Submitted:
23 January 2024
Posted:
24 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
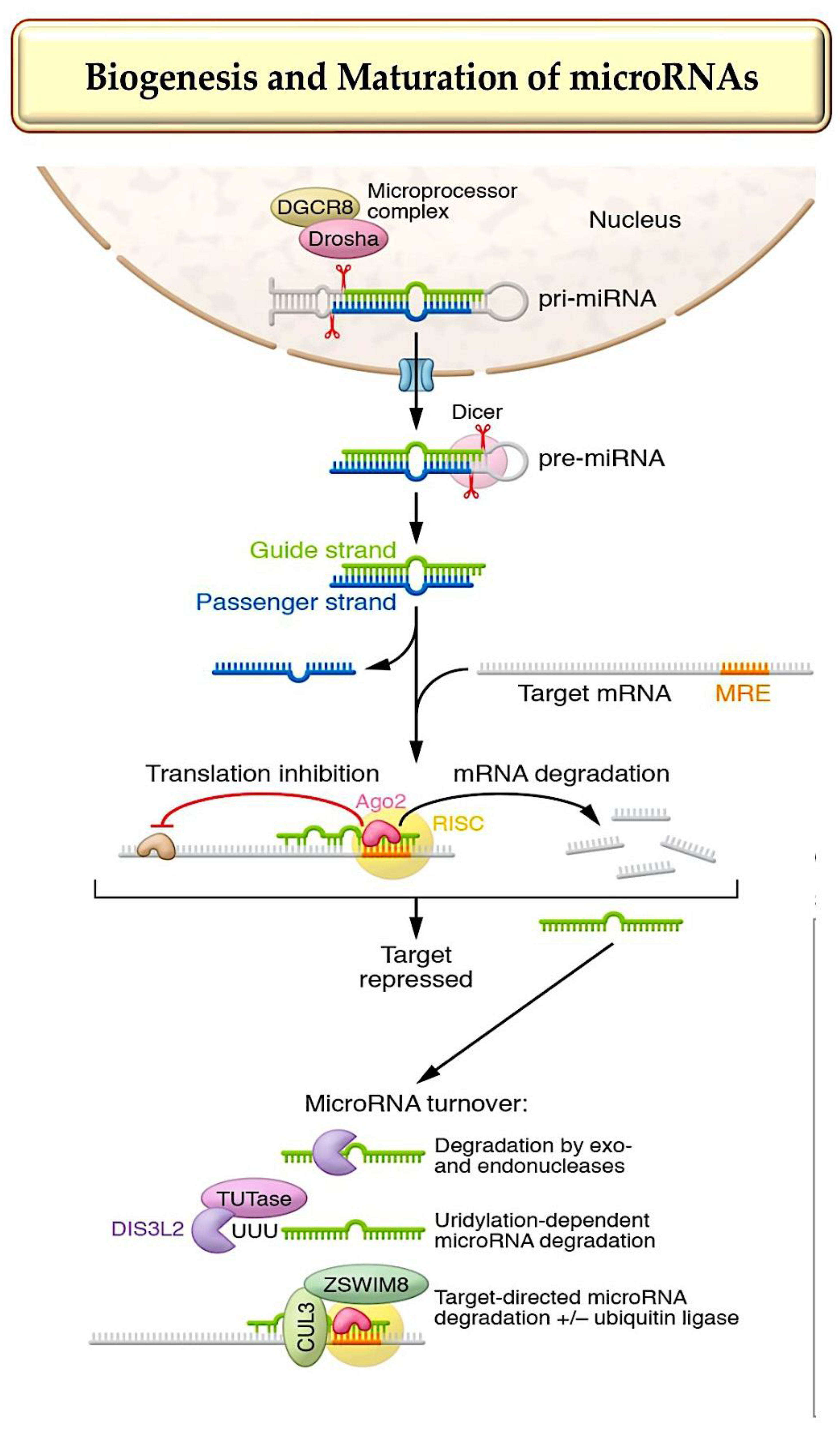
1. MicroRNA Biogenesis, Stability, and Strand Targeting
2. MicroRNA-targeting therapy is advancing towards clinical use.
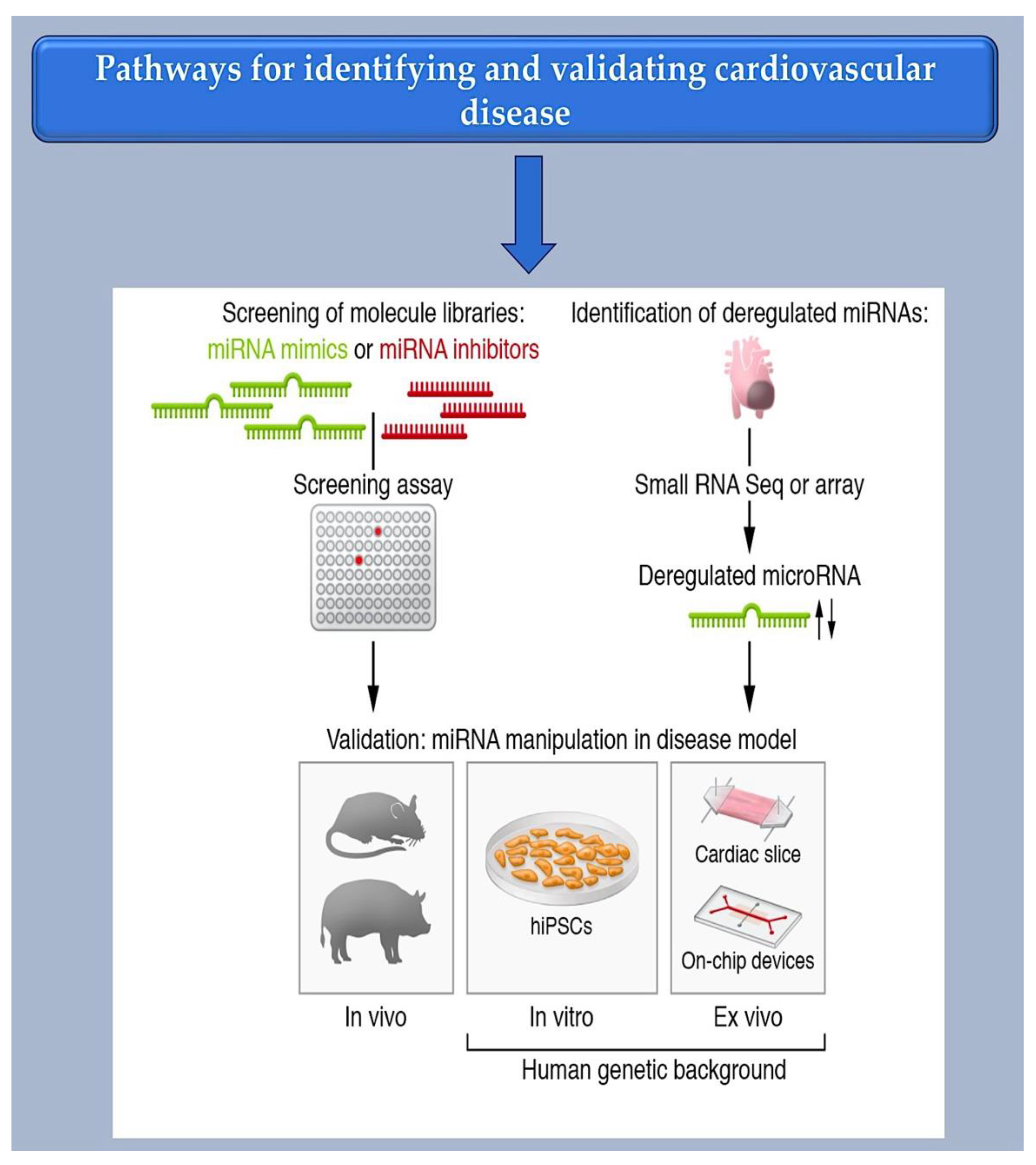
2.1. Investigating Methods for Selecting Therapeutic microRNAs.
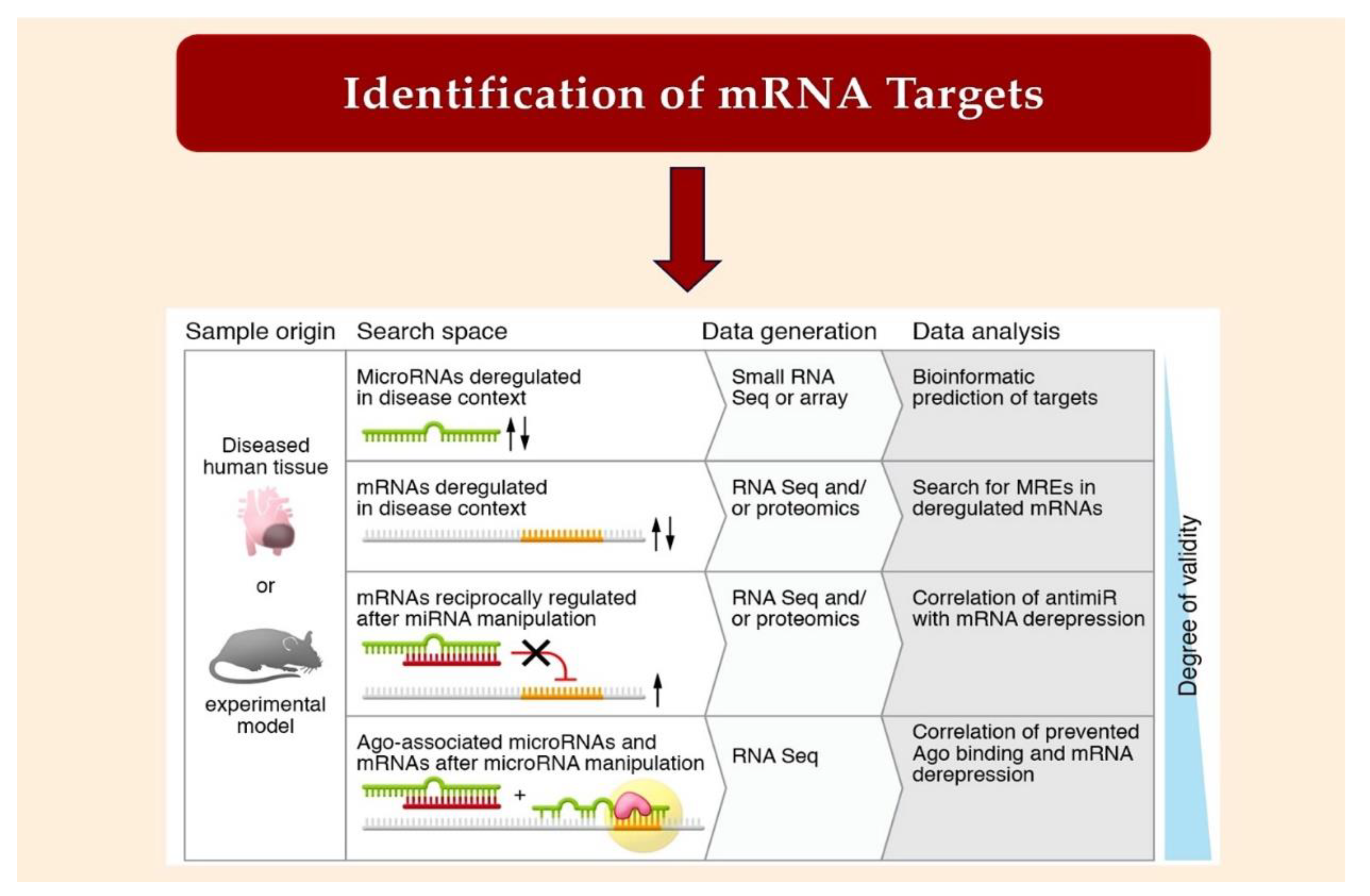
2.2. Bioinformatic Method for MiRNA Characterization through Identification of mRNA Targets
3. Challenges and Potential Solutions for Noncoding RNA Therapeutics
3.1. Types of RNA-targeting therapeutics
3.2. Oligonucleotide-based therapy insight
4. Development of microRNA-based cardiovascular therapeutic approaches in clinical trials
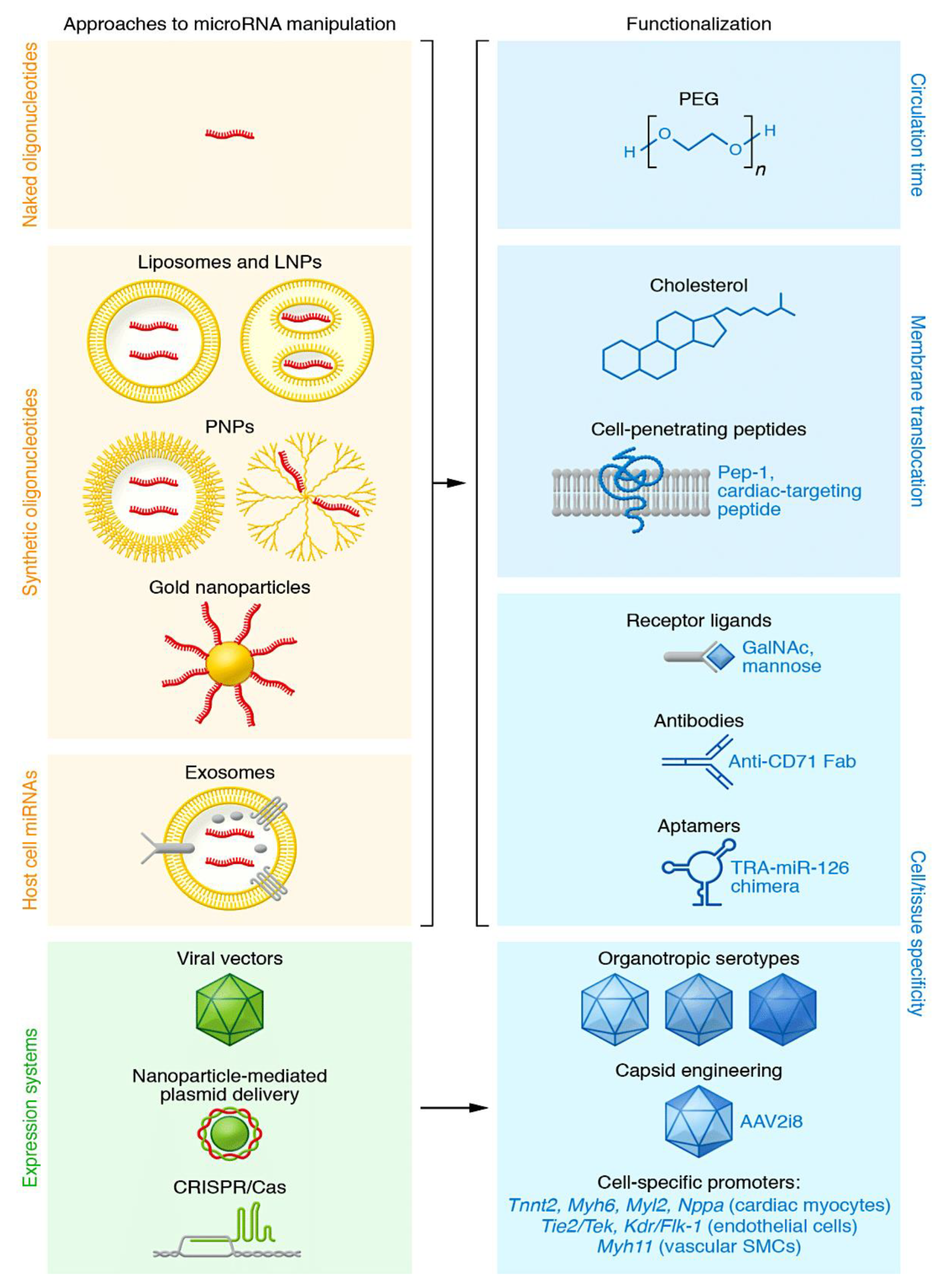
4.1. Evaluating the tropism of oligonucleotides: open questions and major challenges
4.2. Assessing how to manage
4.3. Assessing dosing
4.4. Assessing the risk of adverse effects
- Understanding immune reactions
- Understanding toxicity
- Understanding tumorigenesis
5. Looking ahead
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ha I, Wightman B, Ruvkun G. A bulged lin-4/lin-14 RNA duplex is sufficient for Caenorhabditis elegans lin-14 temporal gradient formation.Genes Dev. 1996 Dec 1;10(23):3041-50. [CrossRef]
- Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):855-62. [CrossRef]
- Lee RC, et al. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense com- plementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843–854.
