Submitted:
25 January 2024
Posted:
26 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and treatments
2.2. Preparation of extracts
2.3. Folin–Ciocalteu assay and determination of ascorbic acid
2.4. UHPLC-MS/MS method
2.5. Determination of enzyme activities involved in phenolic compounds biosynthesis and degradation
2.6. Determination of relative gene expression
2.7. Determination of antioxidant activities
3. Results and Discussion
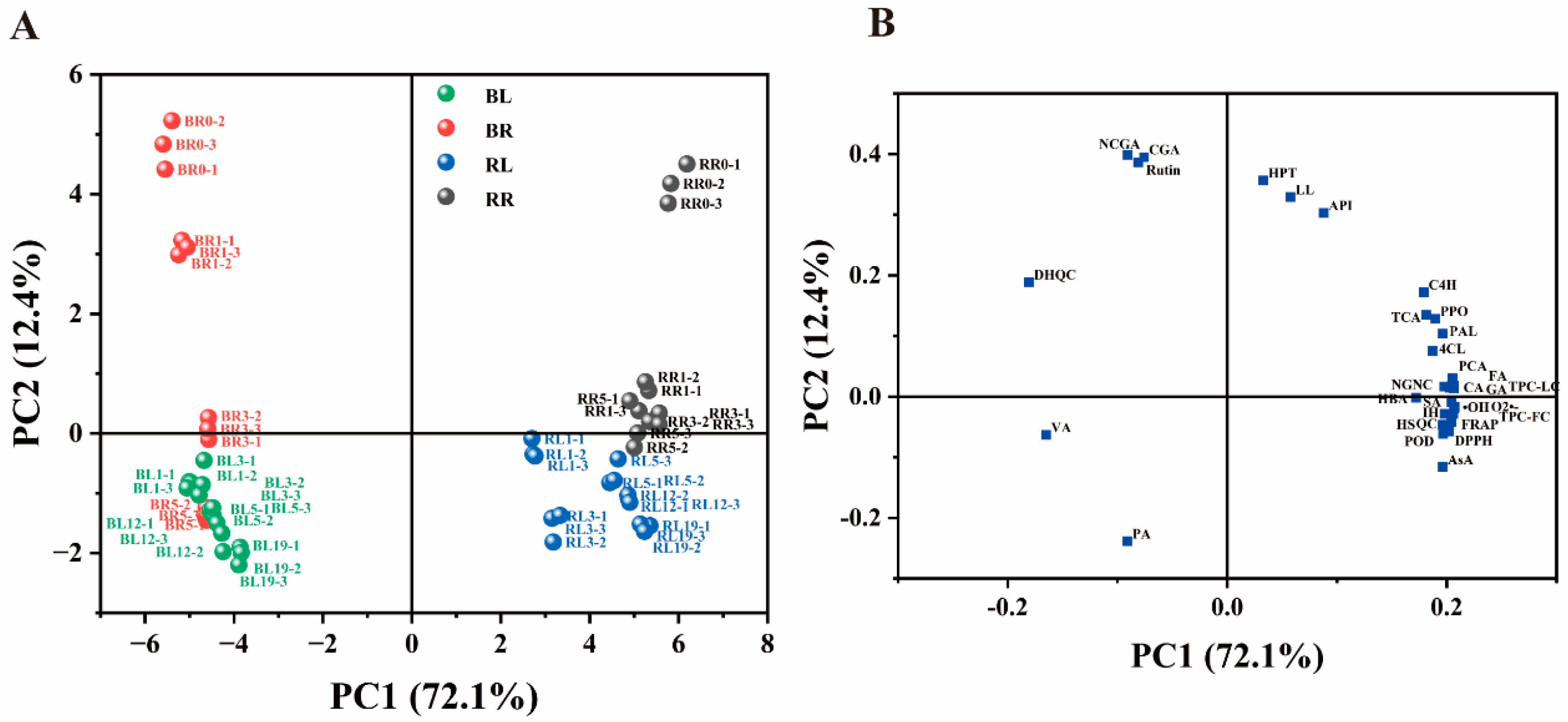
3.1. Principal component analysis
3.2. Dynamics of antioxidant compounds
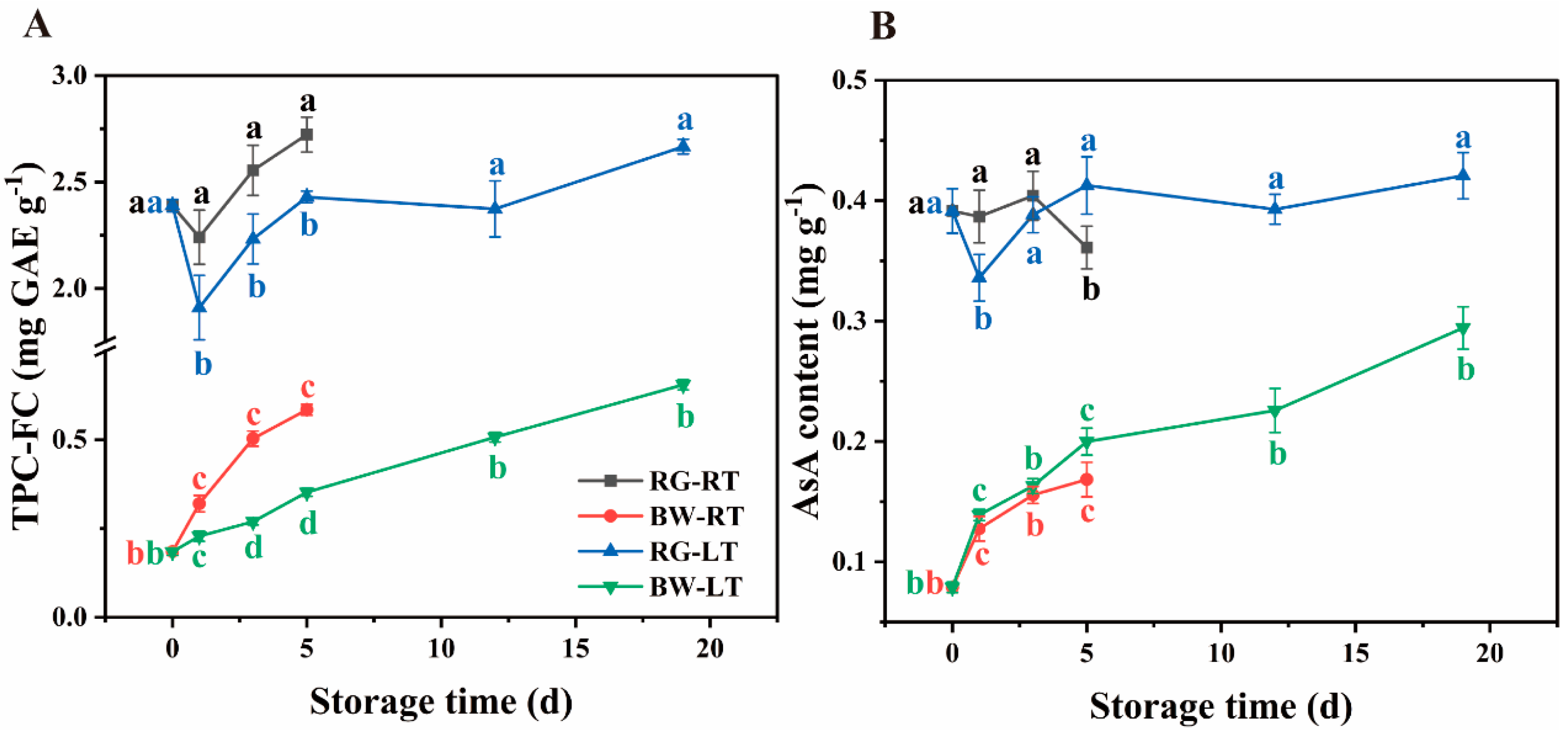
3.2.1. Dynamics of TPC-FC and ascorbic acid
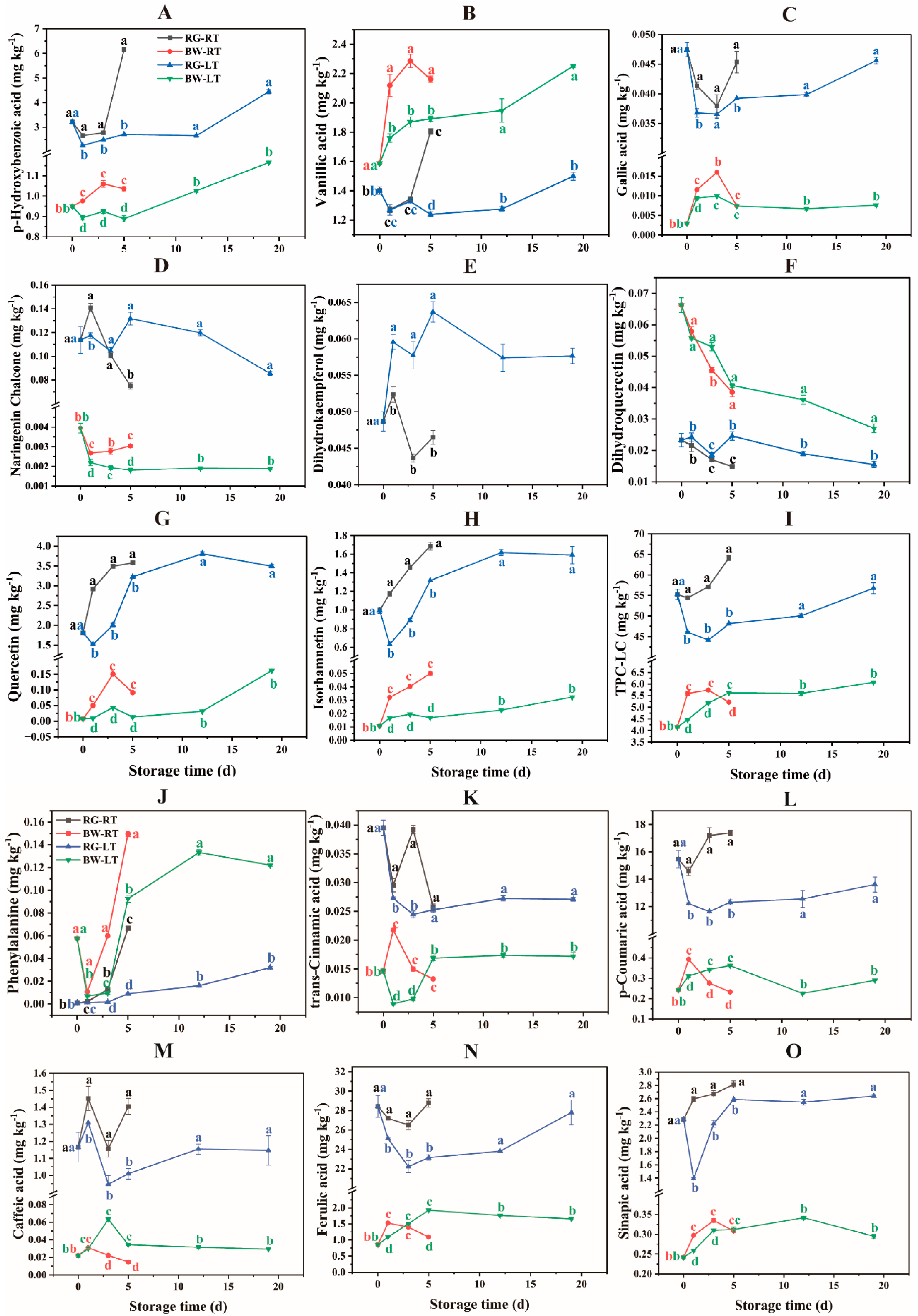
3.2.2. Dynamics of phenolic compounds determined using LC–MS
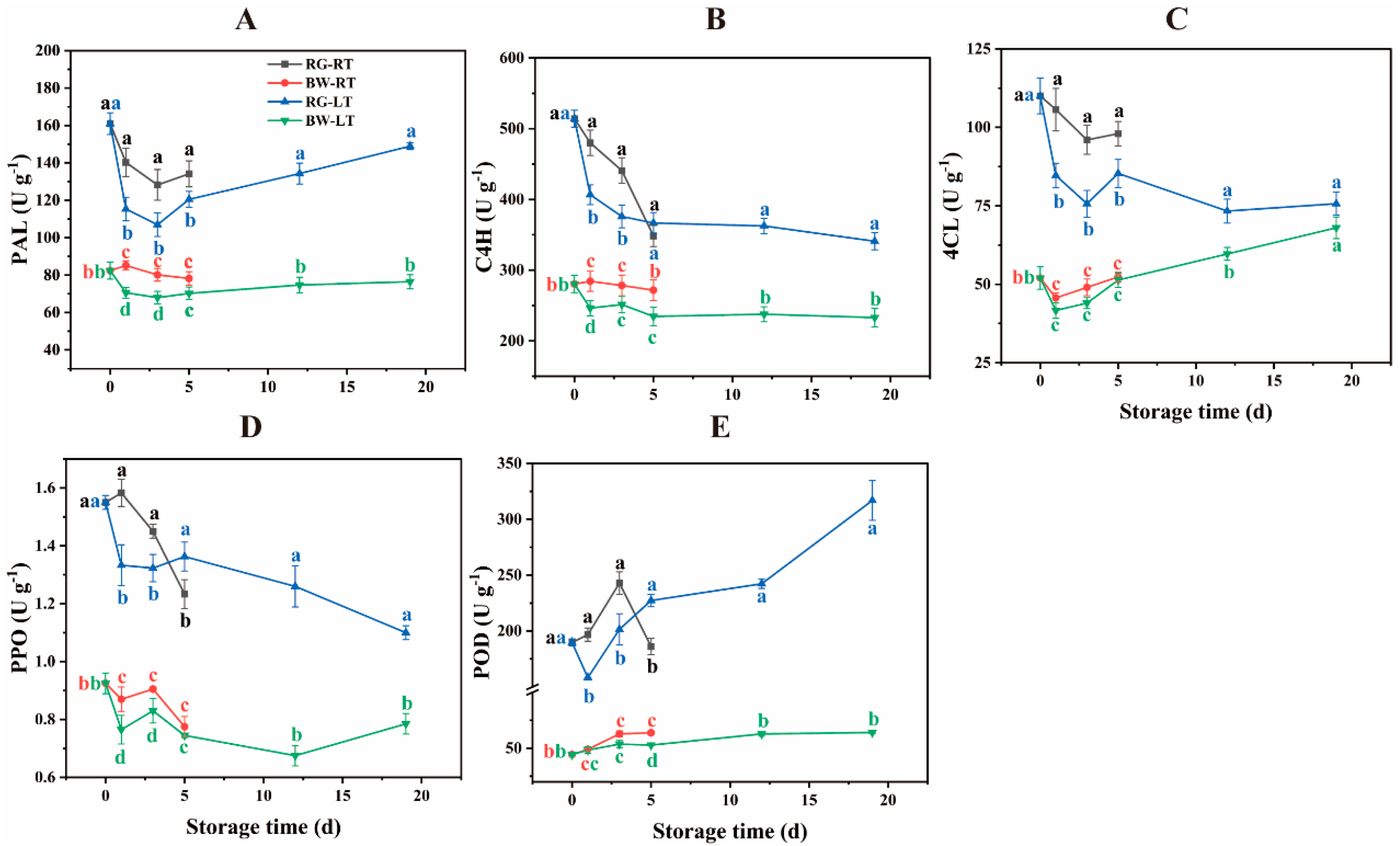
3.3. Dynamics of enzyme activities involved in the metabolism of phenolic compounds in post-harvest chive
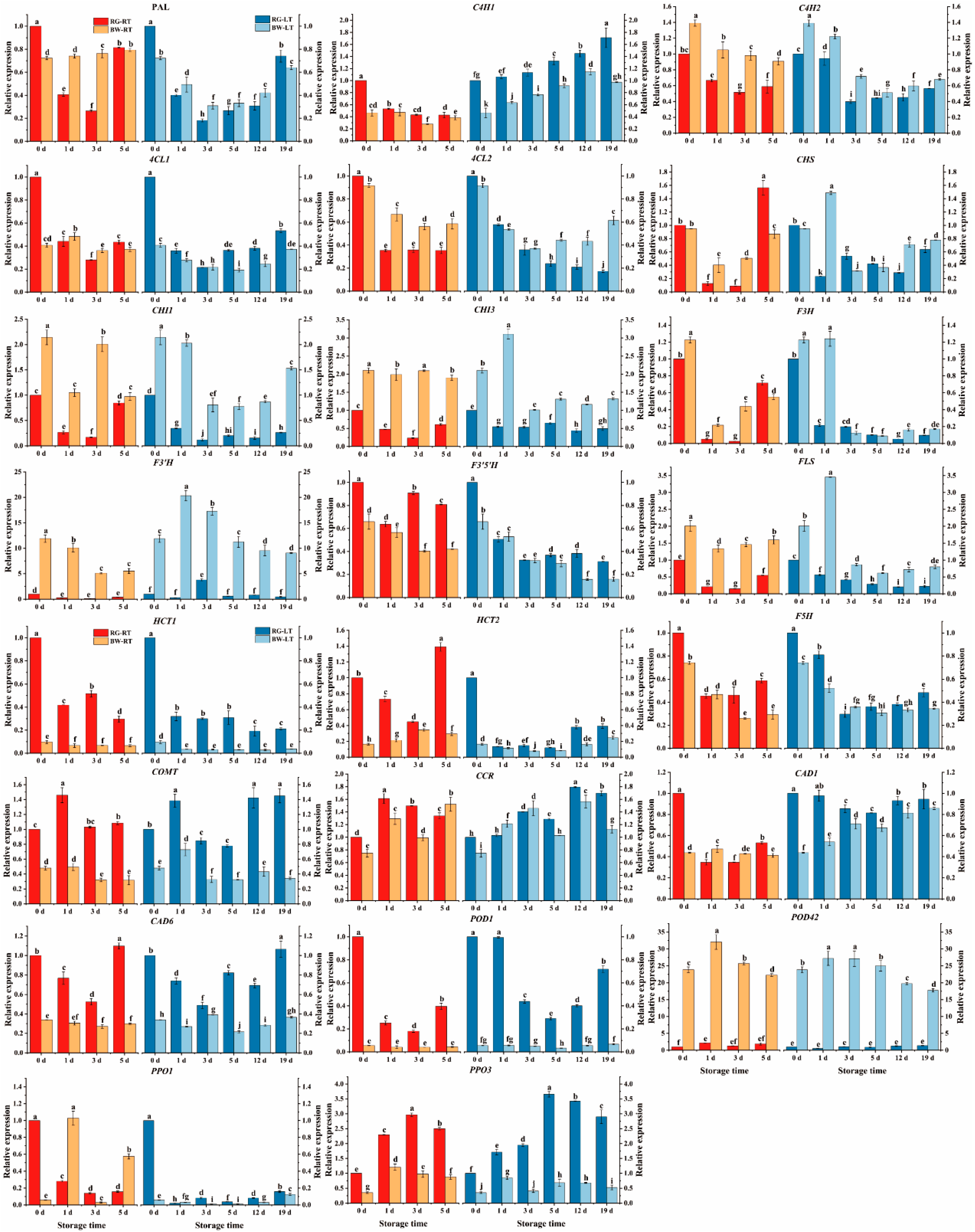
3.4. Dynamics of gene expression
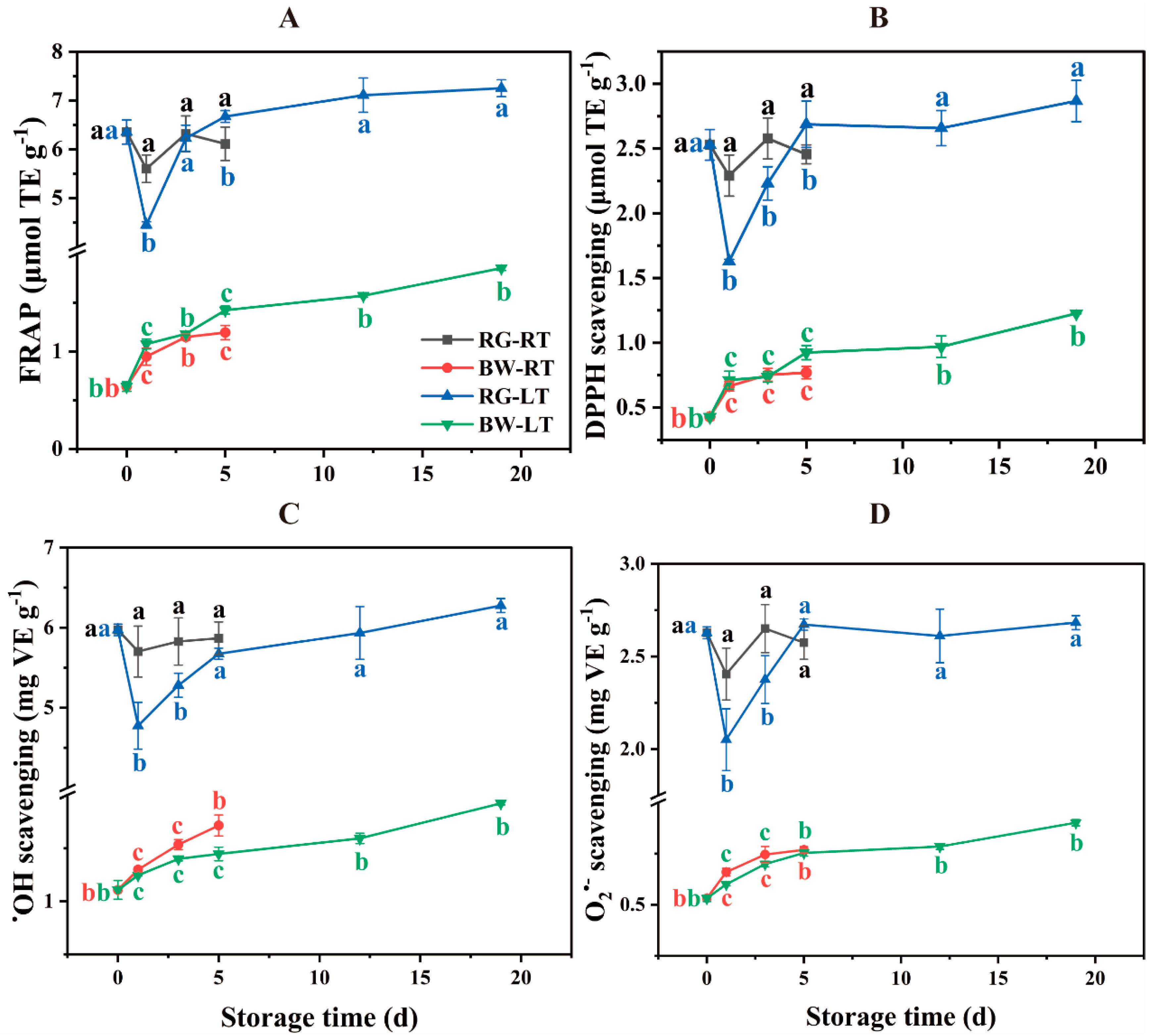
3.5. Dynamics of antioxidant activities in post-harvest chive
3.6. Dynamics of other nutrients
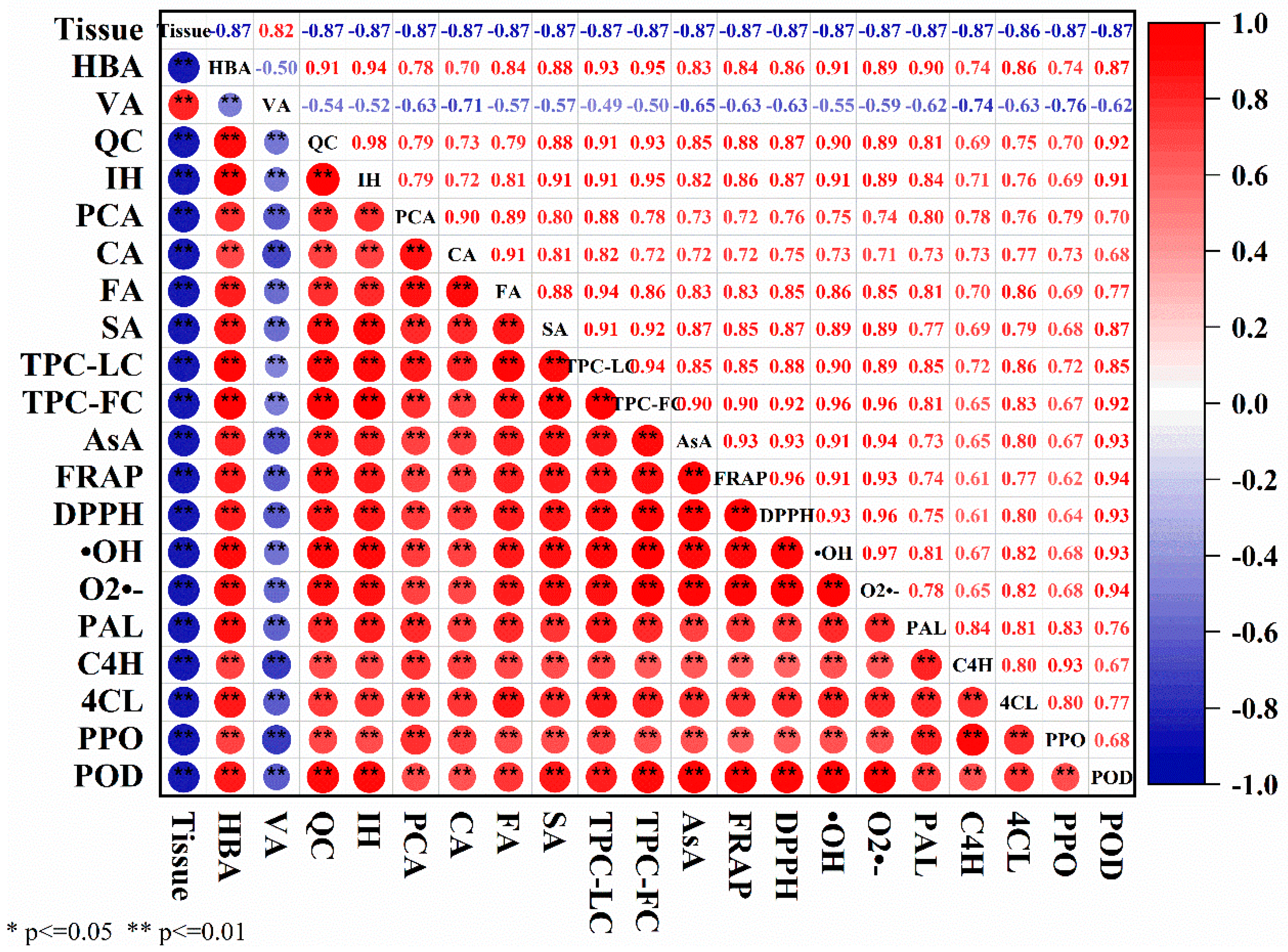
3.7. Correlation analysis
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelrahman, M., Ariyanti, N.A., Sawada, Y., Tsuji, F., Hirata, S., Hang, T.T.M., Okamoto, M., Yamada, Y., Tsugawa, H., Hirai, M.Y., Shigyo, M., 2020. Metabolome-based discrimination analysis of shallot landraces and bulb onion cultivars associated with differences in the amino acid and flavonoid profiles. Molecules 25. [CrossRef]
- Beato, V.M., Orgaz, F., Mansilla, F., Montano, A., 2011. Changes in phenolic compounds in garlic (Allium sativum L.) owing to the cultivar and location of growth. Plant Foods for Humman Nutrition 66, 218-223. [CrossRef]
