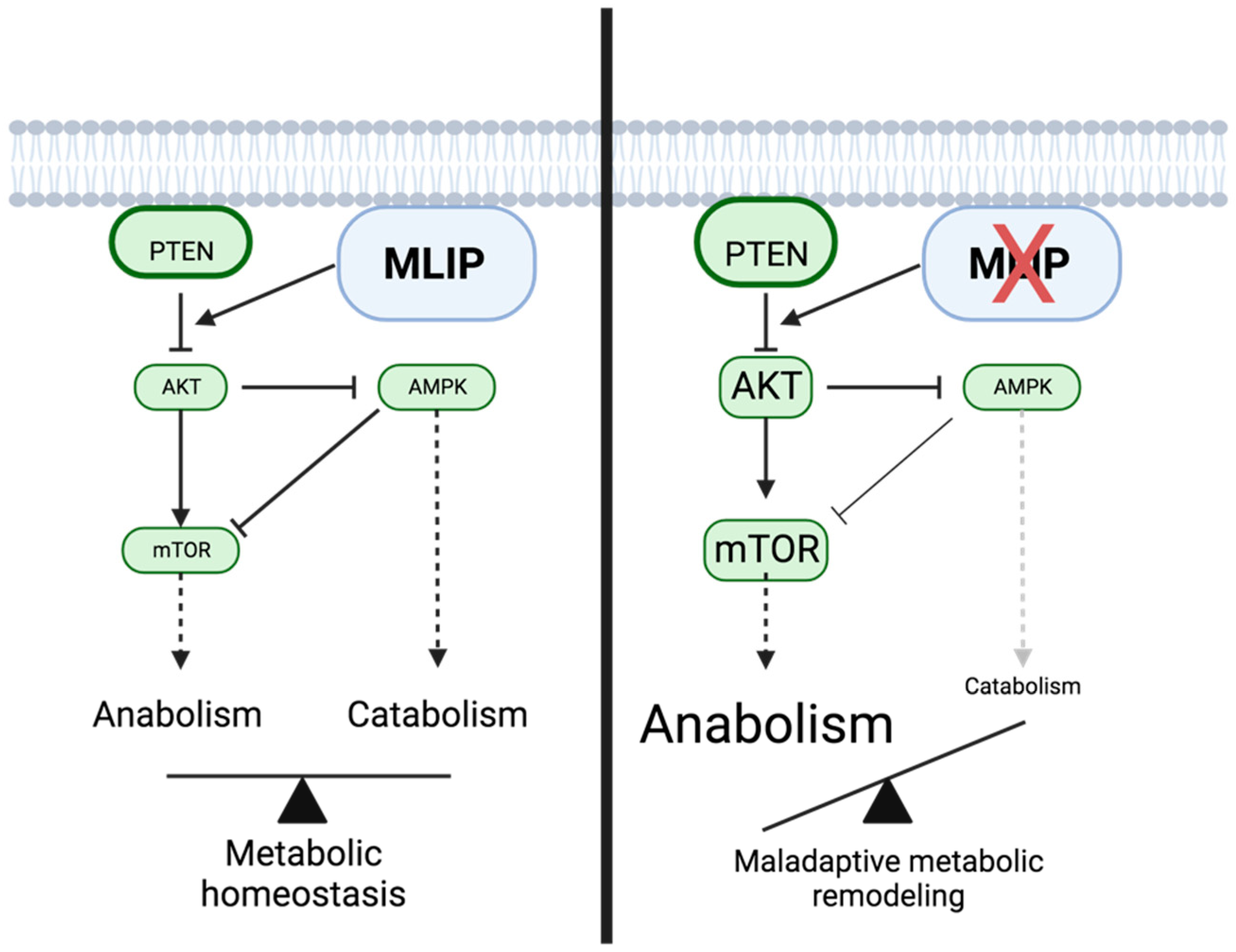
Primary role of AMPK function and dysfunction in cancer
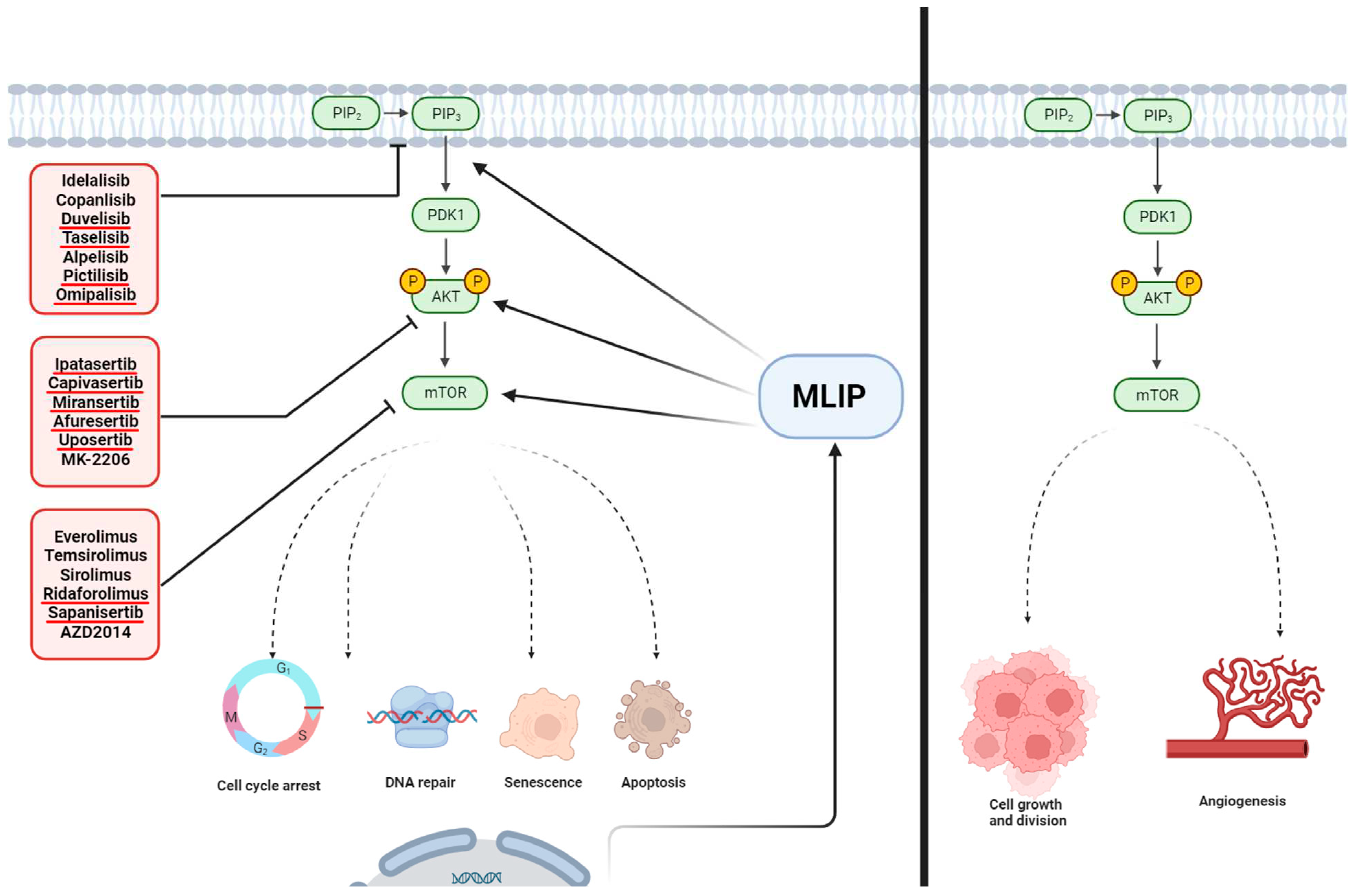
The PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and MLIP
Role of MLIP in FOXO1 signaling
P53 and MLIP
4. Conclusion, MLIP as a potential therapeutic target
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The next Generation. Cell 2011, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, H.K.; Bertoli, C.; de Bruin, R.A.M. Cell Cycle Control in Cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquette, M.; El-Houjeiri, L.; Pause, A. MTOR Pathways in Cancer and Autophagy. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wei, J.; Liu, P. Attacking the PI3K/Akt/MTOR Signaling Pathway for Targeted Therapeutic Treatment in Human Cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 2022, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eijkelenboom, A.; Burgering, B.M.T. FOXOs: Signalling Integrators for Homeostasis Maintenance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2013, 14, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronnebaum, S.M.; Patterson, C. The FoxO Family in Cardiac Function and Dysfunction. Annu Rev Physiol 2010, 72, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousden, K.H.; Ryan, K.M. P53 and Metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 2009, 9, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vousden, K.H.; Prives, C. Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of P53. Cell 2009, 137, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmady, E.; Blais, A.; Burgon, P.G. Muscle Enriched Lamin Interacting Protein (Mlip) Binds Chromatin and Is Required for Myoblast Differentiation. Cells 2021, 10, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmady, E.; Deeke, S.A.; Rabaa, S.; Kouri, L.; Kenney, L.; Stewart, A.F.R.; Burgon, P.G. Identification of a Novel Muscle A-Type Lamin-Interacting Protein (MLIP). J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 19702–19713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattin, M.-E.; Wang, J.; Weldrick, J.J.; Roeske, C.L.; Mak, E.; Thorn, S.L.; DaSilva, J.N.; Wang, Y.; Lusis, A.J.; Burgon, P.G. Deletion of MLIP (Muscle-Enriched A-Type Lamin-Interacting Protein) Leads to Cardiac Hyperactivation of Akt/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (MTOR) and Impaired Cardiac Adaptation. J Biol Chem 2015, 290, 26699–26714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattin, M.-E.; Deeke, S.A.; Dick, S.A.; Verret-Borsos, Z.J.A.; Tennakoon, G.; Gupta, R.; Mak, E.; Roeske, C.L.; Weldrick, J.J.; Megeney, L.A.; et al. Expression of Murine Muscle-Enriched A-Type Lamin-Interacting Protein (MLIP) Is Regulated by Tissue-Specific Alternative Transcription Start Sites. 2018; 293, 19761–19770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes Abath Neto, O.; Medne, L.; Donkervoort, S.; Rodríguez-García, M.E.; Bolduc, V.; Hu, Y.; Guadagnin, E.; Foley, A.R.; Brandsema, J.F.; Glanzman, A.M.; et al. MLIP Causes Recessive Myopathy with Rhabdomyolysis, Myalgia and Baseline Elevated Serum Creatine Kinase. Brain 2021, 144, 2722–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.-P.; Kataoka, M.; Chen, J.; Wu, G.; Ding, J.; Nie, M.; Lin, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Ma, L.; et al. Cardiomyocyte-Enriched Protein CIP Protects against Pathophysiological Stresses and Regulates Cardiac Homeostasis. J Clin Invest 2015, 125, 4122–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tong, G.H.; Wei, X.X.; Chen, H.Y.; Liang, T.; Tang, H.P.; Wu, C.A.; Wen, G.M.; Yang, W.K.; Liang, L.; et al. Identification of Five Cytotoxicity-Related Genes Involved in the Progression of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front Genet 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattin, M.E.; Wang, J.; Weldrick, J.J.; Roeske, C.L.; Mak, E.; Thorn, S.L.; DaSilva, J.N.; Wang, Y.; Lusis, A.J.; Burgon, P.G. Deletion of MLIP (Muscle-Enriched A-Type Lamin-Interacting Protein) Leads to Cardiac Hyperactivation of Akt/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (MTOR) and Impaired Cardiac Adaptation. