Submitted:
22 January 2024
Posted:
22 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
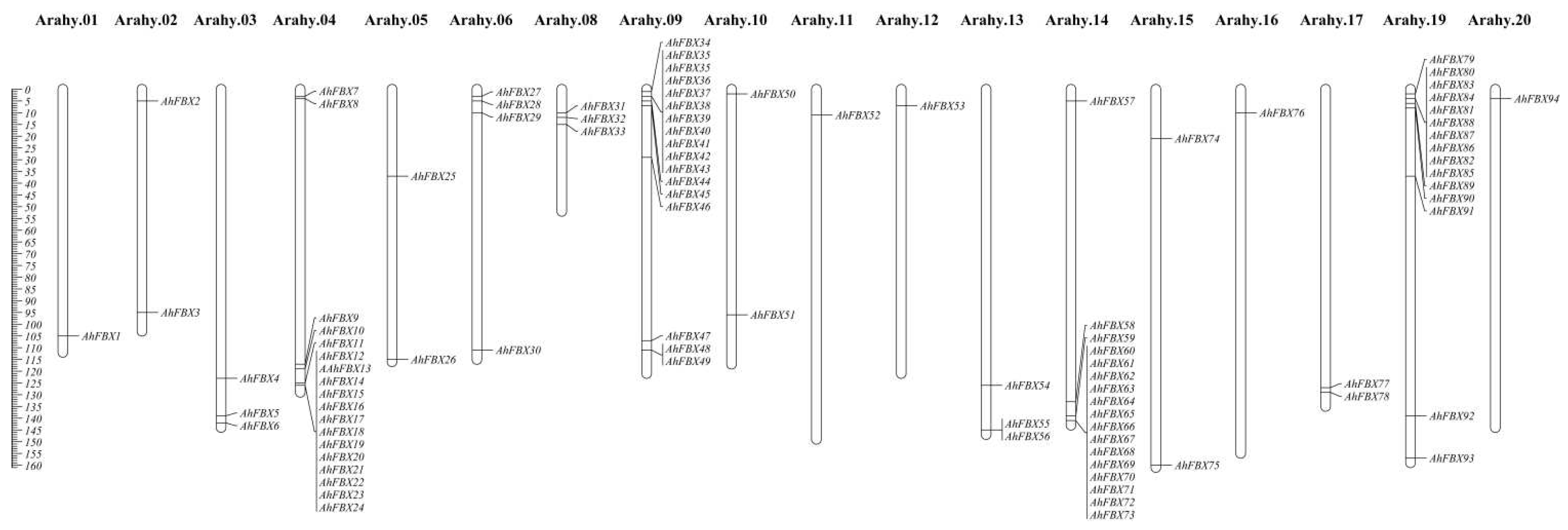
2.1. Genome–wide identification and chromosome localization
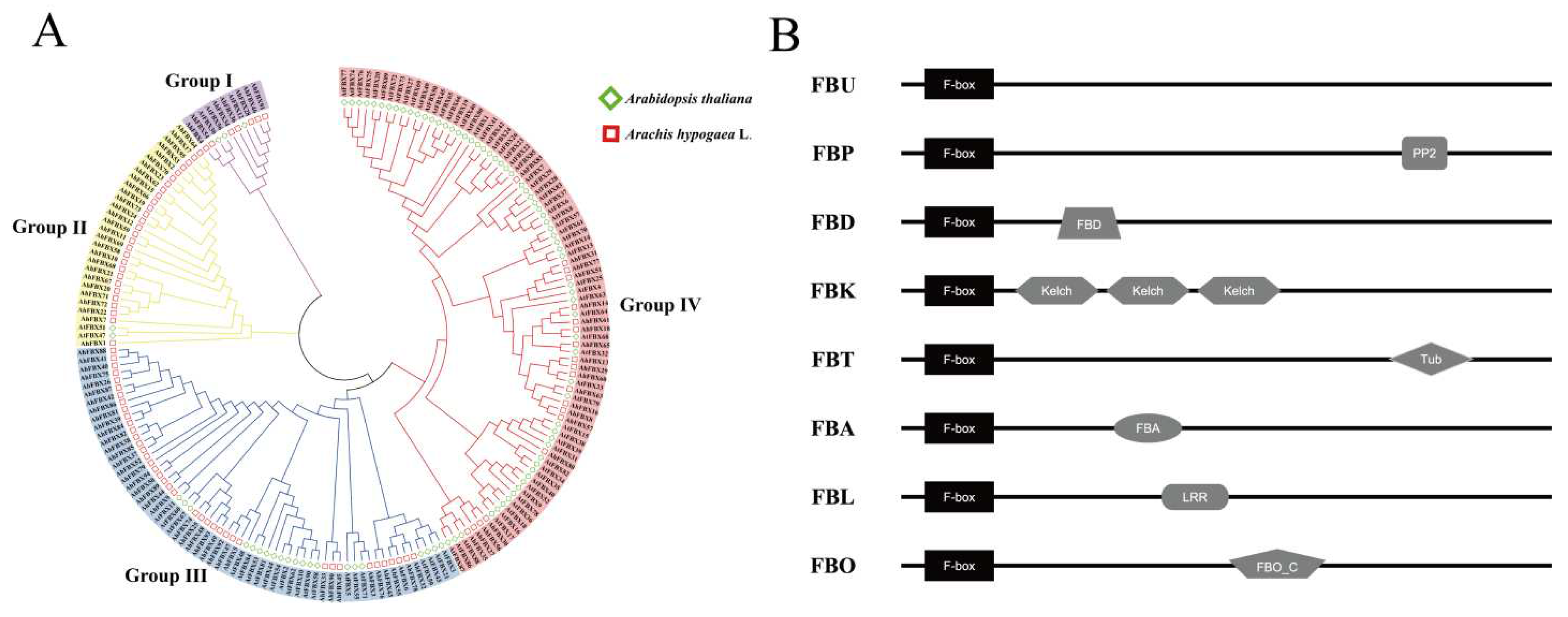
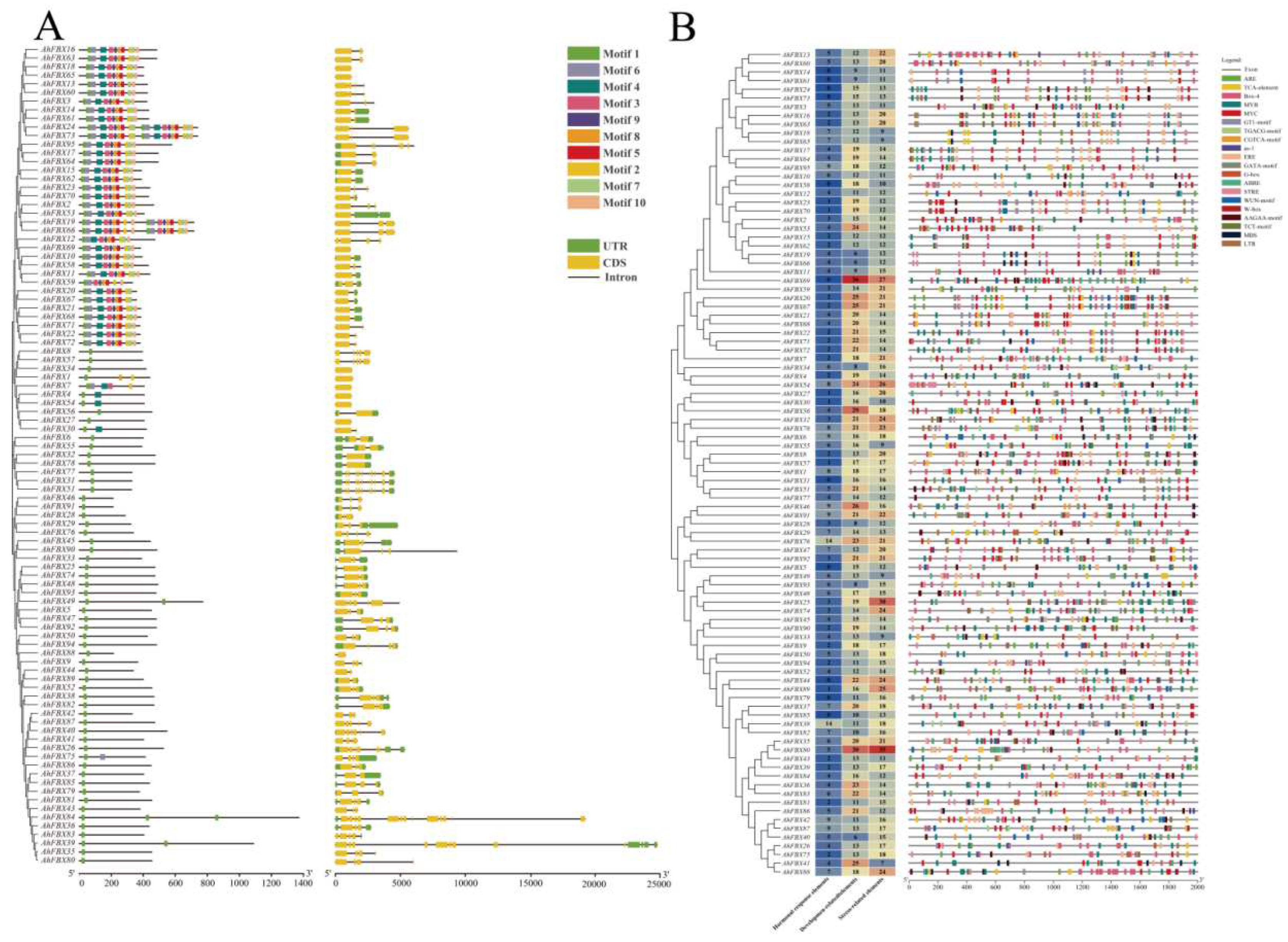
2.2. Physicochemical properties, phylogenetic tree and gene structure analysis
2.3. Prediction of cis–acting elements in the promoter region
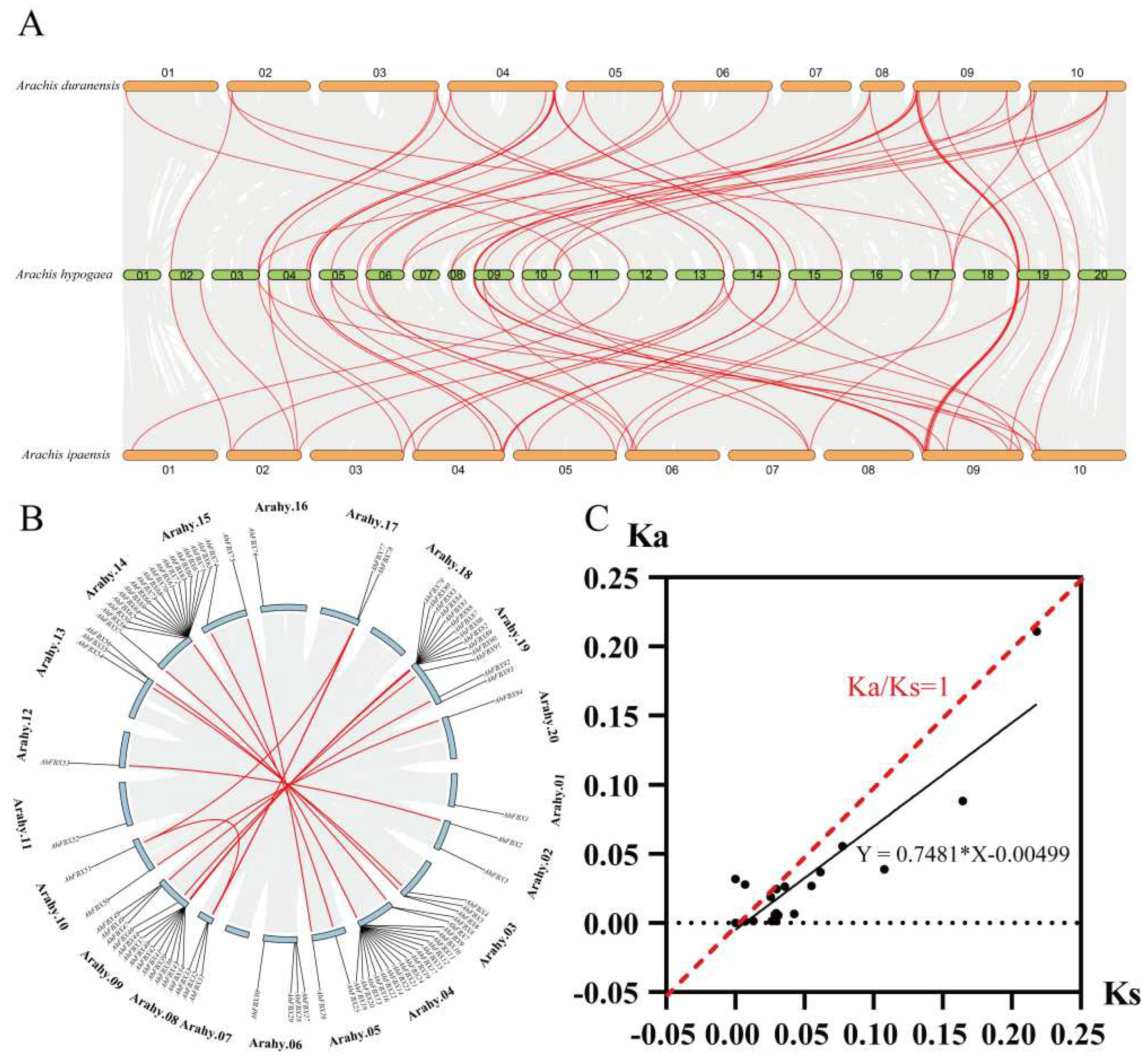
2.4. Collinearity and estimation of Ka/Ks ratios analysis
2.5. In silico expression analysis of AhFBX genes in different tissues
2.6. Expression analysis in lateral branch development of peanut
2.7. RNA extracted and qRT–PCR analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and chromosome location of AhFBXs
3.2. Physicochemical properties and subcellular localization prediction of AhFBXs
3.3. Classification and phylogenetic tree of AhFBXs
3.4. Conserved Motifs and gene structural of AhFBXs
3.6. Cis–acting elements in the promoter region of AhFBXs
3.5. Collinearity and estimation of Ka/Ks ratios of AhFBXs
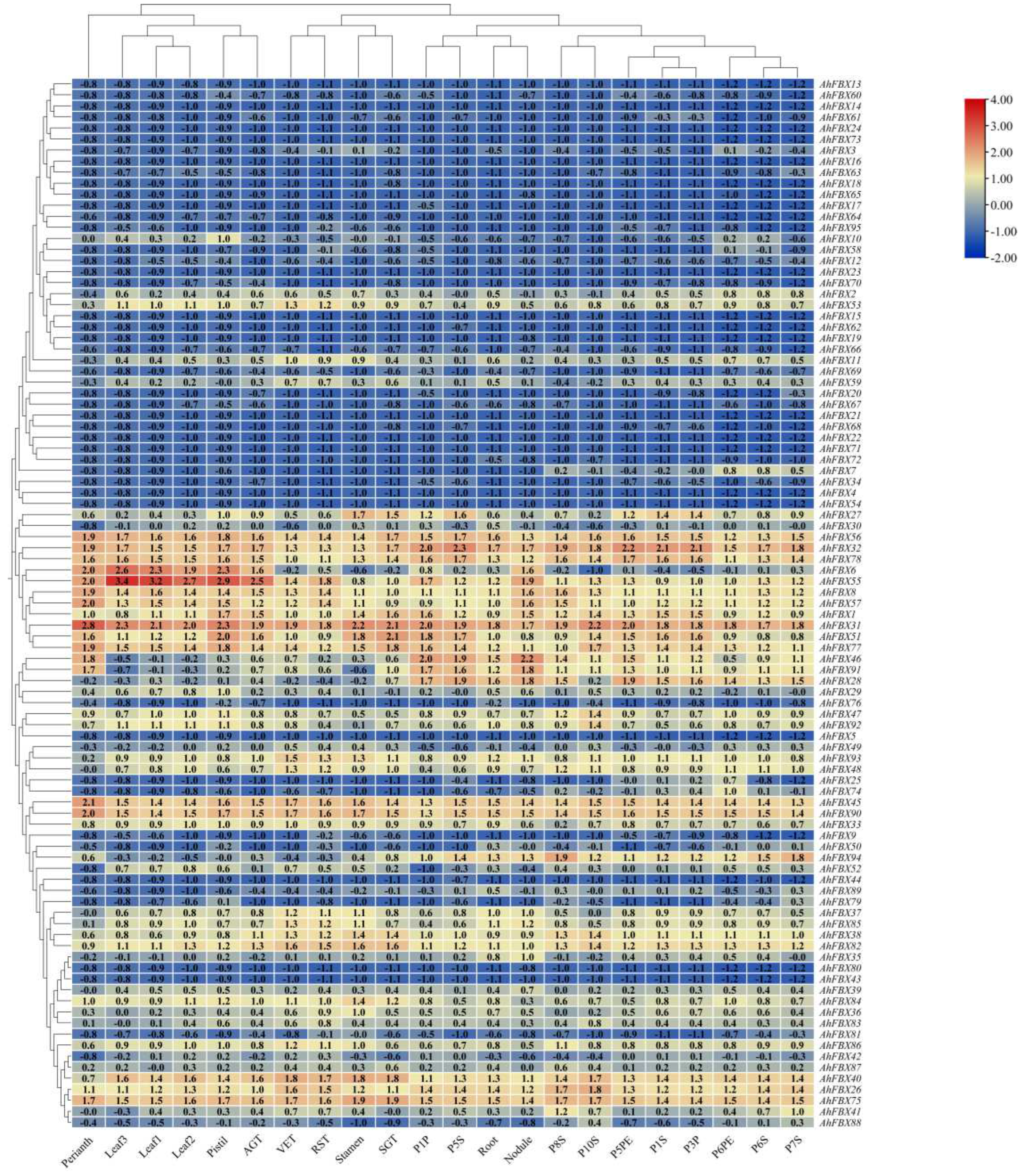
3.7. In silico expression patterns of AhFBXs in different tissues
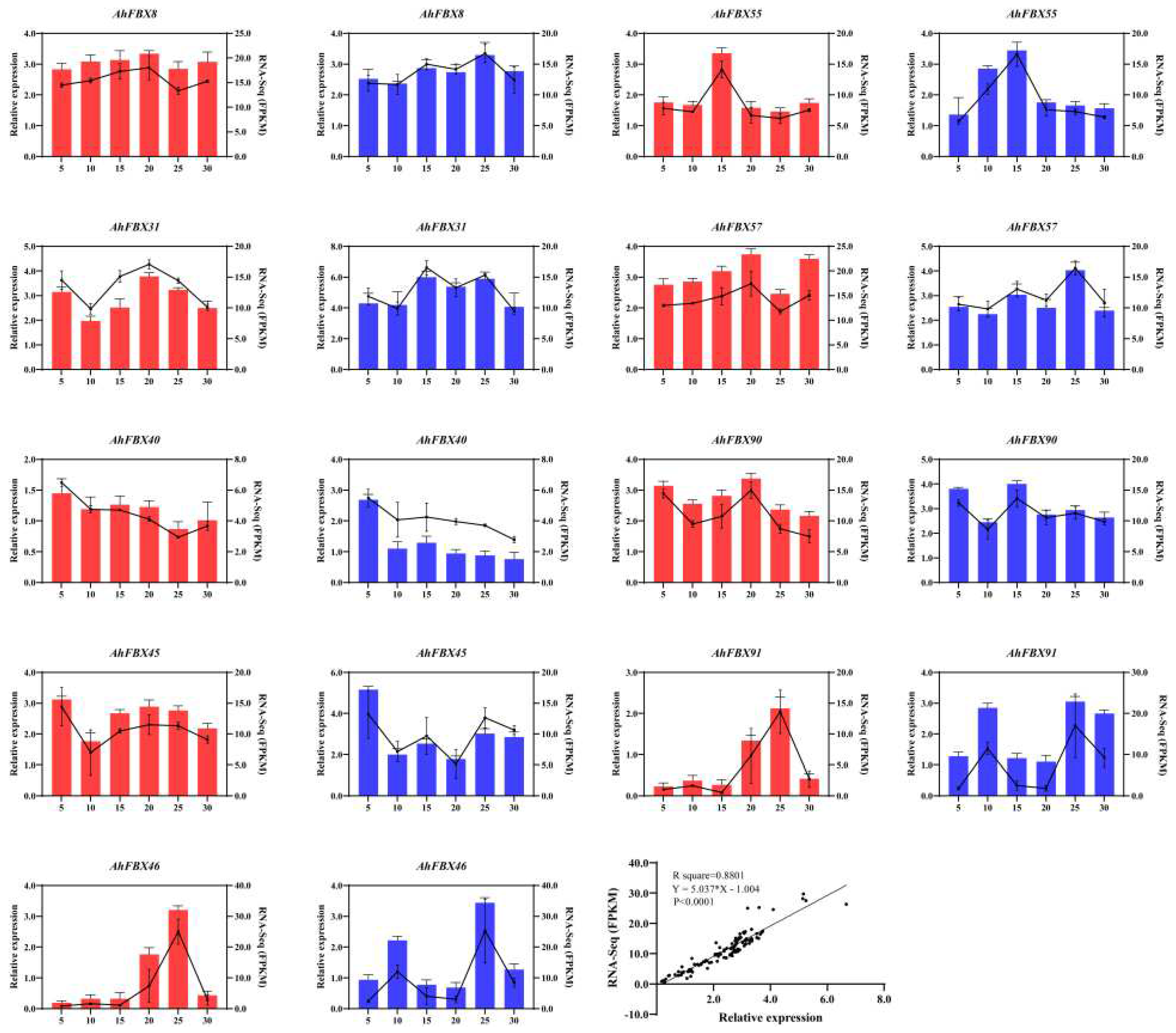
3.8. Expression of AhFBX genes during the lateral branch development
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadanandom, A.; Bailey, M.; Ewan, R.; Lee, J.; Nelis, S. The ubiquitin-proteasome system: Central modifier of plant signalling. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 13-28. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hellmann, H. Plant E3 Ligases: Flexible Enzymes in a Sessile World. Mol. Plant. 2013, 6, 1388-1404. [CrossRef]
