1. Introduction
The expansion of industrial activities has been adversely impacting the water quality and aquatic ecosystem[
1]. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), for instance, halocarbons, aldehydes, ketones, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are one of the most harmful water pollutants[
2]. Industrial manufacture as resin, plastic, paper making, artificial fiber, anticorrosive leather plywood etc., will discharge a large number of formaldehyde wastewater
[3-5]. Formaldehyde has a strong toxic effect on organisms. If people drink water contaminated by formaldehyde for a long time, it will cause dizziness, anemia and other various mental system diseases. Formaldehyde is difficult to biodegrade because it can inhibit the activity of microorganisms. Therefore, there is a critical need to explore efficient purification technologies to treat industrial effluents containing formaldehyde[
6].
Currently, formaldehyde wastewater is mainly treated by Fenton oxidation technique, photocatalytic oxidation technique, wet oxidation technique, chlorine dioxide oxidation technique and other methods. Fenton oxidation technique is one of the Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) applied for degradation of organic pollutants which are difficult to biodegrade in wastewater
[4, 7-9]. The traditional homogeneous Fenton has been widely used in sewage treatment. However, it has some disadvantages, like large consumption of reagents and high operating cost
[10, 11]. Fenton oxidation technique can degrade refractory pollutants completely or partially by the decomposition of H
2O
2 to produce ·OH
[12-18]. Kajitvichyanukul P et al.[
4] evaluated the formaldehyde was almost completely mineralized by photo-Fenton and the environmental toxicity was at a low level after treatment after 240 min. Moussavi G et al.[
19] showed the complete degradation of formaldehyde (8000 mg L
-1) was attained in heterogeneous Fenton after 6 min.
Furthermore, the hydrolysis of Fe(III) is usually performed under acidic conditions (pH 3.0), so the application of conventional Fenton oxidation techniques is limited to a narrow pH range[
20]. Therefore, the development of heterogeneous Fenton catalysts is necessary for heterogeneous Fenton processes based on Fenton chemistry. Fe-based heterogeneous Fenton catalysts are the most widely used catalyst in Fenton technology, which can effectively extend the pH suitability of Fenton application to neutral conditions. For instance, Mohammadifard Z et al.[
21] proposed that combining visible light and H
2O
2 with MIL-100(Fe) could degrade 93% of formaldehyde (700 mg L
-1). Macdonald J et al.[
5] prepared the zeolite Y supported Fe catalyst and used it to degrade formaldehyde by photo-Fenton, which showed the degradation of formaldehyde was still good at neutral solution. In addition, designing heterogeneous catalysts to achieve highly selective Fenton techniques is of significant practical importance
[22, 23].
At the same time, achieving highly selective oxidation is a scientific challenge. Playing an oxidizing role in the Fenton reaction, ·OH has a high oxidation potential of 2.73 V (EHO•
+H
+/H
2O) that can oxidize a wide range of organic substances[
24]. As a result, organics other than target contaminants inevitably consume a substantial portion of ·OH and the demand for reagents (hydrogen peroxide and iron catalyst) is large
[10, 11]. Adhish J et al.[
25] reported an excellent heterogeneous Fenton catalyst copper sulfide nanoparticles for highly selective degradation of dyes. Lei Chen et al.[
26] exploited the selective interfacial oxidation of methylene blue and chrysoidine G, which was based on the heterogeneous Fenton catalytic properties of Fe-OCNT nanocomposites.
ZSM-5 molecular sieve was first developed by American Mobile company in 1972, which is a new zeolite molecular sieve with high silicon three-dimensional channel. The zeolite molecular sieve has high thermal and hydrothermal stability, and most of the pore size is about 0.55 nm, belonging to the middle pore zeolite. Because of its shape selection catalytic performance and unique surface acidity, it is widely used in adsorption separation, cation exchange, fine chemical synthesis and so on. The unique pore structure of the ZSM-5 provides the crystal structure basis for the design of highly selective and highly active catalysts. Xin Xing[
27] studied the Cu-ZSM-5 as selective catalyst for degradation of n-butylamine. The results showed that one of n-butylamine degradation products could reach 90% at 350℃, which suggested the Cu-ZSM-5 catalyst could remove VOCs selectively. Lin-Cong He[
28] studied selective oxidation of diethylamine using the MnO
x/CeO
2/ZSM-5 catalyst.
In this study, the selective catalyst Fe-ZSM-5 was prepared by the infiltration method. The Fe-ZSM-5/H2O2 heterogeneous Fenton system was constructed for the selective oxidation degradation of formaldehyde. The catalyst synthesized fully characterized using spectroscopic and microscopic techniques including XRD, FT-IR, BET and SEM. Based on the results, the Fe-ZSM-5 catalyst had a fine microporous structure and the same phase composition as ZSM-5. The catalyst still exhibited excellent degradation performance on formaldehyde during multiple reuse, and has low iron leaching rate. Importantly, the heterogeneous Fe-ZSM-5/H2O2 Fenton system showed a broad pH suitability and high selectivity of formaldehyde. The underlying mechanism of such systems had been inferred. This system provided the possibility for the efficient and low-energy treatment of formaldehyde wastewater, which helps to reduce the production of secondary pollutants and the use of chemical reagents, so as to achieve sustainable development by reducing energy consumption and secondary pollution to the environment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
ZSM-5, ammonium acetate, acetylacetone, hydrochloride, Iron (III) nitrate nonahydrate (>98%), tert-Butanol, p-Benzoquinone (97%), sodium hydroxide (>96%) were purchased from Miacklin; Glucose Anhydrose (98%), Hydrogen peroxide (30%), 1,10-Phenanthroline, Ascorbic acid (>90%) were obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.; Sodium acetate anhydrous, acetic acid, formaldehyde (37%), sulfuric acid (98%), hydrochloric acid (36%) were supplied by Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.; potassium iodide was obtained from Merck.
2.2. Preparation of the Fe-ZSM-5 Catalyst
2 g ZSM-5 molecular sieve was added to Fe(NO3)3 solution (0.8 mol L-1) at a liquid-solid ratio of 15:1 to obtain the Fe-ZSM-5 catalyst after 4 hours at water bath temperature of 50 ℃. The concentration difference of Iron ions in Fe(NO3)3 solution before and after impregnation was determined, and the iron load on the catalyst was calculated.
Then, in order to study the best impregnation concentration of iron ion, the impregnation concentration of iron ion was changed to 0.1 mol/L, 0.2 mol/L, 0.4 mol/L, 0.8 mol/L and 1.6 mol/L, respectively. The influence of impregnation temperature on the iron loading of ZSM-5 molecular sieve was studied by changing the impregnation temperature in the gradient range of 25-95 ℃. The ratio of impregnating liquid to solid was changed to 10:1, 15:1, 20:1, 25:1 and 30:1 to investigate the optimal ratio of impregnating liquid to solid. Finally, the concentration difference of iron ions in Fe(NO3)3 solution before and after impregnation for 1 h, 2 h, 4 h and 8 h was measured, and the iron load on the catalyst was calculated to obtain the best impregnation time.