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2015, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, X.; Gong, T.; Liang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of LncRNAs, MiRNAs, and MRNAs Forming a Prognostic Scoring System in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PeerJ 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaran, M.; Cass, C.E.; Graham, K.; Mackey, J.R.; Hubaux, R.; Lam, W.; Yasui, Y.; Damaraju, S. Germline Copy Number Variations Are Associated with Breast Cancer Risk and Prognosis. Sci Rep 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breast Cancer Facts & Stats | Incidence, Age, Survival, & More Available online:. Available online: https://www.nationalbreastcancer.org/breast-cancer-facts/ (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Michailidou, K.; Hall, P.; Gonzalez-Neira, A.; Ghoussaini, M.; Dennis, J.; Milne, R.L.; Schmidt, M.K.; Chang-Claude, J.; Bojesen, S.E.; Bolla, M.K.; et al. Large-Scale Genotyping Identifies 41 New Loci Associated with Breast Cancer Risk. Nat Genet 2013, 45, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fachal, L.; Dunning, A.M. From Candidate Gene Studies to GWAS and Post-GWAS Analyses in Breast Cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2015, 30, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaran, M.; Cass, C.E.; Graham, K.; Mackey, J.R.; Hubaux, R.; Lam, W.; Yasui, Y.; Damaraju, S. Germline Copy Number Variations Are Associated with Breast Cancer Risk and Prognosis. Sci Rep 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tong, G.H.; Wei, X.X.; Chen, H.Y.; Liang, T.; Tang, H.P.; Wu, C.A.; Wen, G.M.; Yang, W.K.; Liang, L.; et al. Identification of Five Cytotoxicity-Related Genes Involved in the Progression of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front Genet 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, X.; Gong, T.; Liang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of LncRNAs, MiRNAs, and MRNAs Forming a Prognostic Scoring System in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PeerJ 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salt, I.P.; Johnson, G.; Ashcroft, S.J.H.; Hardie, D.G. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Is Activated by Low Glucose in Cell Lines Derived from Pancreatic Beta Cells, and May Regulate Insulin Release. Biochem J 1998, 335 Pt 3, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhou, X.E.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K. Structure and Physiological Regulation of AMPK. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liong, S.; Lappas, M. Activation of AMPK Improves Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle from Pregnant Women. J Physiol Biochem 2015, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Saud, S.M.; Young, M.R.; Chen, G.; Hua, B. Targeting AMPK for Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Oncotarget 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthana, C.K.; Rayginia, T.P.; Shifana, S.C.; Anto, N.P.; Kalimuthu, K.; Isakov, N.; Anto, R.J. The Role of AMPK in Cancer Metabolism and Its Impact on the Immunomodulation of the Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.C.; Hardie, D.G. AMPK: Sensing Glucose as Well as Cellular Energy Status. Cell Metab 2018, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zang, M.; Guo, W. AMPK as a Metabolic Tumor Suppressor: Control of Metabolism and Cell Growth. Future Oncol 2010, 6, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, M.M.; Zordoky, B.N.; Bujak, A.L.; Lally, J.S.V.; Fung, D.; Young, M.E.; Horman, S.; Miller, E.J.; Light, P.E.; Kemp, B.E.; et al. AMPK Deficiency in Cardiac Muscle Results in Dilated Cardiomyopathy in the Absence of Changes in Energy Metabolism. Cardiovasc Res 2015, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, A.S. PI3K/Akt/MTOR Inhibitors in Cancer: At the Bench and Bedside. Semin Cancer Biol 2019, 59, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ediriweera, M.K.; Tennekoon, K.H.; Samarakoon, S.R. Role of the PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling Pathway in Ovarian Cancer: Biological and Therapeutic Significance. Semin Cancer Biol 2019, 59, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polivka, J.; Janku, F. Molecular Targets for Cancer Therapy in the PI3K/AKT/MTOR Pathway. Pharmacol Ther 2014, 142, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, I.A.; Arteaga, C.L. The PI3K/AKT Pathway as a Target for Cancer Treatment. Annu Rev Med 2016, 67, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, V.S.; Torres, F.F.; da Silva, D.G.H. FoxO3 and Oxidative Stress: A Multifaceted Role in Cellular Adaptation. J Mol Med (Berl) 2023, 101, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitsipatis, D.; Klotz, L.O.; Steinbrenner, H. Multifaceted Functions of the Forkhead Box Transcription Factors FoxO1 and FoxO3 in Skin. