Submitted:
22 January 2024
Posted:
23 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Nuclear Localization Signals of Baculovirus
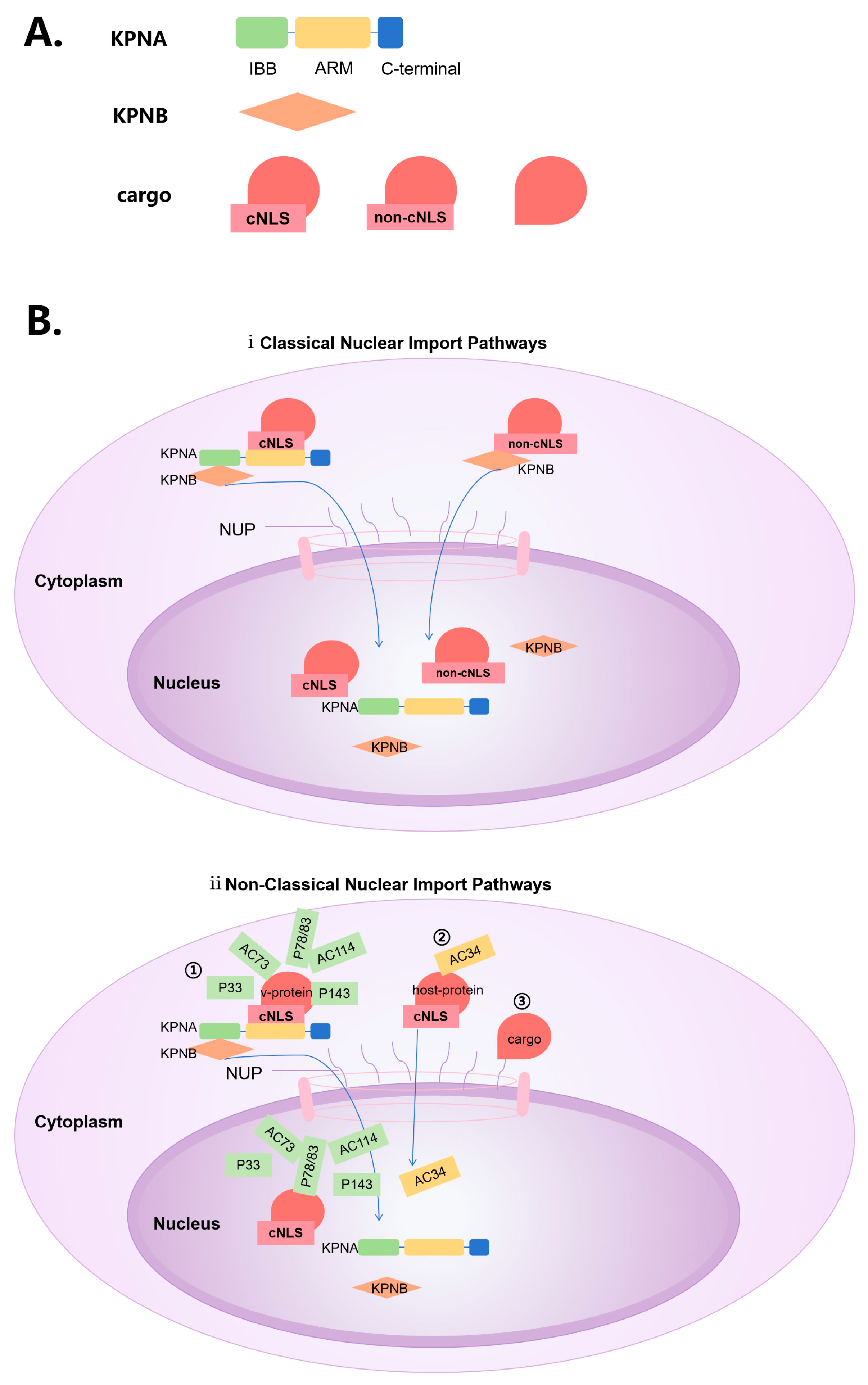
3. Classical Nuclear import Pathways that Directly Rely on NLS
4. Non-Classical Nuclear Import Pathways
4.1. Interaction with Nuclear Entry Proteins
4.2. Direct Interaction with NPC
4.3. Other Pathways
5. Viral regulation of the nuclear import pathway
5.1. Protein Modifications Regulate Transmembrane Transport
5.2. Alteration of Host Structure
6. Summary and Future Prospects
Acknowledgments
Abbreviations
| AcMNPV | Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus |
| ARM | Armadillo |
| BV | Budded virus |
| BmNPV | Bombyx mori multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus |
| CF | cytoplasmic filaments |
| CfNPV | Choristoneura fumiferana nucleopolyhedrovirus |
| CR | cytoplasmic ring |
| cNLS | Classical-nuclear location signal |
| Da | Dalton |
| DNApol | DNA polymerase |
| EBV | Epstein-Barr virus |
| F | phenylalanine,Phe |
| G | Glicine,Gly |
| HCMV | human cytomegalovirus |
| HIV | human immunodeficiencyvirus |
| hnRNP | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins |
| HPV | human papilloma virus |
| IAV | Influenza A virus |
| IBB | importin beta binding |
| IR | inner ring |
| IMP | Integral membrane protein |
| K | lysine,Lys |
| KPN | Karyopherin |
| KPNA | Karyopherin α |
| KPNB | Karyopherin β |
| LR | luminal ring |
| NB | nuclear basket |
| NE | nuclear envelope |
| NES | nuclear export signal |
| NLS | nuclear location signal |