- Somers, D.E.; Fujiwara, S. Thinking outside the F-box: Novel ligands for novel receptors. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 206-213. [CrossRef]
- Lechner, E.; Achard, P.; Vansiri, A.; Potuschak, T.; Genschik, P. F-box proteins everywhere. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 631–638. [CrossRef]
- Kipreos, E.T.; Pagano, M. The F-box protein family. Genome Biology. 2000, 1, s3001-s3002. [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Ma, H.; Nei, M.; Kong, H. Evolution of F-box genes in plants: different modes of sequence divergence and their relationships with functional diversification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.. 2009, 106(3): 835-840. [CrossRef]
- Gagne, J.M.; Downes, B.P.; Shiu, S.; Durski, A.M.; Vierstra, R.D. The F-box subunit of the SCF E3 complex is encoded by a diverse superfamily of genes in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2002, 99, 11519-11524. [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Nijhawan, A.; Arora, R.; Agarwal, P.; Ray, S.; Sharma, P.; Kapoor, S.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. F-Box Proteins in Rice. Genome-Wide Analysis, Classification, Temporal and Spatial Gene Expression during Panicle and Seed Development, and Regulation by Light and Abiotic Stress. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 1467-1483. [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Wu, B.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Zheng, C. Genome-wide identification and characterisation of F-box family in maize. Mol. Genet. Genomics. 2013, 288, 559-577. [CrossRef]