- Jan CH, Friedman RC, Ruby JG, Bartel DP. Formation, regulation and evolution of Caenorhabditis elegans 3'UTRs. Nature. 2011 Jan 6;469(7328):97-101. [CrossRef]
- Friedman RC, et al. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009;19(1):92–105.
- Grimson A, Farh KK, Johnston WK, Garrett-Engele P, Lim LP, Bartel DP. MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol Cell. 2007 Jul 6;27(1):91-105. [CrossRef]
- Kozomara A, et al. miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(d1):D155–D162.
- Huang W, Paul D, Calin GA, Bayraktar R. miR-142: A Master Regulator in Hematological Malignancies and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cells. 2023 Dec 30;13(1):84. [CrossRef]
- Fromm B, et al. MirGeneDB 2.0: the metazo- an microRNA complement. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(d1):132–141.
- Kim K, Baek SC, Lee YY, Bastiaanssen C, Kim J, Kim H, Kim VN. A quantitative map of human primary microRNA processing sites.Mol Cell. 2021 Aug 19;81(16):3422-3439.e11. [CrossRef]
- Nappi F, Alzamil A, Avtaar Singh SS, Spadaccio C, Bonnet N. Current Knowledge on the Interaction of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection, Encoded miRNAs, and Acute Aortic Syndrome. Viruses. 2023 Sep 29;15(10):2027. [CrossRef]
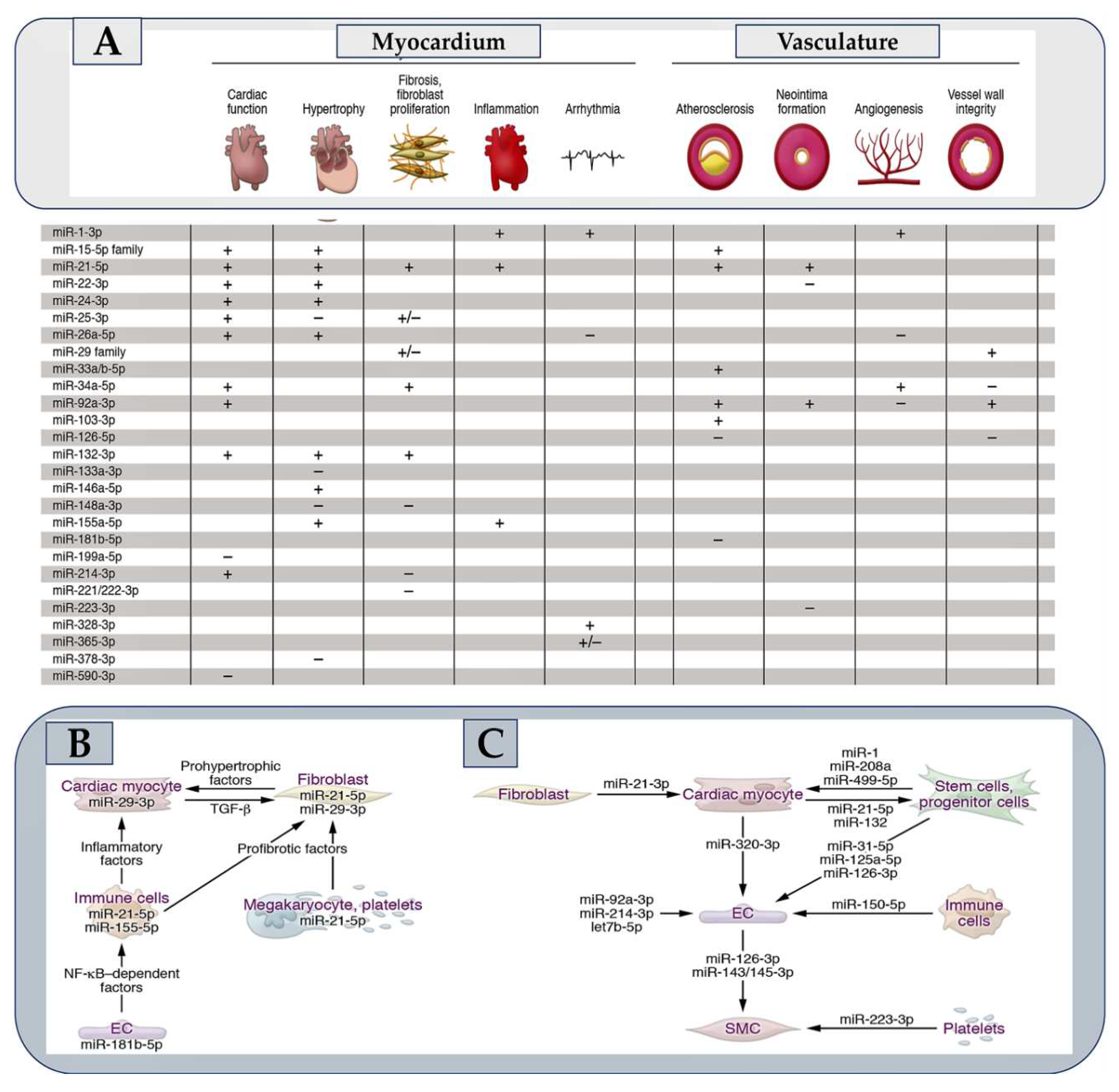
- Nappi F, Avtaar Singh SS, Jitendra V, Alzamil A, Schoell T. The Roles of microRNAs in the Cardiovascular System.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 19;24(18):14277. [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Prakash, T.P.; Corey, D.R. Argonaute 2-dependent regulation of gene expression by single-stranded miRNA mimics. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 946–955.
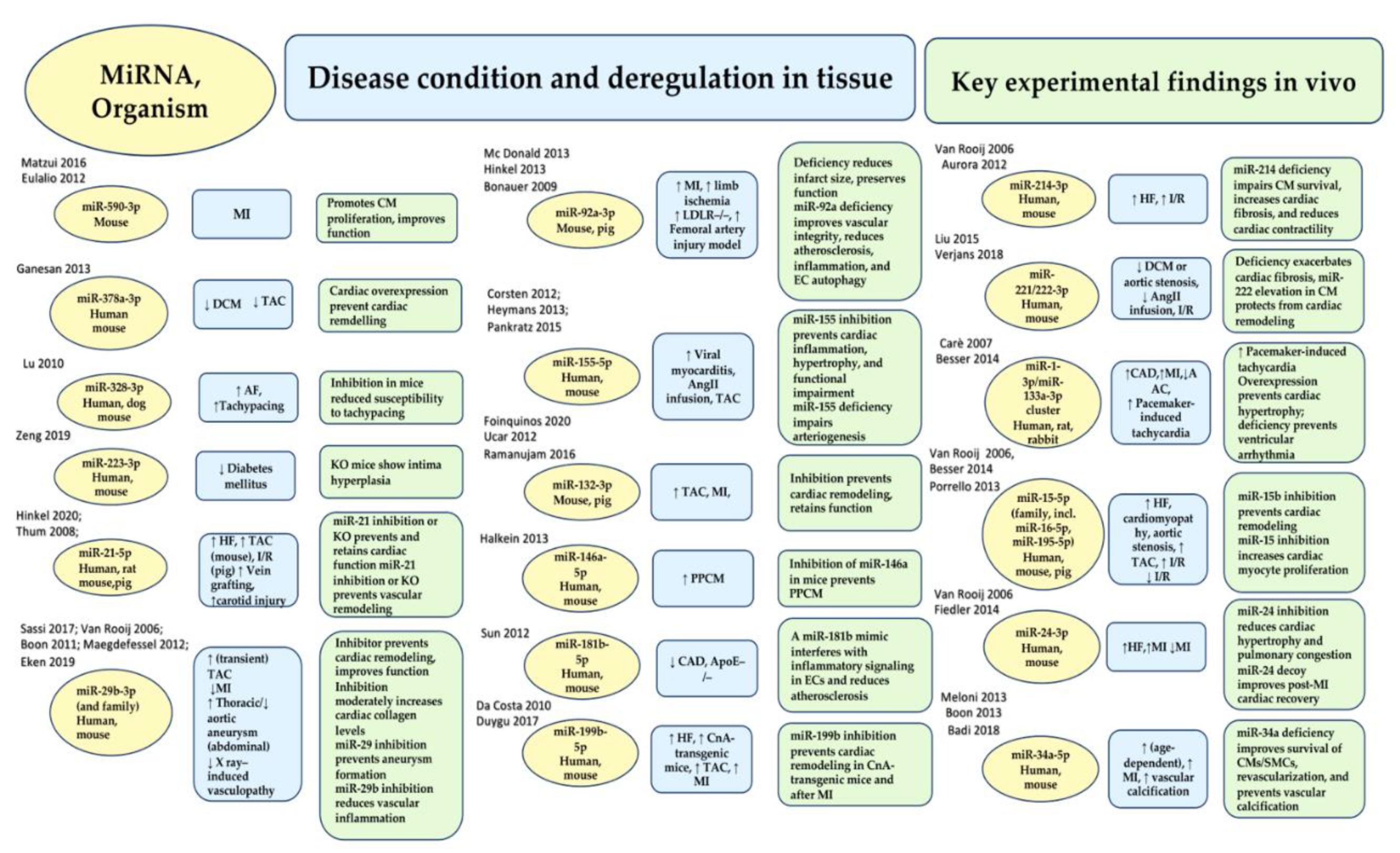
- Eulalio, A.; Mano, M.; Dal Ferro, M.; Zentilin, L.; Sinagra, G.; Zacchigna, S.; Giacca, M. Functional screening identifies miRNAs inducing cardiac regeneration. Nature 2012, 492, 376–381.
