Submitted:
26 January 2024
Posted:
26 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
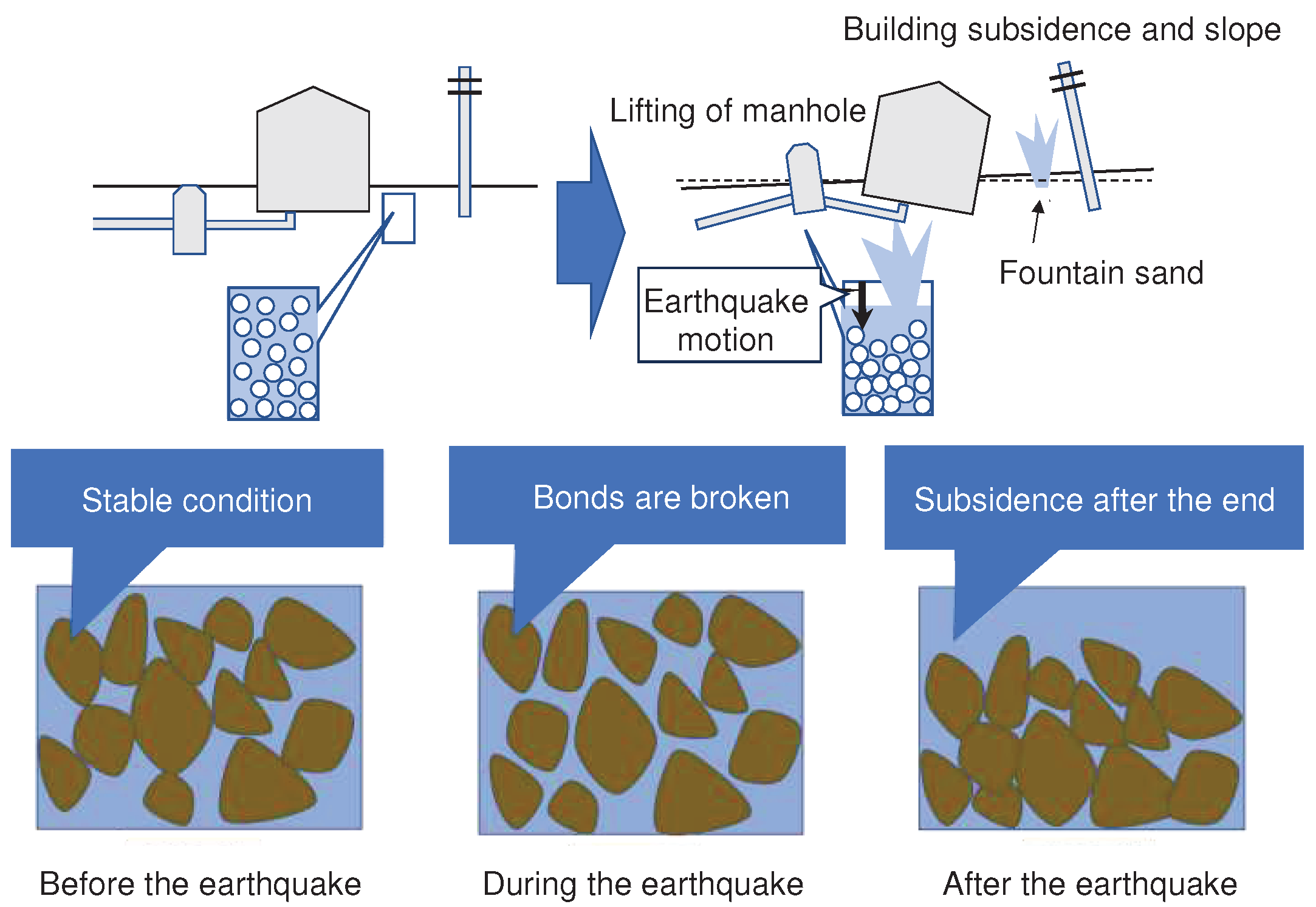
2. General Evaluation and Countermeasures to Liquefaction of Sandy Soils
2.1. Chemical Injection Method
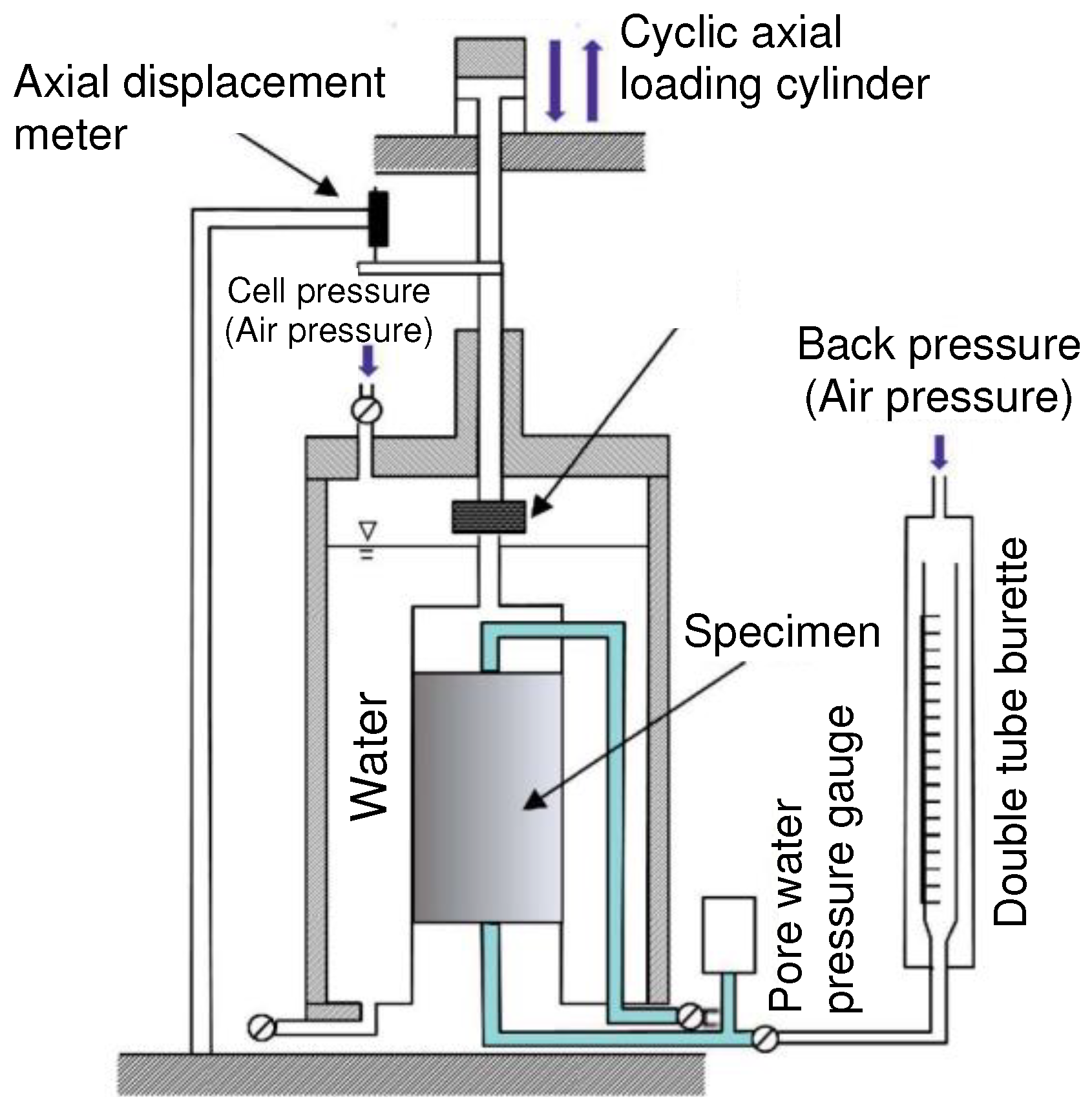
2.2. Cyclic Undrained Triaxial Test
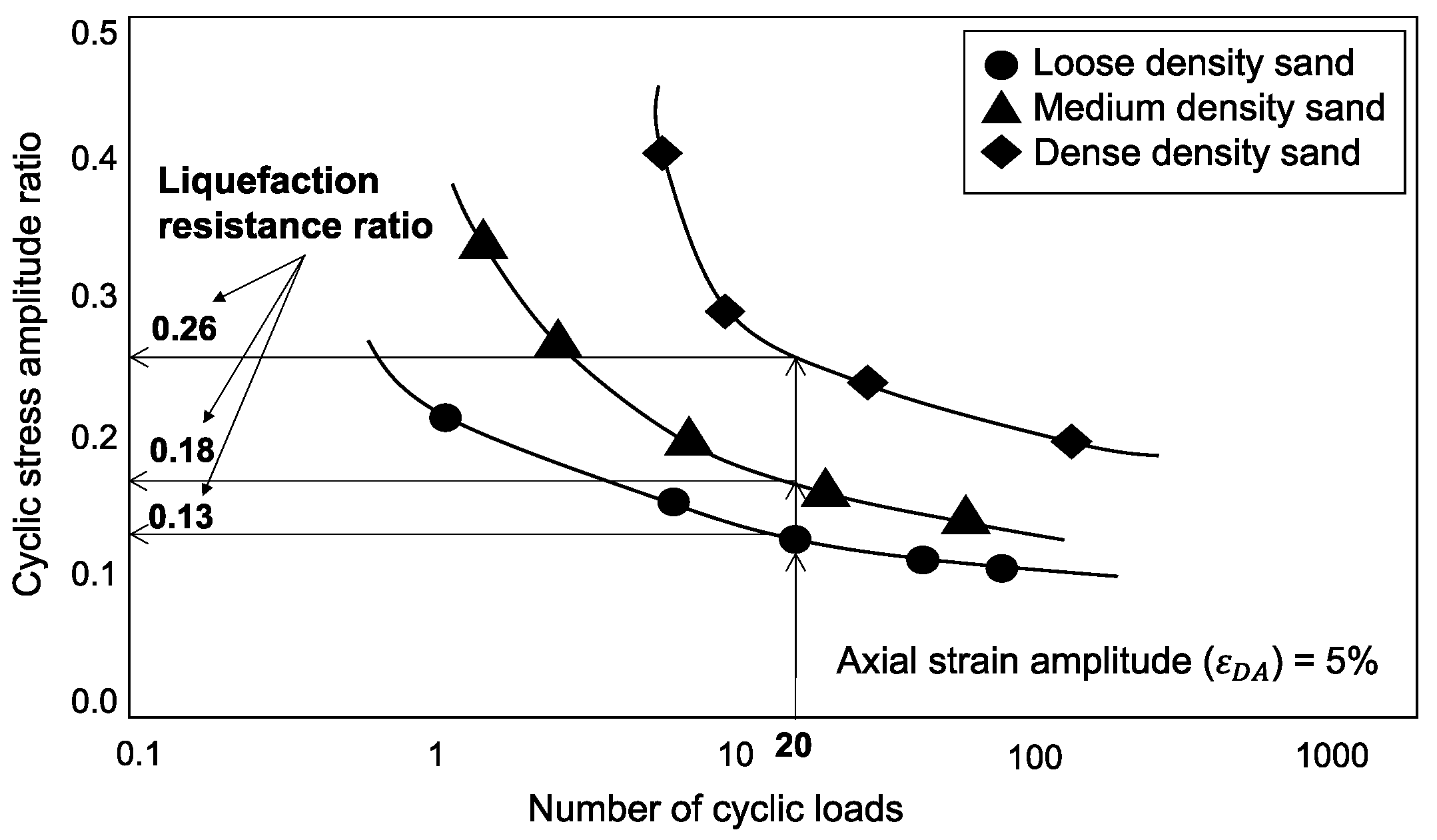
2.3. Liquefaction Resistance Ratio
