Submitted:
23 January 2024
Posted:
25 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
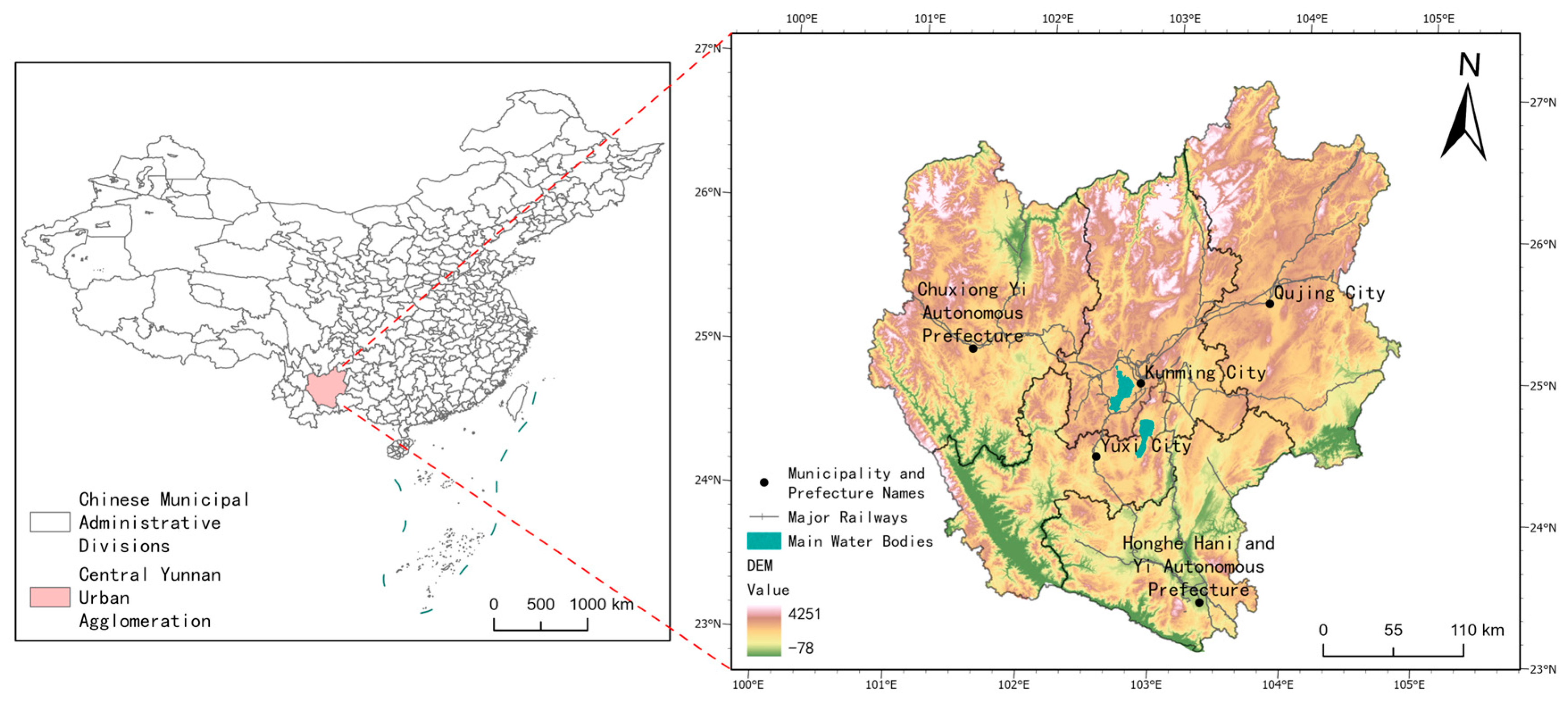
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Construction of Indicator System and Determination of Weights
2.4. Methods for Assessing the Level of Development of Subsystems