- Beretta, H.V., Bannoud, F., Insani, M., Berli, F., Hirschegger, P., Galmarini, C.R., Cavagnaro, P.F., 2017. Relationships Between Bioactive Compound Content and the Antiplatelet and Antioxidant Activities of Six Allium Vegetable Species. Food Technology and Biotechnology 55, 266-275. [CrossRef]
- Bernaert, N., De Clercq, H., Van Bockstaele, E., De Loose, M., Van Droogenbroeck, B., 2013. Antioxidant changes during postharvest processing and storage of leek (Allium ampeloprasum var. porrum). Postharvest Biology and Technology 86, 8-16. [CrossRef]
- Biernacka, B., Dziki, D., Kozlowska, J., Kowalska, I., Soluch, A., 2021. Dehydrated at Different Conditions and Powdered Leek as a Concentrate of Biologically Active Substances: Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Compound Profile. Materials (Basel) 14. [CrossRef]
- Carmona, L., Alquezar, B., Marques, V.V., Pena, L., 2017. Anthocyanin biosynthesis and accumulation in blood oranges during postharvest storage at different low temperatures. Food Chemistry 237, 7-14. [CrossRef]
- Castillejo, N., Martínez-Zamora, L., Gómez, P.A., Pennisi, G., Crepaldi, A., Fernández, J.A., Orsini, F., Artés-Hernández, F., 2021. Postharvest yellow LED lighting affects phenolics and glucosinolates biosynthesis in broccoli sprouts. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 103. [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, L., Ieri, F., Vignolini, P., Mulinacci, N., Romani, A., 2020. Characterization of Volatile and Flavonoid Composition of Different Cuts of Dried Onion (Allium cepa L.) by HS-SPME-GC-MS, HS-SPME-GCxGC-TOF and HPLC-DAD. Molecules 25. [CrossRef]
