1. Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease with a systemic inflammatory response characterized by joint inflammation and swelling. Overactive immune systems caused by RA commonly result in extra-articular manifestations, such as cardiovascular and respiratory dysfunction [
1]. Approximately 66% of patients with RA have lung involvement in a way of interstitial, airway, pleural, vascular, and parenchymal diseases [
2,
3]. The most prevalent form of lung involvement in patients with RA is interstitial lung disease (ILD), which is the chronic inflammation of the interstitial space that causes fibrosis and scarring of the lung tissue [
4]. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) constitutes 13% of the total deaths of patients with RA, and patients with RA-ILD show a significantly low 5-year survival rate of 35–39% [
5]. Overall, patients with RA-ILD have a death risk three times higher than those with RA without ILD [
6].
Pulmonary fibrosis is the fundamental cause of the high mortality and morbidity rates in patients with RA-ILD. The progression of fibrosis can be observed in wide fibrotic areas in the lungs using computed tomography scans with histological patterns, such as usual or nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (abbreviated as UIP and NSIP, respectively) [
7]. Aggravated lung function caused by fibrosis results in a decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) and gas exchange (diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide [DLCO] ), while reducing exercise capacity and the health-related quality of life of patients [
1]. If the condition worsens during successive fibrotic events, acute exacerbation, infection, or malignancy, death can occur.
The control of fibrosis is important for determining the prognosis of RA-ILD. However, predicting and diagnosing the onset of fibrotic phases in RA-ILD remain challenging. Genetic factors, such as the rs35705950 variant in the MUC5B gene and short telomere length, or environmental factors, such as smoking, sex, age, underlying diseases, and a high rheumatoid factor, increase the risk of ILD; however, a distinct correlation remains lacking [
8,
9]. Although genetic biomarkers, such as KL-6, SP-D, and HLA-DR2 alleles, or antibodies in the serum of patients with RA, such as anti-cyclic citrullinated or anti-citrullinated protein antibodies, have been suggested as biomarkers to detect the onset of fibrosis, their detection accuracy is limited [
10]. Owing to difficulties in identifying the emergence of fibrosis, the rudimentary inhibition of immune responses and hindrance of fibrosis progression are of vital importance in RA-ILD treatment.
Currently, the first-line treatment for RA-ILD primarily relies on drugs used for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) because the two diseases share similar clinical, radiological, and molecular patterns. Two major drugs, pirfenidone and nintedanib, are FDA-approved antifibrotic agents for IPF but are commonly used as off-label treatments for RA-ILD. These anti-fibrotic drugs can directly interfere with specific signaling pathways to block or slow the progression of fibrosis and reverse the morphological changes induced by fibrosis. Several immunosuppressants and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), the primary treatments for RA, have also been shown to slow fibrotic progression in RA-ILD by reducing the autoimmune response, which is the causative factor of pulmonary fibrosis.
However, the limitations of current drugs and need for basic inhibition of the autoimmune-induced fibrosis phase necessitate the development of new drugs for RA-ILD. While continuous research and development is in progress, drug repositioning is one of the primary strategies to be explored. Because multi-organ fibrotic diseases share similar clinical and pathological characteristics, these drugs can be repurposed to benefit the fibrotic manifestation of RA-ILD. With adequate targets that can hinder the progression of fibrosis in RA-ILD and a set of drug candidates, computational analysis can aid and accelerate the process by predicting the drug–target interactions (DTIs) between them to recommend favorable pairs for further confirmation.
2. Currently used antifibrotic agents for RA-ILD
To date, the most widely used drugs for the treatment of RA-ILD are pirfenidone and nintedanib, which were initially developed and approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for IPF. Their antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory potentials stem from the strong resemblance of RA-ILD and IPF in terms of pulmonary fibrotic patterns and prognosis. RA-UIP, a prevalent subtype of RA-ILD, is considered the most analogous to IPF because both show identical UIP fibrotic patterns and similar prognoses. RA-ILD and IPF are associated with pulmonary fibrosis and acute exacerbations, respectively. In addition, the upregulation of several genetic markers, such as eotaxin, IL-8, MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, and Flt-3L, and genetic mutations in TERT, RTEL1, PARN, and SFTPC have been observed in patients with RA-ILD and IPF [
11,
12]. These similarities support the implementation of therapeutic strategies for IPF in patients with RA-ILD.
However, RA-ILD and IPF differ in several aspects that can cause adverse effects during treatment. RA-ILD is a multi-system disease stemming from an autoimmune response. In contrast, IPF includes only lung-limited fibrosis without a specific cause. Therefore, their responses to treatment may differ based on their contrasting pathogenic pathways. For instance, an immunosuppressive approach to IPF therapy is contraindicated due to its inefficiency and increased mortality and morbidity [
13]. However, immunosuppression is the standard of care for patients with RA-ILD because the disease is derived from an autoimmune disorder [
14]. Moreover, while IPF exclusively presents UIP histological patterns in pulmonary fibrosis, RA-ILD can include other patterns, such as NSIP, organizing pneumonia (OP), and mixed or indeterminate forms [
15]. Different histological patterns affect disease prognosis and treatment effectiveness. RA-ILD with NSIP or OP responds better than RA-UIP to immunosuppressive treatment, while also showing preferable disease prognosis [
16,
17]. Thus, while the similarities between RA-ILD and IPF can guide the discovery of novel treatments for RA-ILD, their differences should be considered in the process of drug development. This section provides an overview of the anti-fibrotic mechanisms and clinical trials of pirfenidone and nintedanib in patients with RA-ILD.
2.1. Nintedanib
Nintedanib is an FDA-approved antifibrotic agent used for the treatments of IPF, systemic sclerosis-ILD, and chronic fibrosing ILD with a progressive phenotype, regardless of the underlying cause [
18]. Using nintedanib for the treatment of RA-ILD has attracted increased attention. Nintedanib functions as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor for several receptors that contribute to fibrogenesis, including PDGFR α and ß, FGFR 1-3, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) 1-3, colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R), and lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase (Lck) [
19]. Thus, it exerts its anti-fibrotic effect via a multifaceted inhibitory mechanism. It also regulates the activity of Lck, which is essential for T cell proliferation and the release of pro-fibrotic mediators, such as IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-12p70, IL-13, and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) [
20,
21]. By specifically targeting PDGF, FGF2, VEGF-A, and other growth factors, nintedanib suppresses the function of fibrocytes, consequently inhibiting fibrocyte migration, differentiation, and proliferation [
22]. The study also mentioned the ability of nintedanib to suppress transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-ß)-induced fibroblast myofibroblast transition and TGF-ß-stimulated collagen secretion [
22]. In pulmonary fibrosis, nintedanib significantly decreases certain markers, indicating M2 macrophage polarization. M2 macrophage polarization is a major contributor of pulmonary fibrogenesis because it releases fibrotic factors, such as TGF-ß and gelectin-3, which accordingly stimulate epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), endothelial mesenchymal transition (EndoMT), and fibroblast proliferation [
23,
24].
Several clinical trials have been conducted using nintedanib in patients with RA-ILD. The INBUILD trial was a phase 3 clinical trial conducted to evaluate the efficacy of nintedanib in patients with progressive fibrosing ILD [
25]. Of the 663 patients enrolled in the trial, 89 had RA-ILD, and a retrospective subgroup analysis was performed [
26]. Compared with the placebo, nintedanib demonstrated an improvement in patients with RA-ILD by significantly lowering the average rate of FVC decline by 59% over 52 weeks and reducing the risk of acute exacerbation or death. The most common adverse effect associated with nintedanib was diarrhea, which occurred in 61.9% of patients in the nintedanib group; however, the symptoms were still manageable. In addition, its concomitant use with other DMARDs showed no differences in effectiveness or safety profile. Thus, nintedanib demonstrated sufficient efficacy and safety as a potential treatment option for patients with RA-ILD. A recent retrospective cohort study from Portugal suggested the importance of the early initiation of nintedanib treatment in halting ILD progression. Patients treated with nintedanib within 3 years of their initial ILD diagnosis exhibited significantly improved respiratory function within 24 months of treatment [
27].
Nintedanib also affects arthritis in murine models. In a zymosan-induced arthritis SKG mouse model, nintedanib treatment reversed joint swelling and decreased the arthritis score compared to placebo saline treatment. Moreover, while the talus and calcaneus bones of the nintedanib-treated mice were negligibly changed, those of the saline-treated mice were irregular and deformed, suggesting severe erosion [
28]. Based on these in vivo results, future clinical trials are required to determine the efficacy of nintedanib against arthritis involvement.
2.2. Pirfenidone
Pirfenidone has been FDA-approved for IPF treatment since 2014. Phase 3 trials, such as ASCEND in 2014 and CAPACITY 1 and 2, have supported its efficacy and safety for IPF treatment as an antifibrotic agent. Thus, several attempts have been made to use pirfenidone to treat diseases similar to pulmonary fibrosis, including RA-ILD.
Pirfenidone is a pyridine derivative with anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-oxidant properties, which collectively contribute to the inhibition of pulmonary fibrosis. The anti-fibrotic activity of pirfenidone originates from suppressing TGF- ß1, which is a master regulator of fibrosis. Through TGF- ß1, pirfenidone reduces fibroblast proliferation, myofibroblast differentiation, extracellular matrix (ECM) production, and TGF-ß1-induced SMAD3 phosphorylation [
29]. Anti-inflammatory effects of pirfenidone can be observed via a translational level decrease of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ, and the upregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10 [
30]. By controlling the balance between pro-inflammatory cytokines, pirfenidone regulates tissue injury and the subsequent restoration process of wound healing. Regulating oxidative stress is also crucial for pulmonary fibrosis treatment because reactive oxygen species participate in the diverse molecular mechanisms of fibrogenesis [
31]. By eliminating hydroxyl radicals and controlling oxidative stress, pirfenidone establishes itself as a potent antifibrotic agent [
32].