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 2017, 1861, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosaka, T.; Biggs, W.H.; Tieu, D.; Boyer, A.D.; Varki, N.M.; Cavenee, W.K.; Arden, K.C. Disruption of Forkhead Transcription Factor (FOXO) Family Members in Mice Reveals Their Functional Diversification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004, 101, 2975–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Tindall, D.J. Dynamic FoxO Transcription Factors. J Cell Sci 2007, 120, 2479–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiramongkol, Y.; Lam, E.W.F. FOXO Transcription Factor Family in Cancer and Metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2020, 39, 681–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Colman, M.J.; Dansen, T.B.; Burgering, B.M.T. FOXO Transcription Factors as Mediators of Stress Adaptation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freycon, C.; Lupo, P.J.; Witkowski, L.; Budd, C.; Foulkes, W.D.; Goudie, C. A Systematic Review of the Prevalence of Pathogenic or Likely Pathogenic Germline Variants in Individuals with FOXO1 Fusion-Positive Rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2023, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ao, X.; Ding, W.; Ponnusamy, M.; Wu, W.; Hao, X.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Critical Role of FOXO3a in Carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habrowska-Górczyńska, D.E.; Kozieł, M.J.; Kowalska, K.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. FOXO3a and Its Regulators in Prostate Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, M. FOXO Factors and Breast Cancer: Outfoxing Endocrine Resistance. Endocr Relat Cancer 2016, 23, R113–R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Chen, C.; Cheng, J. The Role and Molecular Mechanism of FoxO1 in Mediating Cardiac Hypertrophy. ESC Heart Fail 2020, 7, 3497–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helton, E.S.; Chen, X. P53 Modulation of the DNA Damage Response. J Cell Biochem 2007, 100, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.B.; Schumacher, B. P53 in the DNA-Damage-Repair Process. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnanasundram, S.V.; Bonczek, O.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Fahraeus, R. P53 MRNA Metabolism Links with the DNA Damage Response. Genes (Basel) 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrechtsen, N.; Dornreiter, I.; Grosse, F.; Ella, K.; Wiesmüller, L.; Deppert, W. Maintenance of Genomic Integrity by P53: Complementary Roles for Activated and Non-Activated P53. Oncogene 1999, 18, 7706–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Ho, T.L.F.; Hariharan, A.; Goh, H.C.; Wong, Y.L.; Verkaik, N.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Tam, W.L.; van Gent, D.C.; Venkitaraman, A.R.; et al. Rapid Recruitment of P53 to DNA Damage Sites Directs DNA Repair Choice and Integrity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatz, S.A.; Wiesmüller, L. P53 in Recombination and Repair. Cell Death Differ 2006, 13, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J.; Synnott, N.C.; O’Grady, S.; Crown, J. Targeting P53 for the Treatment of Cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 2022, 79, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J.; Synnott, N.C.; McGowan, P.M.; Crown, J.; O’Connor, D.; Gallagher, W.M. P53 as a Target for the Treatment of Cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 2014, 40, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, N.; Nagano, H.; Tanaka, T. The Role of Tumor Suppressor P53 in Metabolism and Energy Regulation, and Its Implication in Cancer and