3. Machine Learning Predictive Analysis
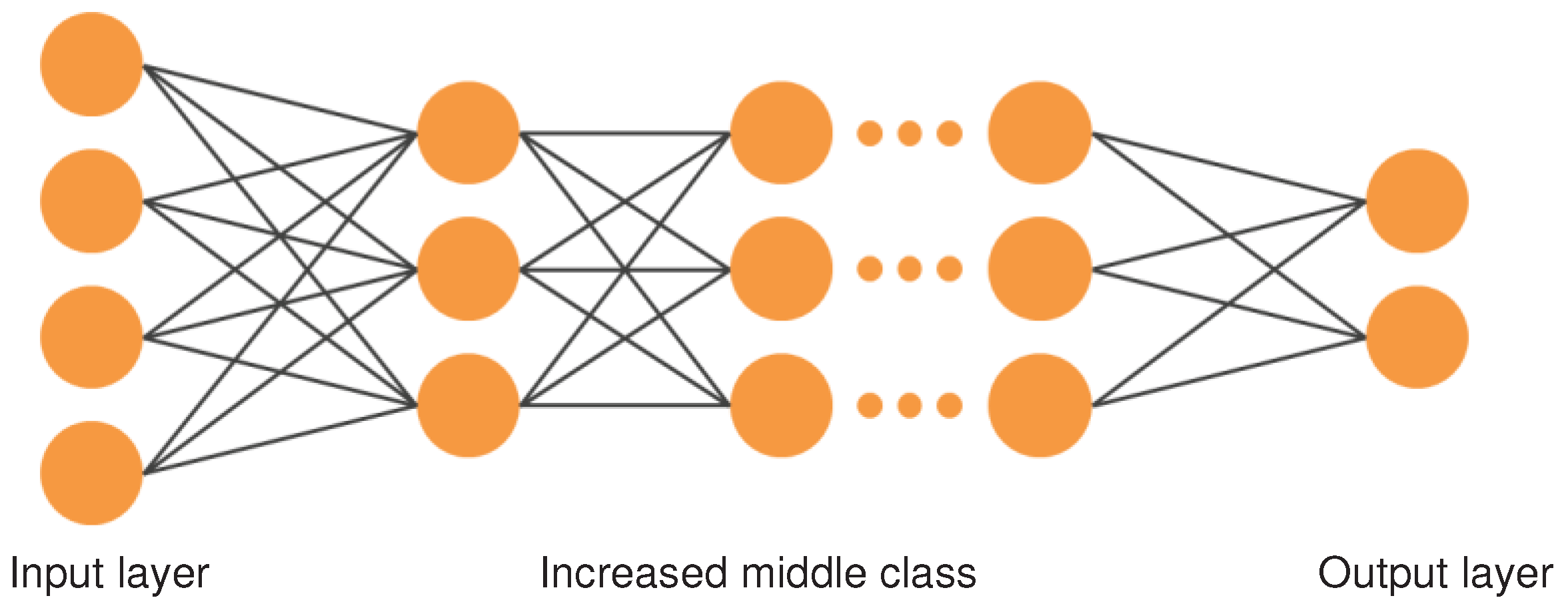
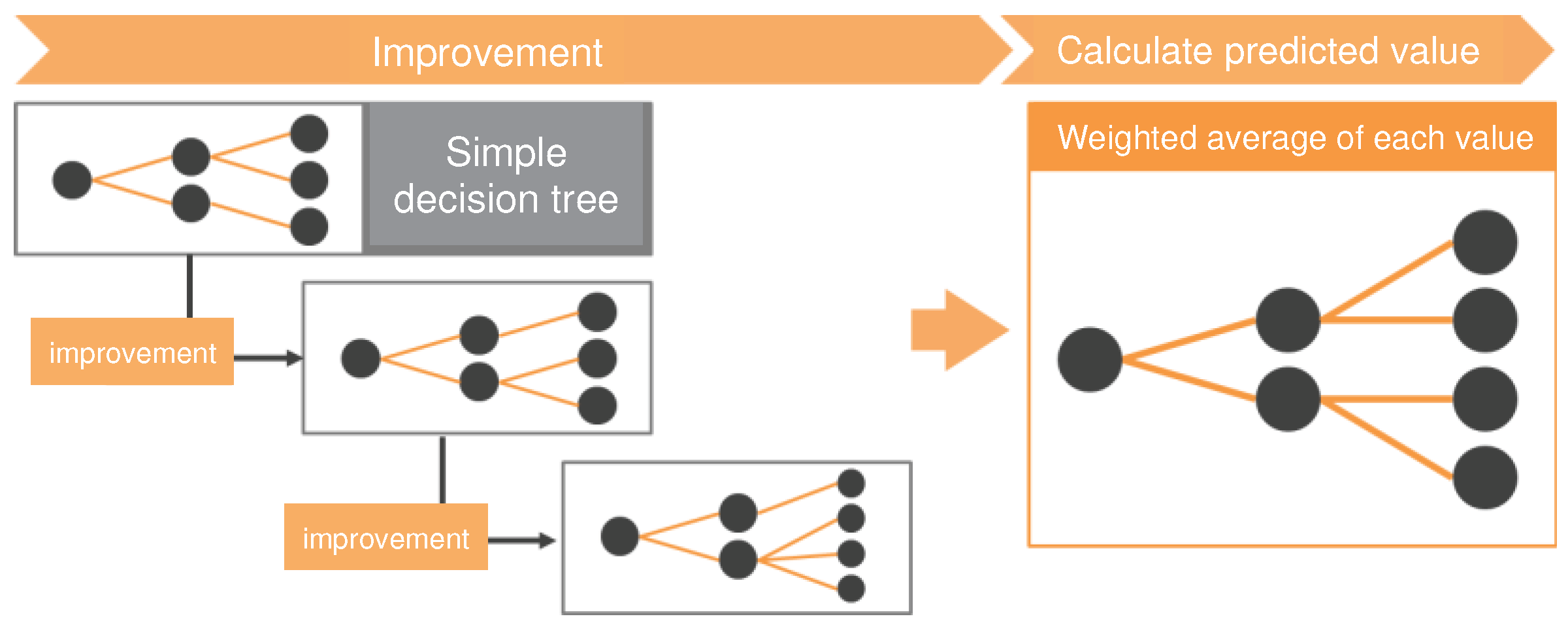
3.1. Ensemble Learning
3.2. Preparation of Dataset
3.2.1. Details of training data
3.2.2. Details of test data
3.3. Distinguishing Explanatory and Target Variables
3.4. Evaluation of Prediction Accuracy
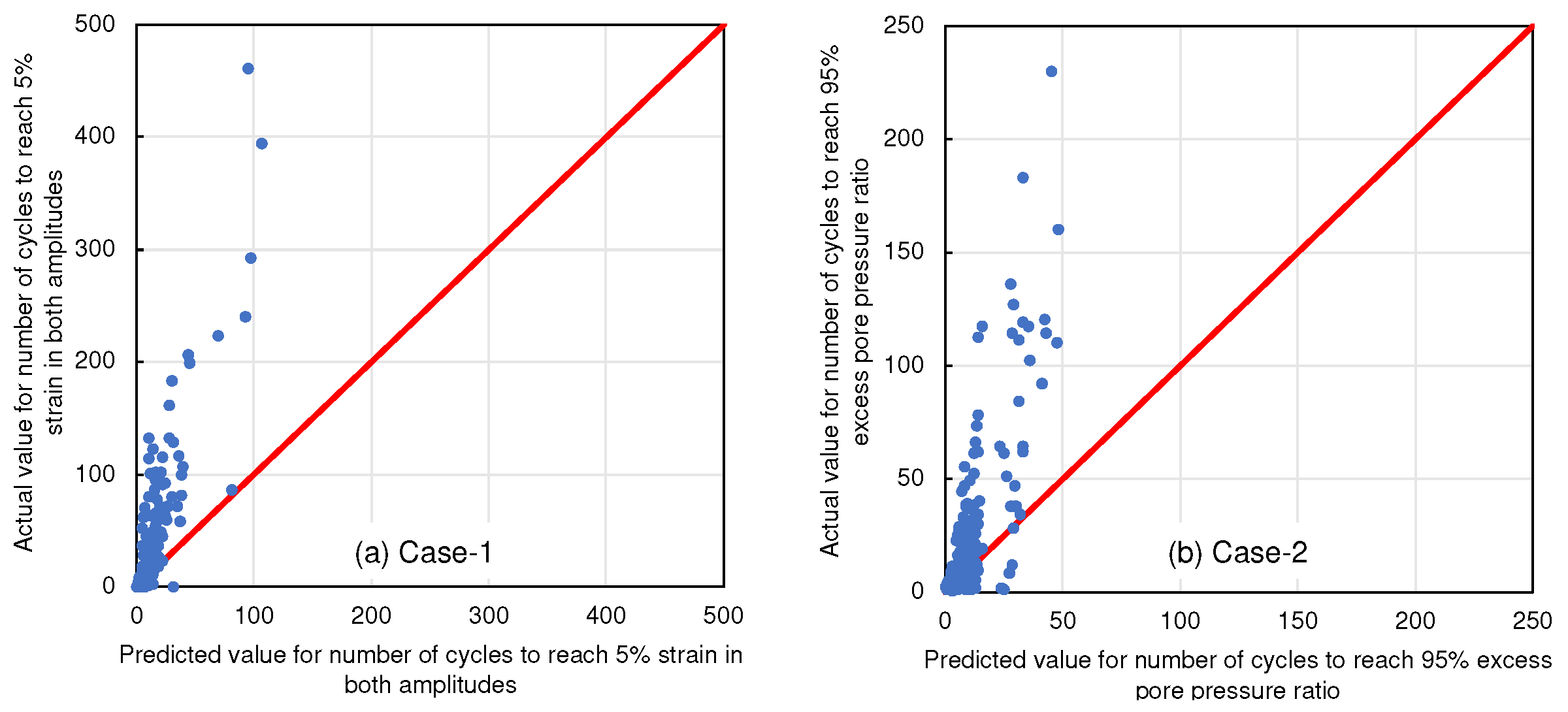