In addition to its strong antifibrotic capacity, pirfenidone has been repurposed as an antirheumatic drug. Gan et al. [
33] demonstrated a reduction in joint synovial inflammation and swelling in a collagen-induced arthritis rat model treated with pirfenidone.
In vitro and bioinformatic analyses supported the antirheumatic effect of pirfenidone via the inhibition of inflammatory cytokines and cell migration, rendering it more suitable for RA-ILD treatment.
Multiple clinical trials have demonstrated the promising potential of pirfenidone for the treatment of RA-ILD. Recently, a phase 2 trial (TRAIL-1) using pirfenidone in patients with RA-ILD was attempted, but was terminated early due to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, certain data indicated that pirfenidone was effective in the treatment of RA-ILD. Pirfenidone lowered the rate of FVC decline compared to the placebo without presenting any new adverse effects. In addition, this study demonstrated that pirfenidone combined with DMARD therapy had an acceptable safety profile and tolerability [
34]. The RELIF trial, another phase 2 study with 127 non-IPF patients with ILD, included 17 patients with RA-ILD. In the trial, patients treated with pirfenidone experienced a lower decline in FVC, indicating decelerated pulmonary aggravation, compared to those who received the placebo, showing that pirfenidone alleviated RA-ILD symptoms [
35].
A prospective controlled cohort study was conducted to investigate the efficacy and safety of pirfenidone combined with immunosuppressant therapy in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease (CTD-ILD). Of the 111 patients, 17 were diagnosed with RA-ILD. While all patients in the study were prescribed immunosuppressants, those in the test group concomitantly received pirfenidone. Pirfenidone-treated patients with RA-ILD exhibited an enhancement in DLCO%, a measure of gas exchange, by 7.40% compared to the baseline, while the control group showed a 5.5% decrease [
36].
A phase 2 study of pirfenidone for the treatment of unclassifiable progressive fibrosing ILD was also conducted. Although patients diagnosed with RA-ILD were not included in the study population, pirfenidone enhanced pulmonary function and exercise capacity compared with the placebo, without presenting extensive adverse effects [
37]. When an ongoing randomized controlled trial for patients with CTD-ILD with a subpopulation of patients with RA-ILD is completed as expected, we will obtain a clearer picture of the potential of pirfenidone for RA-ILD treatment [
38].
3. Immunosuppressants for RA-ILD
Immunosuppressants are early stage drugs used to treat patients with RA. Immunosuppressive agents can hinder the progression of RA to RA-ILD by reducing the autoimmune response that is responsible for lung fibrosis. Although there are currently no FDA-approved immunosuppressants for improving pulmonary function in patients with RA-ILD, several drugs that have shown efficacy against similar or related diseases are being tested. Thus, several immunosuppressants should be considered as plausible treatments for RA-ILD.
3.1. Anti-metabolites
Anti-metabolites suppress immune reactions by inhibiting nucleic acid synthesis. Although these drugs are primarily used as anticancer drugs, some have the potential to relieve RA-ILD. However, owing to their toxicity, they are typically recommended to be administered along with other agents. The following section reviews three anti-metabolites that have shown improvements in RA-ILD.
3.1.1. Methotrexate (MTX)
MTX, a folate derivative, is considered the first-line DMARD for RA. However, its use for RA-ILD treatment is limited owing to MTX-related pulmonary adverse effects, including hypersensitivity pneumonitis, which are presumed to be associated with RA-ILD progression [
39]. Several studies have since overturned the original beliefs of the clinicians. In a retrospective multicenter study conducted by Kiely et al. [
40], MTX exposure did not result in RA-ILD, but rather delayed its onset. Juge et al. [
41] further advocated the positive effect of MTX using a case-control study that revealed a lower risk of RA-ILD in MTX ever-users compared to MTX-never users, with an average delay of 3.6 years in ILD detection [
41]. MTX has also been suggested to be a protective factor against lung function decline and mortality in cohorts of patients with RA-ILD when provided after RA-ILD incidence [
42]. A phase 4 randomized controlled trial (PULMORA) is in progress to compare the effects of MTX with those of the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor tofacitinib [
43]. Through this clinical trial, we expect to gain a better understanding of the effects of MTX on RA-ILD.
3.1.2. Cyclophosphamide (Cyc)
Cyc is a DNA alkylating immunosuppressive agent that hydrolyzes into phosphor mustard when activated, consequently resulting in DNA damage and the inhibition of cell proliferation [
25]. Although the underlying mechanism is not fully understood, the immunosuppressive effect of Cyc has been shown to benefit patients with RA-ILD [
26]. A 10-year retrospective study in Germany by Schupp et al. [
27] demonstrated the ability of Cyc to stabilize lung function in patients with both inflammatory and fibrotic ILD. Randomized controlled trials also support the ability of Cyc to improve lung conditions in patients with CTD-ILD with better FVC results compared to the placebo [
28,
29]. Cyc also relieved tender and swollen joints in patients with RA, which confirms its antirheumatic effects [
30]. However, certain studies have reported that the mortality rate of patients with acute exacerbation of RA-ILD treated with Cyc did not significantly differ from that of the control group [169]. Moreover, the administration of Cyc alone is not recommended because of its high toxicity and adverse effects [
4].
3.1.3. Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF)
MMF is less toxic than Cyc and inhibits inosine-5’-monophosphate dehydrogenase and de novo guanine syntheses, which are critical elements for DNA synthesis and the proliferation of T and B lymphocytes [
32]. In addition to its immunosuppressive effects, studies have supported the antifibrotic capability of MMF by suppressing fibroblast proliferation and the expression of fibrosing cytokines, such as TGF-ß and IL-6 [
33,
34]. Because MMF can control both the inflammatory response and pulmonary fibrosis, it is considered a promising option for the treatment of RA-ILD. Although controlled studies of MMF for RA-ILD are still needed, MMF has shown positive results in several studies, with improved or stabilized pulmonary physiology in patients with CTD-ILD, including subgroups of patients with RA-ILD [
35,
36]. While the frequent adverse events of MMF include gastrointestinal symptoms, bone marrow suppression, and infection due to immunosuppression, it remains an appealing option compared with the safety profiles of other immunosuppressive drugs [
37]. However, MMF is known to have no benefit in treating the articular manifestations of RA [
38]. Thus, it is recommended to be used in combination with a different immunosuppressant that can target joint involvement.
3.2. Therapeutic antibodies
Antibodies can disable specific cells and the immune system, primarily during organ rejection or in autoimmune diseases. Rituximab (RTX) is an anti-B-cell antibody widely used to alleviate joint inflammation in RA. Recently, clinical trials have proven their auxiliary efficacy not only in joint inflammation, but also in delaying fibrosis. Anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) agents have limited clinical evidence against RA-ILD, but are widely used in RA treatments.
3.2.1. RTX
RTX is a chimeric monoclonal antibody that targets the CD20 surface marker on both B cell precursors and mature B cells [
39]. RTX binding can result in B cell depletion via several mechanisms, including complement-dependent cytotoxicity, cell-mediated cytotoxicity, and apoptosis [
40]. With its anti-arthritic effect, RTX treatment has shown clinically significant improvements with articular involvement and has been approved by the FDA as a biologic DMARD for RA in the REFLEX and DANCER trials [
41,
42,
43]. Promising results were also observed in the lung function of patients with CTD-ILD and RA-ILD, showing improved or maintained pulmonary function and slower progression of the disease [
44,
45,
46,
47]. Recently, a randomized controlled trial was conducted to compare the efficacy of RTX and Cyc in patients with CTD-ILD (RECITAL). This study demonstrated the ability of RTX and Cyc to improve the pulmonary function and quality of life of patients without significant differences, with RTX causing fewer adverse effects [
29].
3.2.2. Infliximab, Adalimumab, and Etanercept
Although few clinical studies have been conducted, three anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α inhibitors, infliximab, adalimumab, and etanercept, exhibit positive effects on patients with RA-ILD. The intravenous infusion of infliximab showed the radiographic stabilization of pulmonary functions, such as dyspnea, cough, and exercise tolerance, and improvement in joints [167]. However, a retrospective study of 100 patients with RA-ILD demonstrated that anti-TNF-α therapy of adalimumab and infliximab should be used with caution in older patients with RA-ILD, because lung complication can occur within months of initial anti-TNF-α treatment [166]. Etanercept was also suggested to be used with caution because the exacerbation of ILD was observed in a specific case [168].
3.3. Signaling inhibitors
3.3.1. Abatacept (ABA)
ABA is a co-stimulation blocker comprising the extracellular domain of human cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA4) and a modified Fc portion of human immunoglobulin G1. By binding to CD80/CD86, ABA hinders the CD80/86-CD28 interaction, consequently inhibiting co-stimulatory signals essential for T cell activation [
48]. Although ABA is an FDA-approved drug for the treatment of RA, studies have shown that it also has favorable effects on the treatment of RA-ILD. In vivo studies demonstrated the potency of ABA in inhibiting lung inflammation and fibrosis in murine models [
49,
50]. In an observational study of 263 patients with RA-ILD, approximately 80% of patients treated with ABA maintained stable or improved pulmonary function with better FVC and DLCO, as well as a reduced DAS28esr score, indicating RA disease activity [
51]. Other studies and systematic reviews have also supported the efficacy and safety of ABA in patients with RA-ILD [
52,
53,
54]. Although terminated because of the COVID-19 pandemic, a phase II study of ABA in patients with RA-ILD (APRIL) indicated an acceptable safety profile with no serious adverse reactions [
55]. Thus, randomized controlled trials are necessary to further investigate the potential of ABA as a treatment for RA-ILD.
