Submitted:
18 January 2024
Posted:
19 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction: the neuropeptides as the modulators of the connectome
2. The hypocretin/orexin peptide family: an indispensable neuroendocrine switch of circadian activities.
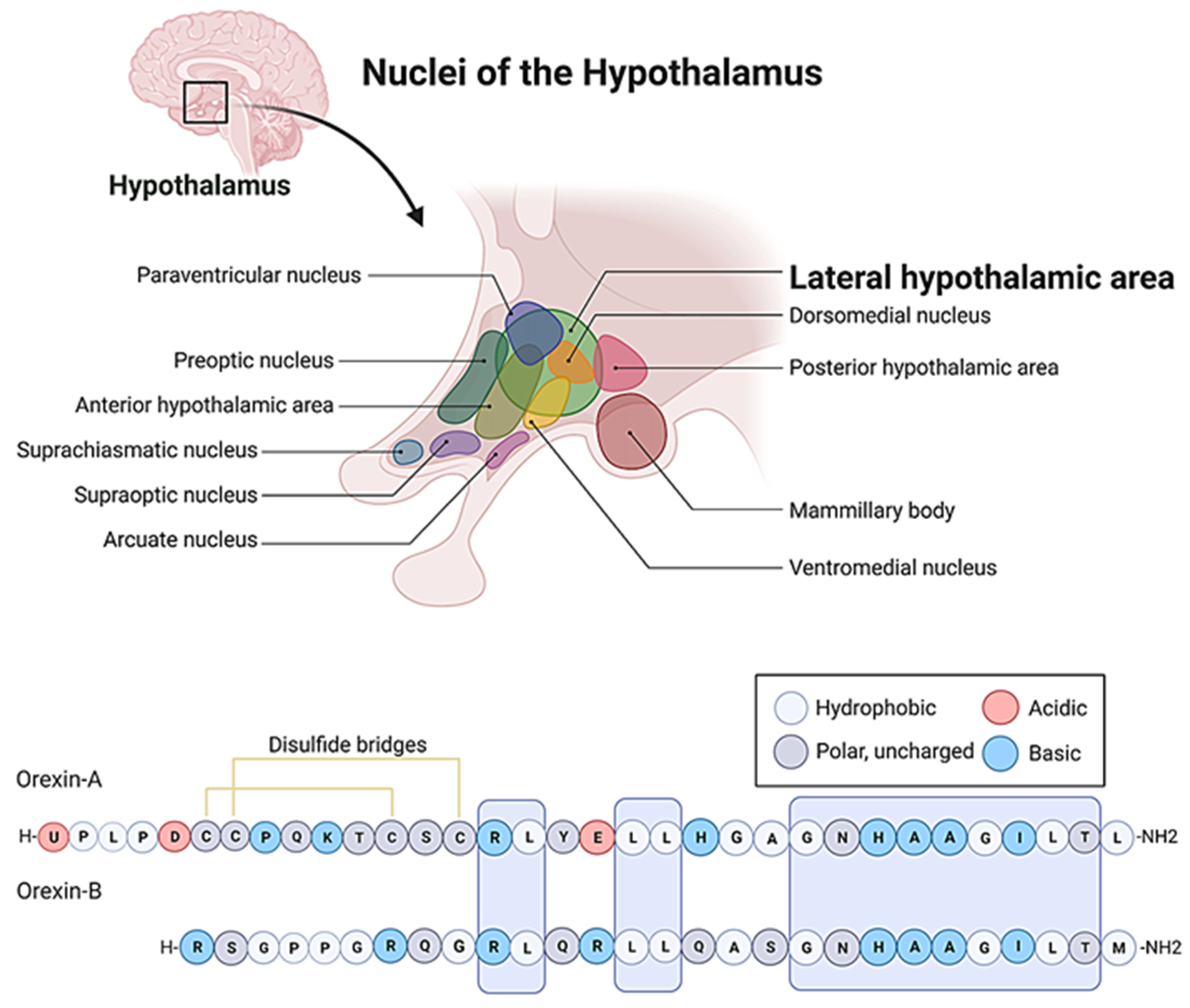
3. The role of orexins in the regulation of the stress response.
4. The role of the orexins in the regulation of behavior.
5. The cooperation between the orexinergic and other peptidergic neuronal networks.
6. Aspects of human pathophysiology: present and future therapeutic potential of orexin receptor ligands.
7. Promising results in translational pharmacology
8. Discussion
9. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTH | adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| ALS | ascending reticular activation system |
| ARAS | ascending reticular activation system |
| ARC | arcuate nucleus |
| BBB | blood brain barrier |
| BNST | bed nucleus of stria terminalis |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| CRH | corticotrope-releasing hormone |
| DMH | dorsomedial hypothalamus |
| DR | dorsal raphe |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GABA | -amino-butyric-acid |
| GAS | General adaptation syndrome |
| GPCRs | G-protein-coupled receptors |
| HPA | hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal cortex |
| LA | lateral amygdala |
| LC | locus coeruleus |
| LHA | lateral hypothalamic area |
| MCH | melanin-concentrating hormone |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| NAc | nucleus accumbens |
| NIBS | non-invasive brain stimulation techniques |
| NM | neuromedin |
| NMS | neuromedin S |
| NPY | neuropeptide Y |
| NST | nucleus of the solitary tract |
| NT | neurotensin |
| OX | orexin receptors |
| PAG | periaqueductal grey |
| PFA | perifornical area |
| POA | preoptic area |
| POMC | pro-opiomelanocortin |
| PPT | pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus |
| PVN | paraventricular nuclei |
| RVLM | rostral ventrolateral medulla |
| RVMM | rostral ventromedial medulla |
| SA | sympathoadrenal |
| SCN | suprachiasmatic nucleus |
| SON | supraoptic nucleus |
| tDCS | transcranial direct current stimulation |
| TMs | transcranial magnetic stimulation |
| TMN | tuberomammillary nucleus |
| VTA | ventral tegmental area |
| VLPO | ventrolateral preoptic nucleus |
References
- Oliver, G.; Schafer, E.A. On the Physiological Action of Extracts of Pituitary Body and certain other Glandular Organs: Preliminary Communication. J Physiol 1895, 18, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, H.H. On some physiological actions of ergot. J Physiol 1906, 34, 163–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US, V.E.; Gaddum, J.H. An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J Physiol 1931, 72, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Pol, A.N. Neuropeptide transmission in brain circuits. Neuron 2012, 76, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elphick, M.R.; Mirabeau, O.; Larhammar, D. Evolution of neuropeptide signalling systems. J Exp Biol 2018, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvar, P.J.; Andero, R.; Hurlemann, R.; Lago, T.R.; Zelikowsky, M.; Dabrowska, J. Limbic Neuropeptidergic Modulators of Emotion and Their Therapeutic Potential for Anxiety and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. J Neurosci 2021, 41, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokfelt, T.; Bartfai, T.; Bloom, F. Neuropeptides: opportunities for drug discovery. Lancet Neurol 2003, 2, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purves, D. Neuroscience, Sixth edition. ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, 2018; p. 1 volume (various pagings). [Google Scholar]
- Seguin, C.; Sporns, O.; Zalesky, A. Brain network communication: concepts, models and applications. Nat Rev Neurosci 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Spekker, E.; Szabó, Á.; Polyák, H.; Vécsei, L. Modelling the neurodevelopmental pathogenesis in neuropsychiatric disorders. Bioactive kynurenines and their analogues as neuroprotective agents—In celebration of 80th birthday of Professor Peter Riederer. Journal of Neural Transmission 2022, 129, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Editorial of special issue ‘dissecting neurological and neuropsychiatric diseases: Neurodegeneration and neuroprotection’. 2022, 23, 6991. [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, T.; Mieda, M. Connectomics of orexin-producing neurons: interface of systems of emotion, energy homeostasis and arousal. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2011, 32, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Diano, M.; Battaglia, S. Insights into structural and functional organization of the brain: evidence from neuroimaging and non-invasive brain stimulation techniques. Frontiers in Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1225755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaszberenyi, M.; Bujdoso, E.; Pataki, I.; Telegdy, G. Effects of orexins on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system. J Neuroendocrinol 2000, 12, 1174–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaszberenyi, M.; Bujdoso, E.; Kiss, E.; Pataki, I.; Telegdy, G. The role of NPY in the mediation of orexin-induced hypothermia. Regul Pept 2002, 104, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaszberenyi, M.; Bujdoso, E.; Telegdy, G. The role of neuropeptide Y in orexin-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal activation. J Neuroendocrinol 2001, 13, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaszberenyi, M.; Bujdoso, E.; Telegdy, G. Behavioral, neuroendocrine and thermoregulatory actions of apelin-13. Neuroscience 2004, 129, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palotai, M.; Bagosi, Z.; Jaszberenyi, M.; Csabafi, K.; Dochnal, R.; Manczinger, M.; Telegdy, G.; Szabo, G. Ghrelin and nicotine stimulate equally the dopamine release in the rat amygdala. Neurochem Res 2013, 38, 1989–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palotai, M.; Bagosi, Z.; Jaszberenyi, M.; Csabafi, K.; Dochnal, R.; Manczinger, M.; Telegdy, G.; Szabo, G. Ghrelin amplifies the nicotine-induced dopamine release in the rat striatum. Neurochem Int 2013, 63, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaszberenyi, M.; Bujdoso, E.; Bagosi, Z.; Telegdy, G. Mediation of the behavioral, endocrine and thermoregulatory actions of ghrelin. Horm Behav 2006, 50, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Telegdy, G. Neurotransmissions of antidepressant-like effects of neuromedin U-23 in mice. Behav Brain Res 2014, 259, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telegdy, G.; Adamik, A. Anxiolytic action of neuromedin-U and neurotransmitters involved in mice. Regul Pept 2013, 186, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaszberenyi, M.; Bagosi, Z.; Thurzo, B.; Foldesi, I.; Telegdy, G. Endocrine and behavioral effects of neuromedin S. Horm Behav 2007, 52, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Telegdy, G. Neurotransmissions of antidepressant-like effects of neuromedin U-23 in mice. Behavioural brain research 2014, 259, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Schally, A.; Telegdy, G. Neurotransmission of the antidepressant-like effects of the growth hormone-releasing hormone antagonist MZ-4-71. Behavioural brain research 2012, 228, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Csabafi, K.; Telegdy, G. Neurotransmissions of antidepressant-like effects of kisspeptin-13. Regulatory peptides 2013, 180, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telegdy, G.; Tanaka, M.; Schally, A.V. Effects of the growth hormone-releasing hormone (GH-RH) antagonist on brain functions in mice. Behavioural brain research 2011, 224, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rákosi, K.; Masaru, T.; Zarándi, M.; Telegdy, G.; Tóth, G.K. Short analogs and mimetics of human urocortin 3 display antidepressant effects in vivo. Peptides 2014, 62, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, K.N.; Nguyen, N.P.K.; Nguyen, L.T.H.; Shin, H.