1. Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is a clinical syndrome consisting of several symptoms (shortness of breath, swelling of the legs, fatigue), which could be accompanied by clinical signs (elevated jugular venous pressure, pulmonary rales, peripheral edema). HF is due to structural and/or functional abnormalities of the heart that result in increased pressure in the cardiac chambers and/or decreased cardiac output at rest and during activity [
1]. In Europe, the incidence of heart failure was estimated to be 3 in 1000 of the population [
1,
2].
Based on the European Society of Cardiology classification, heart failure could be classified into heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) of < 40%, heart failure with a mildly–reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF) of 40% – 49%, and heart failure with a normal ejection fraction, with an ejection fraction value (HFpEF) of > 50% [
3].
Diagnosing patients with HFpEF is quite complicated, and based on studies that have been carried out, HFpEF could be diagnosed if it meets the following criteria: 1. The presence of signs and symptoms of heart failure; 2. Ejection fraction > 50%; 3. There is objective evidence indicating left ventricular (LV) structural and/or functional abnormalities consistent with diastolic dysfunction or increased LV filling pressure, including an increase in natriuretic–peptide [
1,
2].
The pathophysiology of HFpEF is often caused by an increase in the filling pressure of the left ventricle (LV Filling Pressure [LVFP]). The increase in LVFP is largely due to the presence of diastolic dysfunction [
1,
4]. Diastolic dysfunction could be defined as impaired relaxation of the LV, accompanied by LV wall rigidity and increased filling pressure of the LV. Early detection of diastolic dysfunction could lead to appropriate therapy induction and reduce morbidity and mortality related to diastolic dysfunction in patients with heart failure[
5].
Echocardiography is a non–invasive examination widely used to assess diastolic function. Based on the American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI), the assessment of diastolic function could use the following parameters including early diastolic transmitral flow velocity (E' septal and E' lateral), mean E/E', left atrial volume index (LAVI), and tricuspid regurgitation (TR) peak velocity [
6]. But, in some cases of HFpEF patients, the values of the echocardiographic parameters used, such as LAVI, E' septal and/or E' lateral, E/E' show normal values in HFpEF patients [
7].
Several other parameters that could be used to measure diastolic function, but are not routinely used, include colour M–mode propagation velocity (Vp). Colour M–mode propagation velocity (Vp) could represent LV relaxation time constant (τ) and studies have shown that Vp had an inverse correlation with isovolumetric relaxation used in invasive diastolic function measurements. Vp has sparked interest in its usefulness in determining diastolic function and prognosis in patients with ischemic heart disease, myopathy, and HFrEF [
8].The role of Vp in determining diastolic function in patients with HFpEF has not been studied yet. This study aims to determine the role and use of Vp in diastolic dysfunction assessment in HFpEF patients with acute heart failure.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data source
The primary data in this study are obtained by echocardiography examinations by a certified cardiologist at the Dr. Soetomo General Hospital Surabaya and were all acute heart failure patients with normal ejection fraction (HFpEF).
2.2. Study population and design
Our observational analytic study used a cross–sectional design. This study and patient treatment were conducted at Dr. Soetomo General Academic Hospital from April 2022 – June 2022. The population in this study were all acute heart failure patients with normal ejection fraction (HFpEF).
2.3. Data collection
Data was collected by consecutive sampling, where data on all patients who met this study's inclusion and exclusion criteria were collected. Primary data were obtained from interviews and examinations of patients, including physical, laboratory, and echocardiographic examinations.
2.4. Statistical analysis
The independent and dependent variable data were analysed by inferential statistical analysis. The data were tested for normality using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. The statistical difference test used the independent t–test if the data were normally distributed, or the Mann–Whitney U test if the data were not normally distributed. The Pearson or Spearman correlation test was used to test the bivariate correlation between the dependent and independent variables with α = 0.05. If r > 0.6, then the two variables could be concluded as strongly and positively correlated. The test on the degree of diastolic dysfunction was carried out using the ANOVA test because it compared > 2 groups, namely, grades I–II–III diastolic dysfunction based on Vp and E/Vp values. Specificity and sensitivity of predictive value were measured for Vp, E/Vp, and diastolic dysfunction parameters. All analysis results will be presented as narratives, tables, and diagrams. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS (Chicago, IBM) version 26 [
9].