3.4. Corticosteroid (Glucocorticoid)
Glucocorticoids, also known as corticosteroids or steroids, are conventional treatments for autoimmune diseases. They function via multiple mechanisms, including the blocking synthesis of cytokines and cell surface molecules necessary for the activation of the immune system via the inhibition of NF-κB [
17]. Owing to their anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects, glucocorticoids are favored for treating inflammatory RA-ILD with NSIP or OP [
18,
19]. Positive results have also been observed with steroid treatments for fibrotic RA-ILD with UIP. In a retrospective study conducted by Song et al. [
20], approximately 50% of patients with RA-UIP showed improvement or stabilization following glucocorticoid treatment. In contrast, glucocorticoid treatment in patients with IPF resulted in higher morbidity and mortality; therefore, it is contraindicated in IPF [
21,
22]. Despite the high histopathological similarity between IPF and RA-ILD, the same treatment might have disputed pharmacological effects. Moreover, the use of glucocorticoids in patients with RA-ILD carries potential risks, such as an increased risk of infection or osteoporosis development; therefore, additional caution is needed [
23,
24].
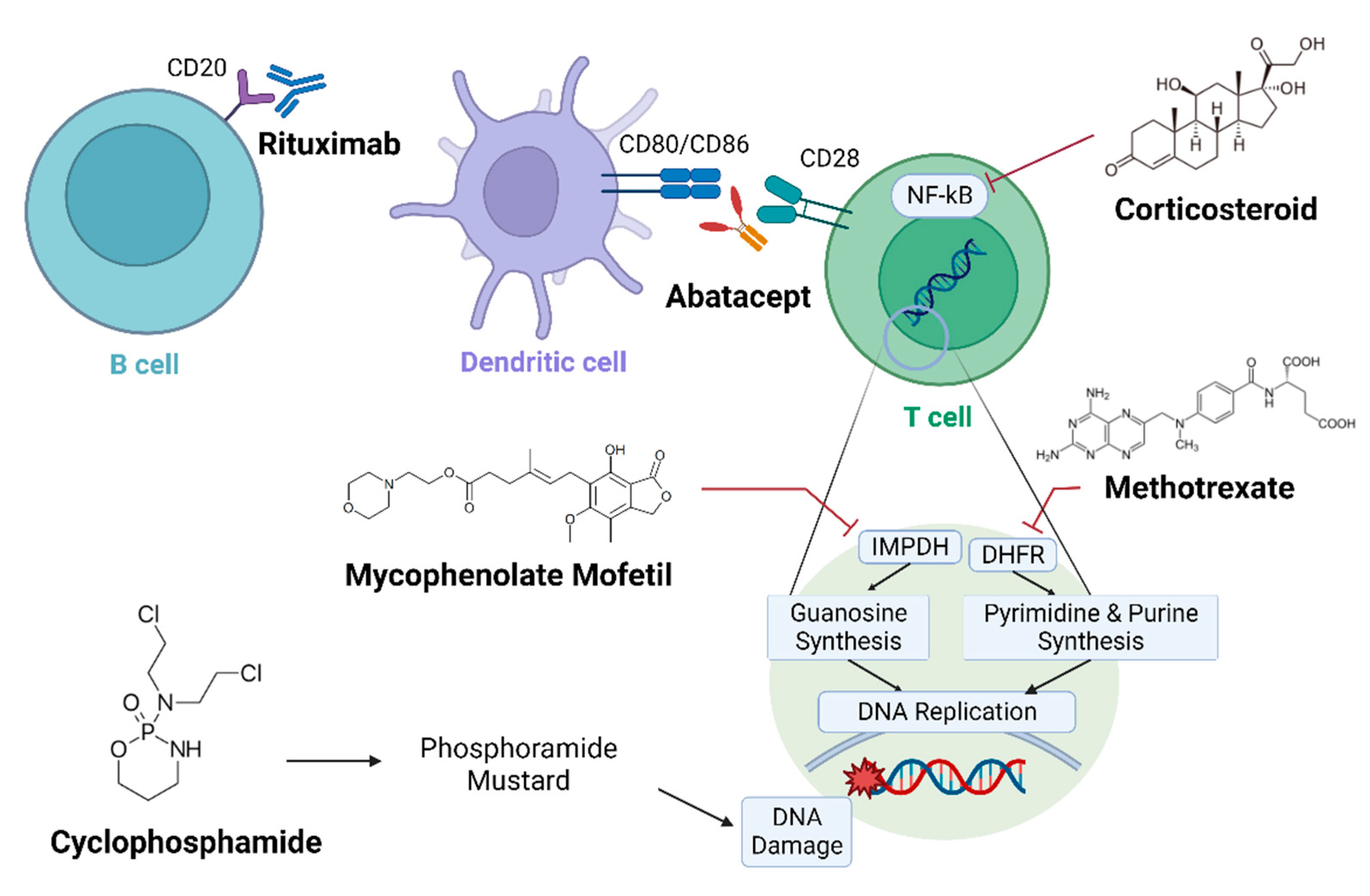
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram in which immunosuppressants target rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD). Mechanisms of several immunosuppressants against RA-ILD are presented. Therapeutic antibodies, such as rituximab and abatacept, immobilize immune cells, and anti-metabolites cause DNA damage. Multiple clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate their efficacy against RA-ILD.
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram in which immunosuppressants target rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD). Mechanisms of several immunosuppressants against RA-ILD are presented. Therapeutic antibodies, such as rituximab and abatacept, immobilize immune cells, and anti-metabolites cause DNA damage. Multiple clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate their efficacy against RA-ILD.
4. DMARDs with anti-fibrotic effects
To date, there are no FDA-approved anti-fibrotic agents specific to RA-ILD. However, multiple drugs have shown efficacy against RA-ILD, and some are undergoing clinical trials. Although pirfenidone and nintedanib are the most used drugs, their application is limited because of their adverse effects. Most anti-fibrotic drugs are multi-targeting, but primarily target proteins, specific pathways, or extracellular molecules that initiate a cascade of events. This section summarizes anti-fibrotic drugs based on their primary functional methods.
4.1. JAK inhibitors
JAKs are a group of intracellular tyrosine kinases that participate in signaling pathways that regulate several physiological cell processes, including differentiation and metabolism [
56]. Transcription factors, called STATS, an oncoprotein family encoded by tumor-associated genes, jointly form a signaling pathway with JAK. JAK and STATS have several subtypes, but JAK2/STAT3 is the most prevalent in ILD [
10,
57,
58]. STAT3 transduces peptide hormone signals from the cell surface to the nucleus and is activated by cytokines, growth factors, and several peptide hormones. While RA-ILD with UIP shares almost identical clinical patterns with IPF, RNA transcriptomic data show that RA-UIP has a nuclear form of phosphorylated JAK2, whereas most patients with IPF have a cytoplasmic form of phosphorylated JAK2 [
59]. Such variations imply that applying therapeutic approaches for IPF in patients with RA-ILD may not yield the same effects and may even cause unexpected adverse effects. The JAK/STAT pathway is activated by a number of pro-fibrotic or pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-11, and IL-13, or growth factors, such as platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs), TGF-ß1, and fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) [
57]. Blocking these signals inactivates the JAK/STAT pathway, which consequently arrests fibrosis. JAK inhibitors also exhibit anti-fibrotic effects by directly affecting fibroblast activation [
60].
Tofacitinib, ruxolitinib, and baricitinib are FDA-approved JAK inhibitors used for the treatment of RA [
61,
62,
63]. They show significant improvement in joints by controlling the plasma levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, reducing joint destruction, and exerting anti-fibrotic effects by directly affecting fibroblasts. Research on macrophages has revealed that they can be effective in controlling diseases characterized by concomitant inflammation and fibrotic manifestations, which also supports their efficacy against RA-ILD [
20,
64].
4.1.1. Tofacitinib
Tofacitinib is a JAK 3/2 inhibitor with strong regulatory effects on IL-17A. IL-17A is secreted by T helper 17 cells and functions cooperatively with IL-17RA and IL-17RC during fibrosis. Large areas of IL-17RA-induced fibroblast accumulation and fibrosis have been observed in patients with RA-ILD. IL-17A plays a distinct role in RA-ILD compared with other normal lung diseases or even IPF [
65]. The suppression of IL-17A ameliorates the activity of inflammatory T helper 17 cells, thereby alleviating fibrosis. In vivo research using SKG mice showed that tofacitinib slowed the progression of RA-ILD by increasing the number of myeloid-derived suppressor cells [
66]. A phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trial indicated that 5 and 10 mg of tofacitinib administered twice a day demonstrated maximal healing effects at 6 months. Signs, symptoms, and pain caused by RA were reduced, physical lung function improved, and the progression of fibrosis or structural damage decreased. However, 28% of the patients discontinued treatment because of adverse events [
67]. Tofacitinib can be applied either alone or in combination with immunosuppressants, such as MTX, without affecting its efficacy [
68]. For instance, tofacitinib was administered to a 52-year-old man after signs of ILD were diagnosed without immunosuppressants. Tofacitinib successfully controlled frequent inflammation and improved respiratory functions [
69]. Multiple studies have shown that tofacitinib retains or slows the progression of RA-ILD, reduces the risk of RA leading to ILD, and exceeds other biological DMARDs (bDMARDs) in restoring pulmonary function. The administration of tofacitinib over an 8–12 month period to two patients with RA-ILD successfully controlled inflammation in the joints without exacerbations or hospitalizations due to lung disease [
70]. In another study, among 31 patients with RA-ILD, 13 were treated with tofacitinib, and 83.9% exhibited overall stability or improvement in RA-ILD symptoms [
71]. Tofacitinib exceeded other bDMARDS in reducing the risk of ILD, and another post hoc analysis of 21 clinical trials supported this finding by concluding that the incidence rate of ILD following tofacitinib treatment was extremely low (0.18).
4.1.2. Ruxolitinib
Ruxolitinib, a specific JAK2 inhibitor, regulates the activity of pro-fibrotic M2 and pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages [
72]. IL-13- and IFN-γ-activated macrophages followed a signaling pathway that involved JAK2, to which ruxolitinib indicated direct repression. Polarization markers, such as MHC II and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), which indicate the differentiation process of M1 and M2, respectively, were decreased, as well as the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as CXCL10, IL-6, and TNF-α [
72].
