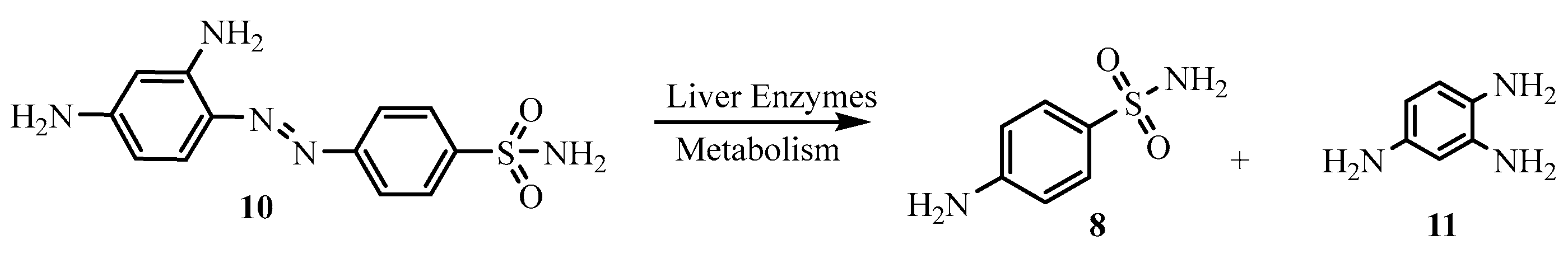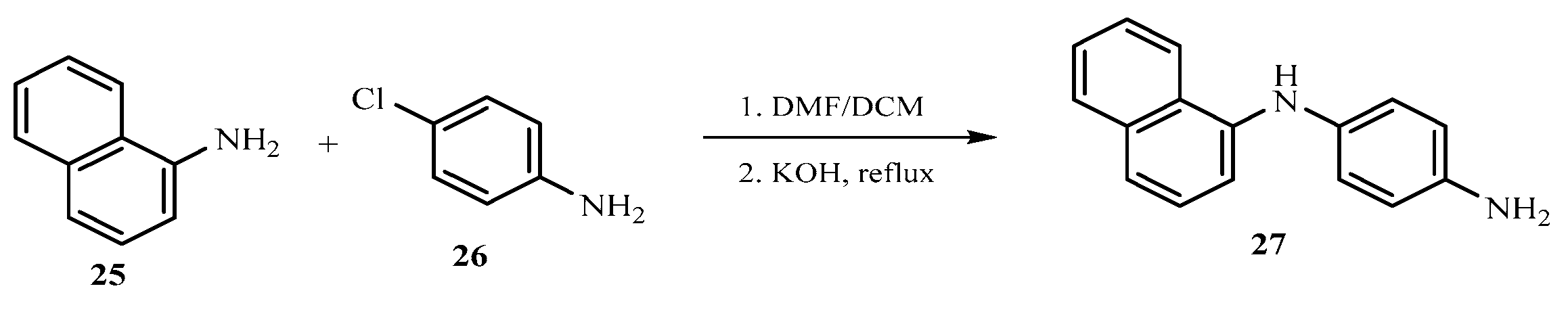1. Introduction
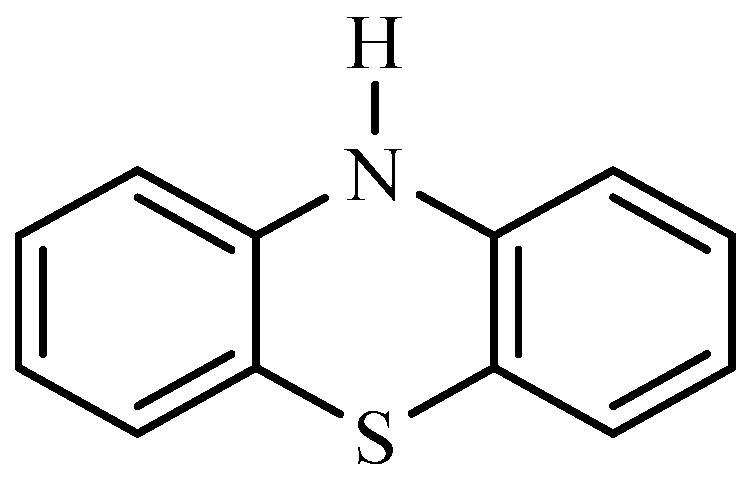
Due to their wide range of pharmacological effects, phenothiazine derivatives have attracted a great deal of attention in the field of medicinal chemistry [
1]. The phenothiazine molecule,
1 is a tricyclic molecule made of two benzene rings joined to a heterocyclic ring containing nitrogen and a sulphur atom [
2,
3]. Numerous biological activities, such as antibacterial, anticancer, antipsychotic, and anti-inflammatory properties, have been reported about these compounds and for that reason they are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry as starting materials for drug molecules [
4].
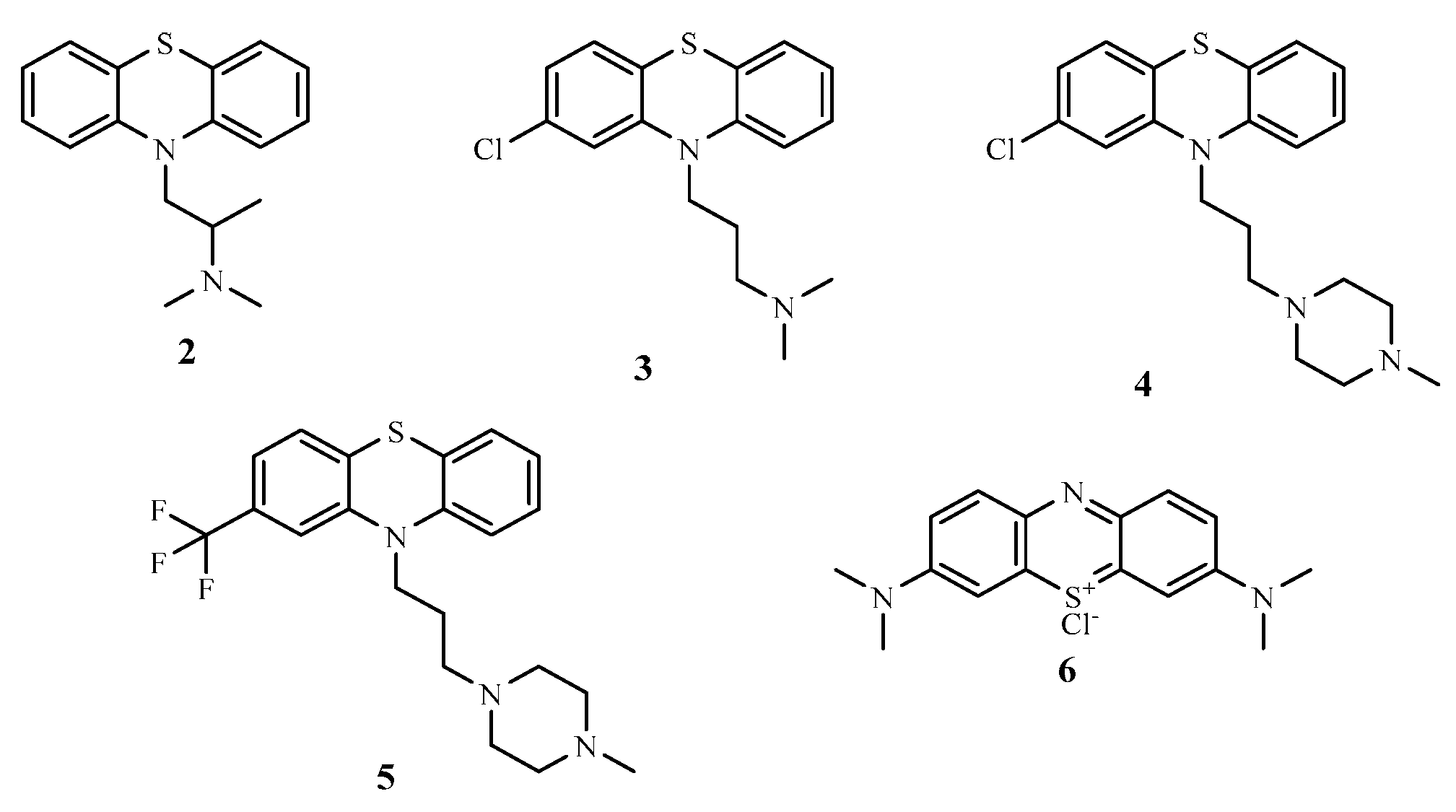
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of some phenothiazine compounds.
