Submitted:
23 January 2024
Posted:
23 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
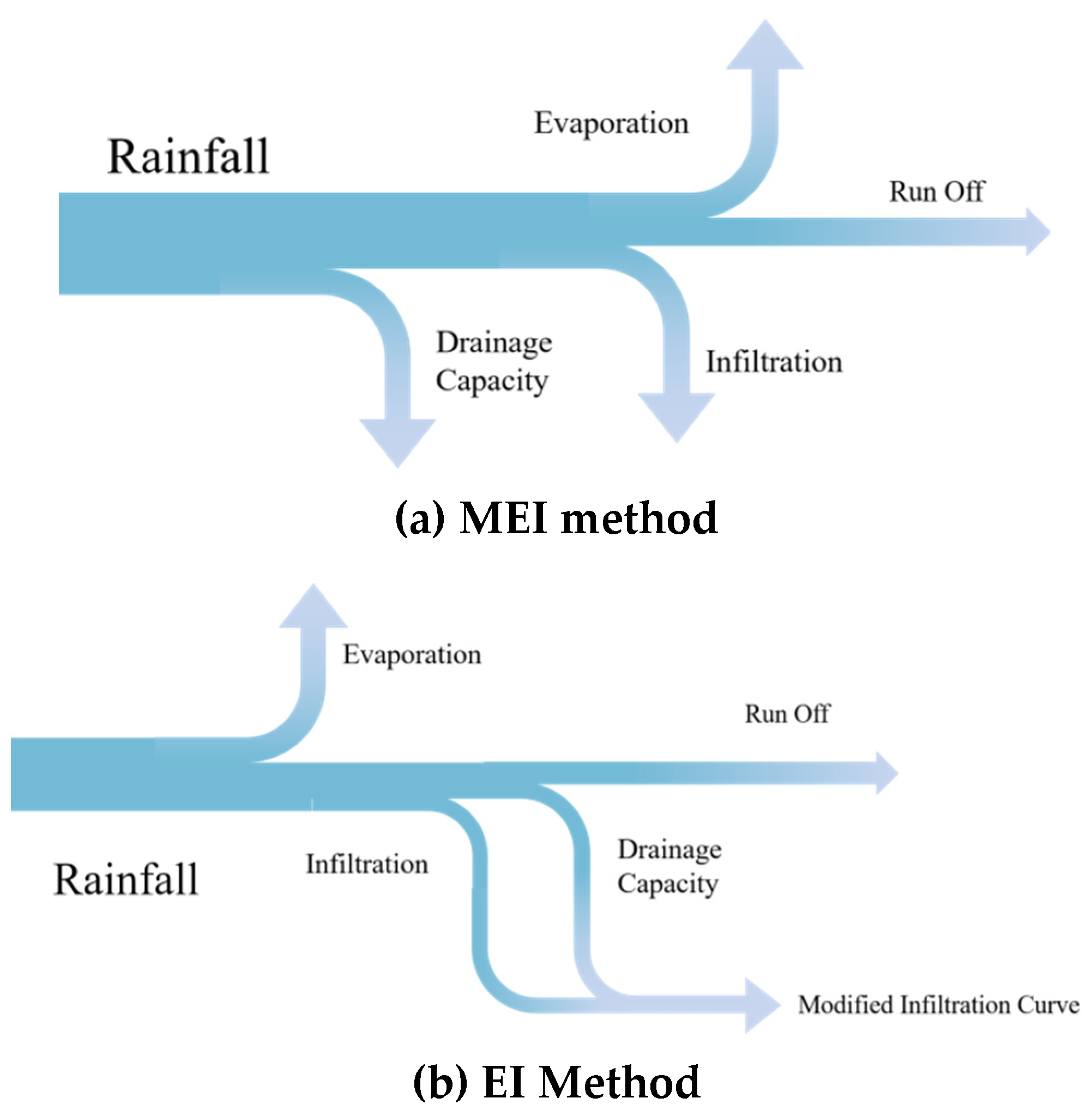
2.1. Principle of the MEI
2.2. Evaluation indicators
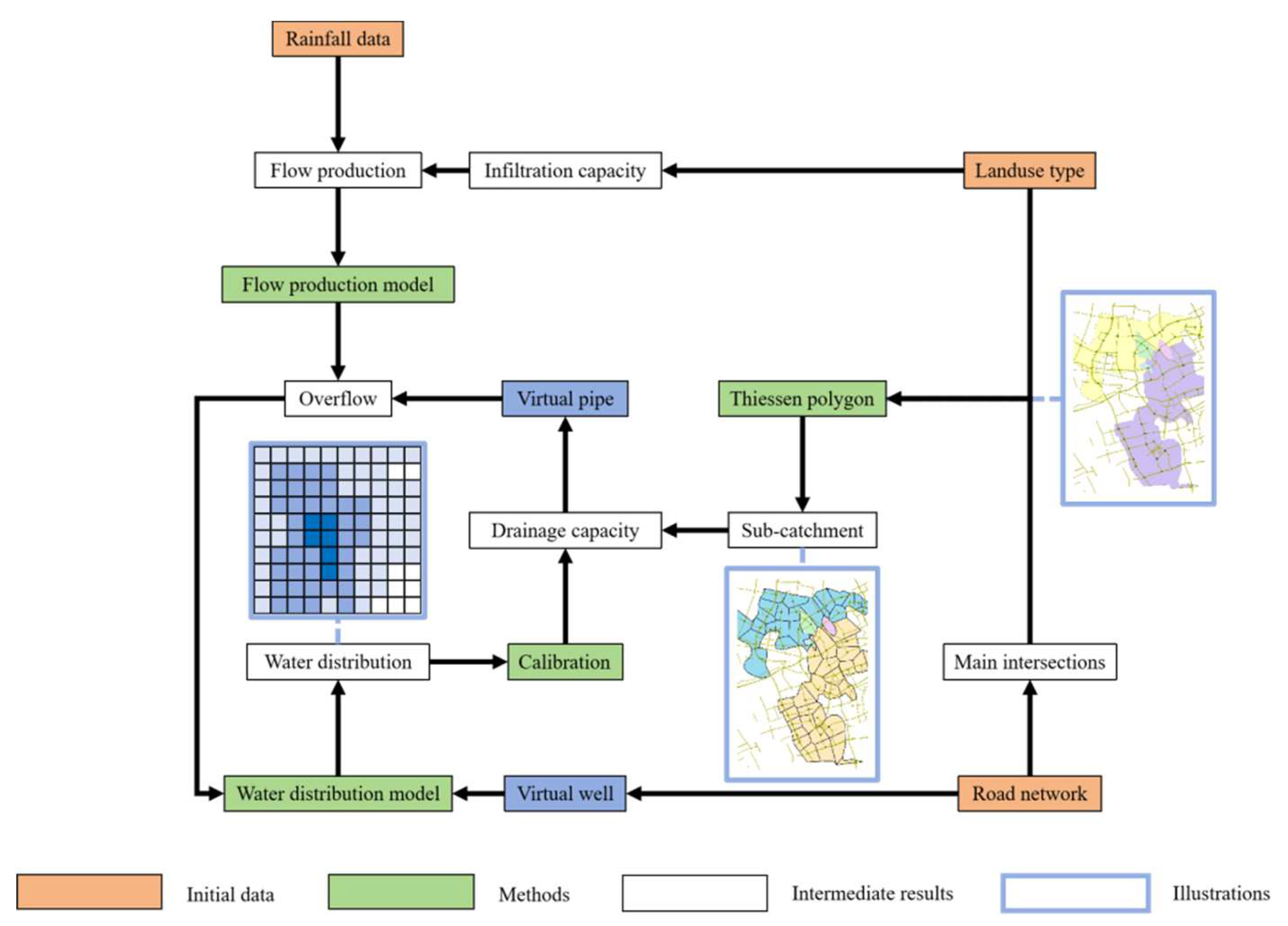
2.3 Preprocessing of data
3. Case Study
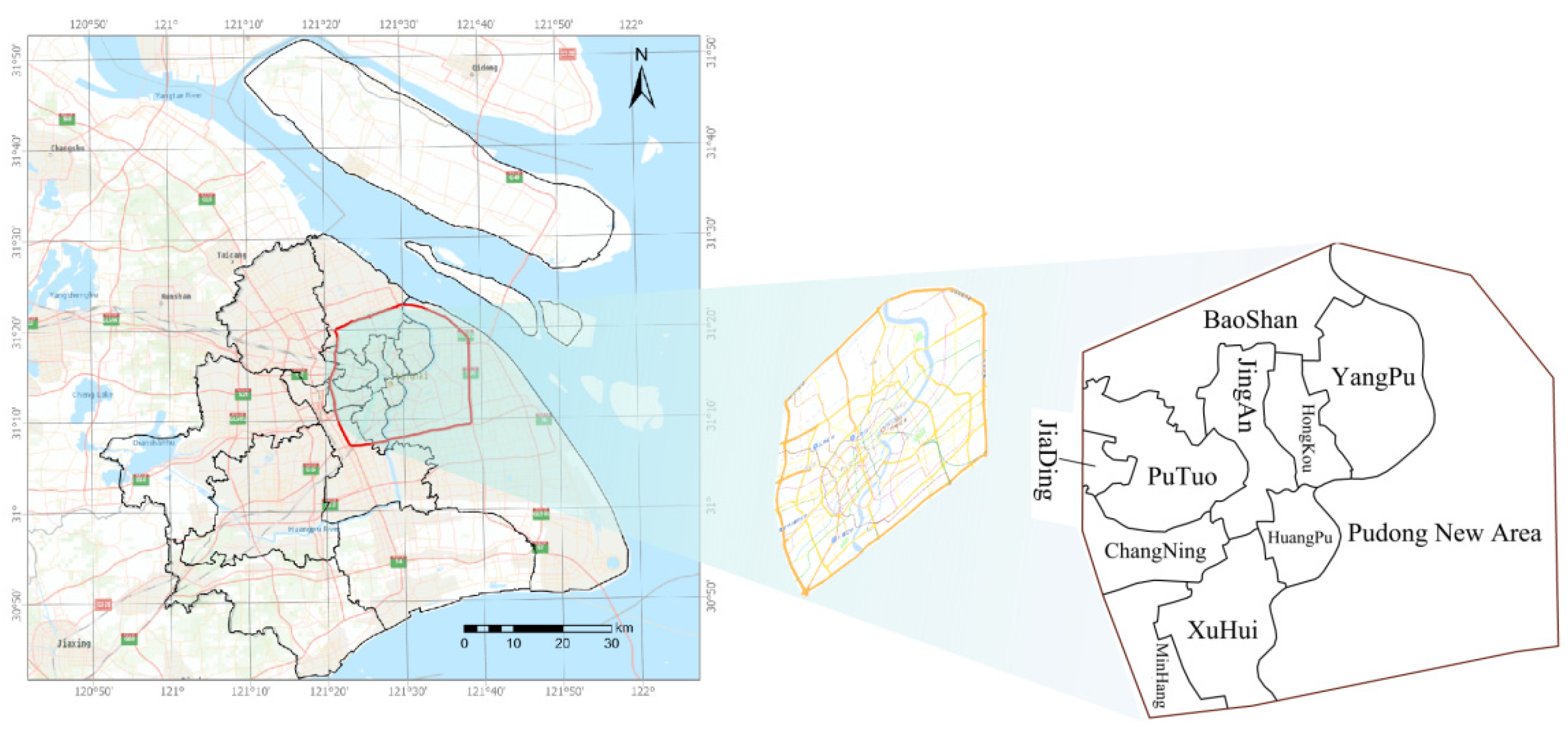
3.1. Research Site
4. Results and discussion
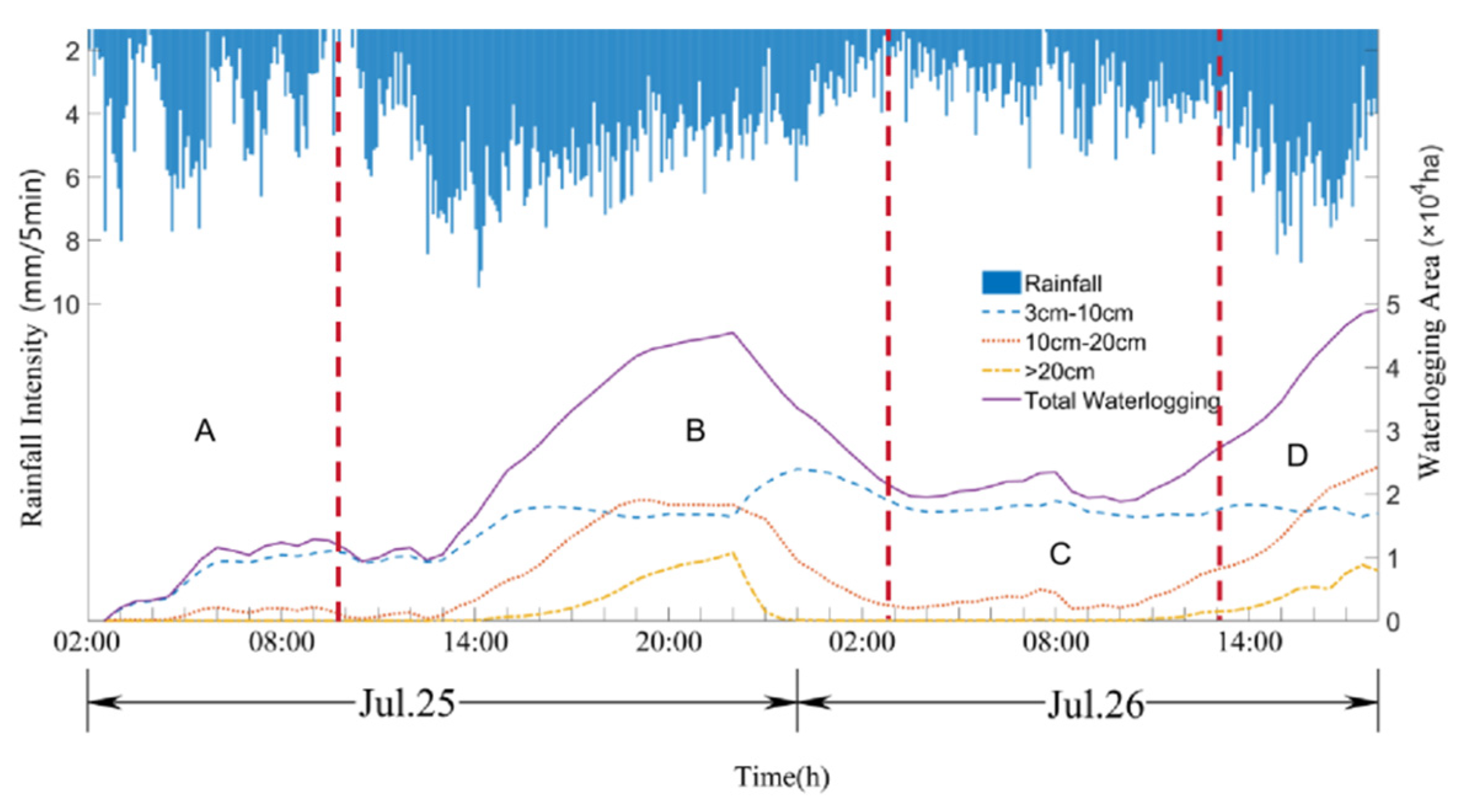
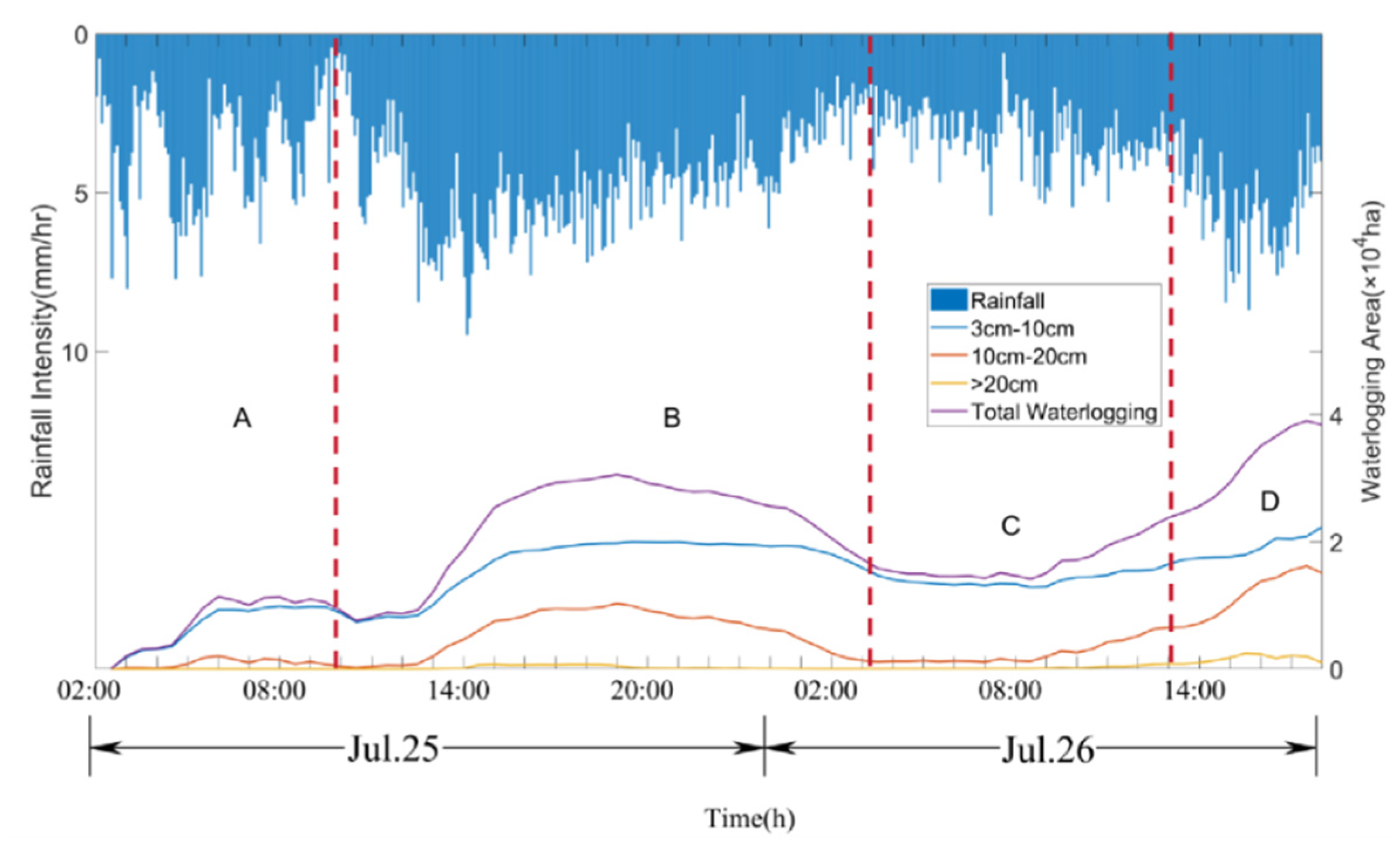
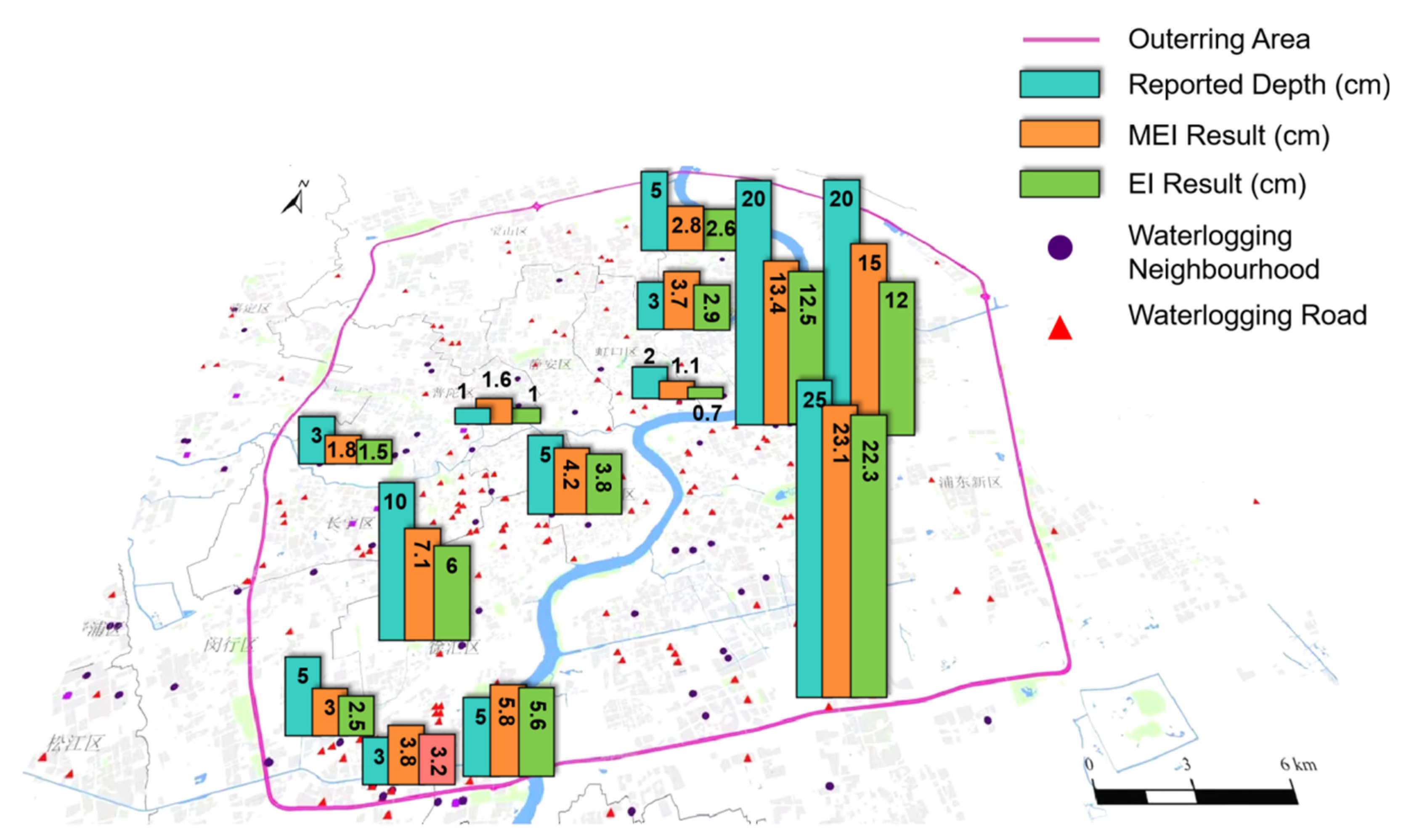