2.4.1. Methodology for Assessing the Level of Economic and Social Development
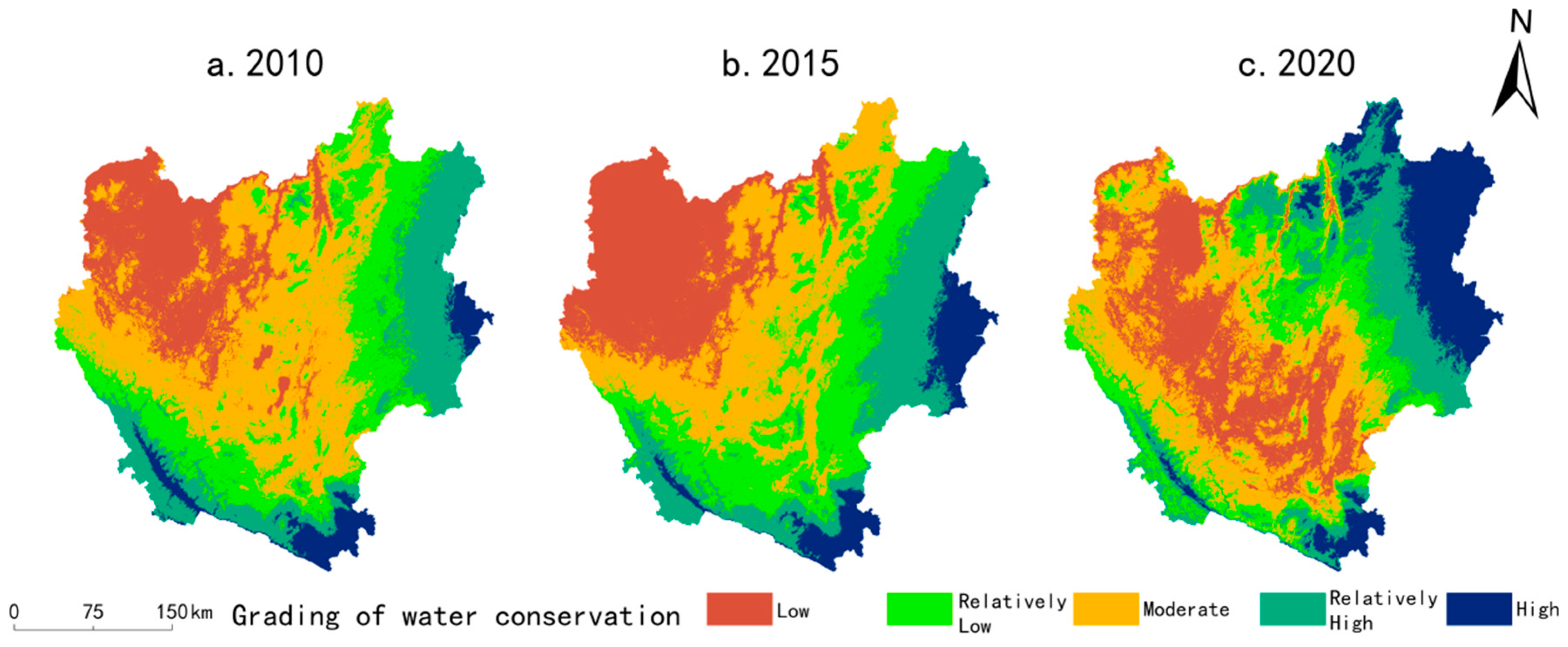
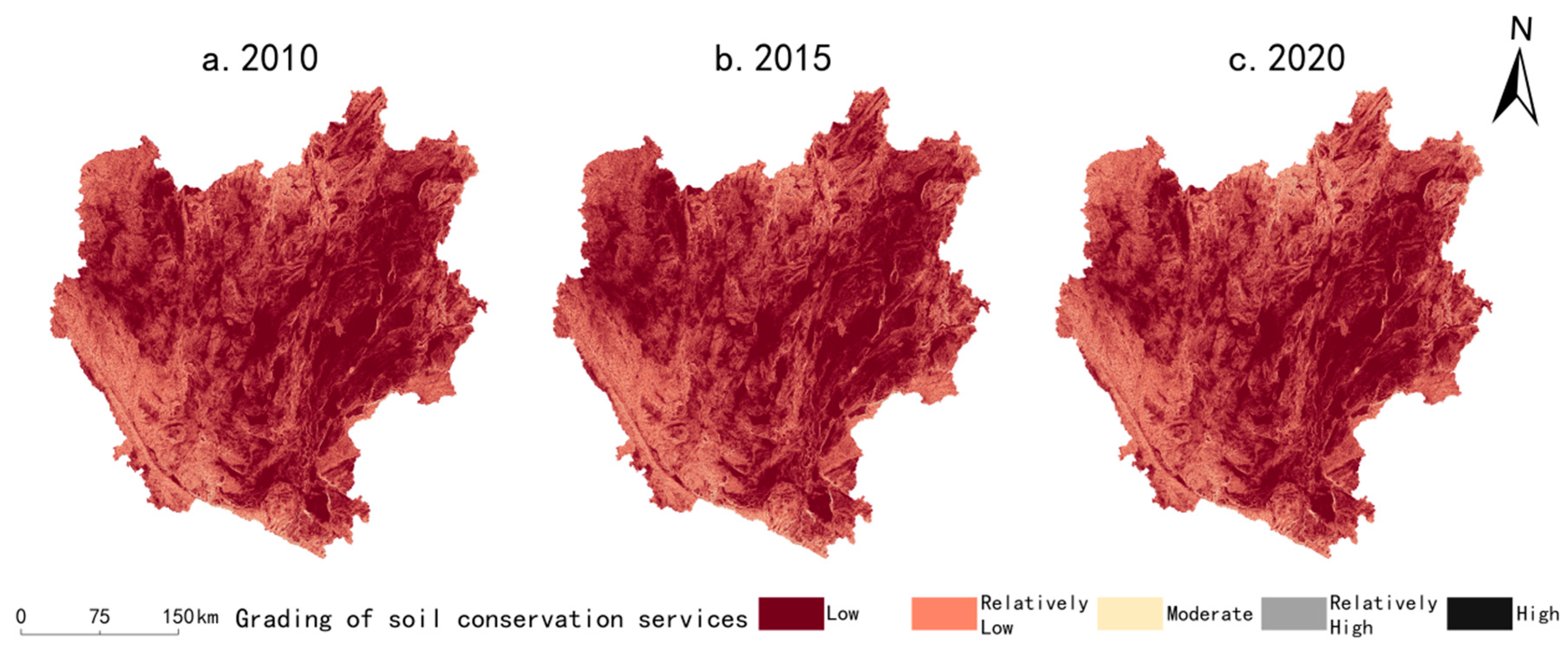
2.4.2. Methodology for Evaluating the Level of Ecological Services of Natural Subsystems
- Water conservation services
- 2.