2.3. Characterization
The microstructure characteristics of the samples were observed by a JSM-7600F thermal field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM). The Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area and pore volume of the samples were measured by a Micromeritics ASAP-2020 analyzer while the samples were dried at 110 ℃ for 6 hours. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of the samples was measured using an Ultima IV assembled multifunctional X-ray diffractometer at a scanning rate of 8˚/min and a scanning range of 5˚ to 80˚. The Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrum of the samples was measured using a Nicolet iS5 infrared spectrometer to qualitatively analyze the functional groups and chemical bond compositions of materials and deduce the structures of materials and molecules, and the powder samples were tested after drying under ATR.
2.4. Heterogeneous Fenton Catalytic Performance
The Fe-ZSM-5 catalyst was evaluated for the heterogeneous Fenton degradation of formaldehyde at different H
2O
2 concentrations, pH, temperature and catalyst dosage respectively. The calculated amount of catalyst and H
2O
2 were added to an equal molar concentration of glucose and formaldehyde,the reaction was carried out under constant temperature conditions afterwards. At set intervals, Glucose concentration was determined by liquid chromatography. the characteristic absorbance of formaldehyde solution was measured by a UV–vis spectrophotometer at wavelength 414 nm which an appropriate amount of acetyl acetone and ammonium salt were added into the separation solution. The selectivity of the catalyst to the target pollutant could be expressed as follows:
Where A and B are the concentrations (mg L
-1) of the target pollutants adsorbed and the total pollutant adsorbed respectively. The higher the calculated selectivity value, the better the selectivity of the catalyst to the target pollutant. The selectivity coefficient (D) was also used to evaluate the selectivity of catalyst. The value of D represented the level of selectivity. The selectivity coefficient could be expressed as follows:
Where K1 and K2 respectively represent quasi-second-order kinetic reaction rate constants.
2.5. Stability and Reusability Measurements
The stability and reusability of this catalyst were measured at a mixture of glucose 100mg L
-1 and formaldehyde 100mg L
-1, solution pH 3, 10 g L
-1catalyst dose, 385 mmol L
-1 H
2O
2, contact time 360 min and the reaction temperature 55 ℃ in a water bath. After each heterogeneous Fenton catalytic cycle, this catalyst was centrifuged from the solution while the eluted Fe and the concentrations of residual formaldehyde in the solution were determined by phenanthroline spectrophotometry (GB/T 9739-2006) and acetyl acetone spectrophotometry (HJ 601-2011) respectively. The separated catalyst was washed and dried for 8 h at 110 ℃ to be used for the next catalytic cycle, with a total of 5 cycles. The dissolution rate of iron was calculated by the formula as follows:
Where , and represent the mass (g) of granular catalyst added, the concentration (mg L-1) of iron and the residual volume (L) of the solution after the reaction respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fe3+ Loading Condition of Catalyst
3.1.1. Influence of Different Impregnation Concentration on Catalyst Performance
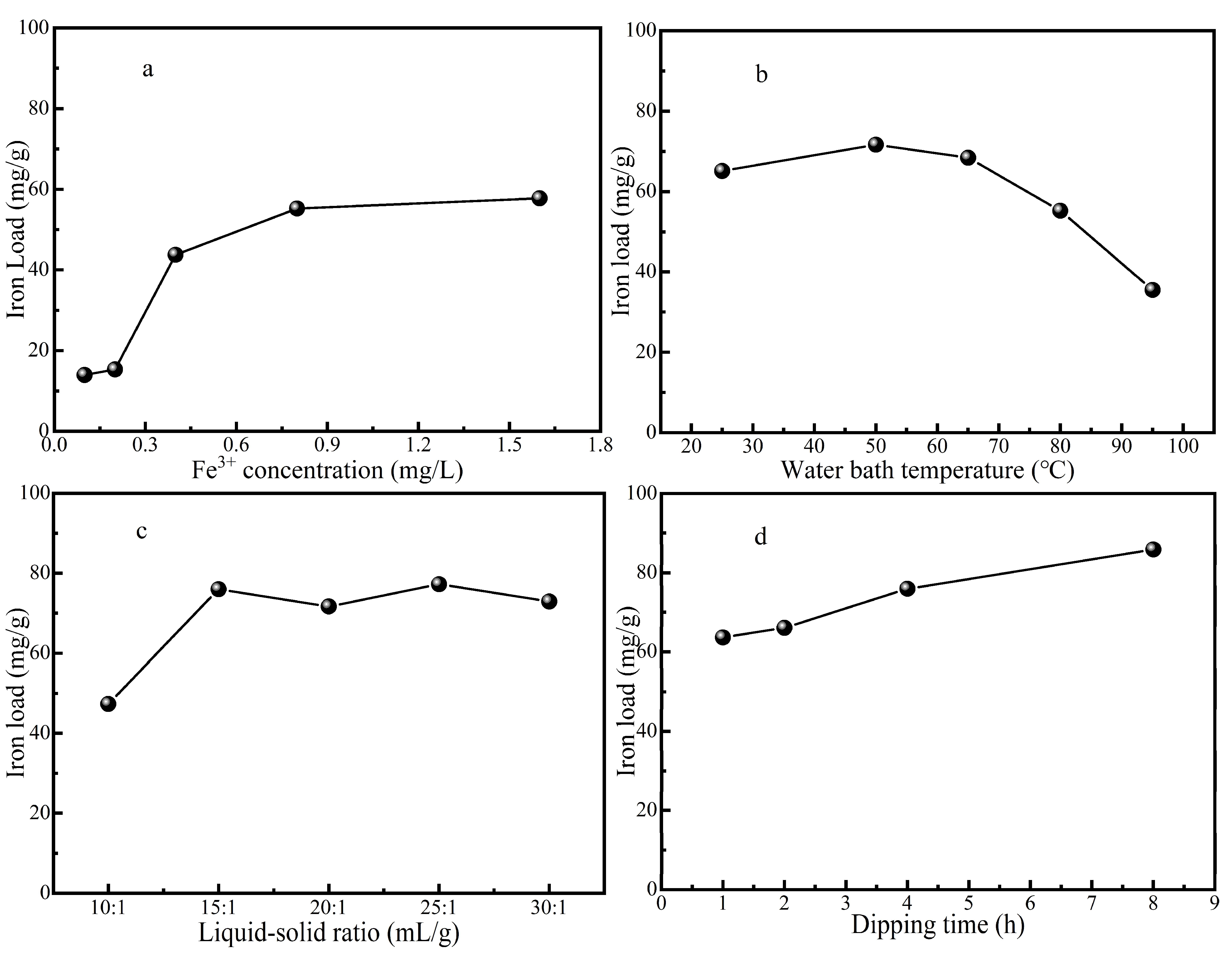
It can be seen from
Figure 1a that the iron load increases with the increase of the impregnation concentration of iron ion, because the driving force of the difference of iron ion concentration makes the adsorption amount of iron ion on ZSM-5 molecular sieve or the ion exchange capacity on the surface of ZSM-5 molecular sieve gradually increase.When the impregnation concentration of Fe(NO
3)
3 solution increases from 0.8 mol/L to 1.6 mol/L, the iron load of ZSM-5 molecular sieve does not increase significantly, which may be due to the fact that the adsorption of Iron ions on ZSM-5 molecular sieve tends to be saturated and the iron load reaches a stable state. At this time, increasing the concentration of Fe(NO
3)
3 solution has little effect on the iron loading capacity of catalyst, and the iron loading efficiency is not high.The optimal impregnation concentration is 0.8 mol/L of Fe(NO
3)
3 solution from the economic point of view and the efficiency of carrying iron.