| NPC | nuclear pore complex |
| NPV | Nucleopolyhedrovirus |
| NR | nucleoplasmic ring |
| NTR | nuclear transport receptor |
| Nup | nucleoporin |
| ODV | Occlusion-derived virus |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| P | Proline,Pro |
| PiraGV | Pieris rapae granulovirus |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
| PY-NLS | Proline-Tyrosine Nuclear Localization Signal |
| R | arginine,Arg |
| Sf | Spodoptera frugiperda |
| SV40 | simian vacuolating virus 40 |
| VS | Viral stroma |
| v-Ubi | v-Ubiquitin |
| WNV | West Nile virus |
| Y | Tyrosine,Tyr |
References
- Martin AJ, Jans DA. Antivirals that target the host IMPα/β1-virus interface. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Feb 26;49(1):281-295.
- Cautain B, Hill R, de Pedro N, Link W. Components and regulation of nuclear transport processes. FEBS J. 2015 Feb;282(3):445-62. [CrossRef]
- Wente SR. Gatekeepers of the nucleus. Science. 2000 May 26;288(5470):1374-7.
- He L, Shao W, Li J, Deng F, Wang H, Hu Z, Wang M. Systematic analysis of nuclear localization of Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus proteins. J Gen Virol. 2021 Mar;102(3). [CrossRef]
- Yarbrough ML, Mata MA, Sakthivel R, Fontoura BM. Viral subversion of nucleocytoplasmic trafficking. Traffic. 2014 Feb;15(2):127-40. [CrossRef]
- Caly L, Wagstaff KM, Jans DA. Nuclear trafficking of proteins from RNA viruses: potential target for antivirals? Antiviral Res. 2012 Sep;95(3):202-6.
- Rohrmann, GF. Polyhedrin structure. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67 ( Pt 8):1499-513.
