Submitted:
24 January 2024
Posted:
24 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The ATR Pathway in the DNA Damage Response Network
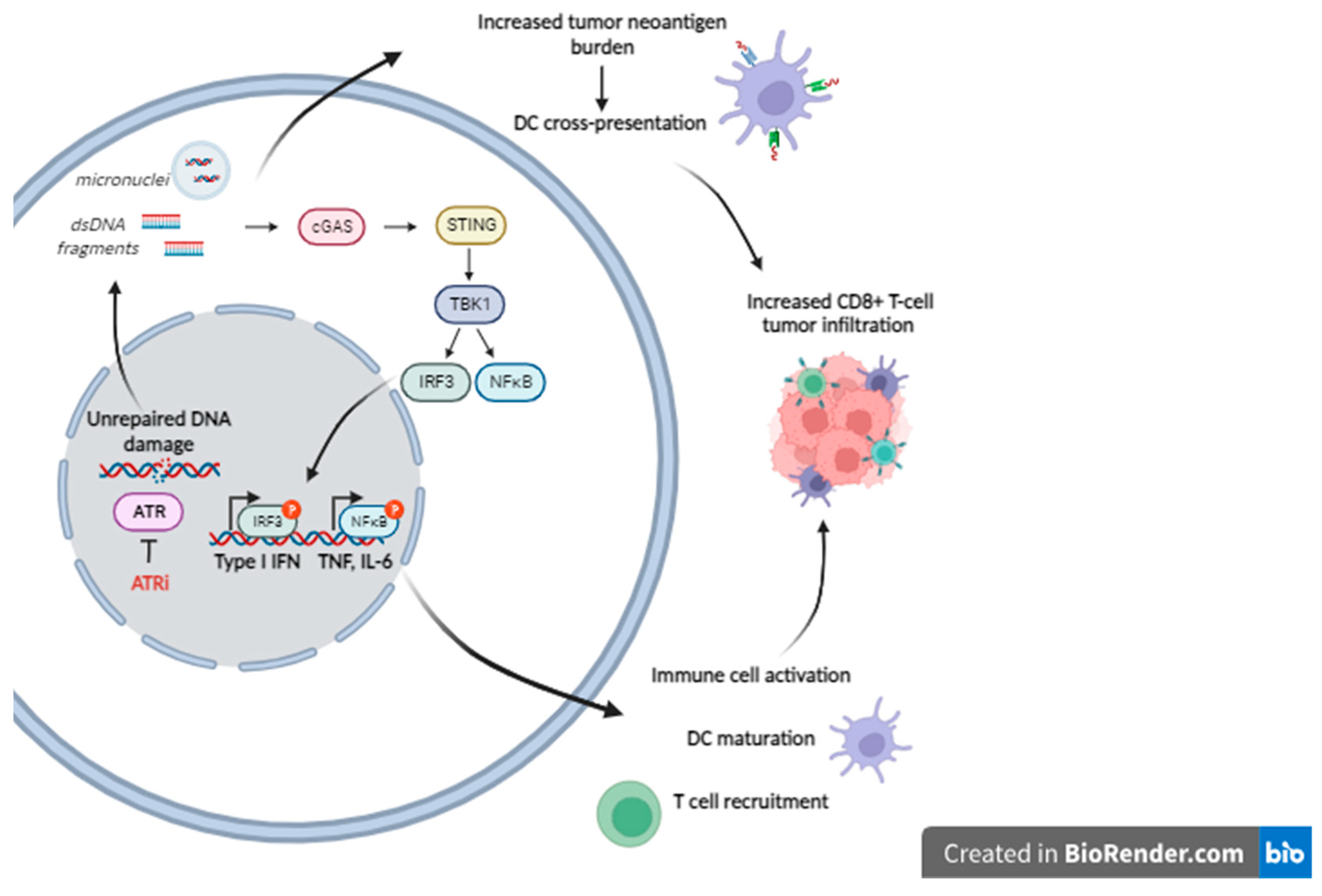
3. The ATR Pathway and the Interplay between the DDR Network and the Immune System
- The induction of immunogenic cell death, i.e., cell death which elicits an immune response [38]. Not all modes of cell death induce such a response which requires, in addition to neoantigen exposure, the presence of additional danger signals [39]. Such signals are provided by damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), i.e., molecules released from dying tumor cells that stimulate the recruitment of antigen-presenting cells to the site, where they process and present tumor neoantigens, thereby priming an adaptive immune response. DAMPs released during chemotherapy-induced immunogenic cell death include, among others, DNA release in the cytoplasm where it leads to activation of stimulator-of-interferon genes (STING) and induction of type I interferon (IFN) and pro-inflammatory cytokines [40].
- The increase in antigen presentation through the upregulation of MHC-1 (major histocompatibility complex type 1) expression on tumor cells and promotion of dendritic cell maturation, priming them for an adaptive immune response [41].
- Increase of the tumor neoantigen burden. There are indications that genotoxic drugs may enhance tumor immunogenicity by causing, thanks to their mutagenicity, an increase of tumor neoantigens, which appear to play a critical role in the effectiveness of immune checkpoint blockade immunotherapy [48,49,50].
