Submitted:
24 January 2024
Posted:
25 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
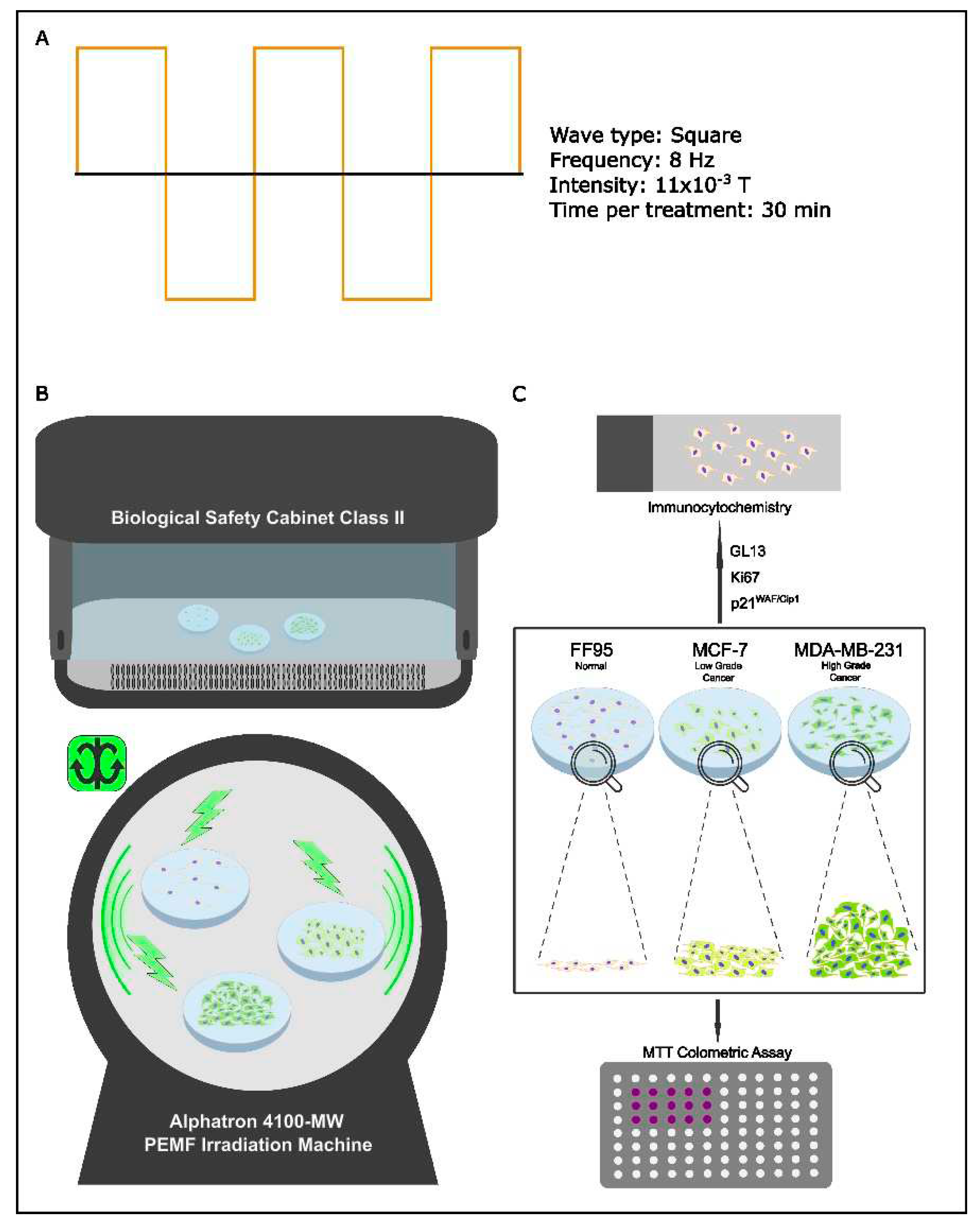
2.2. In Vitro PEMF Irradiation Device
Multi Pulse Magnetic Field Therapy Device Alphatron 4100-MW
2.3. Cytotoxicity Test (MTT Assay)
2.4. Immunocytochemistry for Anti-Biotin, p21WAF1/Cip1, and Ki67 Staining
2.5. GL13 (SenTraGorTM) Staining
2.6. Estimation of Cell Proliferation Rate
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
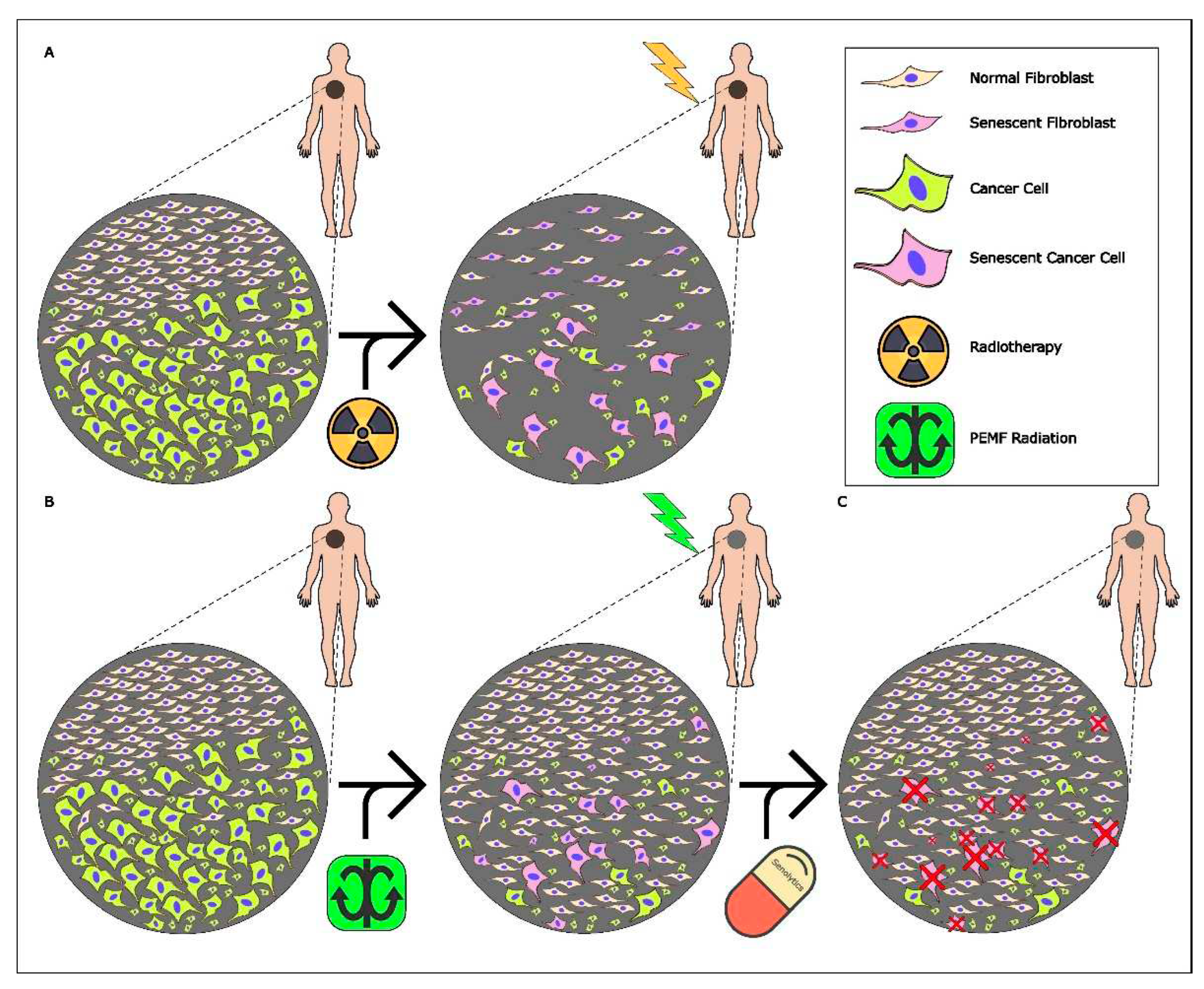
3.1. Experimental Design
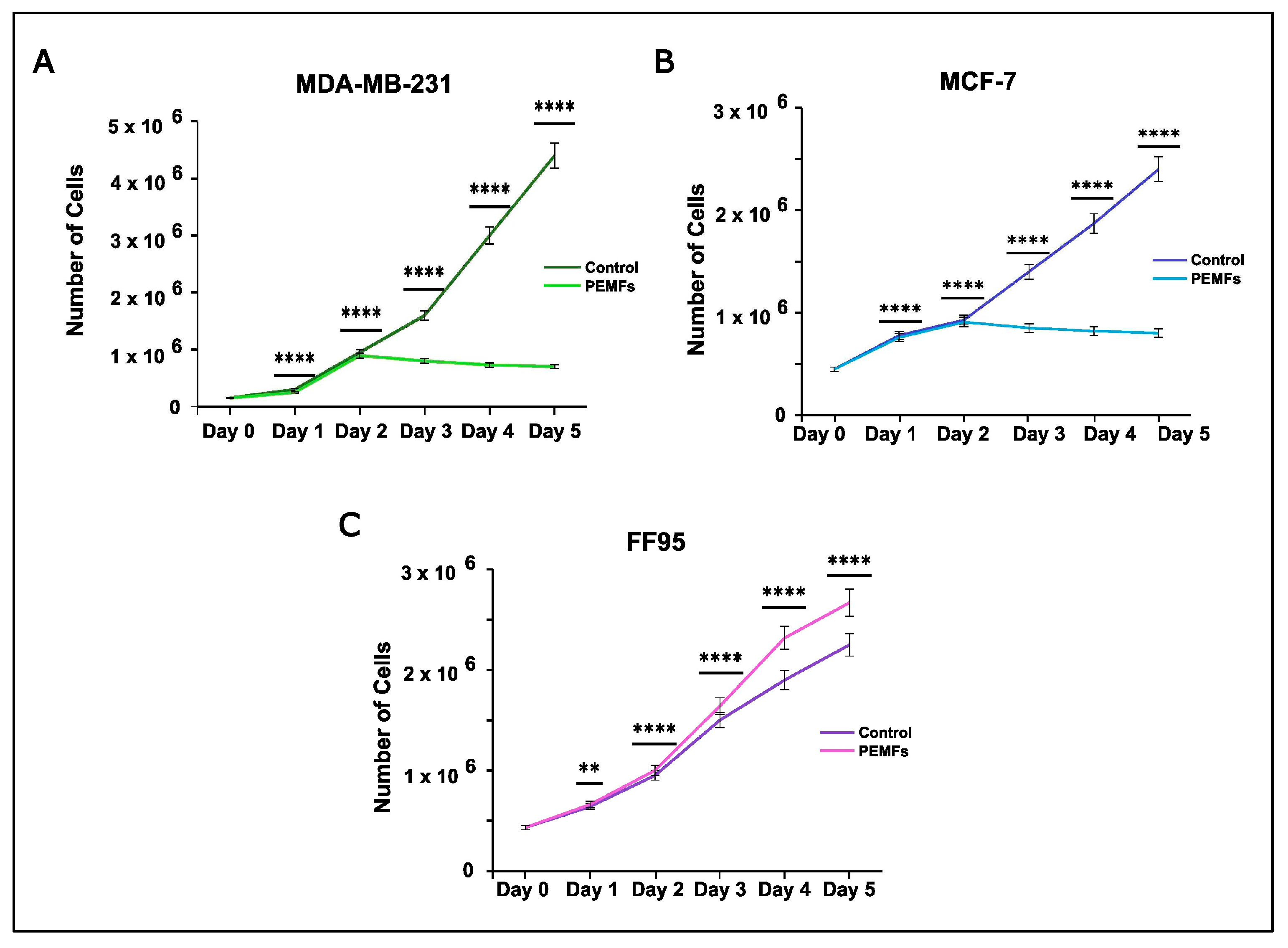
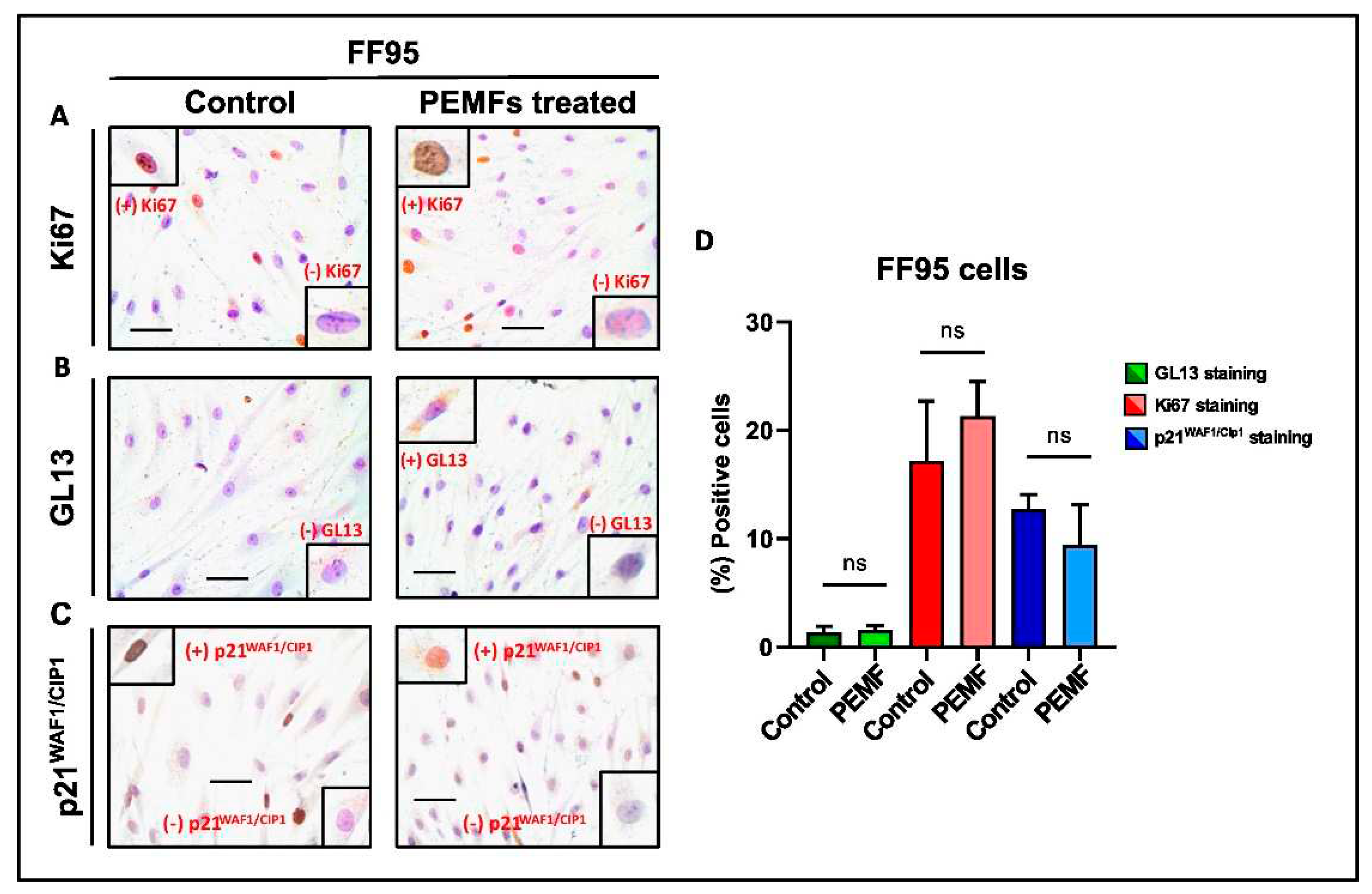
3.2. Pulse Electromagnetic Fields (PEMFs) Trigger Cell Death and Cellular Senescence
Effect on Cell Proliferation Rate
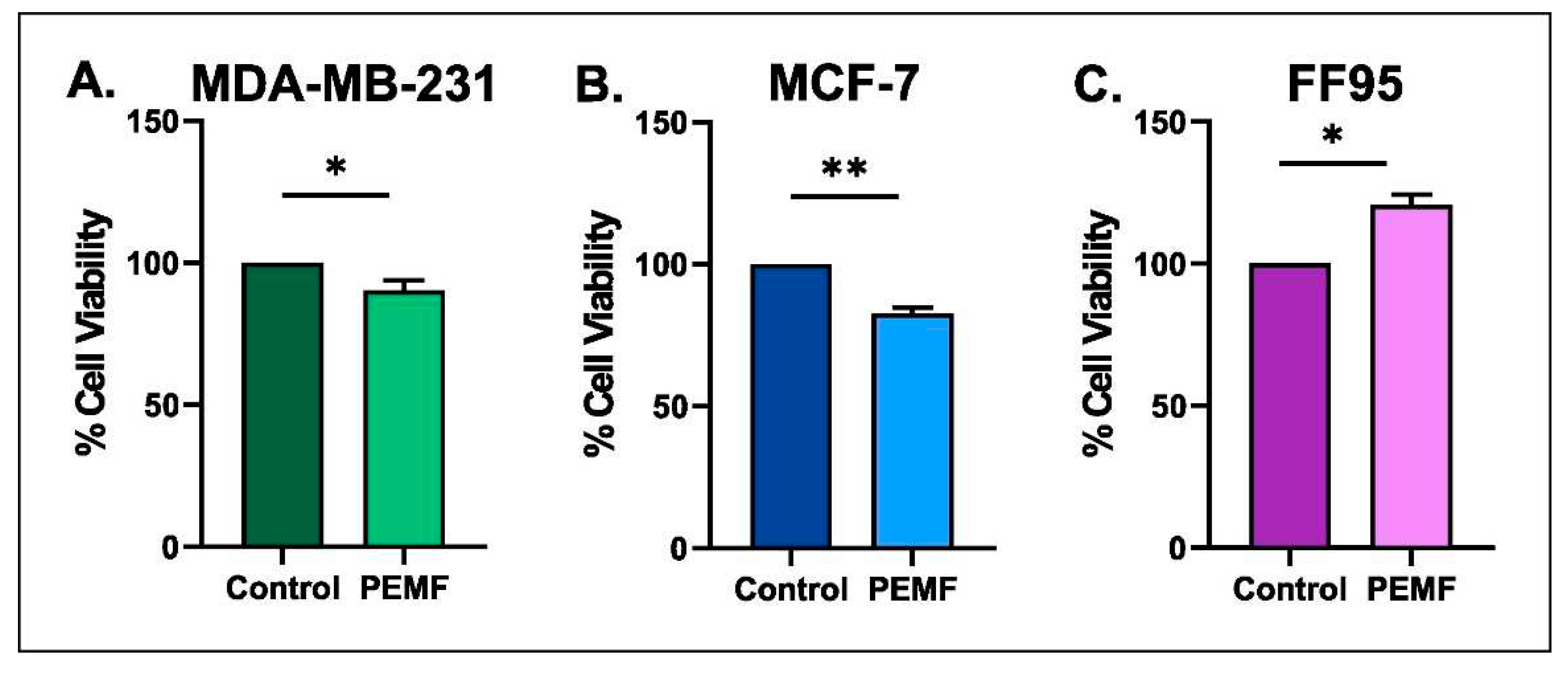
3.3. Effect on Cytotoxicity
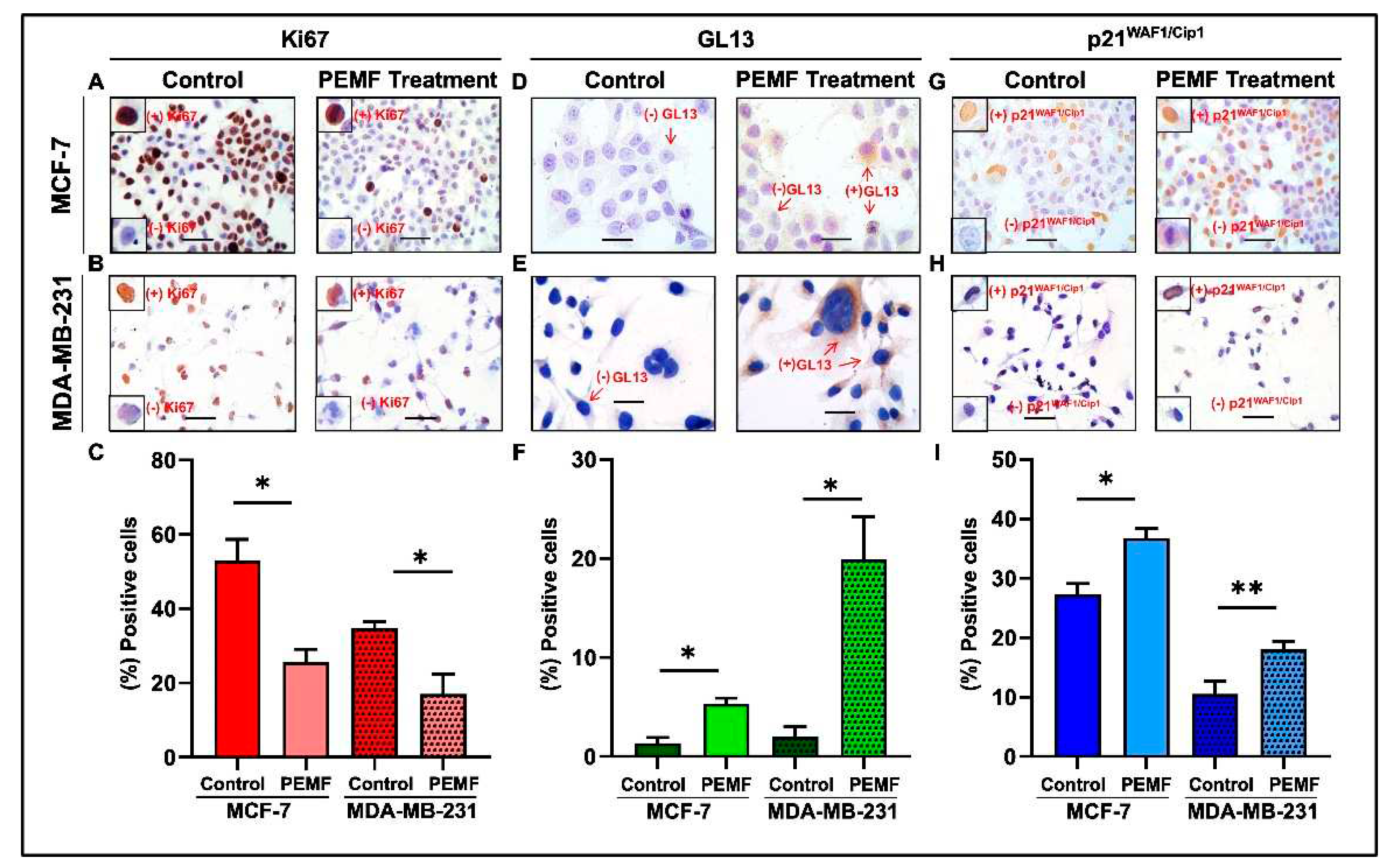
3.4. Detection of Cellular Senescence
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization, Health Topics, Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cancer#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 19/12/2023).
- Fisher, R.; Pusztai, L.; Swanton, C. Cancer heterogeneity: implications for targeted therapeutics. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffray, D.A.; Gospodarowicz, M.K. Radiation Therapy for Cancer. In Radiation Therapy for Cancer Cancer: Disease Control Priorities, Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, 3rd ed.; Gelband, H., Jha, P., Sankaranarayanan, R., Horton, S., Eds.; The World Bank 2015; Volume 3.