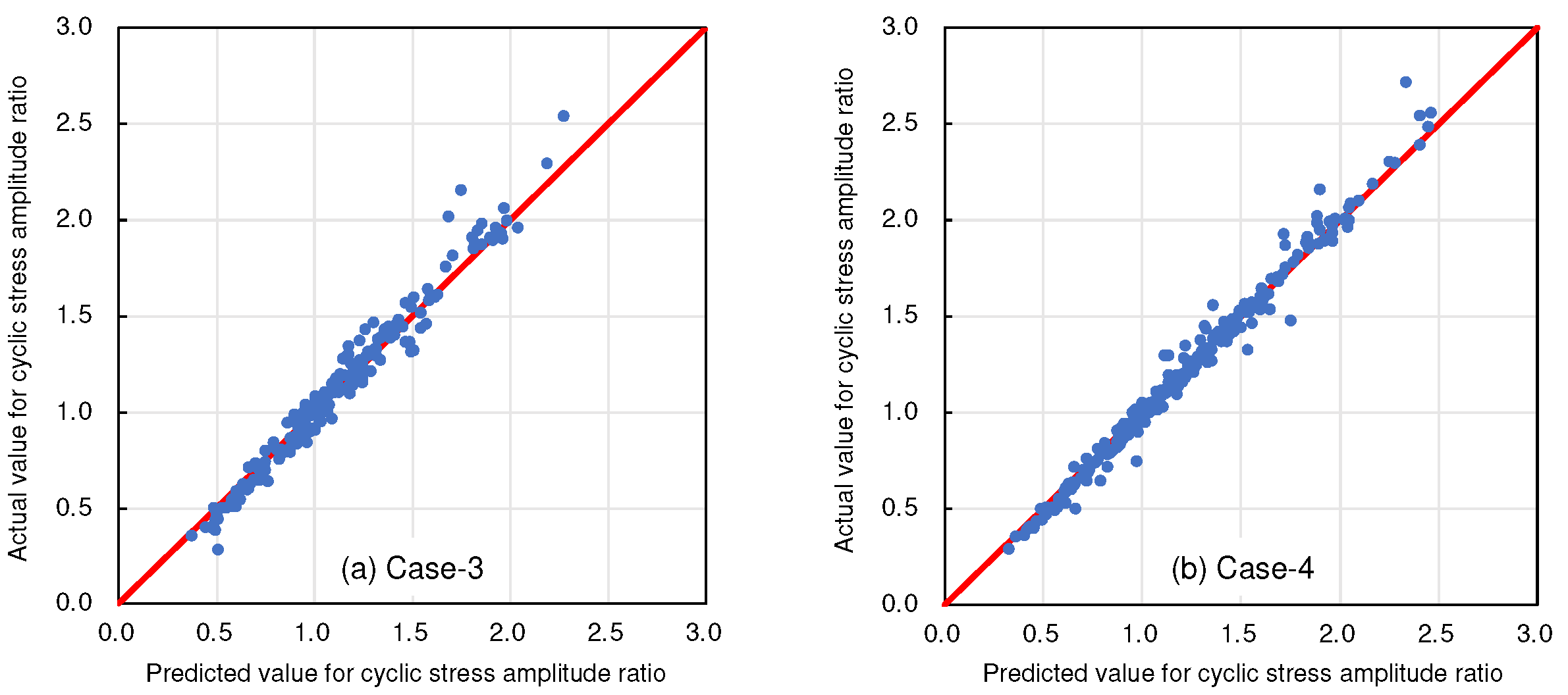
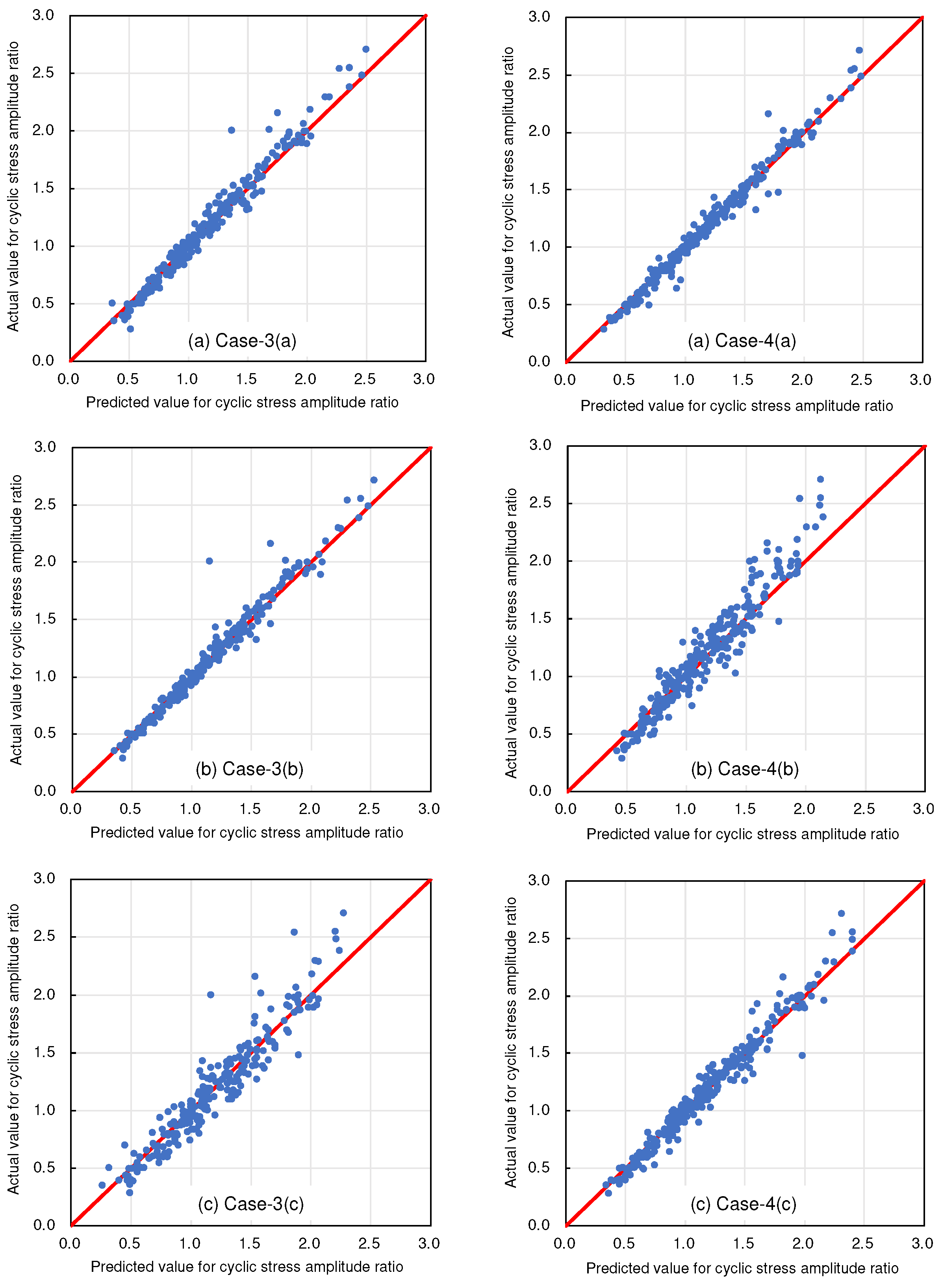
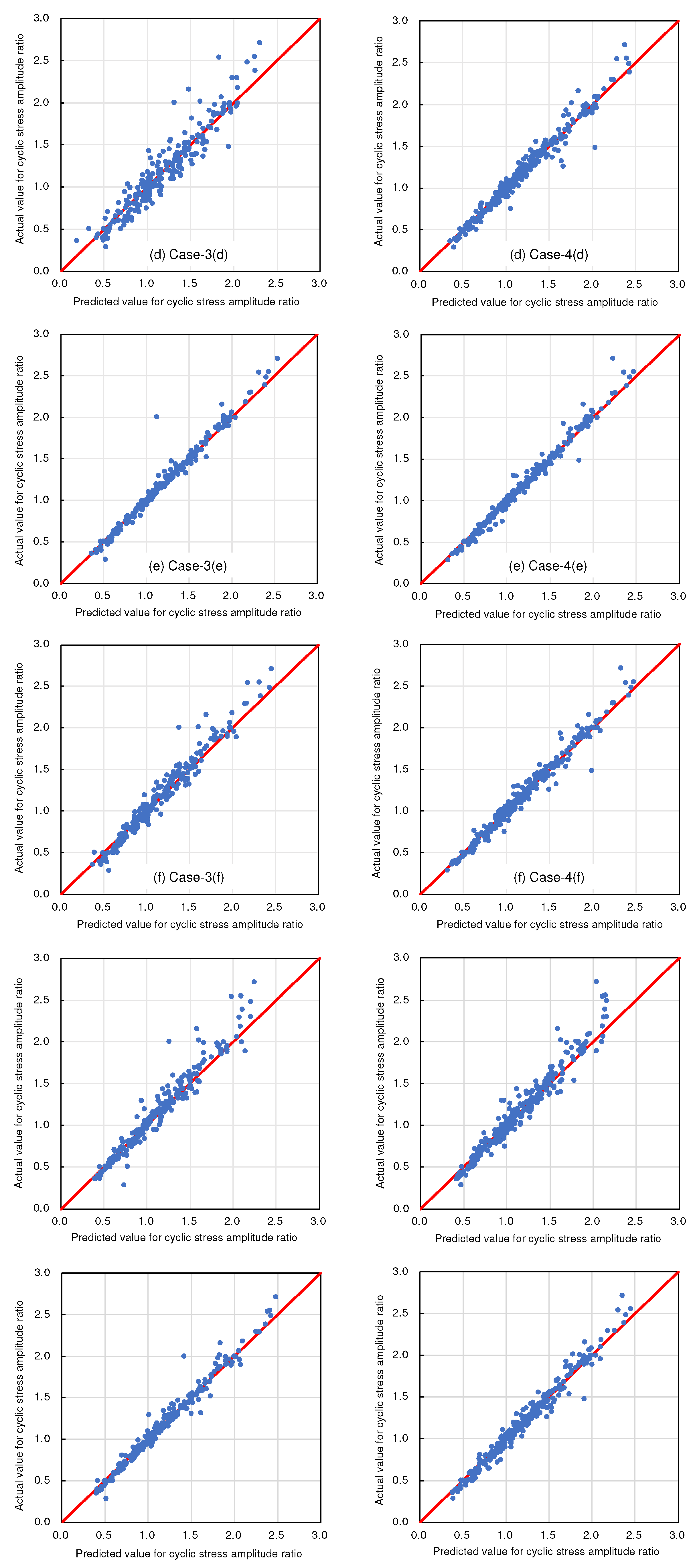
4. Results And Discussion
4.1. Selecting Target Variables
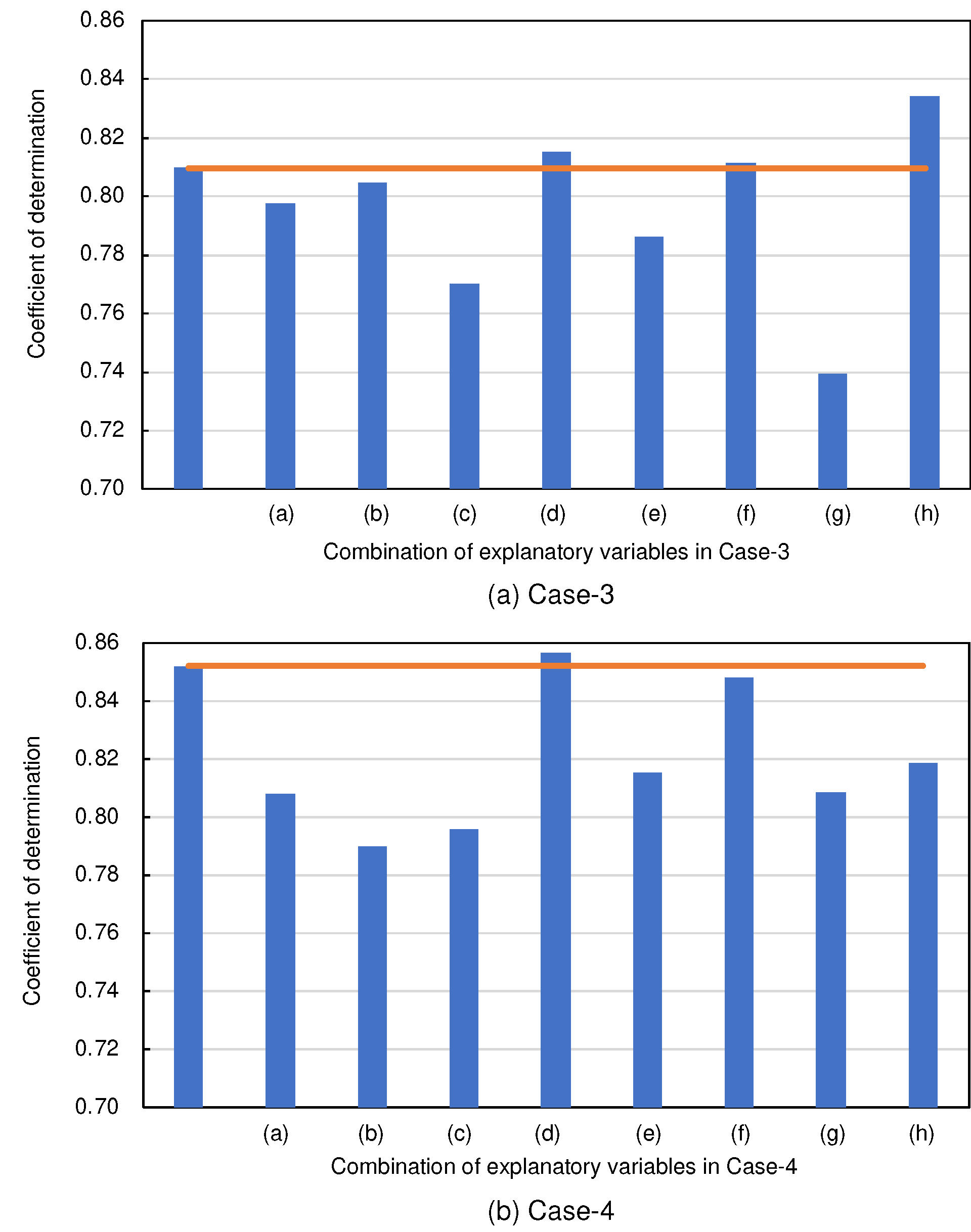
4.2. Selecting Explanatory Variables
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- For the development of a predictive model, it is highly recommended to designate the liquefaction resistance ratio as a dependent variable and the other parameters as explanatory variables. This approach allows a more focused analysis and provides more reliable predictions of the soil behavior under liquefaction conditions.
- (2)
- The exploration of combinations of explanatory variables revealed that using all available variables tends to produce a more stable coefficient of determination (). This stability is critical to the reliability of the model, especially in applications where precision is paramount.
- (3)
- Including the liquefaction resistance ratio in the training data set significantly increases the predictive accuracy of the model. This finding underscores the importance of this particular variable in understanding and predicting the behavior of chemically enhanced sandy soils under stress.
- (4)
- The results of using AI for making predictions highlight the potential of accurately predicting liquefaction resistance using historical data. This approach not only saves time and resources, but also opens new avenues for studies in soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering.