4. The ATR Pathway as a Therapeutic Target
4.1. ATM Functionality as a Predictive Biomarker of ATR-Blockade Response
4.2. ATR Inhibitors Synergy with Other Anti-Tumor Therapies
4.3. ATR Inhibition in Clinical Studies
4.3.1. Breast Cancer
4.3.2. Lung Cancer
4.3.3. Gynaecological cancers
4.3.4. Other Solid Tumors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cadet, J.; Wagner, J.R. DNA Base Damage by Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidizing Agents, and UV Radiation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a012559–a012559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Walker, G.C. Mechanisms of DNA damage, repair, and mutagenesis. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganai, R.A.; Johansson, E. DNA Replication—A Matter of Fidelity. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubbs, A.; Nussenzweig, A. Endogenous DNA Damage as a Source of Genomic Instability in Cancer. Cell 2017, 168, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houten, B.; Santa-Gonzalez, G.A.; Camargo, M. DNA repair after oxidative stress: Current challenges. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Nowsheen, S.; Deng, M. DNA Repair Deficiency Regulates Immunity Response in Cancers: Molecular Mechanism and Approaches for Combining Immunotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Pan, W.; Xing, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z. Recent advances in DDR (DNA damage response) inhibitors for cancer therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 230, 114109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, R.; Brown, J.; Ingles Russo, A.; Yap, T.A. Targeting ATR in cancer medicine. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2017, 41, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavin, M.; Kozlov, S.; Gatei, M.; Kijas, A. ATM-Dependent Phosphorylation of All Three Members of the MRN Complex: From Sensor to Adaptor. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 2877–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carusillo, A.; Mussolino, C. DNA Damage: From Threat to Treatment. Cells 2020, 9, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, A.A.B.A.; Chowdhury, D.; Shapiro, G.I.; D’Andrea, A.D.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A. Targeting replication stress in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.L.; Southgate, H.; Tweddle, D.A.; Curtin, N.J. DNA damage checkpoint kinases in cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2020, 22, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Mun Tho, L.; Xu, N.; A. Gillespie, D. The ATM–Chk2 and ATR–Chk1 Pathways in DNA Damage Signaling and Cancer. In Advances in Cancer Research; Elsevier, 2010; Vol. 108, pp. 73–112 ISBN 978-0-12-380888-2.
- Gusho, E.; Laimins, L. Human Papillomaviruses Target the DNA Damage Repair and Innate Immune Response Pathways to Allow for Persistent Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, Md.; Lin, Y.; Yan, S. Single-Strand Break End Resection in Genome Integrity: Mechanism and Regulation by APE2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Elledge, S.J. Sensing DNA Damage Through ATRIP Recognition of RPA-ssDNA Complexes. Science 2003, 300, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durocher, D.; Jackson, S.P. DNA-PK, ATM and ATR as sensors of DNA damage: variations on a theme? Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldivar, J.C.; Cortez, D.; Cimprich, K.A. The essential kinase ATR: ensuring faithful duplication of a challenging genome. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.C.; Hoegel, T.J.; Lynch, M.L.; Woloszynska, A.; Melendy, T.; Ohm, J.E. Exploiting Replication Stress as a Novel Therapeutic Intervention. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecona, E.; Fernandez-Capetillo, O. Targeting ATR in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokas, E.; Prevo, R.; Hammond, E.M.; Brunner, T.B.; McKenna, W.G.; Muschel, R.J. Targeting ATR in DNA damage response and cancer therapeutics. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiotani, B.; Zou, L. ATR signaling at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazayeri, A.; Falck, J.; Lukas, C.; Bartek, J.; Smith, G.C.M.; Lukas, J.; Jackson, S.P. ATM- and cell cycle-dependent regulation of ATR in response to DNA double-strand breaks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.S.; Cortez, D. Rapid Activation of ATR by Ionizing Radiation Requires ATM and Mre11. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 9346–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkovich, E.; Monnat, R.J.; Kastan, M.B. Roles of ATM and NBS1 in chromatin structure modulation and DNA double-strand break repair. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falck, J.; Coates, J.; Jackson, S.P. Conserved modes of recruitment of ATM, ATR and DNA-PKcs to sites of DNA damage. Nature 2005, 434, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, R.; Bakkenist, C.J.; McKinnon, P.J.; Kastan, M.B. Phosphorylation of SMC1 is a critical downstream event in the ATM–NBS1–BRCA1 pathway. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1423–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Paull, T.T. Activation and regulation of ATM kinase activity in response to DNA double-strand breaks. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7741–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Bailis, J.M.; Johnson, S.A.; Dilworth, S.M.; Hunter, T. Rapid activation of ATM on DNA flanking double-strand breaks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDougall, C.A.; Byun, T.S.; Van, C.; Yee, M.; Cimprich, K.A. The structural determinants of checkpoint activation. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacroix, S.; Wagner, J.M.; Kobayashi, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Karnitz, L.M. The Rad9–Hus1–Rad1 (9–1–1) clamp activates checkpoint signaling via TopBP1. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1472–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnitz, L.M.; Zou, L. Molecular Pathways: Targeting ATR in Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4780–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, A.J.; Elledge, S.J.; Zou, L. Checking on the fork: the DNA-replication stress-response pathway. Trends Cell Biol. 2002, 12, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, R.; Dozier, C.; Ducommun, B. The when and wheres of CDC25 phosphatases. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006, 18, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson-Rosenthal, C.; Millar, J.B.A. Cdc25: mechanisms of checkpoint inhibition and recovery. Trends Cell Biol. 2006, 16, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.P.; Bruce, A.T.; Ikeda, H.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezu, L.; Gomes-de-Silva, L.C.; Dewitte, H.; Breckpot, K.; Fucikova, J.; Spisek, R.; Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Kroemer, G. Combinatorial Strategies for the Induction of Immunogenic Cell Death. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Buqué, A.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, G.N. STING: infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.M.; Fowler, D.W.; Smith, P.; Dalgleish, A.G. Pre-treatment with chemotherapy can enhance the antigenicity and immunogenicity of tumours by promoting adaptive immune responses. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzinikolaou, G.; Karakasilioti, I.; Garinis, G.A. DNA damage and innate immunity: links and trade-offs. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaquin, N.; Carrier-Leclerc, A.; Dessureault, M.; Rodier, F. DDR-mediated crosstalk between DNA-damaged cells and their microenvironment. Front. Genet. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banissi, C.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Chen, L.; Carpentier, A.F. Treg depletion with a low-dose metronomic temozolomide regimen in a rat glioma model. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2009, 58, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.; Mignot, G.; Chalmin, F.; Ladoire, S.; Bruchard, M.; Chevriaux, A.; Martin, F.; Apetoh, L.; Rébé, C.; Ghiringhelli, F. 5-Fluorouracil Selectively Kills Tumor-Associated Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Resulting in Enhanced T Cell–Dependent Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3052–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Fang, W.; Yu, J.; Chen, N.; Zhan, J.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L. Expression of programmed death ligand-1 on tumor cells varies pre and post chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebeh, H.; Lehe, C.; Barhoush, E.; Al-Romaih, K.; Tulbah, A.; Al-Alwan, M.; Hendrayani, F.; Manogaran, P.; Alaiya, A.; Al-Tweigeri, T.; et al. RDesoeaxrcoh arrtuiclbe icin downregulates cell surface B7-H1 expression and upregulates its nuclear expression in breast cancer cells: role of B7-H1 as an anti-apoptotic molecule. 2010.
- Rizvi, N.A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Snyder, A.; Kvistborg, P.; Makarov, V.; Havel, J.J.; Lee, W.; Yuan, J.; Wong, P.; Ho, T.S.; et al. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non–small cell lung cancer. Science 2015, 348, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.K.; Davis, A.A.; Raparia, K.; Agte, S.; Pan, A.; Mohindra, N.; Villaflor, V.; Giles, F. Association of Tumor Mutational Burden With DNA Repair Mutations and Response to Anti–PD-1/PD-L1 Therapy in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, K.C.; Howitt, B.E.; Shukla, S.A.; Rodig, S.; Ritterhouse, L.L.; Liu, J.F.; Garber, J.E.; Chowdhury, D.; Wu, C.J.; D’Andrea, A.D.; et al. Association and prognostic significance of BRCA1/2-mutation status with neoantigen load, number of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and expression of PD-1/PD-L1 in high grade serous ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13587–13598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härtlova, A.; Erttmann, S.F.; Raffi, F.Am.; Schmalz, A.M.; Resch, U.; Anugula, S.; Lienenklaus, S.; Nilsson, L.M.; Kröger, A.; Nilsson, J.A.; et al. DNA Damage Primes the Type I Interferon System via the Cytosolic DNA Sensor STING to Promote Anti-Microbial Innate Immunity. Immunity 2015, 42, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, K.J.; Carroll, P.; Martin, C.-A.; Murina, O.; Fluteau, A.; Simpson, D.J.; Olova, N.; Sutcliffe, H.; Rainger, J.K.; Leitch, A.; et al. cGAS surveillance of micronuclei links genome instability to innate immunity. Nature 2017, 548, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdal, E.; Haider, S.; Rehwinkel, J.; Harris, A.L.; McHugh, P.J. A prosurvival DNA damage-induced cytoplasmic interferon response is mediated by end resection factors and is limited by Trex1. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, S.M.; Benci, J.L.; Irianto, J.; Discher, D.E.; Minn, A.J.; Greenberg, R.A. Mitotic progression following DNA damage enables pattern recognition within micronuclei. Nature 2017, 548, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, K.; Knittler, K.; Borowski, C.; Rudnik, S.; Damme, M.; Aden, K.; Spehlmann, M.E.; Frey, N.; Saftig, P.; Chalaris, A.; et al. Absence of RNase H2 triggers generation of immunogenic micronuclei removed by autophagy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 3960–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablasser, A.; Chen, Z.J. cGAS in action: Expanding roles in immunity and inflammation. Science 2019, 363, eaat8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Ma, Z.; Barber, G.N. STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature 2009, 461, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, E.J.; Vance, R.E. Taking the STING out of cytosolic DNA sensing. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Liu, F. The cGAS-cGAMP-STING Pathway: A Molecular Link Between Immunity and Metabolism. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shu, C.; Yi, G.; Chaton, C.T.; Shelton, C.L.; Diao, J.; Zuo, X.; Kao, C.C.; Herr, A.B.; Li, P. Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase Is Activated by Double-Stranded DNA-Induced Oligomerization. Immunity 2013, 39, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Xu, H.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.; Brautigam, C.A.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.J. The Cytosolic DNA Sensor cGAS Forms an Oligomeric Complex with DNA and Undergoes Switch-like Conformational Changes in the Activation Loop. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilger, D.; Seymour, L.W.; Jackson, S.P. Interfaces between cellular responses to DNA damage and cancer immunotherapy. Genes Dev. 2021, 35, 602–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paludan, S.R.; Reinert, L.S.; Hornung, V. DNA-stimulated cell death: implications for host defence, inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Xia, T.; Konno, H.; Konno, K.; Ruiz, P.; Barber, G.N. Inflammation-driven carcinogenesis is mediated through STING. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Bakhoum, S.F. The Cytosolic DNA-Sensing cGAS–STING Pathway in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruand, M.; Barras, D.; Mina, M.; Ghisoni, E.; Morotti, M.; Lanitis, E.; Fahr, N.; Desbuisson, M.; Grimm, A.; Zhang, H.; et al. Cell-autonomous inflammation of BRCA1-deficient ovarian cancers drives both tumor-intrinsic immunoreactivity and immune resistance via STING. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevtsov, M.; Sato, H.; Multhoff, G.; Shibata, A. Novel Approaches to Improve the Efficacy of Immuno-Radiotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Limbergen, E.J.; De Ruysscher, D.K.; Olivo Pimentel, V.; Marcus, D.; Berbee, M.; Hoeben, A.; Rekers, N.; Theys, J.; Yaromina, A.; Dubois, L.J.; et al. Combining radiotherapy with immunotherapy: the past, the present and the future. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20170157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.K.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A. Combined PARP and Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in Ovarian Cancer. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoi, N.Y.L.; Peng, G.; Yap, T.A. A Tale of Two Checkpoints: ATR Inhibition and PD-(L)1 Blockade. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, E.E.; Walker, S.M.; Taggart, L.E.; McCabe, N.; Knight, L.A.; Wilkinson, R.; McCloskey, K.D.; Buckley, N.E.; Savage, K.I.; Salto-Tellez, M.; et al. Activation of STING-Dependent Innate Immune Signaling By S-Phase-Specific DNA Damage in Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djw199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabanon, R.M.; Muirhead, G.; Krastev, D.B.; Adam, J.; Morel, D.; Garrido, M.; Lamb, A.; Hénon, C.; Dorvault, N.; Rouanne, M.; et al. PARP inhibition enhances tumor cell–intrinsic immunity in ERCC1-deficient non–small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 1211–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonen, P.M.; Kok, Y.P.; Wierenga, E.; Bakker, B.; Foijer, F.; Spierings, D.C.J.; Van Vugt, M.A.T.M. Premature mitotic entry induced by ATR inhibition potentiates olaparib inhibition-mediated genomic instability, inflammatory signaling, and cytotoxicity in BRCA2-deficient cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 2422–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Mann, C.C.; Kranzusch, P.J. cGAS Conducts Micronuclei DNA Surveillance. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 697–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenech, M.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Natarajan, A.T.; Surralles, J.; Crott, J.W.; Parry, J.; Norppa, H.; Eastmond, D.A.; Tucker, J.D.; Thomas, P. Molecular mechanisms of micronucleus, nucleoplasmic bridge and nuclear bud formation in mammalian and human cells. Mutagenesis 2011, 26, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatch, E.M.; Fischer, A.H.; Deerinck, T.J.; Hetzer, M.W. Catastrophic Nuclear Envelope Collapse in Cancer Cell Micronuclei. Cell 2013, 154, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Z.; Ghosh, K.; Vizioli, M.G.; Zhu, J.; Sen, P.; Wangensteen, K.J.; Simithy, J.; Lan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Cytoplasmic chromatin triggers inflammation in senescence and cancer. Nature 2017, 550, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glück, S.; Guey, B.; Gulen, M.F.; Wolter, K.; Kang, T.