Introduction
Today, there is an increasing need to replace or regenerate damaged tissue due to age-related and other degenerative diseases, tumors, trauma, and congenital defects [
1]. Various tissue engineering methods including functional biomaterials, drug-eluting systems, and stem cell therapies have been used to enhance tissue regeneration [
2,
3,
4]. Restoring damaged tissues is vital for survival. Regenerative medicine is an interdisciplinary field that incorporates stem cell-based therapies, tissue generation and repair, and disease modeling [
5,
6]. Despite many efforts in the past, embryonic stem cells (ESCs), mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and other cells have become key players in regenerative medicine [
7,
8]. Moreover, these cells have been the basis of numerous clinical trials, but problems such as tumorigenicity, immune rejection, remarkable ethical issues, and difficulties in obtaining large numbers of adult stem cells have been exposed in the progress of therapeutic research [
9,
10,
11,
12].
Multilineage-differentiating stress-enduring (Muse) cells, a cell subgroup from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) with self-renewal and multi-differentiation potential, differentiated into three parent cell layers with non-tumorigenic and low-end granite activity [
13,
14]. When tissues and organs are damaged, enough Muse cells are crucial for maintaining tissue regeneration and functional integrity. It is an ideal seed cell in the fields of tissue engineering, cell transplantation, and gene therapy. It is also the best candidate cell for endogenous repair and may also be the breakthrough for disease treatment [
15]
.
Muse cells can selectively accumulate at the site of injury in both circulation and tissue because they express sphingosine-monophosphate (S1P) receptor 2 (S1PR2), which senses the S1P produced by damaged tissue, enabling it to migrate and homing to the site of tissue injury, in contrast to other stem cells, they can be obtained from living organisms, do not require genetic manipulation, and maintain their stem cell potential through naturally occurring mechanisms [
16]. The most striking advantages are, first of all, the absence of the side effect of the formation of teratomas [
17,
18]. Secondly, there is also no induction of host immune rejection during autografting to produce tissue-compatible cells, with little error and minimal immune rejection, and they can also tolerate harsh environments that support their survival in damaged/injured tissues [
13,
19]. Thus, it plays a key role in tissue healing and regenerative medicine.
This paper reviews its related research (existing mechanism of treatment of disease, clinical research progress), and highlights Muse cells’ potential for clinical application on tissue regeneration and their possible mechanisms of action. Besides, the safety and reliability of Muse cells overcome the defects of most stem cells and are an excellent alternative to ESCs and iPSCs in the field of regenerative medicine. It’s a valuable addition to the toolbox of future clinical treatments for major diseases, offering broad prospects for the treatment of a wide range of clinical diseases.
1. The discovery of Muse cells
1.1. The source
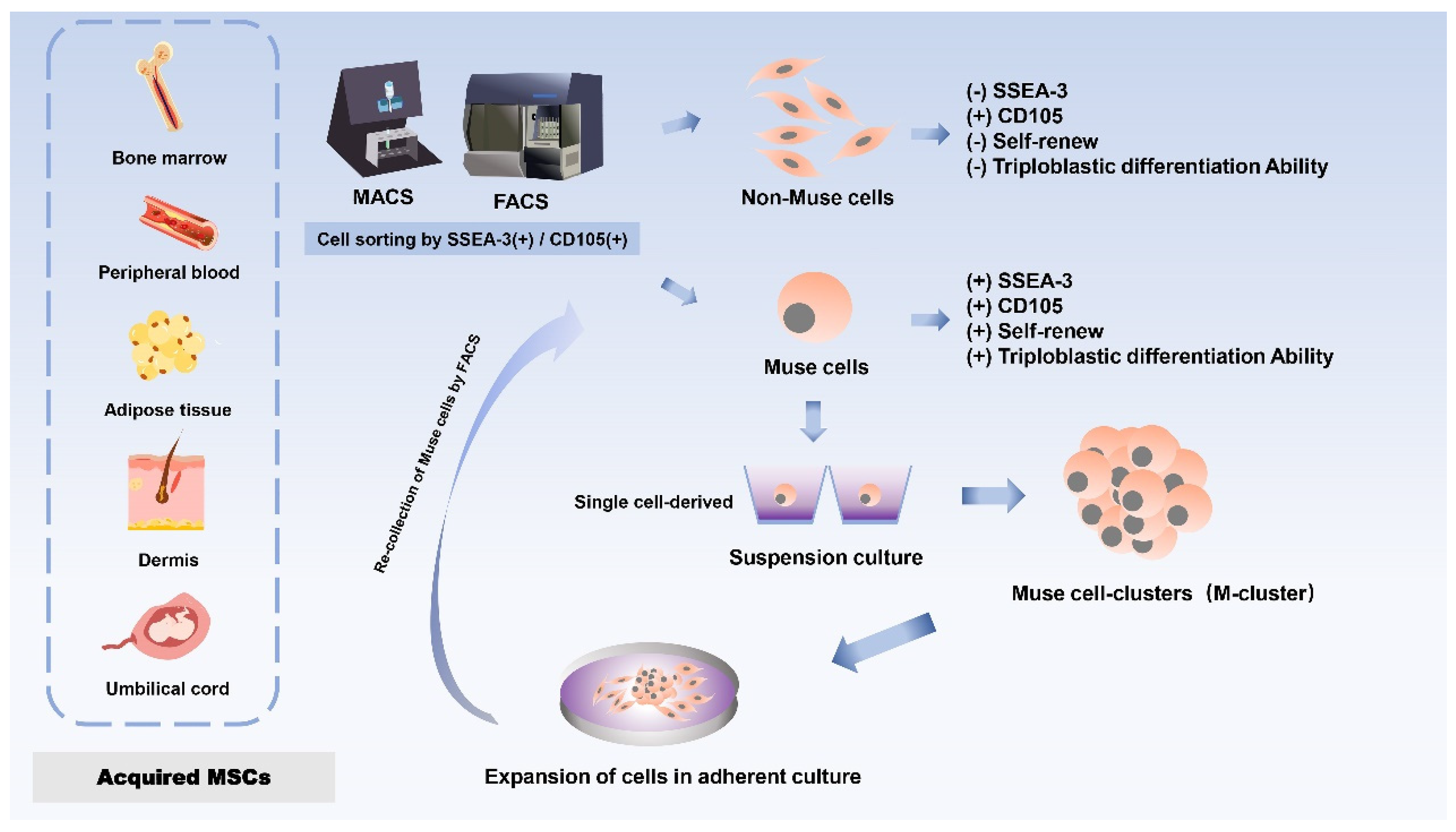
Dezawa’s group first isolated and discovered a distinct cell subpopulation of MSCs in 2010 in bone marrow (BM) aspirates under prolonged trypsin incubation, which was named Muse cells because of their stress-tolerant properties [
13]. Stage-specific embryonic antigen 3 (SSEA-3), a sphingolipid, is a marker for identifying Muse cells and is used to isolate this population from mesenchymal stromal cells [
20,
21]. Since almost all MSCs are positive for CD 105, a single application of SSEA-3 will be sufficient to purify Muse cells from MSCs. Muse cells showed expression of CD105 (a marker for MSCs) and SSEA3 (a marker for ESCs) double-positive cells, and primitive MSCs were separated into Muse cells (SSEA-3+) and non-Muse cells (SSEA-3-) by either fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) or magnetically-affinitive cell sorting (MACS) [
13,
22]. Briefly, Non-Muse cells are mesenchymal stem cells that do not express SSEA-3 but only express general mesenchymal markers. Muse cells gradually give rise to non-Muse cells, resulting in a reduced proportion of Muse cells, which make up about 1-3% of MSCs but can differentiate into endodermal, ectodermal, and mesodermal phenotypes and are capable of self-renewal [
22,
23]. Therefore, SSEA-3 can be directly applied to separate Muse cells from non-Muse cells.
Furthermore, the pluripotency of Muse cells does not need to be induced by the introduction of exogenous genes; they can be isolated from skin and bone marrow obtained from individuals or cell banks[
13]. Although each tissue contains a very small number of stem cells and the proportion of Muse cells in bone marine-derived monocytes is small, a large number of Muse cells can be obtained from mesenchymal cell populations through a series of culture steps, such as Muse cell selection, M-cluster formation in suspension culture, and cell amplification in adherent culture [
13,
24] (
Figure 1).To date, Muse cells can be successfully isolated from many adult tissues, mainly bone marrow (BM)[
13,
24], peripheral blood (PB) [
21], adipose tissue (AT)[
25,
26], dermal fibroblasts [
22,
24,
27], and umbilical cord (UC) [
28]. The most common sources of Muse cells are bone marrow-derived MSCs (BM-MSCs) and umbilical cord-derived MSCs (UC-MSCs). The primary source of Muse cells of peripheral blood origin is thought to be the bone marrow, and given that Muse cells in the peripheral blood enter the tissues from the circulatory system, they are first naturally localized to connective tissues and are thought to be continuously mobilized from the bone marrow to the peripheral blood, where they are then supplied to each organ via the bloodstream [
21,
29]. Once in the organ, they are sparsely distributed throughout the connective tissues of the organ, such as the dermis, liver, spleen, pancreas, trachea, adipose tissue, dental pulp, and synovial tissue [
15,
19,
26,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34], so that Muse cells are spread throughout the different mesenchymal tissues. Muse cells that can be isolated and characterized from menstrual blood-derived endometrial stem cells (MenSC) have been reported to provide another source of inspiration [
35].
Thus, the distributional characteristics of Muse cells make them different from other somatic cells, and Muse cells are naturally occurring endogenous cells. Notably, Muse cells found by cell sorting from bone marrow aspirates resulted in a low yield of approximately 1% Muse cells in the total population (8000 cells/ml initial culture) [
13]. In contrast, Muse-AT cell isolation greatly increased this yield capacity through severe cellular stress [
26], opening up the possibility of viable clinical doses of Muse cells in humans.
1.2. Characteristics of Muse cell
Importantly, Muse cells are indistinguishable from other predominantly mesenchymal cells in adherent cultures, but when they are transferred to suspension cultures, they form characteristic clusters of cells, are positive for pluripotency markers, and exhibit self-renewal and differentiation [
13,
22]. It should be noted that Muse cells are a subpopulation of MSCs and can be distinguished from other cells by SSEA-3 [
13]. Therefore, Muse cells were positive for both pluripotent and mesenchymal markers, while non-Muse MSCs were positive only for mesenchymal markers[
36]. In addition, when Muse and non-Muse cells were isolated from MSCs by cell sorting, Muse and non-Muse cells did not differ greatly in cell size [
13]. Both sections contain a range of cell sizes, and there is no significant size difference trend. Besides, Muse cells express the pluripotency genes, such as octamer binding transcription factor 3/4 (OCT3/4), sex-determining region Y box 2 (SOX2), Nanog (homeobox protein NANOG), reduced expression 1 (REX1) [
13,
15], while cells other than Muse cells containing MSCs did not express pluripotent genes and did not cross the oligonucleotide boundaries between mesoderm, ectoderm, and endoderm [
18,
25,
26,
37].