- Song, J.B.; Wang, Y.X.; Li, H.B.; Li, B.W.; Zhou, Z.S.; Gao, S.; Yang, Z.M. The F-box family genes as key elements in response to salt, heavy mental, and drought stresses in Medicago truncatula. Funct Integr Genomics 2015, 15, 495-507. [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Xiao, Z.X.; Wong, F.L.; Sun, S.; Liang, K.J.; Lam, H.M. Genome-Wide Analyses of the Soybean F-Box Gene Family in Response to Salt Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 818. [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Zhang, N.; Qiu, Y.; Meng, L.; Cheng, M.; Liu, J.; Yao, L.; Lv, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, A. Molecular Characterization, Gene Evolution and Expression Analysis of the F-Box Gene Family in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Genes (Basel). 2021, 12(3): 417. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Yan, S.; Yu, B.; Gan, Y.; Liu, R.; Qiu, Z.; Cao, B. Genome-Wide Analysis and Characterization of Eggplant F-Box Gene Superfamily: Gene Evolution and Expression Analysis under Stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23(24):16049. [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.H.; Niu, M.X.; Liu, X.; Bao, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, M.; He, F.; Han, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.L.; Yin, W.; Su, Y.; Xia X. Genome-Wide Analysis of the FBA Subfamily of the Poplar F-Box Gene Family and Its Role under Drought Stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24(5):4823. [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Luong, P.; Huq, E. The F-Box Protein MAX2 Functions as a Positive Regulator of Photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 1471-1483. [CrossRef]
- Song, J.B.; Huang, S.Q.; Dalmay, T.; Yang, Z.M. Regulation of leaf morphology by microRNA394 and its target LEAF CURLING RESPONSIVENESS. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 1283-1294. [CrossRef]