- Dai, X., Jia, C., Lu, J., Yu, Z., 2023. The dynamics of bioactive compounds and their contributions to the antioxidant activity of postharvest chive (Allium schoenoprasum L.). Food Research International 174. [CrossRef]
- Dai, X., Lu, Y., Yang, Y., Yu, Z., 2021. 1-Methylcyclopropene preserves the quality of chive (Allium schoenoprasum L.) by enhancing its antioxidant capacities and organosulfur profile during storage. Foods 10. [CrossRef]
- Dai, X., Yu, H., Zhu, L., Yu, Z., 2022a. S-alk(en)ylcysteine sulfoxides biosynthesis and free amino acids profile in different parts of postharvest chive (Allium schoenoprasum L.). Scientia Horticulturae 303. [CrossRef]
- Dai, X., Yu, Z., 2022b. Transcriptome analysis reveals the genes involved in S-alk(en)ylcysteine sulfoxide biosynthesis and its biosynthetic location in postharvest chive (Allium schoenoprasum L.). Food Research International 158, 111548. [CrossRef]
- Emir, A., Emir, C., 2020b. Chemical profiles and biological properties of methanol extracts of Allium pallens L. from different localities in Turkey. Archives of Biological Sciences 72, 193-201. [CrossRef]
- Emir, A., Emir, C., Yildirim, H., 2020a. Characterization of phenolic profile by LC-ESI-MS/MS and enzyme inhibitory activities of two wild edible garlic: Allium nigrum L. and Allium subhirsutum L. Journal of Food Biochemistry 44, e13165. [CrossRef]
- Emir, C., Emir, A., 2021. Phytochemical analyses with LC-MS/MS and in vitro enzyme inhibitory activities of an endemic species "Allium stylosum O. Schwarz" (Amaryllidaceae). South African Journal of Botany 136, 70-75. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.S., de Oliveira, V.S., Chavez, D.W.H., Chaves, D.S., Riger, C.J., Sawaya, A., Guizellini, G.M., Sampaio, G.R., Torres, E., Saldanha, T., 2022. Bioactive compounds of parsley (Petroselinum crispum), chives (Allium schoenoprasum L) and their mixture (Brazilian cheiro-verde) as promising antioxidant and anti-cholesterol oxidation agents in a food system. Food Research International 151, 110864. [CrossRef]
- Gouda, M., Nassarawa, S.S., Gupta, S.D., Sanusi, N.I., Nasiru, M.M., 2023. Evaluation of carbon dioxide elevation on phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of red onion (Allium cepa L.) during postharvest storage. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 200, 107752. [CrossRef]
- Han, C., Ji, Y., Li, M., Li, X., Jin, P., Zheng, Y., 2016. Influence of wounding intensity and storage temperature on quality and antioxidant activity of fresh-cut Welsh onions. Scientia Horticulturae 212, 203-209. [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.T., Phan, A.D.T., O'Hare, T.J., 2021. Temperature and Maturity Stages Affect Anthocyanin Development and Phenolic and Sugar Content of Purple-Pericarp Supersweet Sweetcorn during Storage. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 69, 922-931. [CrossRef]
- Kadyrbayeva, G., Zagorska, J., Grzegorczyk, A., Gawel-Beben, K., Strzepek-Gomolka, M., Ludwiczuk, A., Czech, K., Kumar, M., Koch, W., Malm, A., Glowniak, K., Sakipova, Z., Kukula-Koch, W., 2021. The Phenolic Compounds Profile and Cosmeceutical Significance of Two Kazakh Species of Onions: Allium galanthum and A. turkestanicum. Molecules 26. [CrossRef]
- Kampfenkel, K., Vanmontagu, M., Inze, D., 1995. Extraction and Determination of Ascorbate and Dehydroascorbate from Plant Tissue. Analytical biochemistry 225, 165-167. [CrossRef]