Oct3/4, SOX2, and Nanog are embryonic stem cell markers, which are also core transcription factors maintaining cell pluripotency. Single Muse cells could form ESCs-like clusters in suspension, showing triploblastic differentiation potential and self-renewability, while single non-Muse cells could not survive in suspension and self-renewal is not feasible in [
13]. Because Muse cells can differentiate into mesodermal cells (skeletal muscle [
38], cardiomyocytes [
39], glomerular cells [
40]), endodermal cells (hepatocytes [
41], bile duct cells [
42]), and ectodermal cells (melanocytes [
33], nerve cells [
43], keratinocytes [
44]), while the differentiation ability of non-Muse MSCs was limited to adipocytes, bone cells, and chondrocytes, and their differentiation ratio was lower than that of Muse cells [
15].
1.3. Different culture systems of Muse cell
Muse cells were obtained from cultured MSC by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Such cells proliferate asymmetrically in the adherent culture state, giving rise to a new Muse cell in addition to a non-Muse cell. The flat and elongated non-Muse cells surround the Muse cells to form a sheath. The sheathed Muse cells then proliferate by symmetric division to produce mature clusters of 50-150 μm in size within two weeks. When mature clusters were cultured in an adherent state, internal Muse cells proliferated by asymmetric division after moving out of the cluster [
45]. As a result, the number of Muse cells gradually decreases, eventually accounting for only a certain percentage of the total number of cells, which is consistent with the proportion of Muse cells in MSCs and fibroblasts [
13].
It is worth mentioning that the pluripotency of Muse cells is regulated by an “adherence-suspension switch”, which is different from MSCs because Muse cells can survive and proliferate in both adherent and suspension states [
46]. Adhesion-suspension switch may control Muse cell pluripotency. The “adherence-suspension switch” is involved in the control of Muse cell pluripotency. Some researchers found that Nanog, SOX2, Oct3/4, transcription factors that maintain stem cell pluripotency, are distributed in the cytoplasm when they are attached to the wall, while in suspension culture they are present in the nucleus, thus explaining why the expression of these genes is 50 to hundreds of times higher in suspension than in walled culture [
13,
25,
41]. Moreover, the expression levels of these pluripotent genes are reversible between adherent and suspension states, which alter the epigenetics of Muse cells [
41].
Therefore, the Muse cells in the organ’s connective tissue, including the Muse cells in the bone marrow, are considered to have lower pluripotency. However, once the Muse cells are mobilized into the peripheral blood and kept in suspension, their pluripotent factors are activated and highly activated, and the suspension environment enhances the pluripotency of the Muse cells. Pb-Muse cells are considered to have high pluripotency due to the significantly increased pluripotency of Muse cells in suspension [
21]. Indeed, Muse cells in different tissue-derived, the core characteristics, the expression of pluripotent genes, and the ability of triploid differentiation and self-renewal at the individual cell level are consistent. Interestingly, Muse cells show their differentiation direction according to their origin, it may be related to the mobilization of Muse cells into peripheral blood circulation after tissue injury. Amin, et
al. treated Muse cells with DNA methylation inhibitors to increase pluripotent gene expression levels in suspension [
39]. This provides a bright idea for improving the pluripotency of Muse cells in the later stage. Nevertheless, the relationship between the suspension state of Muse cells and the methylation state of pluripotent genes is unknown. The molecular mechanisms by which adherence-suspension switches control the localization and expression of pluripotent genes still require further investigation.
A study comparing the pluripotent gene expression of human ESC/Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and human Muse and non-Muse cells found that the pluripotent gene expression patterns of Muse cells and ESC/iPSCs were very similar. Importantly, non-Muse cells did not express pluripotent genes [
22]. This is in stark contrast to the Muse cell. Moreover, although the gene expression patterns of cell cycle-related factors (i.e. Tumorigenesis factors) were different between ESC/iPSCs and Muse cells, these tumorigenic factors were generally highly expressed in ESC/iPSCs, while they were very low expressed in Muse cells, and their levels and patterns were similar to those of non-Muse cells, which highlighted Muse cells have a low risk of tumorigenesis [
22].
It has been reported that Muse cells can detect DNA damage quickly and activate the DNA damage repair system better than MSCs and non-Muse cells, these two types of cells were treated with H
2O
2 and ultraviolet light to induce DNA damage. Then, cells were collected for DNA damage response (DDR) analysis at 1, 6, and 48 h after stress treatment. Finally confirmed that Muse cells showed better resistance to physical and chemical genotoxic stress than non-Muse cells. Although the efficiency of the single-strand repair system was equal in both populations, the double-strand repair system (non-homologous terminating) of Muse cells was more powerful than that of non-Muse cells. Hence, the high ability of Muse cells to cope with genotoxic stress was related to its rapid and efficient sensing of DNA damage and activation of the DNA repair system. In previously reported models of fulminant hepatitis, skeletal muscle degeneration, stroke, and skin regeneration, Muse cells actively migrated to and integrated into the damaged site with higher efficiency than non-Muse cells [
31,
38,
47,
48]. In addition, Muse cells were able to return to damaged tissues and survive after integration, while non-Muse cells were not. Thus, Muse cells can work as repairing cells for a wide range of tissues and organs.
Indeed, when Muse cells are fully utilized, the low homing rate of intravenous MSCs will be greatly improved because Muse cells homed to the injury site at a higher rate than MSCs due to their ability to sense injury signals[
15,
47]. In light of the above, the differences between Muse and non-Muse cells are shown in
Table 1.
2. Muse cell repairs the location of the damage
2.1. The S1P-S1PR2 system is the main axis that controls the selective homing of circulating Muse cells
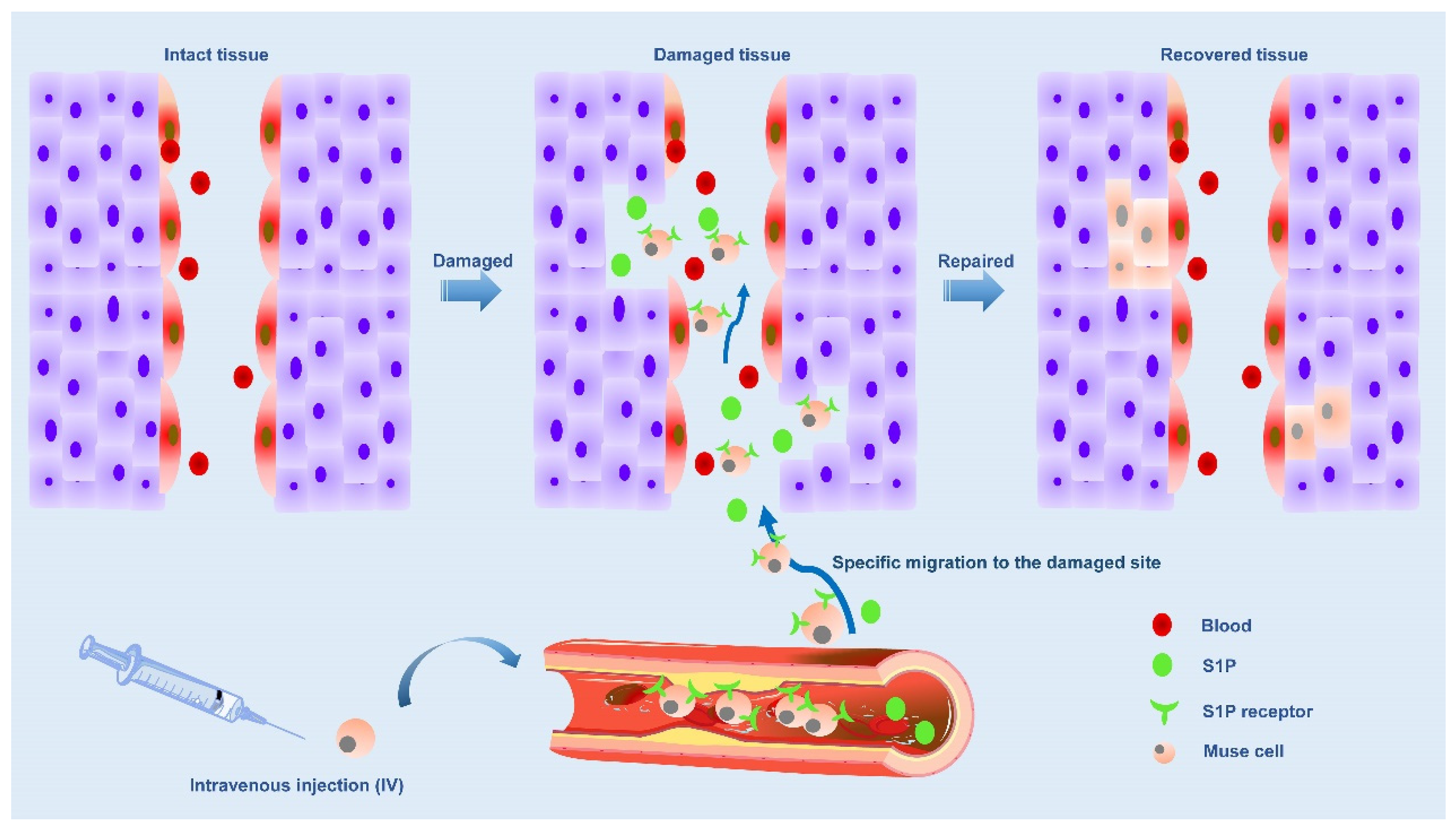
The ability to strongly perceive damage signals released by injured/damaged tissues is a unique and prominent feature of Muse cells due to the selective accumulation of damage sites mediated by sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P)-S1P receptor 2 (S1PR2)-axis [
49]. S1P is an alarm signal of acute inflammation/injury and is actively produced by damaged cells by phosphorylating S1P, a cell membrane component [
50]. In a word, when cells are damaged, S1P is produced. There are five subtypes of S1P receptors, including S1PR1, S1PR2, S1PR3, S1PR4, and S1PR5 [
51]. Previous studies have found that S1P is involved in the proliferation, movement, morphology and differentiation of tumor cells, neurons, vascular smooth muscle cells and vascular endothelial cells, which is associated with S1P receptors [
50,
51,
52,
53,
54]. Muse cells express S1PR2, allowing them to keenly sense S1P signals produced by damaged tissue and selectively return to the site of injury where they have accumulated. Therefore, Muse cells were guided to migrate to the site of injury by the S1P-S1PR2 system. Once tissue injury occurs, Muse cells will be mobilized from bone marrow to peripheral blood, and endogenous and exogenous Muse cells (in the case of transplantation) return to the injured site via the S1P-S1PR2 system [
49](
Figure 2).
Based on clinical data from patients with acute myocardial infarction and stroke, the level of S1P in serum increased before the number of endogenous PB-Muse cells increased. Shortly after injury, S1P was released into the peripheral blood, and this increase in the acute phase was significantly associated with functional recovery at 6 months, supporting the repair function of Muse cells in vivo [
49,
55,
56]. In acute myocardial infarction (AMI), S1P is produced from the infarct area as an alarm signal and transmitted to the bone marrow, where S1P is mobilized to the peripheral blood to increase the number of circulating Muse cells. In addition, circulating Muse cells migrated axially to infarct area via S1P-S1PR2, and replaced damaged cells through spontaneous differentiation into tissue suitable cells to repair heart tissue. When the number of endogenous Muse cells was insufficient, intravenous injection of exogenous Muse cells enhanced the repair activity, leading to successful tissue repair [
55]. Muse cells were inhibited by S1PR2 antagonists to migrate to myocardial infarction sections in vitro and myocardial infarction tissues in vivo. Compared with unsilenced Muse cells, Muse cells migrated to S1PR2-specific agonist SID46371153 and AMI heart tissue, suggesting Muse cells migrated through S1P-S1PR2 axis, which was a “targeting” effect [
49]. These findings support the central role of the S1P-S1PR2 axis in Muse cell-specific homing. At the same time, S1PR2 antagonist also showed that the therapeutic effect of Muse cells was weakened.