3.1.2. Influence of Different Impregnation Temperature on Catalyst
As can be seen from
Figure 1b, when the temperature rises to 50 ℃, the iron loading of ZSM-5 molecular sieve increased, due to the high solution temperature increases the internal energy and the molecular movement becomes violent, which is conducive to the entry of iron ions into ZSM-5 molecular sieve and promotes its iron loading process. But when the temperature continues to rise from 50 ℃ to 95 ℃, the iron load of ZSM-5 molecular sieve decreases constantly, too high temperature will have a negative effect on the iron load process.This will make the adsorption of iron ions desorption again.Therefore, 50℃ is the best water bath temperature for carrying iron.
3.1.3. Influence of Different Impregnation Liquid to Solid Ratio on Iron Loading
It can be seen from
Figure 1c that with the increase of impregnation liquid to solid ratio, the iron load on ZSM-5 molecular sieve also increased. The iron loading increases obviously while the ratio of liquid to solid increased from 10:1 to 15:1. However, when the ratio of liquid to solid continues to increase, the improvement effect on the iron loading becomes weak, fluctuates or slightly decreases. From the economic point of view and iron carrying efficiency, the impregnation liquid-solid ratio of 15:1 is more appropriate.
3.1.4. Effect of Different Impregnation Time on Iron Load
As can be seen from
Figure 1d, the iron load on ZSM-5 molecular sieve increases with the increase of impregnation time. After calculation, the increase percentage of iron load of immersion time 2 h compared with that of immersion time 1h is 3.88%, the increase percentage of iron load of immersion time 4h compared with that of immersion time 2 h is 14.93%, and the increase percentage of iron load of immersion time 8h compared with that of immersion time 4h is 12.99%. It can be seen that the iron load efficiency is higher when immersion time 4 h. The iron loading efficiency began to decrease gradually with additional time, so 4 h impregnation time was selected as the optimal time.
3.2. Characterization of Catalysts
The shape, size, chemical composition, and crystal structure of the synthesized Fe-ZSM-5 nanoparticles were determined by various evaluation techniques. They are presented in the following paragraphs.
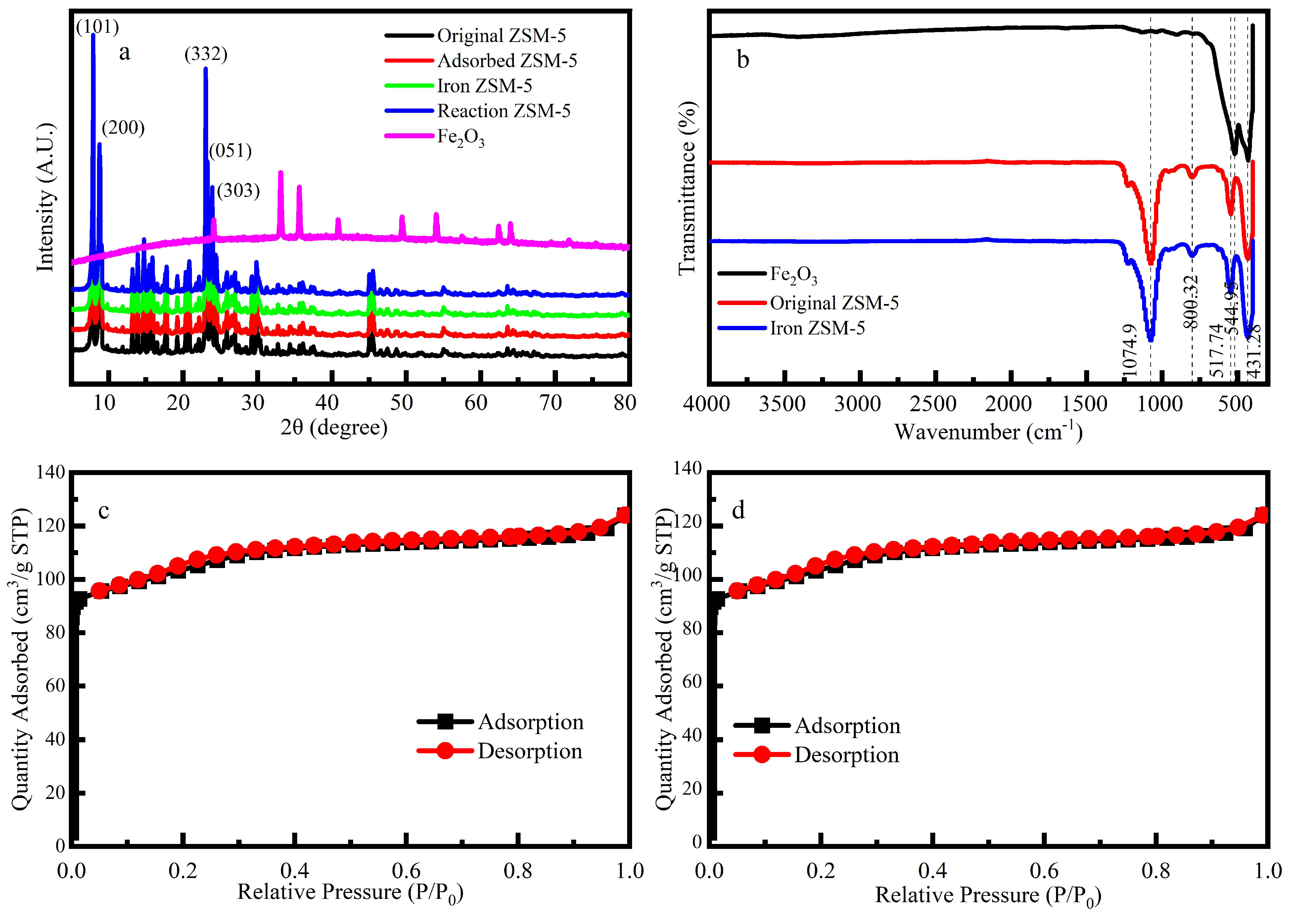
The XRD (
Figure 1a) of the Fe-ZSM-5, ZSM-5 and Fe
2O
3 NPs, acquired from XRD (Ultima IV). The Fe-ZSM-5 characteristic peaks appeared at 2θ=23.9˚, 23.3˚, 23.0˚, 8.8˚and 7.9˚, corresponding to the (303), (051), (332), (200) and (101) crystal planes of the ZSM-5 respectively. The characteristic peaks of Iron-rich lepidolite were found in the samples at 2θ=8.8˚, 26.8˚, 36.1˚and 45.6˚, which were associated with the crystal planes of (001), (003), (113) and (005) respectively. Three typical peaks were observed for Fe
2O
3 NPs at 2θ=24.1˚, 33.1˚and 35.6˚, respectively, which were coincided with previous research. The weak peak strength was due to the low iron content or iron only adhering to the surface of the catalyst[
8]. The characteristic peaks of Fe-ZSM-5 were well consistent with characteristic peaks of Fe
