Submitted:
19 January 2024
Posted:
22 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related works
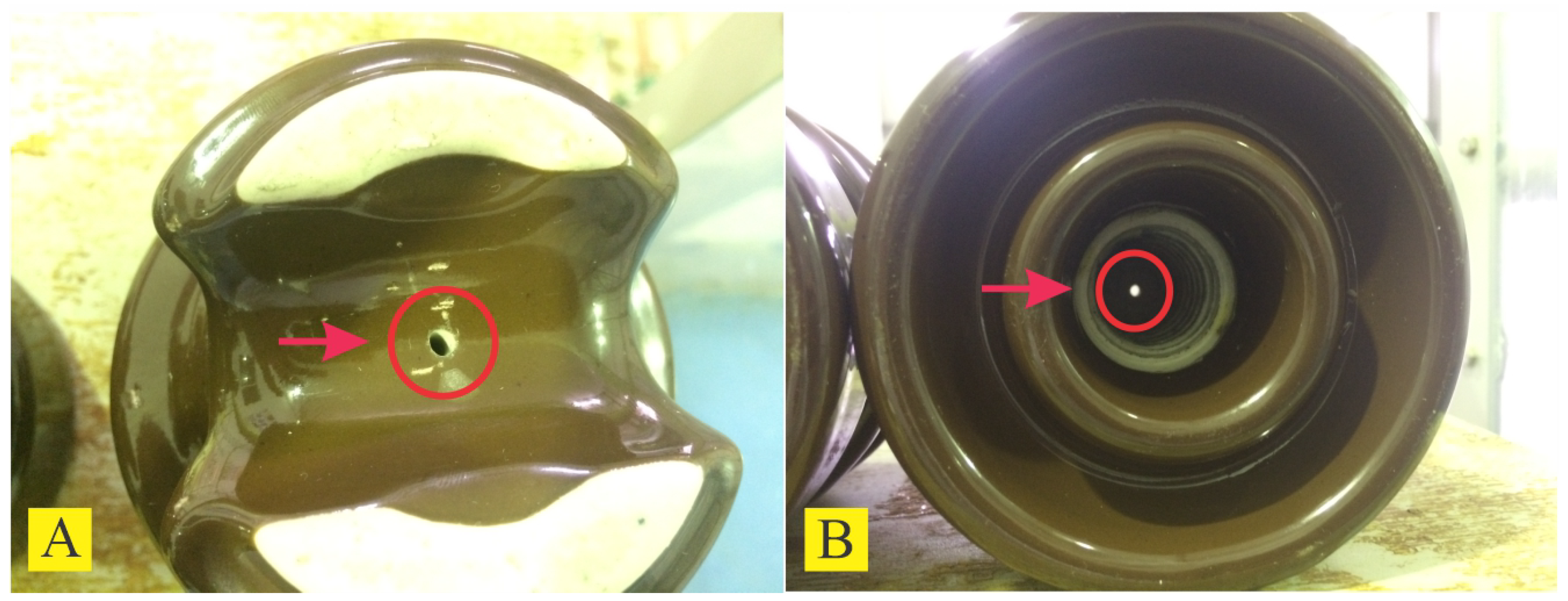
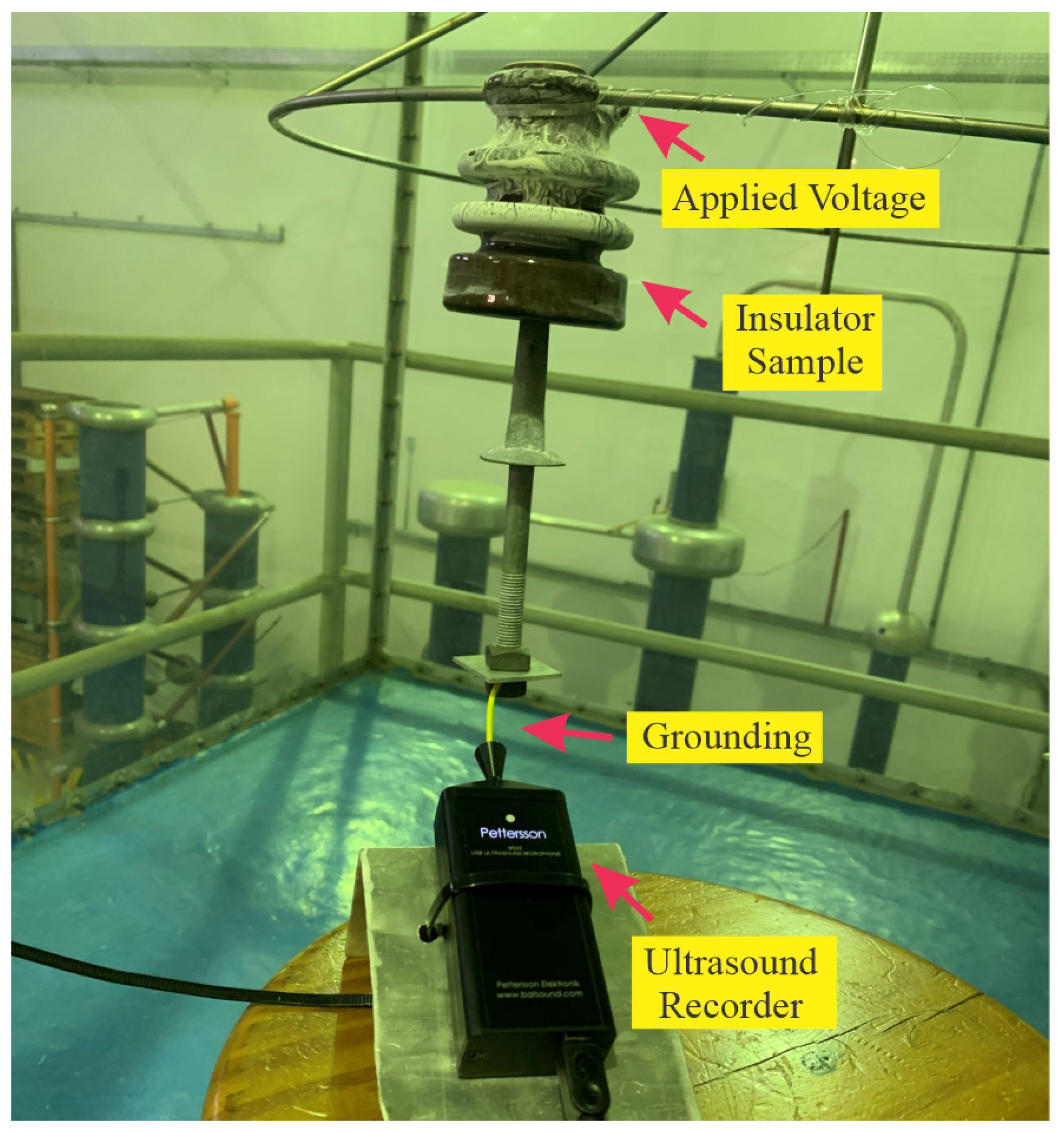
3. Insulators Ultrasound Measurement
4. Methodology
4.1. Empirical Mode Decomposition
| Algorithm 1:EWT |
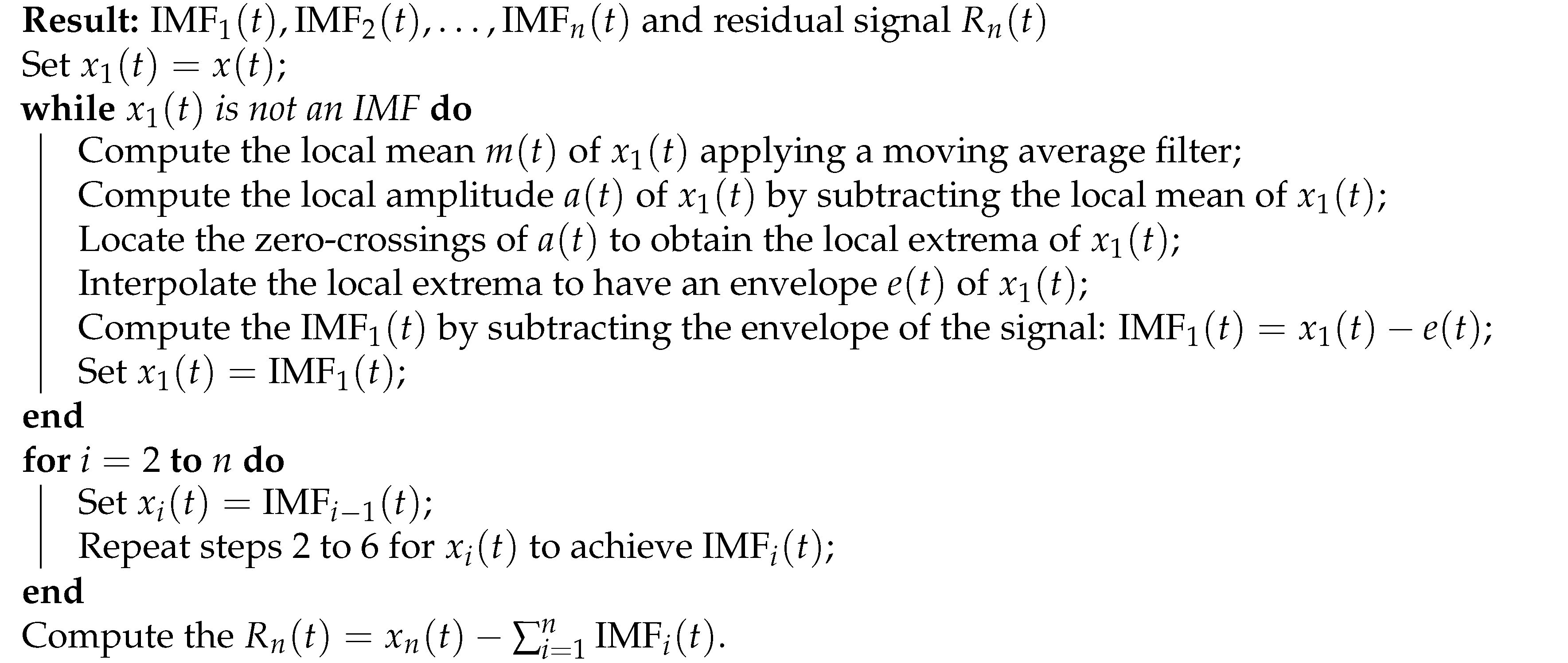 |