4.1. Model validation
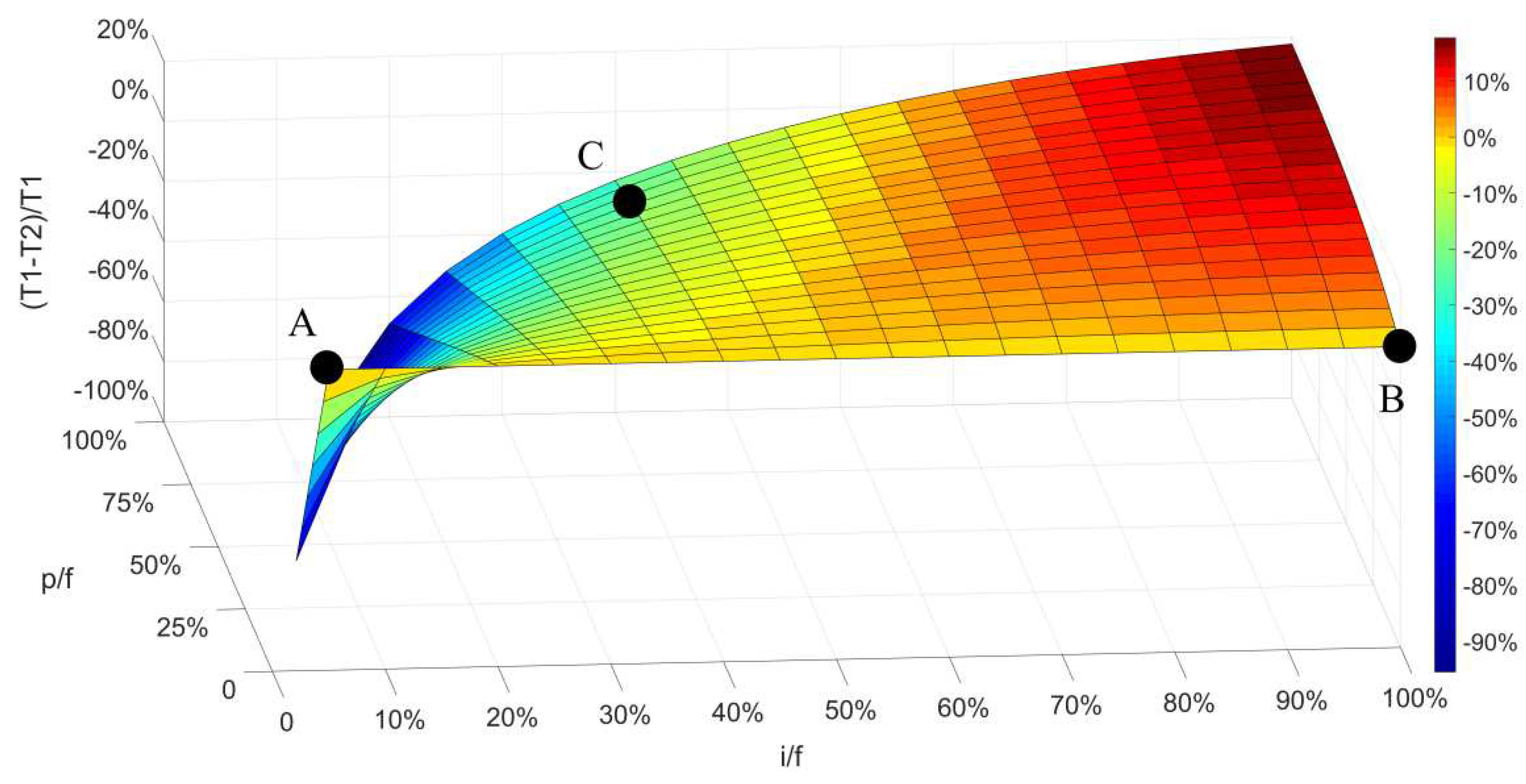
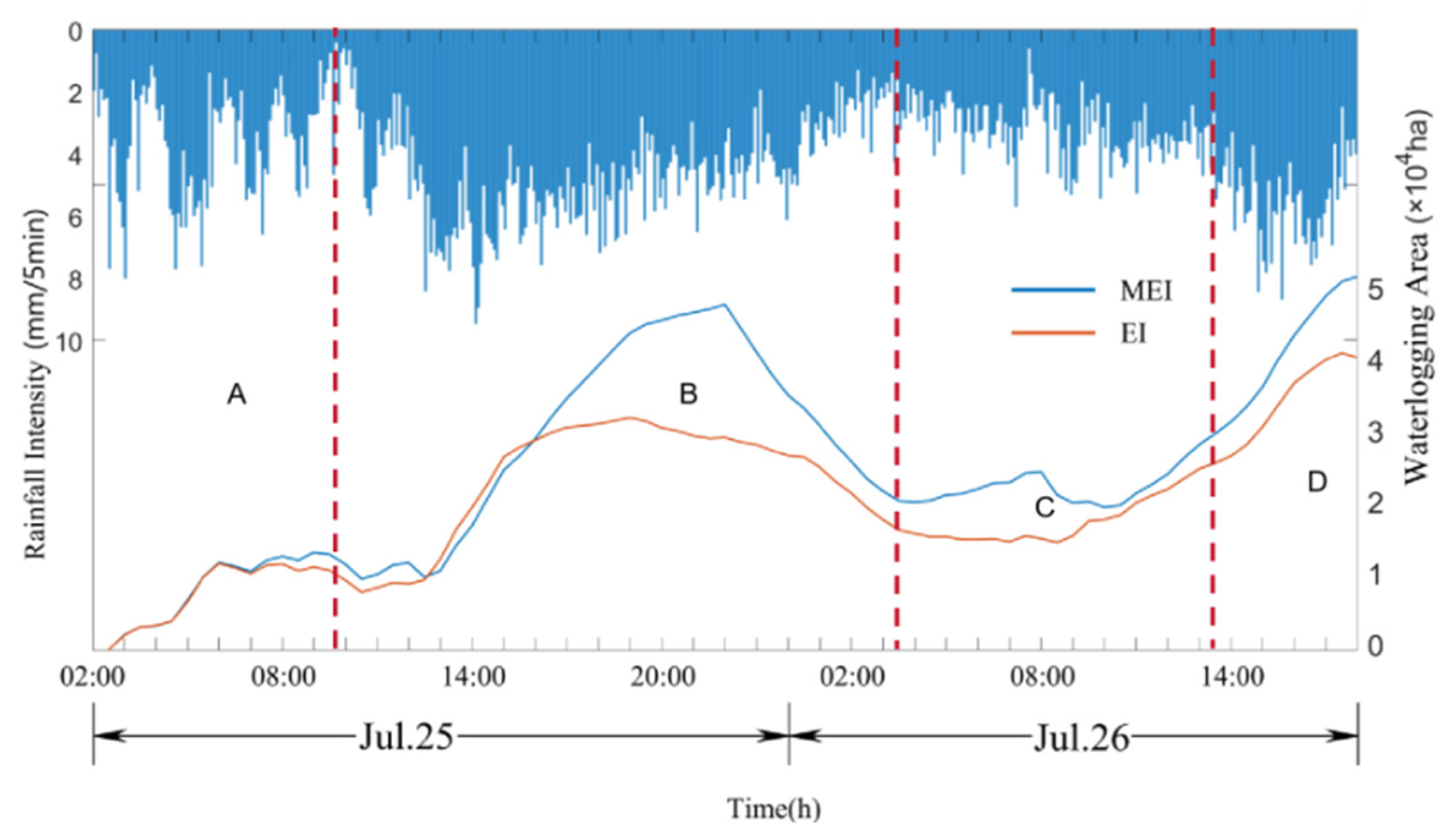
4.2. Comparison between EI and MEI
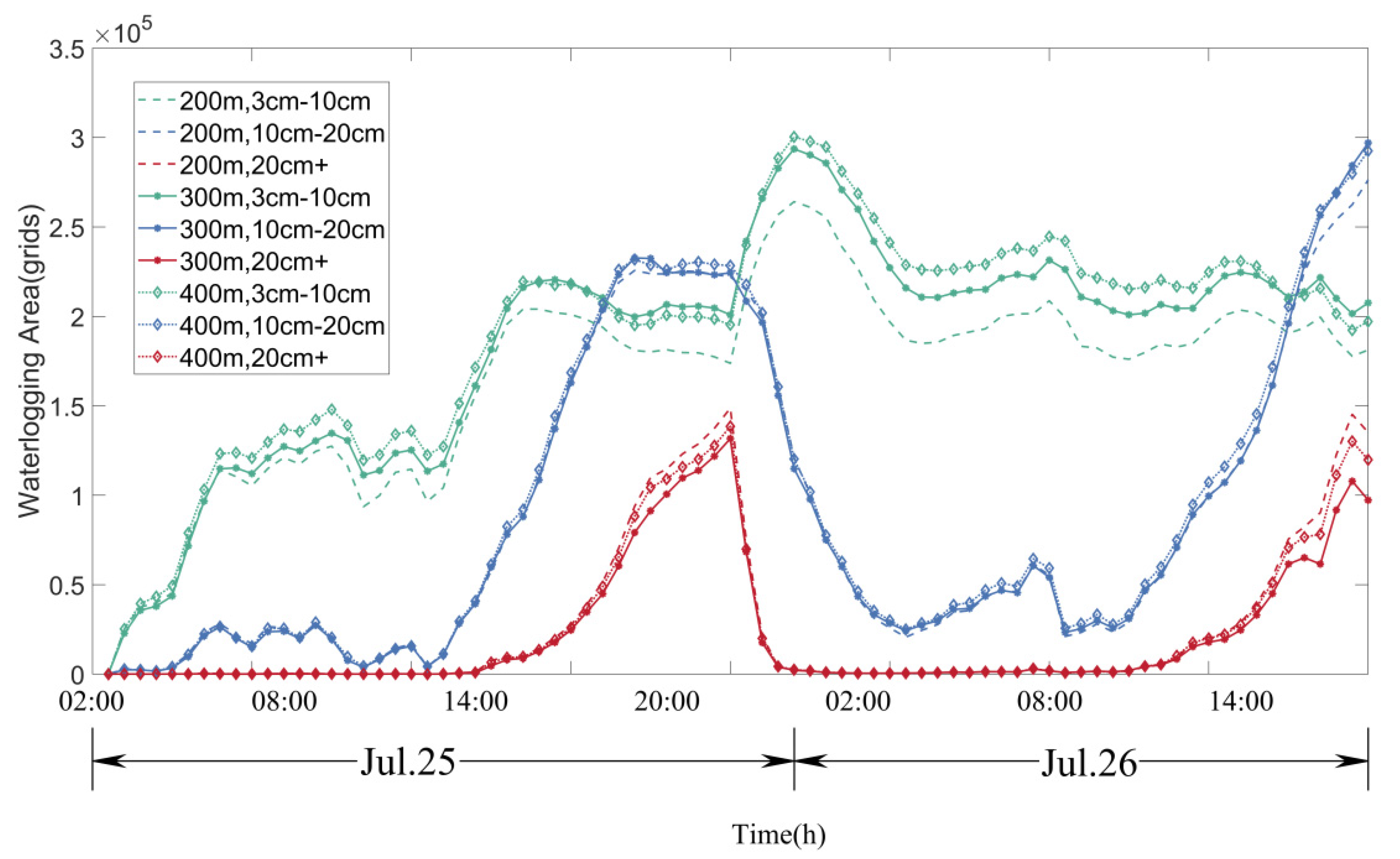
4.3. Effect of spatial distribution of virtual well
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teng, J.; Jakeman, A.J.; Vaze, J.; Croke, B.F.; Dutta, D.; Kim, S.J.E.M. Flood inundation modelling: A review of methods, recent advances and uncertainty analysis. Environmental modelling & software 2017, 90, 201–216. [Google Scholar]