- Jiang L, Goldsmith MR, Xia Q. Advances in the Arms Race Between Silkworm and Baculovirus. Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 9;12:628151. [CrossRef]
- Wang M, Hu Z. Cross-talking between baculoviruses and host insects towards a successful infection. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019 Mar 4;374(1767):20180324. [CrossRef]
- Saxena A, Byram PK, Singh SK, Chakraborty J, Murhammer D, Giri L. A structured review of baculovirus infection process: integration of mathematical models and biomolecular information on cell-virus interaction. J Gen Virol. 2018 Sep;99(9):1151-1171. [CrossRef]
- Wang M, Hu Z. Advances in Molecular Biology of Baculoviruses. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2020;34:183-214. [CrossRef]
- Wubben JM, Atkinson SC, Borg NA. The Role of Protein Disorder in Nuclear Transport and in Its Subversion by Viruses. Cells. 2020 Dec 10;9(12):2654. [CrossRef]
- Li G, Qi X, Hu Z, Tang Q. Mechanisms Mediating Nuclear Trafficking Involved in Viral Propagation by DNA Viruses. Viruses. 2019 Nov 7;11(11):1035. [CrossRef]
- Jarvis DL, Bohlmeyer DA, Garcia A Jr. Enhancement of polyhedrin nuclear localization during baculovirus infection. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):6903-11. [CrossRef]
- Hu Z, Luijckx T, van Dinten LC, van Oers MM, Haj S JP, Bianchi FJ, van Lent JW, Zuidema D, Vlak JM. Specificity of polyhedrin in the generation of baculovirus occlusion bodies. J Gen Virol. 1999 Apr;80 ( Pt 4):1045-1053. [CrossRef]
- Jarvis DL, Bohlmeyer DA, Garcia A Jr. Requirements for nuclear localization and supramolecular assembly of a baculovirus polyhedrin protein. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):795-810. [CrossRef]
- Bae SM, Kim HJ, Lee JB, Choi JB, Shin TY, Koo HN, Choi JY, Lee KS, Je YH, Jin BR, Yoo SS, Woo SD. Hyper-enhanced production of foreign recombinant protein by fusion with the partial polyhedrin of nucleopolyhedrovirus. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 9;8(4):e60835. [CrossRef]
- Feng G, Krell PJ. Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus DNA polymerase C terminus is required for nuclear localization and viral DNA replication. J Virol. 2014 Sep;88(18):10918-33. [CrossRef]
- Chen T, Dong Z, Hu N, Hu Z, Dong F, Jiang Y, Li J, Chen P, Lu C, Pan M. Baculovirus LEF-11 nuclear localization signal is important for viral DNA replication. Virus Res. 2017 Jun 15;238:133-140. [CrossRef]
- Olson VA, Wetter JA, Friesen PD. Baculovirus transregulator IE1 requires a dimeric nuclear localization element for nuclear import and promoter activation. J Virol. 2002 Sep;76(18):9505-15. [CrossRef]
- Katsuma, S. Mutations in the polyhedrin NLS affect the assembly and polyhedral shape of alphabaculovirus occlusion bodies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Sep 24;622:15-21.
- Guo ZJ, Wang DX, Yao Q, Chen KP, Zhang CX. Identification of a novel functional nuclear localization signal in the protein encoded by open reading frame 47 of Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus. Arch Virol. 2010 Dec;155(12):1943-50. [CrossRef]
- Liu G, Carstens EB. Site-directed mutagenesis of the AcMNPV p143 gene: effects on baculovirus DNA replication. Virology. 1999 Jan 5;253(1):125-36.
- Li G, Qi X, Chen H, Hu Z, Chen F, Deng L, Guo Z, Chen K, Tang Q. The Motif of 76KRKCSK in Bm65 Is an Efficient Nuclear Localization Signal Involved in Production of Infectious Virions. Front Microbiol. 2019 Nov 26;10:2739. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Wei G, Wang L, Qian C, Li K, Zhang C, Dai L, Sun Y, Liu D, Zhu B, Liu C. KPNA3-knockdown eliminates the second heat shock protein peak associated with the heat shock response of male silkworm pupae (Bombyx mori) by reducing heat shock factor transport into the nucleus. Gene. 2016 Jan 10;575(2 Pt 2):452-457. [CrossRef]
- Shen Q, Wang YE, Palazzo AF. Crosstalk between nucleocytoplasmic trafficking and the innate immune response to viral infection. J Biol Chem. 2021 Jul;297(1):100856. [CrossRef]
- Kosyna FK, Depping R. Controlling the Gatekeeper: Therapeutic Targeting of Nuclear Transport. Cells. 2018 Nov 21;7(11):221. [CrossRef]
- Chang CC, Hsia KC. More than a zip code: global modulation of cellular function by nuclear localization signals. FEBS J. 2021 Oct;288(19):5569-5585. 8l'. [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto Y., Yamada K., Yoneda Y. Importin alpha: A key molecule in nuclear transport and non-transport functions. *J. Biochem.* 2016;160:69–75. [CrossRef]
- Katsuma S, Deng DX, Zhou CL, Iwanaga M, Noguchi Y, Kobayashi M, Maeda S. Identification of novel residues involved in nuclear localization of a baculovirus polyhedrin protein. Virus Genes. 2000 Oct;21(3):233-40. [CrossRef]
- Braunagel SC, Williamson ST, Ding Q, Wu X, Summers MD. Early sorting of inner nuclear membrane proteins is conserved. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 May 29;104(22):9307-12. [CrossRef]
- Au S, Wu W, Zhou L, Theilmann DA, Panté N. A new mechanism for nuclear import by actin-based propulsion used by a baculovirus nucleocapsid. J Cell Sci. 2016 Aug 1;129(15):2905-11.