- Lyra, M.; Lagopati, N.; Charalambatou, P.; Vamvakas, I. Patient-specific dosimetry in radionuclide therapy. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2011, 147, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russ, E.; Davis, C.M.; Slaven, J.E.; Bradfield, D.T.; Selwyn, R.G.; Day, RM. Comparison of the Medical Uses and Cellular Effects of High and Low Linear Energy Transfer Radiation. Toxics 2022, 10, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskar, R.; Dai, J.; Wenlong, N.; Yeo, R.; Yeoh, K.W. Biological response of cancer cells to radiation treatment. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2014, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirresh, A.; White, L.; Mitchell, A.; Ahmad, S.; Obika, B.; Davis, S.; Ahmad, M.; Candilio, L. Radiation-induced coronary artery disease: a difficult clinical conundrum. Clin Med (Lond) 2022, 22, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.H.W.; Kuo, M.T. Improving radiotherapy in cancer treatment: Promises and challenges. Oncotarget 2017, 37, 62742–62758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, S. Biomechanics and biophysics of cancer cells. Acta Biomater. 2007, 413, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, B.S.; Pye, H.; Whitaker, H.C. The oncological relevance of fragile sites in cancer. Commun Biol 2021, 4, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carew, J.S.; Huang, P. Mitochondrial defects in cancer. Mol Cancer 2002, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseervatham, J. Cytoskeletal Remodeling in Cancer. Biology 2020, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denais, C.; Lammerding, J. Nuclear mechanics in cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 773, 435–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.; Son, S.; Amodei, D.; Cermak, N.; Shaw, J.; Kang, J.H.; Hecht, V.C.; Winslow, M.M.; Jacks, T.; Mallick, P.; Manalis, S.R. Characterizing deformability and surface