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of some phenothiazine compounds.
Heinrich August Bernthsen, German Chemist, produced phenothiazine for the first time in 1876 [
5]. However, it wasn't until a few decades later that its prospective applications were looked into. Paul Charpentier and Henri Laborit led a research team at the French pharmaceutical company, Rhône-Poulenc, where they examined numerous substances for their antihistaminic qualities in the 1930s. They discovered that phenothiazine derivatives exhibited amazing antihistaminic properties [
6]. During World War II, the antimalarial and antiparasitic effects of phenothiazine compounds were investigated, amongst these were promethazine
2 and chlorpromazine
3 just to mention but a few and were discovered to possessed good antimalarial properties [
4]. However, some of the derivatives were ineffective against the
plasmodium parasites that cause malaria. Instead, they had tranquil and relaxing effects, which raised curiosity about their possible psychiatric applications [
7].
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of some phenothiazine compounds.
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of some phenothiazine compounds.
In the 1950s, French researchers Jean Delay, Pierre Deniker and others discovered that phenothiazine compounds had potent antipsychotic properties [
8]. Consequently, the first-generation antipsychotic medications were synthesized when it was discovered that chlorpromazine
3, originally produced as an antihistamine could also reduce psychotic symptoms [
9]. These discoveries completely changed how mental diseases, notably schizophrenia, were treated [
10].
Further investigations on phenothiazine derivatives as therapeutic agents was sparked by the success of chlorpromazine
3 in psychiatry [
11]. Over time, scientists synthesized a variety of phenothiazine compounds with unique pharmacological characteristics namely; prochlorperazine
4 (an antiemetic), promethazine
2 (an antihistamine and an antiemetic), trifluoperazine
5 (an antipsychotic), and methylene blue
6 (an antimalarial and a diagnostic agent) are a few famous examples [
12].
The discovery of phenothiazine and its derivatives brought considerable impact in medicine, especially in the treatment of psychiatric diseases, thereby clearing the pathway for the production of antipsychotic medications for the treatment of mental diseases (Varga et al., 2017).
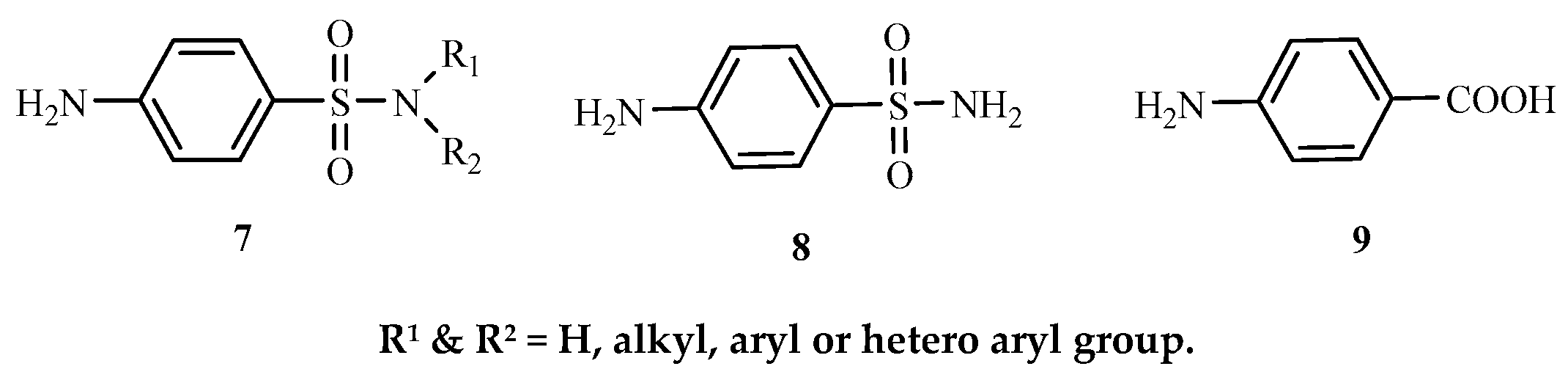
Sulphonamide
7 is a general term for
p-aminobenzenesulphonamide
8 derivatives which resemble
p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). According to Lavanya [
13], sulphonamides were among the first effective antibacterial medications used for treating bacterial infections in humans. Sulphonamides are frequently employed as diuretics, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, and antibacterials [
14].
Figure 3.
Structures of sulphonamide, p- aminobenzenesulphonamide and p-aminobenzoic acid.
Figure 3.
Structures of sulphonamide, p- aminobenzenesulphonamide and p-aminobenzoic acid.
Nobel Prize winner Gerhard Domagk discovered prontosil and its antibacterial properties in the early 1900s. In an effort to keep
streptococci from harming his daughter, he discovered that the sulphonamide dye (prontosil) could selectively inhibit the infectious bacterium cells [
15]. In 1936, Ernest Fourneau identified the protosil pathway in the human body by reporting that the dye was a prodrug (
N-4 substituted sulphonamide)
10 which metabolizes when ingested into sulphanilamide,
8, the active ingredient as an antibacterials, in the human body.
Figure 4.
Metabolism of prontosil (a prodrug) to sulphonmaide (a metabolite form).
Figure 4.
Metabolism of prontosil (a prodrug) to sulphonmaide (a metabolite form).