4.2. Classification Methods
5. Results
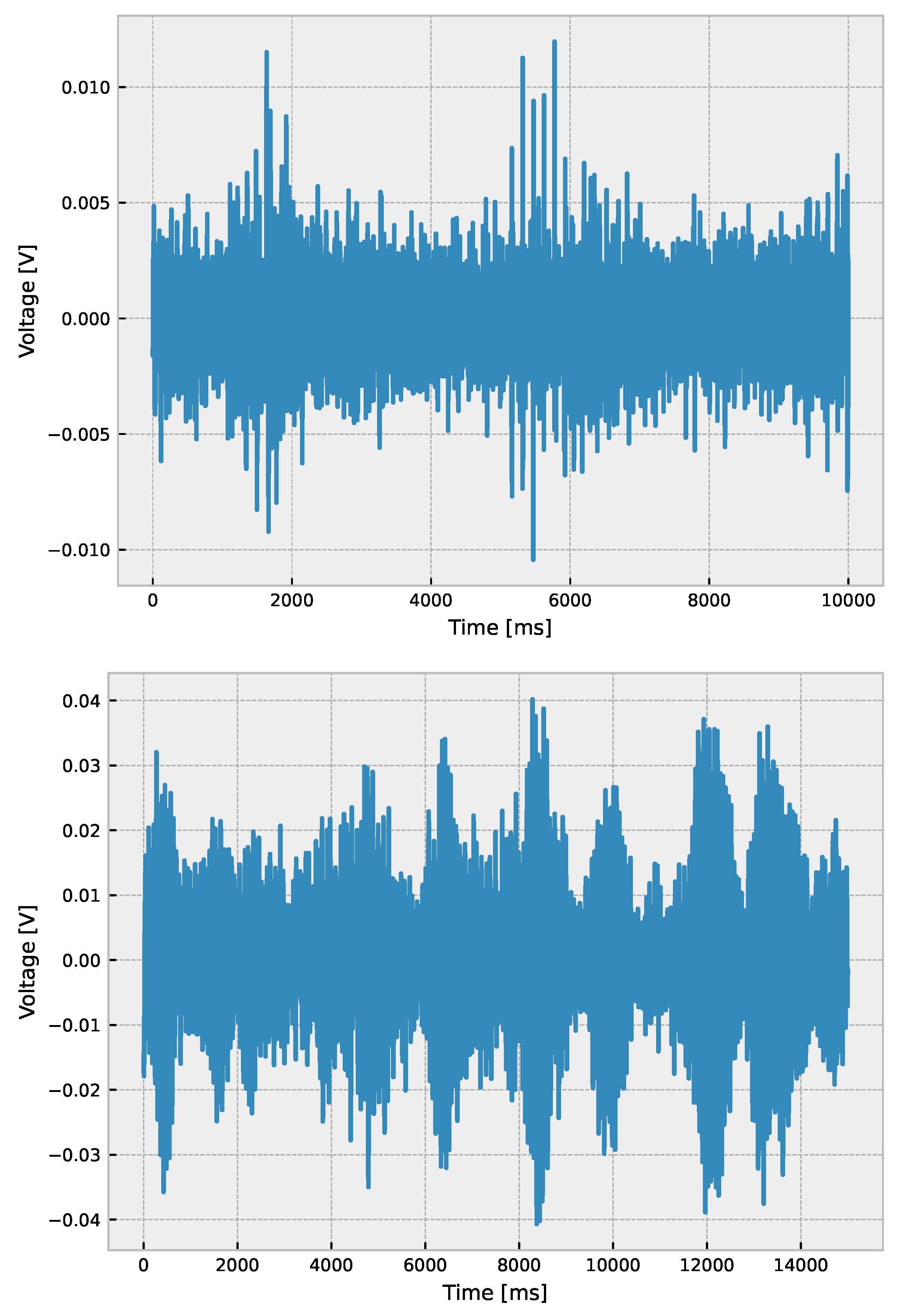
5.1. Empirical Mode Decomposition
5.2. Discussion
- Consider the trade-offs with computational resources and training timeframes carefully when using longer time windows to increase the fault detection models’ accuracy.