friction of cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7580–7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, L. Centrosome dysfunction: a link between senescence and tumor immunity. Sig Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagopati, N.; Kotsinas, A.; Veroutis, D.; Evangelou, K.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Arfanis, M.; Falaras, P.; Kitsiou, P. V.; Pateras, I.; Bergonzini, A.; Frisan, T.; Kyriazis, S.; Tsoukleris, D. S.; Tsilibary, E. C.; Gazouli, M.; Pavlatou, E. A.; Gorgoulis, V. G. Biological Effect of Silver-modified Nanostructured Titanium Dioxide in Cancer. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2021, 3, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vines, J.B.; Yoon, J.H.; Ryu, N.E.; Lim, D.J.; Park, H. Gold Nanoparticles for Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moslemi, S.; Ghotbi Ravandi, M.R.; Zare, S.; Tohidi, N.H. Measuring and assessing the effects of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields (ELF-EMF) on blood parameters and liver enzymes of personnel working in high voltage power stations in a petrochemical industry. Heliyon 2023, 14, 9–15414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirson, E. D.; Gurvich, Z.; Schneiderman, R.; Dekel, E.; Itzhaki, A.; Wasserman, Y.; Schatzberger, R.; Palti, Y. Disruption of cancer cell replication by alternating electric fields. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3288–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, B.A. PEMF The Fifth Element of Health: Learn Why Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF); Balboa Press, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.H.; Chen, K.W.; Ni, D.X.; Fang, H.J.; Jang, L.S.; Chen, C.H. Effect of extremely low frequency electromagnetic field parameters on the proliferation of human breast cancer. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2021, 40, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou-Fermeli, N.; Lagopati, N.; Pippa, N.; Sakellis, E.; Boukos, N.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Gazouli, M.; Pavlatou, E.A. Composite Nanoarchitectonics of Photoactivated Titania-Based Materials with Anticancer Properties. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagopati, N.; Tsilibary, E. P.; Falaras, P.; Papazafiri, P.; Pavlatou, E. A.; Kotsopoulou, E.; Kitsiou, P. Effect of nanostructured TiO₂ crystal phase on photoinduced apoptosis of breast cancer epithelial cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3219–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, J.A. Cell sensitivity assays: the MTT assay. Methods Mol. Med. 2004, 88, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelou, K.; Lougiakis, N.; Rizou, S.V.; Kotsinas, A.; Kletsas, D.; Muñoz-Espín, D.; Kastrinakis, N.G.; Pouli, N.; Marakos, P.; Townsend, P.; Serrano, M.; Bartek, J.; Gorgoulis, V.G. Robust, universal biomarker assay to detect senescent cells in biological specimens. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, J.; Wang, B.; Brandenburg, S.M.; Basisty, N.; Evangelou, K.; Varela-Eirin, M.; Campisi, J.; Schilling, B.; Gorgoulis, V.G; Demaria, M. Algorithmic assessment of cellular senescence in experimental and clinical specimens. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 2471–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinini, F.; Tesei, A.; Arienti, C.; Bevilacqua, A. Cell Counting and Viability Assessment of 2D and 3D Cell Cultures: Expected Reliability of the Trypan Blue Assay. Biol. Proced. Online 2017, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, D.; Pal, D.; Sharma, R.; Garg, V. K.; Goel, N.; Koundal, D.; Zaguia, A.; Koundal, S.; Belay, A. Global Increase in Breast Cancer Incidence: Risk Factors and Preventive Measures. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 9605439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliogna, L.; Medetti, M.; Bina, V.; Brancato, A.M.; Castelli, A.; Jannelli, E.; Ivone, A.; Gastaldi, G.; Annunziata, S.; Mosconi, M.; Pasta, G. Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields in Bone Healing: Molecular Pathways and Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 1 4, 7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgoulis, V.G; Adams, P.D.; Alimonti, A.; Bennett, D.C.; Bischof, O.; Bishop, C.; Campisi, J.; Collado, M.; Evangelou, K.; Ferbeyre, G.; Gil, J.; Hara, E.; Krizhanovsky, V.; Jurk, D.; Maier, A.B.; Narita, M.; Niedernhofer, L.; Passos, J.F.; Robbins, P.D.; Schmitt, C.A.; Sedivy, J.; Vougas, K.; von Zglinicki, T.; Zhou, D.; Serrano, M.; Demaria, M. Cellular Senescence: Defining a Path Forward. Cell 2019, 179, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Espín, D.; Serrano, M. Cellular senescence: from physiology to pathology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgakopoulou, E.A.; Tsimaratou, K.; Evangelou, K.; Fernandez-Marcos, P.J.; Zoumpourlis, V.; Trougakos, I.P.; Kletsas, D.; Bartek, J.; Serrano, M.; Gorgoulis, V.G. Specific lipofuscin staining as a novel biomarker to detect replicative and stress-induced senescence. A method applicable in cryo-preserved and archival tissues. Aging (Albany NY) 2013, 5, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, C.A.; Buckner, A.L.; Koren, S.A.; Persinger, M.A.; Lafrenie, RM. Inhibition of cancer cell growth by exposure to a specific time-varying electromagnetic field involves T-type calcium channels. PLoS ONE 2015, 4, 0124136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.H.; Chen, K.W.; Ni, DX.; Fang, HJ.; Jang, LS.; Chen, CH. Effect of extremely low frequency electromagnetic field parameters on the proliferation of human breast cancer. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2021, 40(3), 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omote, Y.; Hosokawa, M.; Komatsumoto, M.; Namieno, T.; Nakajima, S.; Kubo, Y.; Kobayashi, H. Treatment of Experimental Tumours with a Combination of a Pulsing Magnetic Field and an Antitumor Drug. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1990, 9, 81,9,956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivancsits, S.; Pilger, A.; Diem, E.; Jahn, O.; Rüdiger, H.W. Cell type-specific genotoxic effects of intermittent extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields. Mutat. Res. 2005, 583, 184–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, K.; Henderson, A. MAP kinase activation in cells exposed to a 60 Hz electromagnetic field. J. Cell Biochem. 2003, 90, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawluk, W.; Layne, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Caitlin, J. Power tools for health, How Pulsed Magnetic Fields (PEMFs) Help You; Friesen Press, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Crocetti, S.; Beyer, C.; Schade, G.; Egli, M.; Fröhlich, J.; Franco-Obregón, A. Low intensity and frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields selectively impair breast cancer cell viability. PLoS ONE 2013, 11, 72944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halazonetis, T.D.