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Subjects Included
The basic characteristics of the study subjects, including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), systolic and diastolic blood pressure, comorbidities, and the degree of diastolic dysfunction, are described in
Table 1. Echocardiographic parameters carried out in this study include ejection fraction value using the biplane method, the diastolic function measured by standard parameters, including MV E Vel, Septal E' and Lateral E', mean E', E/E' ratio, E/A ratio, TR Vmax and LAVI. N Measurement of colour M–mode propagation velocity included Vp value and E/Vp ratio and PCWP estimation based on E/E' and E/Vp methods.
Echocardiographic parameters were tested for data normality using the Saphiro–Wilk test [
10], and if the data were normally distributed, the parameters would be presented in the form of mean and standard deviation. If the parameters were not normally distributed, the parameters would be presented in the form of the median and range in
Table 2.
3.2. Vp Correlation with Left Ventricular Diastolic Function Parameters
A Spearman test was used to determine the correlation between colour M–mode propagation velocity (Vp) value with diastolic function in HFpEF patients because the variable distribution was not normal [
11].
Table 3.
Standard Echocardiographic Parameters.
Table 3.
Standard Echocardiographic Parameters.
| Independent Variables |
Vp |
| ρ |
ρ |
| E/E' |
–0.379 |
0.029 |
| MV E vel |
0.226 |
0.206 |
| E/A |
0.213 |
0.234 |
| Sept E' |
0.636 |
< 0.001 |
| Lat E' |
0.650 |
< 0.001 |
| TR Vmax |
–0.079 |
0.663 |
| LAVI |
–0.231 |
0.195 |
The echocardiographic parameter correlation test results between a left ventricular diastolic function with Vp significantly correlated with E/E', Septal E', and Lateral E' parameters. Vp was negatively correlated with E/E' (p = 0.029; r = –0.37). The results of the correlation test between Vp and Septal E' was a positive correlation (p = < 0.001; r = 0.636). Meanwhile, the results of the correlation test between Vp and Lateral E' was a positive correlation (p = < 0.001; r = 0.650).
3.3. The Echocardiographic Parameter Correlation Test Results with The Degree of Diastolic Dysfunction
The correlation test result between the Vp, PCWP E/Vp, and PCWP E/E' value and the degree of diastolic dysfunction (Grade I, II, or III). Grading of diastolic dysfunction is divided as follows : grade I, impaired relaxation and decreased suction of the LV; grade II, pseudo normalization, increased stiffness of the LV, and possible elevated filling pressure; and grade III, restrictive filling with elevated filling pressure and noncompliant LV [
12]. The degree of diastolic dysfunction can be seen in the cross–tabulation in
Table 4. Statistical calculations showed no correlation between the degree of diastolic dysfunction and Vp, with a significance value of 0.360 (p > 0.05). Meanwhile, the correlation between the degree of diastolic dysfunction and PCWP E/VP ratio and PCWP E/E' value showed a significant correlation, with a significance value of 0.005 (p > 0.05) and 0.013 (p > 0.05).