2O
3 NPs and ZSM-5, suggesting the successful synthesis of Fe-ZSM-5 catalysts.
When P/P
0<0.05 (
Figure 1c, 1d), N
2 adsorption was increased rapidly, indicating that a large number of microporous structures existed on ZSM-5 and Fe-ZSM-5. The average pore size diameter of Fe-ZSM-5 was of about 2.247 nm further proving that this catalyst was mostly composed of microporous (
Table 1)[
29]. The catalytic performance of the catalyst is positively correlated with the number of active sites. After loading Fe, the pore volume and the specific surface area of micropores were reduced by 0.57% and 1.81% respectively, indicating that the number of active sites was decreased in comparison to ZSM-5.
The FT-IR spectrums (
Figure 1b) show that the process of loading iron did not change the internal functional groups of ZSM-5, and the loading might only occur on the surface of the ZSM-5. The bands at 800 cm
-1 and 1074 cm
-1 were attributed to the Si-O-Si stretching modes of the Fe-ZSM-5[
30]. The band at 544 cm
-1 was assigned to the unique chain structure unit of the ZSM-5, which the structure consisted of eight five-membered rings connected by edges to form a symmetrical structure unit[
31]. A band was detected at 544 cm
-1, which was related to the Si-O bending vibration of the ZSM-5 molecular sieve.
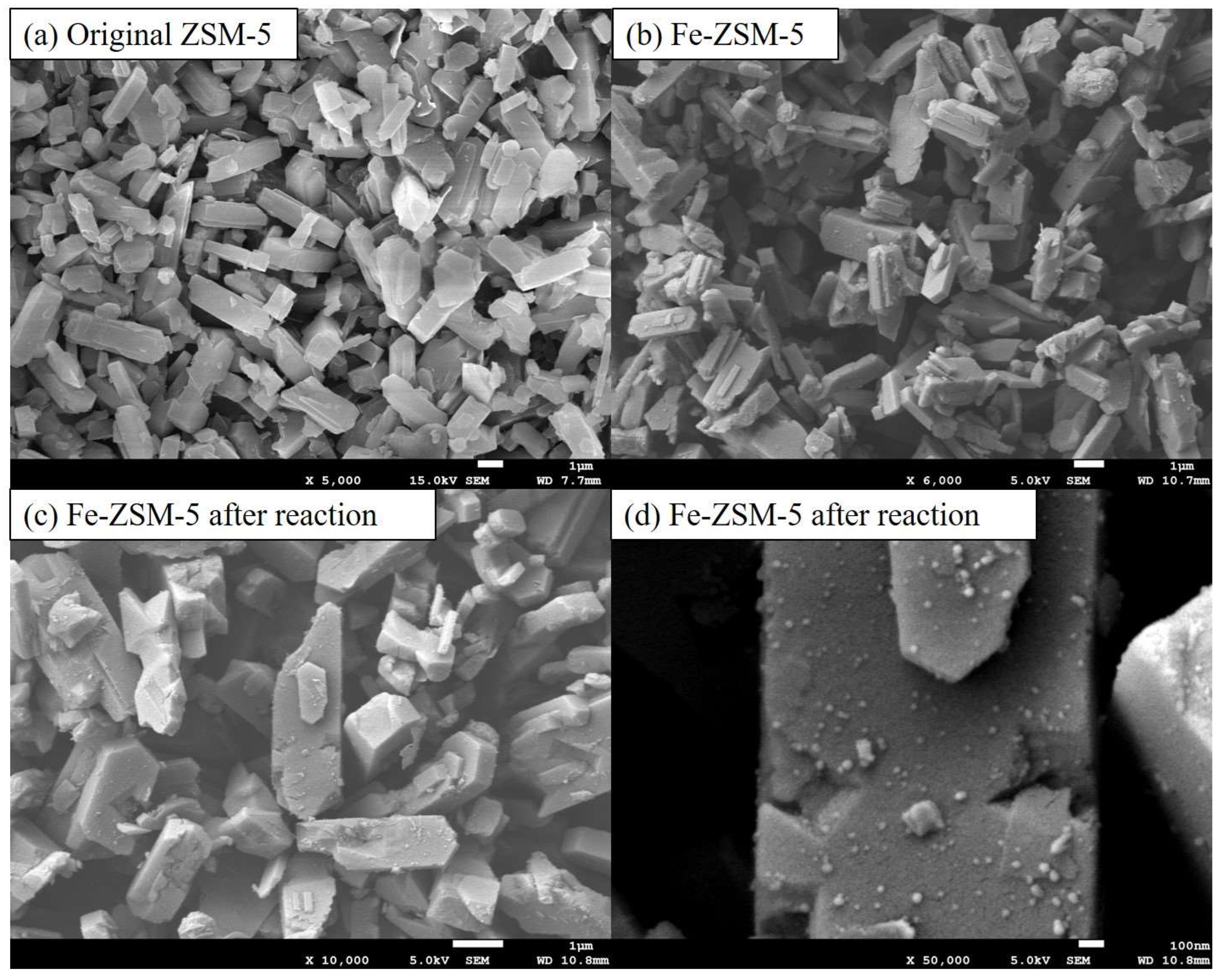
The SEM images (
Figure 2) show that the Fe-ZSM-5 has a smooth surface with a regular shape and uniform pore structure, similar to ZSM-5[
30]. Many fine particles could be clearly observed on the surface of ZSM-5 (
Figure 2c), which reveals Fe was uniformly attached to the grain surface with no apparent agglomeration. The surface of Fe-ZSM-5 catalyst appeared a few cracks appear but the grain shape and structure are still intact after the Fenton reaction.