-W.; Schmacke, N.A.; Bridgeman, A.; Rehwinkel, J.; Zender, L.; Ablasser, A. Innate immune sensing of cytosolic chromatin fragments through cGAS promotes senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Ren, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Z.J. cGAS is essential for cellular senescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, J.; Brooks, T.; Landras, A.; Massey, A.J. Targeting DNA damage response pathways to activate the STING innate immune signaling pathway in human cancer cells. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 4507–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.A.; da Costa, F.H.B.; Adebayo, A.A.; Bartels, M.D.; Xie, T.; Amit, M.; Kawabe, M.; Rangel, R.; Frederick, M.J.; Sandulache, V.; et al. Abstract PO-085: Inhibition of ATR as a therapeutic strategy to enhance immunotherapy in head and neck cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, PO–085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendetti, F.P.; Karukonda, P.; Clump, D.A.; Teo, T.; Lalonde, R.; Nugent, K.; Ballew, M.; Kiesel, B.F.; Beumer, J.H.; Sarkar, S.N.; et al. ATR kinase inhibitor AZD6738 potentiates CD8+ T cell–dependent antitumor activity following radiation. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 128, 3926–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, M.T.; Bergerhoff, K.F.; Pedersen, M.; Whittock, H.; Crespo-Rodriguez, E.; Patin, E.C.; Pearson, A.; Smith, H.G.; Paget, J.T.E.; Patel, R.R.; et al. ATR Inhibition Potentiates the Radiation-induced Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3392–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Shen, M.; Zhou, P.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Dai, W.; et al. ATR inhibitor AZD6738 enhances the antitumor activity of radiotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors by potentiating the tumor immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.; Mayor-Ruiz, C.; Lafarga, V.; Murga, M.; Vega-Sendino, M.; Ortega, S.; Fernandez-Capetillo, O. A Genome-wide CRISPR Screen Identifies CDC25A as a Determinant of Sensitivity to ATR Inhibitors. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dok, R.; Glorieux, M.; Bamps, M.; Nuyts, S. Effect of ATR Inhibition in RT Response of HPV-Negative and HPV-Positive Head and Neck Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.-H.; Karagounis, I.V.; Thomas, C.; François, N.B.; Facciabene, A.; Koumenis, C.; Maity, A. Combination of CHEK1/2 inhibition and ionizing radiation results in abscopal tumor response through increased micronuclei formation. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4344–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Niimi, A.; Yasuhara, T.; Permata, T.B.M.; Hagiwara, Y.; Isono, M.; Nuryadi, E.; Sekine, R.; Oike, T.; Kakoti, S.; et al. DNA double-strand break repair pathway regulates PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-L.; Yang, R.-Y.; Li, C.-W.; Chen, M.-K.; Shao, B.; Hsu, J.-M.; Chan, L.-C.; Yang, Y.; Hsu, J.L.; Lai, Y.-J.; et al. Inhibition of ATR downregulates PD-L1 and sensitizes tumor cells to T cell-mediated killing. Am J Cancer Res 2018, 8, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Buisson, R.; Boisvert, J.L.; Benes, C.H.; Zou, L. Distinct but Concerted Roles of ATR, DNA-PK, and Chk1 in Countering Replication Stress during S Phase. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Qin, W.; Tu, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, W.; Ma, L.; Liu, B.; Qiu, H.; Yuan, X. Combining radiation and the ATR inhibitor berzosertib activates STING signaling and enhances immunotherapy via inhibiting SHP1 function in colorectal cancer. Cancer Commun. 2023, 43, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabanon, R.M.; Rouanne, M.; Lord, C.J.; Soria, J.-C.; Pasero, P.; Postel-Vinay, S. Targeting the DNA damage response in immuno-oncology: developments and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 701–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.A.; Lilly, K.K.; Reynolds, E.A.; Sullivan, W.P.; Kaufmann, S.H.; Cliby, W.A. Ataxia telangiectasia and rad3-related kinase contributes to cell cycle arrest and survival after cisplatin but not oxaliplatin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durinikova, E.; Reilly, N.M.; Buzo, K.; Mariella, E.; Chilà, R.; Lorenzato, A.; Dias, J.M.L.; Grasso, G.; Pisati, F.; Lamba, S.; et al. Targeting the DNA Damage Response Pathways and Replication Stress in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3874–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reaper, P.M.; Griffiths, M.R.; Long, J.M.; Charrier, J.-D.; MacCormick, S.; Charlton, P.A.; Golec, J.M.C.; Pollard, J.R. Selective killing of ATM- or p53-deficient cancer cells through inhibition of ATR. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 428–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, D.L.; Holt, J.; Tang, Y.; Feng, J.; Barsanti, P.; Pan, Y.; Ghoddusi, M.; Zhang, W.; Thomas, G.; Holash, J.; et al. A Synthetic Lethal Screen Reveals Enhanced Sensitivity to ATR Inhibitor Treatment in Mantle Cell Lymphoma with ATM Loss-of-Function. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, N.J. Targeting the DNA damage response for cancer therapy. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2023, 51, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendetti, F.P.; Lau, A.; Schamus, S.; Conrads, T.P.; O’Connor, M.J.; Bakkenist, C.J. The orally active and bioavailable ATR kinase inhibitor AZD6738 potentiates the anti-tumor effects of cisplatin to resolve ATM-deficient non-small cell lung cancer in vivo. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44289–44305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcina, M.M.; Foskolou, I.P.; Anbalagan, S.; Senra, J.M.; Pires, I.M.; Jiang, Y.; Ryan, A.J.; Hammond, E.M. Replication Stress and Chromatin Context Link ATM Activation to a Role in DNA Replication. Mol. Cell 2013, 52, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halazonetis, T.D.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Bartek, J. An Oncogene-Induced DNA Damage Model for Cancer Development. Science 2008, 319, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilad, O.; Nabet, B.Y.; Ragland, R.L.; Schoppy, D.W.; Smith, K.D.; Durham, A.C.; Brown, E.J. Combining ATR Suppression with Oncogenic Ras Synergistically Increases Genomic Instability, Causing Synthetic Lethality or Tumorigenesis in a Dosage-Dependent Manner. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9693–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murga, M.; Campaner, S.; Lopez-Contreras, A.J.; Toledo, L.I.; Soria, R.; Montaña, M.F.; D’Artista, L.; Schleker, T.; Guerra, C.; Garcia, E.; et al. Exploiting oncogene-induced replicative stress for the selective killing of Myc-driven tumors. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoppy, D.W.; Ragland, R.L.; Gilad, O.; Shastri, N.; Peters, A.A.; Murga, M.; Fernandez-Capetillo, O.; Diehl, J.A.; Brown, E.J. Oncogenic stress sensitizes murine cancers to hypomorphic suppression of ATR. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, L.I.; Murga, M.; Zur, R.; Soria, R.; Rodriguez, A.; Martinez, S.; Oyarzabal, J.; Pastor, J.; Bischoff, J.R.; Fernandez-Capetillo, O. A cell-based screen identifies ATR inhibitors with synthetic lethal properties for cancer-associated mutations. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Min, A.; Im, S.; Jang, H.; Lee, K.H.; Lau, A.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.; Yang, Y.; Kim, J.; et al. Anti-tumor activity of the ATR inhibitor AZD6738 in HER2 positive breast cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibrandt, R.C.; Tu, M.-J.; Yu, A.-M.; Lara, P.N.; Parikh, M. ATR Inhibition in Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2023, 21, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.B.; Newsome, D.; Wang, Y.; Boucher, D.M.; Eustace, B.; Gu, Y.; Hare, B.; Johnson, M.A.; Li, H.; Milton, S.; et al. Potentiation of tumor responses to DNA damaging therapy by the selective ATR inhibitor VX-970. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5674–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Ghosh, M.; Kim, T.H.; Park, N.; Pandey, K.; Cho, Y.B.; Hong, S.D.; Katuwal, N.B.; Kang, M.; An, H.J.; et al. Synergism of AZD6738, an ATR Inhibitor, in Combination with Belotecan, a Camptothecin Analogue, in Chemotherapy-Resistant Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallez, Y.; Dunlop, C.R.; Johnson, T.I.; Koh, S.-B.; Fornari, C.; Yates, J.W.T.; Bernaldo De Quirós Fernández, S.; Lau, A.; Richards, F.M.; Jodrell, D.I. The ATR Inhibitor AZD6738 Synergizes with Gemcitabine In Vitro and In Vivo to Induce Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Regression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1670–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallez, Y.; Proia, T.; Cheraghchi-Bashi-Astaneh, A.; Karmokar, A.; Wilson, Z.; Randle, S.; Anderton, M.; Durant, S.; Leo, E.; Lau, A.; et al. Abstract 5298: Activity and tolerability of combinations of trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) with inhibitors of the DNA damage response in preclinical models. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 5298–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.W.; Gosh, M.; Park, N.; Pandey, K.; Katwal, N.B.; Hong, S.D. Abstract P2-26-09: Synergistic activity of PI3K inhibitor in combination with AZD6738, ATR inhibitor in breast cancer preclinical model via DNA damage response pathway. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, P2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhjavani, M.; Hardingham, J.E.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Price, T.J.; Townsend, A.R. Druggable Molecular Targets for the Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J. Breast Cancer 2019, 22, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, R.L.; Wijnhoven, P.W.G.; Ramos-Montoya, A.; Wilson, Z.; Illuzzi, G.; Falenta, K.; Jones, G.N.; James, N.; Chabbert, C.D.; Stott, J.; et al. Combined PARP and ATR inhibition potentiates genome instability and cell death in ATM-deficient cancer cells. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4869–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, Z.; Odedra, R.; Wallez, Y.; Wijnhoven, P.W.G.; Hughes, A.M.; Gerrard, J.; Jones, G.N.; Bargh-Dawson, H.; Brown, E.; Young, L.A.; et al. ATR Inhibitor AZD6738 (Ceralasertib) Exerts Antitumor Activity as a Monotherapy and in Combination with Chemotherapy and the PARP Inhibitor Olaparib. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsels, L.A.; Engelke, C.G.; Parsels, J.; Flanagan, S.A.; Zhang, Q.; Tanska, D.; Wahl, D.R.; Canman, C.E.; Lawrence, T.S.; Morgan, M.A. Combinatorial Efficacy of Olaparib with Radiation and ATR Inhibitor Requires PARP1 Protein in Homologous Recombination–Proficient Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendetti, F.P.; Pandya, P.; Clump, D.A.; Schamus-Haynes, S.; Tavakoli, M.; diMayorca, M.; Islam, N.M.; Chang, J.; Delgoffe, G.M.; Beumer, J.H.; et al. The schedule of ATR inhibitor AZD6738 can potentiate or abolish antitumor immune responses to radiotherapy. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e165615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, E.; Krebs, M.G.; Im, S.-A.; Campone, M.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Arkenau, T.; Lopez, J.; Abida, W.; Jodrell, D.; Lee, K.-W.; et al. Abstract PS11-18: Ceralasertib (cer) in combination with olaparib (ola) in patients (pts) with advanced breast cancer (BC): Results of phase I expansion cohorts. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, PS11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutt, A.; Nowecki, Z.; Szoszkiewicz, R.; Im, S.A.; Arkenau, H.T.; Armstrong, A.C.; Jacot, W.; Kim, J.H.; Webster, M.; Balmana, J.; et al. VIOLETTE: Randomised phase II study of olaparib (ola) plus ceralasertib (cer) or adavosertib (ada) vs ola alone in patients (pts) with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC). 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ring, A.; Kilburn, L.S.; Pearson, A.; Moretti, L.; Afshari-Mehr, A.; Wardley, A.M.; Gurel, B.; Macpherson, I.R.; Riisnaes, R.; Baird, R.D.; et al. Olaparib and Ceralasertib (AZD6738) in Patients with Triple-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer: Results from Cohort E of the plasmaMATCH Trial (CRUK/15/010). Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 4751–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse, B.; Awad, M.; Forde, P.; Thomas, M.; Park, K.; Goss, G.; Rizvi, N.; Huemer, F.; Hochmair, M.; Bennouna, J.; et al. OA07.08 HUDSON: An Open-Label, Multi-Drug, Biomarker-Directed, Phase II Platform Study in Patients with NSCLC, who Progressed on Anti-PD(L)1 Therapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S118–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Mortimer, P.G.; Smith, S.; Kim, H. (Rosa); Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.-M.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Park, W.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; et al. The clinical efficacy of olaparib monotherapy or combination with ceralasertib (AZD6738) in relapsed small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 8562–8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, H.; Hafez, N.; Doroshow, D.; Sohal, D.; Keedy, V.; Do, K.T.; LoRusso, P.; Jürgensmeier, J.; Avedissian, M.; Sklar, J.; et al. Ceralasertib-Mediated ATR Inhibition Combined With Olaparib in Advanced Cancers Harboring DNA Damage Response and Repair Alterations (Olaparib Combinations). JCO Precis. Oncol. 2021, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wethington, S.L.; Shah, P.D.; Martin, L.P.; Tanyi, J.L.; Latif, N.A.; Morgan, M.A.; Torigian, D.A.; Pagan, C.; Rodriguez, D.; Domchek, S.M.; et al. Combination of PARP and ATR inhibitors (olaparib and ceralasertib) shows clinical activity in acquired PARP inhibitor-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 5516–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.D.; Wethington, S.L.; Pagan, C.; Latif, N.; Tanyi, J.; Martin, L.P.; Morgan, M.; Burger, R.A.; Haggerty, A.; Zarrin, H.; et al. Combination ATR and PARP Inhibitor (CAPRI): A phase 2 study of ceralasertib plus olaparib in patients with recurrent, platinum-resistant epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 163, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Leary, A.; Stewart, J.R.; Dewan, M.; Lheureux, S.; Clamp, A.R.; Ray-Coquard, I.L.; Selle, F.; Gourley, C.; Glasspool, R.M. 34O ATR inhibitor alone (ceralasertib) or in combination with olaparib in gynaecological cancers with ARID1A loss or no loss: Results from the ENGOT/GYN1/NCRI ATARI trial. ESMO Open 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, M.T.; Guevara, J.; Mohammed, K.; Patin, E.C.; Smith, S.A.; Dean, E.; Jones, G.N.; Willis, S.E.; Petrone, M.; Silva, C.; et al. Durable responses to ATR inhibition with ceralasertib in tumors with genomic defects and high inflammation. J. Clin. Invest. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.; Umetsu, S.; Dhawan, M.; Grabowsky, J.; Carnevale, J.; Howell, M.; Wilch, L.; Chapman, J.; Alvarez, E.; Calabrese, S. 512O Interim results from a phase II study of the ATR inhibitor ceralasertib in ARID1A-deficient and ARID1A-intact advanced solid tumor malignancies. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Kim, G.; Kim, R.; Kim, K.-T.; Kim, S.T.; Smith, S.; Mortimer, P.G.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Loembé, A.-B.; Irurzun-Arana, I.; et al. Phase II study of ceralasertib (AZD6738) in combination with durvalumab in patients with advanced gastric cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Kwon, M.; An, M.; Kim, S.T.; Smith, S.A.; Loembé, A.B.; Mortimer, P.G.S.; Armenia, J.; Lukashchuk, N.; Shah, N.; et al. Phase II study of ceralasertib (AZD6738) in combination with durvalumab in patients with advanced/metastatic melanoma who have failed prior anti-PD-1 therapy. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2022, 33, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Tae Kim, S.; Smith, S.; Mortimer, P.G.; Loembé, B.; Hong, J.; Kozarewa, I.; Pierce, A.; Dean, E. Results from a phase I, open-label study of ceralasertib (AZD6738), a novel DNA damage repair agent, in combination with weekly paclitaxel in refractory cancer (NCT02630199). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3503–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NCT Number | Study Status | Conditions | Interventions | Primary Outcome | Phase | Enrollment | Completion Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03330847 | Active, not recruiting | mTNBC | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | PFS | 2 | 273 | Sep-24 |
