Submitted:
18 January 2024
Posted:
19 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. The mode of delivery and microbiota transfer
3.1. The mode of delivery and microbiota transmission
3.2. Changes in gut microflora in autism
4. Mode of delivery and autism correlation
5. Microbiota disruption and its potential implications for ASD development
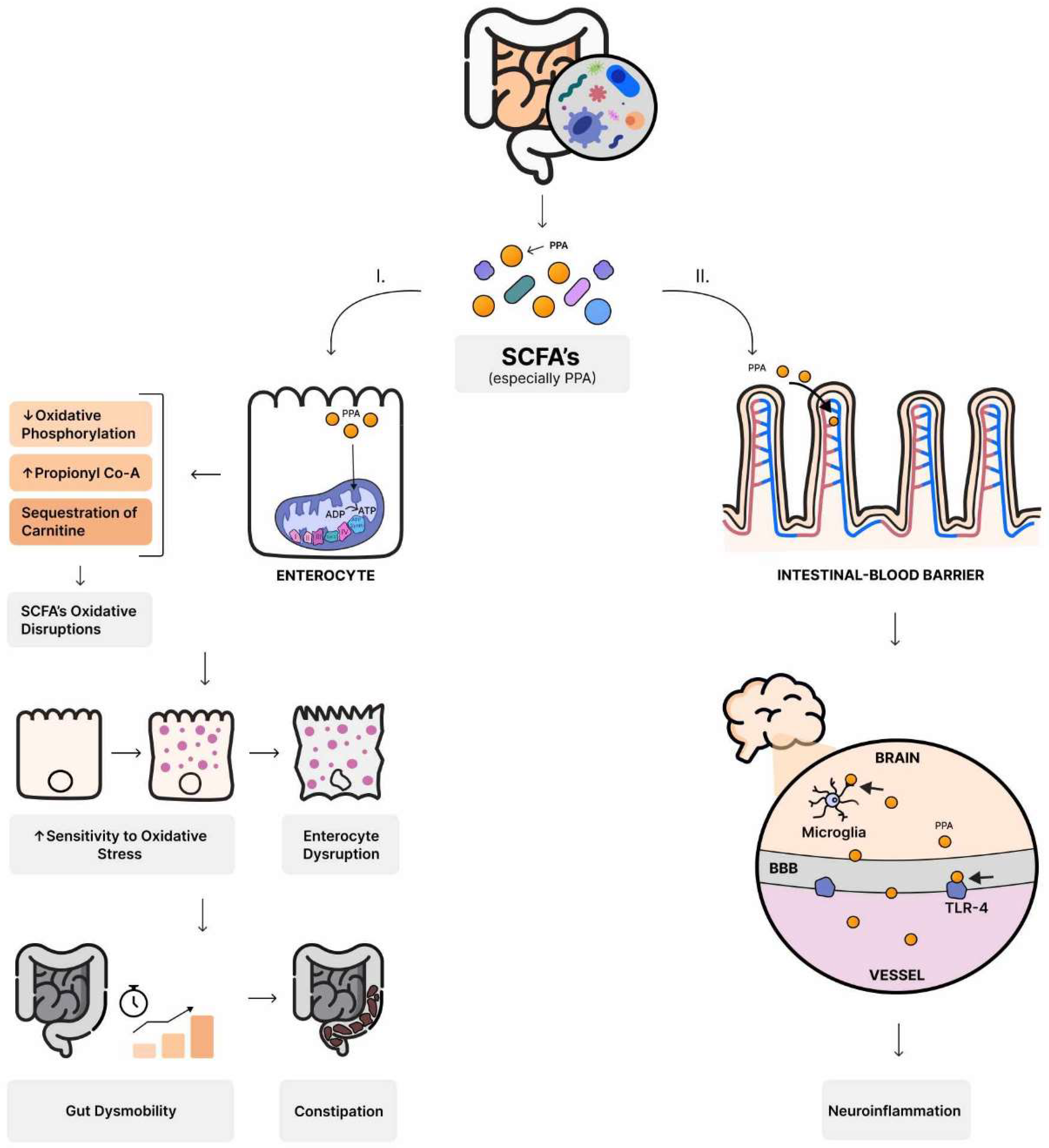
5.1. Bacteria as producers of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)
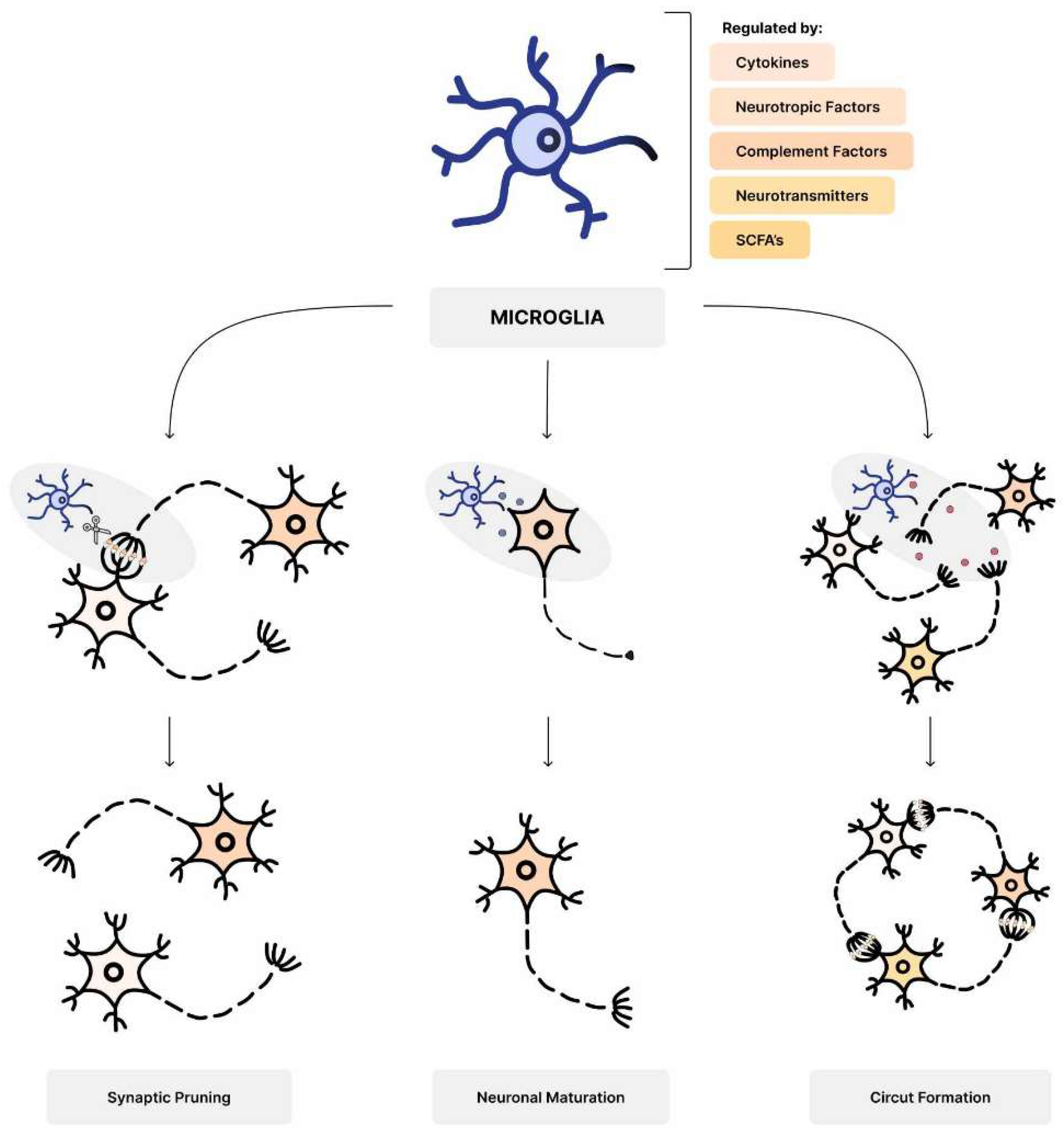
5.2. Microglia dysregulation
6. The gut-brain axis in ASD patients
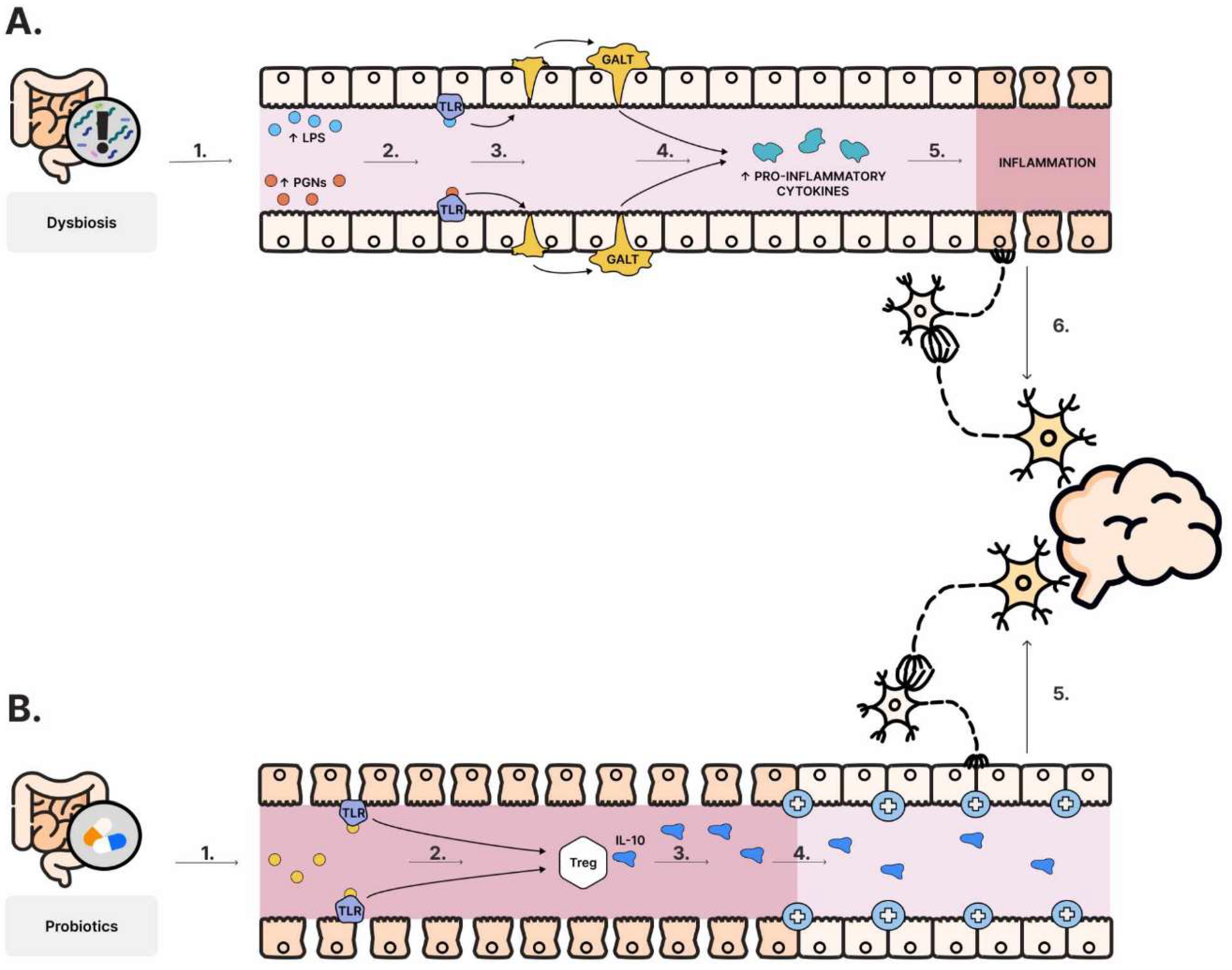
6.1. ’’Leaky gut’’ in ASD
6.2. Enteroendocrine cells and neurotransmiters
6.3. HPA axis
6.4. GALT
7. Gastrointestinal challenges in ASD patients
7.1. Gastrointestinal symptoms in ASD
7.2. Malnutrition
7.3. Gastrointestinal diseases
7.5. Conclusion
8. Maternal microbiome dysregulation
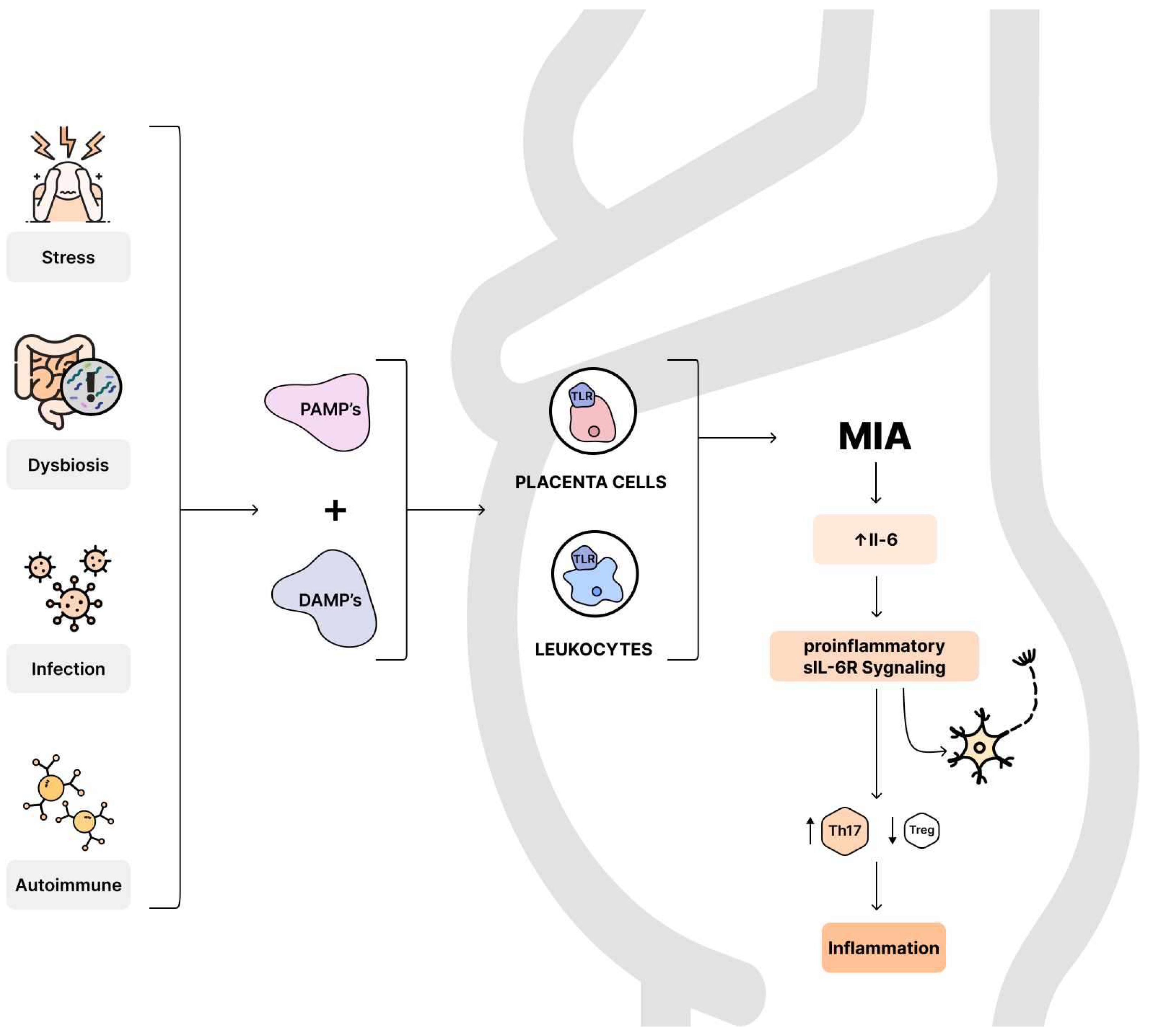
8.1. Maternal immune activation
8.2. MIA and cytokines
8.3. IL-6
8.4. IL-17a
8.5. Cytokine imbalance in ASD
8.6. Gender differences
9. MIA and microbiome dysregulation
9.1. MIA and impaired intestinal integrity
9.2. Gut microflora and MIA
10. Obesity and high-fat diet
10.1. Mother’s obesity and ASD
10.2. Maternal high-fat diet (MHFD)
11. Therapeutic targets
11.1. Probiotisc and prebiotisc
11.2. Antibiotics
11.3. Microbiota Transfer Therapy (MTT)
11.4. Enzymes
11.5. Helminth therapy
11.6. Maternal therapeutic targets
12. Limitations
13. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, C.C.; Lin, L.S.; Long, S.; Ke, X.Y.; Fukunaga, K.; Lu, Y.M.; Han, F. Signalling pathways in autism spectrum disorder: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Sun, M. Autism Spectrum Disorder: Neurodevelopmental Risk Factors, Biological Mechanism, and Precision Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settanni, C.R.; Bibbò, S.; Ianiro, G.; Rinninella, E.; Cintoni, M.; Mele, M.C.; Cammarota, G.; Gasbarrini, A. Gastrointestinal involvement of autism spectrum disorder: focus on gut microbiota. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 599–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saurman, V.; Margolis, K.G.; Luna, R.A. Autism Spectrum Disorder as a Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis Disorder. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, G. When microbe meets human. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gordon, J.I. Honor thy symbionts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10452–10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fang, H.; Li, C.; Wu, G.; Xu, T.; Yang, X.; Zhao, L.; Ke, X.; Zhang, C. Gut Bacteria Shared by Children and Their Mothers Associate with Developmental Level and Social Deficits in Autism Spectrum Disorder. mSphere 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesa, M.D.; Loureiro, B.; Iglesia, I.; Fernandez Gonzalez, S.; Llurba Olivé, E.; García Algar, O.; Solana, M.J.; Cabero Perez, M.J.; Sainz, T.; Martinez, L.; et al. The Evolving Microbiome from Pregnancy to Early Infancy: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, M.D.; Graham, A.M.; Feczko, E.; Miranda-Dominguez, O.; Rasmussen, J.M.; Nardos, R.; Entringer, S.; Wadhwa, P.D.; Buss, C.; Fair, D.A. Maternal IL-6 during pregnancy can be estimated from newborn brain connectivity and predicts future working memory in offspring. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, M.L.; McAllister, A.K. Maternal immune activation: Implications for neuropsychiatric disorders. Science 2016, 353, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.B.; Yim, Y.S.; Wong, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.V.; Hoeffer, C.A.; Littman, D.R.; Huh, J.R. The maternal interleukin-17a pathway in mice promotes autism-like phenotypes in offspring. Science 2016, 351, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; van Jaarsveld, C.H.M.; Llewellyn, C.H.; Fildes, A.; López Sánchez, G.F.; Wardle, J.; Fisher, A. Genetic and Environmental Influences on Developmental Milestones and Movement: Results From the Gemini Cohort Study. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport. 2017, 88, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Shah, Y.A.; Hussain, M.; Rabail, R.; Socol, C.T.; Hassoun, A.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Rusu, A.V.; et al. Human gut microbiota in health and disease: Unveiling the relationship. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 999001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.Y.; Chan, Y.L.; Tsai, M.H.; Wang, C.J.; Chiang, M.H.; Chiu, C.C. Gut microbial dysbiosis is associated with allergen-specific IgE responses in young children with airway allergies. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019, 12, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyté Sjödin, K.; Hammarström, M.L.; Rydén, P.; Sjödin, A.; Hernell, O.; Engstrand, L.; West, C.E. Temporal and long-term gut microbiota variation in allergic disease: A prospective study from infancy to school age. Allergy 2019, 74, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averina, O.V.; Zorkina, Y.A.; Yunes, R.A.; Kovtun, A.S.; Ushakova, V.M.; Morozova, A.Y.; Kostyuk, G.P.; Danilenko, V.N.; Chekhonin, V.P. Bacterial Metabolites of Human Gut Microbiota Correlating with Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, K.; Nakajima, S.; Kurokawa, S.; Barceló-Soler, A.; Ikuse, D.; Hirata, A.; Yoshizawa, A.; Tomizawa, Y.; Salas-Valero, M.; Noda, Y.; et al. Gut microbiota and major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 266, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, C.A.; Diaz-Arteche, C.; Eliby, D.; Schwartz, O.S.; Simmons, J.G.; Cowan, C.S.M. The gut microbiota in anxiety and depression - A systematic review. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 83, 101943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Ju, P.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z.; Yao, L.; Zheng, M.; Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Yu, T.; Xia, Q.; et al. Intricate role of intestinal microbe and metabolite in schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.; Żebrowska-Różańska, P.; Karpiński, P.; Kujawa, D.; Łaczmański, Ł.; Samochowiec, J.; Chęć, M.; Piotrowski, P.; Misiak, B. Profiling gut microbiota signatures associated with the deficit subtype of schizophrenia: Findings from a case-control study. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 127, 110834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, L.; Cantoni, C.; Rotondo, E.; Galimberti, D. The Gut Microbiome-Brain Crosstalk in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Gong, X.; Hu, B.; Lin, L.; Lin, X.; Gong, W.; Zhang, B.; Cao, M.; Xu, Y.; Xia, R.; et al. Altered Gut Microbiota and Short-chain Fatty Acids in Chinese Children with Constipated Autism Spectrum Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Costello, E.K.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11971–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aagaard, K.; Ma, J.; Antony, K.M.; Ganu, R.; Petrosino, J.; Versalovic, J. The placenta harbors a unique microbiome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 237ra265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onderdonk, A.B.; Delaney, M.L.; DuBois, A.M.; Allred, E.N.; Leviton, A.; Investigators, E.L.G.A.N.E.S. Detection of bacteria in placental tissues obtained from extremely low gestational age neonates. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 198, 110.e111-117. [CrossRef]
- Steel, J.H.; Malatos, S.; Kennea, N.; Edwards, A.D.; Miles, L.; Duggan, P.; Reynolds, P.R.; Feldman, R.G.; Sullivan, M.H. Bacteria and inflammatory cells in fetal membranes do not always cause preterm labor. Pediatr. Res. 2005, 57, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widström, A.M.; Brimdyr, K.; Svensson, K.; Cadwell, K.; Nissen, E. Skin-to-skin contact the first hour after birth, underlying implications and clinical practice. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 108, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, K.; Moossavi, S.; Sbihi, H.; Boutin, R.C.T.; Bode, L.; Robertson, B.; Yonemitsu, C.; Field, C.J.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; et al. Breastmilk Feeding Practices Are Associated with the Co-Occurrence of Bacteria in Mothers’ Milk and the Infant Gut: the CHILD Cohort Study. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 285–297.e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdeau-Julien, I.; Castonguay-Paradis, S.; Rochefort, G.; Perron, J.; Lamarche, B.; Flamand, N.; Di Marzo, V.; Veilleux, A.; Raymond, F. The diet rapidly and differentially affects the gut microbiota and host lipid mediators in a healthy population. Microbiome 2023, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubourg, G.; Lagier, J.C.; Robert, C.; Armougom, F.; Hugon, P.; Metidji, S.; Dione, N.; Dangui, N.P.; Pfleiderer, A.; Abrahao, J.; et al. Culturomics and pyrosequencing evidence of the reduction in gut microbiota diversity in patients with broad-spectrum antibiotics. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, H.M.; Konya, T.; Takaro, T.K.; Brook, J.R.; Chari, R.; Field, C.J.; Guttman, D.S.