3.3. Degradation of Formaldehyde in the Fe-ZSM-5/H2O2 System
3.3.1. Effect of Experimental Parameters on Degradation of Formaldehyde
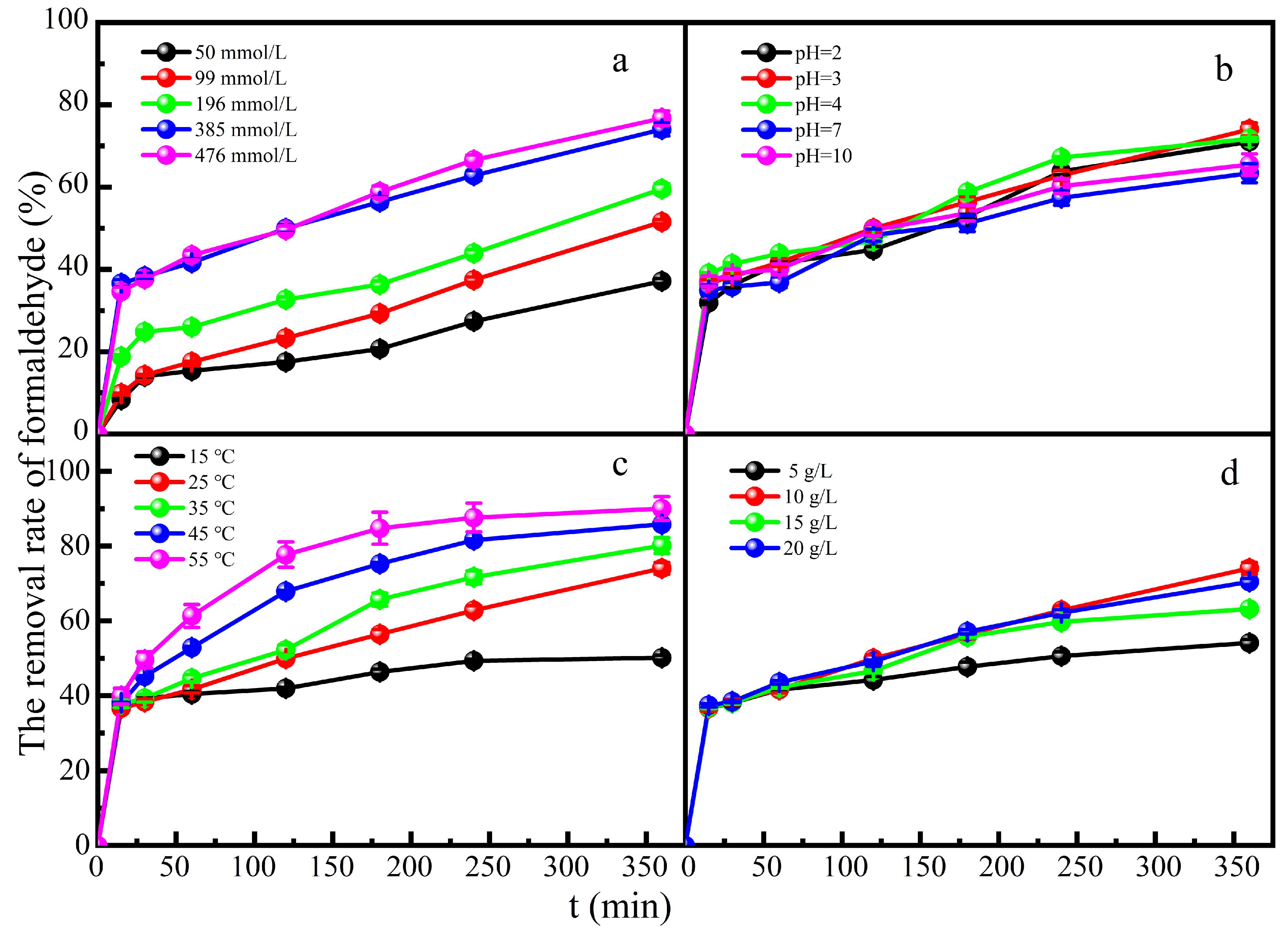
The effect of H
2O
2 concentration on formaldehyde degradation was investigated in a mixed solution of formaldehyde and glucose. When the concentration of H
2O
2 increased to 385 mmol L
-1, it resulted in 74% degradation of formaldehyde at 360 min reaction time (
Figure 3a). However, H
2O
2 doses of 385 mmol L
-1 to 476mmol L
-1 did not improve the formaldehyde degradation significantly. The positive effect of H
2O
2 was attributed to more hydroxyl radicals. While the concentration of H
2O
2 increased to 476 mmol L
-1, hydroxyl radicals might react inefficiently in the catalytic reaction process under the condition of constant catalyst dosage[
32]. The number of active sites was finite, which leaded to little increase in the degradation rate.
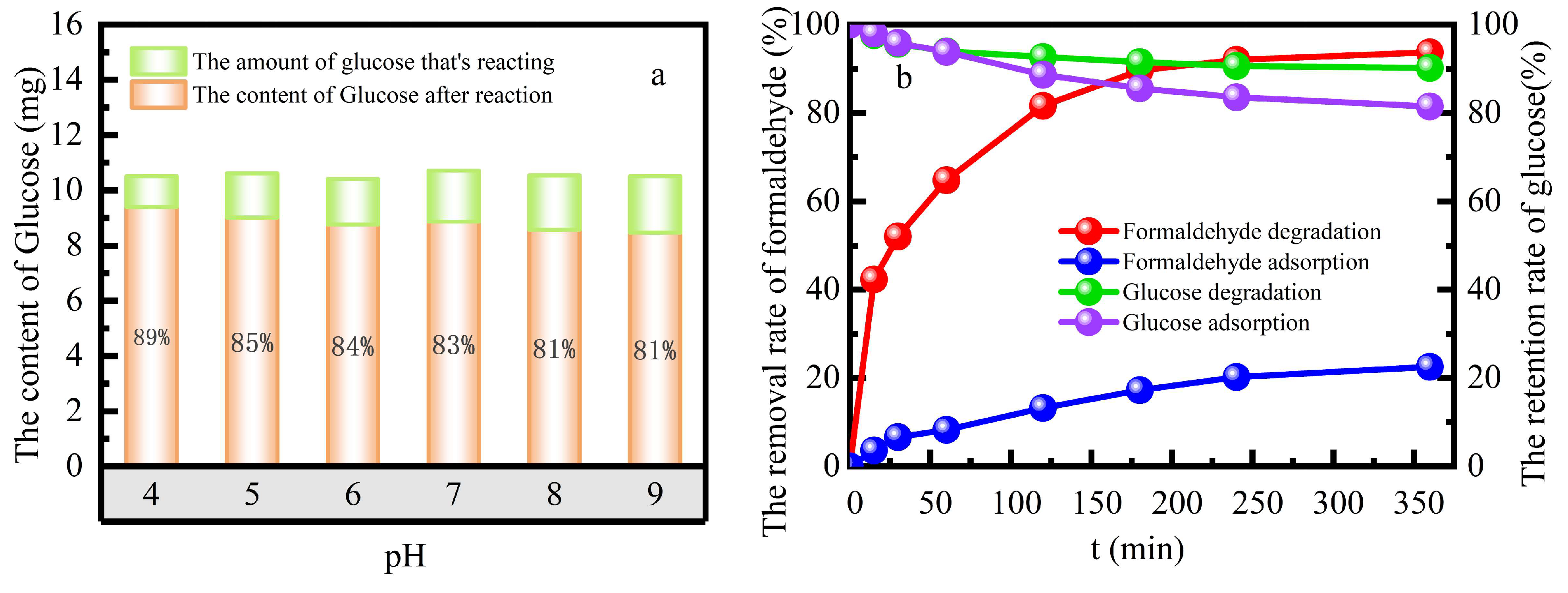
The effect of pH value on formaldehyde degradation was investigated in a mixed solution of formaldehyde and glucose. The catalyst could remove formaldehyde better under acidic than under neutral or alkaline conditions (
Figure 3b). This is because the decomposition products of H
2O
2 are dominantly ·OH under acidic conditions. Alkaline conditions inhibit the generation of ·OH and H
2O
2 are easily hydrolyzed to ·OOH and H
+, while the oxidation ability of ·OH is much stronger than that of ·OOH. When pH=3, the degradation rate of formaldehyde could reach 75% at 360 min contact time. Although the degradation performance was poor in neutral or alkaline medium, about 65%~70% degradation rate of formaldehyde could be reached still. The Fe-ZSM-5 heterogeneous Fenton catalyst greatly widen the pH range of Fenton reaction and is conducive to the application in a broader field.