- Bernet, D.B.; Prasuhn, V.; Weingartner, R. Surface water floods in Switzerland: what insurance claim records tell us about the damage in space and time. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences 2017, 17, 1659–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncoulon, D.; Veysseire, M.; Naulin, J.P.; Wang, Z.X.; Tinard, P.; Desarthe, J.; Hajji, C.; Onfroy, T.; Regimbeau, F.; Déqué, M. Modelling the evolution of the financial impacts of flood and storm surge between 2015 and 2050 in France. International Journal of Safety and Security Engineering 2016, 6, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, X. Assessing influence of future urbanization on hydrological process in typical river basin. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering 2020, 39, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Mignot, E.; Li, X.; Dewals, B. Experimental modelling of urban flooding: A review. Journal of Hydrology 2019, 568, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Guo, G.; Zhang, H.; Tarolli, P. Explicit the urban waterlogging spatial variation and its driving factors: The stepwise cluster analysis model and hierarchical partitioning analysis approach. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 763, 143041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, C.; Liu, J. Review on urban storm water models. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University 2018, 51, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Armson, D.; Stringer, P.; Ennos, A.R. The effect of street trees and amenity grass on urban surface water runoff in Manchester, UK. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening 2013, 12, 282–286. [Google Scholar]
- Skotnicki, M.; Sowiński, M. The influence of depression storage on runoff from impervious surface of urban catchment. Urban Water Journal 2015, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Lai, C.; Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Lin, G.; Zhao, J. Hydrological effect simulation of LID-underground integrated pipe corridors in Yangmei River Basin. Water Resources Protection 2022, 38, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y. (2022). Rainwater Pipe Network and Waterlogging Risk Assessment of Airport Traffic Area Based on SWMM and MIKE Model. Journal of Municipal Technology, 40(07): 242-245(In Chinese).