Lifestyle-Related Diseases. Endocr J 2019, 66, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olovnikov, I.A.; Kravchenko, J.E.; Chumakov, P.M. Homeostatic Functions of the P53 Tumor Suppressor: Regulation of Energy Metabolism and Antioxidant Defense. Semin Cancer Biol 2009, 19, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Hu, W.; Feng, Z. Tumor Suppressor P53 and Metabolism. J Mol Cell Biol 2019, 11, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, M.; Ambroise, G.; Ouchida, A.T.; Lima Queiroz, A.; Smith, D.; Gimenez-Cassina, A.; Iwanicki, M.P.; Muller, P.A.; Norberg, E.; Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg, H. Effect of Mutant P53 Proteins on Glycolysis and Mitochondrial Metabolism. Mol Cell Biol 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yu, L.; Chen, W.; Xu, Y.; Wu, M.; Todorova, D.; Tang, Q.; Feng, B.; Jiang, L.; He, J.; et al. Wild-Type P53 Promotes Cancer Metabolic Switch by Inducing PUMA-Dependent Suppression of Oxidative Phosphorylation. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, W.; Lian, G.; Huang, B.; Du, A.; Gong, J.; Xiao, G.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Xie, L. CPT1 Regulates the Proliferation of Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cells through the AMPK-P53-P21 Pathway in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Mol Cell Biochem 2019, 455, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Hu, W.; Feng, Z. Tumor Suppressor P53 and Its Mutants in Cancer Metabolism. Cancer Lett 2015, 356, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Long, T.; Su, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Yang, T.; Zhao, G.; Ma, Q.; Hu, X.; Liu, C.; et al. Cardiac ISL1-Interacting Protein, a Cardioprotective Factor, Inhibits the Transition From Cardiac Hypertrophy to Heart Failure. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.-P.; Young Seok, H.; Zhou, B.; Chen, J.J.-F.; Chen, J.J.-F.; Tao, Y.; Pu, W.T.; Wang, D.-Z. CIP, a Cardiac Isl1-Interacting Protein, Represses Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy. Circ Res 2012, 110, 818–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaran, M.; Cass, C.E.; Graham, K.; Mackey, J.R.; Hubaux, R.; Lam, W.; Yasui, Y.; Damaraju, S. Germline Copy Number Variations Are Associated with Breast Cancer Risk and Prognosis. Sci Rep 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tong, G.H.; Wei, X.X.; Chen, H.Y.; Liang, T.; Tang, H.P.; Wu, C.A.; Wen, G.M.; Yang, W.K.; Liang, L.; et al. Identification of Five Cytotoxicity-Related Genes Involved in the Progression of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front Genet 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, X.; Gong, T.; Liang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of LncRNAs, MiRNAs, and MRNAs Forming a Prognostic Scoring System in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PeerJ 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bou Zeid, N.; Yazbeck, V. PI3k Inhibitors in NHL and CLL: An Unfulfilled Promise. Blood Lymphat Cancer 2023, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, G.; Hassenrück, F.; Hallek, M. Copanlisib for Treatment of B-Cell Malignancies: The Development of a PI3K Inhibitor with Considerable Differences to Idelalisib. Drug Des Devel Ther 2018, 12, 2577–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Danilov, A. V.; Pagel, J.M. Duvelisib for CLL/SLL and Follicular Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 1573–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, C.J.; Redman, M.W.; Wade, J.L.; Aggarwal, C.; Bradley, J.D.; Crawford, J.; Stella, P.J.; Knapp, M.H.; Miao, J.; Minichiello, K.; et al. SWOG S1400B (NCT02785913), a Phase II Study of GDC-0032 (Taselisib) for Previously Treated PI3K-Positive Patients with Stage IV Squamous Cell Lung Cancer (Lung-MAP Sub-Study). J Thorac Oncol 2019, 14, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, S.; Chia, S.; Kanakamedala, H.; Hsu, W.C.; Park, J.; Chandiwana, D.; Ridolfi, A.; Yu, C.L.; Zarate, J.P.; Rugo, H.S. Effectiveness of Alpelisib + Fulvestrant Compared with Real-World Standard Treatment Among Patients with HR+, HER2-, PIK3CA-Mutated Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2021, 26, e1133–e1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertho, M.; Patsouris, A.; Augereau, P.; Robert, M.; Frenel, J.S.; Blonz, C.; Campone, M. A Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Alpelisib for the Treatment of HR+, HER2-Negative, PIK3CA-Mutated Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2021, 17, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, D.; Ang, J.E.; Baird, R.; Kristeleit, R.; Shah, K.; Moreno, V.; Clarke, P.A.; Raynaud, F.I.; Levy, G.; Ware, J.A.