- Marrocco, K.; Zhou, Y.; Bury, E.; Dieterle, M.; Funk, M.; Genschik, P.; Krenz, M.; Stolpe, T.; Kretsch, T. Functional analysis of EID1, an F-box protein involved in phytochrome A-dependent light signal transduction. Plant J. 2006, 45, 423-438. [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Tian, S.; Zhang, W.; Dong, X.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Yue, B. Q(Dtbn1), an F-box gene affecting maize tassel branch number by a dominant model. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1183-1194. [CrossRef]
- Bertioli, D.J.; Cannon, S.B.; Froenicke, L.; Huang, G.; Farmer, A.D.; Cannon, E.K.; Liu, X.; Gao, D.; Clevenger, J.; Dash, S.; Ren, L.; Moretzsohn, M.C.; Shirasawa, K.; Huang, W.; Vidigal, B.; Abernathy, B.; Chu, Y.; Niederhuth, C.E.; Umale, P.; Araújo, A.C.; Kozik, A.; Kim, K.D.; Burow, M.D.; Varshney, R.K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Barkley, N.; Guimarães, P.M.; Isobe, S.; Guo, B.; Liao, B.; Stalker, H.T.; Schmitz, R.J.; Scheffler, B.E.; Leal-Bertioli, S.C.; Xun, X.; Jackson, S.A.; Michelmore, R.; Ozias-Akins, P. The genome sequences of Arachis duranensis and Arachis ipaensis, the diploid ancestors of cultivated peanut. Nat Genet. 2016, 48(4):438–46. [CrossRef]
- Bertioli, DJ.; Jenkins, J.; Clevenger, J.; Dudchenko, O.; Gao, D.; Seijo, G.; Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M.; Ren, L.; Farmer, A.D.; Pandey, M.K.; Samoluk, S.S.; Abernathy, B.; Agarwal, G.; Ballén-Taborda, C.; Cameron, C.; Campbell, J.; Chavarro, C.; Chitikineni, A.; Chu, Y.; Dash, S.; El, Baidouri, M.; Guo, B.; Huang, W.; Kim, K.D.; Korani, W.; Lanciano, S.; Lui, C.G.; Mirouze, M.; Moretzsohn, M.C.; Pham, M.; Shin, J.H.; Shirasawa, K.; Sinharoy, S.; Sreedasyam, A.; Weeks, N.T.