4.1.3. Baricitinib
Baricitinib is a JAK1/ JAK2 inhibitor suggested as a treatment for patients with RA-ILD who do not respond to the initial treatment with MTX [
73]. An analysis of 3770 patients with RA from eight randomized clinical trials and one long-term extension study on baricitinib showed promising effects in lowering the risk of ILD development [
74]. When 11 patients with RA and 4 patients with RA-ILD were treated with baricitinib for 6 months, a considerable decrease in inflammation was observed in patients with RA-ILD via a reduction in KL-6, a biomarker of RA-ILD. Moreover, improvements in DLCO and diffusion coefficient percentages confirmed that baricitinib restored pulmonary function [
75].
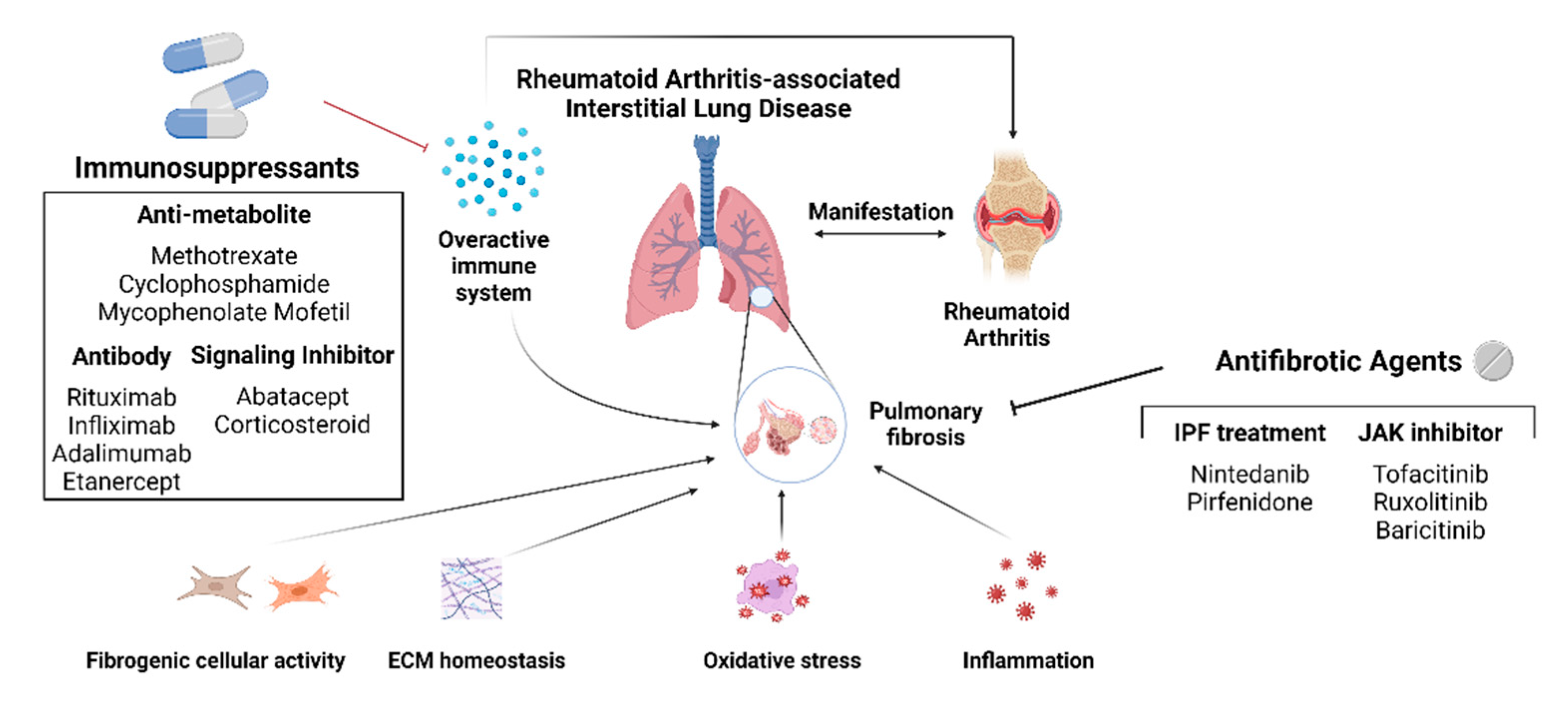
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the currently used drugs against RA-ILD. Immunosuppressants and antifibrotic agents control joint inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis to impede the fibrotic process of RA-ILD. Pulmonary fibrosis can be controlled via four mechanisms: diminishing fibrogenic cellular activity, restoring ECM homeostasis, decreasing oxidative stress, and controling inflammation. Clinical trial results demonstrated that drugs for IPF treatment, nintedanib, and pirfenidone, as well as the three JAK inhibitors, tofacitinib, ruxolitinib, and baricitinib, have anti-fibrotic effects against RA-ILD.
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the currently used drugs against RA-ILD. Immunosuppressants and antifibrotic agents control joint inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis to impede the fibrotic process of RA-ILD. Pulmonary fibrosis can be controlled via four mechanisms: diminishing fibrogenic cellular activity, restoring ECM homeostasis, decreasing oxidative stress, and controling inflammation. Clinical trial results demonstrated that drugs for IPF treatment, nintedanib, and pirfenidone, as well as the three JAK inhibitors, tofacitinib, ruxolitinib, and baricitinib, have anti-fibrotic effects against RA-ILD.
5. Computational methods for further RA-ILD drug development
To prevent fibrosis and the progression of RA-ILD, and because there are limitations in applying IPF treatment to patients with RA-ILD, a novel drug for RA-ILD is necessary. However, considering that diseases with fibrotic characteristics are numerous and that their mechanisms share common molecules and genes, another solution for RA-ILD drug development could be drug repositioning or repurposing.
The first basis for drug repositioning is the phenotypic similarity between diseases, which has already been confirmed by studies demonstrating shared molecules, genes, and signaling pathways between multiple organ fibrotic diseases [150]. Thus, computational drug repositioning is a favorable approach for identifying additional drugs with positive effects on RA-ILD. Drugs currently suggested for RA-ILD treatment also follow this notion, because they were initially implemented for IPF or other CTD-ILDs.
Although demonstrated only by in vitro assessments, certain clinical drugs for distinct diseases show potential for RA-ILD treatment. Cyclosporine, a well-known immunosuppressant, downregulates immune- and fibrosis-related genes, such as insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP2), inhibitor of DNA binding protein 1 (ID1), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) [
123]. Theophylline, a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma drug, is a pan-phosphodiesterase inhibitor that exhibits anti- inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects by interfering with the TGF-ß1 signaling pathway [
90]. Fluvoxamine, a well-known antidepressant drug, showed equivalent anti-fibrotic effects with only one-third the dosage of pirfenidone [
98]. These results suggested that multiple drugs that have already been approved for clinical safety can be used to control fibrosis.
For drug repositioning, potential targets that can effectively impede disease progression must be identified, as discussed in the following section. A computational platform for specifying the optimal targeting drug is introduced in the next section. In the forthcoming therapeutic development, the limitations of implementing RA-ILD in animal models and the great variety of patients with RA-ILD render the computational approach a more favorable option than traditional methods.
5.1. Molecular targets suggested for RA-ILD fibrosis
Fibrosis is regulated by the transition, migration, and metabolic activity of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts. Excessive immune reactions in the lung tissue trigger cytokines and chemokines to be released and fibroblasts to be activated, which then differentiate into α smooth muscle actin expressing myofibroblasts. The invasive nature of pulmonary myofibroblasts stimulates cytoskeletal synthesis and upregulates the expression of contractile proteins. This contracts the lung tissue, and substantial numbers of ECM proteins are produced [
76,
77,
78,
79].
Multiple studies have suggested three molecular targets that can restrict fibroblast activity: TGF-ß, CTGF, and MMP These three targets inhibit and stimulate pulmonary fibrosis via multiple mechanisms and complex interactions. Genetic analysis has demonstrated that they are deeply involved in multiple fibrotic diseases in different organs (eyes, heart, lungs, pancreas, and kidneys) [
76,136].
TGF-ß is a multifunctional cytokine secreted by bronchial structural cells or inflammatory cells that maintain tissue homeostasis. It causes the transition of epithelial and endothelial cells to mesenchymal cells (EMT and EndoMT), activates pericytes and smooth muscle cells related to blood vessels, and induces ECM deposition. Targeting TGF-ß hinders signaling pathways that include SMAD 2/3, Wnt/ß-catenin, MAPK, and PI3K [133–135]. The complex interplay between TGF-ß and CTGF has been reported in pulmonary and renal fibrosis [
76]. Different subtypes of MMPs have dual-purpose properties in pulmonary fibrosis. Dismantling specific collagen via MMP activation may delay fibrotic progression, whereas regulating MMP activity with a tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase reduces inflammatory effects. Among these, MMP-1, -2, and -9 are marked with pulmonary fibrosis [136]. Targeting MMP-1 controls the local epithelial–mesenchymal interaction, MMP-2 plays a significant role in EMT via the Wnt/ß-catenin signaling pathway, and MMP-9 enhances recovery by decreasing IGFBP-3 expression [138–140].
Additional target molecules, including Syndecan-2, which promotes internalization and the degradation of the TGF-ß receptor, are related to citrullinated peptides found in more than half of patients with RA and to the prevalence and exacerbation of ILD in patients with RA [153–155].Additional targets can be found in other CTD-ILDs, including various autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, RA, Sjogren’s syndrome, polymyositis/dermatomyositis, systemic sclerosis (SSc), and mixed connective tissue disease invading the interstitial compartment of the lungs [
126]. TGF-ß, PDGF, and FGF are key growth factors that participate in the fibrotic process of most CTD-ILD diseases. Particularly, the FGF and PDGF receptors and downstream signaling proteins, such as YAP/TAZ, are considered target molecules of SSc-associated lung fibrosis and RA-ILD [
127].