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Study of Pictilisib (GDC-0941), a Potent Pan-Class I Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase (PI3K) Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2015, 21, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munster, P.; Aggarwal, R.; Hong, D.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Van Der Noll, R.; Specht, J.; Witteveen, P.O.; Werner, T.L.; Dees, E.C.; Bergsland, E.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Study of GSK2126458, an Oral Pan-Class I Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumor Malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 2016, 22, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bono, J.S.; De Giorgi, U.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Massard, C.; Bracarda, S.; Font, A.; Arija, J.A.A.; Shih, K.C.; Radavoi, G.D.; Xu, N.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study Evaluating Akt Blockade with Ipatasertib, in Combination with Abiraterone, in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer with and without PTEN Loss. Clin Cancer Res 2019, 25, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, Y.J.; Kang, Y.K.; Ng, M.; Chung, H.C.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Gendreau, S.; Chan, W.Y.; Xu, N.; Maslyar, D.; Meng, R.; et al. A Phase II, Randomised Study of MFOLFOX6 with or without the Akt Inhibitor Ipatasertib in Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Gastric or Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer. Eur J Cancer 2019, 108, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.C.; Oliveira, M.; Howell, S.J.; Dalenc, F.; Cortes, J.; Gomez Moreno, H.L.; Hu, X.; Jhaveri, K.; Krivorotko, P.; Loibl, S.; et al. Capivasertib in Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 2023, 388, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forde, K.; Resta, N.; Ranieri, C.; Rea, D.; Kubassova, O.; Hinton, M.; Andrews, K.A.; Semple, R.; Irvine, A.D.; Dvorakova, V. Clinical Experience with the AKT1 Inhibitor Miransertib in Two Children with PIK3CA-Related Overgrowth Syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolcher, A.W.; Patnaik, A.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Rasco, D.W.; Becerra, C.R.; Allred, A.J.; Orford, K.; Aktan, G.; Ferron-Brady, G.; Ibrahim, N.; et al. Phase I Study of the MEK Inhibitor Trametinib in Combination with the AKT Inhibitor Afuresertib in Patients with Solid Tumors and Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2015, 75, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanian, C.; Bell-McGuinn, K.M.; Burris, H.A.; Siu, L.L.; Stayner, L.A.; Wheler, J.J.; Hong, D.S.; Kurkjian, C.; Pant, S.; Santiago-Walker, A.; et al. A Phase I, Open-Label, Two-Stage Study to Investigate the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of the Oral AKT Inhibitor GSK2141795 in Patients with Solid Tumors. Invest New Drugs 2018, 36, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, A.P.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Barry, W.T.; Luo, W.; Broaddus, R.R.; Makker, V.; Drapkin, R.; Liu, J.; Doyle, A.; Horowitz, N.S.; et al. Phase II, 2-Stage, 2-Arm, PIK3CA Mutation Stratified Trial of MK-2206 in Recurrent Endometrial Cancer. Int J Cancer 2020, 147, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse, B.; Leighl, N.; Bennouna, J.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Blais, N.; Traynor, A.M.; Soria, J.C.; Gogov, S.; Miller, N.; Jehl, V.; et al. Phase II Study of Everolimus-Erlotinib in Previously Treated Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann Oncol 2014, 25, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse, B.; Heist, R.S.; Papadmitrakopoulou, V.