3.4. Correlation of Estimated PCWP Based on E/Vp Ratio with NT–ProBNP
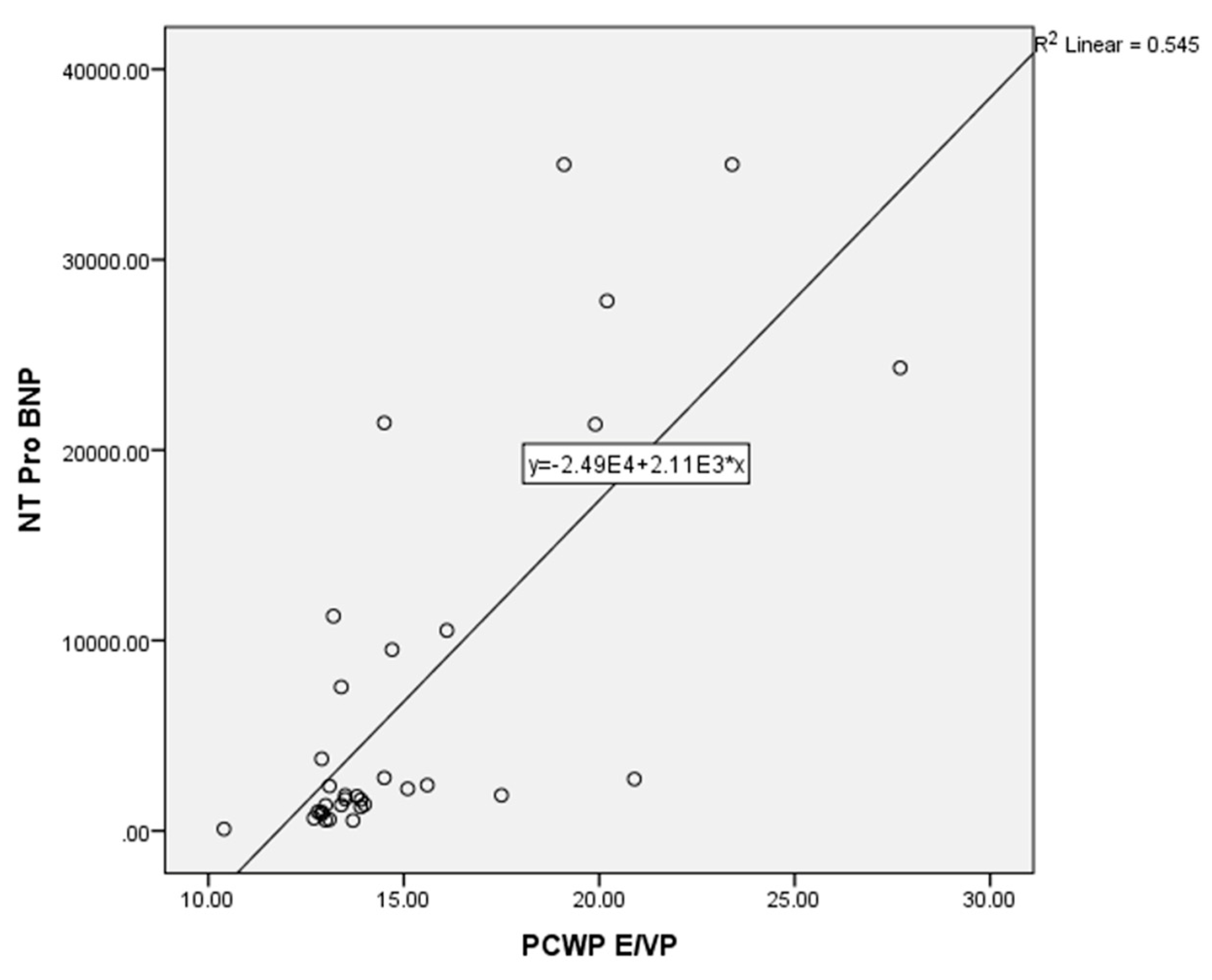
The correlation between the estimated PCWP based on the E/Vp ratio with NT–ProBNP was conducted using a non–parametric Spearman test because the data distribution was not normal for both variables. The results of the correlation test of the two variables showed a strong correlation between estimated PCWP based on E/Vp and NT–ProBNP (p = < 0.001; r = 0.726) (
Figure 1).