- Wulan WN, Heydet D, Walker EJ, Gahan ME, Ghildyal R. Nucleocytoplasmic transport of nucleocapsid proteins of enveloped RNA viruses. Front Microbiol. 2015 Jun 2;6:553. [CrossRef]
- Tessier TM, Dodge MJ, Prusinkiewicz MA, Mymryk JS. Viral Appropriation: Laying Claim to Host Nuclear Transport Machinery. Cells. 2019 Jun 8;8(6):559. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Yu M, Zheng W, Liu W. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of influenza A virus proteins. Viruses. 2015 May 22;7(5):2668-82. [CrossRef]
- Wagstaff KM, Jans DA. Importins and beyond: non-conventional nuclear transport mechanisms. Traffic. 2009 Sep;10(9):1188-98. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, de Jong J, Nagy É, Theilmann DA, Krell PJ. Nuclear Translocation Sequence and Region in Autographa californica Multiple Nucleopolyhedrovirus ME53 That Are Important for Optimal Baculovirus Production. J Virol. 2016 Mar 28;90(8):3953-3965. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Wang Q, Liang C, Song J, Li N, Shi H, Chen X. Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus nucleocapsid protein BV/ODV-C42 mediates the nuclear entry of P78/83. J Virol. 2008 May;82(9):4554-61.
- Qiu J, Tang Z, Yuan M, Wu W, Yang K. The 91-205 amino acid region of AcMNPV ORF34 (Ac34), which comprises a potential C3H zinc finger, is required for its nuclear localization and optimal virus multiplication. Virus Res. 2017 Jan 15;228:79-89. [CrossRef]
- Tang Z, Luo W, Huang Z, Yuan M, Wu W, Yang K. Spodoptera frugiperda mRNA export factor interacts with and mediates the nuclear import of Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus ORF34 (Ac34). Virus Res. 2021 Jul 2;299:198438. [CrossRef]
- CALLAN HG, RANDALL JT, TOMLIN SG. An electron microscope study of the nuclear membrane. Nature. 1949 Feb 19;163(4138):280. [CrossRef]
- Field MC, Dacks JB. First and last ancestors: reconstructing evolution of the endomembrane system with ESCRTs, vesicle coat proteins, and nuclear pore complexes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009 Feb;21(1):4-13. [CrossRef]
- Hoelz A, Debler EW, Blobel G. The structure of the nuclear pore complex. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:613-43. [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazy-Titelman A, Shav-Tal Y, Kehlenbach RH. Into the basket and beyond: the journey of mRNA through the nuclear pore complex. Biochem J. 2020 Jan 17;477(1):23-44. [CrossRef]
- Au S, Wu W, Panté N. Baculovirus nuclear import: open, nuclear pore complex (NPC) sesame. Viruses. 2013 Jul 23;5(7):1885-900. [CrossRef]
- Fulcher AJ, Jans DA. Regulation of nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of viral proteins: an integral role in pathogenesis? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Dec;1813(12):2176-90.
- Shen Q, Feng Q, Wu C, Xiong Q, Tian T, Yuan S, Shi J, Bedwell GJ, Yang R, Aiken C, Engelman AN, Lusk CP, Lin C, Xiong Y. Modeling HIV-1 nuclear entry with nucleoporin-gated DNA-origami channels. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2023 Apr;30(4):425-435. [CrossRef]
- Cohen S, Behzad AR, Carroll JB, Panté N. Parvoviral nuclear import: bypassing the host nuclear-transport machinery. J Gen Virol. 2006 Nov;87(Pt 11):3209-3213. [CrossRef]
- Rohrmann, GF. Polyhedrin structure. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67 ( Pt 8):1499-513.