- (5)
- In addition, this study aimed to validate the effectiveness of the solution-type chemical improvement of sandy soils against liquefaction through AI-based analysis of existing data from cyclic undrained triaxial tests. The results of this study confirmed that high-precision predictions are achievable using the explanatory variables listed in Table 1. In particular, excluding uniaxial compressive strength as an explanatory variable resulted in the highest accuracy, followed closely by scenarios using all explanatory variables. This suggests a nuanced relationship between the variables and their predictive power that warrants further investigation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuribayashi, E.; Tatsuoka, F. Brief review of liquefaction during earthquakes in Japan. Soils and Foundations 1975, 15, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yu, M. Review of soil liquefaction characteristics during major earthquakes of the twenty-first century. Natural Hazards 2013, 65, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasheminezhad, A.; Bahadori, H. Three dimensional finite difference simulation of liquefaction phenomenon. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 2019, 15, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, K.; Inazumi, S.; Takahashi, T.; Nontananandh, S. Numerical simulation of the liquefaction phenomenon by MPSM-DEM coupled CAES. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, R.C.; Wang, Y. Lessons learned from recent earthquakes-geoscience and geotechnical perspectives. Advances in Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering-Soil Liquefaction and Seismic Safety of Dams and Monuments. 2012, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazout, L.; Zitouni, Z.E.A.; Belkhatir, M.; Schanz, T. Evaluation of static liquefaction characteristics of saturated loose sand through the mean grain size and extreme grain sizes. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 2017, 35, 2079–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Ye, B.; Ye, G.; Zhang, F. Co-seismic and post-seismic behavior of a wall type breakwater on a natural ground composed of liquefiable layer. Nat Hazards 2016, 83, 1799–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Jin, Z.; Cui, H.; Chen, X.; Xie, X. Soil liquefaction mitigation in geotechnical engineering: An overview of recently developed methods. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering 2019, 120, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, P.M.; Pamuk, A.; Abdoun, T. Stabilization of liquefiable soils using colloidal silica grout. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 2007, 19, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayehvand, S.; Kalantari, B. Use of grouting method to improve soil stability against liquefaction -A review. Electronic Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 2012, 17, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, H.; Ray, A.; Rai, R.; Gupta, T.; Mehta, N. Ground improvement using chemical methods: A review. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.C.; Su, S.W.; Kim, J.M. Method for prevention of liquefaction caused by earthquakes using grouting applicable to existing structures. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motohashi, T.; Sasahara, S.; Inazumi, S. Strength assessment of water-glass sand mixtures. Gels 2023, 9, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimi, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tokimatsu, K. Liquefaction resistance of a partially saturated sand. Soils and Foundations 1989, 29, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, L.; Flora, A. On the prediction of liquefaction resistance of unsaturated sands. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering 2019, 125, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Nong, Z.Z.; Woo, S.W. Liquefaction resistance of Pohang sand. Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering for Protection and Development of Environment and Constructions 2019, 4359–4365. [Google Scholar]
- Khashila, M.; Hussien, M.N.; Karray, M.; Chekired, M. Liquefaction resistance from cyclic simple and triaxial shearing: a comparative study. Acta Geotechnica 2021, 16, 1735–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, B.; Zhang, S. Unique relation between pore water pressure generated at the first loading cycle and liquefaction resistance. Engineering Geology 2022, 296, 106476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyota, H.; Takada, S. Variation of liquefaction strength induced by monotonic and cyclic loading histories. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering 2017, 143, 04016120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Yang, G.; Li, G.; Liu, J. Liquefaction behavior of fiber-reinforced sand based on cyclic triaxial tests. Geosynthetics International 2021, 28, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashila, M.; Hussien, M.N.; Karray, M.; Chekired, M. Liquefaction resistance from cyclic simple and triaxial shearing: a comparative study. Acta Geotechnica 2021, 16, 1735–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, Z.Z.; Park, S.S.; Lee, D.E. Comparison of sand liquefaction in cyclic triaxial and simple shear tests. Soils and Foundations 2021, 61, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, Z.Z.; Park, S.S.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, D.E. Effect of cyclic loading frequency on liquefaction prediction of sand. Applied Sciences 2021, 10, 4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpit, J.; Mittal, S.; Shukla, S.K. Liquefaction proneness of stratified sand-silt layers based on cyclic triaxial tests. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 2023, 15, 1826–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo, M.; Yasuhara, K.; Hirao, K. Prediction of clay behaviour in undrained and partially drained cyclic triaxial tests. Soils and Foundations 1992, 32, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Wang, J.; Cai, Y.; Yang, Z.; Gao, Y. Undrained cyclic triaxial behavior of saturated clays under variable confining pressure. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering 2012, 40, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayoomi, M.; Suprunenko, G.; Mirshekari, M. Cyclic triaxial test to measure strain-dependent shear modulus of unsaturated sand. International Journal of Geomechanics 2017, 17, 04017043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yu, Z.; Cao, W.; Shi, Y.; Ma, Q. A survey on ensemble learning. Frontiers of Computer Science 2020, 14, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chongzhi, W.; Lin, W.; Zhang, W. Assessment of undrained shear strength using ensemble learning based on Bayesian hyperparameter optimization. Modeling in Geotechnical Engineering 2021, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Hu, Y.; Guo, X.; He, X.; Kek, H.Y.; Ku, T.; Goh, S.H.; Leung, C.F. Predicting geological interfaces using stacking ensemble learning with multi-scale features. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 2023, 60, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M.A. Artificial intelligence in geotechnical engineering: applications, modeling aspects, and future directions. Metaheuristics in Water, Geotechnical and Transport Engineering 2013, 169–204. [Google Scholar]