- Kantakhoo, J., Ose, K., Imahori, Y., 2022. Effects of hot water treatment to alleviate chilling injury and enhance phenolic metabolism in eggplant fruit during low temperature storage. Scientia Horticulturae 304. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R., Kumar, D., 2023. Comprehensive metabolomics and antioxidant activity of Allium species viz. Allium semenovii, A. sativum and A. cepa: An important spice. Food Research International 166, 112584. [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, S., Kolniak-Ostek, J., Oszmiański, J., Wiśniewski, R., 2017. Comparison of Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Capacity of Bear Garlic (Allium ursinum L.) in Different Maturity Stages. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 41. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q., Luo, L., Zheng, L., 2018. Lignins: Biosynthesis and Biological Functions in Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19. [CrossRef]
- Metsämuuronen, S., Sirén, H., 2019. Bioactive phenolic compounds, metabolism and properties: a review on valuable chemical compounds in Scots pine and Norway spruce. Phytochemistry Reviews 18, 623-664. [CrossRef]
- Mollica, A., Zengin, G., Locatelli, M., Picot-Allain, C.M.N., Mahomoodally, M.F., 2018. Multidirectional investigations on different parts of Allium scorodoprasum L. subsp. rotundum (L.) Stearn: Phenolic components, in vitro biological, and in silico propensities. Food Research International 108, 641-649. [CrossRef]
- Naheed, Z., Cheng, Z., Wu, C., Wen, Y., Ding, H., 2017. Total polyphenols, total flavonoids, allicin and antioxidant capacities in garlic scape cultivars during controlled atmosphere storage. Postharvest Biology and Technology 131, 39-45. [CrossRef]