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, Z.; Froenicke, L.; Aiden, E.L.; Michelmore, R.; Varshney, R.K.; Holbrook, C.C.; Cannon, E.K.S.; Scheffler, B.E.; Grimwood, J.; Ozias-Akins, P.; Cannon, S.B.; Jackson, S.A.; Schmutz, J. The genome sequence of segmental allotetraploid peanut Arachis hypogaea. Nat Genet. 2019, 51, 877–884. [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Chen, H.; Yang, M.; Wang, J.; Pandey, M.K.; Zhang, C.; Chang, W.C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Tang, R.; Garg, V.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; Chow, C.N.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, D.; Khan, A.W.; Yang, Q.; Cai, T.; Bajaj, P.; Wu, K.; Guo, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liang, F.; Hu, J.; Liao, B.; Liu, S.; Chitikineni, A.; Yan, H.; Zheng, Y.; Shan, S.; Liu, Q.; Xie, D.; Wang, Z.; Khan, S.A.; Ali, N.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, R.; Peng, Z.; Wang, S.; Mamadou, G.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, W.; Xiong, F.; Quan, W.; Yuan, M.; Li, Y.; Zou, H.; Xia, H.; Zha, L.; Fan, J.; Yu, J.; Xie, W.; Yuan, J.; Chen, K.; Zhao, S.; Chu, W.; Chen, Y.; Sun, P.; Meng, F.; Zhuo, T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; He, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Kavikishor, P.B.; Pan, R.L.; Paterson, A.H.; Wang, X.; Ming, R.; Varshney, R.K. The genome of cultivated peanut provides insight into legume karyotypes, polyploid evolution and crop domestication. Nat Genet. 2019, 51, 865-876. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Hong, Y.; Lan, H.