The effect of reaction temperature on formaldehyde degradation was investigated in a mixed solution of formaldehyde and glucose (
Figure 3c). An increase in temperature could accelerate the movement of molecules and the decomposition of H
2O
2. With the increase of reaction temperature, the degradation rate of formaldehyde increased and could reach 94% at 55 ℃ at 360 min reaction time.
Figure 3d shows the effect of catalyst dose on formaldehyde degradation in a mixed solution of glucose and formaldehyde. As expected, the degradation rate of formaldehyde could reach 70% with the increase of catalyst dose. The appropriate increase of catalyst dose provided more adsorption sites, which could adsorb more formaldehyde molecules and catalyzed the generation of more hydroxyl radicals. However, too much catalyst would promote the occurrence of other side reactions to inhibit the occurrence of catalytic reactions[
31]. Increased Fe
3+ concentration will inhibit the production of ·OH, so excessive catalyst dose will inhibit the generation of ·OH. In a series of Fenton reaction chain reactions, the degradation rate of formaldehyde was relatively reduced when the production rate of Fe
2+ was lower than the accumulation rate of Fe
3+.
3.3.2. Selectivity of the Fe-ZSM-5 Catalyst towards Formaldehyde
The selectivity of the catalyst to simulated formaldehyde wastewater was investigated in the mixed solution of formaldehyde and glucose with both concentrations of 100 mg L
-1, 385 mmol L
-1 H
2O
2, 10 g L
-1 catalyst dose and the reaction temperature 55 ℃ in a water bath at solution pH 3 (
Figure 4). The 98.15% selectivity to formaldehyde in the heterogeneous Fenton system was better than 86.42% selectivity in the adsorption system. The selectivity coefficient of the catalyst was D
formaldehyde =2.3984, D
glucose =3.9962. The concentration gradient promoted the cycle of adsorption-degradation-the continuous absorption-degradation of formaldehyde, and then the cycle continued. This inhibited the adsorption of glucose by catalyst, which made better selective to formaldehyde.
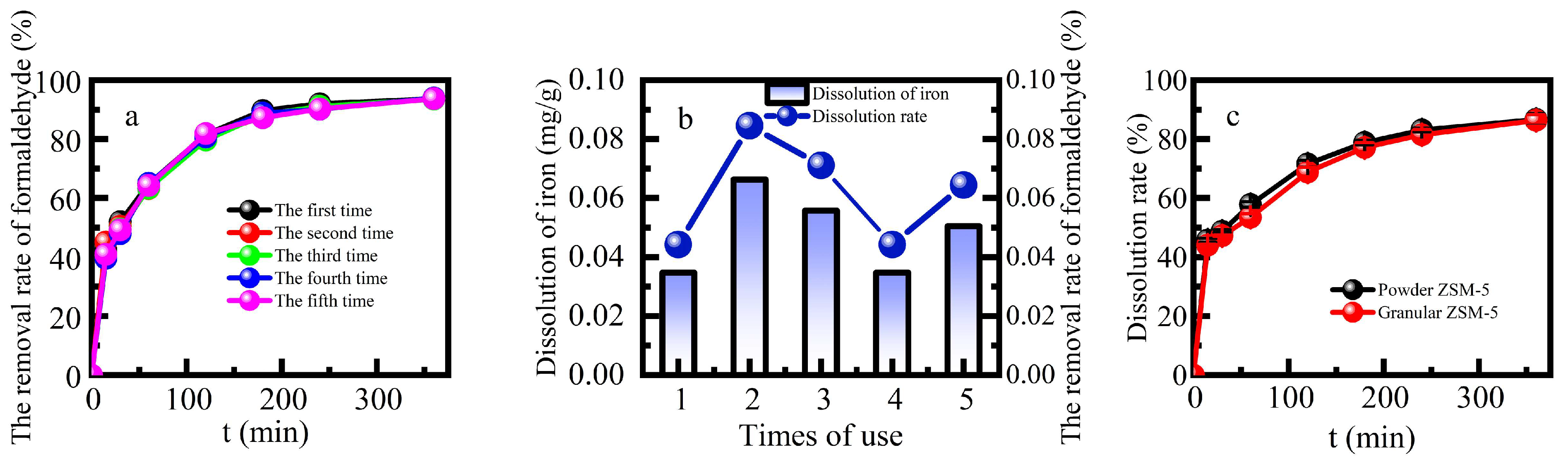
The stability of heterogeneous Fenton catalysts is of great significance in both economic and environmental. This study examined the reusability and stability of Fe-ZSM-5 by measuring the efficiency of formaldehyde degradation and the amount of leaching Fe from Fe-ZSM-5 in multiple cycle (
Figure 5a and
Figure 5b). The percentage removal of formaldehyde was more than 90% after five cycles with no significant decline. The average amount of Fe dissolved was 0.048 mg g
-1 for five continuous cycles, and the average dissolution rate was 0.062%. The Fe supported on the catalyst was completely preserved after the reaction, which was probably the reason for its good reuse performance. This further demonstrated that a large amount of iron sludge would not be generated after the reaction. The heterogeneous Fenton catalytic efficiency and good stability of Fe-ZSM-5 indicated it is appropriate for the removal of formaldehyde in industrial sectors.
