Submitted:
25 January 2024
Posted:
26 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
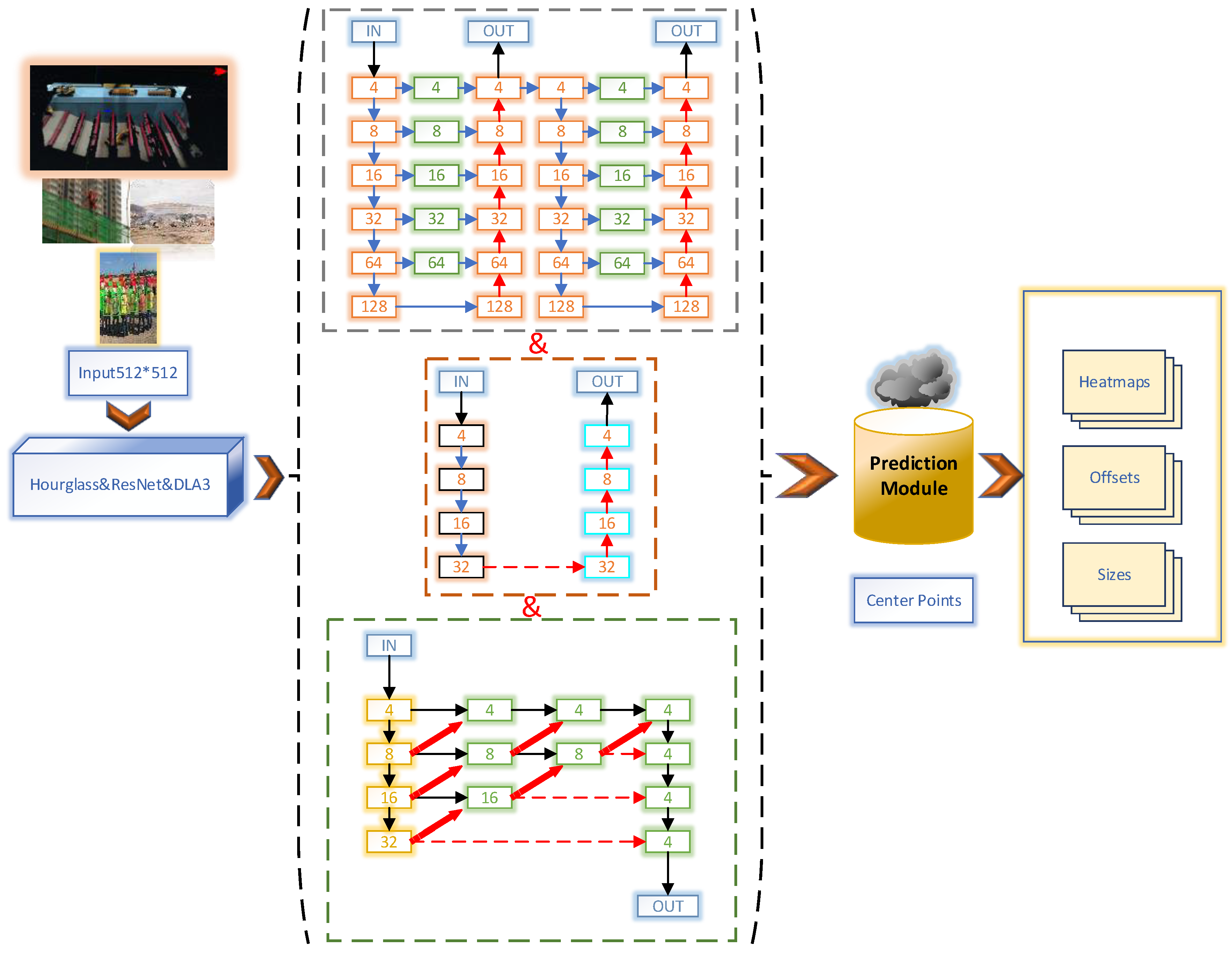
2. CenterNet
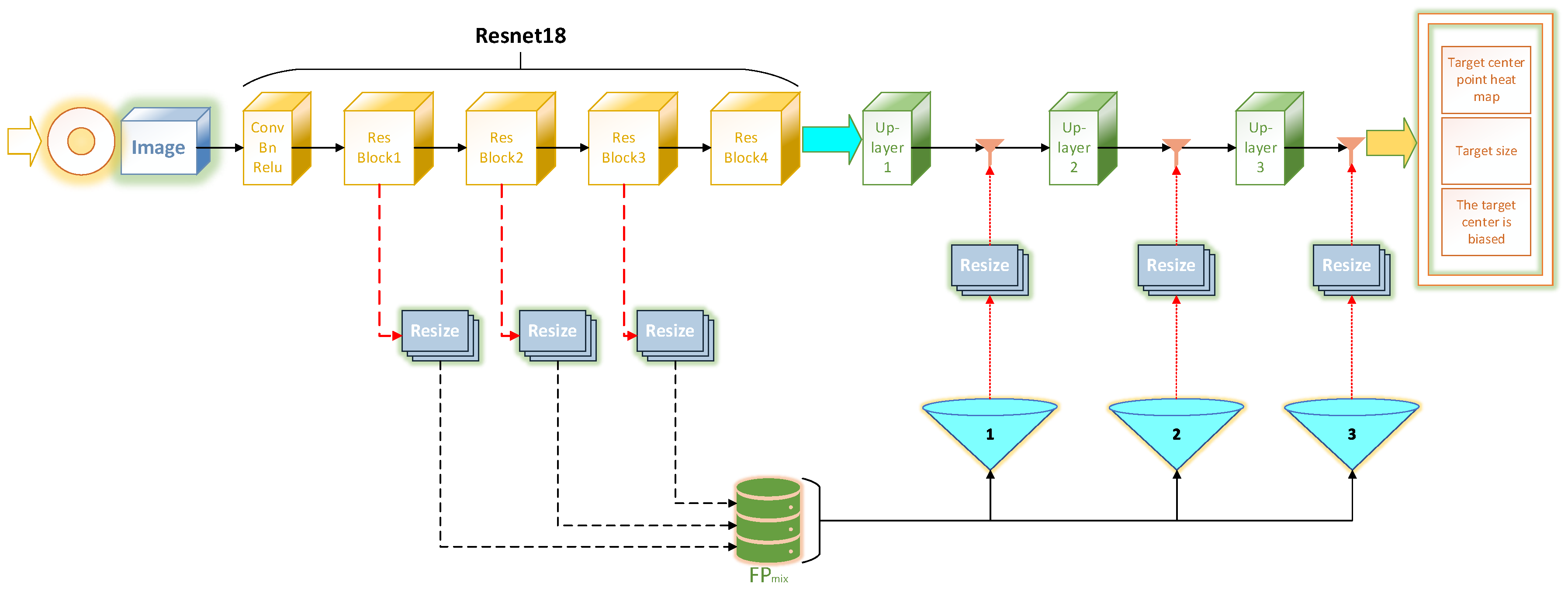
3. CenterNet Optimisation
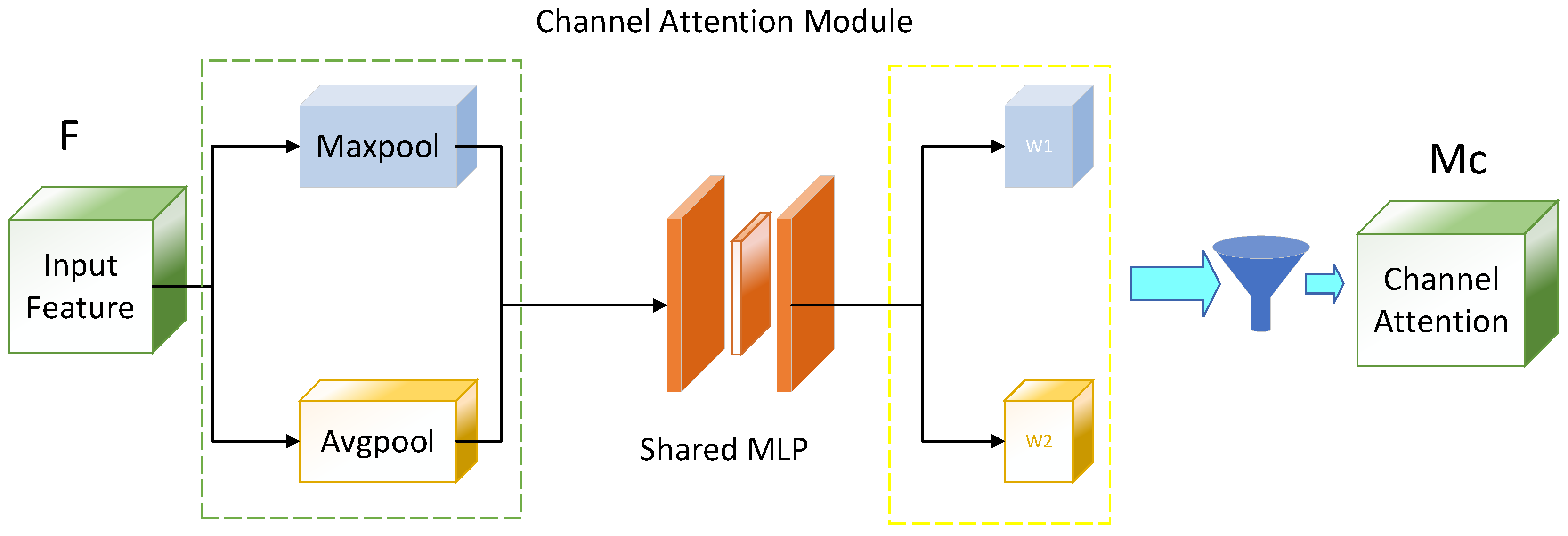
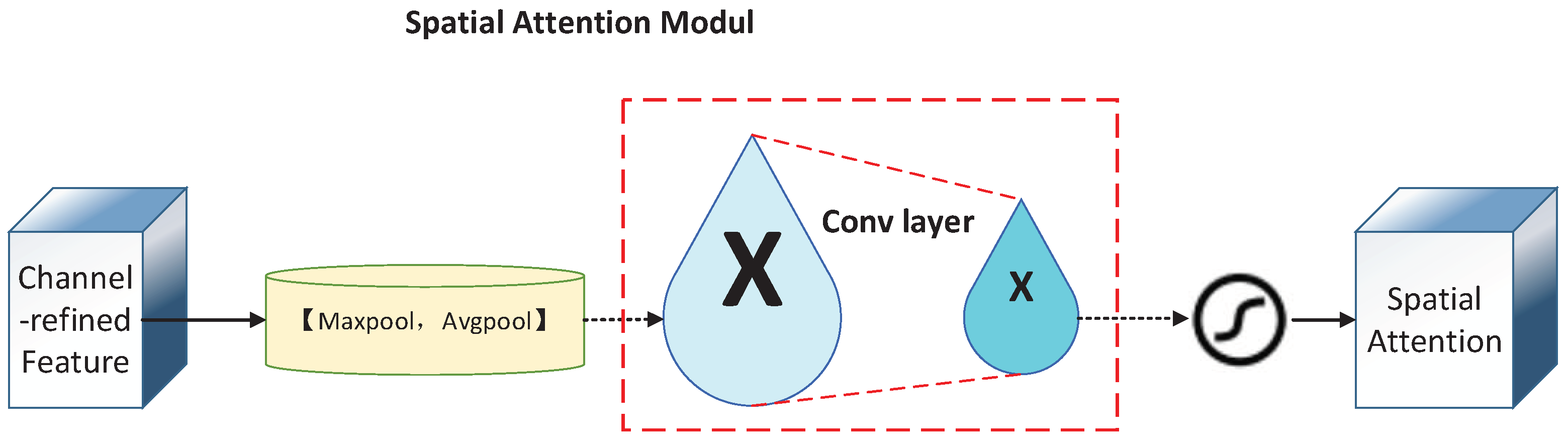
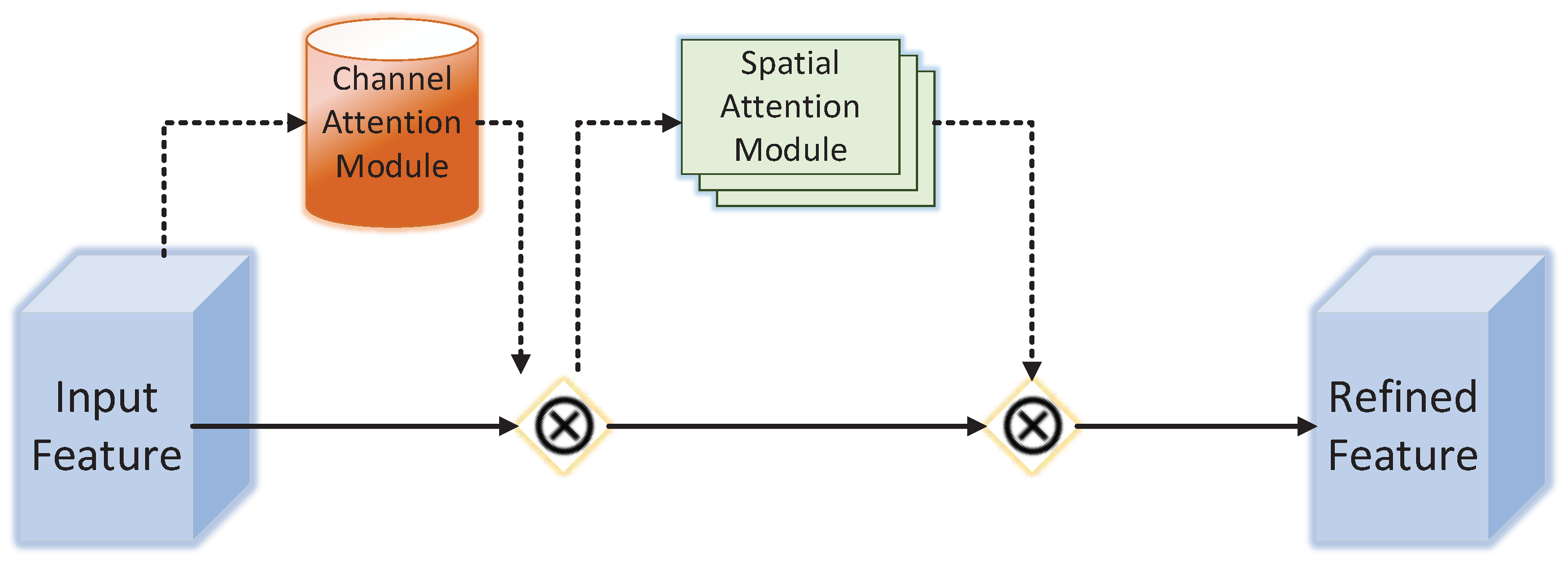
3.1. Addition of Channel Space Attention Mechanism
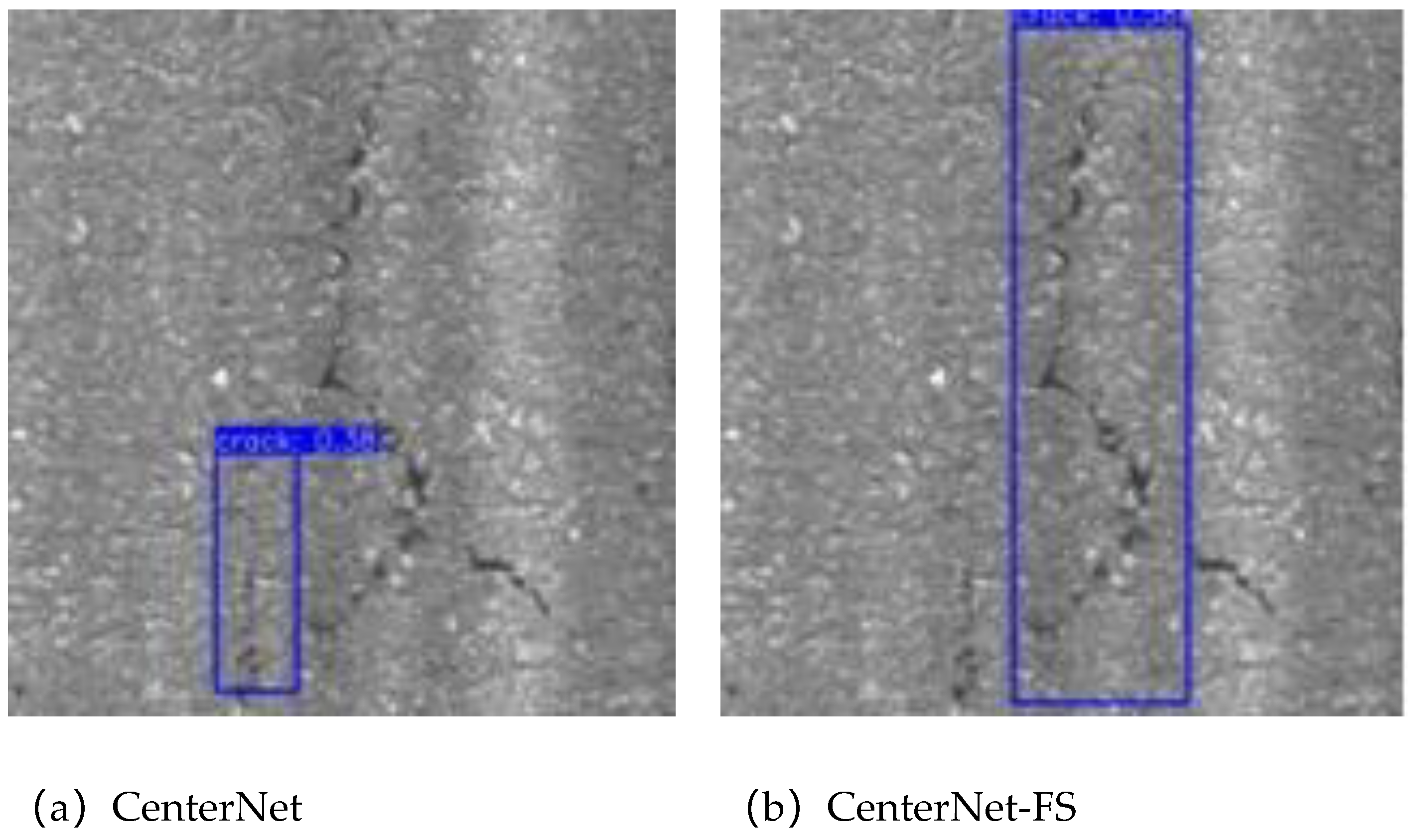