-M.; Yang, I.-J. Screening for Neuroprotective and Rapid Antidepressant-like Effects of 20 Essential Oils. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Kádár, K.; Tóth, G.; Telegdy, G. Antidepressant-like effects of urocortin 3 fragments. Brain Research Bulletin 2011, 84, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Telegdy, G. Antidepressant-like effects of the CRF family peptides, urocortin 1, urocortin 2 and urocortin 3 in a modified forced swimming test in mice. Brain research bulletin 2008, 75, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Liu, H.Y.; Wang, B.Y.; Lin, H.N.; Wang, M.C.; Ren, J.X. A review of physiological functions of orexin: From instinctive responses to subjective cognition. Medicine (Baltimore) 2023, 102, e34206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soya, S.; Sakurai, T. Evolution of Orexin Neuropeptide System: Structure and Function. Front Neurosci 2020, 14, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, T.; Amemiya, A.; Ishii, M.; Matsuzaki, I.; Chemelli, R.M.; Tanaka, H.; Williams, S.C.; Richardson, J.A.; Kozlowski, G.P.; Wilson, S.; et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 1998, 92, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lecea, L.; Kilduff, T.S.; Peyron, C.; Gao, X.; Foye, P.E.; Danielson, P.E.; Fukuhara, C.; Battenberg, E.L.; Gautvik, V.T.; Bartlett, F.S., 2nd; et al. The hypocretins: hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, C.; Tighe, D.K.; van den Pol, A.N.; de Lecea, L.; Heller, H.C.; Sutcliffe, J.G.; Kilduff, T.S. Neurons containing hypocretin (orexin) project to multiple neuronal systems. J Neurosci 1998, 18, 9996–10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, J.C.; Presse, F.; Arias, C.; Peto, C.; Vaughan, J.; Nahon, J.L.; Vale, W.; Sawchenko, P.E. The melanin-concentrating hormone system of the rat brain: an immuno- and hybridization histochemical characterization. J Comp Neurol 1992, 319, 218–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lopez, C.; Dietrich, M.O.; Metzger, F.; Loetscher, H.; Torres-Aleman, I. Disturbed cross talk between insulin-like growth factor I and AMP-activated protein kinase as a possible cause of vascular dysfunction in the amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 2 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 2007, 27, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, J.J.; Leslie, R.A.; Patel, S.; Evans, M.L.; Wattam, T.A.; Holmes, S.; Benham, C.D.; Taylor, S.G.; Routledge, C.; Hemmati, P.; et al. Orexin A activates locus coeruleus cell firing and increases arousal in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999, 96, 10911–10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saper, C.B.; Chou, T.C.; Elmquist, J.K. The need to feed: homeostatic and hedonic control of eating. Neuron 2002, 36, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlet, S.; Tyler, C.J.; Leonard, C.S. Direct and indirect excitation of laterodorsal tegmental neurons by Hypocretin/Orexin peptides: implications for wakefulness and narcolepsy. J Neurosci 2002, 22, 2862–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saper, C.B.; Scammell, T.E.; Lu, J. Hypothalamic regulation of sleep and circadian rhythms. Nature 2005, 437, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Wu, F.; Zhang, M.; Ding, D.; Fan, S.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. The Interaction Between the Ventrolateral Preoptic Nucleus and the Tuberomammillary Nucleus in Regulating the Sleep-Wakefulness Cycle. Front Neurosci 2020, 14, 615854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigoni, E.; Fuller, P.M. The Sleep-Promoting Ventrolateral Preoptic Nucleus: What Have We Learned over the Past 25 Years? Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcomb, K.; Olah, S.S.; Kennedy, M.J.; Ford, C.P. Properties and modulation of excitatory inputs to the locus coeruleus. J Physiol 2022, 600, 4897–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.C.; Bjorkum, A.A.; Gaus, S.E.; Lu, J.; Scammell, T.E.; Saper, C.B. Afferents to the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus. J Neurosci 2002, 22, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, E.; Yanagisawa, M.; Sakurai, T.; Mieda, M. Orexin neurons suppress narcolepsy via 2 distinct efferent pathways. J Clin Invest 2014, 124, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.; Yamanaka, A. The role of orexin neuron activity in sleep/wakefulness regulation. Peptides 2023, 165, 171007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Patterson, L.M.; Berthoud, H.R. Orexin-A projections to the caudal medulla and orexin-induced c-Fos expression, food intake, and autonomic function. J Comp Neurol 2005, 485, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, S.W.; Arseth, H.A.; Johnson, A.K. Orexin neurons couple neural systems mediating fluid balance with motivation-related circuits. Behav Neurosci 2018, 132, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backberg, M.; Hervieu, G.; Wilson, S.; Meister, B. Orexin receptor-1 (OX-R1) immunoreactivity in chemically identified neurons of the hypothalamus: focus on orexin targets involved in control of food and water intake. Eur J Neurosci 2002, 15, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazzi, G.; Moghadam, K.K.; Maggi, L.S.; Donadio, V.; Vetrugno, R.; Liguori, R.; Zoccoli, G.; Poli, F.; Pizza, F.; Pagotto, U.; Ferri, R. Autonomic disturbances in narcolepsy. Sleep Med Rev 2011, 15, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg-Raibstein, D.; Burdakov, D. Do orexin/hypocretin neurons signal stress or reward? Peptides 2021, 145, 170629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafe, L.A.; Bhatnagar, S. Orexins and stress. Front Neuroendocrinol 2018, 51, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargin, D. The role of the orexin system in stress response. Neuropharmacology 2019, 154, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinazzi, R.; Andreis, P.G.; Rossi, G.P.; Nussdorfer, G.G. Orexins in the regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Pharmacol Rev 2006, 58, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Dieguez, C. Cross-talk between orexins (hypocretins) and the neuroendocrine axes (hypothalamic-pituitary axes). Front Neuroendocrinol 2010, 31, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohsaka, A.; Watanobe, H.; Kakizaki, Y.; Suda, T.; Schioth, H.B. A significant participation of orexin-A, a potent orexigenic peptide, in the preovulatory luteinizing hormone and prolactin surges in the rat. Brain Res 2001, 898, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetherington, A.W.; Ranson, S.W. Hypothalamic lesions and adiposity in the rat. The Anatomical Record 1940, 78, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, B.K.; Brobeck, J.R. Hypothalamic control of food intake in rats and cats. Yale J Biol Med 1951, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar]