- Jong, S.C.; Ong, D.E.L.; Oh, E. State-of-the-art review of geotechnical-driven artificial intelligence techniques in underground soil-structure interaction. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 2021, 113, 103946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghbani, A.; Choudhury, T.; Costa, S.; Reiner, J. Application of artificial intelligence in geotechnical engineering: A state-of-the-art review. Earth-Science Reviews 2022, 228, 103991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Ahmed, S.; Naseem, M.; Alnumay, W.S.; Singh, S.; Cho, G.H. A survey on applications of artificial intelligence for pre-parametric project cost and soil shear-strength estimation in construction and geotechnical engineering. Sensors 2021, 21, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wen, Z. Recent developments of soil improvement methods for seismic liquefaction mitigation. Natural Hazards 2015, 76, 1927–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, L.; Flora, A. On the prediction of liquefaction resistance of unsaturated sands. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering 2019, 125, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, A.K.F.; Rahman, M.Z.; Hossain, M.S.; Kamal, A.M. Liquefaction resistance evaluation of soils using artificial neural network for Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Natural Hazards 2022, 113, 933–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsiantis, S.B.; Zaharakis, I.D.; Pintelas, P.E. Machine learning: a review of classification and combining techniques. Artificial Intelligence Review 2006, 26, 159–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pólvora, A.; Nascimento, S.; Lourenço, J.S.; Scapolo, F. Blockchain for industrial transformations: A forward-looking approach with multi-stakeholder engagement for policy advice. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2020, 157, 120091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, M.P.; Hartleb, R.; Wolf, L.; Mayne, P.W. Paleoliquefaction studies and the evaluation of seismic hazard. Geosciences 2019, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, R.; Cubrinovski, M. Geotechnical characterization and liquefaction evaluation of gravelly reclamations and hydraulic fills (Port of Wellington, New Zealand). Soils and Foundations 2020, 60, 1507–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Taiebat, M.; Radjaï, F. Liquefaction of granular materials in constant-volume cyclic shearing: Transition between solid-like and fluid-like states. Computers and Geotechnics 2022, 148, 104800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.K. Mitigation of liquefaction potential of silty sands. From Research to Practice in Geotechnical Engineering 2008, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, S.L. and Mitchell, R. A. Ground motion intensity measures for liquefaction hazard evaluation. Earthquake Spectra 2006, 22, 413–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H. Ensemble Methods: Foundations and Algorithms (Chapman & Hall/CRC Machine Learning & Pattern Recognition). CRC Press 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gurney, K. An Introduction to Neural Networks 1st Edition. CRC Press 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Chow, T.L.; Rees, H.W.; Yang, Q.; Xing, Z. and Meng, F. R. Predict soil texture distributions using an artificial neural network model. Computers and electronics in agriculture 2009, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Guo, X.; Xu, Z.; Ding, M. Soil properties: Their prediction and feature extraction from the LUCAS spectral library using deep convolutional neural networks. Geoderma 2021, 402, 115366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.; Nguyen, M.D.; Ly, H.B.; Pham, T.A.; Hoang, V.; Le, V.H.; Le, T.T.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Bui, G.L. Development of artificial neural networks for prediction of compression coefficient of soft soil. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Geotechnics, Civil Engineering Works and Structures; 2020; pp. 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.; Elhegazy, H.; Elzarka, H.; Gutierrez, L. A novel construction cost prediction model using hybrid natural and light gradient boosting. Advanced Engineering Informatics 2020, 46, 101201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Vo, T.P.; Thai, H.T.; Lee, J.; Patel, V. Strength prediction of concrete-filled steel tubular columns using Categorical Gradient Boosting algorithm. Engineering Structures 2021, 238, 112109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Fu, D. and Sollazzo, G. An ensemble learning model for asphalt pavement performance prediction based on gradient boosting decision tree. International Journal of Pavement Engineering 2022, 23, 3633–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Johnson, P.C.D.; Schielzeth, H. The coefficient of determination R2 and intra-class correlation coefficient from generalized linear mixed-effects models revisited and expanded. Journal of the Royal Society Interface 2017, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Variable elements |
|---|---|
| Condition parameters for specimens of chemically improved sandy soils | Dry density (g/cm3) |
| Fine particle content (%) | |
| Effective confining pressure (kN/m2) | |
| Unconfined compressive strength (kN/m2) | |
| Silica gel concentration of injected chemical solution (%) | |
| Increase in silica content (mg/g) | |
| Results obtained by cyclic undrained triaxial test | Number of cycles to reach 5% strain in both amplitudes |
| Number of cycles to reach 95% excess pore pressure ratio | |
| Cyclic stress amplitude ratio | |
| Liquefaction resistance ratio* | |
| *It refers to the cyclic amplitude stress ratio when the axial strain amplitude reaches 5% or the excess pore water pressure ratio reaches 95% and the number of cyclic loads is 20. | |
| Case | Explanatory variables | Target variables |
|---|---|---|
| Case-1 | Variable elements shown in Table 1 excluding the liquefaction resistance ratio and the target variable | Number of cycles to reach 5% strain in both amplitudes |
| Case-2 | Variable elements shown in Table 1 excluding the liquefaction resistance ratio and the target variable | Number of cycles to reach 95% excess pore pressure ratio |
| Case-3 | Variable elements shown in Table 1 excluding the liquefaction resistance ratio and the target variable | Cyclic stress amplitude ratio |
| Case-4 | Variable elements shown in Table 1 excluding the target variable | Cyclic stress amplitude ratio |
| Variable | Variable elements | Data for 2 of 272 specimens | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Explanatory variables | Dry density (g/cm3) | 1.684 | 1.484 |
| Effective confining pressure (kN/m2) | 90 | 165 | |
| Fine particle content (%) | 14.8 | 11.4 | |
| Unconfined compressive strength (kN/m2) | 539 | 483 | |
| Silica gel concentration of injected chemical solution (%) | 12 | 12 | |
| Increase in silica content (mg/g) | 11.62 | 7.79 | |
| Number of cycles to reach 5% strain in both amplitudes | 18 | 6.5 | |
| Number of cycles to reach 95% excess pore pressure ratio | 37 | 38.4 | |
| Target variable | Repetitive stress amplitude ratio | ||
| Case-3 and Case-4 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explanatory variables | (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | (e) | (f) | (g) | (h) | |
| Dry density (g/cm3) | x | ||||||||
| Effective confining pressure (kN/m2) | x | ||||||||
| Fine particle content (%) | x | ||||||||
| Unconfined compressive strength (kN/m2) | x | ||||||||
| Silica gel concentration of injected chemical solution (%) | x | ||||||||
| Increase in silica content (mg/g) | x | ||||||||
| Number of cycles to reach 5% strain in both amplitudes | x | ||||||||
| Number of cycles to reach 95% excess pore pressure ratio | x | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