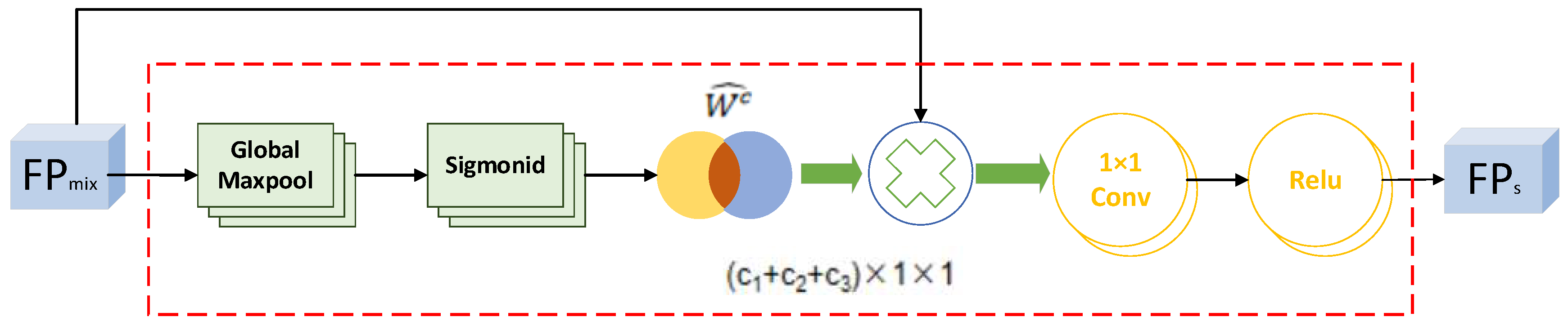
3.2. Addition of Feature Selection Module
3.3. Optimization of the Loss Function
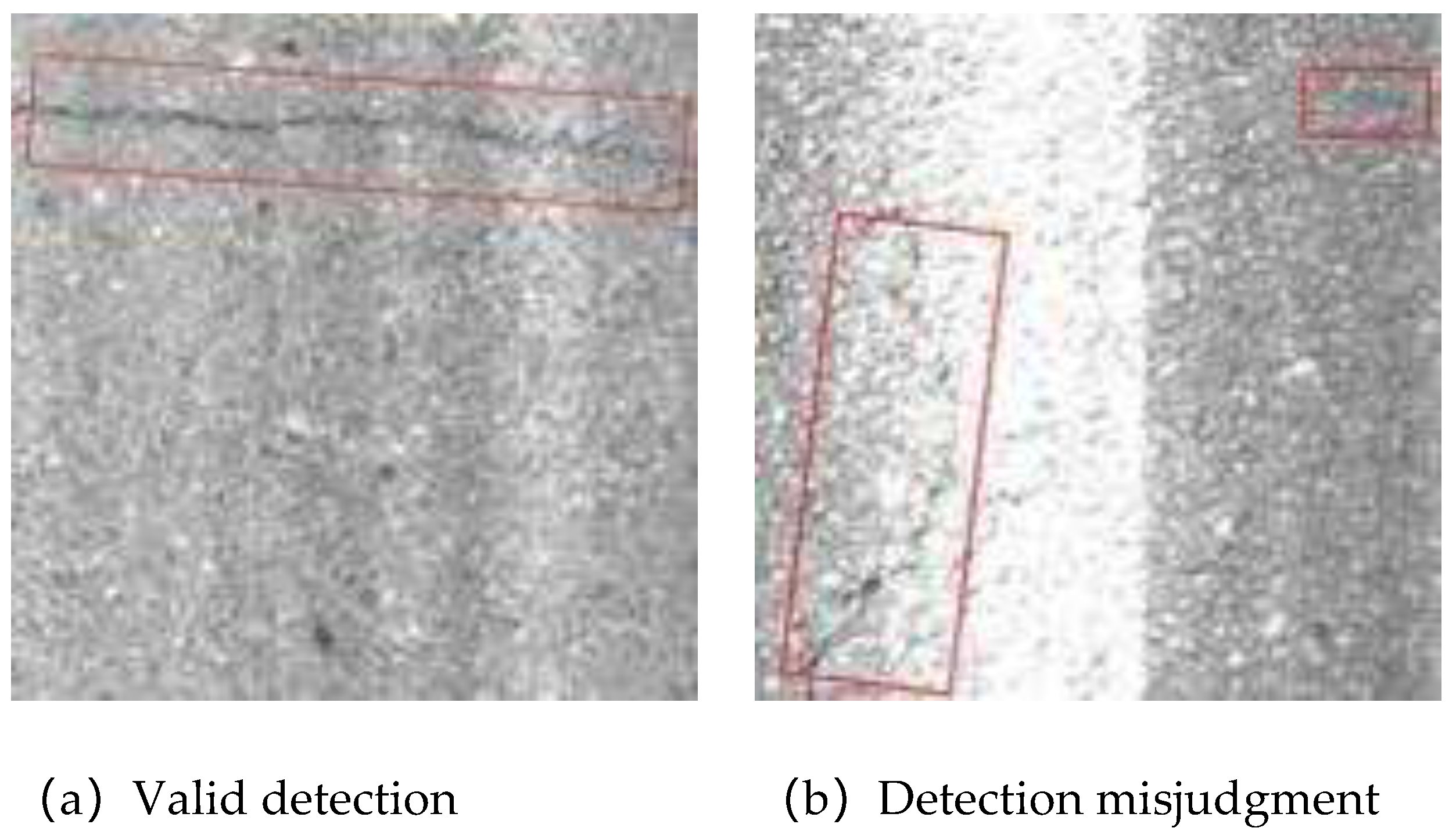
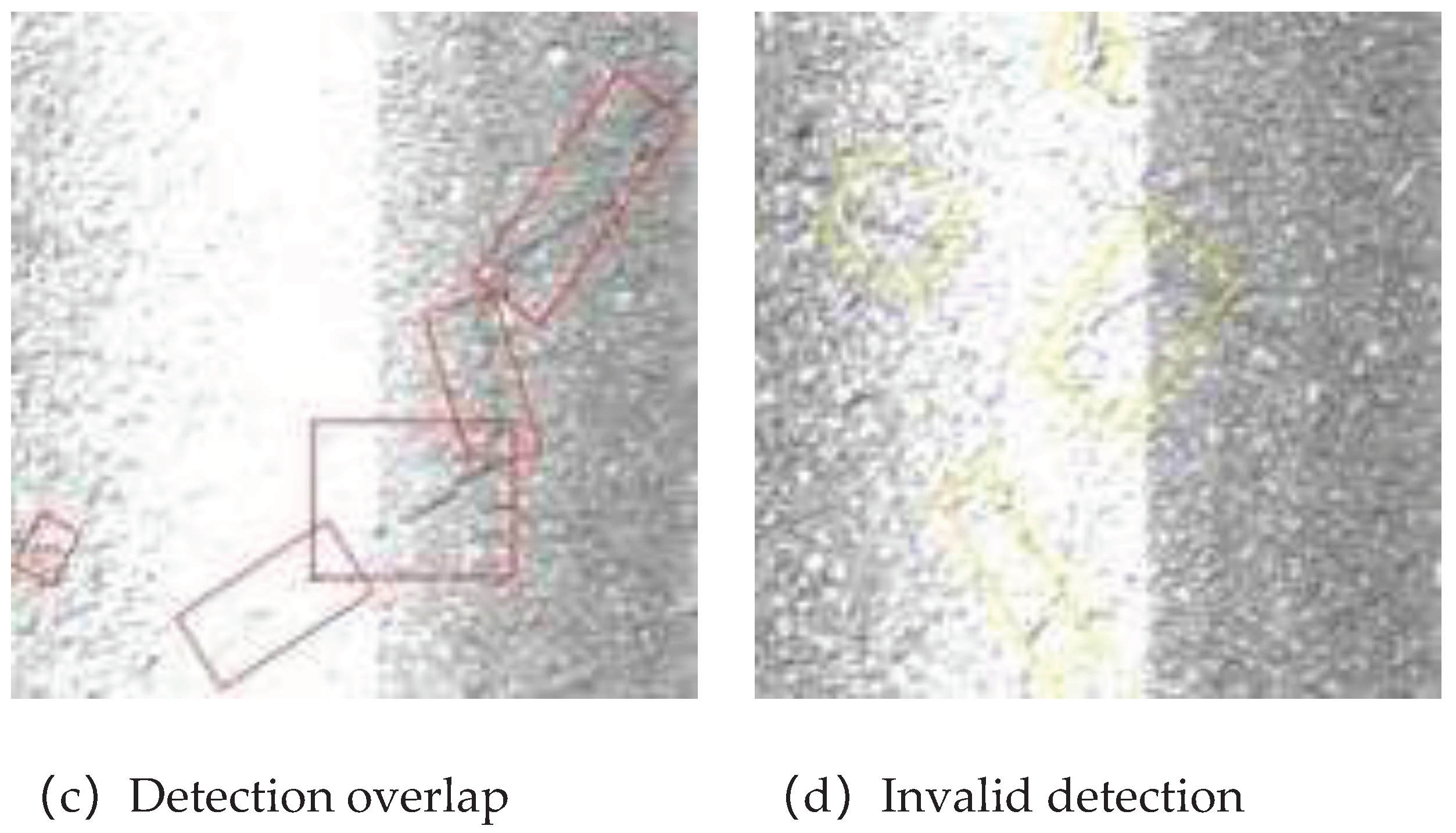
4. Experiment and Result Analysis
4.1. Experimental Environment
4.2. Evaluation Index
| Index | Implication |
|---|---|
| FLOPs | The number of floating-point operations used to measure the computational complexity of the model |