5.2. Computational DTI prediction
Three primary components must be considered in the drug repositioning process: diseases, drugs, and their targets. By understanding their interconnections, researchers can gain insight into the efficacy of plausible treatments and identify potential side effects. Numerous data, such as chemical structures, transcriptional profiles, and phenotypic information, are already available. Thus, holistic data analysis is essential to determine the capacity of drug repositioning, an area in which in silico models have already stood out.
The computational drug repositioning of anti-fibrotic agents is currently in progress. Wu et al. [163] developed Dr AFC, a drug repositioning platform for anti-fibrotic characteristics, using two different models: structure and biological profile prediction models. As their names imply, each model uses chemical structures and compound-induced gene profiles to predict the antifibrotic efficacy of the given compound. Dr AFC demonstrated high predictability for the test sets and proposed several candidates as novel antifibrotic agents. Similar to Dr AFC, similarity-based virtual screening using 2D and 3D structures of possible target molecules of RA-ILD and drug candidates can be performed to predict their affinity. Drugs showing a higher affinity for the target molecule can be selected and evaluated on the cell lines of SKG mouse models to further confirm their effectiveness in RA-ILD. The drug repositioning process can be streamlined by sorting drugs with high structural and biological probabilities using computational methods before proceeding to the next step.
Such DTI prediction not only suggests a new drug but can also increase our knowledge about its potential side effects. For instance, Lounkine et al. [164] created a drug-target-adverse drug reaction network using a similarity ensemble approach, which predicts target binding based on chemical structure similarity with known ligands. New off-target and adverse events can be predicted using the network and can possibly elucidate unknown mechanisms of adverse effects. One of the greatest obstacles to treating RA-ILD is the presence of multiple factors, such as joint, lung, and autoimmunity, that should be considered concurrently. If a drug benefits from one factor, but aggravates others, the drug is ineffective. Thus, we can predict off-target and adverse effects of the drugs in the early stages using these programs and filter out unsuitable options to accelerate the development process.
Scholars are advancing in silico models with better algorithms and strategies to achieve higher prediction accuracy. These advancements have provided possibilities for precision medicine, which is suitable for RA-ILD because different biomarkers and pathogenic pathways are observed depending on the condition of the individual. Therefore, if these models can consider individual factors and help prescribe customized drugs to each patient, this approach will be the optimal direction for future drug development.
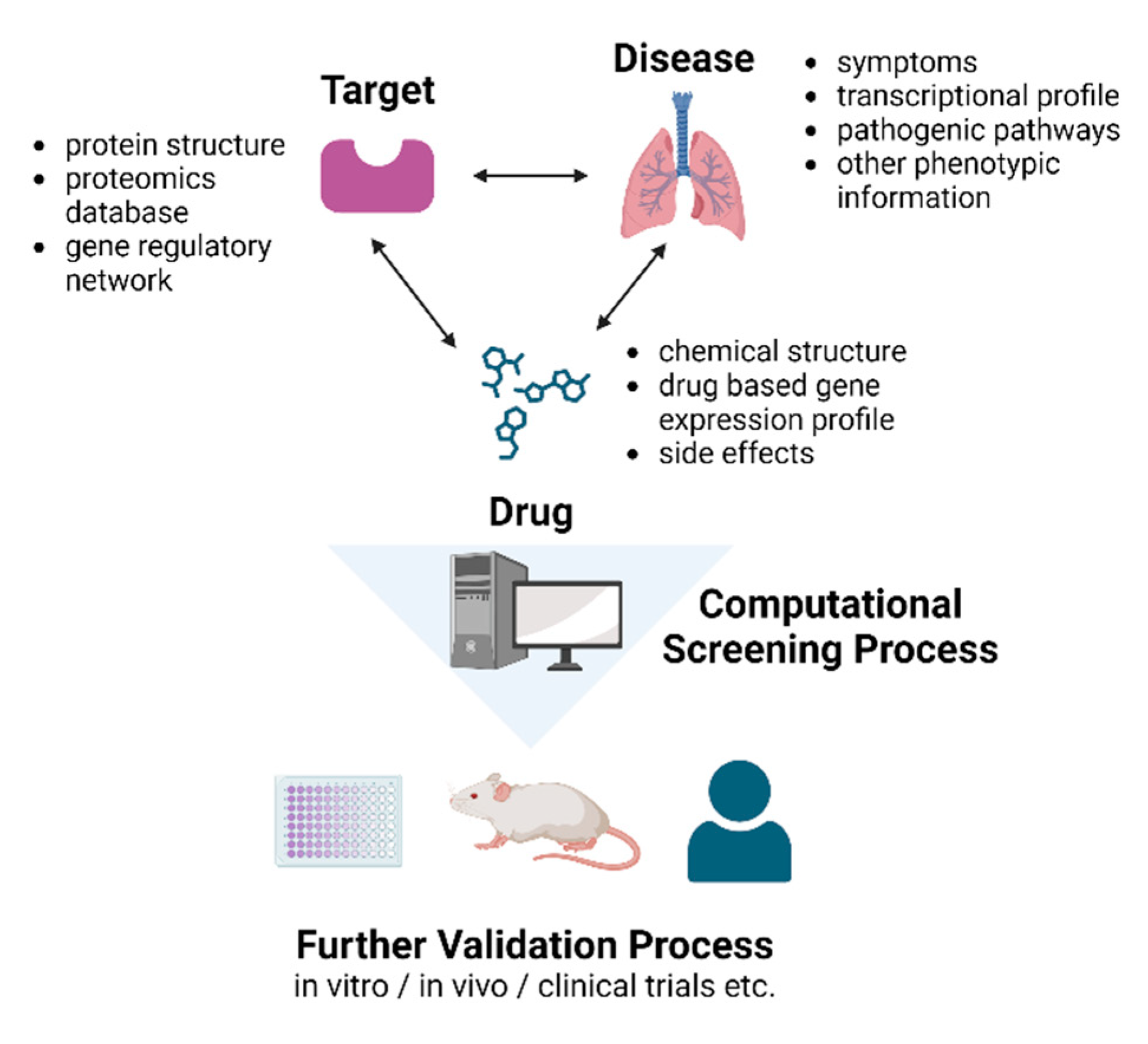
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of using features of the disease to identify potential targets and applying computational screening processes to screen potent drugs for further validation processes. Drug repositioning via computational screening can be an efficient process for further RA-ILD drug development. Pathologic features of RA-ILD can be acquired through its symptoms, transcriptional profile, pathogenic pathways, or other phenotypic information. Through this process, potential targets for drugs can be identified, and three potential targets have been suggested: TGF-ß, CTGF, and MMP. Computational platforms can embody the 2D and 3D structures of a specific target and calculate its interaction with multiple candidate drugs and screen potent drugs. Moreover, possible adverse effects of the drugs can also be identified, which will be helpful in further in vivo and in vitro or clinical trials.
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of using features of the disease to identify potential targets and applying computational screening processes to screen potent drugs for further validation processes. Drug repositioning via computational screening can be an efficient process for further RA-ILD drug development. Pathologic features of RA-ILD can be acquired through its symptoms, transcriptional profile, pathogenic pathways, or other phenotypic information. Through this process, potential targets for drugs can be identified, and three potential targets have been suggested: TGF-ß, CTGF, and MMP. Computational platforms can embody the 2D and 3D structures of a specific target and calculate its interaction with multiple candidate drugs and screen potent drugs. Moreover, possible adverse effects of the drugs can also be identified, which will be helpful in further in vivo and in vitro or clinical trials.
6. Conclusions
RA-ILD is one of the most common lung manifestations of systemic inflammatory autoimmune disease, affecting up to 1% of the population in developed countries [165]. Considering its high morbidity and mortality rates, the control of inflammation and fibrosis is of significant importance. This paper reviews the currently used agents for RA-ILD and describes a computational drug repositioning strategy that can benefit future drug developments for RA-ILD.
Nintedanib and pirfenidone are the most commonly used drugs for RA-ILD. The tyrosine kinase inhibitor, nintedanib, controls the activity of fibrogenic cells (T cells, M2 macrophages, fibroblasts, and myofibroblasts) and decreases oxidative stress. Pirfenidone functions comprehensively via its anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects. Multiple clinical trials have been conducted using pirfenidone and nintedanib. They were shown to restore pulmonary function by slowing FVC decline and improving DLCO% and exercise capacity. Multiple studies have demonstrated that immunosuppressants can stabilize or improve pulmonary function in patients with RA-ILD. However, the specific mechanism has not been clarified. Although more randomized controlled trials are required, regulating the autoimmune response can systematically affect multiple symptoms, including lung and arthritic manifestations. Similarly, several DMARDs exert auxiliary anti-fibrotic effects by controlling specific pathways involved in the progression of fibrogenesis. Drugs target signaling pathways, such as JAK/STAT, Hippo/Yap, Wnt/ß-catenin, cGAS-STING, cAMP-PKA, and PI3K/AKT, to regulate cellular activity (differentiation, metabolic activity, or morphology), ECM homeostasis, and oxidative stress levels. While they differ only in the type of specific enzymes involved, these signaling pathways commonly regulate ECM homeostasis.
Although several drugs have been suggested and investigated, additional research in this area is required. This review summarizes three potent molecular targets that can impede fibrosis and a computational method that can determine the optimal drug to target.
Little is known about the pathogenesis of RA-ILD. Research conducted thus far has identified certain genetic backgrounds, environmental risk factors that trigger RA-ILD, and histologic evidence [8, 124–125]. Thus, further research on the mechanism of RA-ILD, particularly focusing on the onset of the fibrotic stage and molecular correlations between joint inflammation and progressive fibrosis, is urgently needed. If the onset of the fibrotic stage can be clearly identified, preemptive actions, such as aggressive immunosuppressive treatment, can be administered in advance to inhibit subsequent fibrotic progression. Moreover, most drugs against RA are either predetermined to target joint inflammation or partially target fibrosis.