- Oomura, Y.; Ono, T.; Ooyama, H.; Wayner, M.J. Glucose and osmosensitive neurones of the rat hypothalamus. Nature 1969, 222, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, H.; Takenoya, F.; Guan, J.L.; Kageyama, H.; Yada, T.; Shioda, S. Hypothalamic neuronal networks and feeding-related peptides involved in the regulation of feeding. Anat Sci Int 2003, 78, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmquist, J.K.; Elias, C.F.; Saper, C.B. From lesions to leptin: hypothalamic control of food intake and body weight. Neuron 1999, 22, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, T. Roles of orexins in the regulation of body weight homeostasis. Obes Res Clin Pract 2014, 8, e414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuld, A.; Hebebrand, J.; Geller, F.; Pollmacher, T. Increased body-mass index in patients with narcolepsy. Lancet 2000, 355, 1274–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekely, M.; Petervari, E.; Balasko, M. Thermoregulation, energy balance, regulatory peptides: recent developments. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2010, 2, 1009–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federici, L.M.; Caliman, I.F.; Molosh, A.I.; Fitz, S.D.; Truitt, W.A.; Bonaventure, P.; Carpenter, J.S.; Shekhar, A.; Johnson, P.L. Hypothalamic orexin’s role in exacerbated cutaneous vasodilation responses to an anxiogenic stimulus in a surgical menopause model. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 65, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folgueira, C.; Beiroa, D.; Porteiro, B.; Duquenne, M.; Puighermanal, E.; Fondevila, M.F.; Barja-Fernandez, S.; Gallego, R.; Hernandez-Bautista, R.; Castelao, C.; et al. Hypothalamic dopamine signaling regulates brown fat thermogenesis. Nat Metab 2019, 1, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasson, R.; Dearth, R.K.; White, R.S.; Chappell, P.E.; Mellon, P.L. Orexin A induces GnRH gene expression and secretion from GT1-7 hypothalamic GnRH neurons. Neuroendocrinology 2006, 84, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sebastiano, A.R.; Wilson-Perez, H.E.; Lehman, M.N.; Coolen, L.M. Lesions of orexin neurons block conditioned place preference for sexual behavior in male rats. Horm Behav 2011, 59, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.L.; Molosh, A.; Fitz, S.D.; Truitt, W.A.; Shekhar, A. Orexin, stress, and anxiety/panic states. Prog Brain Res 2012, 198, 133–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palotai, M.; Telegdy, G.; Jaszberenyi, M. Orexin A-induced anxiety-like behavior is mediated through GABA-ergic, alpha- and beta-adrenergic neurotransmissions in mice. Peptides 2014, 57, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhaven, M.W.; Cornish, J.L.; Staples, L.G. The orexin-1 receptor antagonist SB-334867 decreases anxiety-like behavior and c-Fos expression in the hypothalamus of rats exposed to cat odor. Behav Brain Res 2015, 278, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, T. The role of orexin in motivated behaviours. Nat Rev Neurosci 2014, 15, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, R.M.; Fink, A.E.; Wigestrand, M.B.; Farb, C.R.; de Lecea, L.; Ledoux, J.E. Orexin/hypocretin system modulates amygdala-dependent threat learning through the locus coeruleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110, 20260–20265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soya, S.; Shoji, H.; Hasegawa, E.; Hondo, M.; Miyakawa, T.; Yanagisawa, M.; Mieda, M.; Sakurai, T. Orexin receptor-1 in the locus coeruleus plays an important role in cue-dependent fear memory consolidation. J Neurosci 2013, 33, 14549–14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telegdy, G.; Adamik, A. The action of orexin A on passive avoidance learning. Involvement of transmitters. Regul Pept 2002, 104, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.; Goadsby, P.J. The hypothalamic orexinergic system: pain and primary headaches. Headache 2007, 47, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, I.; La Marra, M.; Di Maio, G.; Monda, V.; Chieffi, S.; Guatteo, E.; Messina, G.; Moscatelli, F.; Monda, M.; Messina, A. Physiological Role of Orexinergic System for Health. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseghi, S.; Zarrabian, S.; Haghparast, A. Reviewing the role of the orexinergic system and stressors in modulating mood and reward-related behaviors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2022, 133, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Spekker, E.; Polyák, H.; Tóth, F.; Vécsei, L. Mitochondrial impairment: A common motif in neuropsychiatric presentation? The link to the tryptophan–kynurenine metabolic system. Cells 2022, 11, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scammell, T.E. Narcolepsy. N Engl J Med 2015, 373, 2654–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, C.E.; Cogswell, A.; Koralnik, I.J.; Scammell, T.E. The neurobiological basis of narcolepsy. Nat Rev Neurosci 2019, 20, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thannickal, T.C.; Moore, R.Y.; Nienhuis, R.; Ramanathan, L.; Gulyani, S.; Aldrich, M.; Cornford, M.; Siegel, J.M. Reduced number of hypocretin neurons in human narcolepsy. Neuron 2000, 27, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scammell, T.E.; Winrow, C.J. Orexin receptors: pharmacology and therapeutic opportunities. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2011, 51, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, J.A.; Jones, K.A.; Adham, N.; Forray, C.; Artymyshyn, R.; Durkin, M.M.; Smith, K.E.; Tamm, J.A.; Boteju, L.W.; Lakhlani, P.P.; et al. Identification and characterization of two G protein-coupled receptors for neuropeptide FF. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 39324–39331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmle, B.; Schindler, M.; Beilmann, M.; Hamilton, B.S.; Doods, H.N.; Wieland, H.A. Characterization of the NPGP receptor and identification of a novel short mRNA isoform in human hypothalamus. Regul Pept 2003, 111, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Faraco, J.; Li, R.; Kadotani, H.; Rogers, W.; Lin, X.; Qiu, X.; de Jong, P.J.; Nishino, S.; Mignot, E. The sleep disorder canine narcolepsy is caused by a mutation in the hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2 gene. Cell 1999, 98, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemelli, R.M.; Willie, J.T.; Sinton, C.M.; Elmquist, J.K.; Scammell, T.; Lee, C.; Richardson, J.A.; Williams, S.C.; Xiong, Y.; Kisanuki, Y.; et al. Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell 1999, 98, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, C.; Faraco, J.; Rogers, W.; Ripley, B.; Overeem, S.; Charnay, Y.; Nevsimalova, S.; Aldrich, M.; Reynolds, D.; Albin, R.; et al. A mutation in a case of early onset narcolepsy and a generalized absence of hypocretin peptides in human narcoleptic brains. Nat Med 2000, 6, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liblau, R.S.; Vassalli, A.; Seifinejad, A.; Tafti, M. Hypocretin (orexin) biology and the pathophysiology of narcolepsy with cataplexy. Lancet Neurol 2015, 14, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melmed, S.; Auchus, R.J.; Goldfine, A.B.; Koenig, R.J.; Rosen, C.J. Williams textbook of endocrinology, 14th edition. ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, 2020; pp. xiv, 1777 pages. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, W.B. THE EMERGENCY FUNCTION OF THE ADRENAL MEDULLA IN PAIN AND THE MAJOR EMOTIONS. American Journal of Physiology-Legacy Content 1914, 33, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selye, H. A Syndrome produced by Diverse Nocuous Agents. Nature 1936, 138, 32–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, N. Guillemin and schally: a race spurred by rivalry. Science 1978, 200, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, W.; Spiess, J.; Rivier, C.; Rivier, J. Characterization of a 41-residue ovine hypothalamic peptide that stimulates secretion of corticotropin and beta-endorphin. Science 1981, 213, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selye, H. The general adaptation syndrome and the diseases of adaptation. J Allergy 1946, 17, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badami, V.M.; Rice, C.D.; Lois, J.H.; Madrecha, J.; Yates, B.J. Distribution of hypothalamic neurons with orexin (hypocretin) or melanin concentrating hormone (MCH) immunoreactivity and multisynaptic connections with diaphragm motoneurons. Brain Res 2010, 1323, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadel, J.; Pasumarthi, R.; Reznikov, L.R. Stimulation of cortical acetylcholine release by orexin A. Neuroscience 2005, 130, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, L.H.; Hoyer, D.; de Lecea, L. Hypocretins (orexins): The ultimate translational neuropeptides. J Intern Med 2022, 291, 533–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, M. Research progress on the mechanism of orexin in pain regulation in different brain regions. Open Life Sci 2021, 16, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.B.; de Lecea, L. The hypocretin (orexin) system: from a neural circuitry perspective. Neuropharmacology 2020, 167, 107993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu, T.; Sakurai, T.; Mizukami, K.; Hosoya, Y.; Yanagisawa, M.; Goto, K. Distribution of orexin neurons in the adult rat brain. Brain Res 1999, 827, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizza, F.; Barateau, L.; Dauvilliers, Y.; Plazzi, G. The orexin story, sleep and sleep disturbances. J Sleep Res 2022, 31, e13665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorella, S.; Rodrigo-Angulo, M.L.; Núñez, A.; Garzón, M. Synaptic interactions between perifornical lateral hypothalamic area, locus coeruleus nucleus and the oral pontine reticular nucleus are implicated in the stage succession during sleep-wakefulness cycle. Front Neurosci 2013, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujdoso, E.; Jaszberenyi, M.; Tomboly, C.; Toth, G.; Telegdy, G. Behavioral and neuroendocrine actions of endomorphin-2. Peptides 2001, 22, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, G. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis by neuropeptides. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig 2011, 7, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujdoso, E.; Jaszberenyi, M.; Tomboly, C.; Toth, G.; Telegdy, G. Effects of endomorphin-1 on open-field behavior and on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system. Endocrine 2001, 14, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostene, W.H.; Alexander, M.J. Neurotensin and neuroendocrine regulation. Front Neuroendocrinol 1997, 18, 115–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perras, B.; Schultes, B.; Behn, B.; Dodt, C.; Born, J.; Fehm, H.L. Intranasal atrial natriuretic peptide acts as central nervous inhibitor of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal stress system in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004, 89, 4642–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, T.; Ramaswamy, P.; Perumal, M.; Silambanan, S.; Prabu Kumar, A. A short note on oxytocin and stress attenuation. Bioinformation 2021, 17, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaszberenyi, M.; Bujdoso, E.; Telegdy, G. Effects of C-type natriuretic peptide on pituitary-adrenal activation in rats. Neuroreport 1998, 9, 2601–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaszberenyi, M.; Bujdoso, E.; Telegdy, G. Effects of brain natriuretic peptide on pituitary-adrenal activation in rats. Life Sci 2000, 66, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, G.A.; Van de Kar, L.D. Neuroendocrine pharmacology of stress. Eur J Pharmacol 2003, 463, 235–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Kastin, A.J. Urocortin and the brain. Prog Neurobiol 2008, 84, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henckens, M.J.; Deussing, J.M.; Chen, A. Region-specific roles of the corticotropin-releasing factor-urocortin system in stress. Nat Rev Neurosci 2016, 17, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, C.V.; Rosas-Arellano, M.P.; Solano-Flores, L.P.; Ciriello, J. Cardiovascular effects of hypocretin-1 in nucleus of the solitary tract. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2003, 284, H1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, W.K.; Taylor, M.M.; Follwell, M.; Ferguson, A.V. Orexin actions in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: physiological consequences and cellular correlates. Regul Pept 2002, 104, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winsky-Sommerer, R.; Yamanaka, A.; Diano, S.; Borok, E.; Roberts, A.J.; Sakurai, T.; Kilduff, T.S.; Horvath, T.L.; de Lecea, L. Interaction between the corticotropin-releasing factor system and hypocretins (orexins): a novel circuit mediating stress response. J Neurosci 2004, 24, 11439–11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, F.; Yamada, S.; Ueta, Y. Centrally administered orexin-A activates corticotropin-releasing factor-containing neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and central amygdaloid nucleus of rats: possible involvement of central orexins on stress-activated central CRF neurons. Regul Pept 2004, 118, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasiak, A.; Gundlach, A.L.; Hess, G.; Lewandowski, M.H. Interactions of Circadian Rhythmicity, Stress and Orexigenic Neuropeptide Systems: Implications for Food Intake Control. Front Neurosci 2017, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, K.; Kushikata, T.; Kudo, M.; Kudo, T.; Lambert, D.G.; Matsuki, A. Orexin A and B evoke noradrenaline release from rat cerebrocortical slices. Br J Pharmacol 2001, 134, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunton, P.J.; Bales, J.; Russell, J.A. Neuroendocrine stress but not feeding responses to centrally administered neuropeptide Y are suppressed in pregnant rats. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 3737–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.H.; Small, C.J.; Dakin, C.L.; Abbott, C.R.; Morgan, D.G.