- Braunagel SC, Cox V, Summers MD. Baculovirus data suggest a common but multifaceted pathway for sorting proteins to the inner nuclear membrane. J Virol. 2009 Feb;83(3):1280-8. [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi A, Li PP, Qu Q, Jafri QH, Kasamatsu H. Molecular dissection of nuclear entry-competent SV40 during infection. Virus Res. 2007 Mar;124(1-2):226-30. [CrossRef]
- Wang YE, Pernet O, Lee B. Regulation of the nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of viral and cellular proteins by ubiquitin and small ubiquitin-related modifiers. Biol Cell. 2012 Mar;104(3):121-38. [CrossRef]
- Shcherbik, N. and Haines, D.S. Ub on the move. *J. Cell Biochem.* 2004, 93, 11–19.
- Chen BB, Mallampalli RK. Masking of a nuclear signal motif by monoubiquitination leads to mislocalization and degradation of the regulatory enzyme cytidylyltransferase. Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Jun;29(11):3062-75. [CrossRef]
- Pichler A, Melchior F. Ubiquitin-related modifier SUMO1 and nucleocytoplasmic transport. Traffic. 2002 Jun;3(6):381-7. [CrossRef]
- Liang C, Li M, Dai X, Zhao S, Hou Y, Zhang Y, Lan D, Wang Y, Chen X. Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus PK-1 is essential for nucleocapsid assembly. Virology. 2013 Sep 1;443(2):349-57. [CrossRef]
- Chen N, Kong X, Zhao S, Xiaofeng W. Post-translational modification of baculovirus-encoded proteins. Virus Res. 2020 Apr 2;279:197865. [CrossRef]
- Li A, Zhao H, Lai Q, Huang Z, Yuan M, Yang K. Posttranslational Modifications of Baculovirus Protamine-Like Protein P6.9 and the Significance of Its Hyperphosphorylation for Viral Very Late Gene Hyperexpression. J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(15):7646-59. [CrossRef]
- Tsimbalyuk S, Cross EM, Hoad M, Donnelly CM, Roby JA, Forwood JK. The Intrinsically Disordered W Protein Is Multifunctional during Henipavirus Infection, Disrupting Host Signalling Pathways and Nuclear Import. Cells. 2020 Aug 18;9(8):1913.
- Bhuvanakantham R, Cheong YK, Ng ML. West Nile virus capsid protein interaction with importin and HDM2 protein is regulated by protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation. Microbes Infect. 2010 Aug;12(8-9):615-25. [CrossRef]
- Chang CW, Lee CP, Su MT, Tsai CH, Chen MR. BGLF4 kinase modulates the structure and transport preference of the nuclear pore complex to facilitate nuclear import of Epstein-Barr virus lytic proteins. J Virol. 2015 Feb;89(3):1703-18. [CrossRef]
- Biswas S, Willis LG, Fang M, Nie Y, Theilmann DA. Autographa californica Nucleopolyhedrovirus AC141 (Exon0), a Potential E3 Ubiquitin Ligase, Interacts with Viral Ubiquitin and AC66 To Facilitate Nucleocapsid Egress. J Virol. 2018 Jan 17;92(3):e01713-17. [CrossRef]
- Mühlbauer D, Dzieciolowski J, Hardt M, Hocke A, Schierhorn KL, Mostafa A, Müller C, Wisskirchen C, Herold S, Wolff T, Ziebuhr J, Pleschka S. Influenza virus-induced caspase-dependent enlargement of nuclear pores promotes nuclear export of viral ribonucleoprotein complexes. J Virol. 2015 Jun;89(11):6009-21. [CrossRef]
- Au V, Yu M, Carstens EB. Characterization of a baculovirus nuclear localization signal domain in the late expression factor 3 protein. Virology. 2009 Mar 1;385(1):209-17. [CrossRef]
- Chen G, Fang Y, Yan Q, Li P, Wu L, Feng G. The deficiency in nuclear localization signal of Neodiprion lecontei nucleopolyhedrovirus DNA polymerase prevents rescue of viral DNA replication and virus production in dnapol-null Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virus Res. 2019 Jun;266:52-57. [CrossRef]
- Li P, Wu L, Chen G. Identification of a novel bipartite nuclear localization signal in the DNA polymerase of the betabaculovirus Pieris rapae granulovirus. Arch Virol. 2019 Mar;164(3):839-845. [CrossRef]
- Wagstaff KM, Rawlinson SM, Hearps AC, Jans DA. An AlphaScreen®-based assay for high-throughput screening for specific inhibitors of nuclear import. J Biomol Screen. 2011 Feb;16(2):192-200.