- Olivares, D., Contreras, C., Munoz, V., Rivera, S., Gonzalez-Aguero, M., Retamales, J., Defilippi, B.G., 2017. Relationship among color development, anthocyanin and pigment-related gene expression in 'Crimson Seedless' grapes treated with abscisic acid and sucrose. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 115, 286-297. [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, G., Zhang, L., Bocchi, S., Giuberti, G., Ak, G., Elbasan, F., Yildiztugay, E., Ceylan, R., Picot-Allain, M.C.N., Mahomoodally, M.F., Lucini, L., Zengin, G., 2022. The functional potential of nine Allium species related to their untargeted phytochemical characterization, antioxidant capacity and enzyme inhibitory ability. Food Chemistry 368, 130782. [CrossRef]
- Tao, X., Wu, Q., Li, J., Huang, S., Cai, L., Mao, L., Luo, Z., Li, L., Ying, T., 2022. Exogenous methyl jasmonate regulates phenolic compounds biosynthesis during postharvest tomato ripening. Postharvest Biology and Technology 184. [CrossRef]
- Tsaniklidis, G., Kafkaletou, M., Delis, C., Tsantili, E., 2017. The effect of postharvest storage temperature on sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) phenolic metabolism and colour development. Scientia Horticulturae 225, 751-756. [CrossRef]
- Vithana, M.D.K., Singh, Z., Johnson, S.K., 2018. Cold storage temperatures and durations affect the concentrations of lupeol, mangiferin, phenolic acids and other health-promoting compounds in the pulp and peel of ripe mango fruit. Postharvest Biology and Technology 139, 91-98. [CrossRef]