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Pandey, M.K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Yu, J.; Zhang, G.; Yuan, J.; Li, X.; Wen, S.; Meng, F.; Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Liu, Z.J.; Paterson, A.H.; Varshney, R.K.; Liang, X. Sequencing of Cultivated Peanut, Arachis hypogaea, Yields Insights into Genome Evolution and Oil Improvement. Mol Plant. 2019, 12(7):920–934. [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Wan, S. Genome-Wide Analysis of the SNARE Family in Cultivated Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Reveals That Some Members Are Involved in Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7103. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Chi, J.; Li, R.; Han, Y.; Cui, F.; Peng, Z.; Wan, S.; Li, G. Genome-wide identification and expression of SAUR gene family in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and functional identification of AhSAUR3 in drought tolerance. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 178. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Huai, D.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yan, L.; Jiang, H.; Lei, Y.; Liao, B. Genome-wide identification of peanut PIF family genes and their potential roles in early pod development. Gene, 2021, 781, 145539. [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Fan, S.; Wan, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, G. The Major Intrinsic Protein Family and Their Function Under Salt–Stress in Peanut. Front Genet, 2021, 12, 639585. [CrossRef]
- Gallavotti, A. The role of auxin in shaping shoot architecture. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 2593–2608. [CrossRef]
- Pittman, R. N. United States peanut descriptors. ARS (USA), 1995.