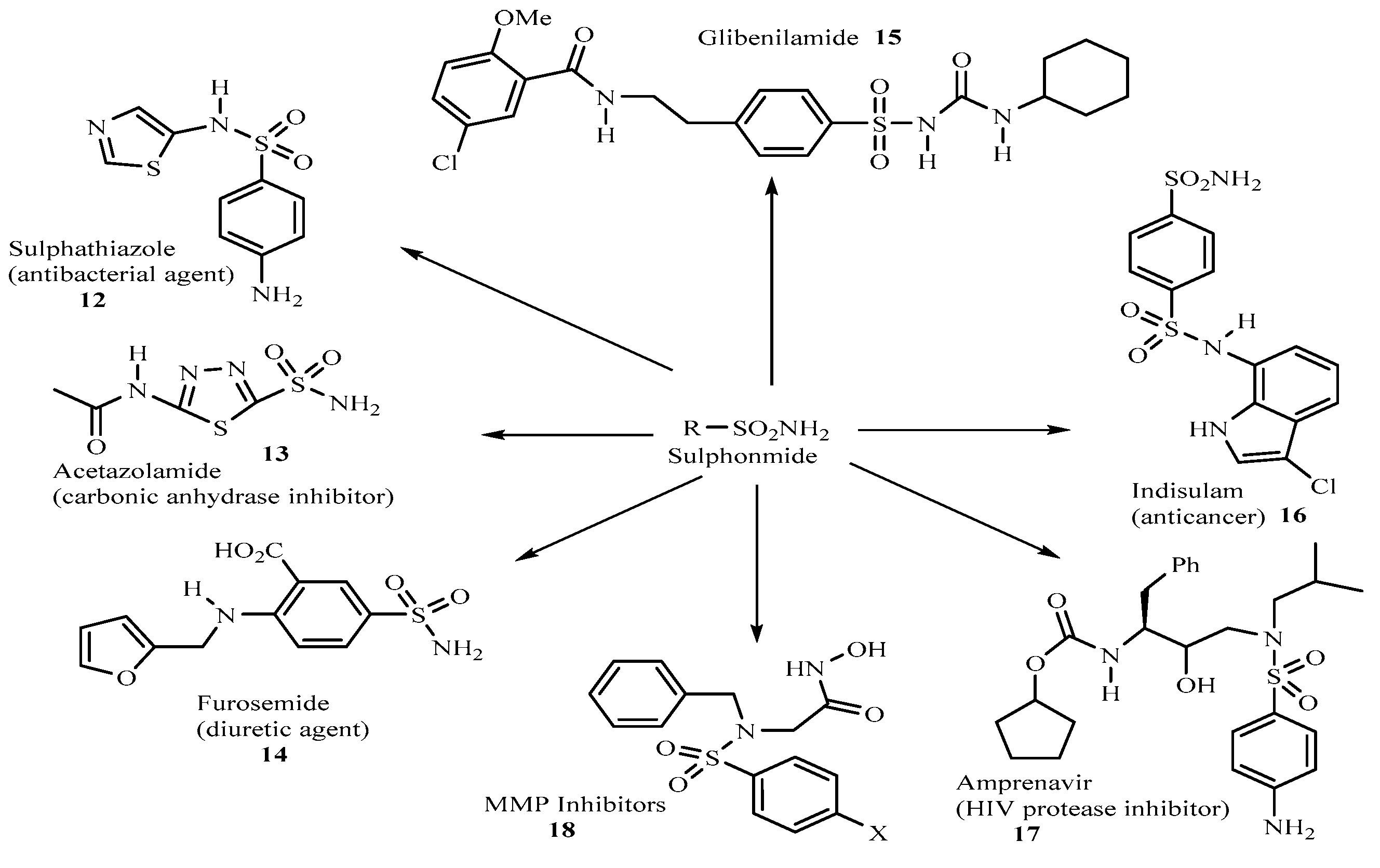
From 1950s till the present day, more potent high-profile sulpha drugs are being produced. These include the antibacterial agent, sulphathiazole
12 [16], the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, acetazolamide
13 [
17,
18] which has been in use clinically for more than 45 years, the diuretic agent, Furosemide
14 [19] the hypoglycemic agent glibenclamide
15 [
20], the anticancer sulphonamide, indisulam
16 [21], the aspartic HIV protease inhibitor amprenavir
17 [
22] used for AIDS and HIV infection management and the metalloprotease (MMP) inhibitors
18 of the sulphonyl amino acid hydroxamate [
23] just to mention but a few (
Figure 5)
Figure 5.
Chemical structures of some sulphonamide drugs.
Figure 5.
Chemical structures of some sulphonamide drugs.
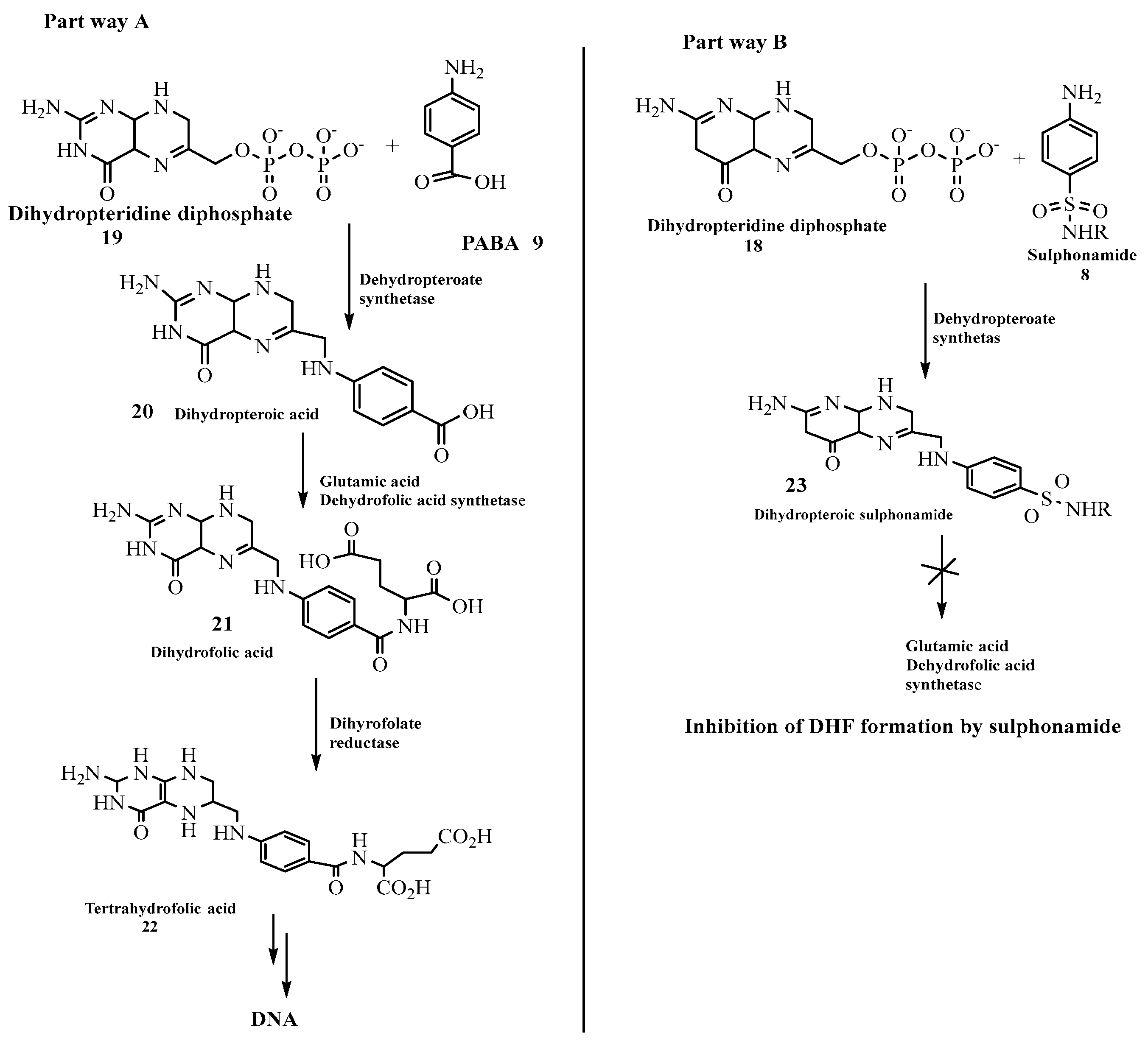
Studies have shown that the presence of folate (folic acid)
22 is very vital in the manufacture of nucleic acids present in the cell wall of bacteria [
24] while its absence renders the cells inactive and prevent DNA synthesis. This can be seen when sulphonamide
8 reacts with dihydropteridine diphosphate
19 to form dihydropteroic sulphonamide
23 in the path way B (
scheme 1) [
25] which hinders further reaction for the formation of folic acid. This is because the formation of dihydropteroic acid
20 which proceeds to yield dihydrofolic acid
21 when dihydropteridine diphosphate
19 reacts with
p-aminobenzoic acid
9 (PABA) in part way A (
scheme 1) cannot take place when sulphonamide is involved [
26]. This clearly shows that sulponamide compounds exhibit bacteriostatic rather than bactericidal effect [
27]. These observations are illustrated in the
Scheme 1 below.