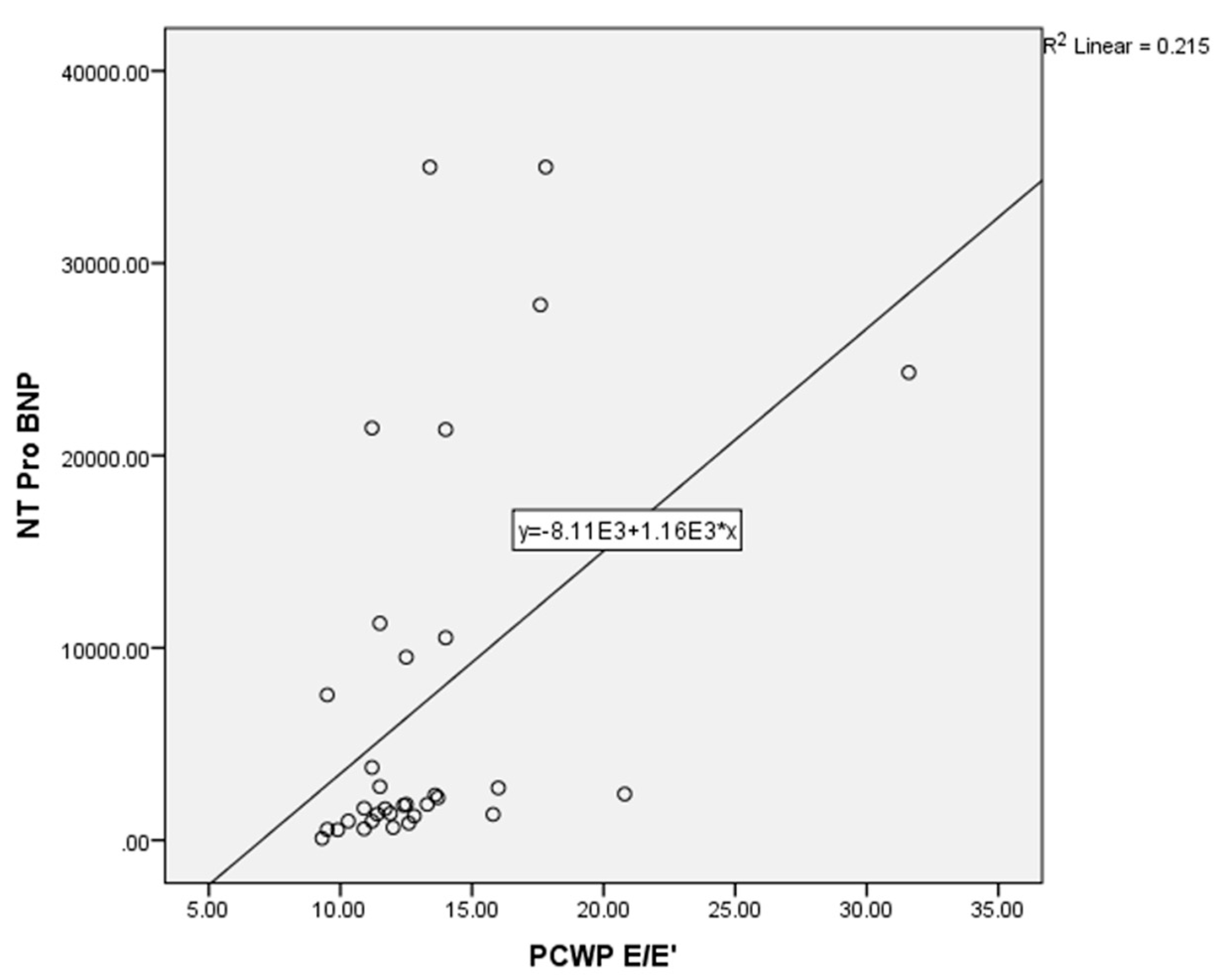
In this study, a correlation test was also conducted between the estimated PCWP based on the E/E’ ratio compared to NT–proBNP as a comparison between the standard method and the E/Vp method. The analysis of the two variables (PCWP E/E' and NT–ProBNP) used a non–parametric Spearman test because the data distribution was abnormal. The results of the correlation test showed a moderate correlation between estimated PCWP based on the E/E ratio and NT–ProBNP (p = < 0.001; r = 0.549) (
Figure 2).
4. Discussion
In our study, the study subjects consisted of 17 females (51.5%) and 16 males (48.5%), with a mean age of 53.55 ± 16.6 years and a mean BMI of 26.4 ± 5 kg/m
2. The characteristics of the study subjects followed the theory that patients with HFpEF tend to be elderly and female, accompanied by an increased BMI [
1,
13,
14]
. In our study subjects, 51.5% of patients had ischemic heart disease (old myocardial infarction & acute coronary syndrome) as the cause of acute heart failure, while 48.5% of other patients had non–ischemic conditions (hypertension, chronic renal failure, preeclampsia, etc.). These findings were different from the theory that HFpEF is more often found in patients without ischemic heart disease; this might happen because, in our study, patients with valvular heart disease or heart rhythm disorders were not included in the study subjects [
1,
13,
14]. Patients with moderate to severe valvular heart disease, such as mitral stenosis, have Vp values like health people because of the high blood flow from LA to LV due to mitral stenosis.