It was found that serum S1P level was positively correlated with the number of Muse cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction, is suggesting that patients with more Muse cells in peripheral blood but less Muse cells in acute stage had improved left ventricular function and remodeled in chronic stage [
55]. Therefore, the number of Muse cells can predict the prognosis of AMI patients.
2.2. Majority of Muse cells escape from lung capillary entrapment is also the reason why Muse cells can be localized to injury sites?
On the base of a great deal of reference literatures, it has been found that when MSCs are injected intravenously into the recipient body, most of them are trapped in the pulmonary capillaries [
57,
58,
59,
60,
61]. In contrast, the majority of Muse cells were able to escape from the coating of lung capillaries because of Muse cells were able to selectively cluster at the site of injury by keenly sensing S1P alarm signals, a key mediator of inflammation, rather than being trapped in lung capillaries and homing in damaged tissue during intravenous injection [
49].
Consistently, the ability to spontaneously differentiate into cells compatible with homing tissues in vivo after integration, even crossing oligonucleotide boundaries from mesoderm to endoderm or between ectoderm cells, is not recognized by other types of stem cells, including ESC/iPSCs and somatic stem cells such as neural and hematopoietic stem cells [
59]. In addition to intravenous injection, Muse cells can also be injected locally to the site of injury. In the study of Yamauchi et
al., Muse cells were injected from the dura mater to the brain parenchyma using a Hamilton syringe. It was found that Muse cells may replace lost neurons by integrating into the peri-infarct cortex and spontaneously differentiating into neuron-labeled positive cells [
62]. Similarly, the study in a mouse intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) model was used in this way, and show that Muse cells can remain in the ICH brain, differentiate into neural lineage cells and restore function without inducing them to enter neuronal cells through gene introduction and cytokine therapy prior to transplantation [
63]. Additionally, Yabuki et
al. show that Muse cells were injected into the pulmonary artery in the model of lung ischemia reperfusion, and more remained in the injured lung than MSCs, which improved the lung function and histological injury associated with IR injury in the rat model at the acute stage [
64].
Therefore, no matter Muse cells are injected locally, injected into pulmonary artery or injected intravenously, as long as they migrate to the damaged site effectively, they will spontaneously differentiate into cells compatible with targeted tissues and secrete factors regulating microenvironment to promote tissue repair. It is known that in animal models of kidney, muscle, brain and liver injury, Muse cells will migrate to damaged tissues after local or systemic administration of drugs and spontaneously differentiate into histocompatibility cells to achieve the recovery of organ functions. Whether Muse cells were injected locally, into pulmonary arteries, or intravenously, there was no mention that Muse cells could be blocked from reaching the injury site due to pulmonary capillaries. It is known that in animal models of kidney, muscle [
34,
65], brain [
63,
66] and liver injury [
67], Muse cells will migrate to damaged tissues after local or systemic administration of drugs and spontaneously differentiate into histocompatibility cells to achieve the recovery of organ functions. Thus, as long as they finally migrate to the damaged site effectively, they will spontaneously differentiate into cells compatible with the targeted tissue and secrete factors that regulate the microenvironment to promote tissue repair.
Microenvironmental cues at the injured site may play an important role in the fate decision of Muse cells. The microenvironment includes a variety of cytokines, growth factors, chemokines and extracellular matrix components. Then, in interaction with local factors, the lineage of Muse cells will be turned on or inhibited [
68,
69]. Perhaps the reason Muse cells end up diverging in a particular direction can be explained by activating cellular and molecular signaling pathways that interact to form a complex regulatory network.
3. Muse cell is an ideal regeneration tool
3.1. No tumorigenic risk has been identified
Pluripotent cells are highly expected to contribute to regenerative medicine because of their ability to differentiate into any type of cell in the body [
7], which means they could be applied to a wide variety of diseases. Muse cells are involved in the multi-lineage differentiation of MSCs. Meanwhile, a single Muse cell can generate cells representing each of the three germ layers and has the ability to self-renew at the single-cell level [
13,
70]. As Muse cells are different from normal ESCs and iPSCs transplanted, Muse cells are naturally occurring in organisms and are autologous, they do not require cytokine pre-treatment before administration or introduction of genes into the cells for differentiation purposes.
Muse cells are able to spontaneously differentiate into tissue-constituent cells so that gene introduction and cytokine treatment are unnecessary, and there is little to no erroneous replacement of damaged/apoptotic cells after homing into damaged tissues. The process progresses rapidly compared to in vitro cytokine-induced differentiation [
13,
18,
46]. Most importantly, Muse are non-tumorigenic, consistent with the fact that they are present in the body. Pluripotency is both a curse and a blessing for stem cells, as the ability of the three germ layers to differentiate and self-renew is often uncontrolled, often resulting in the formation of teratomas. Telomerase activity remains high in stem cells, immortalized cancer cells, and ESCs/iPSCs, possibly to support their proliferation and self-renewal. Telomerase activity is also used as a marker of tumorigenic activity [
25,
27,
71]. The discovery of iPSCs is earlier than Muse cells, and there are many clinical studies. Although unlimited proliferation is the advantage of iPSCs, it has also become a defect that teratomas are easily formed in vivo after transplantation [
72].
On the other hand, the Lin28 gene plays a key role in maintaining the pluripotency of these two types of cells (ESCs and iPSCs) and in generating tumors, and Let-7 is a microRNA that regulates embryonic development, cell differentiation, and tumor inhibition [
73], this phenomenon is thought to prevent tumor formation and promote tissue regeneration [
74]. Unlike ESCs/iPSCs, Muse cells have low telomerase activity and extremely low expression of Lin28, but there is a gradual increase in Let-7 expression, which explains why it is not tumorigenic [
22]. Interestingly, while the proliferation of ESCs and iPSCs is dependent on leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) and bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4), in contrast, Muse cells are dependent on a family of fibroblast cytokines to maintain their self-renewal and proliferative capacity, which may also explain why it is not tumorigenic [
23]. From this, it is clear that Muse cells have evolved multiple fail-safe mechanisms to avoid growing themselves out of control. Previous studies have reported that Muse cells were transplanted into the testicles of immunodeficient mice with Muse iPS cells (treated Muse cells confer iPS properties) that did not form teratomas for up to 6 months, while the formation of teratomas after 12 weeks of implantation of Muse-iPS cells. The result indicated that non-tumorigenic Muse cells were induced by iPS cells to gain tumorigenic proliferative activity [
22]. Nowadays, there are no reports of side effects such as tumorigenicity after Muse cell transplantation in vivo. Based on animal models of existing diseases including acute myocardial infarction (AMI) [
55,
75], stroke [
56,
66], kidney fibrosis [
41], and other diseases [
42,
76,
77,
78], Muse cells not only stimulate tissue regeneration and recovery but also show that they do not form tumors in vivo after transplantation.
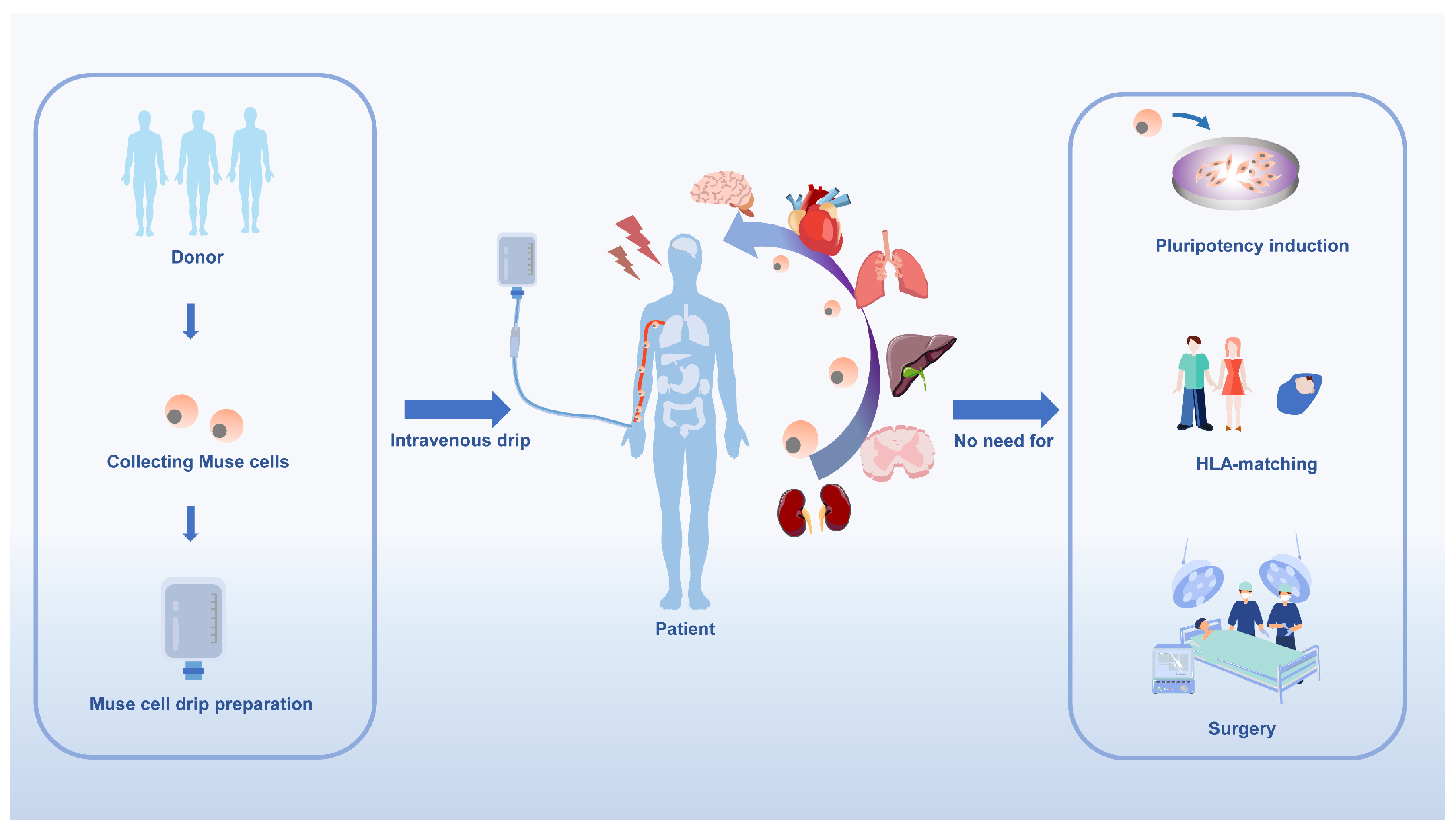
It is important to note that Muse cells can be administered intravenously, eliminating the need for surgery and reducing associated risks. Furthermore, they are a safe choice for clinical regeneration.