- Qiu, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, X. Qiu, R.; Cao, J.; ,Zhang, X. (2022). Parameter Selection of Pollutant Module in SWMM Model Based on the Study of Non-Point Source Pollutants in Old Residential Areas. China Municipal Engineering(04): 51-54(In Chinese).
- Szeląg, B.; Suligowski, R.; De Paola, F.; Siwicki, P.; Majerek, D.; Łagód, G. Influence of urban catchment characteristics and rainfall origins on the phenomenon of stormwater flooding: Case study. Environmental Modelling & Software 2022, 150, 105335. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.; Guan, M.; Yu, D. Urban surface water flood modelling–a comprehensive review of current models and future challenges. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 2021, 25, 2843–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratt, C.B.; Woo, D.K.; Johnson, K.N.; Haagsma, M.; Kumar, P.; Selker, J.; Tyler, S. Field trials to detect drainage pipe networks using thermal and RGB data from unmanned aircraft. Agricultural Water Management 2020, 229, 105895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwori, E.; Pericault, Y.; Ugarelli, R.; Viklander, M.; Hedström, A. Data-driven asset management in urban water pipe networks: a proposed conceptual framework. Journal of Hydroinformatics 2021, 23, 1014–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzenfrei, R.; Möderl, M.; Rauch, W. Assessing the impact of transitions from centralised to decentralised water solutions on existing infrastructures–Integrated city-scale analysis with VIBe. Water research 2013, 47, 7251–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tscheikner-Gratl, F.; Caradot, N.; Cherqui, F.; Leitão, J.P.; Ahmadi, M.; Langeveld, J.G.; Le Gat, Y.; Scholten, L.; Roghani, B.; Rodríguez, J.P. Sewer asset management–state of the art and research needs. Urban Water Journal 2019, 16, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadiun, S.; Yazdi, J.; Hager, J.; Salehi Neyshabouri SA, A.; Sadiq, R.; Hewage, K.; Alavi Gharahbagh, A. Effects of bottleneck blockage on the resilience of an urban stormwater drainage system. Hydrological Sciences Journal 2020, 65, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, N.A.; Hallett, S.H.; Jude, S.R. The challenges of predicting pipe failures in clean water networks: a view from current practice. Water Supply 2022, 22, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, G.; Du, L. (2016). Urban rainfall-runoff simulations and assessment of low impact development facilities using swmm model—a case study of qinghe catchment in beijing. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 35(11):84-93.
- Ma, M.; Li, J.; Deng, C. Analysis of urban waterlogging and pollution load based on swmm model. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering 2017, 36, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Tajima, Y.; Sanuki, H.; Shibuo, Y.; Furumai, H. A novel approach for determining integrated water discharge from the ground surface to trunk sewer networks for fast prediction of urban floods. Journal of Flood Risk Management 2022, 15, e12773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yan, D. Urban flood forecasting based on the coupling of numerical weather model and stormwater model: A case study of Zhengzhou city. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies 2022, 39, 100985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Xia, J.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Tan, Q. Performance assessment of sponge city infrastructure on stormwater outflows using isochrone and SWMM models. Journal of Hydrology 2021, 597, 126151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Mascaro, G.; Garcia, M. Effects of stormwater infrastructure data completeness and model resolution on urban flood modeling. Journal of Hydrology 2022, 607, 127498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Smith, L.; Xia, X. New prospects for computational hydraulics by leveraging high-performance heterogeneous computing techniques. Journal of Hydrodynamics 2016, 28, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasallas, L.; An, H.; Lee, S. Developing synthetic sewer pipe system for data-scarce domains in application for urban flood modeling. Hydrology Research 2023, 54, 1387–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Fu, X.; Wang, D.; Luan, Q. Urban Flood Modeling and Risk Assessment with Limited Observation Data: The Beijing Future Science City of China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2023, 20, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersson, L.; Ten Veldhuis, M.C.; Verhoeven, G.; Kapelan, Z.; Maholi, I.; Winsemius, H.C. Community mapping supports comprehensive urban flood modeling for flood risk management in a data-scarce environment. Frontiers in earth science 2020, 8, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
| D-Imperv | Impermeable depression storage | 1.905 mm |
| D-Perv | Water storage in permeable depressions | 3.81 mm |
| MaxRate | Maximum infiltration rate | 76.2 mm/h |
| MinRate | Minimum infiltration rate | 2.54 mm/h |
| Decay | Attenuation factor | 6 |
| No. | Reporting Depth(cm) | Average Depth(cm) | Relative error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Ⅰ) | 5 | 2.8 | 44 |
| (Ⅱ) | 5 | 3 | 40 |
| (Ⅲ) | 20 | 15 | 25 |
| (Ⅳ) | 5 | 5.8 | 16 |
| (Ⅴ) | 10 | 7.1 | 29 |
| (VI) | 2 | 1.1 | 45 |
| (VII) | 3 | 3.7 | 23 |
| (VIII) | 1 | 1.6 | 60 |
| (IX) | 3 | 3.8 | 27 |
| (X) | 3 | 1.8 | 40 |
| (XI) | 20 | 13.4 | 33 |
| (XII) | 25 | 23.1 | 10 |
| (XIII) | 5 | 4.2 | 22 |
| Average Relative error | 31.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