- Hinkel, R.; Ramanujam, D.; Kaczmarek, V.; Howe, A.; Klett, K.; Beck, C.; Dueck, A.; Thum, T.; Laugwitz, K.L.; Maegdefessel, L.; et al. AntimiR-21 prevents myocardial dysfunction in a pig model of ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1788–1800.
- Ganesan, J.; Ramanujam, D.; Sassi, Y.; Ahles, A.; Jentzsch, C.; Werfel, S.; Leierseder, S.; Loyer, X.; Giacca, M.; Zentilin, L.; et al. MiR-378 controls cardiac hypertrophy by combined repression of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway factors. Circulation 2013, 127, 2097–2106.
- Sassi, Y.; Avramopoulos, P.; Ramanujam, D.; Grüter, L.; Werfel, S.; Giosele, S.; Brunner, A.D.; Esfandyari, D.; Papadopoulou, A.S.; De Strooper, B.; et al. Cardiac myocyte miR-29 promotes pathological remodeling of the heart by activating Wnt signaling. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1614.
- Thum, T.; Gross, C.; Fiedler, J.; Fischer, T.; Kissler, S.; Bussen, M.; Galuppo, P.; Just, S.; Rottbauer, W.; Frantz, S.; et al. MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature 2008, 456, 980–984.
- Ji, R.; Cheng, Y.; Yue, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Dean, D.B.; Zhang, C. MicroRNA expression signature and antisense-mediated depletion reveal an essential role of microRNA in vascular neointimal lesion formation. Circ. Res.2007, 100, 1579–1588.
- Ramanujam, D.; Sassi, Y.; Laggerbauer, B.; Engelhardt, S. Viral vector-based targeting of miR-21 in cardiac nonmyocyte cells reduces pathologic remodeling of the heart. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 1939–1948.
- Van Rooij, E.; Sutherland, L.B.; Thatcher, J.E.; DiMaio, J.M.; Naseem, R.H.; Marshall, W.S.; Hill, J.A.; Olson, E.N. Dysregulation of microRNAs after myocardial infarction reveals a role of miR-29 in cardiac fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13027–13032.
- Boon, R.A.; Seeger, T.; Heydt, S.; Fischer, A.; Hergenreider, E.; Horrevoets, A.J.; Vinciguerra, M.; Rosenthal, N.; Sciacca, S.; Pilato, M.; et al. MicroRNA-29 in aortic dilation: Implications for aneurysm formation. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 1115–1119.
- Maegdefessel, L.; Azuma, J.; Toh, R.; Merk, D.R.; Deng, A.; Chin, J.T.; Raaz, U.; Schoelmerich, A.M.; Raiesdana, A.; Leeper, N.J.; et al. Inhibition of micro-RNA-29b reduces murine abdominal aortic aneurysm development. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 497–506.
- McDonald, R.A.; White, K.M.; Wu, J.; Cooley, B.C.; Robertson, K.E.; Halliday, C.A.; McClure, J.D.; Francis, S.; Lu, R.; Kennedy, S.; et al. miRNA-21 is dysregulated in response to vein grafting in multiple models and genetic ablation in mice attenuates neointima formation. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 1636–1643.
- Eken, S.M.; Christersdottir, T.; Winski, G.; Sangsuwan, T.; Jin, H.; Chernogubova, E.; Pirault, J.; Sun, C.; Simon, N.; Winter, H.; et al. miR-29b mediates the chronic inflammatory response in radiotherapy-induced vascular disease. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2019, 4, 72–82.
- Zeng, Z.; Xia, L.; Fan, X.; Ostriker, A.C.; Yarovinsky, T.; Su, M.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, X.; Xie, Y.; Pi, L.; et al. Platelet-derived miR-223 promotes a phenotypic switch in arterial injury repair. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1372–1386.
- Hinkel, R.; Penzkofer, D.; Zühlke, S.; Fischer, A.; Husada, W.; Xu, Q.F.; Baloch, E.; van Rooij, E.; Zeiher, A.M.; Kupatt, C.; et al. Inhibition of microRNA-92a protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in a large-animal model. Circulation 2013, 128, 1066–1075.
- Foinquinos, A.; Batkai, S.; Genschel, C.; Viereck, J.; Rump, S.; Gyöngyösi, M.; Traxler, D.; Riesenhuber, M.; Spannbauer, A.; Lukovic, D.; et al. Preclinical development of a miR-132 inhibitor for heart failure treatment. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 633.
- Corsten, M.F.; Papageorgiou, A.; Verhesen, W.; Carai, P.; Lindow, M.; Obad, S.; Summer, G.; Coort, S.L.; Hazebroek, M.; van Leeuwen, R.; et al. MicroRNA profiling identifies microRNA-155 as an adverse mediator of cardiac injury and dysfunction during acute viral myocarditis. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 415–425.
- Bonauer, A.; Carmona, G.; Iwasaki, M.; Mione, M.; Koyanagi, M.; Fischer, A.; Burchfield, J.; Fox, H.; Doebele, C.; Ohtani, K.; et al. MicroRNA-92a controls angiogenesis and functional recovery of ischemic tissues in mice. Science 2009, 324, 1710–1713.
- Ucar, A.; Gupta, S.K.; Fiedler, J.; Erikci, E.; Kardasinski, M.; Batkai, S.; Dangwal, S.; Kumarswamy, R.; Bang, C.; Holzmann, A.; et al. The miRNA-212/132 family regulates both cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte autophagy. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1078.
- Heymans, S.; Corsten, M.F.; Verhesen, W.; Carai, P.; van Leeuwen, R.E.; Custers, K.; Peters, T.; Hazebroek, M.; Stöger, L.; Wijnands, Eet al. Macrophage microRNA-155 promotes cardiac hypertrophy and failure. Circulation 2013, 128, 1420–1432.
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Pan, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, H.; Luo, X.; Bai, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-328 contributes to adverse electrical remodeling in atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2010, 122, 2378–2387.
- Pankratz, F.; Bemtgen, X.; Zeiser, R.; Leonhardt, F.; Kreuzaler, S.; Hilgendorf, I.; Smolka, C.; Helbing, T.; Hoefer, I.; Esser, J.S.; et al. MicroRNA-155 exerts cell-specific antiangiogenic but proarteriogenic effects during adaptive neovascularization. Circulation 2015, 131, 1575–1589.
- Halkein, J.; Tabruyn, S.P.; Ricke-Hoch, M.; Haghikia, A.; Nguyen, N.Q.; Scherr, M.; Castermans, K.; Malvaux, L.; Lambert, V.; Thiry, M.; et al. MicroRNA-146a is a therapeutic target and biomarker for peripartum cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2143–2154.
- Sun, X.; Icli, B.; Wara, A.K.; Belkin, N.; He, S.; Kobzik, L.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Vera, M.P.; MICU Registry; Blackwell, T.S.; Baron, R.M.; et al. MicroRNA-181b regulates NF-κB–mediated vascular inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1973–1990.
- da Costa Martins, P.A.; Salic, K.; Gladka, M.M.; Armand, A.S.; Leptidis, S.; el Azzouzi, H.; Hansen, A.; Coenen-de Roo, C.J.; Bierhuizen, M.F.; van der Nagel, R.; et al. MicroRNA-199b targets the nuclear kinase Dyrk1a in an auto-amplification loop promoting calcineurin/NFAT signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 1220–1227.
- Duygu, B.; Poels, E.M.; Juni, R.; Bitsch, N.; Ottaviani, L.; Olieslagers, S.; de Windt, L.J.; da Costa Martins, P.A. miR-199b-5p is a regulator of left ventricular remodeling following myocardial infarction. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2017, 2, 18–26.
- Van Rooij, E.; Sutherland, L.B.; Liu, N.; Williams, A.H.; McAnally, J.; Gerard, R.D.; Richardson, J.A.; Olson, E.N. A signature pattern of stress-responsive microRNAs that can evoke cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18255–18260.
- Aurora, A.B.; Mahmoud, A.I.; Luo, X.; Johnson, B.A.; van Rooij, E.; Matsuzaki, S.; Humphries, K.M.; Hill, J.A.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Sadek, H.A.; et al. MicroRNA-214 protects the mouse heart from ischemic injury by controlling Ca2+ overload and cell death. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1222–1232.
- Liu, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, H.; Wei, X.; Platt, C.; Damilano, F.; Xiao, C.; Bezzerides, V.; Boström, P.; Che, L.; et al. miR-222 is necessary for exercise-induced cardiac growth and protects against pathological cardiac remodeling. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 584–595.
- Verjans, R.; Peters, T.; Beaumont, F.J.; van Leeuwen, R.; van Herwaarden, T.; Verhesen, W.; Munts, C.; Bijnen, M.; Henkens, M.; Diez, J.; et al. MicroRNA-221/222 family counteracts myocardial fibrosis in pressure overload-induced heart failure. Hypertension 2018, 71, 280–288.
- Carè, A.; Catalucci, D.; Felicetti, F.; Bonci, D.; Addario, A.; Gallo, P.; Bang, M.L.; Segnalini, P.; Gu, Y.; Dalton, N.D.; et al. MicroRNA-133 controls cardiac hypertrophy. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 613–618.
- Besser, J.; Malan, D.; Wystub, K.; Bachmann, A.; Wietelmann, A.; Sasse, P.; Fleischmann, B.K.; Braun, T.; Boettger, T. MiRNA-1/133a clusters regulate adrenergic control of cardiac repolarization. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113449.
- Porrello, E.R.; Mahmoud, A.I.; Simpson, E.; Johnson, B.A.; Grinsfelder, D.; Canseco, D.; Mammen, P.P.; Rothermel, B.A.; Olson, E.N.; Sadek, H.A. Regulation of neonatal and adult mammalian heart regeneration by the miR-15 family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 187–192.
- Fiedler, J.; Stöhr, A.; Gupta, S.K.; Hartmann, D.; Holzmann, A.; Just, A.; Hansen, A.; Hilfiker-Kleiner, D.; Eschenhagen, T.; Thum, T. Functional microRNA library screening identifies the hypoxamir miR-24 as a potent regulator of smooth muscle cell proliferation and vascularization. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 1167–1176.
- Meloni, M.; Marchetti, M.; Garner, K.; Littlejohns, B.; Sala-Newby, G.; Xenophontos, N.; Floris, I.; Suleiman, M.S.; Madeddu, P.; Caporali, A.; et al. Local inhibition of micro-RNA-24 improves reparative angiogenesis and left ventricle remodeling and function in mice with myocardial infarction. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1390–1402.
- Boon, R.A.; Iekushi, K.; Lechner, S.; Seeger, T.; Fischer, A.; Heydt, S.; Kaluza, D.; Tréguer, K.; Carmona, G.; Bonauer, A.; et al. MicroRNA-34a regulates cardiac ageing and function. Nature 2013, 495, 107–110.
- Badi, I.; Mancinelli, L.; Polizzotto, A.; Ferri, D.; Zeni, F.; Burba, I.; Milano, G.; Brambilla, F.; Saccu, C.; Bianchi, M.E.; et al. miR-34a promotes vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by downregulating SIRT1 (sirtuin 1) and AXL (AXl receptor tyrosine kinase). Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 2079–2090.
- Laggerbauer B, Engelhardt S. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease.J Clin Invest. 2022 Jun 1;132(11):e159179. [CrossRef]
- Treiber T, et al. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and its crosstalk with other cellular pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(1):5–20.
- Bartel DP. Metazoan microRNAs. Cell. 2018;173(1):20–51.
- Khvorova A, Reynolds A, Jayasena SD.. Functional siRNAs and miRNAs exhibit strand bias. Cell. 2003;115(4):209–216. [CrossRef]
- Schwarz DS, Hutvágner G, Du T, Xu Z, Aronin N, Zamore PD. Asymmetry in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complex. Cell. 2003;115(2):199–208. [CrossRef]
- Bang, C.; Batkai, S.; Dangwal, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Foinquinos, A.; Holzmann, A.; Just, A.; Remke, J.; Zimmer, K.; Zeug, A.; et al. Cardiac fibroblast–derived micro-RNA passenger strand-enriched exosomes mediate cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2136–2146.
- Santovito, D.; Egea, V.; Bidzhekov, K.; Natarelli, L.; Mourão, A.; Blanchet, X.; Wichapong, K.; Aslani, M.; Brunßen, C.; Horckmans, M.; et al. Noncanonical inhibition of caspase-3 by a nuclear microRNA confers endothelial protection by autophagy in atherosclerosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz2294.
- Li H, Zhan J, Zhao Y, Fan J, Yuan S, Yin Z, Dai B, Chen C, Wang DW. Identification of ncRNA-mediated functions of nucleus-localized miR-320 in cardiomyocytes. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020; 19:132–143. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective micro-RNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife. 2015, 4, e05005.
- Broughton, J.P.; Lovci, M.T.; Huang, J.L.; Yeo, G.W.; Pasquinelli, A.E. Pairing beyond the seed supports MicroRNA targeting specificity. Mol. Cell 2016, 64, 320–333.