- Kayam, G.; Brand, Y.; Faigenboim-Doron, A.; Patil, A.; Hedvat, I.; Hovav, R. Fine-Mapping the Branching Habit Trait in Cultivated Peanut by Combining Bulked Segregant Analysis and High-Throughput Sequencing. Front Plant Sci, 2017, 8:467. [CrossRef]
- Donald, C.M. The breeding of crop ideotypes. Euphytica. 1968, 17, 385–403. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, H.; Ma, B.; Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, R.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Qian, Q.; Han, B.; He, Z.; Li, J. A natural tandem array alleviates epigenetic repression of IPA1 and leads to superior yielding rice. Nat Commun. 2017, 8, 14789. [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wang, C.; Xia, J.; Wu, L.; Xu, G.; Wu, W.; Li, D.; Qin, W.; Han, X.; Chen, Q.; Jin, W.; Tian, F. Teosinte ligule allele narrows plant architecture and enhances high-density maize yields. Science. 2016, 16, 365(6454): 658-664. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cui, S.; Dang, P.; Yang, X.; Wei, X.; Chen, K.; Liu, L.; Chen, C.Y. GWAS and bulked segregant analysis reveal the Loci controlling growth habit-related traits in cultivated Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Genom, 2022, 27;23(1):403. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; He, M.; Li, L.; Cui, S.; Hou, M.; Wang, L.; Mu, G.; Liu, L.; Yang, X. Identification and expression analysis of WRKY gene family under drought stress in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). PLoS One, 2020, 15(4): e0231396. [CrossRef]
- Voorrips, R.E. MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; J.J.J.P. GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31(8), 1296–1297. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Tang H, Debarry JD, et al. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(7):e49. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol Plant. 2020, 13(8):1194–1202. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: A Toolkit Incorporating Gamma-Series Methods and Sliding Window Strategies. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics. 2010, 8, 77–80. [CrossRef]
- Clevenger, J., Chu, Y., Scheffler, B., and Ozias-Akins, P. A developmental transcriptome map for allotetraploid Arachis hypogaea. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1446. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Mu, G. Multi-Omics and miRNA Interaction Joint Analysis Highlight New Insights Into Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Peanuts (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022 13:818345. [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Method. Methods. 2001, 25, 402–408. [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Parry, G.; Estelle, M. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and plant development. Plant Cell. 2004, 16(12): 3181-95. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Luo, W.; Li, W.; Chen, N.; Zhang, D.; Chong, K. The F-box protein OsFBK12 targets OsSAMS1 for degradation and affects pleiotropic phenotypes, including leaf senescence, in rice. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163(4):1673-85. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gou, M.; Liu, C.J. Arabidopsis Kelch repeat F-box proteins regulate phenylpropanoid biosynthesis via controlling the turnover of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase. Plant Cell. 2013, 25(12):4994-5010. [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.P.; Lee, C.L.; Chen, P.H.; Wu, S.H.; Yang, C.C.; Shaw, J.F. Molecular analyses of the Arabidopsis TUBBY-like protein gene family. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134(4):1586-97. [CrossRef]
- Swamy, MJ.; Mondal, S. Subunit association, and thermal and chemical unfolding of Cucurbitaceae phloem exudate lectins. A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023, 1; 233: 123434. [CrossRef]