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. The central effects of orexin-A in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in vivo and in vitro in male rats. J Neuroendocrinol 2001, 13, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, T.M.; Vianna, D.M.; Liu, L.; Carrive, P. Hypocretin/orexin contributes to the expression of some but not all forms of stress and arousal. Eur J Neurosci 2009, 30, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, C.M.; Wang, C.; Teske, J.A.; Thorpe, A.J.; Novak, C.M.; Kiwaki, K.; Levine, J.A. Orexin A mediation of time spent moving in rats: neural mechanisms. Neuroscience 2006, 142, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotz, C.M. Integration of feeding and spontaneous physical activity: role for orexin. Physiol Behav 2006, 88, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, I.; Messina, A.; Valenzano, A.; Moscatelli, F.; Esposito, T.; Monda, V.; Esposito, M.; Precenzano, F.; Carotenuto, M.; Viggiano, A.; et al. Basal Forebrain Cholinergic System and Orexin Neurons: Effects on Attention. Front Behav Neurosci 2017, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Wei, C.; Wang, H.; Sui, N.; Kirouac, G.J. Changes in emotional behavior produced by orexin microinjections in the paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2010, 95, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, R.K.; Ruxton, G.D. A review of thanatosis (death feigning) as an anti-predator behaviour. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 2018, 72, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinkhofer, C.; Martial, C.; Cassol, H.; Laureys, S.; Kondziella, D. The evolutionary origin of near-death experiences: a systematic investigation. Brain Commun 2021, 3, fcab132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steimer, T. The biology of fear- and anxiety-related behaviors. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 2002, 4, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Vécsei, L. Preclinical modeling in depression and anxiety: Current challenges and future research directions. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med 2023, 32, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soya, S.; Sakurai, T. Orexin as a modulator of fear-related behavior: Hypothalamic control of noradrenaline circuit. Brain Res 2020, 1731, 146037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soya, S.; Takahashi, T.M.; McHugh, T.J.; Maejima, T.; Herlitze, S.; Abe, M.; Sakimura, K.; Sakurai, T. Orexin modulates behavioral fear expression through the locus coeruleus. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palotai, M.; Telegdy, G.; Ekwerike, A.; Jaszberenyi, M. The action of orexin B on passive avoidance learning. Involvement of neurotransmitters. Behav Brain Res 2014, 272, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, A.; Saravia, R.; Maldonado, R.; Berrendero, F. Orexins and fear: implications for the treatment of anxiety disorders. Trends Neurosci 2015, 38, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; McCormack, S.; Espana, R.A.; Crocker, A.; Scammell, T.E. Afferents to the orexin neurons of the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 2006, 494, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avolio, E.; Alo, R.; Carelli, A.; Canonaco, M. Amygdalar orexinergic-GABAergic interactions regulate anxiety behaviors of the Syrian golden hamster. Behav Brain Res 2011, 218, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, M.A.; Lecourt, H.; Rakotoariniaina, A.; Jenck, F. Favoured genetic background for testing anxiolytics in the fear-potentiated and light-enhanced startle paradigms in the rat. Behav Brain Res 2011, 221, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camina, E.; Guell, F. The Neuroanatomical, Neurophysiological and Psychological Basis of Memory: Current Models and Their Origins. Front Pharmacol 2017, 8, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramzadeh Zoeram, S.; Elahdadi Salmani, M.; Lashkarbolouki, T.; Goudarzi, I. Hippocampal orexin receptor blocking prevented the stress induced social learning and memory deficits. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2019, 157, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzman, M.A.; Katzman, M.P. Neurobiology of the Orexin System and Its Potential Role in the Regulation of Hedonic Tone. Brain Sci 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccoli, L.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Cifani, C.; Costantini, V.J.; Massagrande, M.; Montanari, D.; Martinelli, P.; Antolini, M.; Ciccocioppo, R.; Massi, M.; et al. Role of orexin-1 receptor mechanisms on compulsive food consumption in a model of binge eating in female rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1999–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Garcia, F.; Juarez-Aguilar, E.; Santiago-Garcia, J.; Cardinali, D.P. Ghrelin and its interactions with growth hormone, leptin and orexins: implications for the sleep-wake cycle and metabolism. Sleep Med Rev 2014, 18, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshinai, K.; Date, Y.; Murakami, N.; Shimada, M.; Mondal, M.S.; Shimbara, T.; Guan, J.L.; Wang, Q.P.; Funahashi, H.; Sakurai, T.; et al. Ghrelin-induced food intake is mediated via the orexin pathway. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarta, D.; Smolders, I. Rewarding, reinforcing and incentive salient events involve orexigenic hypothalamic neuropeptides regulating mesolimbic dopaminergic neurotransmission. Eur J Pharm Sci 2014, 57, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzeu, A.; Martin-Fardon, R. Understanding the Role of Orexin Neuropeptides in Drug Addiction: Preclinical Studies and Translational Value. Front Behav Neurosci 2021, 15, 787595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.H.; Stopper, C.M.; Zimmer, B.A.; Koll, N.E.; Bowrey, H.E.; Aston-Jones, G. Increased Number and Activity of a Lateral Subpopulation of Hypothalamic Orexin/Hypocretin Neurons Underlies the Expression of an Addicted State in Rats. Biol Psychiatry 2019, 85, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.K.; Ferris, M.J.; Locke, J.L.; Brodnik, Z.D.; Jones, S.R.; Espana, R.A. Hypocretin/orexin knock-out mice display disrupted behavioral and dopamine responses to cocaine. Addict Biol 2017, 22, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, N.; Rossetti, C.; Sakurai, T.; Yanagisawa, M.; de Lecea, L.; Magistretti, P.J.; Halfon, O.; Boutrel, B. Hypocretin/orexin deficiency decreases cocaine abuse liability. Neuropharmacology 2018, 133, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, R.; Thannickal, T.C.; Siegel, J.M. Pleasure, addiction, and hypocretin (orexin). Handb Clin Neurol 2021, 180, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadkhani, A.; Fragale, J.E.; Pantazis, C.B.; Bowrey, H.E.; James, M.H.; Aston-Jones, G. Orexin-1 Receptor Signaling in Ventral Pallidum Regulates Motivation for the Opioid Remifentanil. J Neurosci 2019, 39, 9831–9840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadkhani, A.; James, M.H.; Pantazis, C.B.; Aston-Jones, G. Persistent effects of the orexin-1 receptor antagonist SB-334867 on motivation for the fast acting opioid remifentanil. Brain Res 2020, 1731, 146461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morganstern, I.; Chang, G.Q.; Barson, J.R.; Ye, Z.; Karatayev, O.; Leibowitz, S.F. Differential effects of acute and chronic ethanol exposure on orexin expression in the perifornical lateral hypothalamus. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2010, 34, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotter, A.; Bayerlein, K.; Hansbauer, M.; Weiland, J.; Sperling, W.; Kornhuber, J.; Biermann, T. Orexin A expression and promoter methylation in patients with cannabis dependence in comparison to nicotine-dependent cigarette smokers and nonsmokers. Neuropsychobiology 2012, 66, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayerlein, K.; Kraus, T.; Leinonen, I.; Pilniok, D.; Rotter, A.; Hofner, B.; Schwitulla, J.; Sperling, W.; Kornhuber, J.; Biermann, T. Orexin A expression and promoter methylation in patients with alcohol dependence comparing acute and protracted withdrawal. Alcohol 2011, 45, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skofitsch, G.; Jacobowitz, D.M.; Zamir, N. Immunohistochemical localization of a melanin concentrating hormone-like peptide in the rat brain. Brain Res Bull 1985, 15, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, M.A.; Smith, R.G.; Diano, S.; Tschop, M.; Pronchuk, N.; Grove, K.L.; Strasburger, C.J.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Esterman, M.; Heiman, M.L.; et al. The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron 2003, 37, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrini, F.; Salio, C.; Lossi, L.; Merighi, A. Ghrelin in central neurons. Curr Neuropharmacol 2009, 7, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Miyazato, M.; Ida, T.; Murakami, N.; Serino, R.; Ueta, Y.; Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Identification of neuromedin S and its possible role in the mammalian circadian oscillator system. EMBO J 2005, 24, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Nagasaki, H. The melanin-concentrating hormone system and its physiological functions. Results Probl Cell Differ 2008, 46, 159–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBona, G.F. Neuropeptide Y. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2002, 282, R635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antushevich, H.; Wojcik, M. Review: Apelin in disease. Clin Chim Acta 2018, 483, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telegdy, G.; Adamik, A.; Jaszberenyi, M. Involvement of neurotransmitters in the action of apelin-13 on passive avoidance learning in mice. Peptides 2013, 39, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telegdy, G.; Jaszberenyi, M. Transmitter mediation of the anxiolytic action of apelin-13 in male mice. Behav Brain Res 2014, 263, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin: structure and function. Physiol Rev 2005, 85, 495–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malendowicz, L.K.; Rucinski, M. Neuromedins NMU and NMS: An Updated Overview of Their Functions. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021, 12, 713961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.R. Biology of Neuropeptides: Orexinergic Involvement in Primary Headache Disorders. Headache 2017, 57 Suppl 2, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, T.L.; Diano, S.; van den Pol, A.N. Synaptic interaction between hypocretin (orexin) and neuropeptide Y cells in the rodent and primate hypothalamus: a novel circuit implicated in metabolic and endocrine regulations. J Neurosci 1999, 19, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, H.; Takenoya, F.; Hirako, S.; Wada, N.; Kintaka, Y.; Inoue, S.; Ota, E.; Ogawa, T.; Shioda, S. Neuronal circuits involving neuropeptide Y in hypothalamic arcuate nucleus-mediated feeding regulation. Neuropeptides 2012, 46, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.H.; Small, C.J.; Kennedy, A.R.; Stanley, S.A.; Seth, A.; Murphy, K.G.; Taheri, S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. Orexin A interactions in the hypothalamo-pituitary gonadal axis. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 5294–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, H.; Yamada, S.; Kageyama, H.; Takenoya, F.; Guan, J.L.; Shioda, S. Co-existence of leptin- and orexin-receptors in feeding-regulating neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus-a triple labeling study. Peptides 2003, 24, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, T.L.; Peyron, C.; Diano, S.; Ivanov, A.; Aston-Jones, G.; Kilduff, T.S.; van Den Pol, A.N. Hypocretin (orexin) activation and synaptic innervation of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system. J Comp Neurol 1999, 415, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Mou, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, F.; Wang, Z.; Jin, K.; Lu, J. Dysregulation of striatal dopamine D2/D3 receptor-mediated by hypocretin induces depressive behaviors in rats. J Affect Disord 2023, 325, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Huang, H.; Chen, X.; Deng, S.; Zhu, C.; Huang, H.; Li, G. Structural and functional characterization of neuromedin S in the teleost fish, zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 2016, 191, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fronczek, R.; Schinkelshoek, M.; Shan, L.; Lammers, G.J. The orexin/hypocretin system in neuropsychiatric disorders: Relation to signs and symptoms. Handb Clin Neurol 2021, 180, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvilliers, Y.; Arnulf, I.; Mignot, E. Narcolepsy with cataplexy. Lancet 2007, 369, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Pan, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, L. Orexin: a potential role in the process of obstructive sleep apnea. Peptides 2013, 42, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, S.; Nishijima, T.; Arihara, Z.; Takahashi, K. Plasma orexin-A levels in obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Chest 2004, 125, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, T.; Sakurai, S.; Arihara, Z.; Takahashi, K. Plasma orexin-A-like immunoreactivity in patients with sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome. Peptides 2003, 24, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifinejad, A.; Ramosaj, M.; Shan, L.; Li, S.; Possovre, M.L.; Pfister, C.; Fronczek, R.; Garrett-Sinha, L.A.; Frieser, D.; Honda, M.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of selected hypothalamic neuropeptides in narcolepsy with cataplexy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2220911120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partinen, M.; Kornum, B.R.; Plazzi, G.; Jennum, P.; Julkunen, I.; Vaarala, O. Narcolepsy as an autoimmune disease: the role of H1N1 infection and vaccination. Lancet Neurol 2014, 13, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorka, S.M.; Khorrami, K.J.; Manzler, C.A.; Phan, K.L. Acute orexin antagonism selectively modulates anticipatory anxiety in humans: implications for addiction and anxiety. Transl Psychiatry 2022, 12, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Q.F.A.; Jufri, N.F.; Hamid, A. Hyperphagia in Prader-Willi syndrome with obesity: From development to pharmacological treatment. Intractable Rare Dis Res 2023, 12, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehr, J.B.; Mitchison, D.; Bowrey, H.E.; James, M.H. Sleep dysregulation in binge eating disorder and "food addiction": the orexin (hypocretin) system as a potential neurobiological link. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 2051–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, L.A.; Brown, T.A.; Lavender, J.M.; Lopez, E.; Wierenga, C.E.; Kaye, W.H. Neuroendocrinology of reward in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa: Beyond leptin and ghrelin. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2019, 497, 110320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Han, F.; Dong, S.X.; Li, J.; An, P.; Zhang, X.Z.