- Seth PP, Tanowitz M, Bennett CF. Selective tissue targeting of synthetic nucleic acid drugs. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(3):915–925. [CrossRef]
- Gebert, L.F.R.; MacRae, I.J. Regulation of micro-RNA function in animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 21–37.
- Yang, A.; Bofill-De Ros, X.; Shao, T.J.; Jiang, M.; Li, K.; Villanueva, P.; Dai, L.; Gu, S. 3′ Uridylation confers miRNAs with non-canonical target repertoires. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 511–522.e4.
- van der Kwast, R.V.C.T.; Parma, L.; van der Bent, M.L.; van Ingen, E.; Baganha, F.; Peters, H.A.B.; Goossens, E.A.C.; Simons, K.H.; Palmen, M.; de Vries, M.R.; et al. Adenosine-to-inosine editing of vasoactive microRNAs alters their targetome and function in ischemia. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 932–953.
- McGahon, M.K.; Yarham, J.M.; Daly, A.; Guduric-Fuchs, J.; Ferguson, L.J.; Simpson, D.A.; Collins, A. Distinctive profile of IsomiR expression and novel microRNAs in rat heart left ventricle. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65809.
- van der Kwast, R.V.C.T.; van Ingen, E.; Parma, L.; Peters, H.A.B.; Quax, P.H.A.; Nossent, A.Y. Adenosine-to-inosine editing of MicroRNA-487b alters target gene selection after ischemia and promotes neovascularization. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 444–456.
- van der Kwast, R.V.C.T.; Woudenberg, T.; Quax, P.H.A.; Nossent, A.Y. MicroRNA-411 and its 5′-isomiR have distinct targets and functions and are differentially regulated in the vasculature under ischemia. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 157–170.
- Kingston, E.R.; Bartel, D.P. Global analyses of the dynamics of mammalian microRNA metabolism. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 1777–1790.
- Marzi, M.J.; Ghini, F.; Cerruti, B.; de Pretis, S.; Bonetti, P.; Giacomelli, C.; Gorski, M.M.; Kress, T.; Pelizzola, M.; Muller, H.; et al. Degradation dynamics of micro-RNAs revealed by a novel pulse-chase approach. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 554–565.
- Han, J.; LaVigne, C.A.; Jones, B.T.; Zhang, H.; Gillett, F.; Mendell, J.T. A ubiquitin ligase mediates target-directed microRNA decay independently of tailing and trimming. Science 2020, 370, eabc9546.
- Shi, C.Y.; Kingston, E.R.; Kleaveland, B.; Lin, D.H.; Stubna, M.W.; Bartel, D.P. The ZSWIM8 ubiquitin ligase mediates target-directed microRNA degradation. Science 2020, 370, eabc9359.
- Bitetti, A.; Mallory, A.C.; Golini, E.; Carrieri, C.; Carreño Gutiérrez, H.; Perlas, E.; Pérez-Rico, Y.A.; Tocchini-Valentini, G.P.; Enright, A.J.; Norton, W.H.J.; et al. MicroRNA degradation by a conserved target RNA regulates animal behavior. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 244–251.
- Cabili, M. Trapnell C, Goff L, Koziol M, Tazon-Vega B, Regev A, Rinn JL. Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev. 2011 Sep 15;25(18):1915-27. [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, M., Girnita, L., Varani, G., Calin, G. A. Decrypting noncoding RNA interactions, structures, and functional networks. Genome Res. 2019 Sep;29(9):1377-1388. [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J. L., Chang, H. Y. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012; 81:145-66. [CrossRef]
- Guttman, M. Rinn, J. L. Modular regulatory principles of large non-coding RNAs. Nature. 2012 Feb 15;482(7385):339-46. [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, M. Calin, G. A. Circular RNAs in cancer- lessons learned from microRNAs. Front Oncol. 2018 Sep 21; 8:307. [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T. B, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J.. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495, 384–388 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; LaVigne, C.A.; Jones, B.T.; Zhang, H.; Gillett, F.; Mendell, J.T. A ubiquitin ligase mediates target-directed microRNA decay independently of tailing and trimming. Science 2020, 370, eabc9546.
- Wang, K.; Jiang, Z.; Webster, K.A.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; et al. Enhanced cardioprotection by human endometrium mesenchymal stem cells driven by exosomal microRNA-21. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 209–222.
- Cheng, M.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, E.; Zeng, Q.; Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, B.; Yi, G.; Mao, X.; et al. Circulating myocardial micro-RNAs from infarcted hearts are carried in exosomes and mobilise bone marrow progenitor cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 959.
- Zheng, D.; Huo, M.; Li, B.; Wang, W.; Piao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, T.; Liu, K. The role of exosomes and exosomal microRNA in cardiovascular disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 616161.
- Kesidou, D.; da Costa Martins, P.A.; de Windt, L.J.; Brittan, M.; Beqqali, A.; Baker, A.H. Extracellular vesicle miRNAs in the promotion of cardiac neovascularisation. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 579892.
- Ottaviani, L.; Sansonetti, M.; da Costa Martins, P.A. Myocardial cell-to-cell communication via microRNAs. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2018, 3, 144–153.
- Zernecke, A.; Bidzhekov, K.; Noels, H.; Shagdarsuren, E.; Gan, L.; Denecke, B.; Hristov, M.; Köppel, T.; Jahantigh, M.N.; Lutgens, E.; et al. Delivery of microRNA-126 by apoptotic bodies induces CXCL12-dependent vascular protection. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra81.
- Martello A, Mellis D, Meloni M, Howarth A, Ebner D, Caporali A, Al Haj Zen A. Phenotypic miRNA screen identifies miR-26b to promote the growth and survival of endothelial cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018; 13:29–43. [CrossRef]
- Eder A, Vollert I, Hansen A, Eschenhagen T. Human engineered heart tissue as a model system for drug testing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016; 96:214–224. [CrossRef]
- Fischer C, Milting H, Fein E, Reiser E, Lu K, Seidel T, Schinner C, Schwarzmayr T, Schramm R, Tomasi R, Husse B, Cao-Ehlker X, Pohl U, Dendorfer A . Long-term functional and structural preservation of precision-cut human myocardium under continuous electromechanical stimulation in vitro. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1–12. [CrossRef]
- Meekel JP, Groeneveld ME, Bogunovic N, Keekstra N, Musters RJP, Zandieh-Doulabi B, Pals G, Micha D, Niessen HWM, Wiersema AM, Kievit JK, Hoksbergen AWJ, Wisselink W, Blankensteijn JD, Yeung KK. An in vitro method to keep human aortic tissue sections functionally and structurally intact. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1–12. [CrossRef]
- Thomas RC, Singh A, Cowley P, Myagmar BE, Montgomery MD, Swigart PM, De Marco T, Baker AJ, Simpson PC. A myocardial slice culture model reveals alpha-1A-adrenergic receptor sig- naling in the human heart. JACC Basic to Transl Sci. 2016;1(3):155–167. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2016.03.005.
- Kang C, Qiao Y, Li G, Baechle K, Camelliti P, Rentschler S, Efimov IR.. Human organotypic cultured car- diac slices: new platform for high throughput preclinical human trials. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:1–13. [CrossRef]
- Esfandyari D, Idrissou BMG, Hennis K, Avramopoulos P, Dueck A, El-Battrawy I, Grüter L, Meier MA, Näger AC, Ramanujam D, Dorn T, Meitinger T, Hagl C, Milting H, Borggrefe M, Fenske S, Biel M, Dendorfer A, Sassi Y, Moretti A, Engelhardt S. MicroRNA-365 regulates human cardiac action potential duration. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):1–15. [CrossRef]
- Mariani SA, Li Z, Rice S, Krieg C, Fragkogianni S, Robinson M, Vink CS, Pollard JW, Dzierzak E. Pro-inflammatory aorta- associated macrophages are involved in embryonic development of hematopoietic stem cells. Immunity. 2019;50(6):1439–1452. [CrossRef]
- Litviňuková M, Talavera-López C, Maatz H, Reichart D, Worth CL, Lindberg EL, Kanda M, Polanski K, Heinig M, Lee M, Nadelmann ER, Roberts K, Tuck L, Fasouli ES, DeLaughter DM, McDonough B, Wakimoto H, Gorham JM, Samari S, Mahbubani KT, Saeb-Parsy K, Patone G, Boyle JJ, Zhang H, Zhang H, Viveiros A, Oudit GY, Bayraktar OA, Seidman JG, Seidman CE, Noseda M, Hubner N, Teichmann SA. Cells of the adult human heart. Nature. 2020;588(7838):466–472. [CrossRef]
- Wang L, Yu P, Zhou B, Song J, Li Z, Zhang M, Guo G, Wang Y, Chen X, Han L, Hu S. Single-cell reconstruction of the adult human heart during heart failure and recovery reveals the cellular landscape underlying cardiac function. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(1):108–119. [CrossRef]
- Hücker SM, Fehlmann T, Werno C, Weidele K, Lüke F, Schlenska-Lange A, Klein CA, Keller A, Kirsch S.. Single-cell microRNA sequencing method comparison and application to cell lines and circulating lung tumor cells. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1–13. [CrossRef]
- Mokou M, Klein J, Makridakis M, Bitsika V, Bascands JL, Saulnier-Blache JS, Mullen W, Sacherer M, Zoidakis J, Pieske B, Mischak H, Roubelakis MG, Schanstra JP, Vlahou A.. Proteomics based identification of KDM5 histone demethylases associated with cardiovascular disease. EBioMedicine. 2019; 41:91–104. [CrossRef]
- Yin X, Wanga S, Fellows AL, Barallobre-Barreiro J, Lu R, Davaapil H, Franken R, Fava M, Baig F, Skroblin P, Xing Q, Koolbergen DR, Groenink M, Zwinderman AH, Balm R, de Vries CJM, Mulder BJM, Viner R, Jahangiri M, Reinhardt DP, Sinha S, de Waard V, Mayr M. Glycoproteomic analysis of the aortic extracellular matrix in Marfan patients. Arterio- scler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(9):1859–1873. [CrossRef]
- Doll S, Dreßen M, Geyer PE, Itzhak DN, Braun C, Doppler SA, Meier F, Deutsch MA, Lahm H, Lange R, Krane M, Mann M. Region and cell-type resolved quantitative proteomic map of the human heart. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1–13. [CrossRef]
- Brunner AD, Thielert M, Vasilopoulou C, Ammar C, Coscia F, Mund A, Hoerning OB, Bache N, Apalategui A, Lubeck M, Richter S, Fischer DS, Raether O, Park MA, Meier F, Theis FJ, Mann M. Ultra-high sensitivity mass spectrometry quantifies single-cell proteome changes upon perturbation. Mol Syst Biol. 2022;18(3): e10798. [CrossRef]
- McGeary SE, Lin KS, Shi CY, Pham TM, Bisaria N, Kelley GM, Bartel DP. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science. 2019 Dec 20;366(6472): eaav1741. [CrossRef]
- Werfel S, Leierseder S, Ruprecht B, Kuster B, Engelhardt S. Preferential microRNA targeting revealed by in vivo competitive binding and differential Argonaute immunoprecipitation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Sep 29;45(17):10218-10228. [CrossRef]
- Bissels U, Wild S, Tomiuk S, Holste A, Hafner M, Tuschl T, Bosio A. Absolute quantification of microRNAs by using a universal reference. RNA. 2009 Dec;15(12):2375-84. [CrossRef]
- Denzler R, Agarwal V, Stefano J, Bartel DP, Stoffel M. Assessing the ceRNA hypothesis with quantitative measurements of mirna and target abundance. Mol Cell. 2014;54(5):766–776. [CrossRef]
- Bosson AD, Zamudio JR, Sharp PA.. Endogenous miRNA and target concentrations determine susceptibil- ity to potential ceRNA competition. Mol Cell. 2014;56(3):347–359. [CrossRef]
- Denzler R, et al. Impact of microRNA levels, target-site complementarity, and cooperativity on competing endogenous RNA-regulated gene expression. Mol Cell. 2016;64(3):565–579.
- Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA-cancer connection: the beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 2006 Aug 1;66(15):7390-4. [CrossRef]
- Lenkala D, LaCroix B, Gamazon ER, Geeleher P, Im HK, Huang RS. The impact of microRNA expression on cellular proliferation.Hum Genet. 2014 Jul;133(7):931-8. [CrossRef]
- Ivey KN, Srivastava D. MicroRNAs as Developmental Regulators.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Jul 1;7(7): a008144. [CrossRef]
- Gutschner T, Diederichs S. The hallmarks of cancer: a long non-coding RNA point of view.RNA Biol. 2012 Jun;9(6):703-19. [CrossRef]
- Schmitt AM, Chang HY. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Pathways. Cancer Cell. 2016 Apr 11;29(4):452-463. [CrossRef]
- Mehta A, Baltimore D. MicroRNAs as regulatory elements in immune system logic. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016 Apr 28;16(5):279-94. [CrossRef]
- Amit M, Takahashi H, Dragomir MP, Lindemann A, Gleber-Netto FO, Pickering CR, Anfossi S, Osman AA, Cai Y, Wang R, Knutsen E, Shimizu M, Ivan C, Rao X, Wang J, Silverman DA, Tam S, Zhao M, Caulin C, Zinger A, Tasciotti E, Dougherty PM, El-Naggar A, Calin GA, Myers JN. Loss of p53 drives neuron reprogramming in head and neck cancer.Nature. 2020 Feb;578(7795):449-454. [CrossRef]
- Andersen RE, Lim DA. Forging our understanding of lncRNAs in the brain. Cell Tissue Res. 2018 Jan;371(1):55-71. [CrossRef]
- Constantin L. Circular RNAs and Neuronal Development. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1087:205-213. [CrossRef]
- Ling H, Fabbri M, Calin GA. MicroRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Nov;12(11):847-65. [CrossRef]
- Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017 Mar;16(3):203-222. [CrossRef]
- van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Thatcher JE, DiMaio JM, Naseem RH, Marshall WS, Hill JA, Olson EN. Dysregulation of microRNAs after myocardial infarction reveals a role of miR-29 in cardiac fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 2;105(35):13027-32. [CrossRef]
- Khvorova A, Watts JK. The chemical evolution of oligonucleotide therapies of clinical utility. Nat Biotechnol. 2017 Mar;35(3):238-248. [CrossRef]
- Ochoa S, Milam VT. Modified Nucleic Acids: Expanding the Capabilities of Functional Oligonucleotides.Molecules. 2020 Oct 13;25(20):4659. [CrossRef]
- Crooke ST. Molecular Mechanisms of Antisense Oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017 Apr;27(2):70-77. [CrossRef]
- Singh NN, Luo D, Singh RN. Pre-mRNA Splicing Modulation by Antisense Oligonucleotides. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1828:415-437. [CrossRef]
- Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells.Nature. 2001 May 24;411(6836):494-8. [CrossRef]
- Rao DD, Senzer N, Wang Z, Kumar P, Jay CM, Nemunaitis J. Bifunctional short hairpin RNA (bi-shRNA): design and pathway to clinical application. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;942:259-78. [CrossRef]
- Rao DD, Jay C, Wang Z, Luo X, Kumar P, Eysenbach H, Ghisoli M, Senzer N, Nemunaitis J. Preclinical Justification of pbi-shRNA EWS/FLI1 Lipoplex (LPX) Treatment for Ewing's Sarcoma. Mol Ther. 2016 Aug;24(8):1412-22. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z, Jay CM, Evans C, Kumar P, Phalon C, Rao DD, Senzer N, Nemunaitis J. Preclinical Biodistribution and Safety Evaluation of a pbi-shRNA STMN1 Lipoplex after Subcutaneous Delivery. Toxicol Sci. 2017 Feb;155(2):400-408. [CrossRef]
- van Rooij E, Kauppinen S. Development of microRNA therapeutics is coming of age. EMBO Mol Med. 2014 Jul;6(7):851-64. [CrossRef]
- Beg MS, Brenner AJ, Sachdev J, Borad M, Kang YK, Stoudemire J, Smith S, Bader AG, Kim S, Hong DS. Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs. 2017 Apr;35(2):180-188. [CrossRef]
- Hong DS, Kang YK, Borad M, Sachdev J, Ejadi S, Lim HY, Brenner AJ, Park K, Lee JL, Kim TY, Shin S, Becerra CR, Falchook G, Stoudemire J, Martin D, Kelnar K, Peltier H, Bonato V, Bader AG, Smith S, Kim S, O'Neill V, Beg MS. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours.
- Br J Cancer. 2020 May;122(11):1630-1637. [CrossRef]
- van Zandwijk N, Pavlakis N, Kao SC, Linton A, Boyer MJ, Clarke S, Huynh Y, Chrzanowska A, Fulham MJ, Bailey DL, Cooper WA, Kritharides L, Ridley L, Pattison ST, MacDiarmid J, Brahmbhatt H, Reid G. Safety and activity of microRNA-loaded minicells in patients with recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma: a first-in-man, phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet Oncol. 2017 Oct;18(10):1386-1396. [CrossRef]
- Krützfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M, Stoffel M. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with 'antagomirs'.Nature. 2005 Dec 1;438(7068):685-9. [CrossRef]
- Gebert LF, Rebhan MA, Crivelli SE, Denzler R, Stoffel M, Hall J. Miravirsen (SPC3649) can inhibit the biogenesis of miR-122.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(1):609-21. [CrossRef]
- Ebert MS, Neilson JR, Sharp PA. MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells.
- Nat Methods. 2007 Sep;4(9):721-6. [CrossRef]
- Lima JF, Cerqueira L, Figueiredo C, Oliveira C, Azevedo NF. Anti-miRNA oligonucleotides: A comprehensive guide for design. RNA Biol. 2018 Mar 4;15(3):338-352. [CrossRef]
- Kluiver J, Slezak-Prochazka I, Smigielska-Czepiel K, Halsema N, Kroesen BJ, van den Berg A. Generation of miRNA sponge constructs. Methods. 2012 Oct;58(2):113-7. [CrossRef]
- Chang S. Construction of Multi-Potent MicroRNA Sponge and Its Functional Evaluation. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1699:201-209. [CrossRef]
- Jung J, Yeom C, Choi YS, Kim S, Lee E, Park MJ, Kang SW, Kim SB, Chang S. Simultaneous inhibition of multiple oncogenic miRNAs by a multi-potent microRNA sponge Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 21;6(24):20370-87. [CrossRef]
- Das S, Kohr M, Dunkerly-Eyring B, Lee DI, Bedja D, Kent OA, Leung AK, Henao-Mejia J, Flavell RA, Steenbergen C. Divergent Effects of miR-181 Family Members on Myocardial Function Through Protective Cytosolic and Detrimental Mitochondrial microRNA Targets. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Feb 27;6(3):e004694. [CrossRef]
- Bernardo BC, Gregorevic P, Ritchie RH, McMullen JR. Generation of MicroRNA-34 Sponges and Tough Decoys for the Heart: Developments and Challenges.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Sep 21; 9:1090. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z. The principles of MiRNA-masking antisense oligonucleotides technology. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;676:43-9. [CrossRef]
- Murakami K, Miyagishi M. Tiny masking locked nucleic acids effectively bind to mRNA and inhibit binding of microRNAs in relation to thermodynamic stability.Biomed Rep. 2014 Jul;2(4):509-512. [CrossRef]
- Gilot D, Migault M, Bachelot L, Journé F, Rogiers A, Donnou-Fournet E, Mogha A, Mouchet N, Pinel-Marie ML, Mari B, Montier T, Corre S, Gautron A, Rambow F, El Hajj P, Ben Jouira R, Tartare-Deckert S, Marine JC, Felden B, Ghanem G, Galibert MD. A non-coding function of TYRP1 mRNA promotes melanoma growth.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 Nov;19(11):1348-1357. [CrossRef]
- Slack FJ, Chinnaiyan AM. The Role of Non-coding RNAs in Oncology. Cell. 2019 Nov 14;179(5):1033-1055. [CrossRef]
- Shah MY, Ferrajoli A, Sood AK, Lopez-Berestein G, Calin GA. microRNA Therapeutics in Cancer - An Emerging Concept. EBioMedicine. 2016 Oct; 12:34-42. [CrossRef]
- Calin GA, Cimmino A, Fabbri M, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE, Shimizu M, Taccioli C, Zanesi N, Garzon R, Aqeilan RI, Alder H, Volinia S, Rassenti L, Liu X, Liu CG, Kipps TJ, Negrini M, Croce CM. MiR-15a and miR-16-1 cluster functions in human leukemia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 1;105(13):5166-71. [CrossRef]
- Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Aqeilan RI, Zupo S, Dono M, Rassenti L, Alder H, Volinia S, Liu CG, Kipps TJ, Negrini M, Croce CM. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 27;102(39):13944-9. [CrossRef]
- Arun G, Diermeier SD, Spector DL. Therapeutic Targeting of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer.
- Trends Mol Med. 2018 Mar;24(3):257-277. [CrossRef]
- Modarresi F, Faghihi MA, Lopez-Toledano MA, Fatemi RP, Magistri M, Brothers SP, van der Brug MP, Wahlestedt C. Inhibition of natural antisense transcripts in vivo results in gene-specific transcriptional upregulation. Nat Biotechnol. 2012 Mar 25;30(5):453-9. [CrossRef]
- Hsiao J, Yuan TY, Tsai MS, Lu CY, Lin YC, Lee ML, Lin SW, Chang FC, Liu Pimentel H, Olive C, Coito C, Shen G, Young M, Thorne T, Lawrence M, Magistri M, Faghihi MA, Khorkova O, Wahlestedt C. Upregulation of Haploinsufficient Gene Expression in the Brain by Targeting a Long Non-coding RNA Improves Seizure Phenotype in a Model of Dravet Syndrome. EBioMedicine. 2016 Jul;9:257-277. [CrossRef]
- Padmakumar S, Jones G, Pawar G, Khorkova O, Hsiao J, Kim J, Amiji MM, Bleier Minimally Invasive Nasal Depot (MIND) technique for direct BDNF AntagoNAT delivery to the brain. BS.J Control Release. 2021 Mar 10; 331:176-186. [CrossRef]
- Moulder SL, Symmans WF, Booser DJ, Madden TL, Lipsanen C, Yuan L, Brewster AM, Cristofanilli M, Hunt KK, Buchholz TA, Zwiebel J, Valero V, Hortobagyi GN, Esteva FJ. Phase I/II study of G3139 (Bcl-2 antisense oligonucleotide) in combination with doxorubicin and docetaxel in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Dec 1;14(23):7909-16. [CrossRef]
- Croce CM, Reed JC. Finally, An Apoptosis-Targeting Therapeutic for Cancer.Cancer Res. 2016 Oct 15;76(20):5914-5920. [CrossRef]
- Gallant-Behm CL, Piper J, Lynch JM, Seto AG, Hong SJ, Mustoe TA, Maari C, Pestano LA, Dalby CM, Jackson AL, Rubin P, Marshall WS. A MicroRNA-29 Mimic (Remlarsen) Represses Extracellular Matrix Expression and Fibroplasia in the Skin.J Invest Dermatol. 2019 May;139(5):1073-1081. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty C, Sharma AR, Sharma G, Bhattacharya M, Lee SS. SARS-CoV-2 causing pneumonia-associated respiratory disorder (COVID-19): diagnostic and proposed therapeutic options.
- Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Apr;24(7):4016-4026. [CrossRef]
- Roberts TC, Langer R, Wood MJA. Advances in oligonucleotide drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19(10):673–694. [CrossRef]
- Hu Y, Matkovich SJ, Hecker PA, Zhang Y, Edwards JR, Dorn GW 2nd. Epitranscriptional orchestration of genetic reprogramming is an emergent property of stress-regulated cardiac microRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(48):19864–19869.
- Bagnall RD, Tsoutsman T, Shephard RE, Ritchie W, Semsarian C. Global microRNA profiling of the mouse ventricles during development of severe hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and heart failure. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44744.
- Raso A, Dirkx E, Sampaio-Pinto V, El Azzouzi H, Cubero RJ, Sorensen DW, Ottaviani L, Olieslagers S, Huibers MM, de Weger R, Siddiqi S, Moimas S, Torrini C, Zentillin L, Braga L, Nascimento DS, da Costa Martins PA, van Berlo JH, Zacchigna S, Giacca M, De Windt LJ. A microRNA program regulates the balance between cardiomyocyte hyperplasia and hypertrophy and stimulates cardiac regeneration. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4808. [CrossRef]
- Ganesan J, Ramanujam D, Sassi Y, Ahles A, Jentzsch C, Werfel S, Leierseder S, Loyer X, Giacca M, Zentilin L, Thum T, Laggerbauer B, Engelhardt S. MiR-378 controls cardiac hyper- trophy by combined repression of mitogen- activated protein kinase pathway factors. Circulation. 2013;127(21):2097–2106. [CrossRef]
- Ray KK, Wright RS. Clinical Update on Novel Lipid-Lowering Therapies to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk.
- JAMA. 2021 Dec 7;326(21):2205. [CrossRef]
- Janssen HLA, Reesink HW, Lawitz EJ, Zeuzem S, Rodriguez-Torres M, Patel K, van der Meer AJ, Patick AK, Chen A, Zhou Y, Persson R, King BD, Kauppinen S, Levin AA, Hodges MR. Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(18):1685–1694. [CrossRef]
- Sioud M. Single-stranded small interfering RNA are more immunostimulatory than their double-stranded counterparts: a central role for 2'-hydroxyl uridines in immune responses. Eur J Immunol. 2006 May;36(5):1222-30. [CrossRef]
- Morrissey DV, Lockridge JA, Shaw L, Blanchard K, Jensen K, Breen W, Hartsough K, Machemer L, Radka S, Jadhav V, Vaish N, Zinnen S, Vargeese C, Bowman K, Shaffer CS, Jeffs LB, Judge A, MacLachlan I, Polisky B. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2005 Aug;23(8):1002-7. [CrossRef]
- Judge AD, Bola G, Lee AC, MacLachlan I. Design of noninflammatory synthetic siRNA mediating potent gene silencing in vivo. Mol Ther. 2006 Mar;13(3):494-505. [CrossRef]
- Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X, Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, Wiggins JF, Bader AG, Fagin R, Brown D, Tang DG. The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 2011 Feb;17(2):211-5. [CrossRef]
- Bader AG. miR-34 - a microRNA replacement therapy is headed to the clinic.Front Genet. 2012 Jul 2;3:120. [CrossRef]
- Daige CL, Wiggins JF, Priddy L, Nelligan-Davis T, Zhao J, Brown D. Systemic delivery of a miR34a mimic as a potential therapeutic for liver cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Oct;13(10):2352-60. [CrossRef]
- Tolcher AW, Rodrigueza WV, Rasco DW, Patnaik A, Papadopoulos KP, Amaya A, Moore TD, Gaylor SK, Bisgaier CL, Sooch MP, Woolliscroft MJ, Messmann RA. A phase 1 study of the BCL2-targeted deoxyribonucleic acid inhibitor (DNAi) PNT2258 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014 Feb;73(2):363-71. [CrossRef]
- Kelnar K, Bader AG. A qRT-PCR Method for Determining the Biodistribution Profile of a miR-34a Mimic.