3.3.3. Mechanism of the Formaldehyde Degradation
The Fe-ZSM-5/H
2O
2 system was based on the active radicals generated by the decomposition of H
2O
2 to degrade target pollutants. Formaldehyde was degraded by reactive radicals after it was adsorbed by the Fe-ZSM-5, and the above reaction occurred on the catalyst surface.
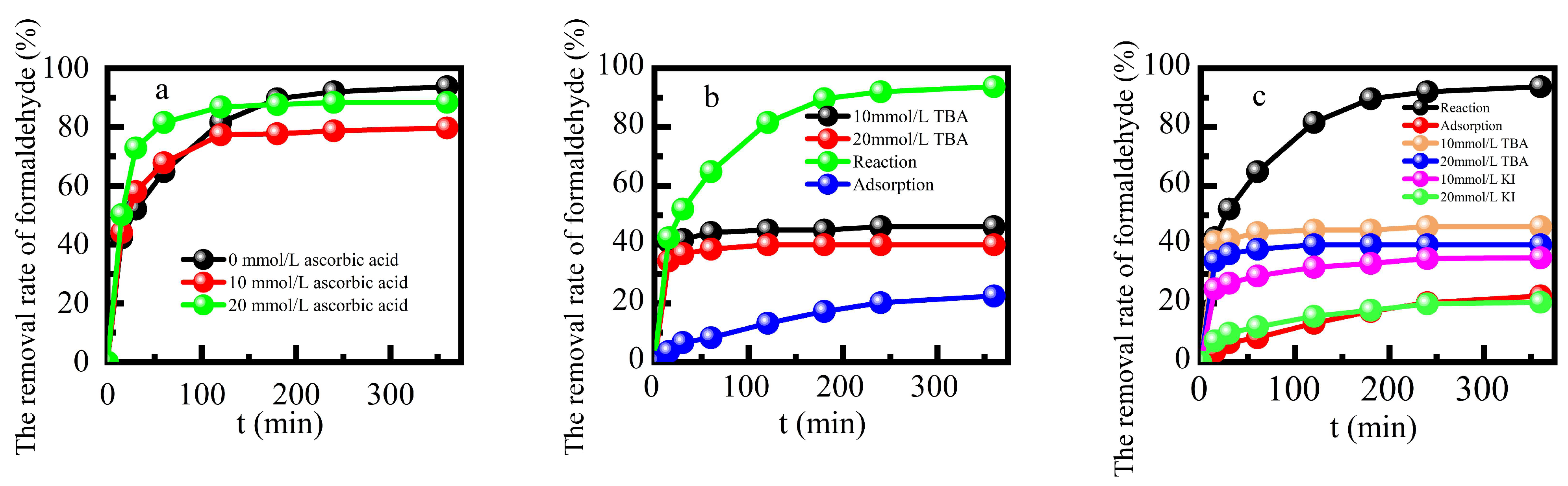
Figure 6 shows the effects of adding ascorbic acid, tert-butanol, KI solution, or benzoquinone[
14] at a concentration of 10 mmol L
-1 on formaldehyde degradation efficiency respectively. The addition of free radical quenchers inhibited formaldehyde degradation. Hydroxyl radical played a dominant role while peroxide radical played a limited catalytic role in the reaction process[
33]. The degradation of formaldehyde in this reaction system mainly occurred on the surface of this catalyst.
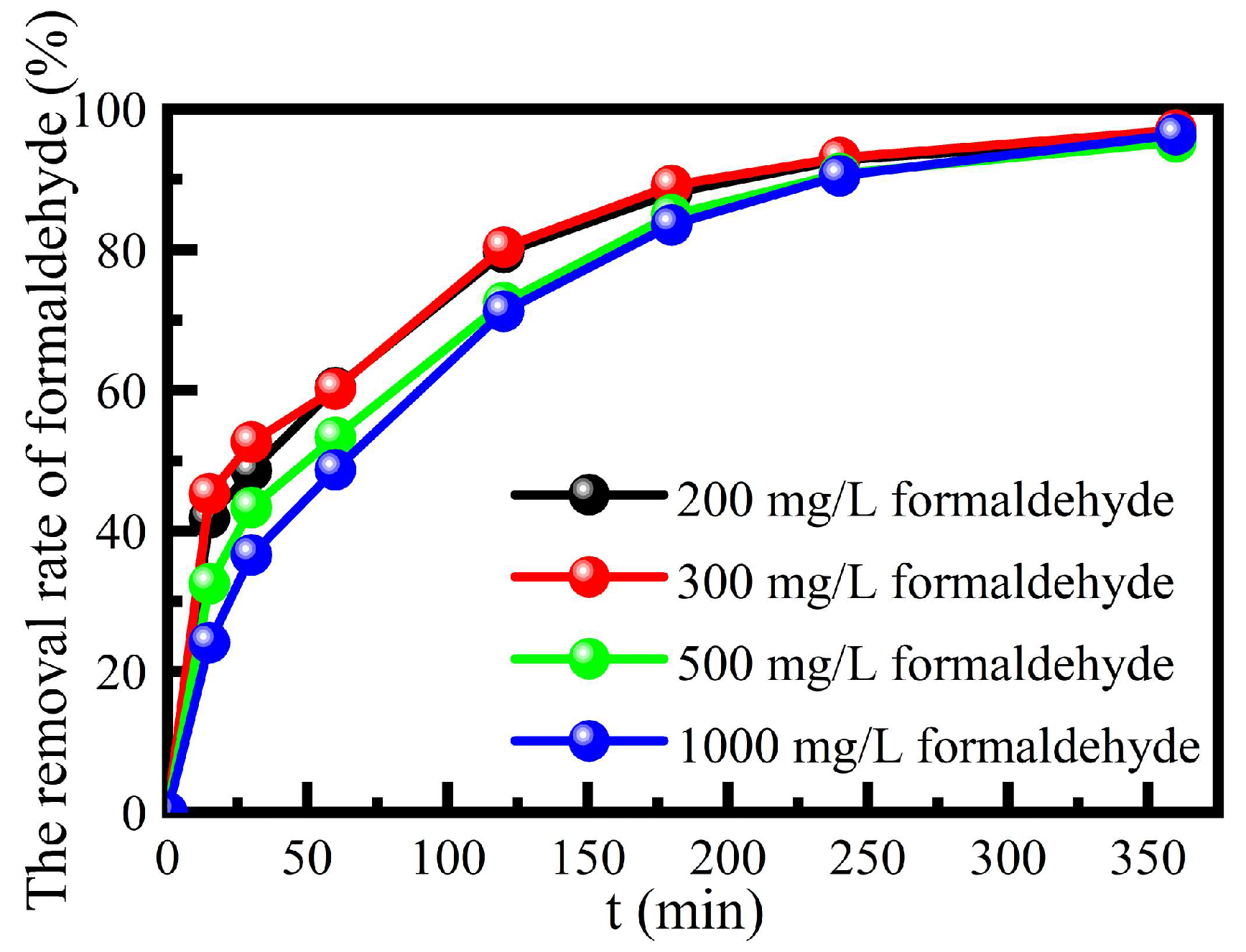
3.3.4. Degradation of the Catalyst on a High Concentration of Formaldehyde Wastewater
The degradation performance of this catalyst on the high concentration of formaldehyde was investigated, at solution pH 3, 385 mmol L
-1 H
2O
2, contact time 360 min and the reaction temperature 55 ℃ in a water bath (
Figure 7). The catalyst still had a good degradation performance on the high concentration of formaldehyde simulated wastewater, and the degradation rate was more than 95%. It could be seen that the catalyst not only solved the defects of the traditional homogeneous Fenton reaction and also had a good degradation performance of high concentration of formaldehyde simulated wastewater.