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Beck, J.T.; Schmid, P.; Mulatero, C.; Miller, N.; Dimitrijevic, S.; Urva, S.; et al. A Phase Ib Dose-Escalation Study of Everolimus Combined with Cisplatin and Etoposide as First-Line Therapy in Patients with Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann Oncol 2014, 25, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, L.; Bahleda, R.; Tolaney, S.M.; Kwak, E.L.; Cleary, J.M.; Pandya, S.S.; Hollebecque, A.; Abbas, R.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Berkenblit, A.; et al. Phase I Study of Neratinib in Combination with Temsirolimus in Patients with Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Dependent and Other Solid Tumors. J Clin Oncol 2014, 32, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, T.; Palmero, R.; Provencio, M.; Insa, A.; Majem, M.; Reguart, N.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Isla, D.; Costa, E.C.; Lee, C.; et al. A Phase Ib Trial of Continuous Once-Daily Oral Afatinib plus Sirolimus in Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and/or Disease Progression Following Prior Erlotinib or Gefitinib. Lung Cancer 2017, 108, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, A.D.J.; Federico, S.M.; Aerts, I.; Hargrave, D.R.; DuBois, S.G.; Iannone, R.; Geschwindt, R.D.; Wang, R.; Haluska, F.G.; Trippett, T.M.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of Oral Ridaforolimus in Pediatric Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 84736–84747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Saenz, J.A.; Martínez-Jañez, N.; Cubedo, R.; Jerez, Y.; Lahuerta, A.; Gonzalez-Santiago, S.; Ferrer, N.; Ramos, M.; Alonso-Romero, J.L.; Anton, A.; et al. Sapanisertib plus Fulvestrant in Postmenopausal Women with Estrogen Receptor-Positive/HER2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer after Progression on Aromatase Inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res 2022, 28, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heudel, P.; Frenel, J.S.; Dalban, C.; Bazan, F.; Joly, F.; Arnaud, A.; Abdeddaim, C.; Chevalier-Place, A.; Augereau, P.; Pautier, P.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the MTOR Inhibitor, Vistusertib, Combined With Anastrozole in Patients With Hormone Receptor-Positive Recurrent or Metastatic Endometrial Cancer: The VICTORIA Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase 1/2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol 2022, 8, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, F.; Wunderle, L.; Badura, S.; Schleyer, E.; Brüggemann, M.; Serve, H.; Schnittger, S.; Gökbuget, N.; Pfeifer, H.; Wagner, S.; et al. A Phase I Study of a Dual PI3-Kinase/MTOR Inhibitor BEZ235 in Adult Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukemia. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Lackner, M.R.; Oudard, S.; Escudier, B.; Ralph, C.; Brown, J.E.; Hawkins, R.E.; Castellano, D.; Rini, B.I.; Staehler, M.D.; et al. Randomized Open-Label Phase II Trial of Apitolisib (GDC-0980), a Novel Inhibitor of the PI3K/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Pathway, versus Everolimus in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016, 34, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolly, S.O.; Wagner, A.J.; Bendell, J.C.; Kindler, H.L.; Krug, L.M.; Seiwert, T.Y.; Zauderer, M.G.; Lolkema, M.P.; Apt, D.; Yeh, R.F.; et al. Phase I Study of Apitolisib (GDC-0980), Dual Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2016, 22, 2874–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantelli, C.; Gaudio, E.; Arribas, A.J.; Kwee, I.; Hillmann, P.; Rinaldi, A.; Cascione, L.; Spriano, F.; Bernasconi, E.; Guidetti, F.; et al. PQR309 Is a Novel Dual PI3K/MTOR Inhibitor with Preclinical Antitumor Activity in Lymphomas as a Single Agent and in Combination Therapy. Clin Cancer Res 2018, 24, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilley-Olson, J.E.; Bedard, P.L.; Fasolo, A.; Cornfeld, M.; Cartee, L.; Razak, A.R.A.; Stayner, L.A.; Wu, Y.; Greenwood, R.; Singh, R.; et al. A Phase Ib Dose-Escalation Study of the MEK Inhibitor Trametinib in Combination with the PI3K/MTOR Inhibitor GSK2126458 in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Invest New Drugs 2016, 34, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, P.; Aggarwal, R.; Hong, D.