In contrast, antifibrotic agents inhibit joint inflammation. This implies that fibrosis and joint inflammation are interrelated in RA-ILD. In addition, deeper insights into the pathogenesis can resolve adverse events that frequently occur with current therapeutic treatments. Ultimately, the pathogenesis of RA-ILD must be elucidated to develop new drugs and reverse adverse effects.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K. K.; writing—original draft preparation, E. J. and S. H.; writing—review and editing, E. J., S. H., and K. K.; supervision, K. K.; funding acquisition, K. K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), which is funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (Grant number 2021R1F1A1048536) and by The present study was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant HI17C0658).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| RA |
Rheumatoid arthritis |
| ILD |
Interstitial lung disease |
| IPF |
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| ECM |
Extracellular matrix |
| CT |
Computed tomography |
| UIP |
Usual interstitial pneumonia |
| NSIP |
Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia |
| FVC |
Forced vital capacity |
| DLCO |
Diffusing capacity of lungs for carbon monoxide |
| RF |
Rheumatoid factor |
| ACCP |
Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody |
| ACPA |
Anti-citrullinated protein antibody |
| DTI |
Drug-target interaction |
| OP |
Organizing pneumonia |
| SSc-ILD |
Systemic sclerosis-interstitial lung disease |
| VEGFR |
Vascular growth factor receptor |
| CSF1R |
Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor |
| Lck |
Lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase |
| IFN-γ |
Interferon gamma |
| TGF-ß |
Tumor growth factor beta |
| EMT |
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| EndoMT |
Endothelial–mesenchymal transition |
| TNF-α |
Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| ROS |
Reactive oxygen species |
| CIA |
Collagen-induced arthritis |
| CTD-ILD |
Connective tissue disease-interstitial lung disease |
| MTX |
Methotrexate |
| DMARD |
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug |
| CYC |
Cyclophosphamide |
| MMF |
Mycophenolate mofetil |
| IMPDH |
Inosine-5’-monophosphate dehydrogenase |
| RTX |
Rituximab |
| CTLA4 |
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 |
| DAS28esr |
Disease activity score in 28 joints |
| JAK |
Janus kinase |
| PDGF |
Platelet-derived growth factor |
| FGF |
Fibroblast growth factor |
| bDMARD |
Biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drug |
| MHCⅡ |
Major histocompatibility complex II |
| CTLA4 |
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte association protein 4 |
| KCO |
Diffusion coefficient |
| IGFBP2 |
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 |
| ID1 |
Inhibitor of DNA binding protein 1 |
| PPARγ |
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| αSMA |
Alpha smooth muscle actin |
| TIMP |
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase |
| SLE |
Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| SS |
Sjogren’s syndrome |
| PM/DM |
Polymyositis / dermatomyositis |
| MTCD |
Mixed connective tissue disease |
| SPPM |
Structure profile prediction model |
| BPPM |
Biological profile prediction model |
| DTI |
Drug–target interaction |
| SEA |
Similarity ensemble approach |
References
- Liang, M.; Matteson, E.L.; Abril, A.; Distler, J.H.W. The role of antifibrotics in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis–associated interstitial lung disease. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2022, 14, 1759720X2210744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, S.; Koduri, G.; Nikiphorou, E.; Dixey, J.; Williams, P.; Young, A. A study of baseline prevalence and cumulative incidence of comorbidity and extra-articular manifestations in RA and their impact on outcome. Rheumatology. 2013, 52, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilsher, M.; Voight, L.; Milne, D.; Teh, M.; Good, N.; Kolbe, J.; et al. Prevalence of airway and parenchymal abnormalities in newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis. Respir Med. 2012, 106, 1441–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Kronzer, V.L.; Dellaripa, P.F.; Deane, K.D.; Bolster, M.B.; Nagaraja, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: Current update on prevalence, risk factors, and pharmacologic treatment. Curr Treat Options Rheumatol. 2020, 6, 337–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, H.; Sato, S.; Nishizawa, T.; Kawabe, R.; Oba, T.; Kato, A.; et al. Impact of radiological honeycombing in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. BMC Pulm Med. 2020, 20, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongartz, T.; Nannini, C.; Medina-Velasquez, Y.F.; Achenbach, S.J.; Crowson, C.S.; Ryu, J.H.; et al. Incidence and mortality of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1583–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoulis, G.E.; Nikiphorou, E.; Larsen, J.; Korsten, P.; Conway, R. Methotrexate-Associated Pneumonitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis-Interstitial Lung Disease: Current Concepts for the Diagnosis and Treatment. Front Med. 2019, 6, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, M.S.; Khaychuk, V.; Wittstock, K.; Han, X.; Crocket, G.; Lin, M.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: epidemiology, risk/prognostic factors, and treatment landscape. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 1108–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Kelly, C. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a perspective review. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2015, 7, 247–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Oka, S.; Higuchi, T.; Shimada, K.; Hashimoto, A.; Matsui, T.; et al. Biomarkers for interstitial lung disease and acute-onset diffuse interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021, 13, 1759720X211022506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, S.; Lee, J.; Eickelberg, O. Two sides of the same coin? A review of the similarities and differences between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2021, 57, 2002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, D.J.; Nouraie, M.; Glassberg, M.K.; Ramreddy, N.; Fernandez, K.; Harlow, L.; et al. Comparative Profiling of Serum Protein Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Arthritis Rheumatol Hoboken NJ. 2020, 72, 409–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical Research Network Raghu, G.; Anstrom, K.J.; King, T.E.; Lasky, J.A.; Martinez, F.J. Prednisone, azathioprine, and N-acetylcysteine for pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2012, 366, 1968–77.
- Papiris, S.A.; Kagouridis, K.; Papadaki, G.; Kolilekas, L.; Manali, E.D. Treating CTDs related fibrotic ILDs by immunosuppressants: “facts and faults. ” Lung. 2014, 192, 221–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, N.A.; Strek, M.; Noth, I.; Gordon, I.O.; Charbeneau, J.; Krishnan, J.A.; et al. Pathologic quantification of connective tissue disease-associated versus idiopathic usual interstitial pneumonia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012, 136, 1253–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassone, G.; Manfredi, A.; Vacchi, C.; Luppi, F.; Coppi, F.; Salvarani, C.; et al. Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: Lights and Shadows. J Clin Med. 2020, 9, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Elicker, B.M.; Maldonado, F.; Webb, W.R.; Ryu, J.H.; Van Uden, J.H.; et al. Usual interstitial pneumonia in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2010, 35, 1322–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, K.M.; Wuyts, W.; Wijsenbeek, M.; Wells, A.U. Medical Therapy in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2016, 37, 368–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hilberg, F.; Roth, G.J.; Krssak, M.; Kautschitsch, S.; Sommergruber, W.; Tontsch-Grunt, U.; et al. BIBF 1120, triple angiokinase inhibitor with sustained receptor blockade and good antitumor efficacy. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4774–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollin, L.; Distler, J.H.W.; Redente, E.F.; Riches, D.W.H.; Stowasser, S.; Schlenker-Herceg, R.; et al. Potential of nintedanib in treatment of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir J. 2019, 54, 1900161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollin, L.; Ostermann, A.; Williams, C. Nintedanib inhibits pro-fibrotic mediators from T cells with relevance to connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2017, 50 suppl 61.
- Sato, S.; Shinohara, S.; Hayashi, S.; Morizumi, S.; Abe, S.; Okazaki, H.; et al. Anti-fibrotic efficacy of nintedanib in pulmonary fibrosis via the inhibition of fibrocyte activity. Respir Res. 2017, 18, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, T.T.; Agudelo, J.S.H.; Camara, N.O.S. Macrophages During the Fibrotic Process: M2 as Friend and Foe. Front Immunol. 2015, 6, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, K.; Herrmann, F.; Ayaub, E.; Parthasarathy, P.; Ackermann, M.; Inman, M.D.; et al. Nintedanib Attenuates the Polarization of Profibrotic Macrophages Through the Inhibition of Tyrosine Phosphorylation on CSF1 Receptor In: A72. AMECHANISMS DRIVING FIBROSIS. American Thoracic Society; 2017. p. A2397–A2397.
- Flaherty, K.R.; Wells, A.U.; Cottin, V.; Devaraj, A.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Nintedanib in Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. N Engl J Med. 2019, 381, 1718–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteson, E.L.; Aringer, M.; Burmester, G.R.; Mueller, H.; Moros, L.; Kolb, M. Effect of nintedanib in patients with progressive pulmonary fibrosis associated with rheumatoid arthritis: data from the INBUILD trial. Clin Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 2311–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elefante, E.; Gualtieri, L.; Cardelli, C.; Battista, M.D.; Carli, L.; Rossa, A.D.; et al. Pos1306 Health-Related Quality of Life (hrqol) Across Different Connective Tissue Diseases (ctds): Analysis of a Monocentric Experience. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023, 82 Suppl 1, 1000–1. [Google Scholar]
- Redente, E.F.; Aguilar, M.A.; Black, B.P.; Edelman, B.L.; Bahadur, A.N.; Humphries, S.M.; et al. Nintedanib reduces pulmonary fibrosis in a model of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018, 314, L998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Gili, E.; Fagone, E.; Fruciano, M.; Iemmolo, M.; Vancheri, C. Effect of pirfenidone on proliferation, TGF-β-induced myofibroblast differentiation and fibrogenic activity of primary human lung fibroblasts. Eur J Pharm Sci Off J Eur Fed Pharm Sci. 2014, 58, 13–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazato, H.; Oku, H.; Yamane, S.; Tsuruta, Y.; Suzuki, R. A novel anti-fibrotic agent pirfenidone suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha at the translational level. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002, 446, 177–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheresh, P.; Kim, S.-J.; Tulasiram, S.; Kamp, D.W. Oxidative stress and pulmonary fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013, 1832, 1028–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, H.P.; Rabideau, C. Pirfenidone inhibits NADPH-dependent microsomal lipid peroxidation and scavenges hydroxyl radicals. Mol Cell Biochem. 2000, 204, 119–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, D.; Cheng, W.; Ke, L.; Sun, A.R.; Jia, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. Repurposing of Pirfenidone (Anti-Pulmonary Fibrosis Drug) for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 631891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, J.J.; Danoff, S.K.; Woodhead, F.A.; Hurwitz, S.; Maurer, R.; Glaspole, I.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of pirfenidone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Respir Med. 2023, 11, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, J.; Prasse, A.; Kreuter, M.; Johow, J.; Rabe, K.F.; Bonella, F.; et al. Pirfenidone in patients with progressive fibrotic interstitial lung diseases other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (RELIEF): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2021, 9, 476–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Qi, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, T.; Cui, Y.; et al. The Efficacy and Safety of Pirfenidone Combined With Immunosuppressant Therapy in Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: A 24-Week Prospective Controlled Cohort Study. Front Med. 2022, 9, 871861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, T.M.; Corte, T.J.; Fischer, A.; Kreuter, M.; Lederer, D.J.; Molina-Molina, M.; et al. Pirfenidone in patients with unclassifiable progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2020, 8, 147–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q. Efficacy, Safety, Immune Function of Pirfenidone in the Treatment of Connetive Tissue Disease -Related Interstitial Lung Disease(CTD-LID). Clinical trial registration. clinicaltrials.gov; 2022.