3.2. No human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-matching or immunosuppressive treatment.
It is well known that an issue that should be considered in allogeneic therapy is the immune response of the recipient after transplantation. This response has been recognized in organ and hematopoietic transplantation, so the use of immunosuppression is needed to protect allogeneic grafts from rejection [
79]. It is also important to consider that in vivo infusion or transplantation of allogeneic cells without appropriate human leukocyte antigen (HLA) or major histocompatibility complex (MHC) matching or the use of immunosuppression, the problem of cell rejection by the host’s immune system can quickly arise [
79,
80,
81]. In conclusion, immune rejection is the greatest challenge to allogeneic cell therapy [
82].
Surprisingly, allogeneic Muse cell transplants are free of immune rejection, eliminating the need to acquire immune tolerance through autologous or allogeneic transplantation[
83]. Donor-derived allogeneic Muse cells have the very beneficial feature of being administered directly to the patient without the need for HLA-matching and immunosuppressive treatment. Donor-derived Muse cells can migrate directly into patients without HLA-matching and immunosuppressive treatment [
55,
83,
84]. In a study of Muse cell entry into infarcted rabbit hearts, Muse cells expressed HLA-G higher than MSCs and were found that intravenously infused Muse cells could survive as differentiated cells in host tissues for more than 6 months, even without immunosuppressive treatment. This anti-immune property makes Muse cells useful not only in tissue repair but also in suppressing autoimmunity [
49]. Human leukocyte antigen G (HLA-G) is a mechanism evolved by placental mammals to prevent immune rejection of the placenta and the fetus it nurtures[
80,
85,
86]. Whereas Indoleamine 2,3- dioxygenase (IDO) inhibits the kynurenine pathway by promoting the degradation of tryptophan in T cells, thereby inhibiting T cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis [
86]. IDO is also involved in the maturation of regulatory T cells (Treg), which are necessary for the acquisition of immune tolerance, and it has been shown that Muse cells produce IDO at levels similar to MSC [
66,
86]. HLA-G is expressed in immune-exempt extravillous trophoblasts in the placenta and has a strong immunosuppressive effect, effectively inhibiting the proliferation and maturation of maternal macrophages, T-cells, B-cells, NK-cells, dendritic cells, and neutrophils [
15,
80,
81]; therefore, the expression of HLA-G may have a protective effect on Muse cells.
Briefly, the powerful anti-immune mechanism of Muse cells is due to the high expression of HLA-G and the immunomodulator IDO to suppress cellular and humoral immunity (
Figure 3). Muse cells may be used as immunomodulators to treat immune-related diseases.
3.3. Superior survivability in vivo
In the field of regenerative medicine, the use of stem cells is often limited by low survival rates, which often do not exceed 3% when exposed to high-stress transplantation environments[
87]. Stem cells may be subjected to multiple rounds of internal and external stresses and therefore must have robust and efficient DNA damage checkpoints and DNA repair mechanisms to promote full cellular recovery rather than triggering senescence and/or apoptosis in the event of a genotoxic event [
69,
87,
88]. Muse cells can be isolated by severe cellular stress conditions, including prolonged exposure to the protein hydrolase collagenase, serum deprivation, hypothermia, and hypoxia [
13,
22,
24,
25,
89]. At the same time, Muse cells display highly conserved cellular mechanisms essential for cell survival and proliferation in response to extreme cellular stress[
74].
Serpins are superfamily proteins that inhibit trypsin, thrombin, and neutrophil elastase with protease inhibitory activity[
90,
91]. Comparing the secretion sets of Muse cells, BM-MSCs, and adipose-derived MSCs (AD-MSCs), Serpins were only expressed in Muse cells, but not in BM-MSCs and AD-MSCs[
91,
92]. This may explain the high tolerance of Muse cells to prolonged pancreatic enzyme incubation [
13]. Moreover, most of the 14-3-3 isomers were involved in anti-apoptotic activity in the Muse cell secretion group [
68]. The 14-3-3-3 protein is a highly conserved family of 30 kDa molecules that form stable homo-and heterodimers [
93]. Accumulating evidence suggests that 14-3-3 protein plays a particularly important role in the activation, maintenance, and release of G1/S and G2/M cell cycle checkpoint activation. Besides, the 14-3-3 protein also plays a crucial role in regulating the response to DNA damage after intracellular and extracellular injury[
93,
94,
95,
96]. If cell damage occurs, the 14-3-3 protein prevents mitosis from entering the cell by regulating cyclin-related protein kinases and phosphatases [
93]. Therefore, Muse cells are stress-resistant, and their active secretion of pro-survival factors such as 14-3-3 proteins and serpins, may be the reason why they can survive in the hostile microenvironment of damaged tissues. These factors play a key role in regulating the cell’s response to DNA damage after internal or external damage. At the same time, it also reduces cell stress and subsequent damaged cell apoptosis.
Available studies show that human Muse cells survive as physiologically active cardiomyocytes in post-infarct cardiac tissue for 2 weeks after administration in rabbits [
49]. Similarly, human Muse cells were found to survive for 4 weeks in chemically induced Hunner-type interstitial cystitis-like rats [
65]. The harsh microenvironment of lung ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury contains both pro-apoptotic and pro-inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species [
97,
98]. In a study of acute lung ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury in a rat model, the results showed that human Muse cells were more effective at homing into damaged lung tissue, inhibiting apoptosis and promoting proliferation of host alveolar cells than MSCs [
64].
In certain diseases, such as stroke, myocardial infarction or renal failure, there is a high level of apoptosis and degeneration of tissue cells. This leads to a very stressful environment in the body and stem cell therapies may fail as the stem cells may be damaged before they can play a regenerative role. However, Muse cells show a strong ability to sense and survive DNA damage in these diseases and play a reparative role [
35,
39,
40,
75,
99]. In summary, Muse cells have a very active anti-stress and anti-cellular transformation protection mechanism, which is undoubtedly a very important property that contributes to the maintenance of their function and the promotion of tissue and organ homeostasis.
3.4. Tissue-protection effects
When tissues are damaged, the damage persists due to the inflammatory response in the microenvironment surrounding the injury that exacerbates apoptosis at the site of injury. Muse cells are able to spontaneously differentiate into cells compatible with their tissues [
47,
100], leading to robust tissue repair by replenishing functional cells. Indeed, Muse cells replace damaged/dead cells by differentiating into tissue-forming cells in vivo, which are immunomodulated and release anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and anti-fibrotic-related factors for tissue protection.
Due to the Muse cell’s pluripotent differentiation capacity, Muse cell-based therapy has been explored in a broad range of diseases. In a study of cell fate and function of human skin fibroblast-derived Muse cells were evaluated in a rat stroke model [
48], they differentiate with a high ratio into neuronal cells after integration with host brain microenvironment, possibly reconstructing the neuronal circuit to mitigate stroke symptoms. Muse cells not only home to damaged tissues, they also directly participate in the formation of new blood vessels by spontaneously differentiating into vascular cells, a process that involves the production of neovascularization activators VEGF and HGF, as shown by typical animal models of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) [
49], liver damage [
101,
102] and aortic aneurism [
103]. Thus, Muse cells have roles in both vascular protection and neovascularization. The above studies have shown that it can spontaneously differentiate into three germ layer lineages adapted to the tissue microenvironment, thereby protecting damaged tissue. The potent anti-inflammatory effects of Muse cells are augmented by the ability to survive for a long period as integrated cells in host tissues, whether autologous or allogeneic [
15,
104]. Macrophages also significantly reduced tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) production when co-cultured with Muse cells in vitro. Muse cells had a significant protective effect on the proliferative maintenance of TNF-α-injured intestinal epithelial crypt cells and on the intestinal barrier structure by decreasing the secretion of IL-6 and IFN-γ and increasing the release of TGF-β and IL-10 in the inflammatory microenvironment [
105]. In rat models of interstitial cystitis [
65] and severe pancreatitis [
42,
106], the administration of Muse cells significantly inhibited the infiltration of inflammatory cells such as macrophages and neutrophils and effectively reduced oedema at the site of injury, thereby protecting the tissues against further damage.
Muse cells survive in host tissues and remain integrated for an extended period of time, and their anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and paracrine effects are correspondingly long-lasting and effective. Thus, the pleiotropic nature of Muse cells allows them to exert potent tissue-protective effects, and their unique ability to provide viable therapeutic approaches for many diseases.
4. The regenerative potential of Muse cells has been confirmed.
To date, Muse cells have been used in neurological diseases [
63,
66,
107,
108,
109,
110,
111,
112], cardiac systemic diseases [
39,
49,
55,
75,
113,
114,
115,
116], renal diseases [
40,
99,
117], dermatological diseases [
44,
78,
118,
119,
120], liver diseases [
29,
41,
67,
101,
121], and other diseases to demonstrate their desirable effects in treating and repairing damaged tissues. In these disease models, Muse cells can migrate to the lesion site and spontaneously differentiate into histocompatible cells such as neurons (ectoderm) [
43,
111,
122], cardiomyocytes (mesoderm) [
115,
123], glomerulocytes (mesoderm) [
40,
117], vascular endothelial cells (mesoderm) [
34,
120]and hepatocytes (entoderm) [
41,
101,
121]. We have summarized the available preclinical studies in
Table 2.
4.1. The role of Muse cells in nervous system diseases
Currently, it is crucial to develop treatments that promote neurological recovery and rebuild damaged neural circuits. Neurological related diseases face a variety of obstacles and challenges. Lack of neuronal regenerative capacity leads to disability and death in many neurological disorders including stroke, and more typically neuroinflammation impedes central nervous system (CNS) repair, i.e., a massive loss and ineffective replenishment of neuronal cells, resulting in difficulty in regeneration of damaged neural tissue [
124]. Microglia are important immune cells in the CNS, which can be divided into two cell types, M1 and M2, and are sensitive to changes in the external environment, affecting the status of surrounding astrocytes and neuronal cells and regulating the immune response in the vicinity [
125,
126,
127]. Recent studies have found that Muse cells reduce neuroinflammatory responses in vitro by regulating the ratio of M1-type to M2-type microglia, possibly by inhibiting the small TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and p38 MAPK signalling pathways in microglia to exert anti-neuroinflammatory effects, providing new ideas for further application of Muse cells in the treatment of CNS diseases and Injuries [
107].
Among the available studies, Human BM-Muse cells cultured in serum-free/allogeneic medium were transplanted into an immunodeficient mouse model of lacunar cerebral infarction for 2 weeks, and it was found that after 8 weeks, approximately 28% of the initially transplanted Muse cells remained in the host brain and spontaneously differentiated into cells expressing NeuN (~62%), MAP2 (~30%), and GSTpi (~12%), and the final results showed that the model mice recovered their neurological function well, and the transplanted Muse cells differentiated into neurons and oligodendrocytes and participated in the reconstruction of cone fascicles, and have a favorable safety profile [
66]. Moreover, experiments with middle cerebral artery occlusion in immunodeficient mice demonstrated that Muse cells incorporated into the peri-infarct cortex were able to spontaneously differentiate into cells positive for the neuronal markers Tuj-1 (45.3 ± 13.9%) and NeuN (20.5 ± 8.7%), replenishing lost neurons and thus restoring motor function [
62]. In a mouse model of ICH, Muse cells can integrate into the region of cerebral vascular injury and differentiate into Neu N- and MAP-2-positive neurons, improving survival and motor function [
63]. In addition, in model studies of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy [
109], amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) [
128], and E. coli-associated encephalopathy [
112], Muse cells have therapeutically mitigated the lethality of the disease and facilitated tissue repair through spontaneous differentiation into neurons and neuroglia after homing into the damaged central nervous system.