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; et al. Exposure to household furry pets influences the gut microbiota of infant at 3-4 months following various birth scenarios. Microbiome 2017, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; Erez-Granat, O.; Braun, T.; Sosnovski, K.; Hadar, R.; BenShoshan, M.; Heiman, S.; Abbas-Egbariya, H.; Glick Saar, E.; Efroni, G.; et al. Gut microbiome development in early childhood is affected by day care attendance. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedermann, L.; Zeitz, J.; Mwinyi, J.; Sutter-Minder, E.; Rehman, A.; Ott, S.J.; Steurer-Stey, C.; Frei, A.; Frei, P.; Scharl, M.; et al. Smoking cessation induces profound changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota in humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyman, M.; van Houten, M.A.; van Baarle, D.; Bosch, A.A.T.M.; Man, W.H.; Chu, M.L.J.N.; Arp, K.; Watson, R.L.; Sanders, E.A.M.; Fuentes, S.; et al. Impact of delivery mode-associated gut microbiota dynamics on health in the first year of life. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Forster, S.C.; Tsaliki, E.; Vervier, K.; Strang, A.; Simpson, N.; Kumar, N.; Stares, M.D.; Rodger, A.; Brocklehurst, P.; et al. Stunted microbiota and opportunistic pathogen colonization in caesarean-section birth. Nature 2019, 574, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wampach, L.; Heintz-Buschart, A.; Fritz, J.V.; Ramiro-Garcia, J.; Habier, J.; Herold, M.; Narayanasamy, S.; Kaysen, A.; Hogan, A.H.; Bindl, L.; et al. Birth mode is associated with earliest strain-conferred gut microbiome functions and immunostimulatory potential. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.M.; Ma, J.; Prince, A.L.; Antony, K.M.; Seferovic, M.D.; Aagaard, K.M. Maturation of the infant microbiome community structure and function across multiple body sites and in relation to mode of delivery. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya-Williams, D.; Lemas, D.J.; Spiryda, L.; Patel, K.; Carney, O.O.; Neu, J.; Carson, T.L. The Neonatal Microbiome and Its Partial Role in Mediating the Association between Birth by Cesarean Section and Adverse Pediatric Outcomes. Neonatology 2018, 114, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, H.E.; Abrahamsson, T.R.; Jenmalm, M.C.; Harris, K.; Quince, C.; Jernberg, C.; Björkstén, B.; Engstrand, L.; Andersson, A.F. Decreased gut microbiota diversity, delayed Bacteroidetes colonisation and reduced Th1 responses in infants delivered by caesarean section. Gut 2014, 63, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.J.; Lynch, D.B.; Murphy, K.; Ulaszewska, M.; Jeffery, I.B.; O’Shea, C.A.; Watkins, C.; Dempsey, E.; Mattivi, F.; Tuohy, K.; et al. Evolution of gut microbiota composition from birth to 24 weeks in the INFANTMET Cohort. Microbiome 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.H. Functional brain development in humans. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulikkan, J.; Maji, A.; Dhakan, D.B.; Saxena, R.; Mohan, B.; Anto, M.M.; Agarwal, N.; Grace, T.; Sharma, V.K. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis in Indian Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 76, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Vázquez, L.; Van Ginkel Riba, G.; Arija, V.; Canals, J. Composition of Gut Microbiota in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parracho, H.M.; Bingham, M.O.; Gibson, G.R.; McCartney, A.L. Differences between the gut microflora of children with autistic spectrum disorders and that of healthy children. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristori, M.V.; Quagliariello, A.; Reddel, S.; Ianiro, G.; Vicari, S.; Gasbarrini, A.; Putignani, L. Autism, Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Nutritional Interventions. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.S.; Zheng, L.J.; Rowehl, L.M.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Litcher-Kelly, L.; Gadow, K.D.; Gathungu, G.; Robertson, C.E.; et al. Comparison of Fecal Microbiota in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders and Neurotypical Siblings in the Simons Simplex Collection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuele, E.; Orsi, P.; Boso, M.; Broglia, D.; Brondino, N.; Barale, F.; di Nemi, S.U.; Politi, P. Low-grade endotoxemia in patients with severe autism. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 471, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomova, A.; Husarova, V.; Lakatosova, S.; Bakos, J.; Vlkova, B.; Babinska, K.; Ostatnikova, D. Gastrointestinal microbiota in children with autism in Slovakia. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 138, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M.; Piccolo, M.; Vannini, L.; Siragusa, S.; De Giacomo, A.; Serrazzanetti, D.I.; Cristofori, F.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Gobbetti, M.; Francavilla, R. Fecal microbiota and metabolome of children with autism and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, F.; Liu, Y.; Rhoads, J.M. Can probiotics benefit children with autism spectrum disorders? World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 10093–10102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Góralczyk-Bińkowska, A.; Szmajda-Krygier, D.; Kozłowska, E. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovene, M.R.; Bombace, F.; Maresca, R.; Sapone, A.; Iardino, P.; Picardi, A.; Marotta, R.; Schiraldi, C.; Siniscalco, D.; Serra, N.; et al. Intestinal Dysbiosis and Yeast Isolation in Stool of Subjects with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Mycopathologia 2017, 182, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikantha, P.; Mohajeri, M.H. The Possible Role of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain-Axis in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socała, K.; Doboszewska, U.; Szopa, A.; Serefko, A.; Włodarczyk, M.; Zielińska, A.; Poleszak, E.; Fichna, J.; Wlaź, P. The role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 172, 105840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarcioglu, A.S.; Kiraz, N.; Aydin, A. Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: Yeast Species Isolated from Stool Samples of Children with Suspected or Diagnosed Autism Spectrum Disorders and In Vitro Susceptibility Against Nystatin and Fluconazole. Mycopathologia 2016, 181, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, B.H.K.; Leonard, H.; Stock, S.; Stoltenberg, C.; Francis, R.W.; Gissler, M.; Gross, R.; Schendel, D.; Sandin, S. Caesarean section and risk of autism across gestational age: a multi-national cohort study of 5 million births. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zalabani, A.H.; Al-Jabree, A.H.; Zeidan, Z.A. Is cesarean section delivery associated with autism spectrum disorder? Neurosciences (Riyadh) 2019, 24, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.Y.; Teitler, J.O.; Rajananda, S.; Chegwin, V.; Bearman, P.S.; Hegyi, T.; Reichman, N.E. Elective Deliveries and the Risk of Autism. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2022, 63, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huberman Samuel, M.; Meiri, G.; Dinstein, I.; Flusser, H.; Michaelovski, A.; Bashiri, A.; Menashe, I. Exposure to General Anesthesia May Contribute to the Association between Cesarean Delivery and Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 3127–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, L.N.; Lin, H.C.; Shao, Y.H.; Chiou, S.T.; Chiou, H.Y. Risk of autism associated with general anesthesia during cesarean delivery: a population-based birth-cohort analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2015, 45, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, J.; Lu, X.; Xun, G.; Wu, R.; Li, Y.; Ou, J.; Shen, Y.; Xia, K.; Zhao, J. Anesthesia, sex and miscarriage history may influence the association between cesarean delivery and autism spectrum disorder. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.P.; Lee, J.R.; Lee, C.S.; Deng, M.; Loepke, A.W. Do anesthetics harm the developing human brain? An integrative analysis of animal and human studies. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2017, 60, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, D.; Barone, S. Critical periods of vulnerability for the developing nervous system: evidence from humans and animal models. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108 Suppl. 3, 511–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, E.A.; Dalman, C.; Kearney, P.M.; Kenny, L.C.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Khashan, A.S. Association Between Obstetric Mode of Delivery and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Population-Based Sibling Design Study. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A. Gut feelings: the emerging biology of gut-brain communication. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, B.; Engevik, M.A.; Ganesh, B.P.; Lackey, E.P.; Lin, T.; Balderas, M.; Major, A.; Runge, J.; Luna, R.A.; Sillitoe, R.V.; et al. Bifidobacteria shape host neural circuits during postnatal development by promoting synapse formation and microglial function. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascale, A.; Marchesi, N.; Marelli, C.; Coppola, A.; Luzi, L.; Govoni, S.; Giustina, A.; Gazzaruso, C. Microbiota and metabolic diseases. Endocrine 2018, 61, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Knauf, C. How gut microbes talk to organs: The role of endocrine and nervous routes. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boets, E.; Gomand, S.V.; Deroover, L.; Preston, T.; Vermeulen, K.; De Preter, V.; Hamer, H.M.; Van den Mooter, G.; De Vuyst, L.; Courtin, C.M.; et al. Systemic availability and metabolism of colonic-derived short-chain fatty acids in healthy subjects: a stable isotope study. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFabe, D.F. Enteric short-chain fatty acids: microbial messengers of metabolism, mitochondria, and mind: implications in autism spectrum disorders. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 28177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, S.; Bennuri, S.C.; Murray, K.F.; Buie, T.; Winter, H.; Frye, R.E. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the gastrointestinal mucosa of children with autism: A blinded case-control study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFabe, D.F.; Cain, D.P.; Rodriguez-Capote, K.; Franklin, A.E.; Hoffman, J.E.; Boon, F.; Taylor, A.R.; Kavaliers, M.; Ossenkopp, K.P. Neurobiological effects of intraventricular propionic acid in rats: possible role of short chain fatty acids on the pathogenesis and characteristics of autism spectrum disorders. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 176, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.E.; Rose, S.; Slattery, J.; MacFabe, D.F. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in autism spectrum disorder: the role of the mitochondria and the enteric microbiome. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 27458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeel, W.A.; Meguid, N.A.; Bjørklund, G.; Eid, E.M.; Farid, M.; Mohamed, S.K.; Wakeel, K.E.; Chirumbolo, S.; Elsaeid, A.; Hammad, D.Y. Impact of Clostridium Bacteria in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder and Their Anthropometric Measurements. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 70, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argou-Cardozo, I.; Zeidán-Chuliá, F. Clostridium Bacteria and Autism Spectrum Conditions: A Systematic Review and Hypothetical Contribution of Environmental Glyphosate Levels. Med. Sci. (Basel) 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, R.H.; Finegold, S.M.; Bolte, E.R.; Buchanan, C.P.; Maxwell, A.P.; Väisänen, M.L.; Nelson, M.N.; Wexler, H.M. Short-term benefit from oral vancomycin treatment of regressive-onset autism. J. Child. Neurol. 2000, 15, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pequegnat, B.; Monteiro, M.A. Carbohydrate Scaffolds for the Study of the Autism-associated Bacterium, Clostridium bolteae. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 6341–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfabe, D.F. Short-chain fatty acid fermentation products of the gut microbiome: implications in autism spectrum disorders. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2012, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, S.R.; Macfabe, D.F.; Martin, S.; Jackson, J.; Taylor, R.; Boon, F.; Ossenkopp, K.P.; Cain, D.P. Intracerebroventricular injections of the enteric bacterial metabolic product propionic acid impair cognition and sensorimotor ability in the Long-Evans rat: further development of a rodent model of autism. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 200, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santocchi, E.; Guiducci, L.; Fulceri, F.; Billeci, L.; Buzzigoli, E.; Apicella, F.; Calderoni, S.; Grossi, E.; Morales, M.A.; Muratori, F. Gut to brain interaction in Autism Spectrum Disorders: a randomized controlled trial on the role of probiotics on clinical, biochemical and neurophysiological parameters. BMC Psychiatry 2016, 16, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erny, D.; Dokalis, N.; Mezö, C.; Castoldi, A.; Mossad, O.; Staszewski, O.; Frosch, M.; Villa, M.; Fuchs, V.; Mayer, A.; et al. Microbiota-derived acetate enables the metabolic fitness of the brain innate immune system during health and disease. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 2260–2276.e2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.M.; Yu, R.; Zhang, L.P.; Wen, S.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, Q.; Kong, L.D. Dietary fructose-induced gut dysbiosis promotes mouse hippocampal neuroinflammation: a benefit of short-chain fatty acids. Microbiome 2019, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, H.; Gressens, P.; Mallard, C. Inflammation during fetal and neonatal life: implications for neurologic and neuropsychiatric disease in children and adults. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguzzi, A.; Barres, B.A.; Bennett, M.L. Microglia: scapegoat, saboteur, or something else? Science 2013, 339, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolicelli, R.C.; Bolasco, G.; Pagani, F.; Maggi, L.; Scianni, M.; Panzanelli, P.; Giustetto, M.; Ferreira, T.A.; Guiducci, E.; Dumas, L.; et al. Synaptic pruning by microglia is necessary for normal brain development. Science 2011, 333, 1456–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.K.; Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 2010, 140, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoli-Ferreira, M.; Thomson, C.A.; McCoy, K.D. Microbiota and Microglia Interactions in ASD. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 676255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, D.L.; Nascimbene, C.; Krishnan, C.; Zimmerman, A.W.; Pardo, C.A. Neuroglial activation and neuroinflammation in the brain of patients with autism. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 57, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokusaeva, K.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; van Sinderen, D. Carbohydrate metabolism in Bifidobacteria. Genes. Nutr. 2011, 6, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Yu, J.S.; Min, B.H.; Gupta, H.; Won, S.M.; Park, H.J.; Han, S.H.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, B.K.; et al. -derived short-chain fatty acids and indole compounds attenuate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating gut-liver axis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1129904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riezzo, G.; Orlando, A.; D’Attoma, B.; Guerra, V.; Valerio, F.; Lavermicocca, P.; De Candia, S.; Russo, F. Randomised clinical trial: efficacy of Lactobacillus paracasei-enriched artichokes in the treatment of patients with functional constipation--a double-blind, controlled, crossover study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Jaitin, D.; Wieghofer, P.; Staszewski, O.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Mahlakoiv, T.; Jakobshagen, K.; Buch, T.; et al. Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Paolicelli, R.C.; Sforazzini, F.; Weinhard, L.; Bolasco, G.; Pagani, F.; Vyssotski, A.L.; Bifone, A.; Gozzi, A.; Ragozzino, D.; et al. Deficient neuron-microglia signaling results in impaired functional brain connectivity and social behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Cho, M.H.; Shim, W.H.; Kim, J.K.; Jeon, E.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Yoon, S.Y. Deficient autophagy in microglia impairs synaptic pruning and causes social behavioral defects. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, D.; Mayer, M.; Hausmann, B.; Pjevac, P.; Giordano, V.; Goeral, K.; Unterasinger, L.; Klebermaß-Schrehof, K.; De Paepe, K.; Van de Wiele, T.; et al. Aberrant gut-microbiota-immune-brain axis development in premature neonates with brain damage. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1558–572.e1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Lin, A.; Tao, K.; Yang, M.; Ye, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lin, Z.; He, M.; et al. Intestinal Klebsiella pneumoniae infection enhances susceptibility to epileptic seizure which can be reduced by microglia activation. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, N.J.; Hu, H. Enteric nervous system: sensory transduction, neural circuits and gastrointestinal motility. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.M.; Bon-Frauches, A.C.; Keszthelyi, D.; Melotte, V.; Boesmans, W. The enteric nervous system in gastrointestinal disease etiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 4713–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.A.; Rinaman, L.; Cryan, J.F. Stress & the gut-brain axis: Regulation by the microbiome. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 7, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, S.L.; Liberles, S.D. Internal senses of the vagus nerve. Neuron 2022, 110, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, K.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Mayer, E.A. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: From Motility to Mood. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, K.N.; Verheijden, S.; Boeckxstaens, G.E. The Vagus Nerve in Appetite Regulation, Mood, and Intestinal Inflammation. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 730–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercik, P.; Park, A.J.; Sinclair, D.; Khoshdel, A.; Lu, J.; Huang, X.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.A.; Fahnestock, M.; Moine, D.; et al. The anxiolytic effect of Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 involves vagal pathways for gut-brain communication. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, B.B.; Mazmanian, S.K. The Enteric Network: Interactions between the Immune and Nervous Systems of the Gut. Immunity 2017, 46, 910–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, M.; Sapone, A.; Senger, S.; Camhi, S.S.; Kadzielski, S.M.; Buie, T.M.; Kelly, D.L.; Cascella, N.; Fasano, A. Blood-brain barrier and intestinal epithelial barrier alterations in autism spectrum disorders. Mol. Autism 2016, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Magistris, L.; Familiari, V.; Pascotto, A.; Sapone, A.; Frolli, A.; Iardino, P.; Carteni, M.; De Rosa, M.; Francavilla, R.; Riegler, G.; et al. Alterations of the intestinal barrier in patients with autism spectrum disorders and in their first-degree relatives. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.T.; Taur, Y.; Walkup, J.T. Gut Microbiota and Autism: Key Concepts and Findings. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. Leaky gut and autoimmune diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 42, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Block, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Breese, G.R.; Hong, J.S.; Knapp, D.J.; Crews, F.T. Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia 2007, 55, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsten, T.B.; Chaves-Kirsten, G.P.; Chaible, L.M.; Silva, A.C.; Martins, D.O.; Britto, L.R.; Dagli, M.L.; Torrão, A.S.; Palermo-Neto, J.; Bernardi, M.M. Hypoactivity of the central dopaminergic system and autistic-like behavior induced by a single early prenatal exposure to lipopolysaccharide. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 90, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, J.J.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Enteroendocrine cells-sensory sentinels of the intestinal environment and orchestrators of mucosal immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Bazin, T.; Pellissier, S. The Vagus Nerve at the Interface of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus, A.; Planchais, J.; Sokol, H. Gut Microbiota Regulation of Tryptophan Metabolism in Health and Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbonnet, L.; Garrett, L.; Clarke, G.; Bienenstock, J.; Dinan, T.G. The probiotic Bifidobacteria infantis: An assessment of potential antidepressant properties in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 43, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicks, L.M.T. Gut Bacteria and Neurotransmitters. Microorganisms 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takumi, T.; Tamada, K.; Hatanaka, F.; Nakai, N.; Bolton, P.F. Behavioral neuroscience of autism. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 110, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marler, S.; Ferguson, B.J.; Lee, E.B.; Peters, B.; Williams, K.C.; McDonnell, E.; Macklin, E.A.; Levitt, P.; Gillespie, C.H.; Anderson, G.M.; et al. Brief Report: Whole Blood Serotonin Levels and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhamzeh, M.; Moravej, F.G.; Arabi, M.; Shahriari, E.; Mehrabi, S.; Ward, R.; Ahadi, R.; Joghataei, M.T. The Roles of Serotonin in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamsen, D.; Ramaekers, V.; Ho, H.T.; Britschgi, C.; Rüfenacht, V.; Meili, D.; Bobrowski, E.; Philippe, P.; Nava, C.; Van Maldergem, L.; et al. Autism spectrum disorder associated with low serotonin in CSF and mutations in the SLC29A4 plasma membrane monoamine transporter (PMAT) gene. Mol. Autism 2014, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.J.; Tan, H.P.; Du, Y.J. The developmental disruptions of serotonin signaling may involved in autism during early brain development. Neuroscience 2014, 267, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzel, T.; Mirowska-Guzel, D. The Role of Serotonin Neurotransmission in Gastrointestinal Tract and Pharmacotherapy. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyte, M. Microbial endocrinology and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyte, M. Probiotics function mechanistically as delivery vehicles for neuroactive compounds: Microbial endocrinology in the design and use of probiotics. Bioessays 2011, 33, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaldi, R.; Cela, D.; Swann, J.R.; Vulevic, J.; Gibson, G.R.; Tzortzis, G.; Costabile, A. In vitro fermentation of B-GOS: impact on faecal bacterial populations and metabolic activity in autistic and non-autistic children. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, C.C.; Dai, Y.; Luo, Q.; Ji, Y.; Wang, K.; Deng, S.; Yu, J.; Xu, M.; Du, X.; et al. Symptom improvement in children with autism spectrum disorder following bumetanide administration is associated with decreased GABA/glutamate ratios. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafet, G.E.; Nemeroff, C.B. Pharmacological Treatment of Anxiety Disorders: The Role of the HPA Axis. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D.N.; Whirledge, S. Stress and the HPA Axis: Balancing Homeostasis and Fertility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiak, B.; Łoniewski, I.; Marlicz, W.; Frydecka, D.; Szulc, A.; Rudzki, L.; Samochowiec, J. The HPA axis dysregulation in severe mental illness: Can we shift the blame to gut microbiota? Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 102, 109951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.A.; Baker, G.B.; Dursun, S.M. The Relationship Between the Gut Microbiome-Immune System-Brain Axis and Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 721126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiertsema, S.P.; van Bergenhenegouwen, J.; Garssen, J.; Knippels, L.M.J. The Interplay between the Gut Microbiome and the Immune System in the Context of Infectious Diseases throughout Life and the Role of Nutrition in Optimizing Treatment Strategies. Nutrients 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borre, Y.E.; O’Keeffe, G.W.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota and neurodevelopmental windows: implications for brain disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elena Franco-Robles and Joel Ramírez-Emiliano and José Sergio López-Briones and Cristina Doriany, B.-P. Prebiotics and the Modulation on the Microbiota-GALT-Brain Axis. In Prebiotics and Probiotics, Elena Franco-Robles and Joel, R.-E., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Kamada, N.; Chen, G.Y.; Inohara, N.; Núñez, G. Control of pathogens and pathobionts by the gut microbiota. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Wouw, M.; Walsh, A.M.; Crispie, F.; van Leuven, L.; Lyte, J.M.; Boehme, M.; Clarke, G.; Dinan, T.G.; Cotter, P.D.; Cryan, J.F. Distinct actions of the fermented beverage kefir on host behaviour, immunity and microbiome gut-brain modules in the mouse. Microbiome 2020, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElhanon, B.O.; McCracken, C.; Karpen, S.; Sharp, W.G. Gastrointestinal symptoms in autism spectrum disorder: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2014, 133, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madra, M.; Ringel, R.; Margolis, K.G. Gastrointestinal Issues and Autism Spectrum Disorder. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 44, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leader, G.; Abberton, C.; Cunningham, S.; Gilmartin, K.; Grudzien, M.; Higgins, E.; Joshi, L.; Whelan, S.; Mannion, A. Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buie, T.; Campbell, D.B.; Fuchs, G.J.; Furuta, G.T.; Levy, J.; Vandewater, J.; Whitaker, A.H.; Atkins, D.; Bauman, M.L.; Beaudet, A.L.; et al. Evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of gastrointestinal disorders in individuals with ASDs: a consensus report. Pediatrics 2010, 125 Suppl 1, S1-18. [CrossRef]
- Black, C.; Kaye, J.A.; Jick, H. Relation of childhood gastrointestinal disorders to autism: nested case-control study using data from the UK General Practice Research Database. BMJ 2002, 325, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.H.; Voigt, R.G.; Katusic, S.K.; Weaver, A.L.; Barbaresi, W.J. Incidence of gastrointestinal symptoms in children with autism: a population-based study. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulceri, F.; Morelli, M.; Santocchi, E.; Cena, H.; Del Bianco, T.; Narzisi, A.; Calderoni, S.; Muratori, F. Gastrointestinal symptoms and behavioral problems in preschoolers with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twachtman-Reilly, J.; Amaral, S.C.; Zebrowski, P.P. Addressing feeding disorders in children on the autism spectrum in school-based settings: physiological and behavioral issues. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Sch. 2008, 39, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marí-Bauset, S.; Zazpe, I.; Mari-Sanchis, A.; Llopis-González, A.; Morales-Suárez-Varela, M. Food selectivity in autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review. J. Child. Neurol. 2014, 29, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, B.; McVeigh, C.; Bendriss, G.; Chaari, A. The Promising Role of Probiotics in Managing the Altered Gut in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, K.A.; Williams, K. Food preferences and factors influencing food selectivity for children with autism spectrum disorders. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2006, 27, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, H.A.; Micali, N.; Moll, H.A.; van Berckelaer-Onnes, I.; Hillegers, M.; Jansen, P.W. The role of food selectivity in the association between child autistic traits and constipation. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.C.; Novak, P.; Withrow, N.; Schmidt, B.; Rarback, S.; Feucht, S.; Criado, K.K.; Sharp, W.G. Nutrition Management of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Guideline from an Expert Panel. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1919–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herndon, A.C.; DiGuiseppi, C.; Johnson, S.L.; Leiferman, J.; Reynolds, A. Does nutritional intake differ between children with autism spectrum disorders and children with typical development? J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2009, 39, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goday, P.S.; Huh, S.Y.; Silverman, A.; Lukens, C.T.; Dodrill, P.; Cohen, S.S.; Delaney, A.L.; Feuling, M.B.; Noel, R.J.; Gisel, E.; et al. Pediatric Feeding Disorder: Consensus Definition and Conceptual Framework. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.; Lu, N.; Liu, N. Hydrogen breath test to detect small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: a prevalence case-control study in autism. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2018, 27, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Krishnamurthy, J.; Susi, A.; Sullivan, C.; Gorman, G.H.; Hisle-Gorman, E.; Erdie-Lalena, C.R.; Nylund, C.M. Association of Autism Spectrum Disorders and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2018, 48, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadik, A.; Dardani, C.; Pagoni, P.; Havdahl, A.; Stergiakouli, E.; Khandaker, G.M.; Sullivan, S.A.; Zammit, S.; Jones, H.J.; Davey Smith, G.; et al. Parental inflammatory bowel disease and autism in children. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A.B.; Ehrenstein, V.; Erichsen, R.; Frøslev, T.; Sørensen, H.T. Autism spectrum disorders in children of parents with inflammatory bowel disease - a nationwide cohort study in Denmark. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2014, 7, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.; Bai, Y.M.; Tsai, S.J.; Chen, T.J.; Liang, C.S.; Chen, M.H. Risks of Major Mental Disorders and Irritable Bowel Syndrome among the Offspring of Parents with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Nationwide Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.B.; Johansen, L.J.; Powell, L.D.; Quig, D.; Rubin, R.A. Gastrointestinal flora and gastrointestinal status in children with autism--comparisons to typical children and correlation with autism severity. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berding, K.; Donovan, S.M. Diet Can Impact Microbiota Composition in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Beltagi, M.; Saeed, N.K.; Bediwy, A.S.; Elbeltagi, R.; Alhawamdeh, R. Role of gastrointestinal health in managing children with autism spectrum disorder. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2023, 12, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atladóttir, H.O.; Thorsen, P.; Østergaard, L.; Schendel, D.E.; Lemcke, S.; Abdallah, M.; Parner, E.T. Maternal infection requiring hospitalization during pregnancy and autism spectrum disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2010, 40, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.S. Epidemiologic studies of exposure to prenatal infection and risk of schizophrenia and autism. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuesel, I.; Chicha, L.; Britschgi, M.; Schobel, S.A.; Bodmer, M.; Hellings, J.A.; Toovey, S.; Prinssen, E.P. Maternal immune activation and abnormal brain development across CNS disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattner, R.J. The role of viruses in congenital defects. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1974, 128, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.K.; Magnusson, C.; Gardner, R.M.; Blomström, Å.; Newschaffer, C.J.; Burstyn, I.; Karlsson, H.; Dalman, C. Maternal hospitalization with infection during pregnancy and risk of autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 44, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Fatemi, S.H.; Sidwell, R.W.; Patterson, P.H. Maternal influenza infection causes marked behavioral and pharmacological changes in the offspring. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin Yim, Y.; Park, A.; Berrios, J.; Lafourcade, M.; Pascual, L.M.; Soares, N.; Yeon Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Waisman, A.; et al. Reversing behavioural abnormalities in mice exposed to maternal inflammation. Nature 2017, 549, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiles, J.; Jernigan, T.L. The basics of brain development. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2010, 20, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, N.; Anixt, J.; Manning, P.; Ping-I Lin, D.; Marsolo, K.A.; Bowers, K. Maternal metabolic risk factors for autism spectrum disorder-An analysis of electronic medical records and linked birth data. Autism Res. 2016, 9, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raz, R.; Roberts, A.L.; Lyall, K.; Hart, J.E.; Just, A.C.; Laden, F.; Weisskopf, M.G. Autism spectrum disorder and particulate matter air pollution before, during, and after pregnancy: a nested case-control analysis within the Nurses’ Health Study II Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, E.L.; Nousen, E.K.; Chamlou, K.A. Maternal high fat diet consumption during the perinatal period programs offspring behavior. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 123, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokosi, T.; Flouri, E.; Midouhas, E. The role of inflammation in the association between poverty and working memory in childhood. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021, 123, 105040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, F.; Brown, A.S. Maternal Immune Activation and Related Factors in the Risk of Offspring Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.K.; Choi, G.B.; Huh, J.R. Maternal inflammation and its ramifications on fetal neurodevelopment. Trends Immunol. 2022, 43, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, V.X.; Patel, S.; Jones, H.F.; Dale, R.C. Maternal immune activation and neuroinflammation in human neurodevelopmental disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 564–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Coyne, C.B.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T. PAMPs and DAMPs: signal 0s that spur autophagy and immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 249, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Fernández, M.A.; Fresno, M. The role of tumour necrosis factor, interleukin 6, interferon-gamma and inducible nitric oxide synthase in the development and pathology of the nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 307–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, U. Prenatal poly(i:C) exposure and other developmental immune activation models in rodent systems. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, L.; Boksa, P. Prenatal and postnatal animal models of immune activation: relevance to a range of neurodevelopmental disorders. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 1335–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska, G.B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Lim, Y.P.; Cummings, E.E.; Makeyev, O.; Besio, W.G.; Gaitanis, J.; Padbury, J.F.; Banks, W.A.; et al. Interleukin-1β transfer across the blood-brain barrier in the ovine fetus. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rite, I.; Machado, A.; Cano, J.; Venero, J.L. Blood-brain barrier disruption induces in vivo degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons. J. Neurochem. 2007, 101, 1567–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, U.; Feldon, J.; Yee, B.K. A review of the fetal brain cytokine imbalance hypothesis of schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2009, 35, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.E.; Li, J.; Garbett, K.; Mirnics, K.; Patterson, P.H. Maternal immune activation alters fetal brain development through interleukin-6. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10695–10702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Yim, Y.S.; Ha, S.; Atarashi, K.; Tan, T.G.; Longman, R.S.; Honda, K.; Littman, D.R.; Choi, G.B.; et al. Maternal gut bacteria promote neurodevelopmental abnormalities in mouse offspring. Nature 2017, 549, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.S.; Sourander, A.; Hinkka-Yli-Salomäki, S.; McKeague, I.W.; Sundvall, J.; Surcel, H.M. Elevated maternal C-reactive protein and autism in a national birth cohort. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, C.; Kushner, I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemi, S.H.; Pearce, D.A.; Brooks, A.I.; Sidwell, R.W. Prenatal viral infection in mouse causes differential expression of genes in brains of mouse progeny: a potential animal model for schizophrenia and autism. Synapse 2005, 57, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, O.; Gong, X.; Rose-John, S.; Heese, K. Interleukin-6 and neural stem cells: more than gliogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- März, P.; Cheng, J.G.; Gadient, R.A.; Patterson, P.H.; Stoyan, T.; Otten, U.; Rose-John, S. Sympathetic neurons can produce and respond to interleukin 6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominitzki, S.; Fantini, M.C.; Neufert, C.; Nikolaev, A.; Galle, P.R.; Scheller, J.; Monteleone, G.; Rose-John, S.; Neurath, M.F.; Becker, C. Cutting edge: trans-signaling via the soluble IL-6R abrogates the induction of FoxP3 in naive CD4+CD25 T cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2041–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockinger, B.; Veldhoen, M.; Martin, B. Th17 T cells: linking innate and adaptive immunity. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Ding, C.; Jin, G.; Wang, Y.; Hu, F.; Yu, L. Inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling in the brain increases sociability in the BTBR mouse model of autism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chang, H.; Kong, Y.; Ni, Y.; Liu, R.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hou, M.; Mao, R.; et al. Rescue of maternal immune activation-induced behavioral abnormalities in adult mouse offspring by pathogen-activated maternal T. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 818–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ayadhi, L.Y.; Mostafa, G.A. Elevated serum levels of interleukin-17A in children with autism. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.I.; McKenzie, B.S.; Zhou, L.; Tadokoro, C.E.; Lepelley, A.; Lafaille, J.J.; Cua, D.J.; Littman, D.R. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell 2006, 126, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Ivanov, I.I.; Spolski, R.; Min, R.; Shenderov, K.; Egawa, T.; Levy, D.E.; Leonard, W.J.; Littman, D.R. IL-6 programs T(H)-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.; Brigas, H.C.; Temido-Ferreira, M.; Pousinha, P.A.; Regen, T.; Santa, C.; Coelho, J.E.; Marques-Morgado, I.; Valente, C.A.; Omenetti, S.; et al. Meningeal γδ T cell-derived IL-17 controls synaptic plasticity and short-term memory. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraco, G.; Brea, D.; Garcia-Bonilla, L.; Wang, G.; Racchumi, G.; Chang, H.; Buendia, I.; Santisteban, M.M.; Segarra, S.G.; Koizumi, K.; et al. Dietary salt promotes neurovascular and cognitive dysfunction through a gut-initiated TH17 response. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienecke, J.; Hebel, K.; Hegel, K.J.; Pierau, M.; Brune, T.; Reinhold, D.; Pethe, A.; Brunner-Weinzierl, M.C. Pro-inflammatory effector Th cells transmigrate through anti-inflammatory environments into the murine fetus. Placenta 2012, 33, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goines, P.E.; Ashwood, P. Cytokine dysregulation in autism spectrum disorders (ASD): possible role of the environment. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2013, 36, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwood, P.; Anthony, A.; Torrente, F.; Wakefield, A.J. Spontaneous mucosal lymphocyte cytokine profiles in children with autism and gastrointestinal symptoms: mucosal immune activation and reduced counter regulatory interleukin-10. J. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 24, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, C.A.; Morrow, A.L.; Meinzen-Derr, J.; Schleifer, K.; Dienger, K.; Manning-Courtney, P.; Altaye, M.; Wills-Karp, M. Elevated cytokine levels in children with autism spectrum disorder. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 172, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFelice, M.L.; Ruchelli, E.D.; Markowitz, J.E.; Strogatz, M.; Reddy, K.P.; Kadivar, K.; Mulberg, A.E.; Brown, K.A. Intestinal cytokines in children with pervasive developmental disorders. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Zou, H.; Sheikh, A.M.; Malik, M.; Dobkin, C.; Brown, W.T.; Li, X. IL-6 is increased in the cerebellum of autistic brain and alters neural cell adhesion, migration and synaptic formation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, M.W.; Larsen, N.; Grove, J.; Nørgaard-Pedersen, B.; Thorsen, P.; Mortensen, E.L.; Hougaard, D.M. Amniotic fluid inflammatory cytokines: potential markers of immunologic dysfunction in autism spectrum disorders. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 14, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goines, P.E.; Croen, L.A.; Braunschweig, D.; Yoshida, C.K.; Grether, J.; Hansen, R.; Kharrazi, M.; Ashwood, P.; Van de Water, J. Increased midgestational IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-5 in women bearing a child with autism: A case-control study. Mol. Autism 2011, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwood, P.; Enstrom, A.; Krakowiak, P.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.L.; Croen, L.A.; Ozonoff, S.; Pessah, I.N.; Van de Water, J. Decreased transforming growth factor beta1 in autism: a potential link between immune dysregulation and impairment in clinical behavioral outcomes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 204, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalcman, S.; Green-Johnson, J.M.; Murray, L.; Nance, D.M.; Dyck, D.; Anisman, H.; Greenberg, A.H. Cytokine-specific central monoamine alterations induced by interleukin-1, -2 and -6. Brain Res. 1994, 643, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, D.M.; Lapchak, P.A.; Collier, B.; Quirion, R. Localization of interleukin-2 immunoreactivity and interleukin-2 receptors in the rat brain: interaction with the cholinergic system. Brain Res. 1989, 498, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornig, M.; Weissenböck, H.; Horscroft, N.; Lipkin, W.I. An infection-based model of neurodevelopmental damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12102–12107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Pan, T.; Kendrick, K.M.; Xu, W. Immunological cytokine profiling identifies TNF-α as a key molecule dysregulated in autistic children. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82390–82398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, G.; Lladó, J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha: a link between neuroinflammation and excitotoxicity. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 861231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, J.; Ryu, J.; Park, S.G.; Cho, S.; Park, B.C.; Lee, D.H. Activation of autophagy during glutamate-induced HT22 cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheray, M.; Joseph, B. Epigenetics Control Microglia Plasticity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousset, C.I.; Chalon, S.; Cantagrel, S.; Bodard, S.; Andres, C.; Gressens, P.; Saliba, E. Maternal exposure to LPS induces hypomyelination in the internal capsule and programmed cell death in the deep gray matter in newborn rats. Pediatr. Res. 2006, 59, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makinodan, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Manabe, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Makinodan, E.; Matsuyoshi, H.; Shimoda, S.; Noriyama, Y.; Kishimoto, T.; Wanaka, A. Maternal immune activation in mice delays myelination and axonal development in the hippocampus of the offspring. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 2190–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.; Allen, N.J.; Vazquez, L.E.; Howell, G.R.; Christopherson, K.S.; Nouri, N.; Micheva, K.D.; Mehalow, A.K.; Huberman, A.D.; Stafford, B.; et al. The classical complement cascade mediates CNS synapse elimination. Cell 2007, 131, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, D.; Loos, M. In vitro modulation of C1q mRNA expression and secretion by interleukin-1, interleukin-6, and interferon-gamma in resident and stimulated murine peritoneal macrophages. Immunobiology 2002, 206, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leviton, A.; Gressens, P. Neuronal damage accompanies perinatal white-matter damage. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, U.; Nyffeler, M.; Engler, A.; Urwyler, A.; Schedlowski, M.; Knuesel, I.; Yee, B.K.; Feldon, J. The time of prenatal immune challenge determines the specificity of inflammation-mediated brain and behavioral pathology. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4752–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S.H.; Stary, J.M.; Egan, E.A. Reduced blood levels of reelin as a vulnerability factor in pathophysiology of autistic disorder. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2002, 22, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brimberg, L.; Sadiq, A.; Gregersen, P.K.; Diamond, B. Brain-reactive IgG correlates with autoimmunity in mothers of a child with an autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, M.D.; Iosif, A.M.; Ashwood, P.; Braunschweig, D.; Lee, A.; Schumann, C.M.; Van de Water, J.; Amaral, D.G. Maternal antibodies from mothers of children with autism alter brain growth and social behavior development in the rhesus monkey. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fombonne, E. Epidemiology of pervasive developmental disorders. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 65, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandy, W.; Chilvers, R.; Chowdhury, U.; Salter, G.; Seigal, A.; Skuse, D. Sex differences in autism spectrum disorder: evidence from a large sample of children and adolescents. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2012, 42, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron-Cohen, S. The extreme male brain theory of autism. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2002, 6, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuse, D.H.; James, R.S.; Bishop, D.V.; Coppin, B.; Dalton, P.; Aamodt-Leeper, G.; Bacarese-Hamilton, M.; Creswell, C.; McGurk, R.; Jacobs, P.A. Evidence from Turner’s syndrome of an imprinted X-linked locus affecting cognitive function. Nature 1997, 387, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.; Sheth, D.; Ghaziuddin, M. Autism spectrum disorder and Klinefelter syndrome. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2007, 16, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.V.; Jacobs, P.A.; Lachlan, K.; Wellesley, D.; Barnicoat, A.; Boyd, P.A.; Fryer, A.; Middlemiss, P.; Smithson, S.; Metcalfe, K.; et al. Autism, language and communication in children with sex chromosome trisomies. Arch. Dis. Child. 2011, 96, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.L.; Roeltgen, D.P.; Kushner, H.; Zinn, A.R.; Reiss, A.; Bardsley, M.Z.; McCauley, E.; Tartaglia, N. Behavioral and social phenotypes in boys with 47,XYY syndrome or 47,XXY Klinefelter syndrome. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglione, A.M.; Villani, A.; Ajmone-Cat, M.A.; Minghetti, L.; Ricceri, L.; Pazienza, V.; De Simone, R.; Calamandrei, G. Maternal immune activation induces autism-like changes in behavior, neuroinflammatory profile and gut microbiota in mouse offspring of both sexes. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thion, M.S.; Low, D.; Silvin, A.; Chen, J.; Grisel, P.; Schulte-Schrepping, J.; Blecher, R.; Ulas, T.; Squarzoni, P.; Hoeffel, G.; et al. Microbiome Influences Prenatal and Adult Microglia in a Sex-Specific Manner. Cell 2018, 172, 500–516.e516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffington, S.A.; Di Prisco, G.V.; Auchtung, T.A.; Ajami, N.J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Costa-Mattioli, M. Microbial Reconstitution Reverses Maternal Diet-Induced Social and Synaptic Deficits in Offspring. Cell 2016, 165, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkova, N.V.; Yu, C.Z.; Hsiao, E.Y.; Moore, M.J.; Patterson, P.H. Maternal immune activation yields offspring displaying mouse versions of the three core symptoms of autism. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukiw, W.J. Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract Microbiome-Derived Neurotoxins-Potent Neuro-Inflammatory Signals From the GI Tract via the Systemic Circulation Into the Brain. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Shen, B.; Huang, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Song, M.; Liu, K.; Lin, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. strain ZY-312 promotes intestinal barrier integrity via upregulating the STAT3 pathway in a radiation-induced intestinal injury mouse model. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1063699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, M.H.; Wu, Y.; Ticer, T.; Schutt, S.; Bastian, D.; Choi, H.J.; Tian, L.; Mealer, C.; Liu, C.; Westwater, C.; et al. A single strain of Bacteroides fragilis protects gut integrity and reduces GVHD. JCI Insight 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmel, J.; Ghanayem, N.; Mayouf, R.; Saleev, N.; Chaterjee, I.; Getselter, D.; Tikhonov, E.; Turjeman, S.; Shaalan, M.; Khateeb, S.; et al. Bacteroides is increased in an autism cohort and induces autism-relevant behavioral changes in mice in a sex-dependent manner. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2023, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, J.T.; Jin, D.M.; Mills, R.H.; Shao, Y.; Rahman, G.; McDonald, D.; Zhu, Q.; Balaban, M.; Jiang, Y.; Cantrell, K.; et al. Multi-level analysis of the gut-brain axis shows autism spectrum disorder-associated molecular and microbial profiles. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Niu, M.; Bi, J.; Du, N.; Liu, S.; Yang, K.; Li, H.; Yao, J.; Du, Y.; Duan, Y. Protective effects of a new generation of probiotic Bacteroides fragilis against colitis in vivo and in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paysour, M.J.; Bolte, A.C.; Lukens, J.R. Crosstalk Between the Microbiome and Gestational Immunity in Autism-Related Disorders. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, M.P. Vancomycin. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1991, 66, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.; Bik, E.M.; DiGiulio, D.B.; Relman, D.A.; Brown, P.O. Development of the human infant intestinal microbiota. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisula, E.; Ziegart-Sadowska, K. Broader Autism Phenotype in Siblings of Children with ASD--A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 13217–13258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakowiak, P.; Walker, C.K.; Bremer, A.A.; Baker, A.S.; Ozonoff, S.; Hansen, R.L.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Maternal metabolic conditions and risk for autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, O.; Olefsky, J.M. The cellular and signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caesar, R.; Reigstad, C.S.; Bäckhed, H.K.; Reinhardt, C.; Ketonen, M.; Lundén, G.; Cani, P.D.; Bäckhed, F. Gut-derived lipopolysaccharide augments adipose macrophage accumulation but is not essential for impaired glucose or insulin tolerance in mice. Gut 2012, 61, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, J.; Burcelin, R.; Ruidavets, J.B.; Cani, P.D.; Fauvel, J.; Alessi, M.C.; Chamontin, B.; Ferriéres, J. Energy intake is associated with endotoxemia in apparently healthy men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 2012, 489, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Farias, C.; Slezak, K.; Fuller, Z.; Duncan, A.; Holtrop, G.; Louis, P. Effect of inulin on the human gut microbiota: stimulation of Bifidobacterium adolescentis and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbonaite, G.; Knyzeliene, A.; Bunn, F.S.; Smalskys, A.; Neniskyte, U. The impact of maternal high-fat diet on offspring neurodevelopment. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 909762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Sun, Q. Macrophage recruitment in obese adipose tissue. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, J.D.; Bailey, M.; Kamp Dush, C.; Schoppe-Sullivan, S.; Christian, L.M. Maternal obesity is associated with alterations in the gut microbiome in toddlers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, M.A.; Hoffmann, C.; Sherrill-Mix, S.A.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Hamady, M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Knight, R.; Ahima, R.S.; Bushman, F.; Wu, G.D. High-fat diet determines the composition of the murine gut microbiome independently of obesity. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1716-1724.e1711-1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poutahidis, T.; Kearney, S.M.; Levkovich, T.; Qi, P.; Varian, B.J.; Lakritz, J.R.; Ibrahim, Y.M.; Chatzigiagkos, A.; Alm, E.J.; Erdman, S.E. Microbial symbionts accelerate wound healing via the neuropeptide hormone oxytocin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasue, H.; Domes, G. Oxytocin and Autism Spectrum Disorders. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 35, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wied, D.; Diamant, M.; Fodor, M. Central nervous system effects of the neurohypophyseal hormones and related peptides. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1993, 14, 251–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domes, G.; Heinrichs, M.; Michel, A.; Berger, C.; Herpertz, S.C. Oxytocin improves "mind-reading" in humans. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modahl, C.; Green, L.; Fein, D.; Morris, M.; Waterhouse, L.; Feinstein, C.; Levin, H. Plasma oxytocin levels in autistic children. Biol. Psychiatry 1998, 43, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, K.J.; Garner, J.P.; Libove, R.A.; Hyde, S.A.; Hornbeak, K.B.; Carson, D.S.; Liao, C.P.; Phillips, J.M.; Hallmayer, J.F.; Hardan, A.Y. Plasma oxytocin concentrations and OXTR polymorphisms predict social impairments in children with and without autism spectrum disorder. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12258–12263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintál, K.; Tóth, A.; Hormay, E.; Kovács, A.; László, K.; Bufa, A.; Marosvölgyi, T.; Kocsis, B.; Varga, A.; Vizvári, Z.; et al. Novel probiotic treatment of autism spectrum disorder associated social behavioral symptoms in two rodent models. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, L.M.; Smith, E.G.; Pedapati, E.V.; Horn, P.S.; Will, M.; Lamy, M.; Barber, L.; Trebley, J.; Meyer, K.; Heiman, M.; et al. Results of a phase Ib study of SB-121, an investigational probiotic formulation, a randomized controlled trial in participants with autism spectrum disorder. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Yang, J.J.; Zhao, D.M.; Chen, B.; Zhang, G.Q.; Chen, S.; Cao, R.F.; Yu, H.; Zhao, C.Y.; et al. Probiotics and fructo-oligosaccharide intervention modulate the microbiota-gut brain axis to improve autism spectrum reducing also the hyper-serotonergic state and the dopamine metabolism disorder. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Q.X.; Loke, W.; Venkatanarayanan, N.; Lim, D.Y.; Soh, A.Y.S.; Yeo, W.S. A Systematic Review of the Role of Prebiotics and Probiotics in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Medicina (Kaunas) 2019, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, W.; Tang, F.; Chen, X.; Song, G. Effects of Probiotics on Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Cho, J.; Kim, K.Y. The Association between Autism Spectrum Disorder and Pre- and Postnatal Antibiotic Exposure in Childhood-A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wink, L.K.; Minshawi, N.F.; Shaffer, R.C.; Plawecki, M.H.; Posey, D.J.; Horn, P.S.; Adams, R.; Pedapati, E.V.; Schaefer, T.L.; McDougle, C.J.; et al. d-Cycloserine enhances durability of social skills training in autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Autism 2017, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Miguel, D.; Lamanna-Rama, N.; Casquero-Veiga, M.; Gómez-Rangel, V.; Desco, M.; Soto-Montenegro, M.L. Minocycline in neurodegenerative and psychiatric diseases: An update. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 1056–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, O.M.; Data-Franco, J.; Giorlando, F.; Berk, M. Minocycline: therapeutic potential in psychiatry. CNS Drugs 2012, 26, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panizzutti, B.; Skvarc, D.; Lin, S.; Croce, S.; Meehan, A.; Bortolasci, C.C.; Marx, W.; Walker, A.J.; Hasebe, K.; Kavanagh, B.E.; et al. Minocycline as Treatment for Psychiatric and Neurological Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleiha, A.; Alikhani, R.; Kazemi, M.R.; Mohammadi, M.R.; Mohammadinejad, P.; Zeinoddini, A.; Hamedi, M.; Shahriari, M.; Keshavarzi, Z.; Akhondzadeh, S. Minocycline as Adjunctive Treatment to Risperidone in Children with Autistic Disorder: A Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. J. Child. Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Adams, J.B.; Gregory, A.C.; Borody, T.; Chittick, L.; Fasano, A.; Khoruts, A.; Geis, E.; Maldonado, J.; McDonough-Means, S.; et al. Microbiota Transfer Therapy alters gut ecosystem and improves gastrointestinal and autism symptoms: an open-label study. Microbiome 2017, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.W.; Adams, J.B.; Coleman, D.M.; Pollard, E.L.; Maldonado, J.; McDonough-Means, S.; Caporaso, J.G.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Long-term benefit of Microbiota Transfer Therapy on autism symptoms and gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Adams, J.B.; Vargason, T.; Santiago, M.; Hahn, J.; Krajmalnik-Brown, R. Distinct Fecal and Plasma Metabolites in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders and Their Modulation after Microbiota Transfer Therapy. mSphere 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, K.; Papadimitriou, J.C.; Rabsztyn, A.; Drachenberg, C.; Tildon, J.T. Gastrointestinal abnormalities in children with autistic disorder. J. Pediatr. 1999, 135, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, K.; Eltayeb, A.A.; Mohamad, I.L.; Al-Atram, A.A.; Elserogy, Y.; Bjørklund, G.; El-Houfey, A.A.; Nicholson, B. A Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial of Digestive Enzymes in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2015, 13, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.B.; Audhya, T.; Geis, E.; Gehn, E.; Fimbres, V.; Pollard, E.L.; Mitchell, J.; Ingram, J.; Hellmers, R.; Laake, D.; et al. Comprehensive Nutritional and Dietary Intervention for Autism Spectrum Disorder-A Randomized, Controlled 12-Month Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo-López, C. Helminth therapy for autism under gut-brain axis- hypothesis. Med. Hypotheses 2019, 125, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, E.; Uzunova, G.; Taylor, B.P.; Noone, R.; Racine, E.; Doernberg, E.; Freeman, K.; Ferretti, C.J. Randomized crossover feasibility trial of helminthic. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 21, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, D.; et al. Correlation of Gut Microbiome Between ASD Children and Mothers and Potential Biomarkers for Risk Assessment. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2019, 17, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.L.; Lu, C.C.; Chen, T.W.; Huang, C.W.; Lu, J.J.; Lai, W.F.; Wu, T.S.; Lai, C.H.; Lai, H.C.; Chen, Y.L. Amelioration of Maternal Immune Activation-Induced Autism Relevant Behaviors by Gut Commensal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Yao, Z. Oral probiotic administration during pregnancy prevents autism-related behaviors in offspring induced by maternal immune activation via anti-inflammation in mice. Autism Res. 2019, 12, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, C.; Martinez Sanchez, I.; Cherifi, Y.; Chartrel, N.; Diaz Heijtz, R. Perturbation of maternal gut microbiota in mice during a critical perinatal window influences early neurobehavioral outcomes in offspring. Neuropharmacology 2023, 229, 109479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humann, J.; Mann, B.; Gao, G.; Moresco, P.; Ramahi, J.; Loh, L.N.; Farr, A.; Hu, Y.; Durick-Eder, K.; Fillon, S.A.; et al. Bacterial Peptidoglycan Traverses the Placenta to Induce Fetal Neuroproliferation and Aberrant Postnatal Behavior. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, J.; Coppola, G.; Zhang, P.; Abyzov, A.; Provini, L.; Tomasini, L.; Amenduni, M.; Szekely, A.; Palejev, D.; Wilson, M.; et al. FOXG1-Dependent Dysregulation of GABA/Glutamate Neuron Differentiation in Autism Spectrum Disorders. Cell 2015, 162, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atladóttir, H.; Henriksen, T.B.; Schendel, D.E.; Parner, E.T. Autism after infection, febrile episodes, and antibiotic use during pregnancy: an exploratory study. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lin, C.H.; Lin, M.C. The Association of Prenatal Antibiotic Use with Attention Deficit and Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Children (Basel) 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitschke, A.S.; do Valle, H.A.; Vallance, B.A.; Bickford, C.; Ip, A.; Lanphear, N.; Lanphear, B.; Weikum, W.; Oberlander, T.F.; Hanley, G.E. Association between prenatal antibiotic exposure and autism spectrum disorder among term births: A population-based cohort study. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2023, 37, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, A.F.; Alessi-Severini, S.; Mahmud, S.M.; Brownell, M.; Kuo, I.F. Prenatal antibiotics exposure and the risk of autism spectrum disorders: A population-based cohort study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haddad, B.J.S.; Oler, E.; Armistead, B.; Elsayed, N.A.; Weinberger, D.R.; Bernier, R.; Burd, I.; Kapur, R.; Jacobsson, B.; Wang, C.; et al. The fetal origins of mental illness. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 221, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Children born by Caesarean section |
Children born by vaginal delivery |
Children with ASD |
|---|---|---|
| ⬆ Staphylococcus, Corynebacterium, and Propionibacterium spp. [23] ⬆Enterococcus, Enterobacter, and Klebsiella [36] |
⬆Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium (Chu et al. 2017, Reyman et al. 2019) [34,37] |
1. ⬆ Bacteroidetes, Parabacteroides, Faecalibacterium, Phascolarctobacterium, Lactobacillus, Clostridioides, Desulfovibrio, Caloramator, and Sarcina [43,44] 2. ⬆ Clostridioides [45] 3. ⬇ Lactobacillus [50] 4. ⬇Coprococcus and Bifidobacterium [44] 3. ⬇ Prevotella, Coprococcus, Enterococcus, Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Lactococcus, Staphylococcus, Ruminococcus, and Bifidobacterium ⬆Clostridia and Desulfovibrio. [46] 5. No significant differences in gut microbiota diversity [47] |
| Frequency | Symptoms | Gastrointestinal disorders |
|---|---|---|
| between 17% and 86% of gastrointestinal symptoms in individuals diagnosed with ASD [55,139] | Predominant: diarrhea and constipation [139,140] Other: abdominal pain, vomiting, bloating, and gastric reflux [141] feeding disorders - often described as “picky eaters” [147] [154] |
higher prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), compared to healthy controls [155] |
| Bifidocaterium | Lactobacillus spp. | Bacteroides spp. |
|---|---|---|
| producing SCFAs [90,91,92] GABA releasing [127] preventing MIA-Induced ASD-relevant deficits in adult offspring [289] preventing parvalbumin-positive neuron loss, increased proinflammatory cytokines levels in maternal serum and fetal brain, and decreased GABA levels [289] |
||
| intestinal refilling of tryptophan (Bifidobacterium infantis) [118] |
inducing changes in γ-aminobutyric acid (L. Rhamnosus) [105] taking part in maintaining tight junctions between cells [53] preventing the overgrowth of Candida [54] promoting oxytocin levels (L. Reuteri) [262] |
B. fragilis: regulating intestinal barrier integrity [108] lowering Il-6 in colon [108] [244] reducing gut permeability [51] promoting stem cell regeneration and increase mucus secretion in intestines [239] promoting the development of regulatory T cells and IL-22 secretion [240] ⬆ B. fragilis may reduce integrity due to the secreting fragilinase [238] Bacteroides spp.: improving communicative, repetitive, anxiety-like, and sensorimotor behavior associated with ASD in mice (Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron) [108] ⬆ levels in autistic individuals [242] exacerbate social behaviors in mice [241] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