- Fragoulis, G.E.; Conway, R.; Nikiphorou, E. Methotrexate and interstitial lung disease: controversies and questions. A narrative review of the literature. Rheumatol Oxf Engl. 2019, 58, 1900–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiely, P.; Busby, A.D.; Nikiphorou, E.; Sullivan, K.; Walsh, D.A.; Creamer, P.; et al. Is incident rheumatoid arthritis interstitial lung disease associated with methotrexate treatment? Results from a multivariate analysis in the ERAS and ERAN inception cohorts. BMJ Open. 2019, 9, e028466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juge, P.-A.; Lee, J.S.; Lau, J.; Kawano-Dourado, L.; Rojas Serrano, J.; Sebastiani, M.; et al. Methotrexate and rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2021, 57, 2000337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Woo, A.; Park, Y.; Yong, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Protective effect of methotrexate on lung function and mortality in rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: a retrospective cohort study. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2022, 16, 17534666221135314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastra Gotaland Region. Effects of Tofacitinib vs Methotrexate on Clinical and Molecular Disease Activity Markers in Joints and Lungs in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (PULMORA) - A Randomized, Controlled, Open-label, Assessor-blinded, Phase IV Trial. Clinical trial registration. clinicaltrials.gov; 2022.
- Ahmed, A.R.; Hombal, S.M. Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan). A review on relevant pharmacology and clinical uses. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984, 11, 1115–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlmann, M.; Hempel, G. The effect of cyclophosphamide on the immune system: implications for clinical cancer therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 661–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupp, J.C.; Köhler, T.; Müller-Quernheim, J. Usefulness of Cyclophosphamide Pulse Therapy in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Respir Int Rev Thorac Dis. 2016, 91, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.; Holland, A.E.; Westall, G.P.; Goh, N.S.; Glaspole, I.N. Cyclophosphamide for connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018, 1, CD010908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, T.M.; Tudor, V.A.; Saunders, P.; Gibbons, M.A.; Fletcher, S.V.; Denton, C.P.; et al. Rituximab versus intravenous cyclophosphamide in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease in the UK (RECITAL): a double-blind, double-dummy, randomised, controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2023, 11, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Almazor, M.E.; Belseck, E.; Shea, B.; Wells, G.; Tugwell, P. Cyclophosphamide for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000, :CD001157.
- Nakamura, K.; Ohbe, H.; Ikeda, K.; Uda, K.; Furuya, H.; Furuta, S.; et al. Intravenous cyclophosphamide in acute exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: A propensity-matched analysis using a nationwide inpatient database. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 977–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, M.L.; Pirofski, L. Mycophenolate mofetil: effects on cellular immune subsets, infectious complications, and antimicrobial activity. Transpl Infect Dis Off J Transplant Soc. 2009, 11, 290–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morath, C.; Schwenger, V.; Beimler, J.; Mehrabi, A.; Schmidt, J.; Zeier, M.; et al. Antifibrotic actions of mycophenolic acid. Clin Transplant. 2006, 20 Suppl 17, 25–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saketkoo, L.A.; Espinoza, L.R. Rheumatoid Arthritis Interstitial Lung Disease: Mycophenolate Mofetil as an Antifibrotic and Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drug. Arch Intern Med. 2008, 168, 1718–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.; Brown, K.K.; Du Bois, R.M.; Frankel, S.K.; Cosgrove, G.P.; Fernandez-Perez, E.R.; et al. Mycophenolate mofetil improves lung function in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 640–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omair, M.A.; Alhamad, E.H. Mycophenolate mofetil is an effective therapy for connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. Int J Clin Rheumatol. 2017, 12, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Cassone, G.; Sebastiani, M.; Vacchi, C.; Erre, G.L.; Salvarani, C.; Manfredi, A. Efficacy and safety of mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of rheumatic disease-related interstitial lung disease: a narrative review. Drugs Context. 2021, 10, 2020–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, M.; Beaulieu, A.; Scott, D.L.; Rashford, M. Mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of adults with advanced rheumatoid arthritis: three 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo- or ciclosporin-controlled trials. Clin Drug Investig. 2010, 30, 613–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescovitz, M.D. Rituximab, an anti-cd20 monoclonal antibody: history and mechanism of action. Am J Transplant Off J Am Soc Transplant Am Soc Transpl Surg. 2006, 6 5 Pt 1, 859–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R. Rituximab (monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody): mechanisms of action and resistance. Oncogene. 2003, 22, 7359–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Nadeem, A.; Attia, S.M.; Bakheet, S.A.; Alasmari, A.F.; Alomar, H.A.; et al. Rituximab exerts its anti-arthritic effects via inhibiting NF-κB/GM-CSF/iNOS signaling in B cells in a mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis. Heliyon. 2023, 9, e16673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.B.; Emery, P.; Greenwald, M.W.; Dougados, M.; Furie, R.A.; Genovese, M.C.; et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, P.; Fleischmann, R.; Filipowicz-Sosnowska, A.; Schechtman, J.; Szczepanski, L.; Kavanaugh, A.; et al. The efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment: results of a phase IIB randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fui, A.; Bergantini, L.; Selvi, E.; Mazzei, M.A.; Bennett, D.; Pieroni, M.G.; et al. Rituximab therapy in interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Intern Med J. 2020, 50, 330–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadillo, C.; Nieto, M.A.; Romero-Bueno, F.; Leon, L.; Sanchez-Pernaute, O.; Rodriguez-Nieto, M.J.; et al. Efficacy of rituximab in slowing down progression of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: data from the NEREA Registry. Rheumatol Oxf Engl. 2020, 59, 2099–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Yusof, M.Y.; Kabia, A.; Darby, M.; Lettieri, G.; Beirne, P.; Vital, E.M.; et al. Effect of rituximab on the progression of rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: 10 years’ experience at a single centre. Rheumatol Oxf Engl. 2017, 56, 1348–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, R.; Matteson, E.; Thomas, C.F. Clinical response of rheumatoid arthritis-associated pulmonary fibrosis to tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibition. Chest. 2002, 122, 1093–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.S.; Hong, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, C.-K.; Yoo, B. Mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease treated with an anti-tumor necrosis factor agent. Korean J Intern Med. 2015, 30, 104–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, K.; Sato, T.; Takagi-Kobayashi, S.; Hasegawa, S.; Shigihara, N.; Akiyama, O. Acute exacerbation of preexisting interstitial lung disease after administration of etanercept for rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2007, 34, 1151–4. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, R.; Moilanen, E. Abatacept, a novel CD80/86-CD28 T cell co-stimulation modulator, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2009, 104, 276–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israël-Assayag, E.; Fournier, M.; Cormier, Y. Blockade of T cell costimulation by CTLA4-Ig inhibits lung inflammation in murine hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Immunol Baltim Md 1950. 1999, 163, 6794–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleto, G.; Guignabert, C.; Pezet, S.; Cauvet, A.; Sadoine, J.; Tu, L.; et al. T-cell costimulation blockade is effective in experimental digestive and lung tissue fibrosis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018, 20, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Díaz, C.; Castañeda, S.; Melero-González, R.B.; Ortiz-Sanjuán, F.; Juan-Mas, A.; Carrasco-Cubero, C.; et al. Abatacept in interstitial lung disease associated with rheumatoid arthritis: national multicenter study of 263 patients. Rheumatol Oxf Engl. 2020, 59, 3906–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardella, M.; Di Carlo, M.; Carotti, M.; Giovagnoni, A.; Salaffi, F. Abatacept in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: short-term outcomes and predictors of progression. Clin Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 4861–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; Atienza-Mateo, B.; Blanco, R.; Cavagna, L.; Ancochea, J.; Castañeda, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of abatacept in interstitial lung disease of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic literature review. Autoimmun Rev. 2021, 20, 102830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Vázquez N, Rojas-Gimenez M, Fuego-Varela C, García-Studer A, Perez-Gómez N, Romero-Barco CM, et al. Safety and Effectiveness of Abatacept in a Prospective Cohort of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Biomedicines. 2022, 10, 1480.
- Gudu, T.; Stober, C.; Fifield, M.; Babar, J.; Ostor, A.; Parfrey, H.; et al. P147 Safety of AbatacePt in Rheumatoid arthritis associated Interstitial Lung disease (APRIL). Rheumatol Oxf Engl. 2021, 60 Suppl 1, keab247.143.
