Submitted:
22 January 2024
Posted:
22 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Single-agent Deep Reinforcement Learning in Traffic Signal Control
2.2. Multi-agent Deep Reinforcement Learning in Traffic Signal Control
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Definition
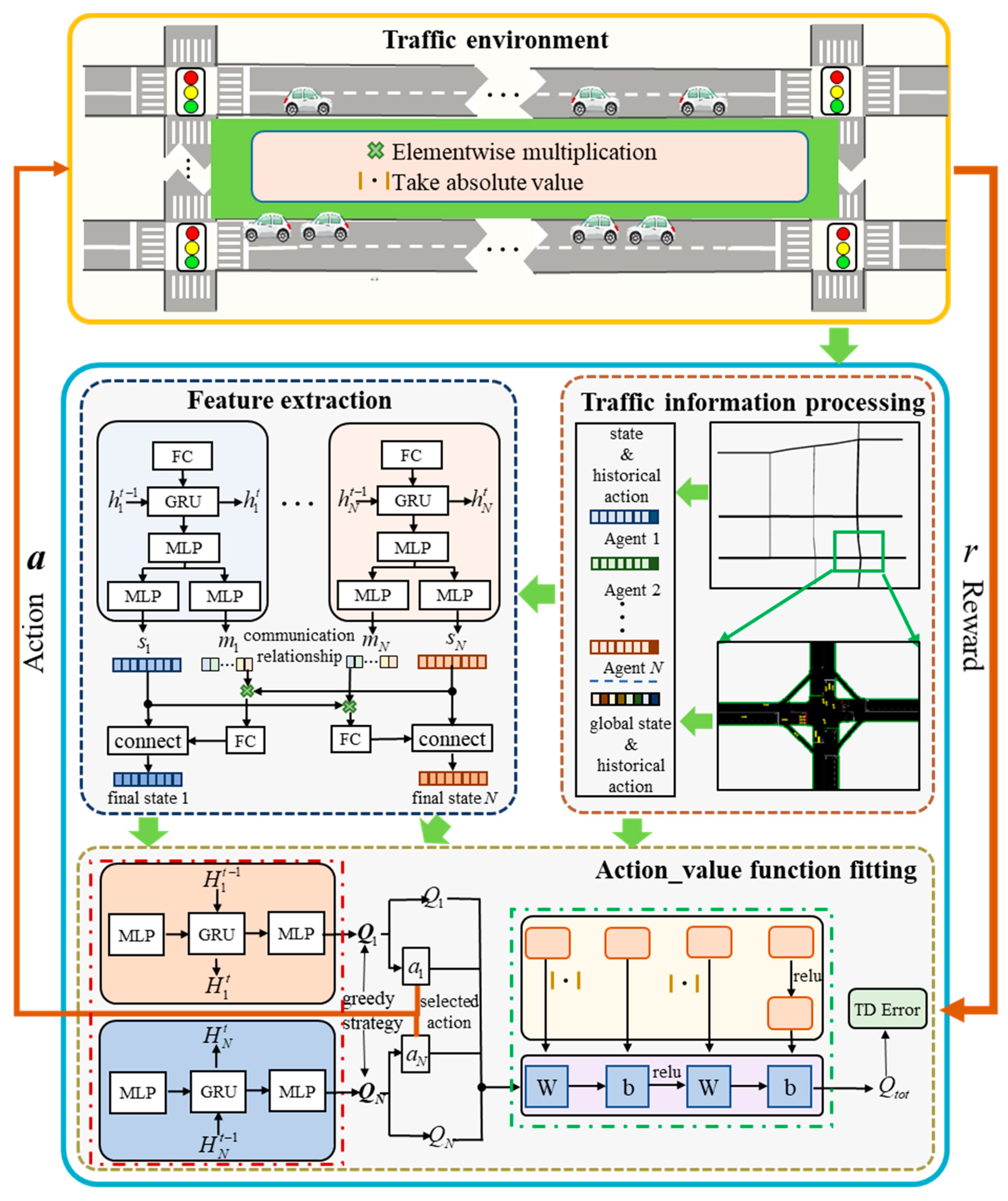
3.2. Model Structure
3.3. Feature Extraction Module
3.4. Action_value Function Fitting Module
- This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
3.5. Model Update

4. Experiments
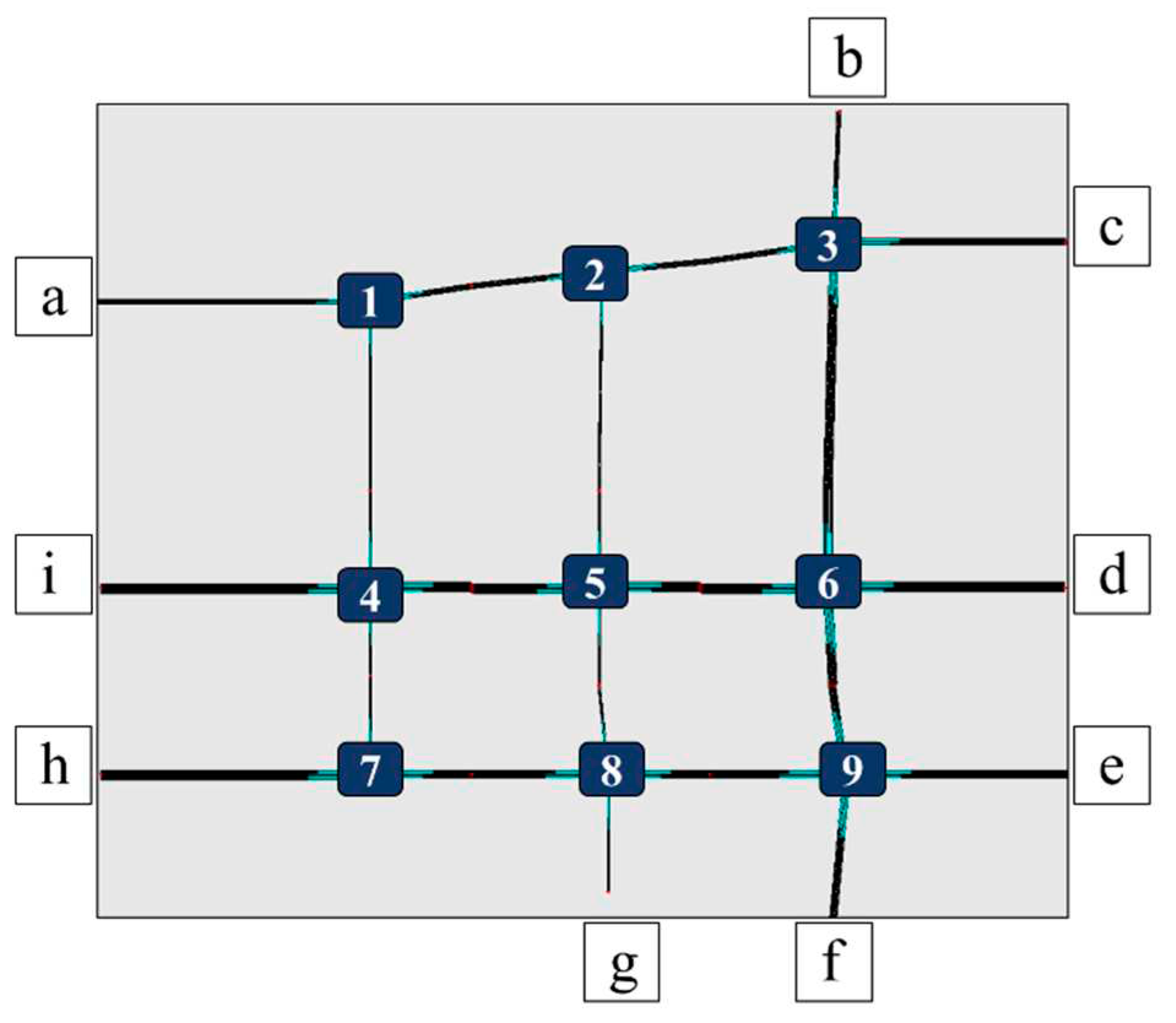
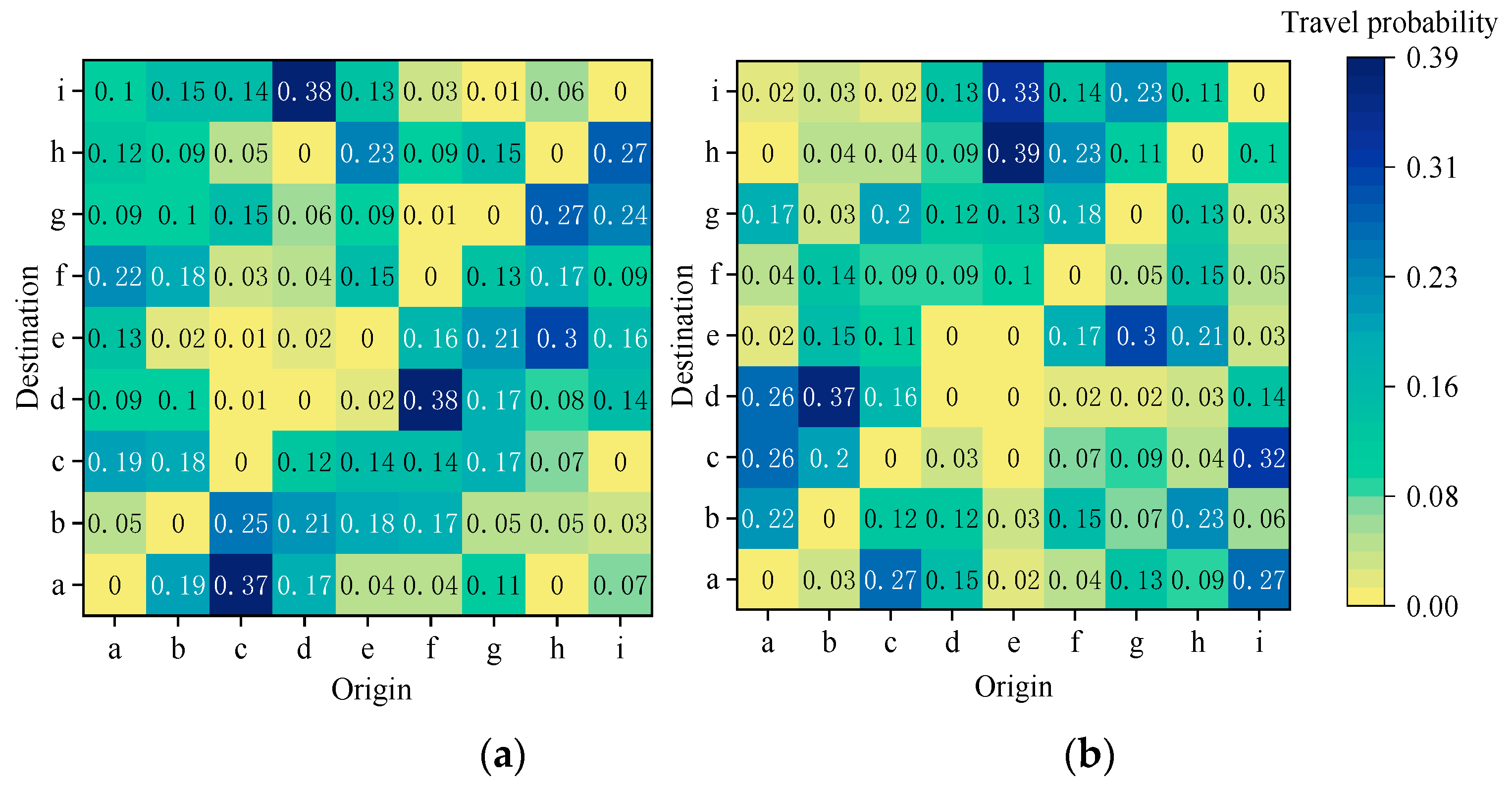
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Simulation Setting
| Stage | Duration (s) | Arrival rate (veh/300s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Max | Min | ||
| Off-peak hours | 0-7200 | 103.55 | 15.15 | 139 | 89 |
| Peak hours | 7200-14400 | 177.20 | 48.92 | 255 | 132 |
4.1.2. Training Parameters Setting
4.1.3. Baseline
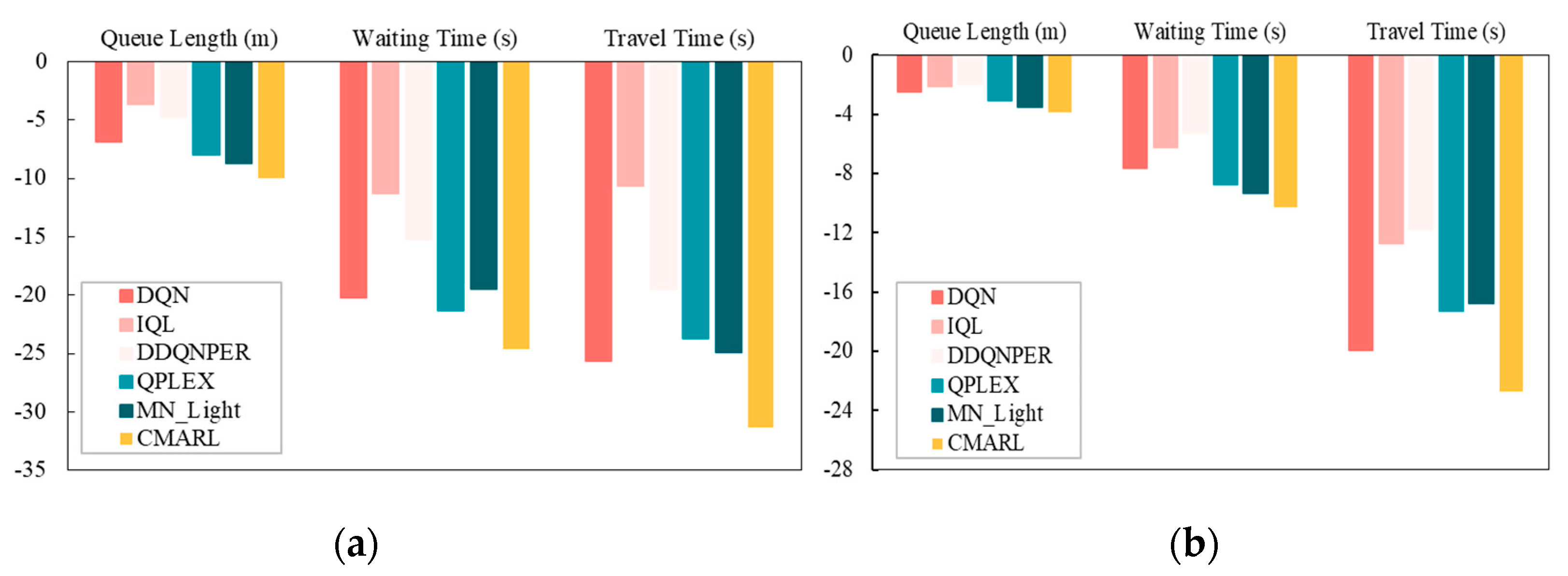
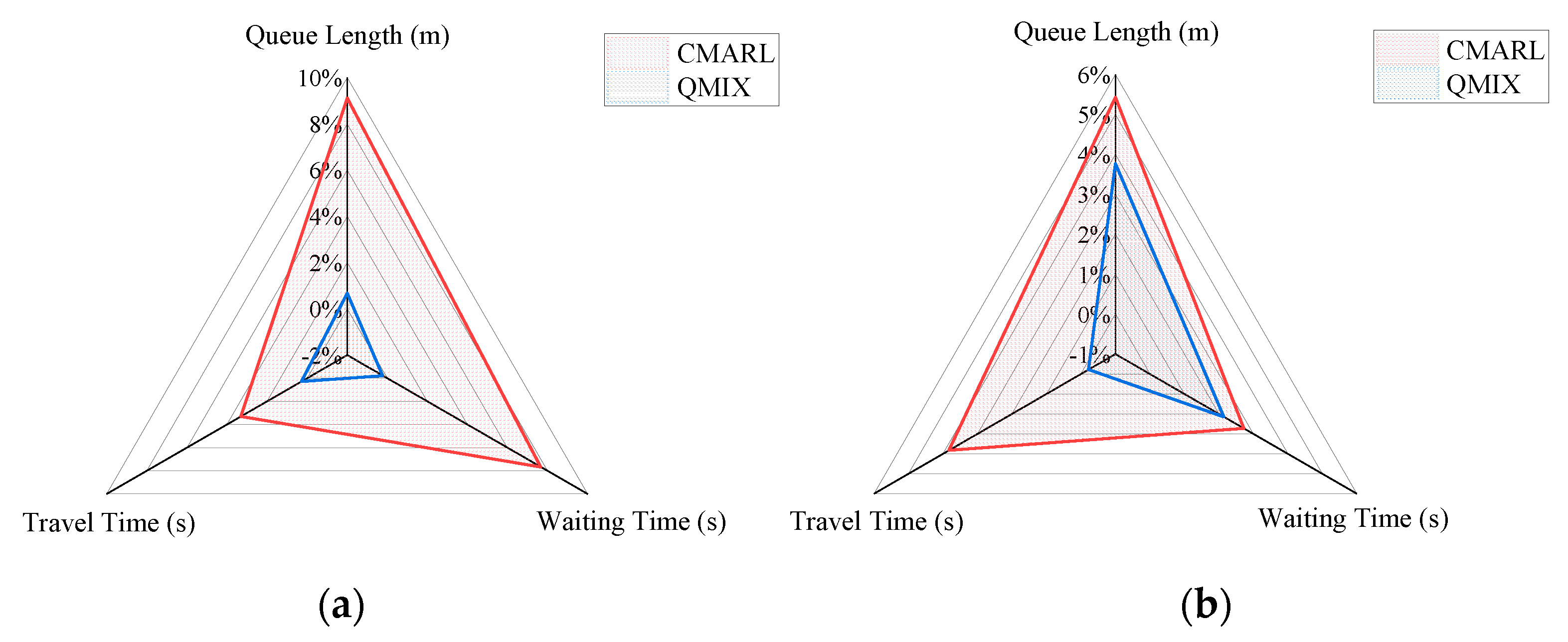
4.2. Experimental Results
4.2.1. Comparative Experiment
4.2.2. Ablation experiment
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
References
- Zhao, D.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, Z. Computational intelligence in urban traffic signal control: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews) 2011, 42, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Wang, H.; Bie, Y.; Wu, J. Double-battery configuration method for electric bus operation in cold regions. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review 2023, 180, 103362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, L. HVAC operation planning for electric bus trips based on chance-constrained programming. Energy 2022, 258, 124807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Li, Z.; Li, L. A comparison of deep reinforcement learning models for isolated traffic signal control. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine 2022, 15, 160–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.; He, J.; Mokbal, F. M. M.; Zhu, N.; Qureshi, S. Ml-lgbm: A machine learning model based on light gradient boosting machine for the detection of version number attacks in rpl-based networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 83654–83665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B. Energy-efficient driving for adaptive traffic signal control environment via explainable reinforcement learning. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, R.; Ye, J.; Qu, X. How machine learning informs ride-hailing services: A survey. Communications in Transportation Research 2022, 2, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Keskin, M. F.; Kulcsár, B.; Wymeersch, H. Connected autonomous vehicles for improving mixed traffic efficiency in unsignalized intersections with deep reinforcement learning. Communications in Transportation Research 2021, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.; LaClair, T. J.; Wang, C.; Shao, Y.; Yuan, J. A Novel Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach to Traffic Signal Control with Connected Vehicles. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Gu, B. Model-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning with Traffic Inference for Traffic Signal Control. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.; Wang, J.; Codecà, L.; Li, Z. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for large-scale traffic signal control. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2019, 21, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cao, J.; Hussain, A. Adaptive Traffic Signal Control for large-scale scenario with Cooperative Group-based Multi-agent reinforcement learning. Transportation research part C: emerging technologies 2021, 125, 103046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannion, P.; Duggan, J.; Howley, E. An