10 To avoid bias in the Vp values in patients with moderate to severe valvular heart disease, the population with this condition was not included in this study.
In this study, subjects who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria were subjected to echocardiography and blood sampling (NT–proBNP) less than 24 hours after the patient was diagnosed with acute heart failure with a normal ejection fraction. Thirty–six patients met the criteria, and 33 patients were willing to participate in the study. The 33 subjects were then measured for echocardiographic parameters, including Ejection Fraction (Simpson's method) [
15], peak velocity of E wave, mean velocity of peak E' wave (septal E' and lateral E'), the ratio of E wave peak to wave A (ratio of E' /A), the ratio of E peak of the E wave to the mean of E' wave peak (E/E' ratio), the LA volume index (LAVI), and the maximal tricuspid regurgitation velocity (TR Vmax). These parameters are used to calculate diastolic function according to the recommendations of ASE/EACVI [
6]. The study subjects were then examined for the colour M–mode propagation velocity (Vp) and the ratio of the E wave peaks to Vp (Ratio E/Vp). Vp was taken on the apical four–chamber view, and the cursor was placed ± 4 cm from the mitral valve, using M–Mode and colour mode on an echocardiography machine [
16].
4.1. Vp Correlation with Left Ventricular Diastolic Function Parameters
The colour M–mode technique can visualize the blood flow propagation throughout the left ventricle during all diastole phases; thus, time, velocity, and space analysis could be performed. Doppler echocardiographic studies have shown that Vp could be used as a parameter for measuring relaxation and pressure during the filling of the left ventricle. Recommendations from ASE / EACVI in calculating the left ventricle diastolic function require several parameters, which are early diastole velocity of the septal and lateral mitral annulus (septal E' / lateral E'), LA Volume Index (LAVI), the maximal tricuspid regurgitation velocity (TR Vmax), E/E' Ratio and E/A Ratio [
6,
17]. In this study, there was a strong positive correlation between Vp and echocardiographic parameters septal E' (p = < 0.001; r = 0.636) and lateral E' (p = < 0.001; r = 0.650), which indicates the higher the septal E' value and lateral E', the higher the Vp value; if septal E' and lateral E' decrease, the Vp value also decreased. The correlation between E/E' and Vp was negatively correlated (p = 0.029; r = –0.37), where the higher the E/E' ratio, the lower the Vp value. Meanwhile, other standard parameters, such as mitral E wave velocity, TR VMax, and LAVI had no statistically significant correlation with Vp.
The results of this study differ from those of Nagueh [
6] where Vp was not correlated with diastolic dysfunction in patients with normal ejection fraction. However, their study also involved many patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), where the Vp value would be normal despite signs of diastolic dysfunction through other examinations [
6,
18]. In our study, none of the study subjects had HCM, and consistently, Vp in acute heart failure patients with normal ejection fraction (EF > 50%) showed abnormal Vp values (< 50 cm/s). Based on our study and comparative studies, it could be concluded that in patients with normal ejection fraction, acute heart failure, Vp value < 50 cm/s with Septal E' value < 70 cm/s and/or Lateral E' < 100 cm/s could be used in diastolic dysfunction diagnosis. The positive correlation between Vp with Septal E' and Lateral E' could occur because the three echocardiographic parameters represent the relaxation time constant of the left ventricle (τ) at the beginning of diastole. The difference between Vp with Septal E' and Lateral E' is that Vp is not affected by the volume status or age of the patient, whereas Septal E' and Lateral E' will decrease with age and increase in conditions of excess volume preload. The use of Septal E' and Lateral E' parameters in acute heart failure patients with normal ejection fraction could lead to errors in diastolic function interpretation [
6,
17].