- Dinant, S.; Clark, A.M.; Zhu, Y.; Vilaine, F.; Palauqui, J.C.; Kusiak, C.; Thompson, G.A. Diversity of the superfamily of phloem lectins (phloem protein 2) in angiosperms. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131(1):114-28. [CrossRef]
- DeFalco, T.A.; Anne, P.; James, S.R.; Willoughby, A.C.; Schwanke, F.; Johanndrees, O.; Genolet, Y.; Derbyshire, P.; Wang, Q.; Rana, S.; Pullen, A.M.; Menke, F.L.H.; Zipfel, C.; Hardtke, C.S.; Nimchuk, Z.L. A conserved module regulates receptor kinase signalling in immunity and development. Nat Plants. 2022, 8(4):356-365. [CrossRef]
- Young, N.D.; Debellé, F.; Oldroyd, G.E.; Geurts, R.; Cannon, S.B.; Udvardi, M.K.; Benedito, V.A.; Mayer, K.F.; Gouzy, J.; Schoof, H.; Van, de, Peer, Y.; Proost, S.; Cook, D.R.; Meyers, B.C.; Spannagl, M.; Cheung, F.; De, Mita, S.; Krishnakumar, V.; Gundlach, H.; Zhou, S.; Mudge, J.; Bharti, A.K.; Murray, J.D.; Naoumkina, M.A.; Rosen, B.; Silverstein, K.A.; Tang, H.; Rombauts, S.; Zhao, P.X.; Zhou, P.; Barbe, V.; Bardou, P.; Bechner, M.; Bellec, A.; Berger, A.; Bergès, H.; Bidwell, S.; Bisseling, T.; Choisne, N.; Couloux, A.; Denny, R.; Deshpande, S.; Dai, X.; Doyle, J.J.; Dudez, A.M.; Farmer, A.D.; Fouteau, S.; Franken, C.; Gibelin, C.; Gish, J.; Goldstein, S.; González, A.J.; Green, P.J.; Hallab, A.; Hartog, M.; Hua, A.; Humphray, S.J.; Jeong, D.H.; Jing, Y.; Jöcker, A.; Kenton, S.M.; Kim, D.J.; Klee, K.; Lai, H.; Lang, C.; Lin, S.; Macmil, S.L.; Magdelenat, G.; Matthews, L.; McCorrison, J.; Monaghan, E.L.; Mun, J.H.; Najar, F.Z.; Nicholson, C.; Noirot, C.; O'Bleness, M.; Paule, C.R.; Poulain, J.; Prion, F.; Qin, B.; Qu, C.; Retzel, E.F.; Riddle, C.; Sallet, E.; Samain, S.; Samson, N.; Sanders, I.; Saurat, O.; Scarpelli, C.; Schiex, T.; Segurens, B.; Severin, A.J.; Sherrier, D.J.; Shi, R.; Sims, S.; Singer, S.R.; Sinharoy, S.; Sterck, L.; Viollet, A.; Wang, B.B.; Wang, K.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Warfsmann, J.; Weissenbach, J.; White, D.D.; White, J.D.; Wiley, G.B.; Wincker, P.; Xing, Y.; Yang, L.; Yao, Z.; Ying, F.; Zhai, J.; Zhou, L.; Zuber, A.; Dénarié, J.; Dixon, R.A.; May, G.D.; Schwartz, D.C.; Rogers, J.; Quétier, F.; Town, C.D.; Roe, B.A. The Medicago genome provides insight into the evolution of rhizobial symbioses. Nature. 2011, 480, 520-524. [CrossRef]
- Gilmartin, PM.; Sarokin, L.; Memelink, J.; Chua, N.H. Molecular light switches for plant genes. Plant Cell. 1990, 2(5):369-78. [CrossRef]
- Schindler, U.; Menkens, A.E.; Beckmann, H.; Ecker, J.R.; Cashmore, A.R. Heterodimerization between light-regulated and ubiquitously expressed Arabidopsis GBF bZIP proteins. EMBO J. 1992, 11(4):1261-73. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.L.; Newton, L.; Liu, M.J.; Shiu, S.H.; Farré, E.M. A G-Box-Like Motif Is Necessary for Transcriptional Regulation by Circadian Pseudo-Response Regulators in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170(1):528-39. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xue, S.; He, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Zou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, C.; Fan, Z.; Yue, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, K.; Le, J. Arabidopsis F-BOX STRESS INDUCED 4 is required to repress excessive divisions in stomatal development. J Integr Plant Biol. 2022, 64(1):56-72. [CrossRef]
- Lama, S.; Broda, M.; Abbas, Z.; Vaneechoutte, D.; Belt, K.; Säll, T.; Vandepoele, K.; Van, Aken. O. Neofunctionalization of Mitochondrial Proteins and Incorporation into Signaling Networks in Plants. Mol Biol Evol. 2019, 36(5): 974-989. [CrossRef]
- Schwager, K.M.; Calderon-Villalobos, L.I.; Dohmann, E.M.; Willige, B.C.; Knierer, S.; Nill, C.; Schwechheimer, C. Characterization of the VIER F-BOX PROTEINE genes from Arabidopsis reveals their importance for plant growth and development. Plant Cell. 2007, 19(4):1163-78. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Abrahan, C.; Colquhoun, T.A.; Liu, C.J. A Proteolytic Regulator Controlling Chalcone Synthase Stability and Flavonoid Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2017, 29(5):1157-1174. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