experimental review of reinforcement learning algorithms for adaptive traffic signal control. Autonomic road transport support systems 2016, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A. A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M. G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A. K.; Ostrovski, G. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydari, A.; Yılmaz, Y. Deep reinforcement learning for intelligent transportation systems: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2020, 23, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Du, X.; Wang, G.; Han, Z. A deep reinforcement learning network for traffic light cycle control. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2019, 68, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Li, L.; Wu, S.; Lv, P.; Li, Y.; Xu, M. Multi-agent broad reinforcement learning for intelligent traffic light control. Information Sciences 2023, 619, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, M.; Leclercq, L. Leveraging reinforcement learning for dynamic traffic control: A survey and challenges for field implementation. Communications in Transportation Research 2023, 3, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.; Lim, Y. Intelligent traffic signal phase distribution system using deep Q-network. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Wang, C.; Bie, Y. Optimal Traffic Control for a Tandem Intersection With Improved Lane Assignments at Presignals. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lyu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yu, W.; Qu, X. DeepTSP: Deep traffic state prediction model based on large-scale empirical data. Communications in transportation research 2021, 1, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhou, P.; Liu, K.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Wu, D. O. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for urban traffic light control in vehicular networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2020, 69, 8243–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Lei, C.; Chen, Y.; Tan, X. Cooperative Decision-Making for Mixed Traffic at an Unsignalized Intersection Based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kővári, B.; Szőke, L.; Bécsi, T.; Aradi, S.; Gáspár, P. Traffic signal control via reinforcement learning for reducing global vehicle emission. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Gao, K.; Wu, N.; Suganthan, P. N. Scheduling Eight-Phase Urban Traffic Light Problems via Ensemble Meta-Heuristics and Q-Learning Based Local Search. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2023, 24, 14414–14426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayode, I. O.; Tartibu, L. K.; Okwu, M. O.; Severino, A. Comparative traffic flow prediction of a heuristic ANN model and a hybrid ANN-PSO model in the traffic flow modelling of vehicles at a four-way signalized road intersection. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Afzal, M. K.; Ahmad, S.; Mostafa, A. M. Intelligent traffic flow prediction using optimized GRU model. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 100736–100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, L.; Li, M.; Wu, D.; Shi, X.; Ma, C. Meta-learning based spatial-temporal graph attention network for traffic signal control. Knowledge-based systems 2022, 250, 109166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhou, B.; Song, X.; Dai, H. A deep reinforcement learning approach to traffic signal control with temporal traffic pattern mining. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2021, 23, 11789–11800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Ahn, K.; Park, J.; Yeo, H. Transferable traffic signal control: Reinforcement learning with graph centric state representation. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 2021, 130, 103321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhu, L.; Song, K.; Yuan, Z.; Yan, Y.; Tang, Y.; Peng, C. Graph cooperation deep reinforcement learning for ecological urban traffic signal control. Applied Intelligence 2023, 53, 6248–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Di, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, X.; Yang, H. AGNP: Network-wide short-term probabilistic traffic speed prediction and imputation. Communications in Transportation Research 2023, 3, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, T.; Samvelyan, M.; De Witt, C. S.; Farquhar, G.; Foerster, J.; Whiteson, S. Monotonic value function factorisation for deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. The Journal of Machine Learning Research 2020, 21, 7234–7284. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ren, Z.; Liu, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C. Qplex: Duplex dueling multi-agent q-learning. arXiv preprint, arXiv:2008.01062 2020.
- Ji, J.; Bie, Y.; Wang, L. Optimal electric bus fleet scheduling for a route with charging facility sharing. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 2023, 147, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; Hu, K. Adaptive traffic signal control model on intersections based on deep reinforcement learning. Journal of Advanced Transportation 2020, 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Sarvi, M.; Bagloee, S. A.; Nassir, N.; Price, J.; Parineh, H. Intelligent vehicle pedestrian light (IVPL): A deep reinforcement learning approach for traffic signal control. Transportation research part C: emerging technologies 2023, 149, 103991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouktif, S.; Cheniki, A.; Ouni, A. Traffic signal control using hybrid action space deep reinforcement learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducrocq, R.; Farhi, N. Deep reinforcement Q-learning for intelligent traffic signal control with partial detection. International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research 2023, 21, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, G.; Dong, S.; Xu, C.