- Soil conservation services
- 3.
- Carbon sequestration services
- 4.
- Habitat quality
- 5.
- Integrated ecosystem services
2.4.3. Coupling Coordination Model
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Economic-Social-Ecological Subsystem Development Chronology
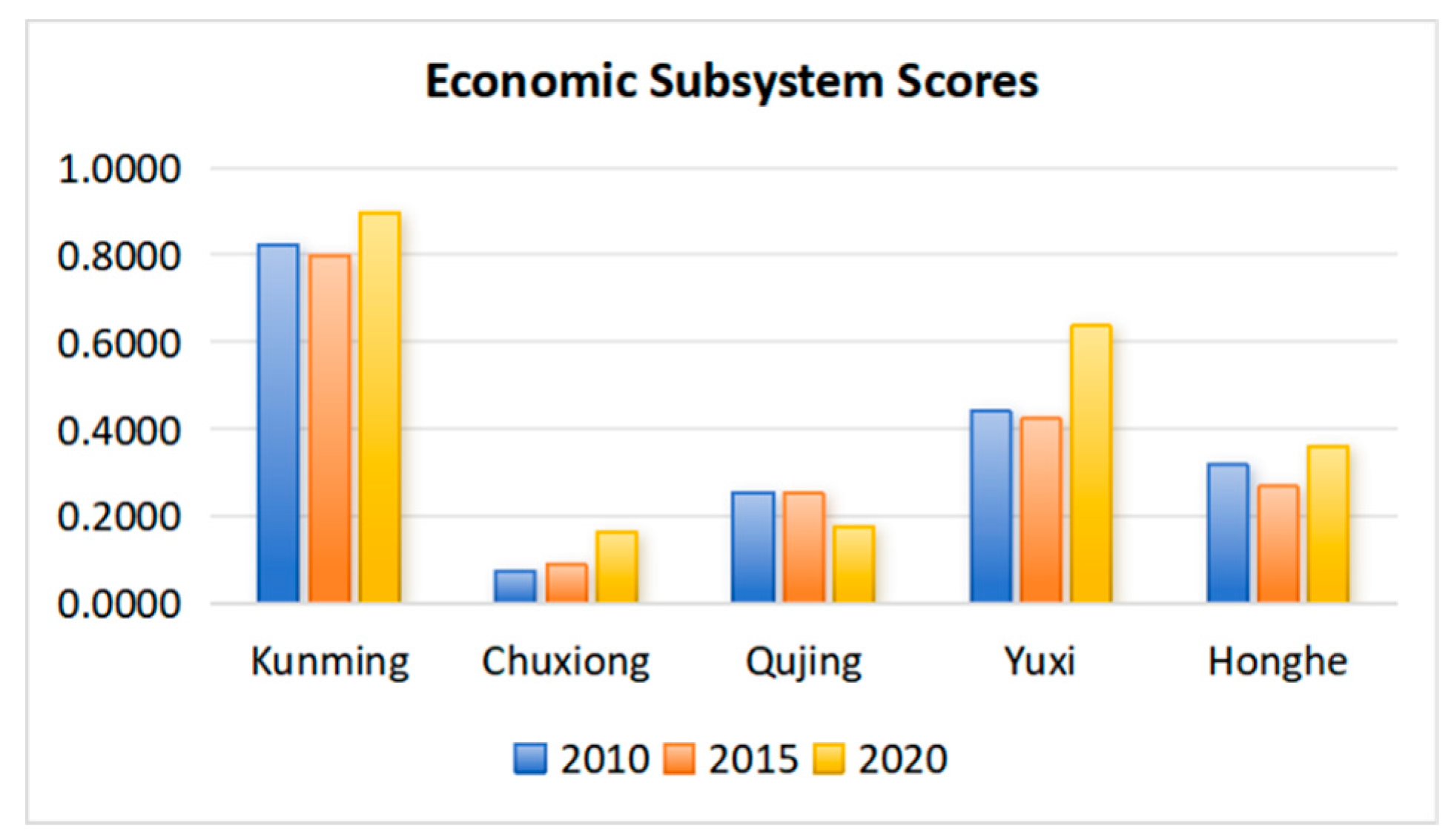
3.1.1. Characteristics of Economic Subsystem Development Chronology
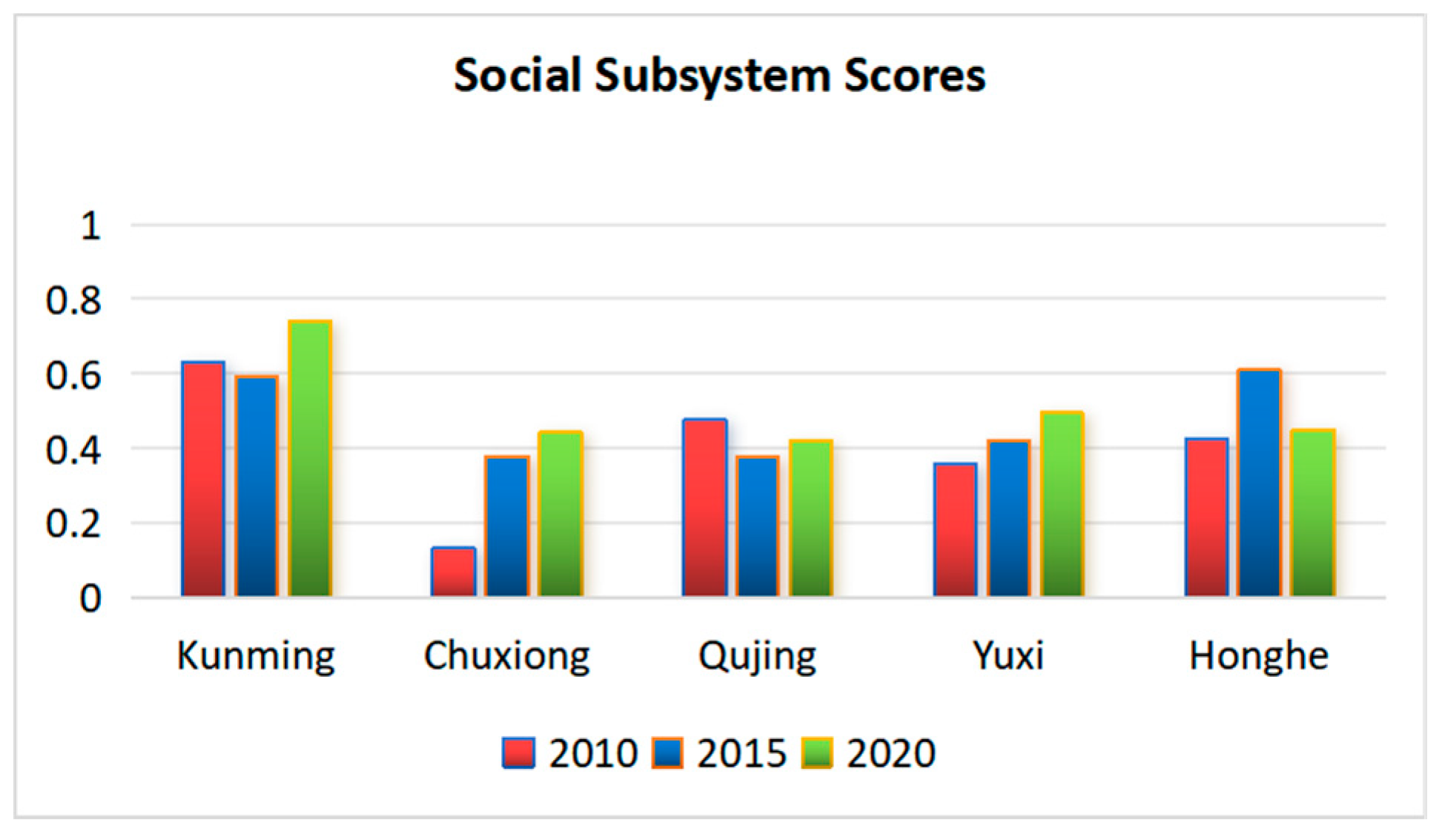
3.1.2. Characteristics of Social Subsystem Development Chronology
3.1.3. Characteristics of Natural Subsystem Development Chronology
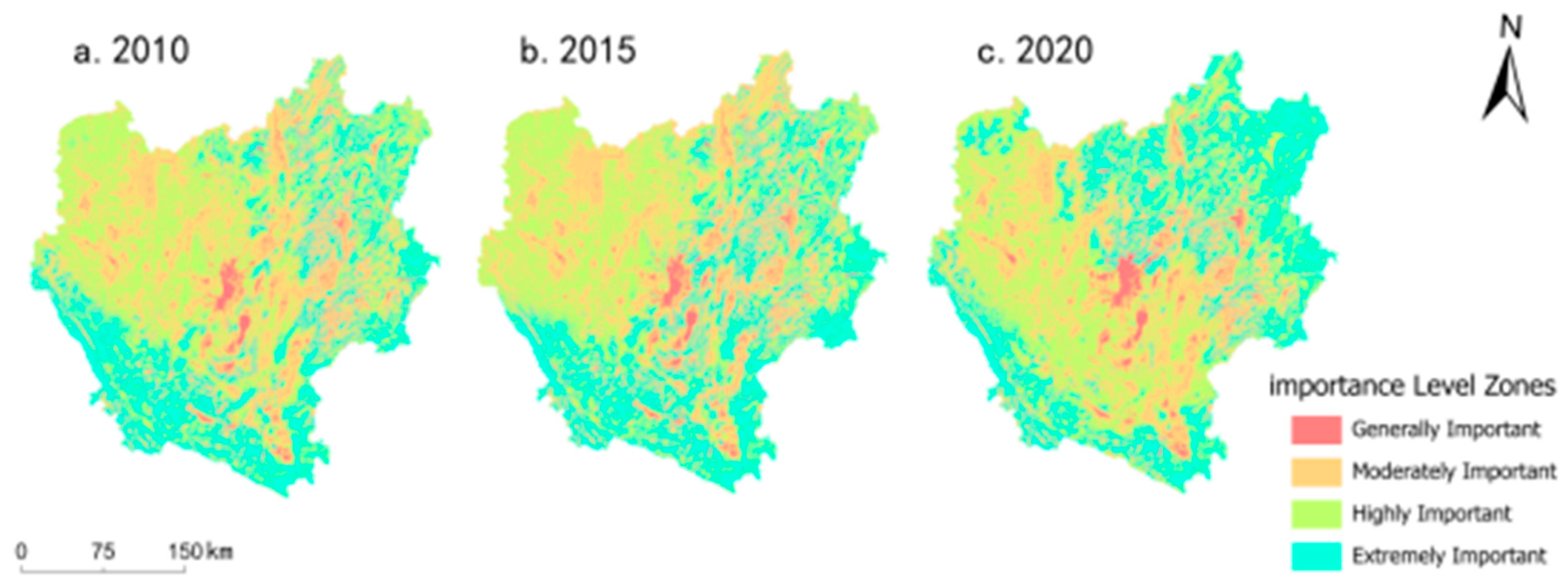
3.2. Coupling and Coordination Relationships in Composite Ecosystems
3.2.1. Status of Development of Coupling in Composite Ecosystems
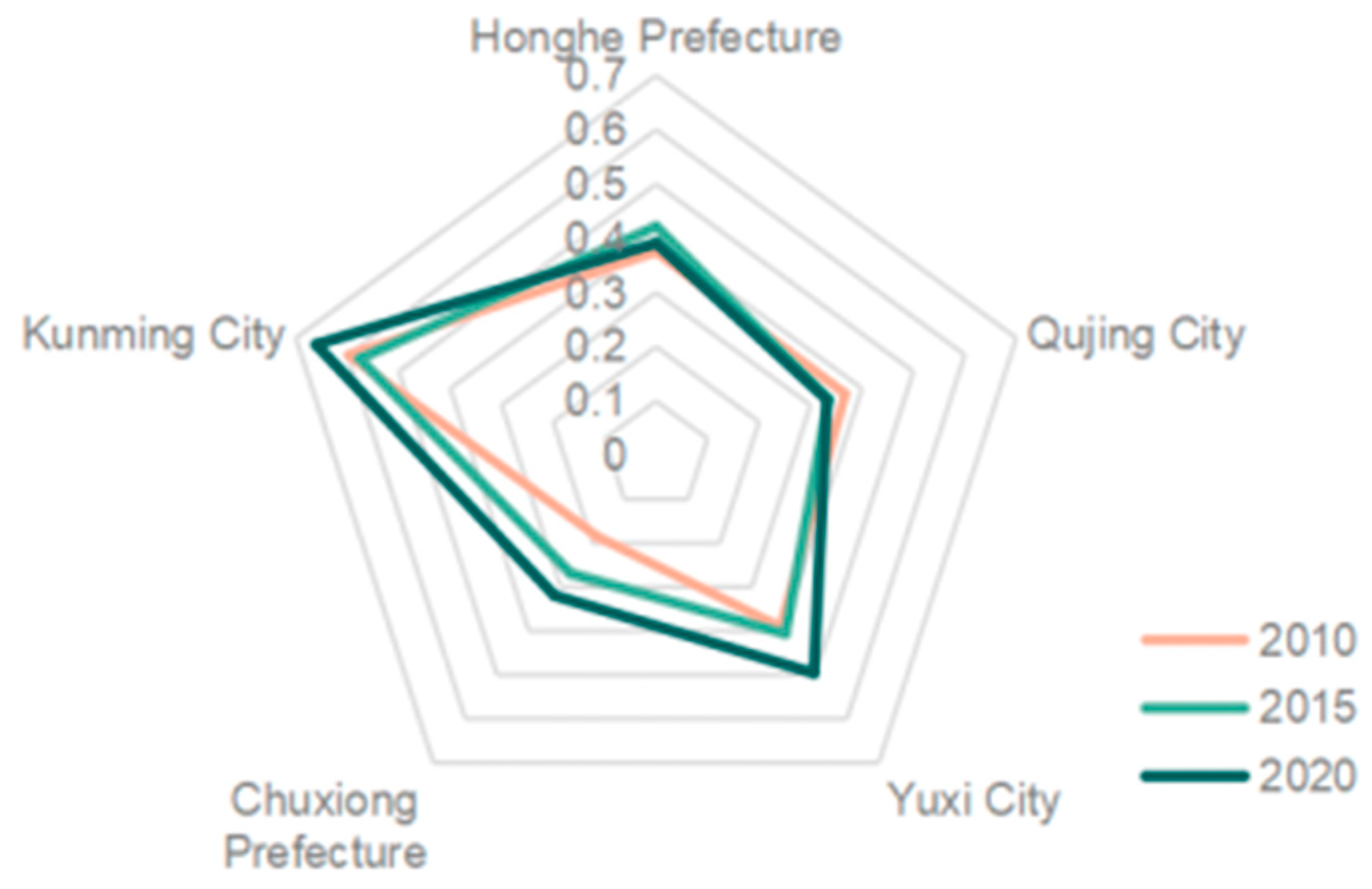
3.2.2. Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Variability of Coordination in Composite Ecosystems
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
References
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, R. Social Economic Natural Composite Ecosystem. Acta Ecologica Sinica 1984, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, D. A Framework of China’s High-quality Economic Development. Research on Economics and Management 2019, 40, 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Yuan, J. An Analyzing M odel System on Population, Resources, Environment and Economics. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice. 2002, 67-72.
- Lin, Y.; Yang, P. Research on Rural Human Settlement Environment Based on Composite Ecosystem Theory. Spatial Governance for High-Quality Development: Proceedings of the 2021 China Urban Planning Annual Conference 2021, 16, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Yang, J.; Li, Z. Evolution and Driving Mechanism of Temporal and Spatial Patterns of Regulation Services of Urban Complex Ecosystem in Taiyuan. Scientia Geographica Sinica 2021, 41, 463–472. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, K; Han, X. Rural landscape planning in hilly areas based on complex ecosystem theory. Ecology and Environmental Sciences 2018, 27, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C. Feng, X. Analysis and Forecast of Coupling Coordination Development among the Regional Economy-Ecological Environment-Tourism Industry —A Case Study of Provinces Along the Yangtze Economic Zone. ECONOMIC GEOGRAPHY 2016, 36, 186–193. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Wang, Y. Quantitative investigation of the interactive coupling relationship between urbanization and eco-environment. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2015, 35, 2244–2254. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Zhou, C. Theoretical analysis of interactive coupled effects between urbanization and eco-environment in mega-urban agglomerations. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2016, 71, 531–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Fang, S. Coupling Coordination Between the Socio-Economic Benefits and Eco-Environmental Benefits of the Songshan Global Geopark. Resources Science 2014, 36, 206–216. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, W. The Coupling and Coordination Relationship and Their Spatial Pattern of Urban Land Use Economic, Social and Ecological Benefits of Cities in Three Largest Urban Agglomerations in China. Urban Development Studies 2016, 23, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, P. Coupling Coordination Degree of Regional Forest Ecological-Nature-Economy-Society Complex System: a Case Study in Changsha. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 2023, 59, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Liao, P. Urbanization Quality over Time and Space as Well as Coupling Coordination of Land, Population and Industrialization in Chongqing. Economic Geography 2015, 35, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yuan, Y. Assessment of Regional Green Finance and Coupled Coordinated Development of the Ecological Environment. Statistics & Decision 2019, 35, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, R. Analysis of Coupling Degrees of Urbanization and Ecological Environment in China. Journal of Natural Resources 2005, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Xu, H. Analysis on Spatial- temporal Coupling Coordinate Degree among Population, Land and Economy Urbanization: Based on China Provincial Panel Data. Urban Development Studies 2014, 21, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Hong, W. Coupling Degrees of Land Ecosystem Services and Urbanization of Fuzhou City. Scientia Geographica Sinica 2013, 33, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W.; Jin, X. “Production-Living-Ecological” Function Evaluation and Coupling Coordination Analysis of Land Use in Jiangsu Province. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 1541–1551. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, X.; Huang, Y. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Coupled Coordination Degree of Ecotourism and Tourism Environment of Jilin Province. Scientia Geographica Sinica 2019, 39, 496–505. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. An analysis of coupling between the bearing capacity of the ecological environment and the quality of new urbanization in Chongqing. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2016, 71, 817–828. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Huang, Z. The Spatial Characteristics and Drive Mechanism of Coupling Relationship between Urbanization and Eco-Environment in the Pan Yangtze River Delta. Economic Geography 2017, 37, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Cui, Z. Coupling relationship between urbanization and ecological resilience in the Pearl River Delta. Acta Geographica Sinica 2021, 76, 973–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, D. The Coupled Coordination Relationship between Land Urbanization and Population Urbanization—A Case Study of the Central Plains Economic Region. Economic Geography 2017, 37, 145–154. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, W. The Coupled Relationship and Spatial Differences between Population Urbanization and Land Urbanization: A Case Study of the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration. Ecological Economy 2019, 35, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Zhao, J. Identification of Territory Space Pattern and Spatio-temporal Evolution Analysis of Urban Agglomeration in Central Yunnan. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 2019, 50, 176–191. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Jiao, H. Coupling and Coordinating Between Economic Development and Ecological Environment in the Pan Yangtze River Delta. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 719–727. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, T.; Wu, S. otemporal variation of water source supply service in Three Rivers Source Area of China based on InVEST model. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology. 2013, 24, 183-189. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, G. Study on change in carbon storage and its spatial pattern in Mata Watershed from 1999 to 2016 based on InVEST model. Arid Zone Research 2021, 38, 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, J. Analysis on spatial and temporal changes of regional habitat quality based on the spatial pattern reconstruction of land use. Acta Geographica Sinica 2020, 75, 160–178. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Shi, P. Ecological risk assessment and identification of priority areas for management and control based on the perspective of ecosystem services equilibrium: A case study of Lanzhou. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 2020, 40, 724–733. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, X. Coupling coordination and interaction between urbanization and eco-environment in ChengYu urban agglomeration, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 2021, 32, 993–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Yang, X. Research on the coupling coordination of water-energy-food system and its temporal and spatial characteristics. China Environmental Science 2022, 42, 4444–4456. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Bai, L. Coupling and Coordinating Degrees of Provincial Economy, Resources and Environment in China. Journal of Natural Resources 2017, 32, 788–799. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Liu, Y. The Belt and Road and Development of Marginal Growth Centers in Yunnan Province. Journal of Boundary and Ocean Studies 2022, 7, 84–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Evolution of Ecosystem Services of Weihe River Basin in ShaanXi Qinling Mountain based on InVEST Model. Master, Northwest University, Xi’an City, Shaanxi Province, 2022.
- Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Spatio-temporal variations of ecosystem service value and its spatial heterogeneity mechanism in the Dongjiang River Basin, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 2023, 34, 2498–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Liu, F. Study on temporal and spatial evolution of production-living-ecological space in central Yunnan urban agglomeration based on LUCC. Shanghai Land & Resources 2023, 44, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, D.; Jiang, X. Economic Development of Urban Agglomeration in Central.


| Data | Source | Preprocessing |
|---|---|---|
| Meteorological data such as temperature, precipitation, actual water pressure, etc. | Weather Science Data Center (http://data.cma.cn) | To account for inter-annual fluctuations in the data, local annual average meteorological data were selected for the calculations. |
| Potential evapotranspiration | Annual mean potential evapotranspiration was calculated using the Modified-Hargreaves method with refined interpolation. | |