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.L.; Liu, Y.N.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Orexin A Levels and Autonomic Function in Kleine-Levin Syndrome. Sleep 2016, 39, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzoli, M.; Bartolomucci, A. The Dichotomous Effect of Chronic Stress on Obesity. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2016, 27, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Celik, O.; Celik, N.; Celik, E.; Turkcuoglu, I.; Simsek, Y.; Minareci, Y.; Boz, M.; Aydin, S. Maternal and fetal serum orexin-A levels in gestational diabetes mellitus. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2013, 39, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Celik, O.; Celik, N.; Simsek, Y.; Celik, E.; Yildirim, E. Serum orexin-A (OXA) level decreases in polycystic ovarian syndrome. Gynecol Endocrinol 2013, 29, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, O.; Aydin, S.; Celik, N.; Yilmaz, M. Peptides: Basic determinants of reproductive functions. Peptides 2015, 72, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jequier, E. Leptin signaling, adiposity, and energy balance. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2002, 967, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopf, F.W. Recent perspectives on orexin/hypocretin promotion of addiction-related behaviors. Neuropharmacology 2020, 168, 108013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Proudnikov, D.; Yuferov, V.; Kreek, M.J. Drug-induced and genetic alterations in stress-responsive systems: Implications for specific addictive diseases. Brain Res 2010, 1314, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berteotti, C.; Calvello, C.; Liguori, C. Role of the orexin system in the bidirectional relation between sleep and epilepsy: New chances for patients with epilepsy by the antagonism to orexin receptors? Epilepsia 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, A.R.; Molosh, A.I.; Johnson, P.L.; Shekhar, A. Role of medial hypothalamic orexin system in panic, phobia and hypertension. Brain Res 2020, 1731, 145942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.B.; Lakis, G.A.; Zhoba, H. Sleep-wake and arousal dysfunctions in post-traumatic stress disorder: Role of orexin systems. Brain Res Bull 2022, 186, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brundin, L.; Bjorkqvist, M.; Petersen, A.; Traskman-Bendz, L. Reduced orexin levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of suicidal patients with major depressive disorder. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2007, 17, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, R.M.; Ripley, B.; Kennedy, J.S.; Johnson, B.; Schmidt, D.; Zeitzer, J.M.; Nishino, S.; Mignot, E. Diurnal variation of cerebrospinal fluid hypocretin-1 (Orexin-A) levels in control and depressed subjects. Biol Psychiatry 2003, 54, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Abdulhadi, M.H.; Hussien, N.R.; Al-Niemi, M.S.; Rasheed, H.A.; Al-Gareeb, A.I. Involvement of orexinergic system in psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders: A scoping review. Brain Circ 2020, 6, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, B.; Ray, L.B.; Pozzobon, A.; Fogel, S.M. Sleep, Orexin and Cognition. Front Neurol Neurosci 2021, 45, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarakeh, J.I.; Takahashi, K.; Sakurada, S.; Nishino, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kato, M.; Naghdi, N.; Yanai, K. Enhanced antinociception by intracerebroventricularly administered orexin A in histamine H1 or H2 receptor gene knockout mice. Pain 2005, 118, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Kuwaki, T.; Yanagisawa, M.; Fukuda, Y.; Shimoyama, M. Persistent pain and stress activate pain-inhibitory orexin pathways. Neuroreport 2005, 16, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.B.; Jones, J.R.; de Lecea, L. Hypocretins, Neural Systems, Physiology, and Psychiatric Disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep 2016, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalliomaki, M.L.; Panula, P. Neuropeptide FF, but not prolactin-releasing peptide, mRNA is differentially regulated in the hypothalamic and medullary neurons after salt loading. Neuroscience 2004, 124, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehrs, T.; Withrow, D.; Koshorek, G.; Verkler, J.; Bazan, L.; Roth, T. Sleep and pain in humans with fibromyalgia and comorbid insomnia: double-blind, crossover study of suvorexant 20 mg versus placebo. J Clin Sleep Med 2020, 16, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, J.; May, A. Diagnosis, pathophysiology, and management of cluster headache. Lancet Neurol 2018, 17, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, S.; Schmidt, A.; Hassel, S.; Tanaka, M. Editorial: Case reports in neuroimaging and stimulation. Front Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1264669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Diano, M.; Battaglia, S. Editorial: Insights into structural and functional organization of the brain: evidence from neuroimaging and non-invasive brain stimulation techniques. Front Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1225755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgomaneri, S.; Battaglia, S.; Sciamanna, G.; Tortora, F.; Laricchiuta, D. Memories are not written in stone: Re-writing fear memories by means of non-invasive brain stimulation and optogenetic manipulations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2021, 127, 334–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, V.M. Metabolic regulation of kisspeptin - the link between energy balance and reproduction. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2020, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvineau, A.; Nicole, P.; Gratio, V.; Voisin, T. The Orexin receptors: Structural and anti-tumoral properties. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 931970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, T.; Nicole, P.; Gratio, V.; Chassac, A.; Mansour, D.; Rebours, V.; Couvelard, A.; Couvineau, A. The Orexin-A/OX1R System Induces Cell Death in Pancreatic Cancer Cells Resistant to Gemcitabine and Nab-Paclitaxel Treatment. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 904327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, M.; Detheux, M.; Vandenbogaerde, A.; Communi, D.; Vanderwinden, J.M.; Le Poul, E.; Brezillon, S.; Tyldesley, R.; Suarez-Huerta, N.; Vandeput, F.; et al. The metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes kisspeptins, the natural ligands of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR54. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 34631–34636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, F.; Atika, B.; Shahab, M.; Behr, R. Kisspeptin signalling in the physiology and pathophysiology of the urogenital system. Nat Rev Urol 2016, 13, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten-Blanco, M.; Flores, A.; Cristino, L.; Pereda-Perez, I.; Berrendero, F. Targeting the orexin/hypocretin system for the treatment of neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases: From animal to clinical studies. Front Neuroendocrinol 2023, 69, 101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropper, A.H.; Samuels, M.A.; Klein, J.; Prasad, S. Adams and Victor’s principles of neurology. 2023, 1 online resource.