4.2. Vp Correlation with Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction Degree
The degree of diastolic dysfunction indicates diastolic dysfunction severity, whether the dysfunction only results in an increase in left ventricular filling pressure (LVFP) without an increase in left atrial pressure (LAP) as in grade I diastolic dysfunction. Alternatively, diastolic dysfunction is accompanied by an increase in LVFP and LAP as in grade II and III diastolic dysfunction [
19]. Our study showed no statistical correlation between Vp value and the degree of diastolic dysfunction in acute heart failure patients with normal ejection fraction. As far as the authors are aware, there are currently no studies that have tested the correlation between the degree of diastolic dysfunction and Vp value in acute heart failure patients or other cardiovascular disease conditions. A study by Naugeh [
6]
11 had revealed that Vp is reliable as an index of LV relaxation in patients with depressed LVEFs and dilated left ventricle but not in patients with normal EFs. In patients with normal LV volumes and LVEF but elevated LV filling pressures, Vp can be misleadingly normal. It concluded that Vp also has no correlation with patients with normal EFs.
The E/Vp ratio could be used for estimated LVFP with an E/Vp ratio > 2.5 having PCWP correlation > 15 mm Hg [
6] The more severe the LVFP in patients with heart failure, the more severe the diastolic dysfunction. This study also tested the correlation between the degree of diastolic dysfunction with E/Vp ratio and estimated PCWP. The results obtained in our study showed a statistically moderate correlation between the degree of diastolic dysfunction with E/Vp ratio value and estimated PCWP (p = 0.005; r = 0.478). The grade I diastolic dysfunction group's E/Vp ratio was < 2.5, with a mean estimated PCWP of 14.22 mm Hg. In the second–degree diastolic dysfunction group, the E/Vp ratio is > 2.5, with a mean estimated PCWP of 18.12 mm Hg. In the third–degree diastolic dysfunction group, the E/Vp ratio is > 2.5, with a mean estimated PCWP of 19.96 mm Hg.
The correlation between E/E' and the degree of of diastolic dysfunction showed almost similar results. Statistical analysis showed a moderate correlation between E/E' and the degree of diastolic dysfunction (p = 0.013; r = 0.427). Statistically, there was a moderate correlation between the degree of diastolic dysfunction and E/Vp and E/E' ratios. A study conducted by Andersen et al. also obtained similar results, where there was a gradual increase between the degree of diastolic dysfunction and LVFP as measured non–invasively by echocardiography using E/E' of 10 mm Hg in grade I (7 – 12 mm Hg), 18 mm Hg in grade II (14 – 24 mm Hg) and 24 mm Hg in grade III (19 – 30 mm Hg) (grade I vs. grade II: p < 0.001; grade I vs. grade III: p < 0.001; grade II vs. III degrees: p 0.006) [
20].
Several parameters can be used to determine the degree of diastolic dysfunction in patients with acute heart failure with a normal ejection fraction or decreased ejection fraction, including E Velocity, E/A ratio, Septal E' / Lateral E', LAVI, and TR V Max. For patients with normal ejection fraction, it is necessary to combine standard examination, 2–D echocardiography, and other echocardiographic parameters in diastolic dysfunction interpretation [
1,
6,
17].
4.3. Correlation of Estimated PCWP Based on E/Vp Ratio with NT–ProBNP
Measurement of PCWP in heart failure patients aims to measure the filling pressure in the left ventricle (LV Filling Pressure [LVFP]). Non–invasive measurement of LVFP with echocardiography could be done in 2 ways: Tissue Doppler Imaging (TDI) to measure E/E', or by colour M–mode to measure E/Vp. Several studies have shown some diagnostic superiority of E/E' in heart failure conditions with decreased EF function, but in patients with normal EF, this has not been widely studied. In the guidelines issued by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), the PCWP value that could cause symptoms of heart failure is PCWP > 15 mm Hg. However, the recommendations of the American Society of Echocardiography (ASE) and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI) indicate normal PCWP value ranges from 6 – 12 mm Hg; if PCWP > 12 mm Hg is obtained, it is likely that an increase in left ventricular filling pressure has been found [
1,
6,
17]. Hence, in this study, the PCWP value > 12 mm Hg was used as a sign of heart failure with a normal ejection fraction.