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Van Der Noll, R.; Specht, J.; Witteveen, P.O.; Werner, T.L.; Dees, E.C.; Bergsland, E.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Study of GSK2126458, an Oral Pan-Class I Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumor Malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 2016, 22, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainberg, Z.A.; Alsina, M.; Soares, H.P.; Braña, I.; Britten, C.D.; Del Conte, G.; Ezeh, P.; Houk, B.; Kern, K.A.; Leong, S.; et al. A Multi-Arm Phase I Study of the PI3K/MTOR Inhibitors PF-04691502 and Gedatolisib (PF-05212384) plus Irinotecan or the MEK Inhibitor PD-0325901 in Advanced Cancer. Target Oncol 2017, 12, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morscher, R.J.; Brard, C.; Berlanga, P.; Marshall, L. V.; André, N.; Rubino, J.; Aerts, I.; De Carli, E.; Corradini, N.; Nebchi, S.; et al. First-in-Child Phase I/II Study of the Dual MTORC1/2 Inhibitor Vistusertib (AZD2014) as Monotherapy and in Combination with Topotecan-Temozolomide in Children with Advanced Malignancies: Arms E and F of the AcSé-ESMART Trial. Eur J Cancer 2021, 157, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Porta, C.; Suárez, C.; Hainsworth, J.; Voog, E.; Duran, I.; Reeves, J.; Czaykowski, P.; Castellano, D.; Chen, J.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Sapanisertib ± TAK-117 vs. Everolimus in Patients With Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma After VEGF-Targeted Therapy. Oncologist 2022, 27, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starks, D.C.; Rojas-Espaillat, L.; Meissner, T.; Williams, C.B. Phase I Dose Escalation Study of Dual PI3K/MTOR Inhibition by Sapanisertib and Serabelisib in Combination with Paclitaxel in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Gynecol Oncol 2022, 166, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiramongkol, Y.; Lam, E.W.F. FOXO Transcription Factor Family in Cancer and Metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2020, 39, 681–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cancer | Status | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | 1 out of 6 genes associated with breast cancer risk and recurrence free survival | [65] |
| Triple negative breast cancer | Upregulated in and associated with patient survival in triple-negative breast cancer | [66] |
| Esophageal cancer | One of 7 risk RNAs for esophageal cancer | [67] |
| Drug | Molecular Target | Status | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Idelalisib (Zydelig) | PI3K | Relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), follicular lymphoma, and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) | [68] |
| Copanlisib (Aliqopa) | PI3K | relapsed follicular lymphoma | [69] |
| Duvelisib (Copiktra) | PI3K | relapsed or refractory CLL, SLL, and follicular lymphoma | [70] |
| Taselisib (GDC-0032) | PI3K | investigational drug clinical trials for various types of cancer, including breast cancer and lung cancer | [71] |
| Alpelisib (Piqray) | PI3K | HR-positive, HER2-negative, PIK3CA-mutated advanced or metastatic breast cancer | [72,73] |
| Pictilisib (GDC-0941) | PI3K | investigational drug clinical trials for various types of cancer, including breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. | [74] |
| Omipalisib (GSK2126458) | PI3K | investigational drug clinical trials for various types of cancer, including melanoma and pancreatic cancer. | [75] |
| Ipatasertib (GDC-0068) | AKT | investigational drug clinical trials for various types of cancer, including breast cancer, prostate cancer, and ovarian cancer. | [76,77] |
| Capivaserib (AZD5363) | AKT | investigational drug clinical trials for various types of cancer, including breast cancer, prostate cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer. | [78] |
| Miransertib (ARQ092) | AKT | investigational drug clinical trials for various types of cancer, including endometrial cancer, solid tumors, and proteus syndrome. | [79] |
| Afuresertib (GSK2110183) | AKT | investigational drug clinical trials for multiple myeloma and other hematologic malignancies | [80] |