Scheme 1.
Reaction path ways for both para-aminobenzoic and sulphonamide molecules.
Scheme 1.
Reaction path ways for both para-aminobenzoic and sulphonamide molecules.
Studies have shown that sulphonamides and phenothiazine derivatives respectively coupled with other moieties tend to exhibit tremendous pharmacological activities [
28,
29,
30,
31]. For instance Hasti
et al [
32] reported that substitution of electron withdrawing group at position 2 of the phenothiazine ring increases antipsychotic activity. The effect of groups on antipsychotic activity can be ranked as: R
2 = -SO
2NR
2> -CF
3> -COCH
3> -Cl, while substitution at position 3, can improve activity more than non-substituted compounds, but not significantly. Furthermore the authors Hasti
et al [
32] also claimed that substituent at position 4 might hinder the receptor from binding to sulphur at position 5 due to stearic hindrance. In addition to the above observations made by Hasti et al [
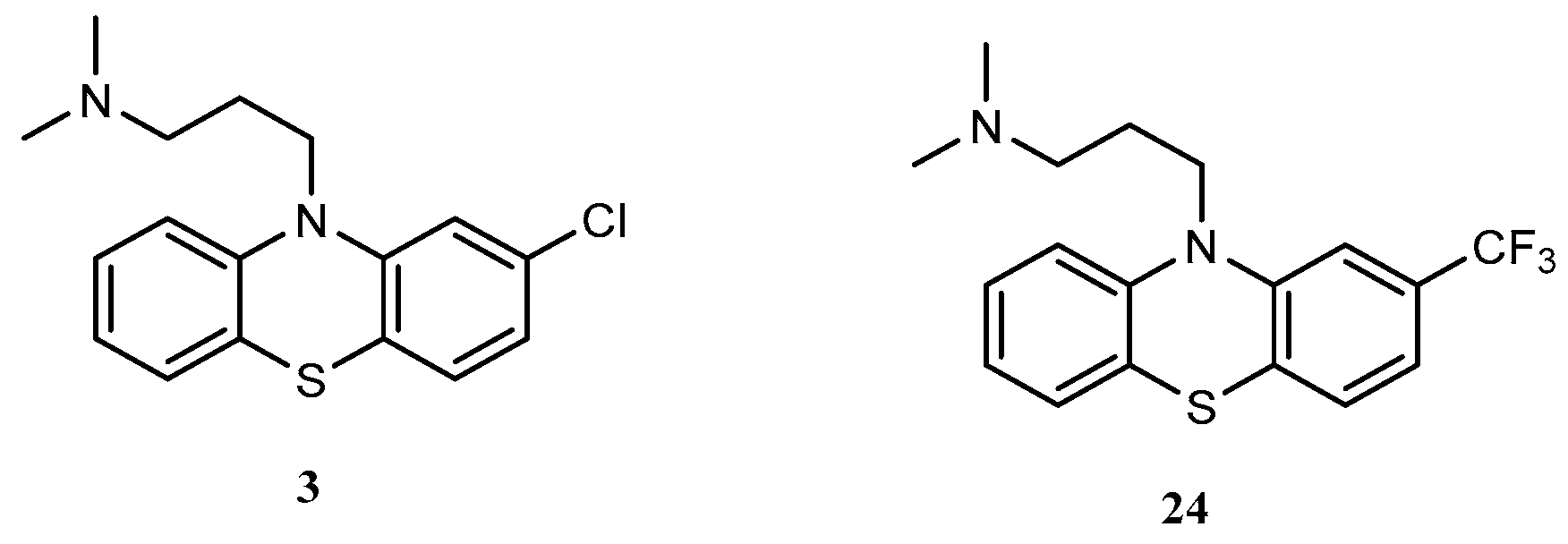
32] they also maintained that the nature of substituent at position 10 also influences pharmacological activity. This observation explains why compounds with aliphatic side chain e.g. chlorpromazine
3 and triflupromazine
24 are less potent, but clinically effective.
Figure 6.
Structures of chlorpromazine and triflupromazine.
Figure 6.
Structures of chlorpromazine and triflupromazine.
These findings underscore the importance of substituted penothiazines surrogates as targeted materials for drug synthesis. Therefore, since penothiazines and sulphonamides derivatives exhibit pharmacological properties, it is our expectation that the coupling of these classes of compounds through organic synthesis would yield derivatives with a broad spectrum of pharmacological properties. Consequently, this expectations inspired the research work reported in this article.