- Methods Mol Biol. 2015; 1317:125-33. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Li J, Dong K, Lin F, Long M, Ouyang Y, Wei J, Chen X, Weng Y, He T, Zhang H. Tumor suppressor miR-34a targets PD-L1 and functions as a potential immunotherapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia.
- Cell Signal. 2015 Mar;27(3):443-52. [CrossRef]
- Täubel J, et al. Novel antisense therapy targeting microRNA-132 in patients with heart failure: results of a first-in-human phase 1b randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(2):178–188.
- Hinkel R, et al. AntimiR-132 attenuates myocar- dial hypertrophy in an animal model of percu- taneous aortic constriction. J Am Col Cardiol. 2021;77(23):2923–2935.
- Van Der Ree MH, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of microRNA-targeted therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients. Antiviral Res. 2014; 111:53–59.
- Van Der Ree MH, et al. Miravirsen dosing in chronic hepatitis C patients results in decreased microRNA-122 levels without affecting other microRNAs in plasma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;43(1):102–113.
- Natarelli L, et al. miR-103 promotes endothelial maladaptation by targeting lncWDR59. Nat Com- mun. 2018;9(1):2645.
- Deng Y, et al. Randomized clinical trials towards a single-visit cure for chronic hepatitis C: Oral GSK2878175 and injectable RG-101 in chronic hepatitis C patients and long-acting injectable GSK2878175 in healthy participants. J Viral Hepat. 2020;27(7):699–708.
- van der Ree MH, et al. Safety, tolerability, and antiviral effect of RG-101 in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a phase 1B, double- blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10070):709–717.
- van Zandwijk N, et al. Safety and activity of microRNA-loaded minicells in patients with recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma: a first-in-man, phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(10):1386–1396.
- Lee EC, Valencia T, Allerson C, Schairer A, Flaten A, Yheskel M, Kersjes K, Li J, Gatto S, Takhar M, Lockton S, Pavlicek A, Kim M, Chu T, Soriano R, Davis S, Androsavich JR, Sarwary S, Owen T, Kaplan J, Liu K, Jang G, Neben S, Bentley P, Wright T, Patel V.. Discovery and preclinical evalua- tion of anti-miR-17 oligonucleotide RGLS4326 for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1–14. [CrossRef]
- Du W, et al. By targeting Stat3 microRNA-17-5p promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis in response to ischemia followed by reperfusion. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34(3):955–965.
- Anastasiadou E, Seto AG, Beatty X, Hermreck M, Gilles ME, Stroopinsky D, Pinter-Brown LC, Pestano L, Marchese C, Avigan D, Trivedi P, Escolar DM, Jackson AL, Slack FJ. Cobomarsen, an oligo- nucleotide inhibitor of miR-155, slows DLBCL tumor cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(4):1139–1149. [CrossRef]
- Abplanalp WT, et al. Efficiency and target derepres- sion of anti-miR-92a: results of a first in human study. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020;30(6):335–345.
- Boon RA, et al. MicroRNA-34a regulates cardiac ageing and function. Nature. 2013;495(7439):107–110.
- Gabisonia K, Prosdocimo G, Aquaro GD, Carlucci L, Zentilin L, Secco I, Ali H, Braga L, Gorgodze N, Bernini F, Burchielli S, Collesi C, Zandonà L, Sinagra G, Piacenti M, Zacchigna S, Bussani R, Recchia FA, Giacca M. MicroRNA therapy stimulates uncontrolled cardiac repair after myocardial infarction in pigs. Nature. 2019;569(7756):418–422. [CrossRef]
- Juliano RL. The delivery of therapeutic oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(14):6518–6548. [CrossRef]
- Geary RS, Norris D, Yu R, Bennett CF.. Pharmacokinetics, biodistribution and cell uptake of antisense oligonucleotides. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015; 87:46–51. [CrossRef]
- Eding JEC, Demkes CJ, Lynch JM, Seto AG, Montgomery RL, Semus HM, Jackson AL, Isabelle M, Chimenti S, van Rooij E. The efficacy of cardiac anti- miR-208a therapy is stress dependent. Mol Ther. 2017;25(3):694–704. [CrossRef]
- Stein CA, Hansen JB, Lai J, Wu S, Voskresenskiy A, Høg A, Worm J, Hedtjärn M, Souleimanian N, Miller P, Soifer HS, Castanotto D, Benimetskaya L, Ørum H, Koch T. Efficient gene silencing by deliv-ery of locked nucleic acid antisense oligonu-cleotides, unassisted by transfection reagents. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;38(1):1–8. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell MJ, Billingsley MM, Haley RM, Wechsler ME, Peppas NA, Langer R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(2):101–124. [CrossRef]
- Bian J, et al. Effect of cell-based intercellu- lar delivery of transcription factor GATA4 on ischemic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2007;100(11):1626–1633.
- Zahid M, Feldman KS, Garcia-Borrero G, Feinstein TN, Pogodzinski N, Xu X, Yurko R, Czachowski M, Wu YL, Mason NS, Lo CW. Cardiac targeting peptide, a novel cardiac vector: Studies in bio-distribution, imag- ing application, and mechanism of transduction. Biomolecules. 2018;8(4):14296–14296. [CrossRef]
- Grijalvo S, Alagia A, Jorge AF, Eritja R. Covalent strategies for targeting messenger and non-coding RNAs: an updated review on siRNA, miRNA and antimiR conjugates. Genes (Basel). 2018;9(2):74. [CrossRef]
- Sugo T, Terada M, Oikawa T, Miyata K, Nishimura S, Kenjo E, Ogasawara-Shimizu M, Makita Y, Imaichi S, Murata S, Otake K, Kikuchi K, Teratani M, Masuda Y, Kamei T, Takagahara S, Ikeda S, Ohtaki T, Matsumoto H. Development of antibody-siRNA conjugate targeted to cardiac and skeletal muscles. J Control Release. 2016; 237:1–13. [CrossRef]
- Klein D, Goldberg S, Theile CS, Dambra R, Haskell K, Kuhar E, Lin T, Parmar R, Manoharan M, Richter M, Wu M, Mendrola Zarazowski J, Jadhav V, Maier MA, Sepp-Lorenzino L, O'Neil K, Dudkin V. Centyrin ligands for extrahepatic delivery of siRNA. Mol Ther. 2021; 29(6):2053–2066. [CrossRef]
- Orellana EA, Tenneti S, Rangasamy L, Lyle LT, Low PS, Kasinski AL. FolamiRs: Ligand-targeted, vehicle-free delivery of microRNAs for the treatment of cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(401):1–11. [CrossRef]
- Bom APDA, Bonacossa de Almeida CE, Silva D, Missailidis S. Aptamers as delivery agents of siRNA and chimeric formulations for the treat- ment of cancer. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(12):1–16. [CrossRef]
- Rohde JH, Weigand JE, Suess B, Dimmeler S. A universal aptamer chimera for the delivery of functional microRNA-126. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2015;25(3):141–151. [CrossRef]
- Domenger C, Grimm D. Next-generation AAV vectors—do not judge a virus (only) by its cover. Hum Mol Genet. 2019; 28:3–14. [CrossRef]
- Li C, Samulski RJ. Engineering adeno-associated virus vectors for gene therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 2020;21(4):255–272. [CrossRef]
- Asokan A, Conway JC, Phillips JL, Li C, Hegge J, Sinnott R, Yadav S, DiPrimio N, Nam HJ, Agbandje-McKenna M, McPhee S, Wolff J, Samulski RJ. Reengineering a receptor foot- print of adeno-associated virus enables selective and systemic gene transfer to muscle. Nat Bio- technol. 2010;28(1):79–82. [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa K, Fish KM, Tilemann L, Rapti K, Aguero J, Santos-Gallego CG, Lee A, Karakikes I, Xie C, Akar FG, Shimada YJ, Gwathmey JK, Asokan A, McPhee S, Samulski J, Samulski RJ, Sigg DC, Weber T, Kranias EG, Hajjar RJ. Cardiac I-1c overexpression with reengineered AAV improves cardiac func- tion in swine ischemic heart failure. Mol Ther. 2014;22(12):2038–2045. [CrossRef]
- Tabebordbar M, Lagerborg KA, Stanton A, King EM, Ye S, Tellez L, Krunnfusz A, Tavakoli S, Widrick JJ, Messemer KA, Troiano EC, Moghadaszadeh B, Peacker BL, Leacock KA, Horwitz N, Beggs AH, Wagers AJ, Sabeti PC. Directed evolution of a family of AAV capsid variants enabling potent muscle-directed gene delivery across species. Cell. 2021;184(19):4919–4938. [CrossRef]
- Zeng Y, Du WW, Wu Y, Yang Z, Awan FM, Li X, Yang W, Zhang C, Yang Q, Yee A, Chen Y, Yang F, Sun H, Huang R, Yee AJ, Li RK, Wu Z, Backx PH, Yang BB. A circular RNA binds to and acti- vates AKT phosphorylation and nuclear localiza- tion reducing apoptosis and enhancing cardiac repair. Theranostics. 2017;7(16):3842–3855. [CrossRef]
- Gruner HN, McManus MT. Examining the evidence for extracellular RNA function in mam- mals. Nat Rev Genet. 2021;22(7):448–458.
- Sahoo S, et al. Therapeutic and diagnostic trans- lation of extracellular vesicles in cardiovascular diseases: roadmap to the clinic. Circulation. 2021;1426(14):1429–1449.
- Chakraborty R, et al. Promoters to study vascular smooth muscle. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(4):603–612.
- Hullinger TG, et al. Inhibition of miR-15 pro- tects against cardiac ischemic injury. Circ Res. 2012;110(1):71–81.
- Icli B, Wara AK, Moslehi J, Sun X, Plovie E, Cahill M, Marchini JF, Schissler A, Padera RF, Shi J, Cheng HW, Raghuram S, Arany Z, Liao R, Croce K, MacRae C, Feinberg MW. MicroRNA-26a regulates pathological and physiological angiogenesis by targeting BMP/SMAD1 signaling. Circ Res. 2013;113(11):1231–1241. [CrossRef]
- Tijsen AJ, et al. The microRNA-15 family inhibits the TGFβ-pathway in the heart. Cardiovasc Res. 2014;104(1):61–71.
- Yang F, Chen Q, He S, Yang M, Maguire EM, An W, Afzal TA, Luong LA, Zhang L, Xiao Q. miR-22 is a novel mediator of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation and neointima formation. Circulation. 2018;137(17):1824–1841. [CrossRef]
- Dirkx E, et al. Nfat and miR-25 cooperate to reactivate the transcription factor Hand2 in heart failure. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(11):1282–1293.