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Bartek, J. An oncogene-induced DNA damage model for cancer development. Science 2008, 319, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewald, J.A.; Desotelle, J.A.; Wilding, G.; Jarrard, D.F. Therapy-induced senescence in cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer-Dennert, M.; de Wit, R.; Schmitz, P.; Djontono, J.; Beurden, V.v.; Stoter, G.; Verweij, J. Patient perceptions of the side-effects of chemotherapy: the influence of 5HT3 antagonists. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 76, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentzen, S. Preventing or reducing late side effects of radiation therapy: radiobiology meets molecular pathology. Nat Rev Cancer 6 2006, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrianthopoulos, V.; Evangelou, K.; Vasileiou, PVS; Cooks, T.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; Pangalis, G.A.; Kouloukoussa, M.; Kittas, C.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Gorgoulis, V.G. Senescence and senotherapeutics: a new field in cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 193, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veroutis, D.; Argyropoulou, O.D.; Goules, A.V.; Kambas, K.; Palamidas, D.A.; Evangelou, K.; Havaki, S.; Polyzou, A.; Valakos, D.; Xingi, E.; Karatza, E.; Boki, KA.; Cavazza, A.; Kittas, C.; Thanos, D.; Ricordi, C.; Marvisi, C.; Muratore, F.; Galli, E.; Croci, S.; Salvarani, C.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Tzioufas, A.G. Senescent cells in giant cell arteritis display an inflammatory phenotype participating in tissue injury via IL-6-dependent pathways. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 24, 2023–224467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppé, J.P.; Desprez, P.Y.; Krtolica, A.; Campisi, J. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: the dark side of tumor suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2010, 5, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelou, K.; Belogiannis, K.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Petty, R.; Gorgoulis, V.G. Escape from senescence: molecular basis and therapeutic ramifications. J. Pathol. 2023, 260, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkouta, S.; Veroutis, D.; Pousias, A.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Pippa, N.; Lougiakis, N.; Kambas, K.; Lagopati, N.; Polyzou, A.; Georgiou, M.; Chountoulesi, M.; Pispas, S.; Foutadakis, S.; Pouli, N.; Marakos, P.; Kotsinas, A.; Verginis, P.; Valakos, D.; Mizi, A.; Papantonis, A.; Vatsellas, G.; Galanos, P.; Bartek, J.; Petty, R.; Serrano, M.; Thanos, D.; Roussos, C.; Demaria, M.; Evangelou, K.; Gorgoulis, V.G. A fluorophore-conjugated reagent enabling rapid detection, isolation and live tracking of senescent cells. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 3558–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pre-set Program C4 | Manual Program 1 | Manual Program 2 | Manual Program 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 8-31 Hz | 8 Hz | 8 Hz | 8 Hz |
| Wave Type | Sinus-Rechteck | Full square | Full square | Full square |
| Intensity | 0.0033-0.0055 T | 0.0088 T | 0.0044 T | 0.011 T |
| Duration | 30 min (2 times)/ 5 days |
1 h (2 times)/ 5 days |
30 min (2 times)/ 5 days |
30 min (2 times)/ 5 days |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