| Uprosertib (GSK2141795) | AKT | investigational drug clinical trials for various types of cancer, including solid tumors and lymphomas. | [81] |
| MK-2206 | AKT | investigational drug clinical trials for various types of cancer, including breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer. | [82] |
| Everolimus (Afinitor, Zortress) | mTOR | advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), progressive neuroendocrine tumors of pancreatic origin (PNET), advanced hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer, renal angiomyolipoma with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), and subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) associated with TSC. | [83,84] |
| Temsirolimus (Torisel) | mTOR | advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) | [85] |
| Sirolimus (Rapamune) | mTOR | potential anti-cancer properties in certain cancers, such as TSC-associated lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM). | [86] |
| Ridaforolimus (AP23573, MK-8669) | mTOR | investigational drug clinical trials for various types of cancer, including sarcomas, endometrial cancer, and other solid tumors. | [87] |
| Sapanisertib (INK128, TAK-228) | mTOR | investigational drug clinical trials for various types of cancer, including breast cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. | [88] |
| AZD2014 (Vistusertib) | mTOR | investigational drug clinical trials for various types of cancer, including endometrial cancer, breast cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer. | [89] |
| Dactolisib (BEZ235) | dual PI3K/mTOR | preclinical and early-phase clinical trials for various types of solid tumors, including breast, prostate, and renal cell carcinoma. | [90] |
| Apitolisib (GDC-0980) | dual PI3K/mTOR | early-phase clinical trials for various types of solid tumors, including colorectal, breast, and prostate cancer. | [91,92] |
| Bimiralisib (PQR309) | dual PI3K/mTOR | early-phase clinical trials for various types of solid tumors and lymphomas. | [93] |
| Omipalisib (GSK2126458) | dual PI3K/mTOR | early-phase clinical trials for various types of solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. | [94,95] |
| Gedatolisib (PF-05212384) | dual PI3K/mTOR | early-phase clinical trials for various types of solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. | [96] |
| Vistusertib (AZD2014) | dual PI3K/mTOR | early-phase clinical trials for various types of solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. | [97] |
| Serabelisib (INK1117, MLN0128, TAK-228) | dual PI3K/mTOR | early-phase clinical trials for various types of solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. | [98,99] |
| FOXO type | Role in cell biology | Role in cancer | Types of tumors | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOXO1 | Regulation of gluconeogenesis, cell proliferation, apoptosis, metabolism, inflammation, differentiation, and stress resistance. Global deletion causes embryonic cell death due to incomplete vascular development. | Tumor suppressor, regulation of cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and DNA repair | Lymphoma, soft tissue sarcoma, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), breast cancer | [100] |
| FOXO2 | Involved in multiple important biological processes, such as cell-cycle arrest, DNA repair, apoptosis, glucose metabolism, aging, and autophagy. | Tumor suppressor, regulation of cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and DNA repair | Not specified | [100] |
| FOXO3 | Affects lymph proliferation, widespread organ inflammation. Expression found in most tissues, including lymphocytes and myeloid cells. | Tumor suppressor, regulation of cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and DNA repair | Neuroblastoma, breast cancer, colorectal cancer, glioblastoma, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | [100] |
| FOXO4 | Required for stem cell function in multiple tissues, including maintenance of hematopoietic, neural, and muscle stem cell pools. | Tumor suppressor, regulation of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis | Not specified | [100] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