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Jin, S.-M.; Lee, B.J.; Chung, D.H.; Jang, B.-G.; Park, H.S.; et al. Treatment response and long term follow-up results of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. J Korean Med Sci. 2012, 27, 661–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dwyer, D.N.; Armstrong, M.E.; Cooke, G.; Dodd, J.D.; Veale, D.J.; Donnelly, S.C. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) associated interstitial lung disease (ILD). Eur J Intern Med. 2013, 24, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.W.; Lee, H.-K.; Lee, C.K.; Chae, E.J.; Jang, S.J.; Colby, T.V.; et al. Clinical course and outcome of rheumatoid arthritis-related usual interstitial pneumonia. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis Off J WASOG. 2013, 30, 103–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, B.; Branley, H.M.; Egan, J.J.; Greaves, M.S.; Hansell, D.M.; Harrison, N.K.; et al. Interstitial lung disease guideline: the British Thoracic Society in collaboration with the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand and the Irish Thoracic Society. Thorax. 2008, 63 Suppl 5, v1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical Research Network, Martinez FJ, de Andrade JA, Anstrom KJ, King TE, Raghu G. Randomized trial of acetylcysteine in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014, 370, 2093–101.
- Zamora-Legoff, J.A.; Krause, M.L.; Crowson, C.S.; Ryu, J.H.; Matteson, E.L. Risk of serious infection in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 2585–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canalis, E.; Mazziotti, G.; Giustina, A.; Bilezikian, J.P. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: pathophysiology and therapy. Osteoporos Int J Establ Result Coop Eur Found Osteoporos Natl Osteoporos Found USA. 2007, 18, 1319–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013, 188, 733–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, P.; Milara, J.; Roger, I.; Cortijo, J. Role of JAK/STAT in Interstitial Lung Diseases; Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, K.L.; Brockwell, N.K.; Parker, B.S. JAK-STAT Signaling: A Double-Edged Sword of Immune Regulation and Cancer Progression. Cancers. 2019, 11, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, C.; et al. Canonical and noncanonical regulatory roles for JAK2 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol. 2022, 36, e22336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, R.; Chen, C.-W.; Mallano, T.; Dees, C.; Distler, A.; et al. JAK1-dependent transphosphorylation of JAK2 limits the antifibrotic effects of selective JAK2 inhibitors on long-term treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017, 76, 1467–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, V.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Lee, E.B.; Fleischmann, R.; Zwillich, S.H.; Gruben, D.; et al. Tofacitinib or adalimumab versus placebo: patient-reported outcomes from a phase 3 study of active rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Oxf Engl. 2016, 55, 1031–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, J.M.; Bloom, B.J.; Breedveld, F.C.; Coombs, J.H.; Fletcher, M.P.; Gruben, D.; et al. The safety and efficacy of a JAK inhibitor in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: Results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIa trial of three dosage levels of CP-690,550 versus placebo. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. Properties of FDA-approved small molecule protein kinase inhibitors: A 2021 update. Pharmacol Res. 2021, 165, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Roden, A.C.; Zhao, H.; et al. Profibrotic effect of IL-17A and elevated IL-17RA in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and rheumatoid arthritis-associated lung disease support a direct role for IL-17A/IL-17RA in human fibrotic interstitial lung disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019, 316, L487–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendo, S.; Saegusa, J.; Yamada, H.; Nishimura, K.; Morinobu, A. Tofacitinib facilitates the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and ameliorates interstitial lung disease in SKG mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019, 21, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citera, G.; Mysler, E.; Madariaga, H.; Cardiel, M.H.; Castañeda, O.; Fischer, A.; et al. Incidence Rates of Interstitial Lung Disease Events in Tofacitinib-Treated Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Post Hoc Analysis From 21 Clinical Trials. J Clin Rheumatol Pract Rep Rheum Musculoskelet Dis. 2021, 27, e482–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, R.; Mease, P.J.; Schwartzman, S.; Hwang, L.-J.; Soma, K.; Connell, C.A.; et al. Efficacy of tofacitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis stratified by background methotrexate dose group. Clin Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, C.; Manfredi, A.; Cassone, G.; Cerri, S.; Della Casa, G.; Andrisani, D.; et al. Tofacitinib for the Treatment of Severe Interstitial Lung Disease Related to Rheumatoid Arthritis. Case Rep Med. 2021, 2021, 6652845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldarriaga-Rivera, L.M.; López-Villegas, V.J. Janus kinase inhibitors as a therapeutic option in rheumatoid arthritis and associated interstitial lung disease. Report of four cases. Rev Colomb Reumatol Engl Ed. 2019, 26, 137–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tardella, M.; Di Carlo, M.; Carotti, M.; Ceccarelli, L.; Giovagnoni, A.; Salaffi, F. A retrospective study of the efficacy of JAK inhibitors or abatacept on rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease. Inflammopharmacology. 2022, 30, 705–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescoat, A.; Lelong, M.; Jeljeli, M.; Piquet-Pellorce, C.; Morzadec, C.; Ballerie, A.; et al. Combined anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory properties of JAK-inhibitors on macrophages in vitro and in vivo: Perspectives for scleroderma-associated interstitial lung disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020, 178, 114103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.; Bijlsma, J.; Burmester, G.; Chatzidionysiou, K.; Dougados, M.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017, 76, 960–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarani, C.; Sebastiani, M.; Dieude, P.; Garcia, M.; Deberdt, W.; Rogai, V.; et al. Baricitinib and the Risk of Incident Interstitial Lung Disease: A Descriptive Clinical Case Report from Clinical Trials. Rheumatol Ther. 2021, 8, 1435–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Alessandro, M.; Perillo, F.; Metella Refini, R.; Bergantini, L.; Bellisai, F.; Selvi, E.; et al. Efficacy of baricitinib in treating rheumatoid arthritis: Modulatory effects on fibrotic and inflammatory biomarkers in a real-life setting. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020, 86, 106748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, J.-P.; Bureau, R.; Rochais, C.; Dallemagne, P. Drug repositioning: a brief overview. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 1145–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, N.; Ito, T.; Miyazaki, S.; Ebina, M.; Homma, S. Gene expression profiling of lung myofibroblasts reveals the anti-fibrotic effects of cyclosporine. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2014, 233, 283–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik-Pszczoła, K.; Chłoń-Rzepa, G.; Jankowska, A.; Ślusarczyk, M.; Ferdek, P.E.; Kusiak, A.A.; et al. A Novel, Pan-PDE Inhibitor Exerts Anti-Fibrotic Effects in Human Lung Fibroblasts via Inhibition of TGF-β Signaling and Activation of cAMP/PKA Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wu, X.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Du, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Fluvoxamine alleviates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis via regulating the cGAS-STING pathway. Pharmacol Res. 2023, 187, 106577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, B.; Yuan, M.; Zhu, R. Drugs and Targets in Fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, R.C.; Mercer, P.F. Mechanisms of alveolar epithelial injury, repair, and fibrosis. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015, 12 Suppl 1 Suppl 1, S16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, P.W. Epithelial fibroblast triggering and interactions in pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir Rev. 2008, 17, 123–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnato, G.; Harari, S. Cellular interactions in the pathogenesis of interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev Off J Eur Respir Soc. 2015, 24, 102–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalanobish, S.; Saha, S.; Dutta, S.; Sil, P.C. Matrix metalloproteinase: An upcoming therapeutic approach for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pharmacol Res. 2020, 152, 104591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEntee, C.P.; Gunaltay, S.; Travis, M.A. Regulation of barrier immunity and homeostasis by integrin-mediated transforming growth factor β activation. Immunology. 2020, 160, 139–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.; Gunaltay, S.; McEntee, C.P.; Shuttleworth, E.E.; Smedley, C.; Houston, S.A.; et al. Human monocytes and macrophages regulate immune tolerance via integrin αvβ8-mediated TGFβ activation. J Exp Med. 2018, 215, 2725–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarev, E.; Izumchenko, E.; Aihara, F.; Wysocki, P.T.; Zhu, Q.; Buzdin, A.; et al. Common pathway signature in lung and liver fibrosis. Cell Cycle Georget Tex. 2016, 15, 1667–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, I.; Cisneros, J.; Maldonado, M.; Ramírez, R.; Ortiz-Quintero, B.; Anso, E.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 induces lung alveolar epithelial cell migration and proliferation, protects from apoptosis, and represses mitochondrial oxygen consumption. J Biol Chem. 2013, 288, 25964–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Crampton, S.P.; Hughes, C.C.W. Wnt signaling induces matrix metalloproteinase expression and regulates T cell transmigration. Immunity. 2007, 26, 227–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilewski, J.M.; Liu, L.; Henry, A.C.; Knauer, A.V.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 3 and 5 are overexpressed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and contribute to extracellular matrix deposition. Am J Pathol. 2005, 166, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Sugiyama, D.; Kogata, Y.; Tsuji, G.; Nakazawa, T.; Kawano, S.; et al. Meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2007, 146, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska, W.; Kuca-Warnawin, E.H.; Radzikowska, A.; Maśliński, W. The role of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Cent-Eur J Immunol. 2017, 42, 390–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, C.S.; Briones, M.R.; Guo, R.; Ostrowski, R.A. Elevated anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody titer is associated with increased risk for interstitial lung disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 1201–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Shi, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Shu, J.; et al. Interstitial Lung Disease in Connective Tissue Disease: A Common Lesion With Heterogeneous Mechanisms and Treatment Considerations. Front Immunol. 2021, 12, 684699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouawad, J.E.; Feghali-Bostwick, C. The Molecular Mechanisms of Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Lung Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Gao, W.; Li, X.; Tian, C.; Jiao, N.; Fang, S.; et al. Dr AFC: drug repositioning through anti-fibrosis characteristic. Brief Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lounkine, E.; Keiser, M.J.; Whitebread, S.; Mikhailov, D.; Hamon, J.; Jenkins, J.L.; et al. Large-scale prediction and testing of drug activity on side-effect targets. Nature. 2012, 486, 361–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010, 69, 1580–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Lee, J.S.; Sverzellati, N.; Rossi, G.; Cottin, V. The Lung in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Focus on Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol Hoboken NJ. 2018, 70, 1544–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Moreno, J.; Hartson, L.; Navarro, C.; Gaxiola, M.; Selman, M.; Randall, T.D. Inducible bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue (iBALT) in patients with pulmonary complications of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2006, 116, 3183–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).