-Z. Network-wide traffic signal control optimization using a multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 2021, 125, 103059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S. Hierarchical graph multi-agent reinforcement learning for traffic signal control. Information Sciences 2023, 634, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiong, G.; Lv, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, B.; Wang, F.-Y. A Collaborative Communication-Qmix Approach for Large-scale Networked Traffic Signal Control. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, USA, 9-22 September 2021; pp. 3450–3455. [Google Scholar]
- Bokade, R.; Jin, X.; Amato, C. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Based on Representational Communication for Large-Scale Traffic Signal Control. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 47646–47658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | 32 | greedy probability | 0.95-0.01 |
| 0.95 | initial learning rate lr | 0.001 | |
| M | 1000 | 16 | |
| K | 200 | 32 | |
| T | 300 | 32 | |
| p | 10 | 64 |
| Model | Peak hours | Off-peak hours | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Queue length (m) | Waiting time (s) | Travel time (s) | Queue length (m) | Waiting time (s) | Travel time (s) | |
| FixedTime | 23.59 | 86.35 | 218.80 | 10.15 | 44.35 | 173.80 |
| DQN | 16.75 | 66.11 | 193.13 | 7.69 | 36.70 | 153.90 |
| IQL | 19.98 | 75.11 | 208.19 | 8.07 | 38.10 | 161.05 |
| DDQNPER | 18.84 | 71.11 | 199.36 | 8.19 | 39.06 | 162.05 |
| QPLEX | 15.62 | 65.04 | 195.05 | 7.09 | 35.65 | 156.49 |
| MN_Light | 14.91 | 66.83 | 193.88 | 6.63 | 35.02 | 157.05 |
| CMARL | 13.55 | 61.71 | 187.47 | 6.27 | 34.06 | 151.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