4. Conclusion
The Fe-ZSM-5 catalyst was prepared by impregnating the ZSM-5 molecular sieve in ferric chloride solution. Under the conditions of solution pH 3, 385 mmol L-1 H2O2, 10 g L-1 catalyst dose and the reaction temperature 55 ℃ in a water bath, 93.72% of formaldehyde was degraded, and the selectivity of the catalyst for formaldehyde was 98.15% after 360 min. Notably, compared with traditional Fenton technology, the formaldehyde degradation rate of selective heterogeneous Fenton could reach about 75% in neutral and alkaline solutions, which indicated its pH requirements were more relaxed. The degradation rate of formaldehyde could still reach more than 93% after repeated experiments with the catalyst for 5 times, indicating this catalyst had good stability. It was speculated that the degradation mechanism of formaldehyde was mainly surface heterogeneous catalysis mechanism, and the cycle of adsorption-degradation-desorption-re-adsorption-re-degradation-re-desorption was carried out on the catalyst surface. Furthermore, the catalyst prepared in this experiment still had good degradation performance to the high concentration of formaldehyde.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Peiguo Zhou; methodology, Peiguo Zhou; project administration, Peiguo Zhou; writing—original draft , Jiaxin Hou; writing—review and editing, Jiaxin Hou; formal analysis, Donghui Zhang, Ziqiao Liao and Liping Yang; data curation, Wenjing Yang; investigation, Xin Ru and Zongbiao Dai.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program “Key Technology of Safety Production and Pollution Monitoring of Wood-Based Panel” (2016YFD0600703).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhou P, Ru X, Yang W, Dai Z, Ofori M A, Chen J, Hou J, Zhong Z and Jin H. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. 2022, 10, 107138.
- Du L, Gao W, Li Z, Jiao W and Liu Y. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification. 2020, 155, 108053.
- Gu X, Tan C, He L, Guo J, Zhao X, Qi K and Yan Y. Chemosphere. 2022, 304, 135292.
- Kajitvichyanukul P, Lu M-C, Liao C-H, Wirojanagud W and Koottatep T. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2006, 135, 337–343.
- MacDonald M J, Wu Z, Ruzicka J-Y, Golovko V, Tsang D C W and Yip A C K. Separation and Purification Technology. 2014, 125, 269–274.
- Wu Y, Guo Q, Liu H, Wei S and Wang L. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. 2022, 10, 108277.
- Ganiyu S O, van Hullebusch E D, Cretin M, Esposito G and Oturan M A. Separation and Purification Technology. 2015, 156, 891–914.
- Iglesias O, Meijide J, Bocos E, Sanromán M Á and Pazos M. Electrochimica Acta. 2015, 169, 134–141.
- Rayaroth M P, Aravindakumar C T, Shah N S and Boczkaj G. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2022, 430, 133002.
- Moussavi G, Yazdanbakhsh A and Heidarizad M. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2009, 171, 907–913.
- Zhang H, Zheng Z, Yu T, Liu C, Qian H and Li J. Environmental Research. 2022, 205, 112550.
- Du C, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhou L, Yu G, Wen X, Chi T, Wang G, Su Y, Deng F, Lv Y and Zhu H. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2022, 431, 133932.
- He H, Li Y, Wang J, Wu J, Sun L, Cai Y, Cheng H and Wang X. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2022, 450, 138141.
- Huang X, Xiao J, Yi Q, Li D, Liu C and Liu Y. Journal of Environmental Management. 2022, 308, 114613.
- Panda N, Sahoo H and Mohapatra S. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2011, 185, 359–365.
- Shen J, Li Y, Zhu Y, Hu Y and Li C. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. 2016, 4, 2469–2476.
- Silva M and Baltrusaitis, J. Journal of Hazardous Materials Letters. 2021, 2, 100012.
- Tan Y, Zhao W, Sun L, Zhang R, Hou J, Fu S, Xu W and Zhang R. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2022, 369, 133280.
- Moussavi G, Bagheri A and Khavanin A. J Hazard Mater. 2012, 237-238, 147-152.
- Bokare A D and Choi, W. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2014, 275, 121–135.
- Mohammadifard Z, Saboori R, Mirbagheri N S and Sabbaghi S. Environ Pollut. 2019, 251, 783–791.
- Yin D, Zhang L, Zhao X, Chen H and Zhai Q. Chinese Journal of Catalysis. 2015, 36, 2203–2210.
- Ziembowicz S and Kida, M. Chemosphere. 2022, 296, 134041.
- Chen B, Xu J, Dai G, Sun X, Situ Y and Huang H. Separation and Purification Technology. 2022, 299, 121688.
- Raj S I and Jaiswal, A. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry. 2021, 410, 113158.
- Chen L, Wang S, Yang Z, Qian J and Pan B. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2021, 292.
- Xing X, NaCheng, JieSun, YonggangZhang, ZhongshenZhang, XinHao, Zhengping. Journal of environmental sciences. 2020, 96(1).
- He L-C, Wang X-F, Liu C-F, Li B, Luo M-F and Chen J. Applied Catalysis A: General. 2022, 648, 118929.
- Shao J a, Jiang H, Yang M, Xiao J, Yang H, Chen Y, Zhang S and Chen H. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis. 2022, 166, 105628.
- Ahmadi Zahrani A and Ayati, B. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry. 2020, 873, 114456.
- Rostamizadeh M, Jafarizad A and Gharibian S. Separation and Purification Technology. 2018, 192, 340–347.
- Cleveland V, Bingham J-P and Kan E. Separation and Purification Technology. 2014, 133, 388–395.
- Wang J and Tang, J. Journal of Molecular Liquids. 2021, 332, 115755.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).