The use of Muse cells promises to be an effective means of treating CNS disorders. Seed cells that both promote nerve regeneration and improve the CNS microenvironment.
4.2. The role of Muse cells in cardiovascular system diseases
Using Semi-clinical grade human Muse cell product in the Swine model of acute myocardial infarction, Muse cells homed to the infarct margins and differentiated into cardiomyocytes (troponin I-positive) and microvessels (CD31-positive), which were able to reduce the size of the infarcts and improve ventricular function and remodeling[
116]. In an acute myocardial infarction model, Muse cells homed to post-infarct tissue and spontaneously differentiated within 2 weeks into cells positive for cardiomyocyte markers such as troponin-I, α-actinin and connexin 43 proteins, exhibiting calcium inward and outward currents synchronized with electrocardiogram-recorded cardiac activity, and the expression of MLC 2a (Myosin Light Chain 2a) and MLC 2v (Myosin Light Chain 2v), which also demonstrated the ability of Muse cells to differentiate into atrial and ventricular cardiomyocytes [
39].
In conclusion, Muse cells are capable of spontaneous differentiation into cardiac and vascular lineages, and additionally have extraordinary potential for the treatment of cardiovascular disease through regeneration of cardiomyocytes and blood vessels, as well as paracrine effects that more dramatically reduce the size of myocardial infarcts and improve cardiac function [
115].
4.3. The role of Muse cells in skin regeneration
Transplantation of Muse cells promotes reconstruction of damaged skin tissue by replenishing new dermal and epidermal cells. In a report of skin ulcers in type 1 diabetic immunodeficient mice, Muse cell-treated ulcers showed faster healing with thicker epidermis [
34]. In addition, after induction of Muse-AT cells into fibroblasts, keratinocytes and melanocytes, skin sheets were reconstructed by these differentiated cells and collagen gel layers, and the reconstructed hyperpigmented skin formed an epidermal-like structure [
31]. CL2020, a clinical-grade Muse cell product, administered to patients with epidermolysis bullosa reduced painful skin ulcers [
78]. Thus, transplantation of Muse cells may be an effective treatment for skin-related diseases.
4.4. The role of Muse cells in liver diseases
Muse cells are integrated as hepatic progenitor cells in the early stage, and then spontaneously differentiate into major liver components such as hepatocytes, bile duct cells, sinusoidal endothelial cells and Kupffer cells in the physical partial hepatectomy model[
129]. In a mouse model of liver injury, human Muse cells expressing CK19, DLK, OV6 and alpha-fetoprotein (markers of hepatic progenitor cells) 2 days after intravesical injection and expressing the mature hepatocyte markers HepPar1, albumin and antitrypsin within 2 weeks had a very high homing rate in damaged livers and stayed in host tissues for 8 weeks, integrating briefly by intravenous injection into the damaged liver, spontaneously differentiated into hepatocytes in vivo, and finally significantly improved liver function in model mice by attenuating fibrosis [
41]. Postoperative liver failure (PHLF) is a potentially fatal complication. The safety and efficacy of transapical infusion of allogeneic Muse cells in a porcine model of PHLF was assessed. Specific homing of Muse cells to the liver resulted in improved control of hyperbilirubinaemia, the international normalized ratio of prothrombinogen (P = 0.05), and suppression of focal necrosis. The integrated Muse cells spontaneously differentiated into hepatocyte marker-positive cells. Muse cell transplantation may provide a reparative role and functional recovery in a hepatic resection model and thus may contribute to the treatment of PHLF [
67,
129].
These studies suggest that Muse cells are a viable stem cell type for the treatment of liver disease.
4.5. The role of Muse cells in another disease (including lung injuries, kidney disease, osteochondral defects)
Muse cells have also been highlighted in other diseases as follows. Human Muse cell administration improved lung function and histological damage associated with acute phase ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model. Muse cells were more abundant in lung tissue from ischemia-reperfusion injury compared to MSCs. Human Muse cells secreted beneficial substances (KGF, HGF, Ang-1 and PGE 2) in vitro, and it is possible that these protective factors together exert tissue repair, apoptosis prevention and alveolar fluid clearance [
64,
97,
98]. Muse cells also have therapeutic potential for osteochondral repair[
68]. Osteochondral defects were produced in the patellar groove of immunodeficient rats and intra-articular injected with Muse cells. At 12 weeks, the Muse defects were completely filled with smooth homogenous tissue, which made it difficult to clearly identify the defect edges. Although the repaired tissue in the Muse group was negative for type II collagen, indicating unsatisfactory cartilage repair, histological scoring showed better subchondral bone repair at the site of the cartilage defect. Extensive studies on the cartilage-forming potential of Muse cells are needed. Muse cells have great potential for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and other inflammatory diseases of the gut [
105].
In conclusion, it is worth keeping an eye on the powerful regenerative capacity of Muse cells, and I believe there are many more promising therapeutic effects in the pipeline!
Table 2.
Preclinical Studies Using Muse Cells for Various Diseases.
Table 2.
Preclinical Studies Using Muse Cells for Various Diseases.
| Category |
Model of Disease Indications |
Tissue Source of Muse cells |
Mechanisms for repairing damage |
Administration method |
References |
| Nervous system |
Lacunar stroke |
Bone marrow & CL2020* |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration & Local injection |
[66,130] |
| Ischemic stroke |
Bone marrow & Dermal fibroblasts |
Replenishment of neurons and oligodendrocytes, reconstruction of neuronal circuit |
Intravenous administration
& Local injection |
[48,62] |
Intracerebral
Hemorrhage (ICH) |
Bone marrow |
Differentiation |
Local injection |
[63] |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) |
Bone marrow |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[128] |
| Neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy (HIE) |
CL2020* |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[131] |
| spinal cord injury (SCI) |
Bone marrow |
Differentiation |
Local injection |
[108] |
| E. coli-associated encephalopathy |
Bone marrow |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[112] |
| Thoracic spinal cord contusion injury |
Bone marrow & CL2020* |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[110] |
| Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy |
Bone marrow |
Regulation of glutamate metabolism and Reduction of microglial activation. |
Intravenous administration |
[109] |
| Cardiovascular system |
acute myocardial infarction (AMI) |
Bone marrow & CL2020* |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[49,115,116] |
| Dermatosis |
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) |
Bone marrow & CL2020* |
differentiated into keratinocytes and functionally restored basement membrane zone (BMZ) proteins at the injury site |
Intravenous administration |
[78,132] |
| Diabetic skin ulcers |
Adipose |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[34] |
| Atopic dermatitis |
Bone marrow |
promote the migration and proliferation of keratinocytes |
Subcutaneous injection |
[119] |
| Corneal scarring wound |
Abdominal lipoaspirate tissue |
increased corneal re-epithelialization and nerve regrowth, and reduced the severity of corneal inflammation and neovascularization. |
Placed with scaffold |
[118] |
| Kidney disease |
Adriamycin Nephropathy |
Bone marrow |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[40] |
| Liver disease |
Liver fibrosis |
Bone marrow |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[41] |
| Post-hepatectomy liver failure |
Bone marrow |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[129] |
| Lung disease |
Acute lung ischemia-reperfusion Injury |
Bone marrow |
secreted several substances involved in wound healing |
Injected into pulmonary artery |
[64] |
| Another disease |
Aortic aneurysms |
Bone marrow |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[103] |
| Acute pancreatitis |
Bone marrow |
attenuating edema, inflammation and apoptosis |
Intravenous administration |
[42] |
| Cartilage lesions |
Bone marrow |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[133] |
| Cartilage defects |
Synovial tissue & Bone marrow |
Differentiation |
Intravenous administration |
[30,68] |
| Intestinal inflammatory diseases |
Bone marrow |
Anti-inflammatory and immune regulatory functionality |
Intravenous administration |
[105] |
| Hunner-type interstitial cystitis (HIC) |
Bone marrow |
Paracrine effect |
Injected into the anterior and posterior bladder wall |
[65] |
| Diabetes mellitus |
Adipose |
Paracrine effect |
Intravenous administration |
[76,106] |
5. Future Prospects and Challenges
Muse cells have features that compensate for the shortcomings of current stem cells such as iPSCs and ESCs. These cells are naturally occurring reparative stem cells in the body that do not cause tumors, have the ability to differentiate spontaneously, and can be targeted to damaged tissues through the S1P-S1PR2 axis. Furthermore, Muse cells do not require gene introduction or cytokine induction to present pluripotency or induce differentiation into the cell type of interest prior to clinical use before treatment, and it is an expedient for patients to provide viable regenerative therapy through intravenous infusion.
Even though Muse cells have practical advantages for regenerative medicine, there are still unresolved difficulties and some unknown challenges. Although Muse cells naturally exist as endogenous cells rather than immortalized or monoclonal expanded tumorigenic cells, the homogeneity of Muse cells remains unknown. Additionally, Muse cells account for only a small population of various sources and take time to expand to enough cells for clinical administration. Take stroke as an example, the time window is narrow [
134,
135], and patients cannot use freshly prepared Muse cells.
In particular, compared with MSCs, the culture cost of Muse cells is more expensive and the culture procedure is more complex. Moreover, complex steps will introduce more variable parameters, resulting in inconsistent product quality of different batches of cells, and ultimately lead to different treatment outcomes after clinical transplantation. At present, Muse cells clinical trials are limited for diseases. In view of the above-mentioned facts, Muse cells are in urgent need of gold standardization, to establish a strict GMP compliance process, to provide patients with high quality, high consistency Muse cells in urgent need of gold standardization. Furthermore, the complex mechanisms and pathways by which Muse cells differentiate into histocompatibility cells are still far from being fully understood. Therefore, it is necessary to further investigate which signaling pathways or transcription factors control the differentiation of Muse cells into specific directions. For example, by introducing the relevant genes into Muse cells or modifying them with nanomaterials, it may be possible to increase the rate of differentiation into the intended cell line after transplantation to the damaged site.
Its impressive regenerative properties may provide a simple and feasible strategy to treat a variety of diseases. The Muse cell is being used as a delivery system that may play a role in improving the delivery of drugs and lysosomal viruses to recalcitrant tumors, and may also be considered for engineering into molecules with angiogenic, neurotrophic and anti-inflammatory properties to accelerate the repair of damaged or diseased tissues. Therefore, the unique properties of Muse cells and their great potential in repairing damage need further research and development.