- Campbell, W.C. Ivermectin: a potent new antiparasitic agent. Science. 1983;221:823–828. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines 21st List 2019.
- Jans DA, Wagstaff KM. Ivermectin as a Broad-Spectrum Host-Directed Antiviral: The Real Deal? Cells. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):2100.
- Campbell W.C. An introduction to the avermectins. N. Z. Vet. J. 1981;29:174–178. [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme A.J., Rogers A.T. Glutamate-gated chloride channels and the mode of action of the avermectin/milbemycin anthelmintics. Parasitology. 2005;131(Suppl):S85–S95. [CrossRef]
- Laing R, Gillan V, Devaney E. Ivermectin - Old Drug, New Tricks? Trends Parasitol. 2017 Jun;33(6):463-472.
- Jarvis DL, Bohlmeyer DA, Garcia A Jr. Requirements for nuclear localization and supramolecular assembly of a baculovirus polyhedrin protein. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):795-810. [CrossRef]
- Chen Z, Carstens EB. Identification of domains in Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus late expression factor 3 required for nuclear transport of P143. J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(17):10915-22. [CrossRef]
- Wu Y, Carstens EB. A baculovirus single-stranded DNA binding protein, LEF-3, mediates the nuclear localization of the putative helicase P143. Virology. 1998 Jul 20;247(1):32-40. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Dong ZQ, Zhang CD, He Q, Chen XM, Cao MY, Li HQ, Xiao WF, Lu C, Pan MH. Identification of a novel nuclear localization signal of baculovirus late expression factor 11. Virus Res. 2014 May 12;184:111-9. [CrossRef]
- Hu P, Feng F, Xia H, Chen L, Yao Q, Chen K. Molecular cloning and characterization of a Bombyx mori gene encoding the transcription factor Atonal. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 2014 Mar-Apr;69(3-4):155-64. [CrossRef]
- Chen G, Fang Y, Hu Z, Krell PJ, Feng G. Rescue of dnapol-null Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus with DNA polymerase (DNApol) of Spodoptera litura nucleopolyhedrovirus (SpltNPV) and identification of a nuclear localization signal in SpltNPV DNApol. J Gen Virol. 2016 Aug;97(8):1968-1980. [CrossRef]
- Chen GQ, Li P, Yan Q, Wu YH, Wang HR, Chao SF, Wu LJ, Chen L, Feng GZ. Identification of Spodoptera frugiperda importin alphas that facilitate the nuclear import of Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus DNA polymerase. Insect Mol Biol. 2021 Aug;30(4):400-409.
- Blissard GW, Theilmann DA. Baculovirus Entry and Egress from Insect Cells. Annu Rev Virol. 2018 Sep 29;5(1):113-139. [CrossRef]
- Lange A, Mills RE, Lange CJ, Stewart M, Devine SE, Corbett AH. Classical nuclear localization signals: definition, function, and interaction with importin alpha. J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 23;282(8):5101-5. [CrossRef]
- Fraser, M. J. Ultrastructural observations of virion maturation in Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus infected Spodoptera frugiperda cell cultures. J. Ultrastruct. Mol. Struct. Res.1986 95, 189–195. [CrossRef]
- Herniou EA, Olszewski JA, Cory JS, O'Reilly DR. The genome sequence and evolution of baculoviruses. Annu Rev Entomol. 2003;48:211-34. [CrossRef]
- Young J. C., MacKinnon E. A., Faulkner P. The architecture of the virogenic stroma in isolatednuclei of Spodoptera frugiperda cells in vitro infected by Autographa californicanuclearpolyhedrosis virus.J Struct Biol, 1993, 110:141-153.
- Fraser M. J. Ultrastructural observations of virion maturation in Autographa californica nuclearpolyhedrosis virus infected Spodoptera frugiperda cell cultures. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res, 1986.95:189-195.
- Fontes M.R., Teh T., Kobe B. Structural basis of recognition of monopartite and bipartite nuclear localization sequences by mammalian importin-alpha. J. Mol. Biol. 2000;297:1183–1194.
- Cherezova L, Burnside KL, Rose TM. Conservation of complex nuclear localization signals utilizing classical and non-classical nuclear import pathways in LANA homologs of KSHV and RFHV. PLoS One. 2011 Apr 29;6(4):e18920. [CrossRef]
- Moroianu J. Distinct nuclear import and export pathways mediated by members of the karyopherin beta family. J Cell Biochem. 1998 Aug 1;70(2):231-9.