| NCT03801369 | Recruiting | mTNBC | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 132 | Dec-27 |
| NCT03740893 | Recruiting | Operable TNBC | Ceralasertib | Biomarker | 2 | 81 | Dec-25 |
| NCT03182634 | Completed | mBC | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 70 | Nov-23 |
| NCT04090567 | Recruiting | HER2-, BRCA+ mBC | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 60 | Mar-25 |
| NCT05582538 | Recruiting | mTNBC | Ceralasertib followed by Durvalumab/nab-Paclitaxel | PFS | 2 | 37 | Nov-25 |
| NCT05450692 | Recruiting | mNSCLC | Ceralasertib + Durvalumab | OS | 3 | 580 | May-25 |
| NCT03334617 | Active, not recruiting | mNSCLC | Ceralasertib, Ceralasertib + Durvalumab | 12-week ORR | 2 | 531 | Sep-24 |
| NCT02664935 | Active, not recruiting | mNSCLC | Ceralasertib + Durvalumab | ORR, PFS, 24-week DCR | 2 | 423 | Sep-23 |
| NCT03833440 | Recruiting | mNSCLC | Ceralasertib + Durvalumab | 12-week DCR | 2 | 120 | Feb-24 |
| NCT05941897 | Recruiting | mNSCLC | Ceralasertib + Durvalumab | ORR | 2 | 38 | Jun-25 |
| NCT02937818 | Active, not recruiting | ES-SCLC | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 72 | Dec-23 |
| NCT04361825 | Active, not recruiting | ES-SCLC | Ceralasertib + Durvalumab | ORR | 2 | 45 | Dec-23 |
| NCT04699838 | Recruiting | ES-SCLC | Platinum-Etoposide-Durvalumab + maintenance Ceralasertib/Durvalumab | PFS | 2 | 30 | May-24 |
| NCT03428607 | Completed | ES-SCLC | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 26 | Jan-21 |
| NCT03579316 | Recruiting | Ovarian Cancer | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 104 | Dec-24 |
| NCT04239014 | Withdrawn | Ovarian Cancer | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | PFS | 2 | 0 | Jan-21 |
| NCT04065269 | Active, not recruiting | Gynaecological Cancers | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 168 | Mar-23 |
| NCT05061134 | Active, not recruiting | Melanoma | Ceralasertib, Ceralasertib + Durvalumab | ORR | 2 | 186 | Apr-24 |
| NCT03780608 | Active, not recruiting | Melanoma, Gastric cancer | Ceralasertib + Durvalumab | ORR | 2 | 61 | Dec-23 |
| NCT04298021 | Active, not recruiting | Biliary Tract Cancer | Ceralasertib + Durvalumab, Ceralasertib + Olaparib | DCR | 2 | 74 | Dec-24 |
| NCT04298008 | Recruiting | Biliary Tract Cancer | Ceralasertib + Durvalumab | DCR | 2 | 26 | Dec-24 |
| NCT04417062 | Recruiting | Osteosarcoma | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | 4-month EFS | 2 | 63 | Jun-25 |
| NCT03787680 | Active, not recruiting | Prostate Cancer | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 49 | Jan-27 |
| NCT03022409 | Completed | HNSCC | Ceralasertib | Biomarker | 1 | 21 | Jan-21 |
| NCT04704661 | Recruiting | HER2+ GEJ/CRC | Ceralasertib + T-DXd | Toxicity | 1 | 15 | Mar-26 |
| NCT02264678 | Recruiting | Advanced Solid Tumors | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | Toxicity | 1/2 | 466 | Jul-26 |
| NCT03682289 | Recruiting | Advanced Solid Tumors | Ceralasertib, Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 89 | Jul-25 |
| NCT02223923 | Active, not recruiting | Advanced Solid Tumors | Ceralasertib | MTD | 1 | 87 | Dec-23 |
| NCT02576444 | Terminated | Advanced Solid Tumors | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 67 | Nov-19 |
| NCT02630199 | Completed | Advanced Solid Tumors | Ceralasertib + Paclitaxel | Toxicity, MTD | 1 | 65 | Apr-21 |
| NCT03669601 | Recruiting | Advanced Solid Tumors | Ceralasertib + Gemcitabine | DLT | 1 | 55 | Sep-24 |
| NCT04564027 | Active, not recruiting | Advanced Solid Tumors | Ceralasertib | ORR | 2 | 54 | Feb-24 |
| NCT05514132 | Active, not recruiting | Advanced Solid Tumors | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | DLT | 1 | 14 | Apr-25 |
| NCT05469919 | Active, not recruiting | Advanced Solid Tumors | Ceralasertib | DLT | 1 | 12 | Dec-24 |
| NCT03878095 | Suspended | IDH1/2mut Advanced Solid Tumors | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 50 | Mar-24 |
| NCT03330847 | Active, not recruiting | mTNBC | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | PFS | 2 | 273 | Sep-24 |
| NCT03801369 | Recruiting | mTNBC | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 132 | Dec-27 |
| NCT03740893 | Recruiting | Operable TNBC | Ceralasertib | Biomarker | 2 | 81 | Dec-25 |
| NCT03182634 | Completed | mBC | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 70 | Nov-23 |
| NCT04090567 | Recruiting | HER2-, BRCA+ mBC | Ceralasertib + Olaparib | ORR | 2 | 60 | Mar-25 |
| NCT05582538 | Recruiting | mTNBC | Ceralasertib followed by Durvalumab/nab-Paclitaxel | PFS | 2 | 37 | Nov-25 |
| NCT05450692 | Recruiting | mNSCLC | Ceralasertib + Durvalumab | OS | 3 | 580 | May-25 |
| NCT03334617 | Active, not recruiting | mNSCLC | Ceralasertib, Ceralasertib + Durvalumab | 12-week ORR | 2 | 531 | Sep-24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