- Younes, N.A., Anik, T.R., Rahman, M.M., Wardany, A.A., Dawood, M.F.A., Tran, L.P., Abdel Latef, A.A.H., Mostofa, M.G., 2023. Effects of microbial biostimulants (Trichoderma album and Bacillus megaterium) on growth, quality attributes, and yield of onion under field conditions. Heliyon 9, e14203. [CrossRef]
- Younes, N.A., Rahman, M.M., Wardany, A.A., Dawood, M.F.A., Mostofa, M.G., Keya, S.S., Abdel Latef, A.A.H., Tran, L.P., 2021. Antioxidants and Bioactive Compounds in Licorice Root Extract Potentially Contribute to Improving Growth, Bulb Quality and Yield of Onion (Allium cepa). Molecules 26. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F., Xie, Y., Shi, J., Jiang, L., 2022. Effects of 1-methylcyclopropene treatment on phenolic metabolism in postharvest Gynura bicolor DC. Scientia Horticulturae 293. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X., Jiang, H., Silvy, E.M., Zhao, S., Chai, X., Wang, B., Li, Z., Bi, Y., Prusky, D., 2021. Candida Oleophila Proliferated and Accelerated Accumulation of Suberin Poly Phenolic and Lignin at Wound Sites of Potato Tubers. Foods 10. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D., Liu, Q., Peng, J., Tu, S., Pan, L., Tu, K., 2020. Metabolic analysis of phenolic profiles reveals the enhancements of anthocyanins and procyanidins in postharvest peach as affected by hot air and ultraviolet C. Postharvest Biology and Technology 167. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D., Sun, R., Zhu, W., Shi, Y., Ni, S., Wu, C., Li, T., 2023. Impact of dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma on the quality and phenolic metabolism in blueberries based on metabonomic analysis. Postharvest Biology and Technology 197. [CrossRef]
 means increase.