Author Contributions
HQ, JG, and PG conceived the idea, analysis of literature, and writing of the manuscript; WZ, YJ, FH, XL collected, summarized, and read the literature; PG revised the article; EM, YH, HL proofread the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 82174083), and a special fund project for basic research business expenses of the central universities of Southwest Minzu University (Grant Number: 2022NYXXS004).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Abbreviations
Muse, Multilineage-differentiating stress-enduring; S1P, sphingosine-monophosphate; S1PR2, sphingosine-monophosphate receptor 2; MSCs, mesenchymal stromal cells; MSCs, Mesenchymal Stem Cells; BM, bone marrow; SSEA-3, Stage-specific embryonic antigen 3; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; MACS, magnetically-affinitive cell sorting; PB, peripheral blood; AT, adipose tissue; UC, umbilical cord; BMMSCs, bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells; UC -MSCs, umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells; MenSC, menstrual blood-derived endometrial stem cells; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; OCT3/4, octamer binding transcription factor 3/4; SOX2, sex-determining region Y box 2; REX1, reduced expression 1; DDR, DNA damage response; LIF, leukemia inhibitory factor; BMP4, bone morphogenetic protein 4; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; HLA-G, Human leukocyte antigen G; IDO, Indoleamine 2,3- dioxygenase; Treg, regulatory T cells; AD-MSCs, adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells; IR, ischemia-reperfusion; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; S1PR2, specific G-protein-coupled receptors receptor 2; AMI, acute myocardial infarction; ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage; CNS, central nervous system; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; PHLF, Postoperative liver failure; HIE, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; SCI, spinal cord injury; EB, Epidermolysis bullosa; BMZ, basement membrane zone; HIC, Hunner-type interstitial cystitis.
References
- Sobral-Reyes, M.F.; Lemos, D.R. Recapitulating Human Tissue Damage, Repair, and Fibrosis with Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Organoids. Stem Cells Dayt. Ohio 2020, 38, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Walsh, C.; Yue, D.; Dardik, A.; Cheema, U. Current Advancements and Strategies in Tissue Engineering for Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Wound Care 2017, 6, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, M.; Ungaro, F.; Quaglia, F.; Netti, P.A. Controlled Drug Delivery in Tissue Engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, G.; Su, J.; Li, W.; Chen, Q.; Shou, P.; Xu, C.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A New Strategy for Immunosuppression and Tissue Repair. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, J.M.; Harrison, R.S.; Fishman, M.C. Fundamental Science behind Today’s Important Medicines. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaaq1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, N.; Badylak, S. Regenerative Medicine: Today’s Discoveries Informing the Future of Medical Practice. NPJ Regen. Med. 2016, 1, 16007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stem Cells: Therapeutic Applications; Ratajczak, M. Z., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; Vol. 1201, ISBN 978-3-030-31205-3. [Google Scholar]
- Trounson, A.; McDonald, C. Stem Cell Therapies in Clinical Trials: Progress and Challenges. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorecka, J.; Kostiuk, V.; Fereydooni, A.; Gonzalez, L.; Luo, J.; Dash, B.; Isaji, T.; Ono, S.; Liu, S.; Lee, S.R.; et al. The Potential and Limitations of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells to Achieve Wound Healing. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doss, M.X.; Sachinidis, A. Current Challenges of iPSC-Based Disease Modeling and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2019, 8, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volarevic, V.; Markovic, B.S.; Gazdic, M.; Volarevic, A.; Jovicic, N.; Arsenijevic, N.; Armstrong, L.; Djonov, V.; Lako, M.; Stojkovic, M. Ethical and Safety Issues of Stem Cell-Based Therapy. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Daoud, A.M.; Popovic, M.; Dondorp, W.J.; Trani Bustos, M.; Bredenoord, A.L.; Chuva de Sousa Lopes, S.M.; van den Brink, S.C.; Roelen, B.A.J.; de Wert, G.M.W.R.; Heindryckx, B. Modelling Human Embryogenesis: Embryo-like Structures Spark Ethical and Policy Debate. Hum. Reprod. Update 2020, 26, 779–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y.; Kitada, M.; Wakao, S.; Nishikawa, K.; Tanimura, Y.; Makinoshima, H.; Goda, M.; Akashi, H.; Inutsuka, A.; Niwa, A.; et al. Unique Multipotent Cells in Adult Human Mesenchymal Cell Populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107, 8639–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakao, S.; Akashi, H.; Kushida, Y.; Dezawa, M. Muse Cells, Newly Found Non-Tumorigenic Pluripotent Stem Cells, Reside in Human Mesenchymal Tissues. Pathol. Int. 2014, 64, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezawa, M. Muse Cells Provide the Pluripotency of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Direct Contribution of Muse Cells to Tissue Regeneration. Cell Transplant. 2016, 25, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguma, Y.; Kuroda, Y.; Wakao, S.; Kushida, Y.; Dezawa, M. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Different Signatures of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Pluripotent-like and Multipotent Populations. iScience 2022, 25, 105395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wakao, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Kushida, Y.; Dezawa, M. Chapter 7 - Muse Cells as a Robust Source of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. In Cell Sources for iPSCs; Birbrair, A., Ed.; Advances in Stem Cell Biology; Academic Press, 2021; Vol. 7, pp. 137–161 ISBN 978-0-12-822135-8.
- Simerman, A.A.; Perone, M.J.; Gimeno, M.L.; Dumesic, D.A.; Chazenbalk, G.D. A Mystery Unraveled: Nontumorigenic Pluripotent Stem Cells in Human Adult Tissues. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2014, 14, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, D.; Alessio, N.; Demirsoy, I.H.; Squillaro, T.; Peluso, G.; Di Bernardo, G.; Galderisi, U. MUSE Stem Cells Can Be Isolated from Stromal Compartment of Mouse Bone Marrow, Adipose Tissue, and Ear Connective Tissue: A Comparative Study of Their In Vitro Properties. Cells 2021, 10, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-J.; Kuo, H.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Yang, B.-C.; Cheng, Y.-Y.; Yu, A.L.; Khoo, K.-H.; Yu, J. Switching of the Core Structures of Glycosphingolipids from Globo- and Lacto- to Ganglio-Series upon Human Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107, 22564–22569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Wakao, S.; Kushida, Y.; Tatsumi, K.; Kitada, M.; Abe, T.; Niizuma, K.; Tominaga, T.; Kushimoto, S.; Dezawa, M. A Novel Type of Stem Cells Double-Positive for SSEA-3 and CD45 in Human Peripheral Blood. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720923574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakao, S.; Kitada, M.; Kuroda, Y.; Shigemoto, T.; Matsuse, D.; Akashi, H.; Tanimura, Y.; Tsuchiyama, K.; Kikuchi, T.; Goda, M.; et al. Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring (Muse) Cells Are a Primary Source of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in Human Fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2011, 108, 9875–9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakao, S.; Kushida, Y.; Dezawa, M. Basic Characteristics of Muse Cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1103, 13–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, Y.; Wakao, S.; Kitada, M.; Murakami, T.; Nojima, M.; Dezawa, M. Isolation, Culture and Evaluation of Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring (Muse) Cells. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1391–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, F.; Wakao, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Tsuchiyama, K.; Bagheri, M.; Heneidi, S.; Chazenbalk, G.; Aiba, S.; Dezawa, M. Human Adipose Tissue Possesses a Unique Population of Pluripotent Stem Cells with Nontumorigenic and Low Telomerase Activities: Potential Implications in Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cells Dev. 2014, 23, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneidi, S.; Simerman, A.A.; Keller, E.; Singh, P.; Li, X.; Dumesic, D.A.; Chazenbalk, G. Awakened by Cellular Stress: Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Population of Pluripotent Stem Cells Derived from Human Adipose Tissue. PloS One 2013, 8, e64752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Li, D.; Cheng, S.; Yang, Y.; Tian, T.; Pan, X. Muse Cells, a New Type of Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived from Human Fibroblasts. Cell. Reprogramming 2016, 18, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Z.; Sun, D.; Huang, Z.; Tadmori, I.; Chiang, N.; Kethidi, N.; Sabra, A.; Kushida, Y.; Fu, Y.-S.; Dezawa, M.; et al. Quantitative Analysis of SSEA3+ Cells from Human Umbilical Cord after Magnetic Sorting. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Katagiri, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Nitta, H.; Sasaki, A. Mobilization of Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring Cells into the Peripheral Blood in Liver Surgery. PloS One 2022, 17, e0271698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, E.; Sato, M.; Takahashi, T.; Maehara, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Mitani, G.; Takagaki, T.; Hamahashi, K.; Watanabe, M. Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring (Muse)-like Cells Exist in Synovial Tissue. Regen. Ther. 2019, 10, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiyama, K.; Wakao, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Ogura, F.; Nojima, M.; Sawaya, N.; Yamasaki, K.; Aiba, S.; Dezawa, M. Functional Melanocytes Are Readily Reprogrammable from Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring (Muse) Cells, Distinct Stem Cells in Human Fibroblasts. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2425–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimeno, M.L.; Fuertes, F.; Barcala Tabarrozzi, A.E.; Attorressi, A.I.; Cucchiani, R.; Corrales, L.; Oliveira, T.C.; Sogayar, M.C.; Labriola, L.; Dewey, R.A.; et al. Pluripotent Nontumorigenic Adipose Tissue-Derived Muse Cells Have Immunomodulatory Capacity Mediated by Transforming Growth Factor-Β1. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhang, R.-Z.; Yang, Y.-H.; Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Pan, X.-R. Muse Cells Derived from Dermal Tissues Can Differentiate into Melanocytes. Cell. Reprogramming 2017, 19, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, K.; Kuno, S.; Ishimine, H.; Aoi, N.; Mineda, K.; Kato, H.; Doi, K.; Kanayama, K.; Feng, J.; Mashiko, T.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Adipose-Derived SSEA-3-Positive Muse Cells for Treating Diabetic Skin Ulcers. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wei, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Lin, J. Muse Cells: Ushering in a New Era of Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Stroke. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisch, S.C.; Gimeno, M.L.; Phan, J.D.; Simerman, A.A.; Dumesic, D.A.; Perone, M.J.; Chazenbalk, G.D. Pluripotent Nontumorigenic Multilineage Differentiating Stress Enduring Cells (Muse Cells): A Seven-Year Retrospective. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simerman, A.A.; Dumesic, D.A.; Chazenbalk, G.D. Pluripotent Muse Cells Derived from Human Adipose Tissue: A New Perspective on Regenerative Medicine and Cell Therapy. Clin. Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ee, M.; N, K.; R, S.; S, W.; M, D.; N, A.; M, O. Therapeutic Potential of Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring Cells for Osteochondral Repair in a Rat Model. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Kushida, Y.; Wakao, S.; Kitada, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Dezawa, M. Cardiotrophic Growth Factor–Driven Induction of Human Muse Cells Into Cardiomyocyte-Like Phenotype. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, N.; Kushida, Y.; Kitada, M.; Wakao, S.; Kumagai, N.; Kuroda, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Hirohara, Y.; Kure, S.; Chazenbalk, G.