2. Results and Discussions
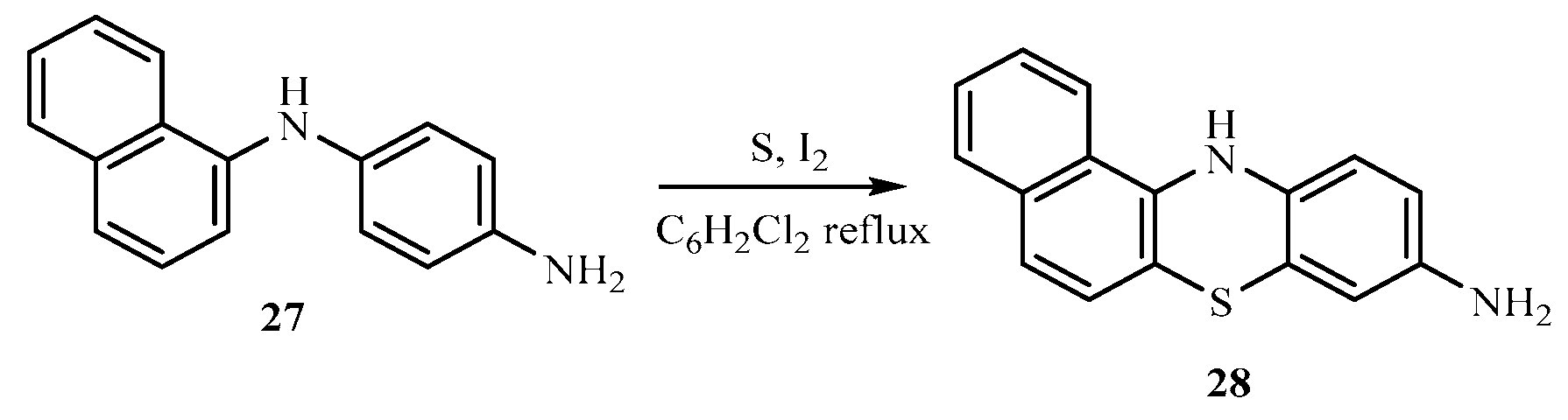
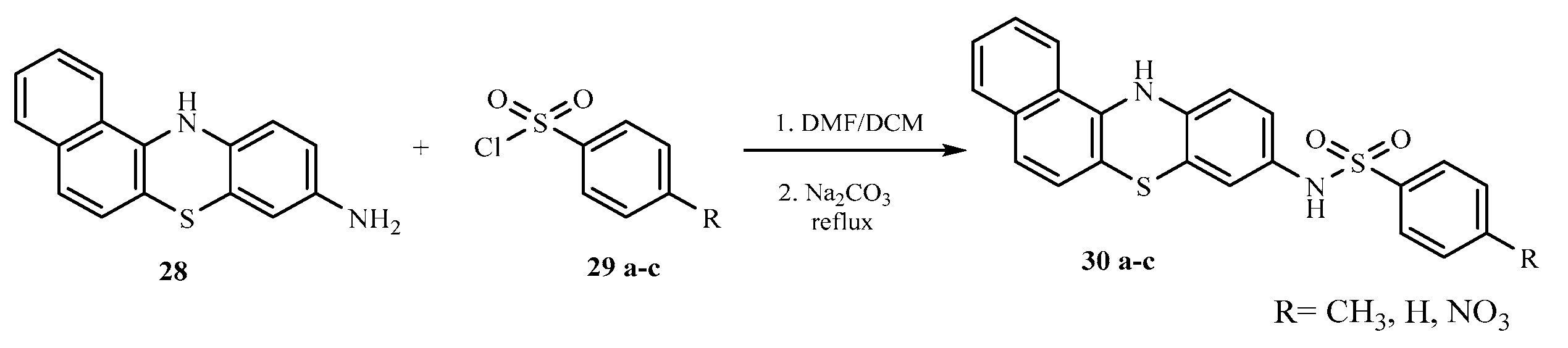
The base catalyzed reaction of 1-naphthylamine 25 and 4-chloroaniline 26 in the presence of dimethylformamide yielded 1-(naphthalen-1-yl) benzene-1,4-diamine 27 one of the key intermediates as shown in scheme 2.0. The FTIR spectrum of this compound gave absorption bands at 3350.9 cm-1 for NH stretch, 3049 cm-1 for C-H aromatic, 1617.7 cm-1 for C=C aromatic, and 1285.9 for C-N bending vibration. In the 1H-NMR spectrum, the peak at δ 8.85 appeared as a singlet and was attributed to NH proton, the peaks at δ 7.71- 6.21 belonged to aromatic protons while the peak at δ 4.95 was for the two protons for NH2 of aniline ring. The 13C-NMR spectrum showed peaks δ 142.7 - 118.5 for aromatic carbons. In order to obtain the phenothiazine derivative 28, 1-(naphthalen-1-yl) benzene-1,4-diamine 27 was treated with sulphur powder and iodine crystals in 1,2-dichlorobenzene to furnish the product, 1-(naphthalen-1-yl)benzene-1,4-diamine and 12H-benzo[a]phenothiazin-9-amine 28 as shown in scheme 2.1 whose FTIR spectrum revealed bands at the following regions 3388.2 cm-1 for NH stretch, 3049 cm-1 for C-H aromatic, 1617.7 cm-1 for C=C aromatic, and 1300.8 cm-1 for C-N. In the 1H-NMR spectrum, there was a single peak at δ 8.21 due to NH proton, δ 7.82 -7.71 for all the aromatic protons and a singlet at δ 4.89 for NH2 proton. The 13C-NMR spectrum showed peaks δ 152.1 - 111.5 which were all assigned to aromatic carbons. The substituted phenothiazine-3-sulphonamide (30 a-c) derivatives were synthesized via a base catalyzed reaction of 12H-benzo[a]phenolthiazin-9-amine and three substituted arylsulphonyl chlorides to yield the final products, phenothiazine-3-sulphonamide derivatives as shown in scheme 2.2. The structures of these derivatives were supported by spectral data. In the FTIR spectrum, the compounds shown almost similar absorption band at 3350.9 cm-1 (NH stretch), 3063.9 cm-1 (Aromatic C-H stretch), 2922.2 cm-1 (aliphatic C-H stretch), 1621.4 cm-1 (C=C aromatic), 1379.1 cm-1 (S=O vibration) and 1330.7 cm-1 was due to C-N bending. The 1H NMR spectra showed peaks at the expected regions for NH at δ 9.8 -9.6, δ 8.37-8.35 for SO2-NH, δ 7.85- 6.61 for aromatic protons while the 13C-NMR spectra of the compounds revealed peaks at δ 144.6 - 111.6 assigned to aromatic carbons and 19.9 to methyl aliphatic carbon.
Scheme 2.
0: Synthesis of 1-(naphthalen-1-yl) benzene-1,4-diamine.
Scheme 2.
0: Synthesis of 1-(naphthalen-1-yl) benzene-1,4-diamine.
Scheme 2.
1: Synthesis of 1-(naphthalen-1-yl) benzene-1,4-diamine and 12H-benzo[a]phenothiaz- in-9-amine.
Scheme 2.
1: Synthesis of 1-(naphthalen-1-yl) benzene-1,4-diamine and 12H-benzo[a]phenothiaz- in-9-amine.
Scheme 2.
2: Synthesis of substituted phenothiazine-3-sulphonamide derivatives.
Scheme 2.
2: Synthesis of substituted phenothiazine-3-sulphonamide derivatives.
2.1. In silico antimicrobial studies
The docking antimicrobial studies were conducted to predict the biological activities of the of both the intermediates
27 and
28 as well the final product (
30 a-c) on the microorganisms using their binding energies as presented on the table below. Higher negative values of the binding energies suggest good activities of the compounds against the tested microorganisms [
33]. The results are presented in
Table 1.
The results on
Table 1, showed compounds
30 b and 30 c exhibited higher binding energy values of 7.1 kcal mol
-1 each for
Salmonella comparable with the standard drugs ciprofloxacin and gentamycin with values of -7.4 and 7.0 kcal mol
-1 respectively. For
S. aureus the intermediate
28 gave the highest binding energy value of -7.3 kcal mol
-1, comparable with the standard drugs ciprofloxacin and gentamycin with values of -7.6 and 7.0 kcal mol
-1. For
E. Coli, the higher binding energy value of -7.20 and -7.0 kcal mol
-1 was obtained for both compound
30 a and
30 b as well as for
30 c while for
S. pyogenes, the highest value of -7.4 was recorded for intermediate
28 when compared with comparable with the standard drugs. For the fungus
A. fumigatus, compound 30 b gave the highest binding energy value of -7.5 kcal mol
-1 comparable to the standard drug ketoconazole. The results obtained from
in silico antimicrobial studies of the above compounds suggested that the phenothiazine and phenothiazine -3-sulphonamide compounds possessed good biological activities comparable with the standard drugs used for the investigation.