| DEM data | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn) | The ASTER GDEM 30m resolution data of the urban agglomeration in central Yunnan were obtained and cropped and spliced by ArcGIS. The watershed boundary was obtained by ArcGIS hydrological analysis. |
| Soil depth data, soil type data, and other soil data such as organic carbon content | Earth System Science Data Sharing Platform, Cold and Arid Regions Science Data Center, China Soil Dataset Based on World Soil Database | PAWC and saturated hydraulic conductivity were calculated using soil properties from the SPAW Hydrology model. |
| Land use data | Center for Resource and Environmental Sciences and Data, Chinese Academy of Sciences (http://www.resdc.cn) | The time span is 2000, 2015 and 2020, and the resolution is 100 m × 100 m. After data processing and with reference to the national county-level land use status classification system, a land use classification map of the urban agglomeration in central Yunnan was generated. |
| Target Level | System Level | Criterion Level | Indicator Level | Unit | Attribute | Weight |
| Urban Composite Ecosystem | Economic Subsystem | Economic Development | Per Capita GDP | Yuan | + | 0.1101 |
| Per Capita Disposable Income | Yuan | + | 0.1107 | |||
| Per Capita Local Fiscal Revenue | Yuan | + | 0.1100 | |||
| Per Capita Fixed Asset Investment | Ten thousand yuan | + | 0.1100 | |||
| Economic Structure | The Proportion of the Secondary Sector in GDP | % | + | 0.1121 | ||
| The Proportion of the Tertiary Sector in GDP | % | + | 0.1123 | |||
| Economic Vitality | Fiscal Self-Sufficiency Ratio | % | + | 0.1100 | ||
| Per Capita Retail Sales of Consumer Goods | Yuan per person | + | 0.1100 | |||
| Total Social Labor Productivity | Yuan per person | + | 0.1108 | |||
| Social Subsystem | Population Factors | Permanent Resident Population | people | + | 0.0910 | |
| Natural Population Growth Rate | ‰ | + | 0.0919 | |||
| Living Standards | Average Wages of Urban Non-profit Unit Employees | Yuan | + | 0.0909 | ||
| Per Capita Net Income of Rural Residents | People per square kilometer | + | 0.0910 | |||
| Registered Urban Unemployment Rate | % | - | 0.0917 | |||
| Infrastructure | Per Capita Road Area | m² | + | 0.0850 | ||
| International Internet Coverage Rate | % | + | 0.0912 | |||
| Gas Penetration Rate | % | + | 0.0925 | |||
| Public Services | Number of Teachers per Ten Thousand People | People | + | 0.0900 | ||
| Number of Health Facilities per Ten Thousand People | Count | + | 0.0900 | |||
| Comprehensive Social Health Insurance Coverage Rate | % | + | 0.0900 | |||