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Systemically Administered Human Muse Cells in Adriamycin Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2017, 28, 2946–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, M.; Kushida, Y.; Wakao, S.; Akimoto, T.; Mizuma, M.; Motoi, F.; Asada, R.; Shimizu, S.; Unno, M.; Chazenbalk, G.; et al. Muse Cells, Nontumorigenic Pluripotent-Like Stem Cells, Have Liver Regeneration Capacity Through Specific Homing and Cell Replacement in a Mouse Model of Liver Fibrosis. Cell Transplant. 2017, 26, 821–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukase, M.; Sakata, N.; Kushida, Y.; Wakao, S.; Unno, M.; Dezawa, M. Intravenous Injection of Human Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring Cells Alleviates Mouse Severe Acute Pancreatitis without Immunosuppressants. Surg. Today 2022, 52, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Kushida, Y.; Abe, K.; Dezawa, M. Non-Tumorigenic Pluripotent Reparative Muse Cells Provide a New Therapeutic Approach for Neurologic Diseases. Cells 2021, 10, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Yamasaki, K.; Tsuchiyama, K.; Koike, S.; Aiba, S. The Potential of Muse Cells for Regenerative Medicine of Skin: Procedures to Reconstitute Skin with Muse Cell-Derived Keratinocytes, Fibroblasts, and Melanocytes. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2639–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushida, Y.; Wakao, S.; Dezawa, M. Muse Cells Are Endogenous Reparative Stem Cells. In Muse Cells; Dezawa, M., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer Japan: Tokyo, 2018; Vol. 1103, pp. 43–68. ISBN 978-4-431-56845-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kushida, Y.; Wakao, S.; Dezawa, M. Muse Cells Are Endogenous Reparative Stem Cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1103, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, H.; Kushida, Y.; Nojima, M.; Kuroda, Y.; Wakao, S.; Ishida, K.; Endo, F.; Kume, K.; Takahara, T.; Nitta, H.; et al. A Distinct Subpopulation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Muse Cells, Directly Commit to the Replacement of Liver Components. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2016, 16, 468–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, H.; Morita, T.; Niizuma, K.; Kushida, Y.; Kuroda, Y.; Wakao, S.; Sakata, H.; Matsuzaka, Y.; Mushiake, H.; Tominaga, T.; et al. Transplantation of Unique Subpopulation of Fibroblasts, Muse Cells, Ameliorates Experimental Stroke Possibly via Robust Neuronal Differentiation. Stem Cells Dayt. Ohio 2016, 34, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Wakao, S.; Kushida, Y.; Minatoguchi, S.; Mikami, A.; Higashi, K.; Baba, S.; Shigemoto, T.; Kuroda, Y.; Kanamori, H.; et al. S1P-S1PR2 Axis Mediates Homing of Muse Cells Into Damaged Heart for Long-Lasting Tissue Repair and Functional Recovery After Acute Myocardial Infarction. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1069–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigert, A.; Olesch, C.; Brüne, B. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate and Macrophage Biology-How the Sphinx Tames the Big Eater. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obinata, H.; Hla, T. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate and Inflammation. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Takuwa, N.; Yoshioka, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Gonda, K.; Sugihara, K.; Fukamizu, A.; Asano, M.; Takuwa, Y. S1P(2), the G Protein-Coupled Receptor for Sphingosine-1-Phosphate, Negatively Regulates Tumor Angiogenesis and Tumor Growth in Vivo in Mice. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Van Brocklyn, J.R.; Thangada, S.; Liu, C.H.; Hand, A.R.; Menzeleev, R.; Spiegel, S.; Hla, T. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate as a Ligand for the G Protein-Coupled Receptor EDG-1. Science 1998, 279, 1552–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Takuwa, N.; Gonda, K.; Okazaki, H.; Chang, K.; Yatomi, Y.; Shigematsu, H.; Takuwa, Y. EDG1 Is a Functional Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor That Is Linked via a Gi/o to Multiple Signaling Pathways, Including Phospholipase C Activation, Ca2+ Mobilization, Ras-Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activation, and Adenylate Cyclase Inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 27104–27110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Nishigaki, K.; Minatoguchi, S.; Nawa, T.; Yamada, Y.; Kanamori, H.; Mikami, A.; Ushikoshi, H.; Kawasaki, M.; Dezawa, M.; et al. Mobilized Muse Cells After Acute Myocardial Infarction Predict Cardiac Function and Remodeling in the Chronic Phase. Circ. J. Off. J. Jpn. Circ. Soc. 2018, 82, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, E.; Hayakawa, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Hori, S.; Okamoto, S.; Shibata, T.; Kubo, M.; Horie, Y.; Sasahara, M.; Kuroda, S. Mobilization of Pluripotent Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring Cells in Ischemic Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2016, 25, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, A.; Futrega, K.; Liang, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Crawford, D.H.G.; Doran, M.R.; Roberts, M.S.; Wang, H. Concise Review: Quantitative Detection and Modeling the In Vivo Kinetics of Therapeutic Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, A.; Futrega, K.; Liang, X.; Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Crawford, D.H.G.; Doran, M.R.; Roberts, M.S.; Wang, H. Concise Review: Quantitative Detection and Modeling the In Vivo Kinetics of Therapeutic Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer-Smith, A.R.; Findlay, I.A.; Bomba, H.N.; Hingtgen, S.D. Intravenously Infused Stem Cells for Cancer Treatment. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2021, 17, 2025–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Mao, N. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alter Migratory Property of T and Dendritic Cells to Delay the Development of Murine Lethal Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease. Stem Cells Dayt. Ohio 2008, 26, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbash, I.M.; Chouraqui, P.; Baron, J.; Feinberg, M.S.; Etzion, S.; Tessone, A.; Miller, L.; Guetta, E.; Zipori, D.; Kedes, L.H.; et al. Systemic Delivery of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to the Infarcted Myocardium: Feasibility, Cell Migration, and Body Distribution. Circulation 2003, 108, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kuroda, Y.; Morita, T.; Shichinohe, H.; Houkin, K.; Dezawa, M.; Kuroda, S. Therapeutic Effects of Human Multilineage-Differentiating Stress Enduring (MUSE) Cell Transplantation into Infarct Brain of Mice. PloS One 2015, 10, e0116009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, N.; Kakuta, K.; Wang, L.; Naraoka, M.; Uchida, H.; Wakao, S.; Dezawa, M.; Ohkuma, H. Neuro-Regeneration Therapy Using Human Muse Cells Is Highly Effective in a Mouse Intracerebral Hemorrhage Model. Exp. Brain Res. 2017, 235, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabuki, H.; Wakao, S.; Kushida, Y.; Dezawa, M.; Okada, Y. Human Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring Cells Exert Pleiotropic Effects to Ameliorate Acute Lung Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in a Rat Model. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, A.; Kuroda, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Egawa, S.; Dezawa, M.; Yoshimura, N. Effects of Human Muse Cells on Bladder Inflammation, Overactivity, and Nociception in a Chemically Induced Hunner-Type Interstitial Cystitis-like Rat Model. Int. Urogynecology J. 2022, 33, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, H.; Niizuma, K.; Kushida, Y.; Wakao, S.; Tominaga, T.; Borlongan, C.V.; Dezawa, M. Human Muse Cells Reconstruct Neuronal Circuitry in Subacute Lacunar Stroke Model. Stroke 2017, 48, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizuka, S.S.; Suzuki, Y.; Katagiri, H.; Takikawa, Y. Liver Regeneration Supported by Muse Cells. In Muse Cells; Dezawa, M., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer Japan: Tokyo, 2018; Vol. 1103, pp. 219–241. ISBN 978-4-431-56845-2. [Google Scholar]
- Alessio, N.; Özcan, S.; Tatsumi, K.; Murat, A.; Peluso, G.; Dezawa, M.; Galderisi, U. The Secretome of MUSE Cells Contains Factors That May Play a Role in Regulation of Stemness, Apoptosis and Immunomodulation. Cell Cycle Georget. Tex 2017, 16, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessio, N.; Squillaro, T.; Özcan, S.; Di Bernardo, G.; Venditti, M.; Melone, M.; Peluso, G.; Galderisi, U. Stress and Stem Cells: Adult Muse Cells Tolerate Extensive Genotoxic Stimuli Better than Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19328–19341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rs, W.; Sl, T.; Sl, H.; Am, B. A New Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Paradigm: Polarization into a pro-Inflammatory MSC1 or an Immunosuppressive MSC2 Phenotype. PloS One 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, F.; Okuka, M.; Liu, N.; Ji, G.; Ye, X.; Zuo, B.; Li, M.; Liang, P.; Ge, W.W.; et al. Association of Telomere Length with Authentic Pluripotency of ES/iPS Cells. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S. Pluripotent Stem Cell-Based Cell Therapy-Promise and Challenges. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.E.; Gregory, R.I. How Does Lin28 Let-7 Control Development and Disease? Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simerman, A.A.; Phan, J.D.; Dumesic, D.A.; Chazenbalk, G.D. Muse Cells: Nontumorigenic Pluripotent Stem Cells Present in Adult Tissues-A Paradigm Shift in Tissue Regeneration and Evolution. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 1463258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minatoguchi, S.; Mikami, A.; Tanaka, T.; Minatoguchi, S.; Yamada, Y. Acute Myocardial Infarction, Cardioprotection, and Muse Cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1103, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perone, M.J.; Gimeno, M.L.; Fuertes, F. Immunomodulatory Properties and Potential Therapeutic Benefits of Muse Cells Administration in Diabetes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1103, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoyama, K.; Saiki, Y. Muse Cells and Aortic Aneurysm. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1103, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Komatsu, M.; Lee, S.E.; Kushida, Y.; Nakayama-Nishimura, C.; Matsumura, W.; Takashima, S.; Shinkuma, S.; Nomura, T.; Masutomi, N.; et al. Intravenous Injection of Muse Cells as a Potential Therapeutic Approach for Epidermolysis Bullosa. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 198–202.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinen, J.; Buckley, R.H. Transplantation Immunology: Solid Organ and Bone Marrow. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, S324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kot, M.; Baj-Krzyworzeka, M.; Szatanek, R.; Musiał-Wysocka, A.; Suda-Szczurek, M.; Majka, M. The Importance of HLA Assessment in “Off-the-Shelf” Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Based-Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankrum, J.A.; Ong, J.F.; Karp, J.M. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Immune Evasive, Not Immune Privileged. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, S.; Yang, P.; Cao, H.; Li, L. The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Prevention and Treatment of Graft-versus-Host Disease. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W. Future of Muse Cells. In Muse Cells; Dezawa, M., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer Japan: Tokyo, 2018; Vol. 1103, pp. 309–315. ISBN 978-4-431-56845-2. [Google Scholar]