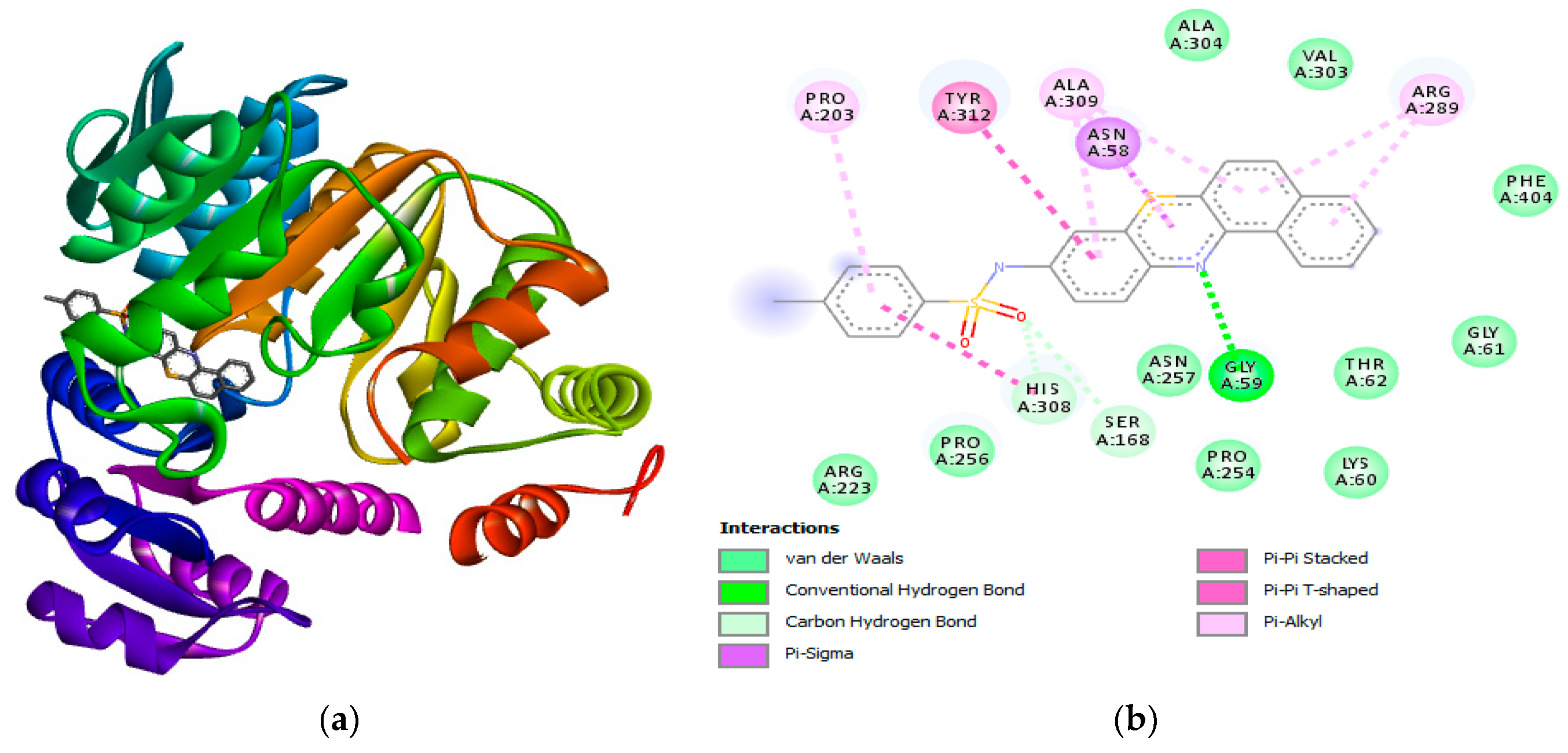
Figure 7.
(a) 3D structure of 30 c bound to E. coli (b) 2D diagram displaying the hydrogen bonding and other interactions between 30 c and the amino acids residues in the active site. (b) showed the formation hydrogen bonding with active site amino acid residues (GLY59). Other interactions formed between 30 c and the active site amino acid residues are Van der Waals interactions, Pi-Pi T-shaped, carbon hydrogen bond.
Figure 7.
(a) 3D structure of 30 c bound to E. coli (b) 2D diagram displaying the hydrogen bonding and other interactions between 30 c and the amino acids residues in the active site. (b) showed the formation hydrogen bonding with active site amino acid residues (GLY59). Other interactions formed between 30 c and the active site amino acid residues are Van der Waals interactions, Pi-Pi T-shaped, carbon hydrogen bond.
These results agree with the experimental results presented in
Table 2 of section
2.3 and will provided more insight into the mechanism of inhibition for the synthesized compounds.
2.2. Comparative estimation of the physiochemical properties of synthesized compounds
The parameters that indicated the drug likeness of the prepared compounds according Lipinski, (2004) include; MW-Molecular Weight, TPSA- Topological Polar Surface Area, HBA- Hydrogen Bond Acceptor, HBD- Hydrogen Bond Donator, Nrotb- Number of rotable bonds, Nviolations- Number of violations, miLogP- Modified molecular hydrophobicity potential. The table below presents a summary of drug likeness properties of the prepared compounds.
Table 2.
Physiochemical or drug likeness properties of synthesized compounds.
Table 2.
Physiochemical or drug likeness properties of synthesized compounds.
| Compounds |
MW* |
miLogP |
LogS# |
TPSA@ |
HBA |
HBD |
Nviolations |
Nrotb |
| 28 |
264.07 |
4.22 |
-4.63 |
41.81 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
| 30a |
418.08 |
6.36 |
-7.11 |
61.96 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
3 |
| 30b |
404.07 |
5.73 |
-7.18 |
61.96 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
3 |
| 30c |
449.05 |
5.91 |
-5.20 |
107.78 |
5 |
2 |
1 |
4 |
| Acceptable threshold |
˂500 Da |
˂5 |
0 – (-6) |
≤140 A2
|
≤10 |
≤5 |
0 |
9 |
An effective drug candidate should have a MW threshold of less than 500 Da (g/mol) based on Lipinski's RO5 [
34,
35,
36,
37]. Studies have proven the relationship between a drug's molecular weight (MW) and toxicity, suggesting that compounds with lower MW have reduced toxicity [
38]. For this reason, a benchmark of 500 Da (g/mol) has been established. Therefore, it is preferable to have low molecular weights [
36]. From the above table above, the four compounds obeyed Lipinski's RO5 of MW threshold ˂500 Da (g/mol), therefore needless for optimisation.
According to Chapman
et al [
38],
LogP is a measure of a chemical's hydrophobicity and is universally defined as the negative of the logarithm of the partition coefficient between n-octanol and water (C
octanol/C
water). Consequently, an increase in
LogP signals a decline in aqueous solubility, which lowers absorption. From the above table above, the compounds obeyed Lipinski's RO5 of
LogP threshold ˂5 except compounds “
30a, 30b and
30c” which suggests a need for structural optimization.
LogS determines the oral bioavailability of drugs in line with membrane permeability [
39].The estimation is crucial because it influences the bioavailability of drugs based on membrane permeability. A look at the table above suggests that compounds “
30a and
30b” did not fall within the acceptable threshold range for
LogS which suggest a need for structural optimization also.
The topological polar surface area (TPSA) parameter totals the polar atoms at the surface which are primarily oxygen and nitrogen in addition to the hydrogen atoms that are attached to them. This parameter predicts the cell penetration ability of chemical compounds. Accordingly, it is said that the lower the TPSA value, the better [
40,
41]. Substances with TPSA values less than 190 Å
2 are more likely to cross the blood-brain barrier than those with TPSA values larger than 140 Å
2. As a result, it is hypothesized that an increase in TPSA will reduce the ability of drugs to be transported, which will impact their biological activities [
42]. A look at the table above suggests that compounds “
28-30c” did fall within the acceptable threshold range for
TPSA, therefore needless for optimization.