means increase.  means decrease.
means decrease.  means change not too much. The thickness of the arrows indicates the extent of the change.
means change not too much. The thickness of the arrows indicates the extent of the change.  means inhibited by low temperature.
means inhibited by low temperature.
 means increase.
means increase.  means decrease.
means decrease.  means change not too much. The thickness of the arrows indicates the extent of the change.
means change not too much. The thickness of the arrows indicates the extent of the change.  means inhibited by low temperature.
means inhibited by low temperature.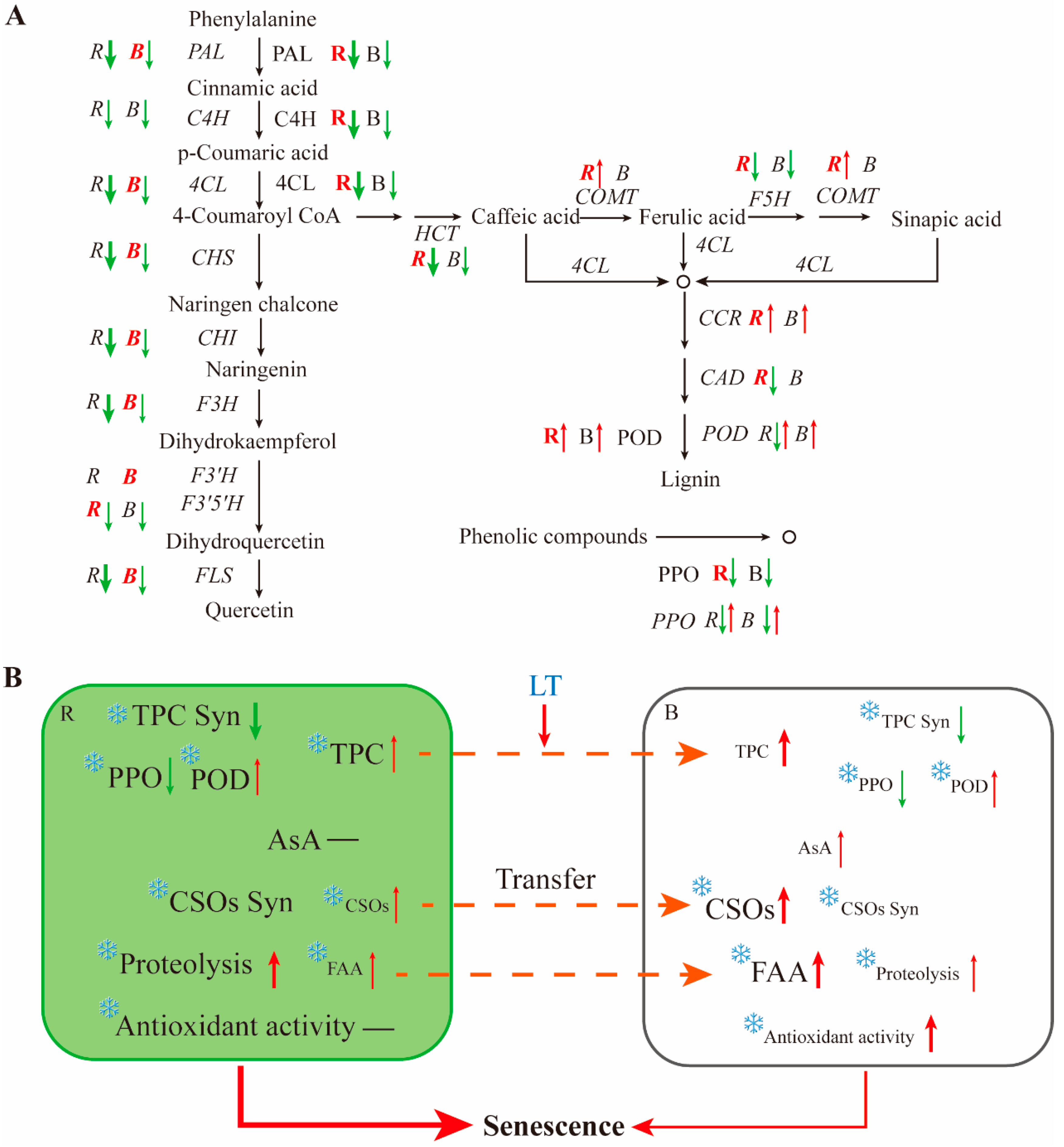
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