The NT–ProBNP level used in this study to determine the presence of acute heart failure was > 300 pg/ml. This value was obtained by the ICON–RELOADED study [
21], which examined the threshold value to exclude the presence of acute heart failure in the emergency room. Meanwhile, according to the recommendations from the ESC, the NT–ProBNP level in the acute phase was not distinguished from the chronic phase and used a lower value of < 125 pg/ml [
1,
21].Based on these studies, the NT–ProBNP value used in this study for the diagnosis of acute heart failure was > 300 pg/ml. By using PCWP cut–off values > 12 mm Hg and NT–ProBNP > 300 pg/ml in acute heart failure diagnosis with normal ejection fraction, we found a strong correlation between estimated PCWP and NT–ProBNP value (p = < 0.001; r = 0.726) compared to estimated PCWP using E/E' with NT–ProBNP (p = < 0.001; r = 0.549). Our study's result is similar to that of Sugimoto et al. who compared estimated PCWP and E/E' with Vp, where E/E' had a worse predictive value of heart failure, especially in patients with normal ejection fraction [
22]. In another study conducted by Kidawa et al., they also showed similar results where the estimated PCWP value with E/Vp had a strong correlation and was better than E/E' [
23].
The E/E ratio was routinely used in patients with acute heart failure to assess estimated PCWP and LVFP. However, studies that have been conducted show a low correlation between the E/E ratio with PCWP and LVFP, especially in people with normal ejection fraction. E' represents regional velocity in the mitral and correlates with LV relaxation. However, LV elasticity and elongation load could also affect E'. In addition, the E wave represents the peak velocity at the beginning of diastole and is influenced by the loading condition of the patient. The E wave will increase at high preload conditions and will decrease at high afterload conditions. Thus, using the E/E ratio to estimate PCWP in acute heart failure patients with normal ejection fraction will result in an incorrect calculation of the estimated PCWP [
20] [
24].
4.4. Study Limitation
In this study, PCWP measured in acute heart failure patients was only measured non–invasively with echocardiography; no invasive PCWP measurements were used as a comparison. The population of moderate–to–severe valvular heart disease or heart rhythm disorder patients was not included in the study subjects because the measurement of standard diastolic function parameters according to ASE/EACVI recommendations could not be carried out completely. Although the measurement of Vp is relatively easy and could be conducted in all echocardiographic machines without special software, the absence of special software for Vp analysis could lead to subjectivity in this study. To prevent subjectivity in our study, the Vp assessment was conducted five times and divided to determine the mean Vp value, and interobserver measurements were conducted to rule out the subjectivity of the Vp measurement.
5. Conclusions
Overall, our study reveals a substantial positive correlation between colour M–mode Vp values and left ventricular diastolic function standard parameters E' Septal and E' Lateral, as well as a negative correlation between Vp and E/E' ratio in patients with acute heart failure and normal ejection fraction. E/Vp and PCWP E/Vp estimation have a moderate association with the degree of diastolic dysfunction; however, there is no correlation between M–mode Vp colour values and the degree of diastolic dysfunction. In addition, there is a positive relationship between the PCWP evaluation based on the E/Vp ratio and the NT–ProBNP value.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.; methodology, I.S.P.; software, I.S.P.; validation, A.S. and A..; formal analysis, R.A.N.; investigation, I.S.P.; resources, A.S.; data curation, I.S.P.; writing—original draft preparation, F.N.F.; writing—review and editing, R.A.N.; visualization, M.R.; supervision, A. and A.S.; project administration, I.S.P.; funding acquisition, A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Dr. Soetomo General Hospital (Ref. number: 0410/KEPK/IV/2022) on 18 April 2022.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the whole staff and residents from Center for Integrated Cardiac Services at the Soetomo General Academic Hospital, Surabaya, Indonesia for their technical contribution.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 2021;42:3599–726. [CrossRef]
- Naing P, Forrester D, Kangaharan N, Muthumala A, Mon Myint S, Playford D. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A growing global epidemic. Aust J Gen Pract 2019;48:465–71. [CrossRef]
- Marco Tubaro, Pascal Vranckx SP, Vrints and C. Acute heart failure: Epidemiology, classification, andpathophysiology. ESC Textb. Intensive AcuteCardiovascular Care (2 ed.). 2 ed, Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2018. [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer MA, Shah AM, Borlaug BA. Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction In Perspective. Circ Res 2019;124:1598–617. [CrossRef]
- Kossaify A, Nasr M. Diastolic Dysfunction and the New Recommendations for Echocardiographic Assessment of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function: Summary of Guidelines and Novelties in Diagnosis and Grading. J Diagnostic Med Sonogr 2019;35:317–25. [CrossRef]
- Nagueh SF, Smiseth OA, Appleton CP, Byrd BF 3rd, Dokainish H, Edvardsen T, et al. Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr Off Publ Am Soc Echocardiogr 2016;29:277–314. [CrossRef]
- Singh A, Mehta Y. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF): Implications for the anesthesiologists. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 2018;34:161–5. [CrossRef]
- Ravi Vishnu Prasad1, Kumar Vikram Singh1, K. K. Sethi2 SS. Role of Flow Propagation Velocity Across Mitral Valve in the Assessment of Diastolic Dysfunction and Prognostication in Acute Myocardial Infarction. J Indian Acad Echocardiogr Cardiovasc Imaging 2020;4:11-7. [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows 2017.