- Dezawa, M. Clinical Trials of Muse Cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1103, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lila, N.; Amrein, C.; Guillemain, R.; Chevalier, P.; Latremouille, C.; Fabiani, J.-N.; Dausset, J.; Carosella, E.D.; Carpentier, A. Human Leukocyte Antigen-G Expression after Heart Transplantation Is Associated with a Reduced Incidence of Rejection. Circulation 2002, 105, 1949–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipnis, S.; Viswanathan, C.; Majumdar, A.S. Immunosuppressive Properties of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Role of B7-H1 and IDO. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2010, 88, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tower, J. Stress and Stem Cells. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2012, 1, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgetts, S.I.; Beilharz, M.W.; Scalzo, A.A.; Grounds, M.D. Why Do Cultured Transplanted Myoblasts Die in Vivo? DNA Quantification Shows Enhanced Survival of Donor Male Myoblasts in Host Mice Depleted of CD4+ and CD8+ Cells or Nk1.1+ Cells. Cell Transplant. 2000, 9, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezawa, M. The Muse Cell Discovery, Thanks to Wine and Science. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aymonnier, K.; Kawecki, C.; Arocas, V.; Boulaftali, Y.; Bouton, M.C. Serpins, New Therapeutic Targets for Hemophilia. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 121, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellici, T.F.; Pilka, E.S.; Bodkin, M.J. Small-Molecule Modulators of Serine Protease Inhibitor Proteins (Serpins). Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakao, S.; Kushida, Y.; Dezawa, M. Basic Characteristics of Muse Cells. In Muse Cells; Dezawa, M., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer Japan: Tokyo, 2018; Vol. 1103, pp. 13–41. ISBN 978-4-431-56845-2. [Google Scholar]
- Clapp, C.; Portt, L.; Khoury, C.; Sheibani, S.; Norman, G.; Ebner, P.; Eid, R.; Vali, H.; Mandato, C.A.; Madeo, F.; et al. 14-3-3 Protects against Stress-Induced Apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardino, A.K.; Yaffe, M.B. 14-3-3 Proteins as Signaling Integration Points for Cell Cycle Control and Apoptosis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, C.C.; Ottmann, C.; Perry, M.W.D. 14-3-3 Modulation of the Inflammatory Response. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obsilova, V.; Obsil, T. Structural Insights into the Functional Roles of 14-3-3 Proteins. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zheng, M.; Hou, H.; Fang, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Yao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Hei, Z. Cellular Senescence in Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuki, H.; Watanabe, T.; Oishi, H.; Katahira, M.; Kanehira, M.; Okada, Y. Muse Cells and Ischemia-Reperfusion Lung Injury. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1103, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, N.; Kumagai, N.; Kondo, Y. Application of Muse Cell Therapy for Kidney Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1103, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushida, Y.; Wakao, S.; Dezawa, M. Muse Cells Are Endogenous Reparative Stem Cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1103, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shono, Y.; Kushida, Y.; Wakao, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Unno, M.; Kamei, T.; Miyagi, S.; Dezawa, M. Protection of Liver Sinusoids by Intravenous Administration of Human Muse Cells in a Rat Extra-Small Partial Liver Transplantation Model. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2021, 21, 2025–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessheimer, A.J.; Vengohechea, J.; Fondevila, C. The Hepatic Sinusoid: The “Muse” in Small-for-Size Liver Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2021, 21, 1998–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoyama, K.; Wakao, S.; Kushida, Y.; Ogura, F.; Maeda, K.; Adachi, O.; Kawamoto, S.; Dezawa, M.; Saiki, Y. Intravenously Injected Human Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring Cells Selectively Engraft into Mouse Aortic Aneurysms and Attenuate Dilatation by Differentiating into Multiple Cell Types. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 155, 2301–2313.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgetts, S.I.; Beilharz, M.W.; Scalzo, A.A.; Grounds, M.D. Why Do Cultured Transplanted Myoblasts Die in Vivo? DNA Quantification Shows Enhanced Survival of Donor Male Myoblasts in Host Mice Depleted of CD4+ and CD8+ Cells or NK1.1+ Cells. Cell Transplant. 2000, 9, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Yang, L.; Cao, H.; Shen, Z.-Y.; Song, H.-L. Study of the Protective Effect on Damaged Intestinal Epithelial Cells of Rat Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring (Muse) Cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, A.M.; Gabr, M.M.; Abdelhady, E.K.; Zakaria, M.M.; Khater, S.M.; Ismail, A.M.; Refaie, A.F. In Vitro Differentiation of Human Multilineage Differentiating Stress-Enduring (Muse) Cells into Insulin Producing Cells. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Du, P.; Wang, X.-S.; Lu, Y.-C.; Sun, Y.-W.; Sun, Y.-H.; Hu, Y.-M.; Chen, X. Muse Cells Decrease the Neuroinflammatory Response by Modulating the Proportion of M1 and M2 Microglia in Vitro. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yin, X.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Du, P.; Lu, Y.-C.; Jin, H.-B.; Yang, C.-C.; Ying, J.-L. Human Muse Cells-Derived Neural Precursor Cells as the Novel Seed Cells for the Repair of Spinal Cord Injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 568, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Sato, Y.; Kushida, Y.; Tsuji, M.; Wakao, S.; Ueda, K.; Imai, K.; Iitani, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Hida, H.; et al. Intravenously Delivered Multilineage-Differentiating Stress Enduring Cells Dampen Excessive Glutamate Metabolism and Microglial Activation in Experimental Perinatal Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2021, 41, 1707–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajitani, T.; Endo, T.; Iwabuchi, N.; Inoue, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Abe, T.; Niizuma, K.; Tominaga, T. Association of Intravenous Administration of Human Muse Cells with Deficit Amelioration in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2021, 34, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, Y.; Kitani, T.; Yanishi, K.; Kusaba, T.; Dezawa, M.; Matoba, S. Intravenous Transplantation of Human Muse Cells Improves Blood Perfusion in a Mouse Model of Limb Ischemia. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, ehaa946.3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozuru, R.; Wakao, S.; Tsuji, T.; Ohara, N.; Matsuba, T.; Amuran, M.Y.; Isobe, J.; Iino, M.; Nishida, N.; Matsumoto, S.; et al. Rescue from Stx2-Producing E. Coli-Associated Encephalopathy by Intravenous Injection of Muse Cells in NOD-SCID Mice. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2020, 28, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, R.; Zhang, K.; Sun, R.; Yang, M.; Li, K.; Liu, H.; Xue, Y.; Xu, H.; Guo, Y. Characterization of Early Myocardial Inflammation in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, M.G.; Peralta, T.M.; Locatelli, P.; Velazquez, C.; Herrero, Y.; Crottogini, A.J.; Olea, F.D.; Cuniberti, L.A. Promoting Early Neovascularization by Allotransplanted Adipose-Derived Muse Cells in an Ovine Model of Acute Myocardial Infarction. PloS One 2023, 18, e0277442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Minatoguchi, S.; Kanamori, H.; Mikami, A.; Okura, H.; Dezawa, M.; Minatoguchi, S. Stem Cell Therapy for Acute Myocardial Infarction - Focusing on the Comparison between Muse Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Minatoguchi, S.; Baba, S.; Shibata, S.; Takashima, S.; Wakao, S.; Okura, H.; Dezawa, M.; Minatoguchi, S. Human Muse Cells Reduce Myocardial Infarct Size and Improve Cardiac Function without Causing Arrythmias in a Swine Model of Acute Myocardial Infarction. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchelder, C.A.; Lee, C.C.I.; Matsell, D.G.; Yoder, M.C.; Tarantal, A.F. Renal Ontogeny in the Rhesus Monkey (Macaca Mulatta) and Directed Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells towards Kidney Precursors. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 2009, 78, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wang, P.; Cui, Z.; Cao, J.; Liu, S.; Yu, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Zhu, D.; Xie, M.; et al. Muse Cell Spheroids Have Therapeutic Effect on Corneal Scarring Wound in Mice and Tree Shrews. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaw1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, W.; Wu, J.; Gao, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Shan, C.; Shen, Y.; Chen, G. Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring Cells Alleviate Atopic Dermatitis-Associated Behaviors in Mice. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Yamasaki, K.; Tsuchiyama, K.; Aiba, S. Artificial Pigmented Human Skin Created by Muse Cells. In Muse Cells; Dezawa, M., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer Japan: Tokyo, 2018; Vol. 1103, pp. 255–271. ISBN 978-4-431-56845-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hessheimer, A.J.; Vengohechea, J.; Fondevila, C. The Hepatic Sinusoid: The “Muse” in Small-for-Size Liver Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 1998–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, B.; Chhatbar, P.Y.; Dong, Y.; Alawieh, A.; Lowe, F.; Hu, X.; Feng, W. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy in Stroke: A Systematic Review of Literature in Pre-Clinical and Clinical Research. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T.; Nishigaki, K.; Minatoguchi, S. Safety and Efficacy of Human Muse Cell-Based Product for Acute Myocardial Infarction in a First-in-Human Trial. Circ. J. Off. J. Jpn. Circ. Soc. 2020, 84, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawcett, J.W. The Struggle to Make CNS Axons Regenerate: Why Has It Been so Difficult? Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransohoff, R.M. A Polarizing Question: Do M1 and M2 Microglia Exist? Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosser, C.-A.; Baptista, S.; Arnoux, I.; Audinat, E. Microglia in CNS Development: Shaping the Brain for the Future. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 149–150, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Itriago, A.; Radford, R.A.W.; Aramideh, J.A.; Maurel, C.; Scherer, N.M.; Don, E.K.; Lee, A.; Chung, R.S.; Graeber, M.B.; Morsch, M. Microglia Morphophysiological Diversity and Its Implications for the CNS. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 997786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Kushida, Y.; Wakao, S.; Tadokoro, K.; Nomura, E.; Omote, Y.; Takemoto, M.; Hishikawa, N.; Ohta, Y.; Dezawa, M.; et al. Therapeutic Benefit of Muse Cells in a Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, M.; Mizuma, M.; Wakao, S.; Kushida, Y.; Kudo, K.; Fukase, M.; Ishida, M.; Ono, T.; Shimura, M.; Ise, I.; et al. The Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of Intravenously Administered Allogeneic Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring Cells in a Swine Hepatectomy Model. Surg. Today 2021, 51, 634–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Aburakawa, D.; Niizuma, K.; Iwabuchi, N.; Kajitani, T.; Wakao, S.; Kushida, Y.; Dezawa, M.; Borlongan, C.V.; Tominaga, T. Intravenously Transplanted Human Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring Cells Afford Brain Repair in a Mouse Lacunar Stroke Model. Stroke 2020, 51, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, N.; Shimizu, S.; Ueda, K.; Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, S.; Miura, R.; Katayama, A.; Ando, M.; Mizuno, M.; Hirakawa, A.; et al. Safety and Tolerability of a Multilineage-Differentiating Stress-Enduring Cell-Based Product in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischaemic Encephalopathy with Therapeutic Hypothermia (SHIELD Trial): A Clinical Trial Protocol Open-Label, Non-Randomised, Dose-Escalation Trial. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e057073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Nohara, T.; Takashima, S.; Natsuga, K.; Adachi, M.; Yoshida, K.; Shinkuma, S.; Takeichi, T.; Nakamura, H.; Wada, O.; et al. Intravenous Allogeneic Multilineage-differentiating Stress-enduring Cells in Adults with Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa: A Phase 1/2 Open-label Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, e528–e531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Ahmed, S.; Fristad, I.; Lie, S.A.; Suliman, S.; Mustafa, K.; Vindenes, H.; Idris, S.B. Adipose-Derived and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Donor-Matched Comparison. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L, L.; X, W.; Z, Y. Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in the Brain: Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Biochem. Pharmacol. Open Access 2016, 5, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.V.; De Silva, D.A.; Macleod, M.R.; Coutts, S.B.; Schwamm, L.H.; Davis, S.M.; Donnan, G.A. Ischaemic Stroke. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2019, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).