| FPS | The number of images the algorithm processes per second, the higher the value, the faster the algorithm processes |
| p | The size of the video memory occupied by the algorithm in the inference stage. The smaller the video memory occupation, the less resources are required |
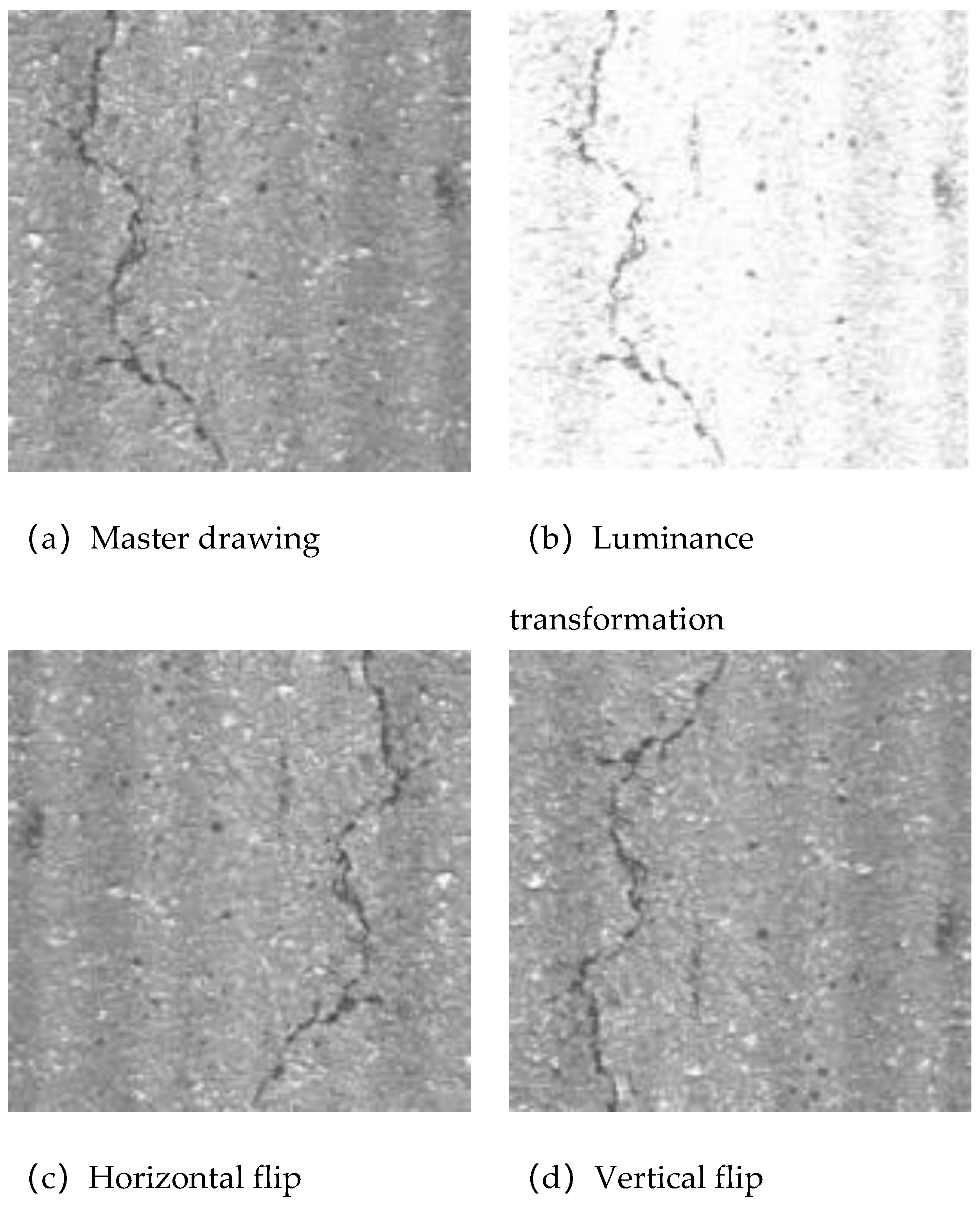
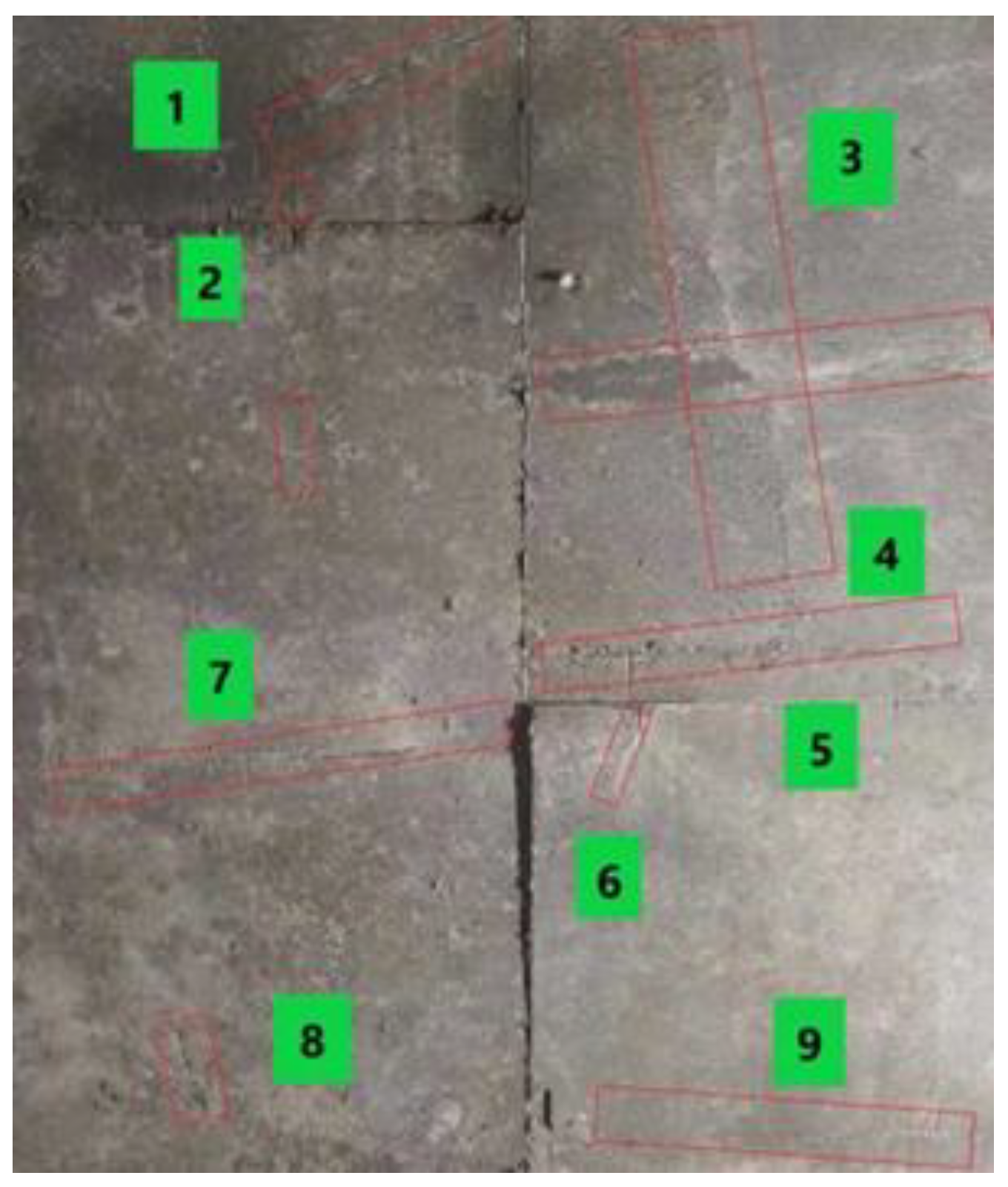
4.3. Data
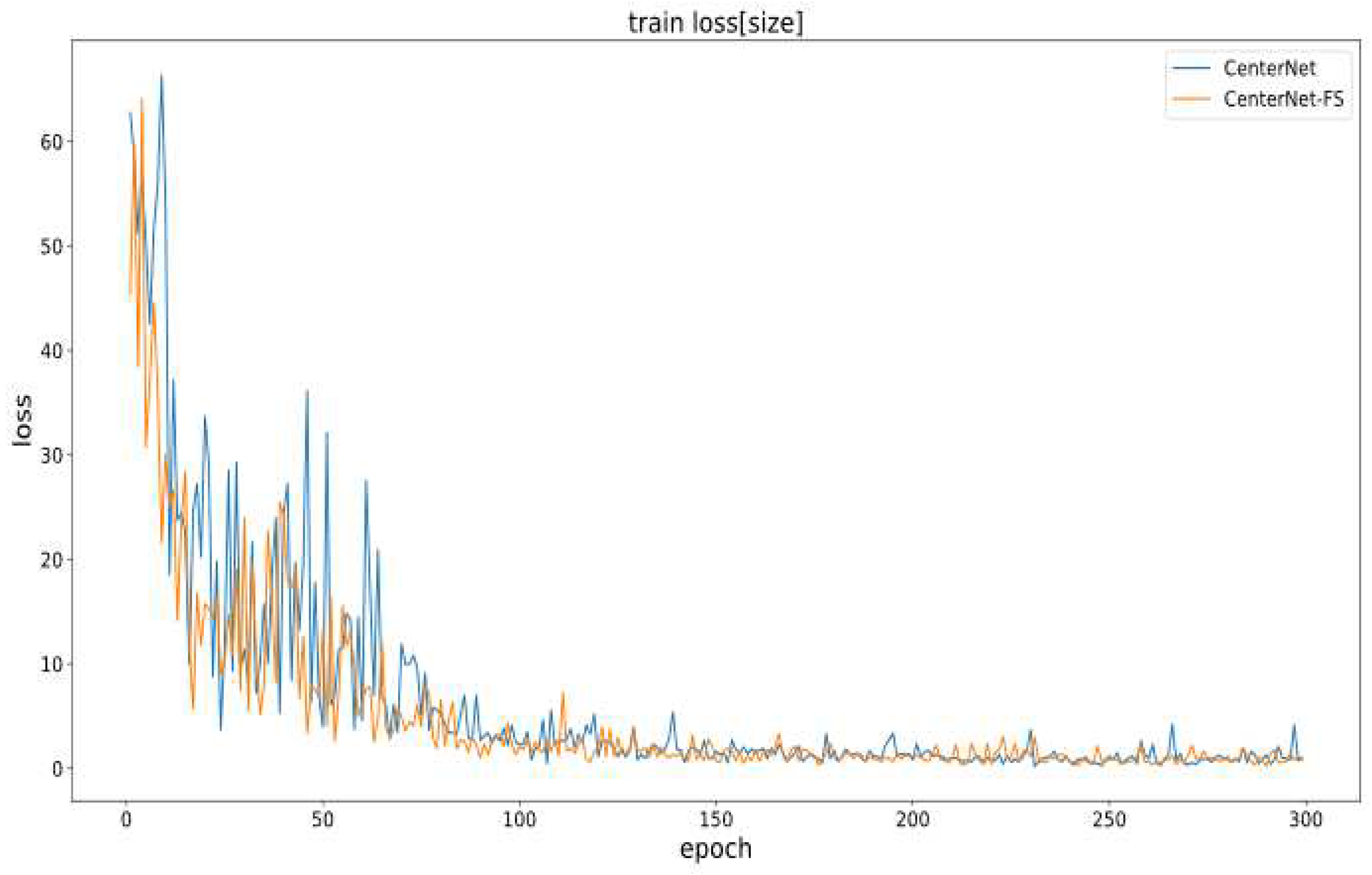