- Bischoff, F.R.; Krebber, H.; Smirnova, E.; Dong, W.; Ponstingl, H. Co-activation of RanGTPase and inhibition of GTP dissociation by Ran-GTP binding protein RanBP1. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti E, Uy M, Leighton L, Blobel G, Kuriyan J. Crystallographic analysis of the recognition of a nuclear localization signal by the nuclear import factor karyopherin alpha. Cell. 1998 Jul 24;94(2):193-204. [CrossRef]
- Fontes MR, Teh T, Kobe B. Structural basis of recognition of monopartite and bipartite nuclear localization sequences by mammalian importin-alpha. J Mol Biol. 2000 Apr 14;297(5):1183-94. [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb DS, Corbett AH, Mason DA, Harreman MT, Adam SA. Importin alpha: a multipurpose nuclear-transport receptor. Trends Cell Biol. 2004 Sep;14(9):505-14. [CrossRef]
- Marfori, M.; Mynott, A.; Ellis, J.J.; Mehdi, A.M.; Saunders, N.F.W.; Curmi, P.M.; Forwood, J.K.; Bodén, M.; Kobe, B. Molecular basis for specificity of nuclear import and prediction of nuclear localization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1562–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, A.; Mills, R.E.; Lange, C.J.; Stewart, M.; Devine, S.E.; Corbett, A.H. Classical Nuclear Localization Signals: Definition, Function, and Interaction with Importin. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5101–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball LA. Virus replication strategies. Fields Virol 2007;5:120–140.
| Baculovirus species | Target proteins | Type | Motif | verified or projected | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AcMNPV | polyhedrin | Monopartite | 29KNAKRKKHF37 | Verified | 4,74 |
| IE-1 | Bipartite | 130TGTKRKLDEYLDNSQGVVGQFNKIKLRPKYK151 | Projected | 4 | |
| Monopartite | 534KVNRR538 | Verified | 20 | ||
| AC13 | Monopartite | 260RHFRKRKMRFE270 | Projected | 4 | |
| DBP (AC25) | Bipartite | 2ATKRKIGDGYSSSDDNQPKRERSE19 | Projected | 4 | |
| LEF-6 (AC28) | Bipartite | 13EKKFSKEFLIHIAPDLKNSVDWNGSTRKQLRV33 | Projected | 4 | |
| PP31 (AC36) | Bipartite | 63ERKMSKRKKKVINNNKYILFNSWYTKIKQPEWP85 | Verified | 1,4 | |
| Bipartite | 234GSRKRKSSVPAKQRSSIKTRRNT253 | Projected | 4 | ||
| LEF-11(AC37) | Bipartite | 76RKVCLHHKRIARLLGIKKIYHQEYKRVVSKVYK100 | Verified | 4,77 | |
| AC39 | Bipartite | 4RANSRKPFLFYNEDYYCEKPKRYFHTNKVIFEK25 | Projected | 4 | |
| GTA(AC42) | Bipartite | 138IKQNKQSSLFSTRWHRVVLDEAHIIKNCKT158 | Projected | 4 | |
| LEF-8 (AC50) | Bipartite | 337RQKMLKQKKDFVKFIGSFFHGEMTVAGKKFFL356 | Projected | 4 | |
| Bipartite | 582RDNKLMTAEDPYIPHIALPICLYNNKVNKLK601 | Projected | 4 | ||
| Bipartite | 661DGRRYKIETCTNGNFNVYKVYVYFRQIKNQKIE684 | Projected | 4 | ||
| AC58 | Monopartite | 3SSRKRRVAKR12 | Projected | 4 | |
| Monopartite | 26VVSTRKRLKQN36 | Projected | 4 | ||
| Bipartite | 5RKRRVAKRAFNAKSKKFPIGEVVSTRKRLKQN29 | Projected | 4 | ||