- Rayner KJ, Sheedy FJ, Esau CC, Hussain FN, Temel RE, Parathath S, van Gils JM, Rayner AJ, Chang AN, Suarez Y, Fernandez-Hernando C, Fisher EA, Moore KJ. Antagonism of miR-33 in mice promotes reverse cholesterol transport and regression of atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(7):2921–2931.. [CrossRef]
- Duygu B, Juni R, Ottaviani L, Bitsch N, Wit JBM, de Windt LJ, da Costa Martins PA.. Comparison of different chem- ically modified inhibitors of miR-199b in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019; 159:106–115. [CrossRef]
- Raso A, Dirkx E, Philippen LE, Fernandez-Celis A, De Majo F, Sampaio-Pinto V, Sansonetti M, Juni R, El Azzouzi H, Calore M, Bitsch N, Olieslagers S, Oerlemans MIFJ, Huibers MM, de Weger RA, Reckman YJ, Pinto YM, Zentilin L, Zacchigna S, Giacca M, da Costa Martins PA, López-Andrés N, De Windt LJ. Therapeutic delivery of miR-148a suppresses ventricular dilation in heart failure. Mol Ther. 2019;27(3):584–599. [CrossRef]
- Yang H, Qin X, Wang H, Zhao X, Liu Y, Wo HT, Liu C, Nishiga M, Chen H, Ge J, Sayed N, Abilez OJ, Ding D, Heilshorn SC, Li K. An in vivo miRNA delivery system for restoring infarcted myocardium. ACS Nano. 2019;13(9):9880–9894. [CrossRef]
- Rayner KJ, Esau CC, Hussain FN, McDaniel AL, Marshall SM, van Gils JM, Ray TD, Sheedy FJ, Goedeke L, Liu X, Khatsenko OG, Kaimal V, Lees CJ, Fernandez-Hernando C, Fisher EA, Temel RE, Moore KJ. Inhibition of miR-33a/b in non-human primates raises plasma HDL and lowers VLDL triglycerides. Nature. 2011;478(7369):404–407. [CrossRef]
- van Meer L, Moerland M, Gallagher J, van Doorn MB, Prens EP, Cohen AF, Rissmann R, Burggraaf J. Injection site reactions after subcutaneous oligonucleotide therapy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;82(2):340–351. [CrossRef]
- Rogg EM, Abplanalp WT, Bischof C, John D, Schulz MH, Krishnan J, Fischer A, Poluzzi C, Schaefer L, Bonauer A, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S. Analysis of cell type-specific effects of microRNA-92a provides novel insights into target regulation and mechanism of action. Circulation. 2018;138(22):2545–2558. [CrossRef]
- Wahlquist C, Jeong D, Rojas-Muñoz A, Kho C, Lee A, Mitsuyama S, van Mil A, Park WJ, Sluijter JP, Doevendans PA, Hajjar RJ, Mercola M. Inhibition of miR-25 improves cardiac contractility in the failing heart. Nature. 2014;508(7497):531–535. [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolskaia MA, McNeil SE. Immunological and hematological toxicities challenging clinical translation of nucleic acid-based therapeutics. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(7):1023–1048.
- Judge AD, Sood V, Shaw JR, Fang D, McClintock K, MacLachlan I. Sequence-dependent stim- ulation of the mammalian innate immune response by synthetic siRNA. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23(4):457–462. [CrossRef]
- Karikó K, Buckstein M, Ni H, Weissman D. Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: the impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity. 2005;23(2):165–175. [CrossRef]
- Broering R, Real CI, John MJ, Jahn-Hofmann K, Ickenstein LM, Kleinehr K, Paul A, Gibbert K, Dittmer U, Gerken G, Schlaak JF. Chemical modifications on siRNAs avoid toll-like-receptor-mediated activa- tion of the hepatic immune system in vivo and in vitro. Int Immunol. 2014;26(1):35–46. [CrossRef]
- Alharbi A, Garcin AJ, Lennox KA, Pradeloux S, Wong C, Straub S, Valentin R, Pépin G, Li HM, Nold MF, Nold-Petry CA, Behlke MA, Gantier MP. Rational design of antisense oligonucleotides modulating the activi-ty of TLR7/8 agonists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(13):7052–7065. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa523.
- Povsic TJ, Lawrence MG, Lincoff AM, Mehran R, Rusconi CP, Zelenkofske SL, Huang Z, Sailstad J, Armstrong PW, Steg PG, Bode C, Becker RC, Alexander JH, Adkinson NF, Levinson AI; REGULATE-PCI Investigators.Pre-existing anti-PEG antibodies are associated with severe immediate allergic reactions to pegnivacogin, a PEGylated aptamer. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138(6):1712–1715. [CrossRef]
- Shen W, De Hoyos CL, Migawa MT, Vickers TA, Sun H, Low A, Bell TA 3rd, Rahdar M, Mukhopadhyay S, Hart CE, Bell M, Riney S, Murray SF, Greenlee S, Crooke RM, Liang XH, Seth PP, Crooke ST. Chemical modification of PS-ASO therapeutics reduces cellular protein-binding and improves the therapeutic index. Nat Biotech- nol. 2019;37(6):640–650. [CrossRef]
- Androsavich JR, Chau BN. Non-inhibited miRNAs shape the cellular response to anti-miR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(11):6945–6955. [CrossRef]
- Khan AA, Betel D, Miller ML, Sander C, Leslie CS, Marks DS.. Transfection of small RNAs globally perturbs gene regulation by endogenous microRNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27(6):549–555. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1543.
- Slack FJ, Chinnaiyan AM. The role of non-coding RNAs in oncology. Cell. 2019;179(5):1033–1055.
- de Boer RA, Hulot JS, Tocchetti CG, Aboumsallem JP, Ameri P, Anker SD, Bauersachs J, Bertero E, Coats AJS, Čelutkienė J, Chioncel O, Dodion P, Eschenhagen T, Farmakis D, Bayes-Genis A, Jäger D, Jankowska EA, Kitsis RN, Konety SH, Larkin J, Lehmann L, Lenihan DJ, et al . Common mechanistic path- ways in cancer and heart failure. A scientific roadmap on behalf of the Translational Research Committee of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur J Heart Fail. 2020;22(12):2272–2289. [CrossRef]
- Sahraei M, Chaube B, Liu Y, Sun J, Kaplan A, Price NL, Ding W, Oyaghire S, García-Milian R, Mehta S, Reshetnyak YK, Bahal R, Fiorina P, Glazer PM, Rimm DL, Fernández-Hernando C, Suárez Y. Suppressing miR-21 activity in tumor-associated macrophages promotes an antitumor immune response. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(12):5518–5536. doi: 10.1172/JCI127125.
- Mastroianni J, Stickel N, Andrlova H, Hanke K, Melchinger W, Duquesne S, Schmidt D, Falk M, Andrieux G, Pfeifer D, Dierbach H, Schmitt-Graeff A, Meiss F, Boerries M, Zeiser R. miR-146a controls immune response in the melanoma microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2019;79(1):183–195. [CrossRef]
- Mu P, Han YC, Betel D, Yao E, Squatrito M, Ogrodowski P, de Stanchina E, D'Andrea A, Sander C, Ventura A. Genetic dissection of the miR-17~92 cluster of microRNAs in Myc-induced B-cell lymphomas. Genes Dev. 2009;23(24):2806–2811. [CrossRef]
- Kilikevicius A, Meister G, Corey DR. Reexamining assumptions about miRNA-guided gene silencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(2):617–634. [CrossRef]
| Table 1: FDA and/or European Medicines Agency approved RNA therapies | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Type | Amendment & product delivery | Mode of delivery | Destination site | Disease |
Target gene and route |
FDA and/or EMA approval year |
| Lumasiran (Oxlumo, ALN-GO1) |
21 nt ds-siRNA |
2nd gen; 2ʹ-F/2ʹ-O-Me; GalNAc-conjugated. |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Primary hyperoxaluria type 1 |
Hydroxyacid oxidase 1 (HAO1) mRNA |
2020 (EMA), 2020 (FDA) |
| Inclisiran (Leqvio, ALN-PCSsc) | 21 nt ds-siRNA |
2nd gen; 2ʹ-F/2ʹ-O-Me; GalNAc-conjugated. |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, elevated cholesterol, homozygous/ heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia |
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) mRNA |
2020 (EMA) |
| Volanesorsen (Waylivra) |
20-mer ASO |
2nd gen; 2′-MOE gapme |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Familial chylomicronaemia syndrome |
Apolipoprotein CIII (APOC3) mRNA |
2019 (EMA) |
| Viltolarsen (Viltepso, NS-065, NCNP-01) |
21-mer ASO |
3rd gen; 2′-MOE PMO |
Intravenous |
Muscle |
Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
DMD pre-mRNA splicing (exon 53 skipping) |
2020 (FDA) |
| Givosiran (Givlaari) |
21 nt ds-siRNA |
2nd gen; 2ʹ-F/2ʹ-O-Me; GalNAc-conjugated |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Acute hepatic porphyria |
Delta aminolevulinic acid synthase 1 (ALAS1) mRNA |
2020 (EMA), 2019 (FDA) |
| Golodirsen (Vyondys 53, SRP-4053) |
25-mer ASO |
3rd gen; 2′-MOE PMO |
Intravenous |
Muscle |
Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
DMD pre-mRNA splicing (exon 53 skipping) |
2019 (FDA) |
| Patisiran (Onpattro) |
21 nt ds-siRNA |
2nd gen; 2ʹ-F/2ʹ-O-Me; liposomal |
Intravenous |
Liver |
Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis |
Transthyretin (TTR) mRNA |
2018 (EMA), 2019 (FDA) |
| Inotersen (Tegsedi, AKCEA-TTR-LRx) |
20-mer ASO |
2nd gen; 2′-MOE; GalNAc-conjugated |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis |
Transthyretin (TTR) mRNA |
2018 (EMA), 2018 (FDA) |
| Eteplirsen (Exondys 51) |
30-mer ASO |
3rd gen; 2′-MOE PMO |
Intravenous |
Muscle |
Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
Dystrophin (DMD) pre-mRNA splicing (exon 51 skipping) |
2016 (FDA) |
| Nusinersen (Spinraza, ASO-10-27) |
18-mer ASO |
2nd gen; 2′-MOE |
Intrathecal |
Central nervous system |
Spinal muscular atrophy |
Survival of motor neuron 2 (SMN2) pre-mRNA splicing (exon 7 inclusion) |
2017 (EMA), 2016 (FDA) |
| Mipomersen (Kynamro) |
20-mer ASO |
2nd gen; 2′-MOE gapmer |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia |
Apolipoprotein B mRNA |
2012 (EMA), 2013 (FDA) |
| Fomivirsen (Vitravene) |
21-mer ASO |
1st gen; PT |
Intravitreal |
Eye |
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis in immunocompromised patients |
CMV IE-2 mRNA |
1998 (FDA), 1999 (EMA)* |
| Table 2. Clinical development of RNA therapeutics that has been discontinued. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λTreatment | Type | Amendment & product delivery | Mode of delivery | Destination site | Disease |
Target gene and route |
Reason for leaving the company. |
| Aprinocarsen (ISIS 3521, LY900003) |
ASO |
1st gen; PT |
Intravenous |
Tumour |
Non-small cell lung cance |
Protein kinase Cα mRNA |
No clinical efficacy improvement |
| ISIS 5132 (CGP 69846 A) |
ASO |
1st gen; PT |
Intravenous |
Tumour |
Breast cancer, ovarian cancer |
Raf mRNA |
No clinical efficacy improvement |
| ISIS 104838 |
ASO |
2nd gen; 2′-MOE gapmer |
Oral |
Joints |
Rheumatoid arthritis |
TNF mRNA |
Company decision related to cost and competition. |
| PF-4523655 (PF-655) |
siRNA |
2nd gen; liposomal |
Intravitreal |
Eye |
Age-related macular degeneration, diabetic macular oedema |
DNA damage- inducible transcript 4 (DDIT4) mRNA |
No clinical efficacy improvement compared to the current standard of care. |
| ISIS 329993 (ISIS-CRPRx) |
ASO |
2nd gen; 2′-MOE |
Subcutaneous or intraperitoneal |
Heart or joints |
Paroxysmalatrial fibrillation, rheumatoid arthritis |
C-reactive protein (CRP) mRNA |
Although it reduced CRP mRNA, clinical efficacy was lacking. |
| AEG35156 (AEG 161, GEM 640) |
ASO |
Mixed backbone oligonucleotides |
Intravenous |
Tumour |
Various malignancies |
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) mRNA |
It lacks clinical efficacy. Increased incidence of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. |
| Custirsen (ISIS 112989, OGX-011, TV-1011) |
ASO |
2nd gen; 2′-MOE gapmer |
Intravenous |
Tumour |
Prostate cancer, breast cancer |
Clusterin (CLU) mRNA |
Primary end points were not met in phase III trials, indicating a lack of clinical efficacy. |
| Bevasiranib (Cand5 |
siRNA |
1st gen; PT |
Intravitreal |
Eye |
Age-related macular degeneration, diabetic macular oedema |
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA |
The therapeutic effect of TLR3 stimulation, which is independent of sequence, has not been clinically effective. |
| Oblimersen sodium (G3139, Genasense) |
ASO |
1st gen; PT |
Subcutaneous |
Tumour |
Various malignancies |
BCL2 mRNA |