- McKnight, R.; Price, J.; Geddes, J. Psychiatry, Fifth edition. ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, 2019; pp. x, 542 pages. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Vécsei, L.; Giménez-Llort, L. Emerging translational research in neurological and psychiatric diseases: from in vitro to in vivo models. 2023, 24, 15739. [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.B.; Amiji, M.M. A review of nanocarrier-based CNS delivery systems. Curr Drug Deliv 2006, 3, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, D.E. Ghrelin and the short- and long-term regulation of appetite and body weight. Physiol Behav 2006, 89, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastin, A.J.; Pan, W.; Maness, L.M.; Banks, W.A. Peptides crossing the blood-brain barrier: some unusual observations. Brain Res 1999, 848, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milbank, E.; Lopez, M. Orexins/Hypocretins: Key Regulators of Energy Homeostasis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2019, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Biswas, D.A. Physiological Role of Orexin/Hypocretin in the Human Body in Motivated Behavior: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e34009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baimel, C.; Borgland, S.L. Orexin Signaling in the VTA Gates Morphine-Induced Synaptic Plasticity. J Neurosci 2015, 35, 7295–7303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baimel, C.; Bartlett, S.E.; Chiou, L.C.; Lawrence, A.J.; Muschamp, J.W.; Patkar, O.; Tung, L.W.; Borgland, S.L. Orexin/hypocretin role in reward: implications for opioid and other addictions. Br J Pharmacol 2015, 172, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baimel, C.; Bartlett, S.E.; Chiou, L.C.; Lawrence, A.J.; Muschamp, J.W.; Patkar, O.; Tung, L.W.; Borgland, S.L. Orexin/hypocretin role in reward: implications for opioid and other addictions. British journal of pharmacology 2015, 172, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brundin, L.; Petersen, A.; Bjorkqvist, M.; Traskman-Bendz, L. Orexin and psychiatric symptoms in suicide attempters. J Affect Disord 2007, 100, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vecsei, L. Editorial of Special Issue "Crosstalk between Depression, Anxiety, and Dementia: Comorbidity in Behavioral Neurology and Neuropsychiatry". Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehlan, C.; Roch, C.; Vaillant, C.; Dingemanse, J. The orexin story and orexin receptor antagonists for the treatment of insomnia. J Sleep Res 2023, 32, e13902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Editorial of special issue “crosstalk between depression, anxiety, and dementia: comorbidity in behavioral neurology and neuropsychiatry”. 2021, 9, 517. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Monitoring the kynurenine system: Concentrations, ratios or what else? Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2021, 30, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Monitoring the redox status in multiple sclerosis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattar, P.; Uribe-Cerda, S.; Pezoa, C.; Guarnieri, T.; Kotz, C.M.; Teske, J.A.; Morselli, E.; Perez-Leighton, C. Brain site-specific regulation of hedonic intake by orexin and DYN peptides: role of the PVN and obesity. Nutr Neurosci 2022, 25, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterick, T.A.; Billington, C.J.; Kotz, C.M.; Nixon, J.P. Orexin: pathways to obesity resistance? Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2013, 14, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Leighton, C.E.; Butterick-Peterson, T.A.; Billington, C.J.; Kotz, C.M. Role of orexin receptors in obesity: from cellular to behavioral evidence. Int J Obes (Lond) 2013, 37, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seale, P. Orexin turns up the heat on obesity. Cell Metab 2011, 14, 441–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Chen, C. Towards a mechanistic understanding of depression, anxiety, and their comorbidity: perspectives from cognitive neuroscience. Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience 2023, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajti, J.; Szok, D.; Csáti, A.; Szabó, Á.; Tanaka, M.; Vécsei, L. Exploring novel therapeutic targets in the common pathogenic factors in migraine and neuropathic pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Szabó, Á.; Körtési, T.; Szok, D.; Tajti, J.; Vécsei, L. From CGRP to PACAP, VIP, and Beyond: Unraveling the Next Chapters in Migraine Treatment. Cells 2023, 12, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Bohár, Z.; Vécsei, L. Are kynurenines accomplices or principal villains in dementia? Maintenance of kynurenine metabolism. Molecules 2020, 25, 564. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, A.; Lott, D.; Brussee, J.M.; Muehlan, C.; Dingemanse, J. Population pharmacokinetic modeling of daridorexant, a novel dual orexin receptor antagonist. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol 2023, 12, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Diseases and disorders |
|---|
| narcolepsy, cataplexy |
| obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome |
| obesity |
| Prader-Willi syndrome |
| bulimia, anorexia nervosa |
| Kleine-Levin syndrome |
| gestational diabetes |
| polycystic ovary syndrome |
| attention deficit hyperactivity disorder |
| epilepsy |
| Panic disorder |
| phobia |
| major depressive disorder |
| post-traumatic stress disorder |
| psychosomatic disorders |
| hypertension |
| fibromyalgia |
| chronic pain disorders (migraine and cluster headaches) |
| schizophrenia |
| Parkinson’s disease |
| Alzheimer’s disease |
| Huntington’s disease |
| multiple sclerosis |
| amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| Cell body location | Target region | Receptor | Function |
| LHA, DMH | VMH, ARC, PVN, NAc | OX1 | Stimulation of feeding |
| LHA, PFA | PAG, NTS, PVN, RVLM, RVMM, VTA | OX1, OX2 | Autonomic responses (RR↑, (tachycardia, thermoregulation) |
| PFA, DMH | LA, LC, PPT | OX1 | Emotions (anxiety, fear, mood) |
| LHA, DMH | VTA, NAc, DR | OX1, OX2 | Reward, addiction |
| LHA, DMH | PVN, POA | OX1, OX2 | Endocrine responses (stress response, gonadal functions) |
| PFA, LHA | LC, DR, VTA, TMN | OX2, OX1 | Arousal, Wakefulness |
| Classes | Indications |
| Hypocretin receptors 1 & 2 antagonists | Insomnia, narcolepsy |
| Hypocretin receptors 1 antagonists | Panic disorder |
| Major depressive disorder | |
| anxiety | |
| Hypocretin receptors 2 antagonist | Binge eating disorder |
| Hypocretin receptors 2 agonist | narcolepsy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