| DNA-Pol (AC65) | Monopartite | 806PGKKRKSTDD815 | Projected | 4 | |
| Monopartite | 819PSPKRRVITV828 | Projected | 4 | ||
| Bipartite | 486RKLIPLKNIPKDAINLGPANQTVKYKGGKVLKP518 | Projected | 4 | ||
| Bipartite | 804DNPGKKRKSTDDNEGPSPKRRVITVARHCREI835 | Projected | 4 | ||
| Monopartite | 939CSVKRKRDDD948 | Verified | 4,18 |
||
| Bipartite | 804DNPGKKRKSTDDNEGPSPKRRVIT827 | Verified | |||
| LEF-3 (AC67) | Bipartite | 18KRMAMASSPKKIREN32 | Verified | 4,64,75 | |
| Bipartite | 2ATKRSLSGESSGEPLIKRMAM16 | Projected | 4 | ||
| HCF-1 (AC70) | Bipartite | 145PSFKAVCFSCIKRIKTCQVCNQPLLKMYKEK164 | Projected | 4 | |
| Ac79 | Monopartite | 72EYNLKRKCSKY82 | Projected | 4 | |
| TLP (AC82) | Monopartite | 165DAPTPKKQKLD175 | Projected | 4 | |
| AC88 | Monopartite | 48IRKIRKRKKVPCPLC62 | Projected | 4 | |
| Bipartite | 35ELDTCKHQLCSMCIRKIRKRKKVP58 | Projected | 4 | ||
| Bipartite | 187ELQLKRITTEKALKSLNDDYAKLASKNAKLS217 | Projected | 4 | ||
| VP80 (AC104) | Bipartite | 368 EIKDSSTPLYNIAMYKSDYDAIKNKNIKT396 | Projected | 4 | |
| Bipartite | 417 PVRKTSGKRSAEDDLLPTRSSKRANRP443 | Projected | 4 | ||
| Bipartite | 467ESKRRKLEDEDFLKLKALEFSKDIVNEKLQKII499 | Projected | 4 | ||
| Monopartite | 464YEKESKRRKLEDEDF480 | Projected | 4 | ||
| AC107 |
Bipartite | 71NERKRKLQNTNSTAKCLLPAPPPQLRKLEKK101 | Projected | 4 | |
| Monopartite | 71NERKRKLQNT80 | Projected | 4 | ||
| PEP (AC131) | Bipartite | 25NLKMPLQAFQQLLFTIPSKHRKMI48 | Projected | 4 | |
| ME53 | Unknown | Unknown | / | 37 | |
| AC11 | None | None | / | 4 | |
| Ac30 | None | None | / | 4 | |
| Ac34 | None | None | / | 39,40 | |
| Ac43 | None | None | / | 4 | |
| PCNA (AC49) | None | None | / | 4 | |
| VP1054 (AC54) | None | None | / | 4 | |
| Ac73 | None | None | / | 4 | |
| Ac114 | None | None | / | 4 | |
| VP78/83 | None | None | / | 32 | |
| P143 | None | None | / | 23,76 | |
| P33 | None | None | / | 4 | |
| BmNPV | polh | Monopartite | 32KRKK35 | Verified | 14-17 |
| VP39 | Monopartite | 52HLIKRFKMS60 | Projected | 13 | |
| 38K | Bipartite | 13RLNDAIIKRHVLVLSEYADLKYLG FEKYKFFEY45 | Projected | 13 | |
| BV/ODV-C42 | Monopartite | 357KRKK360 | Verified | 13,38 | |
| BV/ODV-EC27 |
Bipartite | 2KRIKCNKVRTVTEIVNSDEKIQKTYEL28 | Projected | 13 | |
| VLF-1 | Bipartite | 225LIKRGKLHSDTINLKRKRSRNN246 | Verified | 13 | |
| ORF47 | Bipartite | 117RKRR---144RKR-K | Verified | 22 | |
| LEF-11 | Bipartite | 72RKVCLHHKRIARLLGIKKIYHQEYKRVVSKVYKN105 | Verified | 19,77 | |
| BmAtonal | Bipartite | 62LEGSGKRRGRATSAAVLRRRR82 | Verified | 78 | |
| Bm65 | Monopartite | 76KRKCSK81 | Verified | 24 | |
| LEF-3 | Bipartite | 18KRMAMANSPKKIREN32 | Verified | 64 | |
| PiraGV | DNApol | Bipartite | 4LFKRKLDEPPTDHTLV K AIKLS25 | Verified | 66 |
| SpltNPV | DNApol | Monopartite | 827QEPPAKRARMPT838 | Verified | 79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