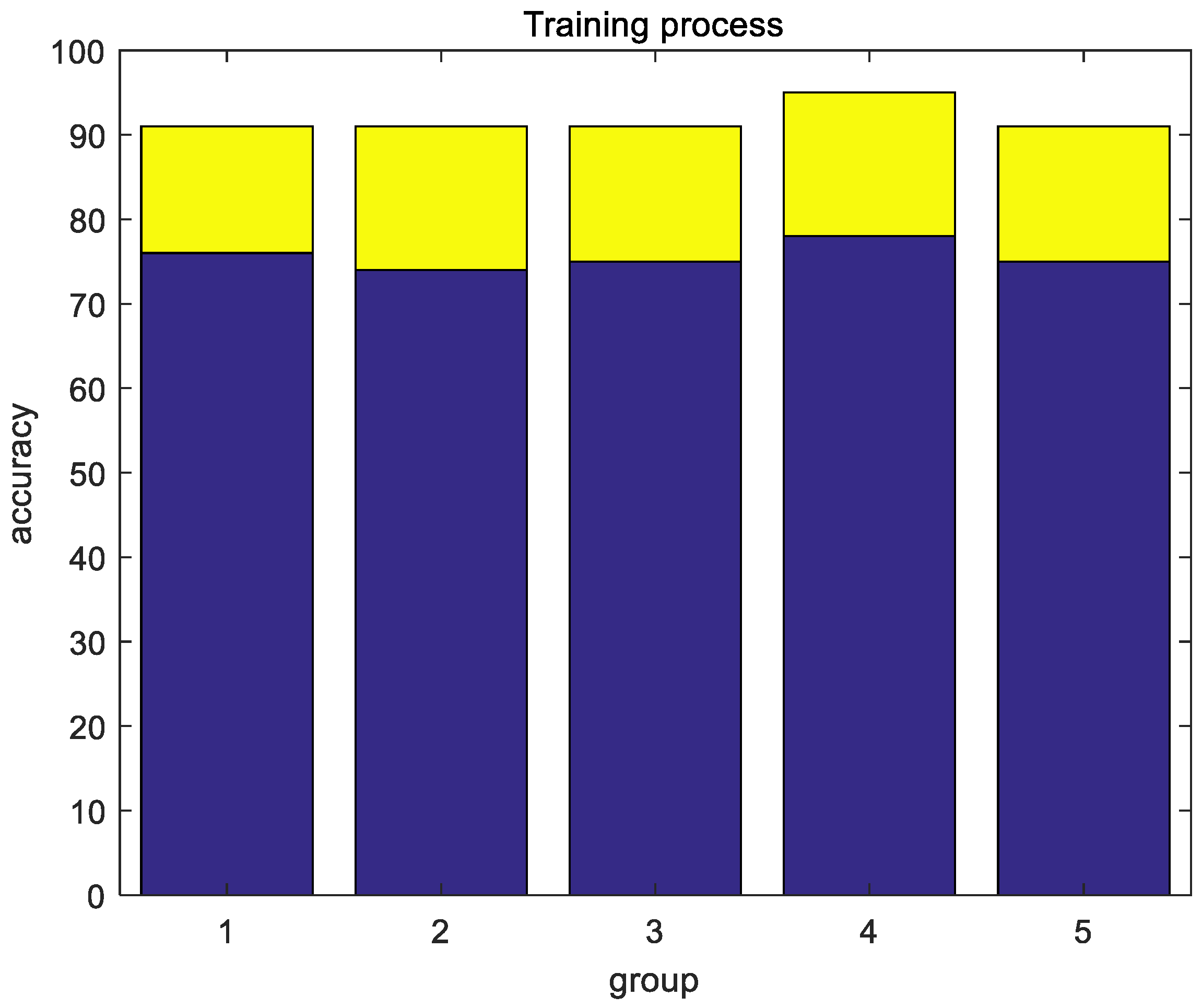
4.4. Training Process and Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ling, Y. Crack Detection and Recognition Based on DeepLearning. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou Jiaotong University: Gansu, China, Gansu.
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y. Research on Concrete Surface Crack Detection Based on SqueezeNet. J. Dalian Minzu Univ. 2021, 23, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, X. Micro-crack quantitative detection technique for metal component surface based on laser ultrasonic. J. Vib. Shock 2019, 38, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Hou, Q.; Yu, J. Contrast analysis of testing methods for tiny crack in parts of weapon. Ordnance Mater. Sci. Eng. 2005, 28, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Long, J.; Liu, C.; Pan, S.; Zuo, C.; Cai, P. Review of the development and application of deformation measurement based on digital holography and digital speckle interferometry. Infrared Laser Eng. 2019, 48, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J. Application of Penetration testing in Nondestructive testing of pressure vessels and Pipelines. China CIO News 2023, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yu, S.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Y. Application of Nondestructive Testing Technology in Detecting Crack of Special Vehicle. Comput. Meas. Control 2011, 19, 2676–2678. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. Research on Aircraft Panel Crack Measurement System Based on Machine Vision. Master’s thesis, Xi’an Engineering University: Shaanxi, China, 2020.