The terms used to describe the hydrogen bonds that exist in a molecule are hydrogen bond donors (
HBD) and acceptors (
HBA). These parameters have been utilized frequently in the analysis of the drug likeness of compounds. According to Lipinski's RO5, a drug must have an HBD count of
≤5 and a HBA of
≤10 in order to be orally active [
43]. A look at the table suggests that compound “
28-30c” did fall within the acceptable threshold range for
HBA and
HBD, therefore needless for optimization.
From the table “compound 30a, compound 30b and compound 30c” suggests a need for structural optimization since they do not meet the acceptable threshold for miLogP which is the reason why we have 3 number of violations.
2.3. In vitro studies
The studies were conducted to determine the effects of the prepared compounds on the following microorganisms
Salmonella typhi, S. aureus, E. coli, S. pyogenes and
A. fumigatus [
44]. The lower the value of the minimum inhibitory concentration, the better the activity of the compound. The results are presented in
Table 3.
Compound 30c exhibited the lowest minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values for the first three tested bacterial strains and the fungus A. fumigatus comparable to the standard drugs Compound 28 showed no result (NR) for E.coli, compounds 28-30c showed no result (NR) for S. pyogenes, while compounds 28-30b showed no result (NR) for A. fumigatus. These observations call for more research on the activities of the compounds on these microorganisms.
3. Material and Methods
All chemical reagents and solvents used were obtained from Aldrich, MolyChem, JHD and Burgoyne, and used without purification. Joel 400MHz spectrometers in CDCl3 using TMS as internal standards were used in recording 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra. FT-IR Spectroscopy of the compounds were run in PerkinElmer Spectrum version 10.03.06 and the bands represented in wave number. Melting points were determined in open capillary tubes and are uncorrected. All experiments were carried out at the Chemistry Laboratory, Department of Chemical Sciences, Godfrey Okoye University, Thinkers Corner in Enugu, Enugu State. Computational Tools: ChemDraw (used specifically in drawing chemical structures and molecular modeling), protein-ligand design and virtual screening (BIOVIA discovery Studio); used in analyzing protein and ligand structures, perform structural alignment, identifying binding sites, and analyzing protein-ligand interactions, molecular docking software (AutoDock Vina); used in predicating the binding affinities and interactions of the synthesized derivatives with target proteins, molecular modeling and visualization software (PyMOL); used for analyzing and visualizing molecular structures and interactions.
3.1. Synthesis of 1-(naphthalen-1-yl) benzene-1,4-diamine (27)
A mixture of 1-naphthylamine 25 (2.0 mmol) and 4-chloroaniline 26 (2.0 mmol) in dimethyl for- mamide (25 ml) was refluxed in the presence of anhydrous potassium hydroxide (2.0 mmol) for three hours using an oil bath. The mixture was filtered and residue was washed with 10.0 ml hot dimethylformamide. The filtrate obtained was poured into ice cold water, followed by acidification with 10.0 ml dilute HCl. The precipitate was washed twice with dichloromethane (30 ml) and finally with ethylacetate (3x 20 ml) in a separating funnel. The organic layers obtained were combined and air dried to give a colored solid product, 1-(naphthalen-1-yl) benzene-1,4-diamine 27. The compounds were characterized as thus;
Yield 75.7%, melting point 190-191C. FTIR (KBr, cm-1): 3350.9 (N-H stretch), 3049 (C-H aromatic), 1617.7 (C=C aromatics), 1285.9 (C-N). 1H NMR (δ): 8.85 (s, 1H, NH proton), 7.71 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 7.34 (d, J = 0.4 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 6.21 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 4.95 (d, J=3.0 Hz, 2H, NH2). 13C NMR (δ): 142.7 (1C), 135.9 (1C), 130.3 (1C), 130.0 (1C), 127.8 (1C), 127.3 (1C), 126.8 (1C), 126.4 (1C), 125.8 (1C), 125.6 (1C), 123.4 (1C), 122.5 (1C), 120.5 (1C), 118.5 (1C) (14 aromatic carbons)
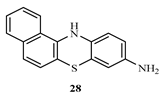
3.2. Synthesis of 12H-benzo[a]phenothiazin-9-amine (28)
A mixture of 1-(naphthalen-1-yl)benzene-1,4-diamine 27 ( 0.4 mmol), sulphur powder (0.8 mmol) and iodine crystals (0.8 mmol) in 1,2-dichlorobenzene (20 ml) was refluxed for five hours in oil bath. The reaction mixture was then distilled to remove excess solvent. The product obtained was then recrystallized from acetone, filtered and allowed to air dry to give a dark colored solid product. The compound was characterized as thus; Yield 83.4%, m.p. 250°C. FT-IR (KBr, cm-1): 3388.2 (N-H stretch), 3049 cm-1 (C-H aromatic), 1617.5 (C=C aromatics), 1248.7(C-N). 1H NMR (δ) 8.21 (d, 1H, NH), 7.82 (s, 1H2, Ar-H), 7.73-7.71 (t, 3H, J=0.8Hz, Ar-H), 7.65 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 7.52-7.54 (m, J=0.8Hz, Ar-H), 7.34-7.32 (d, J=0.8Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 4.89 (s, 1H, NH2). 13C NMR (δ): 152.1-111.5 (16 aromatic carbons).
3.3. General method for the synthesis of phenothiazine-3-sulphonamides derivatives (30a-c)
Sodium carbonate, Na2CO3 (0.5 mmol) was weighed and added to a solution of 12H-benzo[a]phenothiazin-9-amine 28 (0.1 mmol) in dichloromethane (20 ml) and acetone with continuous stirring using a magnetic stirrer until all the solutes were dissolved. The appropriate substituted arylsulphonyl chlorides 29 a-c (1.0 mmol) were added in three portions over a period of 45 minutes. The solution was refluxed for ten hours in water bath. After completion, the pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted from 7 to 2 using HCl (2 mol) and a cloudy solution was obtained. The organic portion was extracted with dichloromethane (50 ml) and ethylacetate (50 ml), and left to air-dry. The compounds were then characterized as follows:
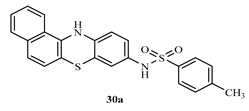
N-(12H-benzo[a]phenothiazine-9-yl)-4-methylbenzenesulphonamide (30a)
Yield 82.5%, melting point 240-241°C. FT-IR (KBr, cm-1) 3369.5 (N-H stretch), 3063.9 (C-H aromatic), 2914.8 (C-H stretch), 1625.1 (C=C aromatics), 1375.4 (S=O vibration of sulphonamide), 1319.5 (C-N). 1H NMR (δ): 9.60 (s, 1H, NH), 8.15 (s, 1H, SO2-NH of amide), 7.81 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 7.79 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 7.50-7.61 (m, 7H, J=4.4Hz, Ar-H), 7.59 (d, 2H, Ar-H, J=0.8Hz), 7.15 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 6.97 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 2.40 (s, 1H, Ar-CH3). 13C NMR (δ): 144.6- 111.6 (18 aromatic carbons).