There was a lack of clinical efficacy due to insufficient delivery, resulting in primary end points not being met. |
| AGN 211745 (AGN-745, siRNA-027) |
siRNA |
Chemical composition unclear; carrier-free |
Intravitreal |
Eye |
Age-related macular degeneration, choroidal neovascularization |
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR1) mRNA |
The therapeutic effect of TLR3 stimulation, which is independent of sequence, has not been clinically effective. |
| PRO-040201 (TKM-ApoB, ApoB SNALP) |
siRNA |
Liposomal (stable nucleic acid lipid particle) |
Intravenous |
Liver |
Hypercholesterol- aemia |
Apolipoprotein B (APOB) mRNA |
Possible to stimulate the immune system, which may cause flu-like symptoms. |
| MRX34 |
miRNA mimic |
Liposomal |
Intravenous or intratumour |
Intravenous or intratumour |
Primary liver cancer, advanced or metastatic cancer with or without liver involvement, haematological malignancies |
miR-34a targetome |
Immune-related adverse events |
| RG-101 |
AntimiR |
GalNAc conjugated |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Hepatitis C infection |
miR-122 |
Immune-related adverse events |
| χCobomarsen (MRG-106) |
AntimiR |
3rd gen; LNA |
Subcutaneous or intravenous |
lood or lymphoid organs |
Various lymphomas |
miR-155 |
Company decision unrelated to safety or efficacy |
| χSuvodirsen (WVE-210201) |
ASO |
1st gen; PT, stereopure |
Intravenous |
Muscle |
Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
Dystrophin (DMD) pre-mRNA splicing (exon 51 skipping) |
The treatment did not show clinical efficacy and did not increase dystrophin levels. |
| χAganirsen (GS-101) |
ASO |
1st gen; PT |
Topical |
Eye |
Ischaemic central retinal vein occlusion, neovascular glaucoma |
Insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) mRNA |
Problems related to the stability of the formulation |
| χDCR-PH1 |
siRNA |
Liposomal |
Intravenous |
Liver |
Primary hyperoxaluria type 1 (PH1) |
Lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) mRNA |
The focus of development has been on the GalNAc conjugation variant, DCR-PHXC. |
| χDCR-MYC (DCR-M1711) |
siRNA |
Liposomal |
Intravenous |
Tumour |
Advanced solid tumours, multiple myeloma, lymphoma |
MYC mRNA |
Despite reducing MYC, there is a lack of clinical efficacy. |
| Table 3: RNA therapies in phase II or III clinical development. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Type | Amendment & product delivery | Mode of delivery | Destination site | Disease |
Target gene and route |
Phase & Identifier |
| RG-125 (AZD4076) |
Anti-miR- 103/107 |
GalNAc- conjugated antagomiR |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Type II diabetes, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. |
miR-103/107 |
I/II NCT04120493 |
| Prexigebersen (BP1001-A) |
ASO |
Liposomal |
Intravenous |
Blood and/or immune cells |
Acute myeloid leukaemia, chronic myeloid leukaemia |
GRB2 mRNA |
II NCT01159028; NCT04196257; NCT02781883 |
| WVE-120102 |
ASO (allele- selectiv) |
Stereopure ASO |
Intrathecal |
Brain |
Huntington disease |
U-variant of SNP rs362331 (SNP2) in HTT mRNA |
I/II NCT03225846, NCT04617860 |
| siG12D-LODER |
siRNA |
Biodegradable polymeric matrix (PLGA) |
Intratumoral |
Tumour |
Advanced pancreatic cancer |
G12D-mutated KRAS mRNA |
II NCT01188785; NCT01676259 |
| rAAV5-miHTT (AMT-130) |
Pri-miR-451 backbone |
Adeno-associated viral vector (AAV5) |
Intrastriatal |
Brain |
Huntington disease |
Huntingtin (HTT) mRNA |
I/II NCT04120493 |
| Remlarsen (MRG-201) |
miR-29 mimic |
Cholesterol conjugated |
Intradermal |
Skin |
Keloid (pathological fibrosis) |
miR-29 targetome |
II NCT02603224, NCT03601052 |
| Miravirsen (SPC3649) |
Anti-miR-122 |
PS-β-d-oxy-LNA gapmer ODN |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Hepatitis C virus infection |
miR-122 |
II NCT01646489, NCT01727934, NCT01872936, NCT01200420 |
| Olpasiran (AMG 890, ARO-LPA |
siRNA |
GalNAc conjugated |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Cardiovascular disease |
Apolipoprotein A (LPA) mRNA |
II NCT03626662, NCT04270760 |
| Vupanorsen (AKCEA- ANGPTL3-LRx) |
ASO |
GalNAc conjugated |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Dyslipidaemias, hyperlipidaemias, hyperlipoprotein- aemias |
Angiopoietin- like 3 (ANGPTL3) mRNA |
II NCT04459767, NCT03371355, NCT04516291 |
| Danvatirsen (IONIS-STAT3- 2.5Rx, AZD9150 |
ASO |
GalNAc conjugated |
Intravenous |
Tumour |
Metastatic NSCLC, resectable early-stage NSCLC, pancreatic cancer, mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancer |
STAT3 mRNA |
II NCT03819465, NCT03794544, NCT0298357 |
| Cemdisiran (ALN-CC5) |
siRNA |
GalNAc conjugated |
Subcutaneous |
Blood |
Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria, IgA nephropathy, Berger disease, glomerulonephritis |
Complement 5 mRNA |
II NCT04601844, NCT02352493, NCT03841448, NCT03999840 |
| BMT 101 (cp-asiRNA) |
Cell- penetrating asymmetrical siRNA |
Carrier-free |
Intradermal |
Skin |
Hypertrophic scar |
Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) mRNA |
II NCT03133130, NCT04012099 |
| Apatorsen (OGX-427) |
ASO |
2′-O-MOE-PTO gapmer |
Intravenous |
Tumour |
Squamous cell lung cancer, non-squamous NSCLC, urological neoplasms, metastatic bladder cancer, urinary tract neoplasms, castration-resistant prostate cancer |
HSP27 mRNA |
II NCT01120470, NCT01454089, NCT01829113, NCT02423590 |
| Bamosiran (SYL040012) |
siRNA |
Carrier-free |
Topical |
Eye |
Ocular hypertension, glaucoma |
β-Adrenergic receptor 2 (ADRB2) mRNA |
II NCT00990743, NCT01227291, NCT01739244, NCT02250612 |
| Donidalorsen (IONIS-PKK-LRx, ISIS 721744) |
ASO |
GalNAc- conjugated PS-2′-MOE ODN |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Hereditary angio-oedema, COVID-19 |
Prekallikrein (PKK) mRNA |
II NCT03263507, NCT04030598, NCT04307381, NCT0454992 |
| Sepofarsen (QR-110) |
ASO |
Chemically modified |
Intravitreal |
Eye |
Leber congenital amaurosis type 10 (LCA10) is a hereditary or congenital eye disease that can cause blindness and vision and sensation disorders. It may also present with neurological manifestations. LCA10 falls under the category of eye diseases. | c.2991+1655A> G-mutated CEP290, pre-mRNA splicing |
II/III NCT03140969, NCT03913143, NCT03913130 |
| Tominersen (RO7234292, HTT ASO, IONIS-HTTRx, ISIS-443139, ISIS-HTTRx, RG 6042) |
ASO (allele- nonselective) |
PS-2′-MOE gapmer |
Intrathecal |
Brain |
Huntington disease |
HTT mRNA |
III NCT02519036, NCT04000594, NCT03342053, NCT03761849, NCT03842969 |
| AKCEA- TTR-LRx |
ASO |
GalNAc conjugated |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Hereditary transthyretin- mediated amyloid polyneuropathy |
Transthyretin (TTR) mRNA |
III NCT04302064; NCT03728634; NCT04136184; NCT04136171 |
| Alicaforsen (ISIS 2302) |
ASO |
Phosphorothioate- modified |
Oral |
Intestine |
Crohn’s disease |
ICAM1 mRNA |
III NCT03473626, NCT00063830, NCT00063414, NCT00048113, NCT02525523 |
| Nedosiran (DCR-PHXC) |
siRNA |
GalNAc conjugated |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Primary hyperoxaluria type 1 and type 2 are kidney and urological diseases characterized by excessive oxalate production. | Lactate dehydrogenase A enzyme (LDHA) mRNA |
III NCT03392896, NCT04555486, NCT04580420, NCT03847909, NCT04042402 |
| Tivanisiran (SYL1001) |
siRNA |
Carrier-free |
Topical |
Eye |
Dry eye disease |
TRPV1 is a member of the transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V. | III NCT01438281, NCT01776658, NCT02455999, NCT03108664 |
| Pelacarsen (AKCEA- APO(a)-LRx, TQJ230) |
siRNA |
GalNAc conjugated |
Subcutaneous |
Liver |
Hyperlipo- proteinaemia |
Apolipoprotein A mRNA |
III NCT03070782, NCT03070782, NCT04023552 |
| Table 4: Clinical trials of miRNAs with therapeutic potential in cardiovascular disease | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active principle/ Therapeutic Drug Name |
Indication |
Clinical phase |
Study no. /status |
Preclinica/ clinical study outcome |
Corporate Sponsor | Related cardiovascular studies |
| miR-132-3p inhibitor (CDR132L) |
Stable heart failure |
Phase I |
NCT04045405 (completed) |
(28, 170) |
Cardior Pharmaceuticals |
(28,31,170,171) |
| miR-122-5p inhibitor (miravirsen) |
HCV |
Phase I Phase I Phase I Phase IIa |
NCT00688012 (completed) NCT00979927 (completed) NCT01646489 (completed) NCT01200420 EudraCT 2010-019057-17 (completed) |
(160, 172, 173) |
Santaris Pharma |
(160, 172, 173) |
| miR-103/107-3p inhibitor (AZD4076) |
T2D with NAFLD T2D with NASH |
Phase I/IIa Phase I |
NCT02826525 (halted for strategic reasons) NCT02612662 (halted for strategic reasons) |
AstraZeneca |
(174) |
|
| miR-122-5p inhibitor (RG-101) |
HCV |
Phase II PhaseII PhaseIIb Phase IIb |
EudraCT 2015-004702-42 (completed) EudraCT 2015-001535-21 (completed) EudraCT 2013-002978-49 (completed) EudraCT 2016-002069-77 (completed) |
(175) (176) |
Regulus Therapeutics |
|
| miR-16-5p mimic (TargomiR) |
Malignant pleural mesothelioma |
Phase I |
NCT02369198 (completed) |
(177) |
Asbestos Diseases Research Foundation |
|
| miR-17-5p inhibitor (RGLS4326) |
ADPKD |
Phase Ib |
NCT04536688 (completed) |
(178) |
Regulus Therapeutics |
(179) |
| miR-155-5p inhibitor cobomarsen (MRG-106) |
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma |
Phase I Phase II |
NCT02580552 (completed) NCT03713320 (terminated for strategic reasons |
(180) |
miRagen Therapeutics (now Viridian Therapeutic) |
(32, 34) |
| miR-92a-3p inhibitor (MRG-110) |
Wound healing |
Phase I Phase I Phase I |
NCT03603431 (completed) NCT03494712 (completed) EUDRA-CT 2017-004180-12 (completed) |
(181) |
miRagen Therapeutics (now Viridian Therapeutic) |
(45, 85, 134) |
| miR-21-5p inhibitor lademirsen (RG-012) |
Alport’s syndrome |
Phase I Phase II |
NCT02603224 (completed) NCT02855268 (ongoing) |
Genzyme/Sanofi |
||
| miR-29-3p mimic remlarsen (MRG-201) |
Keloid scar formation |
Phase I Phase II |
NCT02603224 (completed) NCT03601052 (completed) |
miRagen Therapeutics (now Viridian Therapeutic) |
(17, 22, 23, 173) |
|
| miR-34a-5p mimic (MRX-34) |
Advanced cancer |
Phase I |
NCT01829971 (terminated due to serious adverse effects) |
(128) |
Mirna Therapeutics |
(182, 177) |
| Table 5: Composition, mode of delivery and dosage schedules of selected synthetic inhibitors or mimics of microRNAs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic molecule ϕ Ref |
Organism |
Composition |
MoD | Dosage schedules |
|
AntimiRS | ||||
| LNA-antimiR-29 [17] |
Mouse | Saline | I.V | 20 mg/kg, 1 daily dose for 3 days, starting d1 after surgery. |
| LNA-antimiR-15b [206] |
Mouse |
Saline |
i.v. via catheter |
Up to 33 mg/kg, 1 dose 3 days after AngII infusion. |
| LNA-antimiR-26a or miR-26a mimic [207] |
Mouse |
Matrigel |
s.c | 1 × 106 cells/mL Matrigel transfection: 30–100 nM oligonucleotide/5 × 104 cells |
| LNA-antimiR-15 [208] |
Mouse |
Saline |
s.c | 2 doses with 5 mg/kg each (2–3 days before TAC, 3–4 days after) |
| LNA-antimiR-26a [208] |
Mouse |
Not candidate | i.v | 24 mg/kg, 1 dose 24 hours before MI |
| LNA-antimiR-15b [206] |
Pig | Saline | i.v | Up to 3.3 mg/kg |
| LNA-antimiR-22 [209] |
Mouse |
Hydrogel |
Perivascular |
2.5 nmol Injection concomitant with surgery |
| LNA-antimiR-21 [18] |
Pig |
Saline | i.v | 10 mg each on d5 and d19 after MI |
|
Antagomirs | ||||
| Antagomir-199b [38] |
Mouse |
Saline |
i.p | 0.05–80 mg/kg |
| Antagomir-25 [210] |
Mouse |
Saline |
i.p |
80mg/kg, 1daily dose for 3 days, starting day 1 after surgery |
| Antagomir-21 [18] |
Mouse |
Saline |
i.v. via catheter |
80 mg/kg, 1 daily dose for 2 days, starting d1 or d21 after surgery. |
| Antagomir-29b [117] |
Mouse |
Saline |
i.p | 80 mg/kg, 1 daily dose for 2 days, starting d1 or d21 after surgery |
| Antagomir-146a [211] |
Mouse |
Saline |
Not indicated | 8 mg/kg d2 before delivery and d1, d3 and d7 after surgery |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