- SHAPIRO SS, WILK MB. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965;52:591–611. [CrossRef]
- Spearman Rank Correlation Coefficient BT - The Concise Encyclopedia of Statistics, New York, NY: Springer New York; 2008, p. 502–5. [CrossRef]
- Nagueh SF, Appleton CP, Gillebert TC, Marino PN, Oh JK, Smiseth OA, et al. Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr Off Publ Am Soc Echocardiogr 2009;22:107–33. [CrossRef]
- Maeder MT, Buser M, Brenner R, Rickli H. [Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)]. Ther Umsch 2018;75:161–9. [CrossRef]
- Solomon SD, McMurray JJ V, Anand IS, Ge J, Lam CSP, Maggioni AP, et al. Angiotensin-Neprilysin Inhibition in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. N Engl J Med 2019;381:1609–20. [CrossRef]
- Otterstad JE. Measuring left ventricular volume and ejection fraction with the biplane Simpson’s method. Heart 2002;88:559–60. [CrossRef]
- Hodzic A, Bonnefous O, Langet H, Hamiche W, Chaufourier L, Tournoux F, et al. Analysis of inter-system variability of systolic and diastolic intraventricular pressure gradients derived from color Doppler M-mode echocardiography. Sci Rep 2020;10:7180. [CrossRef]
- Nagueh SF. Diastology: 2020-A practical guide. Echocardiography 2020;37:1919–25. [CrossRef]
- Stewart KC, Kumar R, Charonko JJ, Ohara T, Vlachos PP, Little WC. Evaluation of LV diastolic function from color M-mode echocardiography. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2011;4:37–46. [CrossRef]
- Bavry AA, Anderson RD, Gong Y, Denardo SJ, Cooper-Dehoff RM, Handberg EM, et al. Outcomes Among hypertensive patients with concomitant peripheral and coronary artery disease: findings from the INternational VErapamil-SR/Trandolapril STudy. Hypertens (Dallas, Tex 1979) 2010;55:48–53. [CrossRef]
- Andersen OS, Smiseth OA, Dokainish H, Abudiab MM, Schutt RC, Kumar A, et al. Estimating Left Ventricular Filling Pressure by Echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017;69:1937–48. [CrossRef]
- Januzzi JLJ, Chen-Tournoux AA, Christenson RH, Doros G, Hollander JE, Levy PD, et al. N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in the Emergency Department: The ICON-RELOADED Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018;71:1191–200. [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto T, Dohi K, Tanabe M, Watanabe K, Sugiura E, Nakamori S, et al. Echocardiographic estimation of pulmonary capillary wedge pressure using the combination of diastolic annular and mitral inflow velocities. J Echocardiogr 2013;11:1–8. [CrossRef]
- Kidawa M, Coignard L, Drobinski G, Krzeminska-Pakula M, Thomas D, Komajda M, et al. Comparative value of tissue Doppler imaging and m-mode color Doppler mitral flow propagation velocity for the evaluation of left ventricular filling pressure. Chest 2005;128:2544–50. [CrossRef]
- Kawase Y, Kawasaki M, Tanaka R, Nomura N, Fujii Y, Ogawa K, et al. Noninvasive estimation of pulmonary capillary wedge pressure in patients with mitral regurgitation: A speckle tracking echocardiography study. J Cardiol 2016;67:192–8. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).