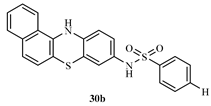
N-(12H-benzo[a]phenothiazine-9-yl)benzenesulphonamide (30b)
Yield 80.6%, melting point 195-196°C. FT-IR (KBr, cm-1): 3350.9cm-1 (N-H stretch), 3063.9 (C-H aromatic), 2922.2 (C-H stretch), 1621.4 (C=C aromatics), 1379.1 (S=O vibration of sulphonamide), 1330.7 (C-N). 1H NMR (δ): 9.60 (s, 1H, NH), 8.15 (s, 1H, SO2-NH of amide), 7.85 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 7.75 (t, 3H, J=0.4Hz, Ar-H), 7.55-7.57 (m, J=0.8Hz, 4H, Ar-H), 7.49 (d, 2H, J=0.2Hz, Ar-H), 7.15 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 6.87 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 6.61 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 6.23 (s, 1H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (δ): 144.6-18.0 (22 aromatic carbons).
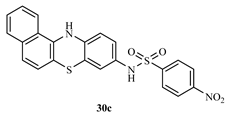
N-(12H-benzo[a]phenothiazine-9-yl)-4-nitrobenzenesulphonamide (30c)
Yield 81.9%, melting point 237-238°C. FT-IR (KBr, cm-1): 3388.2cm-1 (N-H stretch), 2079.9 cm-1 (C-H aromatic), 1625.1 cm-1 (C=C aromatics), 1524.5 cm-1(N-O stretch), 1360.5 cm-1 (S=O vibration of sulphonamide), 1211.4 cm-1 (C-N). 1H NMR (δ): 9.80 (s, 1H, NH), 8.37-8.35 (d, 2H, J=0.8Hz, SO2-NH of amide), 8.21 (s, 1H, Ar-NO2), 8.01 (d, 1H, Ar-H), 7.85 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 7.78 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 7.64 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 7.45-7.44 (d, 2H, J=0.4Hz, Ar-H), 6.80 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 6.75 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 6.69 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 6.60 (s, 1H, Ar-H). 13C NMR (δ): 152.5-111.5 (22 aromatic carbons).
3.4. Biological Studies
The antimicrobial activity of the synthesized phenothiazine-3-sulphonamide derivatives against clinical pathogens was determined by using agar well diffusion method based on the guidelines of the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards NCCLS (2002) [
44]
3.4.1. Preparation of selected derivatives concentrations
The synthesized compounds, 12
H-benzo[a]phenothiazin-9-amine 28,
N-(12
H-benzo[a]phenothia- zine-9-yl)-4-methylbenzenesulponamide
30a,
N-(12
H-benzo[a]phenothiazine-9-yl)benzenesulph- onamide
30b, and
N-(12
H-benzo [a]phenothiazine-9-yl)-4-nitrobenzenesulphonamide
30c were prepared in four different molar concentrations respectively. A stock solution was first prepared for each of the derivatives containing 5mg/ml and this was dissolved in 10 ml of acetone to give the stock solution, of each of the synthesized compounds. From the stock solutions different concentrations of the solutions of the compounds were prepared, thus: 2.5 mg/ml, 1.25 mg/ml, and 0.625 mg/ml [
44,
45].
3.4.2. Nutrient agar preparation
28.0 g of nutrient agar powder was suspended in a conical flask containing 1000 ml of distilled water, mixed and dissolved completely. The flask and its content were sterilized by autoclaving at 121°C for 15 minutes, cooled at 37°C and mixed thoroughly. The molten agar was then poured into the sterilized petri dishes and allowed to solidify [
44].
3.4.3. The test microorganisms used:
Four human pathogenic bacteria made up of two Gram-positive (
Staphylococcus aureus,
Streptococcus pyogenes) and two Gram-negative (
Escherichia coli, and
Salmonella), were used for the antibacterial assay while one fungus (
Aspergillus fumigatus) was used for the antifungal assay. All the organisms were local isolates from the Laboratory bacterial and fungi stock of Lifechart Medical Diagnostic Center, Enugu State, Nigeria and streaked unto already prepared nutrient agar [
44].
3.4.4. Control test (standard):
The standard antibiotics used were ciprofloxacin and gentamycin, while ketoconazole was used as the antifungal drug.
3.4.5. Determination of antimicrobial activity
Sterile Mueller-Hinton agar plates were prepared for bacterial strains and sterile nutrient agar was prepared for fungal strain inoculated by a spread plate method under aseptic condition [
44].
3.4.6. Preparation of nutrient agar for fungal strain
28.0 g of nutrient agar powder was suspended in 1000 ml of distilled water. It was then mixed and dissolved completely,
sterilized by autoclaving at 121°C for 15 minutes. After autoclaving and allowed to cool down, 10mg/ml of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin, was added. This was to stop bacteria inhibition [
44].
3.4.7. Preparation of Mueller-hinton agar for bacterial strains
10.0 g of Mueller-Hinton agar was dissolved in 300 ml of distilled water and dissolved completely. Sterilized by autoclaving at 121°C for 15 minutes, the liquid was then poured into 16 petri dishes and allowed to solidify. After solidification, four wells of about 6 mm diameter were punched in each agar plates using a sterile gel puncher. The nutrient agar grown pathogenic cultures were then streaked on each agar plates using a sterile wire loop, trying as much as possible to avoid the wells while streaking the entire plates [
44,
45,
46]. About 100 µl of the different concentrations of 12
H-benzo[a]phenothiazin-9-amine
28 and its sulphonamide derivatives (
30a-c) were added into the wells using sterile micropipettes. The culture plates were incubated in inverted position at 37°C for 24hours. Positive control was set using standard antibiotics (ciprofloxacin and gentamycin) and antifungal drug (ketoconazole) while a negative control was set using solvent (acetone).
3.6.8. Determination of Minimum Inhibition Concentration (MIC)
12
H-benzo[a]phenothiazin-9-amine
28 and its its sulphonamide derivatives (
30a-c) were used in the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) determination using well diffusion method. The inoculum of microorganisms was prepared from nutrient agar cultures. In this method, the agar dilution technique of the samples were prepared to the highest concentration of 5 mg/ml (stock concentration) in acetone and serially diluted to a working concentration ranging from 5 mg/ml to 0.625 mg/ml using Mueller-Hinton Agar and later inoculated with 1 ml suspension of the test organisms [
44,
45,
46]. The positive control was Nutrient Agar with standard reference antibiotics (gentamycin and ciproflaxin) and antifungal (ketoconazole) and inoculums. After 24 hours of incubation at 37°C, the samples were observed.
Molecular docking studies
Molecular docking was performed to predict and the binding potentials of the synthesized compounds and the standard drugs; ciprofloxacin and gentamycin (antibacterial), ketoconazole (an antifungal) on the active sites of the receptors (proteins) of
Staphylococcus aureus,
Streptococcus pyogenes,
Escherichia coli,
Salmonella,
Aspergillus fumigatus, using AutoDock tools. Their 3D crystal structures of the respective microorganisms were downloaded from protein data bank as follows; (PDB: 5YH5 with 2.90Å resolution) [
47], (PDB: 5YHP with 3.02Å resolution) [
48], (PDB: 6KZV with 2.40Å resolution) [
49], (PDB: 4W4M with 3.20Å resolution) [
50], (PDB: 5ZVP with 1.42Å resolution) [
51], (PDB: 2XCT with 3.35Å resolution) [
52], and (PDB: 2V0M with 2.80Å resolution) [
53]. ChemDraw Professional 15.0 was used in drawing the structures of the different derivatives. BIOVIA Discovery Studio 2017 R2 was then used in editing and removing irrelevant components of the different proteins downloaded from the Protein Data Bank. Lastly, the PyRx app was used in binding the different ligands to the active sites of the selected proteins [
54].