| Natural Subsystem | Water Conservation | Annual Water Production | mm | + | 0.2078 | |
| Soil Conservation | Soil Conservation Quantity | t‧hm-2‧a-1 | + | 0.2301 | ||
| Carbon Sequestration Services | Carbon Storage per Unit Area | t‧hm-2‧a-1 | + | 0.3313 | ||
| Habitat Quality | Habitat Quality | + | 0.4328 |
| serial number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| main class | Dysfunctional recession class | transition class | Coordinated development class | |||||||
| Coordination Degree | 0-0.09 | 0.1-0.19 | 0.2-0.29 | 0.3-0.39 | 0.4-0.49 | 0.5-0.59 | 0.6-0.69 | 0.7-0.79 | 0.8-0.89 | 0.9-1.00 |
| Coordination Degree Level | extreme disorder | severe disorder | intermediate disorder | mild disorder | on the verge of becoming disordered | Barely coordination | Primary coordination | intermediate coordination | good coordination | High-quality coordination |
| Coupling Degree | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kunming City | 0.9368 | 0.9426 | 0.9264 |
| Chuxiong Prefecture | 0.8145 | 0.8362 | 0.9199 |
| Yuxi City | 0.9958 | 0.9983 | 0.9729 |
| Qujing City | 0.9687 | 0.9833 | 0.9323 |
| Honghe Prefecture | 0.9929 | 0.9453 | 0.9947 |
| 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subsystem Pairwise Coupling Degree | Economic-Social | Social-Natural | Economic-Natural | Economic-Social | Social-Natural | Economic-Natural | Economic-Social | Social-Natural | Economic-Natural |
| Kunming City | 0.9913 | 0.9524 | 0.8702 | 0.9889 | 0.9630 | 0.8728 | 0.9954 | 0.9317 | 0.8748 |
| Chuxiong Prefecture | 0.9600 | 0.8928 | 0.8841 | 0.7832 | 0.9984 | 0.9184 | 0.8859 | 0.9937 | 0.9029 |
| Yuxi City | 0.9943 | 0.9997 | 0.8921 | 0.9999 | 0.9982 | 0.8898 | 0.9921 | 0.9868 | 0.8823 |
| Qujing City | 0.9534 | 0.9922 | 0.8977 | 0.9803 | 0.9999 | 0.8949 | 0.9133 | 0.9997 | 0.9200 |
| Honghe Prefecture | 0.9896 | 0.9986 | 0.8967 | 0.9213 | 0.9754 | 0.9137 | 0.9938 | 0.9946 | 0.8861 |
| Region | Coordination Degree | Coordination Degree Level | Lagging Subsystem |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kunming City City | 0.7824 | Intermediate coordination | Natural Subsystem |
| Chuxiong Prefecture Prefecture | 0.5419 | Barely coordination | Economic Subsystem |
| Yuxi City | 0.6947 | Primary coordination | Natural Subsystem |
| Qujing City City | 0.5564 | Barely coordination | Economic Subsystem |
| Honghe Prefecture Prefecture | 0.6235 | Primary coordination | Economic Subsystem |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