- Mohammadkhorasani, A.; Malek, K.; Mojidra, R.; Li, J.; Bennett, C.; Collins, W.; Moreu, F. Augmented Reality-Computer Vision Combination for Automatic Fatigue Crack Detection and Localization. Comput. Ind. 2023, 149, 103936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramanandham, N.; Rajendiran, K.; Poovathy J, F.G.; Premanand, Y.S.; Mallichetty, S.R.; Kumar, P. Pixel Intensity Resemblance Measurement and Deep Learning Based Computer Vision Model for Crack Detection and Analysis. Sensors 2023, 23, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Peng, G.; Xie, H. Strip steel defect detection based on morphological enhancement and image fusion. Laser Infrared 2018, 48, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambon, S.; Moliard, J.-M. Automatic Road Pavement Assessment with Image Processing: Review and Comparison. Int. J. Geophys. 2011, 2011, e989354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Huang, H.; Xue, Y. Development and Application of Machine Vision Inspection system for cracks in Tunnel lining. Highway 2022, 67, 439–446. [Google Scholar]
- Soukup, D.; Huber-Mörk, R. Convolutional Neural Networks for Steel Surface Defect Detection from Photometric Stereo Images. In Advances in Visual Computing; Bebis, G., Boyle, R., Parvin, B., Koracin, D., McMahan, R., Jerald, J., Zhang, H., Drucker, S.M., Kambhamettu, C., El Choubassi, M., Deng, Z., Carlson, M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2014; Vol. 8887, pp. 668–677; ISBN 978-3-319-14248-7. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Chao, W.; Shuangmiao, L.; Baocai, F. Research on Crack Detection Method of Airport Runway Based on Twice-Threshold Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 Fifth International Conference on Instrumentation and Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control (IMCCC); September 2015; pp. 1716–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.-S.; Yang, C.-M.; Huang, C.-W. Thin Crack Observation in a Reinforced Concrete Bridge Pier Test Using Image Processing and Analysis. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2015, 83, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Fernandez, A.; Rodriguez-Lozano, F.J.; Villatoro, R.; Olivares, J.; Palomares, J.M. Efficient Pavement Crack Detection and Classification. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, S.; Ju, Y. Image-Based Method for Concrete Bridge Crack Detection. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2013, 10, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F. Deep Learning Based Animal Detection and Multipleobject Tracking in Modern Livestock Farms. Master’s thesis, Beijing University of posts and Telecommunications: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Wang, Z.; Ye, X.; Han, Y.; Guo, S.; Yan, X.; Wang, S. Improved Real-Time Target Detection Algorithm for Similar Multiple Targets in Complex Underwater Environment Based on YOLOv3. In Proceedings of the Global Oceans 2020: Singapore – U.S. Gulf Coast; October 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, H. Detection of Remote Sensing Targets with Angles via Modified CenterNet. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 100, 107979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Ruan, G. An Algorithm for Target Detection of Engineering Vehicles Based on Improved CenterNet. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, R. Small Object Detection of Improved Lightweight CenterNet. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2023, 59, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, J. Research on Detection Algorithm of Wheel Position Based on CenterNet. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1802, 032126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, J.; Zhao, D.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Quan, X.; Li, X.; Xue, F.; Zhou, M.; Bai, B. LFSCA-UNet: liver fibrosis region segmentation network based on spatial and channel attention mechanisms. J. Image Graph. 2021, 26, 2121–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y. Detection of Solar Panel Defects Based on Separable Convolution and Convolutional Block Attention Module. Energy Sources Part Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 7136–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, M. Convolutional Neural Network with Convolutional Block Attention Module for Finger Vein Recognition Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2022. (submitted).
- Chakraborty, S.K.; A., S.; Dubey, K.; Jat, D.; Chandel, N.S.; Potdar, R.; Rao, N.R.N.V.G.; Kumar, D. Development of an Optimally Designed Real-Time Automatic Citrus Fruit Grading–Sorting Machine Leveraging Computer Vision-Based Adaptive Deep Learning Model. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 120, 105826. [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, C. Learning Global Image Representation with Generalized-Mean Pooling and Smoothed Average Precision for Large-Scale CBIR. IET Image Process. 2023, 17, 2748–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Network | FLOPs | Memory footprint/MB | FPS | Video memory/MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CenterNet | 13.06 | 50.3 | 296.5 | 1347 |
| CenterNet-CBAM | 13.06 | 51.7 | 189.9 | 1349 |
| CenterNet-FS | 16.35 | 51.1 | 250.2 | 1405 |
| Serial number | CenterNet | CBAM | FS | Iou | Memory footprint/MB | FPS | Video memory/MB | FLOPs | AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | √ | × | × | × | 50.3 | 296.5 | 1347 | 13.06 | 0.751 |
| 2 | √ | √ | × | × | 51.7 | 189.9 | 1349 | 13.06 | 0.823 |
| 3 | √ | × | √ | × | 51.1 | 250.2 | 1405 | 16.35 | 0.852 |
| 4 | √ | × | × | √ | 50.8 | 172.8 | 1378 | 15.26 | 0.772 |
| 5 | √ | √ | √ | √ | 52.4 | 270.9 | 1409 | 16.87 | 0.905 |
| Net | Input size | Input channel | Output size | Output channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convolution 1 | 512×512 | 3 | 128×128 | 64 |
| Res-Block1 | 128×128 | 64 | 128×128 | 64 |
| CBAM1 | 128×128 | 64 | 128×128 | 64 |
| Res-Block2 | 128×128 | 64 | 64×64 | 128 |
| CBAM2 | 64×64 | 128 | 64×64 | 128 |
| Res-Block3 | 64×64 | 128 | 32×32 | 256 |
| CBAM3 | 32×32 | 256 | 32×32 | 256 |
| Res-Block4 | 32×32 | 256 | 16×16 | 512 |
| CBAM4 | 16×16 | 512 | 16×16 | 512 |
| Upper sampling layer 1 | 16×16 | 512 | 32×32 | 256 |
| Upper sampling layer 2 | 32×32 | 256 | 64×64 | 128 |
| Upper sampling layer 3 | 64×64 | 128 | 128×128 | 64 |
| Target center point | 128×128 | 64 | 128×128 | 1 |
| The target center is biased | 128×128 | 64 | 128×128 | 2 |
| Target size | 128×128 | 64 | 128×128 | 2 |
| Network | AP |
|---|---|
| CenterNet | 0.751 |
| CenterNet-IOU | 0.772 |
| CenterNet-CBAM | 0.823 |
| CenterNet-FS | 0.852 |
| CenterNet-CBAM-FS-IOU | 0.905 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