- Consider tree-based algorithms for insulator failure detection, such as CatBoost, LightGBM, and gradient boosting, while being cautious of overfitting concerns and using regularization techniques as necessary. To improve the efficiency of linear algorithms and potentially reduce model complexity while retaining high accuracy, use data transforms like Rocket, MiniRocket, or MultiRocket.
- Employ EMD methods to enhance the performance of less complex regression methods by providing a more refined representation of the data and improving fault detection capabilities.
6. Conclusion and future directions of research
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salem, A.A.; Lau, K.Y.; Ishak, M.T.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Al-Gailani, S.A.; Al-Ameri, S.M.; Mohammed, A.; Alashbi, A.A.S.; Ghoneim, S.S.M. Monitoring porcelain insulator condition based on leakage current characteristics. Materials 2022, 15, 6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Dalbah, A.; Abualsaud, A.; Tariq, U.; El-Hag, A. Application of machine learning to evaluate insulator surface erosion. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2020, 69, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Yow, K.C.; Nied, A.; Meyer, L.H. Classification of distribution power grid structures using inception v3 deep neural network. Electrical Engineering 2022, 104, 4557–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Cao, B.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y. On-line monitoring, data analysis for electrolytic corrosion of ±800 kV high voltage direct current insulators. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2021, 131, 107097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilomuanya, C.; Nekahi, A.; Farokhi, S. A study of the cleansing effect of precipitation and wind on polluted outdoor high voltage glass cap and pin insulator. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 20669–20676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Oliveira, J.R.; Coelho, A.S.; Meyer, L.H. Diagnostic of insulators of conventional grid through LabVIEW analysis of FFT signal generated from ultrasound detector. IEEE Latin America Transactions 2017, 15, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corso, M.P.; Stefenon, S.F.; Singh, G.; Matsuo, M.V.; Perez, F.L.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. Evaluation of visible contamination on power grid insulators using convolutional neural networks. Electrical Engineering 2023, 105, 3881–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Seman, L.O.; Sopelsa Neto, N.F.; Meyer, L.H.; Mariani, V.C.; Coelho, L.d.S. Group method of data handling using Christiano-Fitzgerald random walk filter for insulator fault prediction. Sensors 2023, 23, 6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, L.; Liao, R.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L. Nonlinear ultrasonic nondestructive detection and modelling of kissing defects in high voltage composite insulators. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation 2020, 27, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.A.; Lau, K.Y.; Rahiman, W.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Al-Gailani, S.A.; Rahman, R.A.; Al-Ameri, S. Leakage current characteristics in estimating insulator reliability: Experimental investigation and analysis. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 14974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Singh, G.; Souza, B.J.; Freire, R.Z.; Yow, K.C. Optimized hybrid YOLOu-Quasi-ProtoPNet for insulators classification. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution 2023, 17, 3501–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.A.; Lau, K.Y.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Al-Gailani, S.A.; Tan, C.W. Flashover voltage of porcelain insulator under various pollution distributions: Experiment and modeling. Electric Power Systems Research 2022, 208, 107867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanda, A.; Mori, U.; Lozano, J.A. A review on distance based time series classification. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 2019, 33, 378–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faouzi, J. Time series classification: A review of algorithms and implementations. Machine Learning (Emerging Trends and Applications) 2022, 1, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail Fawaz, H.; Forestier, G.; Weber, J.; Idoumghar, L.; Muller, P.A. Deep learning for time series classification: A review. Data mining and knowledge discovery 2019, 33, 917–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.; Petitjean, F.; Webb, G.I. ROCKET: Exceptionally fast and accurate time series classification using random convolutional kernels. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 2020, 34, 1454–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.; Schmidt, D.F.; Webb, G.I. Minirocket: A very fast (almost) deterministic transform for time series classification. Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, 2021, Vol. 27, pp. 248–257. [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Dempster, A.; Bergmeir, C.; Webb, G.I. MultiRocket: Multiple pooling operators and transformations for fast and effective time series classification. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 2022, 36, 1623–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Liu, F.; Cai, R.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ning, M.; Shen, S. Research on seismic signal analysis based on machine learning. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Branco, N.W.; Nied, A.; Bertol, D.W.; Finardi, E.C.; Sartori, A.; Meyer, L.H.; Grebogi, R.B. Analysis of training techniques of ANN for classification of insulators in electrical power systems. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution 2020, 14, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaar, A.C.R.; Stefenon, S.F.; Seman, L.O.; Mariani, V.C.; Coelho, L.d.S. Optimized EWT-Seq2Seq-LSTM with attention mechanism to insulators fault prediction. Sensors 2023, 23, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopelsa Neto, N.F.; Stefenon, S.F.; Meyer, L.H.; Ovejero, R.G.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. Fault prediction based on leakage current in contaminated insulators using enhanced time series forecasting models. Sensors 2022, 22, 6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.; Sartori, A.; Stefenon, S.F.; Meyer, L.H.; Nied, A. Comparison of artificial intelligence techniques to failure prediction in contaminated insulators based on leakage current. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 2022, 42, 3285–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, N.W.; Cavalca, M.S.M.; Stefenon, S.F.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. Wavelet LSTM for fault forecasting in electrical power grids. Sensors 2022, 22, 8323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seman, L.O.; Stefenon, S.F.; Mariani, V.C.; Coelho, L.S. Ensemble learning methods using the Hodrick–Prescott filter for fault forecasting in insulators of the electrical power grids. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2023, 152, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Ribeiro, M.H.D.M.; Nied, A.; Mariani, V.C.; Coelho, L.D.S.; Leithardt, V.R.Q.; Silva, L.A.; Seman, L.O. Hybrid Wavelet Stacking Ensemble Model for Insulators Contamination Forecasting. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 66387–66397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Seman, L.O.; Sopelsa Neto, N.F.; Meyer, L.H.; Nied, A.; Yow, K.C. Echo state network applied for classification of medium voltage insulators. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2022, 134, 107336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.V.; Germano, A.D.; da Costa, E.G. Ultrasound and artificial intelligence applied to the pollution estimation in insulations. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2012, 27, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Freire, R.Z.; Meyer, L.H.; Corso, M.P.; Sartori, A.; Nied, A.; Klaar, A.C.R.; Yow, K.C. Fault detection in insulators based on ultrasonic signal processing using a hybrid deep learning technique. IET Science, Measurement & Technology 2020, 14, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Chatterjee, B.; Chakravorti, S. A novel leakage current index for the field monitoring of overhead insulators under harmonic voltage. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2018, 65, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhouchet, K.; Bayadi, A.; Bendib, M.E. Artificial neural networks (ANN) and genetic algorithm modeling and identification of arc parameter in insulators flashover voltage and leakage current. International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), 2015, Vol. 4, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Bao, Z. Data-based line trip fault prediction in power systems using LSTM networks and SVM. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 7675–7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.; Stefenon, S.F.; Seman, L.O.; Nied, A.; Ferreira, F.C.S.; Subtil, M.C.M.; Klaar, A.C.R.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. Long short-term memory stacking model to predict the number of cases and deaths caused by COVID-19. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 2022, 6, 6221–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Seman, L.O.; Aquino, L.S.; dos Santos Coelho, L. Wavelet-Seq2Seq-LSTM with attention for time series forecasting of level of dams in hydroelectric power plants. Energy 2023, 274, 127350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadykova, D.; Pernebayeva, D.; Bagheri, M.; James, A. IN-YOLO: Real-time detection of outdoor high voltage insulators using UAV imaging. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2020, 35, 1599–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Stefenon, S.F.; Yow, K.C. Interpretable visual transmission lines inspections using pseudo-prototypical part network. Machine Vision and Applications 2023, 34, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, B.J.; Stefenon, S.F.; Singh, G.; Freire, R.Z. Hybrid-YOLO for classification of insulators defects in transmission lines based on UAV. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2023, 148, 108982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prates, R.M.; Cruz, R.; Marotta, A.P.; Ramos, R.P.; Simas Filho, E.F.; Cardoso, J.S. Insulator visual non-conformity detection in overhead power distribution lines using deep learning. Computers & Electrical Engineering 2019, 78, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Singh, G.; Yow, K.C.; Cimatti, A. Semi-ProtoPNet deep neural network for the classification of defective power grid distribution structures. Sensors 2022, 22, 4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polisetty, S.; El-Hag, A.; Jayram, S. Classification of common discharges in outdoor insulation using acoustic signals and artificial neural network. High Voltage 2019, 4, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitiche, I.; Jenkins, M.D.; Boreham, P.; Nesbitt, A.; Morison, G. Deep complex neural network learning for high-voltage insulation fault classification from complex bispectrum representation. European Signal Processing Conference; IEEE,, 2019; Vol. 27, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Dalbah, A.; Abualsaud, A.; Tariq, U.; El-Hag, A. Application of machine learning to evaluate insulator surface erosion. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2020, 69, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santos, H.; Sanz-Bobi, M.A. A machine learning approach for condition monitoring of high voltage insulators in polluted environments. Electric Power Systems Research 2023, 220, 109340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Seman, L.O.; Mariani, V.C.; Coelho, L.S. Aggregating prophet and seasonal trend decomposition for time series forecasting of Italian electricity spot prices. Energies 2023, 16, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Kasburg, C.; Freire, R.Z.; Silva Ferreira, F.C.; Bertol, D.W.; Nied, A. Photovoltaic power forecasting using wavelet neuro-fuzzy for active solar trackers. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 2021, 40, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Kasburg, C.; Nied, A.; Klaar, A.C.R.; Ferreira, F.C.S.; Branco, N.W. Hybrid deep learning for power generation forecasting in active solar trackers. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution 2020, 14, 5667–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Guo, J.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, J.; Fu, W. Quality control for medium voltage insulator via a knowledge-informed SPSA based on historical gradient approximations. Processes 2020, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaar, A.C.R.; Stefenon, S.F.; Seman, L.O.; Mariani, V.C.; Coelho, L.S. Structure optimization of ensemble learning methods and seasonal decomposition approaches to energy price forecasting in Latin America: A case study about Mexico. Energies 2023, 16, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xu, M.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, Z. An insulator in transmission lines recognition and fault detection model based on improved faster RCNN. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2021, 70, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Alam, A.; Kumar, K.V.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, P.; Jaffery, Z.A. Design of thermal imaging-based health condition monitoring and early fault detection technique for porcelain insulators using Machine learning. Environmental Technology & Innovation 2021, 24, 102000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z. Uncertainty-aware accurate insulator fault detection based on an improved YOLOX model. Energy Reports 2022, 8, 12809–12821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantach, S.; Lutfi, A.; Moradi Tavasani, H.; Ashraf, A.; El-Hag, A.; Kordi, B. Deep learning in high voltage engineering: A literature review. Energies 2022, 15, 5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhenhua, L.; Ziyi, C.; Xingxin, C.; Xu, Y. Insulator fouling monitoring based on acoustic signal and one-dimensional convolutional neural network. Frontiers in Energy Research 2023, 10, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Yeh, C.T.; Cho, M.Y.; Chang, C.L.; Chen, M.J. Convolutional neural network bidirectional long short-term memory to online classify the distribution insulator leakage currents. Electric Power Systems Research 2022, 208, 107923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, P.N.; Cho, M.Y. Online leakage current classification using convolutional neural network long short-term memory for high voltage insulators on web-based service. Electric Power Systems Research 2023, 216, 109065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, B.; Asaithambi, P.; Raman, A.A.A.; Ibrahim, S. Hybrid nero-fuzzy methods for estimation of ultrasound and mechanically stirring Influences on biodiesel synthesis through transesterification. Measurement 2017, 103, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, P.; Greco, A.; Conversano, F.; Renna, M.D.; Casciaro, E.; Quarta, L.; Costanza, D.; Muratore, M.; Casciaro, S. A quantitative ultrasound approach to estimate bone fragility: A first comparison with dual X-ray absorptiometry. Measurement 2017, 101, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, P.; Conversano, F.; Chiriacò, F.; Quarta, E.; Quarta, L.; Muratore, M.; Lay-Ekuakille, A.; Casciaro, S. Estimation of femoral neck bone mineral density by ultrasound scanning: Preliminary results and feasibility. Measurement 2016, 94, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, A.; Pisani, P.; Conversano, F.; Soloperto, G.; Renna, M.D.; Muratore, M.; Casciaro, S. Ultrasound fragility Score: An innovative approach for the assessment of bone fragility. Measurement 2017, 101, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Furtado Neto, C.S.; Coelho, T.S.; Nied, A.; Yamaguchi, C.K.; Yow, K.C. Particle swarm optimization for design of insulators of distribution power system based on finite element method. Electrical Engineering 2022, 104, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Americo, J.P.; Meyer, L.H.; Grebogi, R.B.; Nied, A. Analysis of the electric field in porcelain pin-type insulators via finite elements software. IEEE Latin America Transactions 2018, 16, 2505–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopelsa Neto, N.F.; Stefenon, S.F.; Meyer, L.H.; Bruns, R.; Nied, A.; Seman, L.O.; Gonzalez, G.V.; Leithardt, V.R.Q.; Yow, K.C. A study of multilayer perceptron networks applied to classification of ceramic insulators using ultrasound. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Bruns, R.; Sartori, A.; Meyer, L.H.; Ovejero, R.G.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. Analysis of the ultrasonic signal in polymeric contaminated insulators through ensemble learning methods. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 33980–33991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Seman, L.O.; Pavan, B.A.; Ovejero, R.G.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. Optimal design of electrical power distribution grid spacers using finite element method. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution 2022, 16, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Corso, M.P.; Nied, A.; Perez, F.L.; Yow, K.C.; Gonzalez, G.V.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. Classification of insulators using neural network based on computer vision. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution 2021, 16, 1096–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefenon, S.F.; Silva, M.C.; Bertol, D.W.; Meyer, L.H.; Nied, A. Fault diagnosis of insulators from ultrasound detection using neural networks. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 2019, 37, 6655–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlehurst, M.; Large, J.; Flynn, M.; Lines, J.; Bostrom, A.; Bagnall, A. HIVE-COTE 2.0: A new meta ensemble for time series classification. Machine Learning 2021, 110, 3211–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantiskas, L.; Verstoep, K.; Hoogendoorn, M.; Bal, H. Taking ROCKET on an efficiency mission: Multivariate time series classification with LightWaveS. International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems (DCOSS), 2022, Vol. 18, pp. 149–152. [CrossRef]
- Bondugula, R.K.; Udgata, S.K.; Sivangi, K.B. A novel deep learning architecture and MINIROCKET feature extraction method for human activity recognition using ECG, PPG and inertial sensor dataset. Applied Intelligence 2022, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangarajoo, R.G.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Srivastava, G.; Haque, F.; Ali, S.H.M.; Bakar, A.A.A.; Bhuiyan, M.A.S. Machine learning-based epileptic seizure detection methods using wavelet and EMD-based decomposition techniques: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Pan, Z. A new method based CEEMDAN for removal of baseline wander and powerline interference in ECG signals. Optik 2020, 223, 165566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuragi, A.; Sisodia, D.S.; Pachori, R.B. Epileptic-seizure classification using phase-space representation of FBSE-EWT based EEG sub-band signals and ensemble learners. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2022, 71, 103138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Xiao, D.; Li, X. Gear fault diagnosis based on genetic mutation particle swarm optimization VMD and probabilistic neural network algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 18456–18474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.R.; Al-Badrawi, M.H.; Kirsch, N.J. An Optimized De-Noising Scheme Based on the Null Hypothesis of Intrinsic Mode Functions. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 2019, 26, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Su, P. Fault diagnosis of shipboard medium-voltage DC power system based on machine learning. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2021, 124, 106399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, M.; Freire, R.Z.; Seman, L.O.; Stefenon, S.F.; Mariani, V.C.; dos Santos Coelho, L. Optimized hybrid ensemble learning approaches applied to very short-term load forecasting. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2024, 155, 109579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Wei, X.; Gao, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y. Fault location of flexible grounding distribution system based on multivariate modes and kurtosis calibration. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2023, 150, 109108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, D.; Gong, Z.; Jin, T.; Mohamed, M.A. Adaptive spectral trend based optimized EWT for monitoring the parameters of multiple power quality disturbances. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2023, 146, 108797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ding, X.; Zhou, W.; Ding, R. A hybrid electricity price forecasting model with Bayesian optimization for German energy exchange. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2019, 110, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Ma, N.; Qu, M. Bi-level decision matrix based fault location method for multi-branch offshore wind farm transmission lines. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2022, 141, 108137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.S.; Assis, F.A.; Leite da Silva, A.M.; Coelho, A.J.; Moura, R.A.; Schroeder, M.A.O. Reliability evaluation of composite generation and transmission systems via binary logistic regression and parallel processing. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2022, 142, 108380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerl, A.E.; Kennard, R.W. Ridge regression: Biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics 1970, 12, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Mohanty, S.; Swetapadma, A.; Kumar Nayak, P.; Malik, O.P. Decision tree approach for fault detection in a TCSC compensated line during power swing. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2023, 146, 108758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mallick, P.K.; Tripathy, H.K.; Bhoi, A.K.; González-Briones, A. Performance evaluation of a proposed machine learning model for chronic disease datasets using an integrated attribute evaluator and an improved decision tree classifier. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripoppoom, S.; Ma, X.; Yong, R.; Wu, J.; Yu, W.; Sepehrnoori, K.; Miao, J.; Li, N. Assisted history matching in shale gas well using multiple-proxy-based Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm: The comparison of K-nearest neighbors and neural networks as proxy model. Fuel 2020, 262, 116563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zong, M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, R. Efficient k-NN classification With different numbers of nearest neighbors. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2018, 29, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corso, M.P.; Perez, F.L.; Stefenon, S.F.; Yow, K.C.; García Ovejero, R.; Leithardt, V.R.Q. Classification of contaminated insulators using k-nearest neighbors based on computer vision. Computers 2021, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, L.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. Automated detection of Parkinson’s disease based on multiple types of sustained phonations using linear discriminant analysis and genetically optimized neural network. IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachitra, S.; Prasanth, A. Multi-feature analysis for automated brain stroke classification using weighted Gaussian naïve Bayes classifier. Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers 2021, 30, 2150178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, A.; Küçüker, A.; Bayrak, G.; Ertekin, D.; Shafie-Khah, M.; Guerrero, J.M. An improved automated PQD classification method for distributed generators with hybrid SVM-based approach using un-decimated wavelet transform. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2022, 136, 107763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, S. Ensemble decision trees for high impedance fault detection in power distribution network. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2012, 43, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.I.; Islam, N.; Uddin, J.; Islam, S.; Nasir, M.K. Water quality prediction and classification based on principal component regression and gradient boosting classifier approach. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences 2022, 34, 4773–4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Wei, R.; Huang, Y.; Li, X. Damage prediction of 10 kV power towers in distribution network under typhoon disaster based on data-driven model. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2022, 142, 108307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Y.; Yu, J. Prediction of user outage under typhoon disaster based on multi-algorithm Stacking integration. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2021, 131, 107123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; Shouxiang, W.; Qianyu, Z.; Shaomin, W.; Liwei, F. A multi-energy load prediction model based on deep multi-task learning and ensemble approach for regional integrated energy systems. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2021, 126, 106583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Yin, C.; Wan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y. Recognition of diseased Pinus trees in UAV images using deep learning and AdaBoost classifier. Biosystems Engineering 2020, 194, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, C. Detecting travel modes Using rule-based classification system and Gaussian process classifier. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 116741–116752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining; ACM: New York, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Huang, Y.; Lehane, B.; Ma, G. XGBoost algorithm-based prediction of concrete electrical resistivity for structural health monitoring. Automation in Construction 2020, 114, 103155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Xiao, J.W.; Wang, Y.W. A machine learning-based detection framework against intermittent electricity theft attack. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2023, 150, 109075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; Vanderplas, J.; Passos, A.; Cournapeau, D.; Brucher, M.; Perrot, M.; Duchesnay, E. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
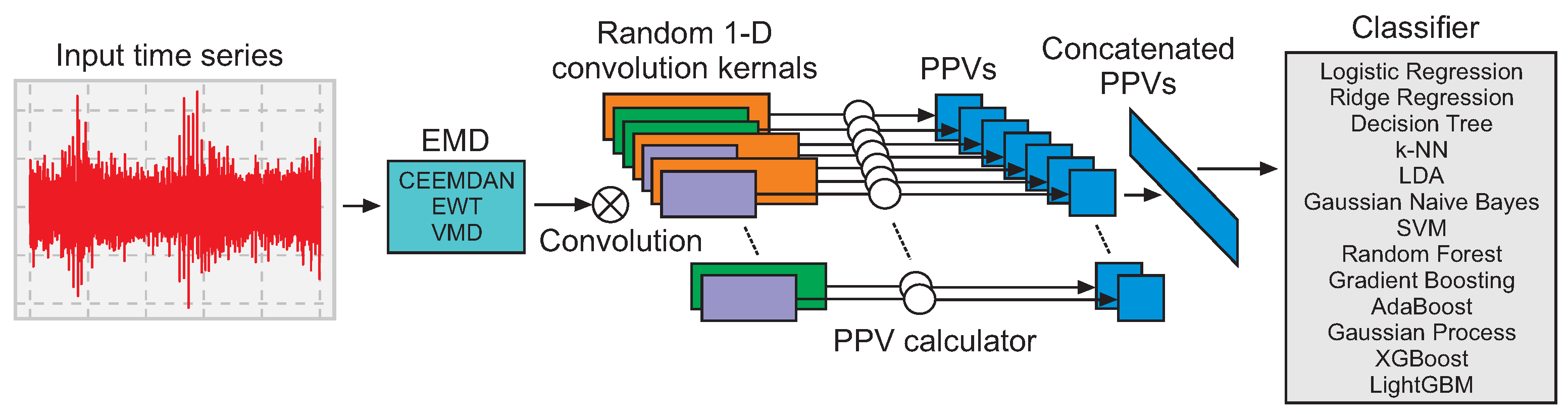
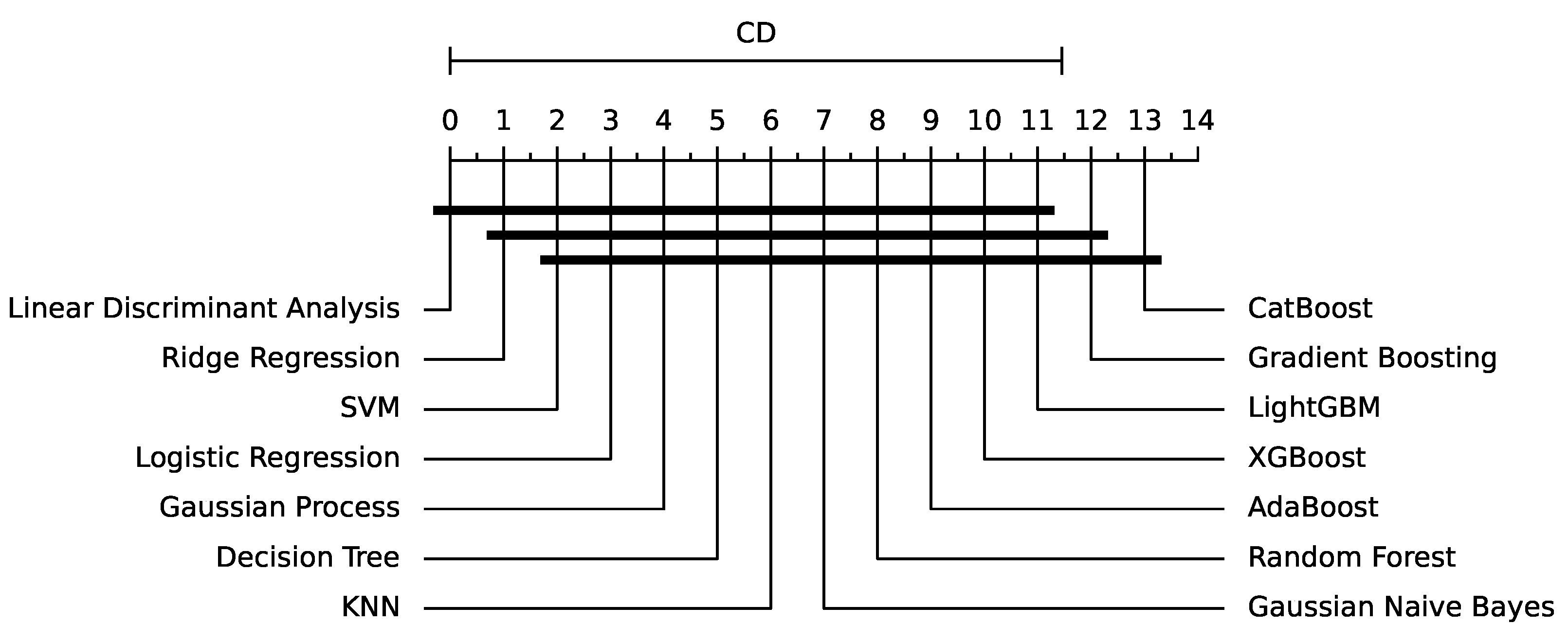
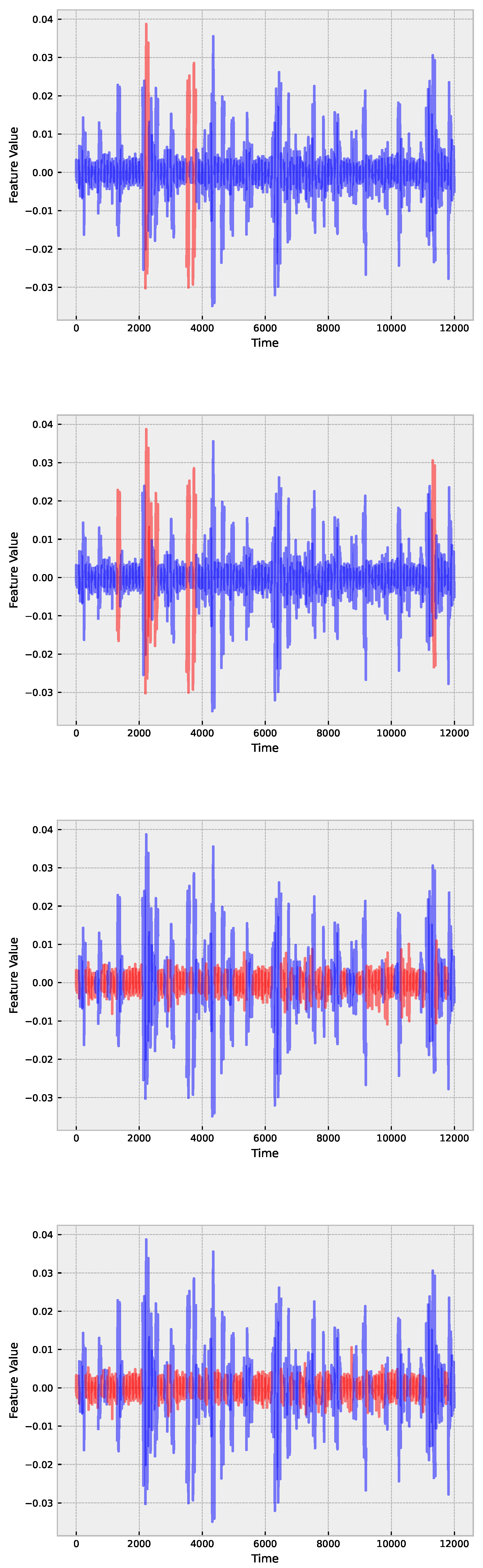
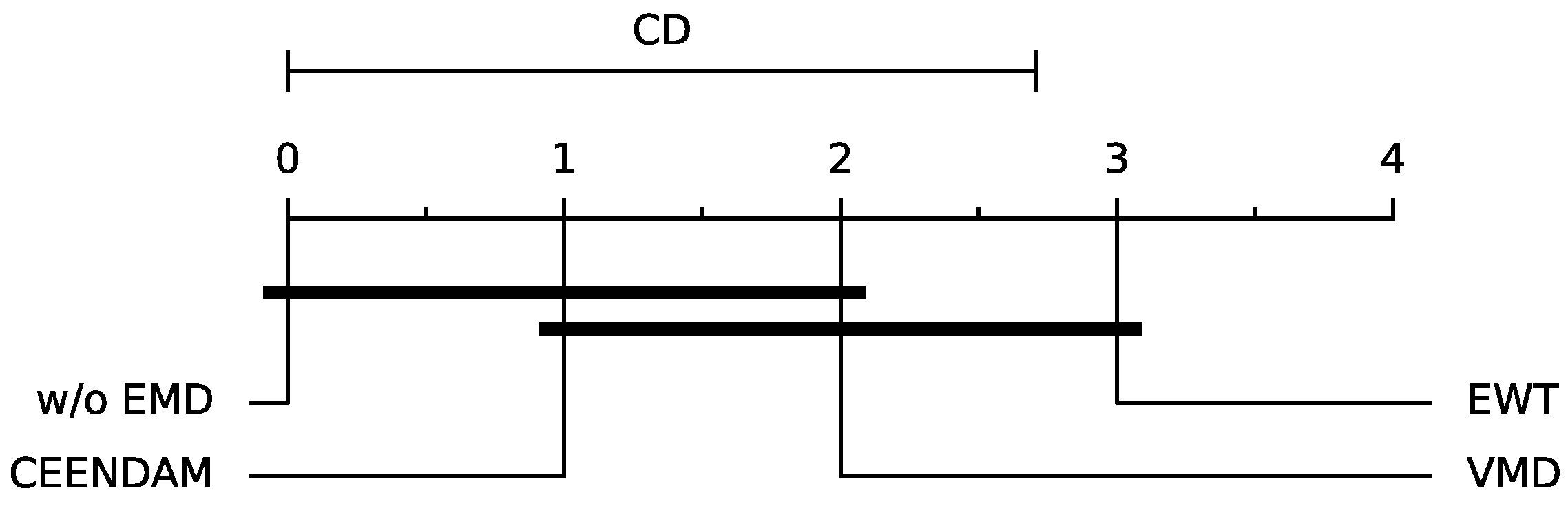
| Model | WS10 | WS50 | WS100 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 0.5193 ± 0.0395 | 0.5167 ± 0.0325 | 0.5683 ± 0.0436 |
| Ridge Regression | 0.4923 ± 0.0134 | 0.5158 ± 0.0308 | 0.58 ± 0.041 |
| Decision Tree | 0.849 ± 0.0832 | 0.8658 ± 0.0789 | 0.8283 ± 0.0759 |
| k-NN | 0.8762 ± 0.0713 | 0.9025 ± 0.0748 | 0.85 ± 0.1182 |
| LDA | 0.4858 ± 0.0147 | 0.495 ± 0.0286 | 0.525 ± 0.0247 |
| Gaussian Naive Bayes | 0.8428 ± 0.0927 | 0.9133 ± 0.0746 | 0.9283 ± 0.0586 |
| SVM | 0.5343 ± 0.0379 | 0.5283 ± 0.0263 | 0.53 ± 0.0306 |
| Random Forest | 0.8672 ± 0.0815 | 0.9225 ± 0.0621 | 0.925 ± 0.0548 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.8792± 0.0694 | 0.9433± 0.0439 | 0.9433 ± 0.0464 |
| AdaBoost | 0.8693 ± 0.07 | 0.9258 ± 0.0504 | 0.9317 ± 0.0593 |
| Gaussian Process | 0.6085 ± 0.0811 | 0.6342 ± 0.0564 | 0.615 ± 0.0883 |
| XGBoost | 0.8753 ± 0.0691 | 0.9417 ± 0.0484 | 0.935 ± 0.0539 |
| LightGBM | 0.8732 ± 0.0695 | 0.94 ± 0.0467 | 0.95± 0.0431 |
| Model | Rocket | MiniRocket | MultiRocket |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 0.7552 ± 0.0353 | 0.8453 ± 0.068 | 0.8465 ± 0.06 |
| Ridge Regression | 0.6762 ± 0.0462 | 0.7943 ± 0.0518 | 0.8068 ± 0.0447 |
| Decision Tree | 0.7427 ± 0.0617 | 0.8635 ± 0.0687 | 0.8687 ± 0.064 |
| k-NN | 0.7375 ± 0.0387 | 0.8488 ± 0.0729 | 0.8623 ± 0.0676 |
| LDA | 0.6048 ± 0.0635 | 0.7832 ± 0.0421 | D.N.C. * |
| Gaussian Naive Bayes | 0.7615 ± 0.0515 | 0.8253 ± 0.0926 | 0.8342 ± 0.0894 |
| SVM | 0.6968 ± 0.0438 | 0.8257 ± 0.0647 | 0.8413 ± 0.0583 |
| Random Forest | 0.762 ± 0.0553 | 0.8788 ± 0.0659 | 0.882 ± 0.0676 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.7735 ± 0.0543 | 0.8837± 0.0655 | 0.8873± 0.0632 |
| AdaBoost | 0.7452 ± 0.0544 | 0.8678 ± 0.0695 | 0.8715 ± 0.0639 |
| XGBoost | 0.7623 ± 0.0472 | 0.8785 ± 0.0687 | 0.8823 ± 0.0638 |
| LightGBM | 0.7713 ± 0.0482 | 0.8832 ± 0.067 | 0.8873± 0.0622 |
| Model | Rocket | MiniRocket | MultiRocket |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 0.955± 0.0395 | 0.955± 0.0395 | 0.955 ± 0.0384 |
| Ridge Regression | 0.9533 ± 0.036 | 0.9533 ± 0.036 | 0.9508 ± 0.0389 |
| Decision Tree | 0.9258 ± 0.0551 | 0.9342 ± 0.0468 | 0.9367 ± 0.0511 |
| k-NN | 0.9483 ± 0.0427 | 0.9483 ± 0.0427 | 0.9433 ± 0.043 |
| LDA | 0.9533 ± 0.0361 | 0.9533 ± 0.0361 | 0.9492 ± 0.0418 |
| Gaussian Naive Bayes | 0.9308 ± 0.0491 | 0.9308 ± 0.0491 | 0.9283 ± 0.0502 |
| SVM | 0.9525 ± 0.0398 | 0.9525 ± 0.0398 | 0.9525 ± 0.0368 |
| Random Forest | 0.9483 ± 0.0459 | 0.9508 ± 0.0461 | 0.9483 ± 0.0402 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.9517 ± 0.042 | 0.9483 ± 0.0452 | 0.9492 ± 0.0414 |
| AdaBoost | 0.9475 ± 0.0416 | 0.9475 ± 0.0416 | 0.955 ± 0.0349 |
| Gaussian Process | 0.9367 ± 0.0509 | 0.9367 ± 0.0509 | D.N.C. * |
| XGBoost | 0.9475 ± 0.044 | 0.9475 ± 0.044 | 0.9575 ± 0.0339 |
| LightGBM | 0.9542 ± 0.0365 | 0.9542 ± 0.0365 | 0.9592± 0.0309 |
| Model | Rocket | MiniRocket | MultiRocket |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 0.9783± 0.0194 | 0.9783± 0.0194 | 0.9733 ± 0.0249 |
| Ridge Regression | 0.9767 ± 0.0193 | 0.9767 ± 0.0193 | 0.9717 ± 0.034 |
| Decision Tree | 0.9633 ± 0.0323 | 0.9667 ± 0.0316 | 0.97 ± 0.0282 |
| k-NN | 0.9567 ± 0.037 | 0.9567 ± 0.037 | 0.9683 ± 0.0309 |
| LDA | 0.97 ± 0.0261 | 0.97 ± 0.0261 | 0.975 ± 0.0247 |
| Gaussian Naive Bayes | 0.945 ± 0.0515 | 0.945 ± 0.0515 | 0.9483 ± 0.0392 |
| SVM | 0.9783 ± 0.018 | 0.9783± 0.018 | 0.9717 ± 0.0277 |
| Random Forest | 0.9717 ± 0.0314 | 0.9767 ± 0.0244 | 0.9733 ± 0.0309 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.9683 ± 0.0271 | 0.97 ± 0.0251 | 0.9717 ± 0.0245 |
| AdaBoost | 0.9783± 0.0201 | 0.9733 ± 0.0295 | 0.965 ± 0.0399 |
| Gaussian Process | 0.96 ± 0.0363 | 0.96 ± 0.0363 | D.N.C. * |
| XGBoost | 0.9767 ± 0.0249 | 0.9767 ± 0.0249 | 0.975± 0.0228 |
| LightGBM | 0.9767 ± 0.022 | 0.9767 ± 0.022 | 0.965 ± 0.0429 |
| Accuracy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Window Size | W/o EMB | EWT | CEENDAM | VMD |
| 10 | ||||
| 50 | ||||
| 100 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





