1. Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by persistent hyperglycemia, resulted from decreased insulin secretion, insulin resistance or both [
1]. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), which accounts more than 90% of all cases of DM, is characterized by deficient insulin secretion through pancreatic β-cells injury and by inability of tissues (liver, adipose tissue and skeletal muscles) to respond properly to insulin [
2]. DM reduces the quality of life, increases the risk factors for mortality and morbidity and is considered one of the five main causes of death in the worldwide. The global prevalence of DM was 537 million in 2021 and is predicted to further increase during the next years, because of the careless lifestyle of people [
3]. Also, it is worrying that the incidence of DM among children and teenagers is increasing [
4]. Moreover, the chronic hyperglycemia is associated with micro and macrovascular complications leading to blindness, kidney failure, heart disease, stroke and gangrene, which often requires foot amputation. It is considered that these complications can be avoided or reduced by achieving a constant glycemic control [
5].
Nowadays, there is many evidences that oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis of DM. The generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) appears through nonenzymatic glycation of protein, glucose oxidation and increasing of lipid peroxidation. The over production of RSO (oxidative stress) contributes to the degradation of enzymes and mitochondria and to the development of insulin resistance. In addition, the oxidative stress decreases the proliferation of pancreatic β-cells, that conducts to impairing of insulin secretion. Normally, the body produces endogenous antioxidants (e.g. superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione S-transferase), that will scavenge the excess of ROS and protect against several diseases, such as DM, cancer and heart disease. When the body's defense capacity,
via endogenous antioxidants, is exceeded, exogenous antioxidants are necessary to be added [
6]. The modern approaches of T2DM management include the reduction of hyperglycemia and also to reduces the oxidative stress. The antidiabetic therapy, based mainly on hypoglycemic drugs are unfortunately often associated with serious side effects.
To assure the success, the antidiabetic therapy should target two important aspects: (i) the optimal glycemic control as soon as possible, in order to reduce the impact of glucose toxicity and (ii) the proper control of associated risk factors, including oxidative stress, dyslipidemia, mitochondrial dysfunction, micro/macro vascular complications [
7].
It is known also that the progress of micro/macro vascular complications of DM is closely associated to oxidative stress and inflammation [
8]. Consequently, the drugs with hypoglycemic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects could be a good option for DM management and the use of combined therapy was recently taken in consideration.
Pioglitazone (Pio), is a reference antidiabetic drug, which belongs to thiazolidine-2,4-diones (TZD), which primarily works by reducing insulin resistance. It acts as a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR-γ) agonist, that modifies the transcription of some genes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism [
8]. In addition, Pio inhibits the expression of proteins with proinflammatory properties such as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), inducible nitric-oxide synthase (iNOS), and several cytokines. There are also evidences which support that Pio decreases the oxidative stress in the pancreatic β-cells of DM mice and improves their function, even if the level of PPAR-γ receptors was low [
8].
Despite its notable biological effects, the use of Pio in T2DM treatment is limited, because it has a very limited water solubility, a low bioavailability, a short half-life of 3-6 hours, and a fast elimination. In order to overcome these disadvantages numerous studies have focused on increasing its bioavailability and half-life, using polymeric nanocarriers, like nanoparticles (NPs) [
9].
NPs are intensively investigated as co-drug delivery systems with different properties; different methods for co-encapsulation being studied. The most used method is physical co-encapsulation, but chemical co-encapsulation (e.g., covalent chemical bonds between polymer and drugs) could be also used [
10].
Furthermore, NPs are intensively investigated for hydrophobic drugs, orally administrated. NPs protect the loaded drugs from the acidic environment of the gastrointestinal tract (GI) and increase drug bioavailability, by promoting the crossing of the GI epithelium, via transcellular or paracellular transport pathways. The easier GI passing is explain based on their unique characteristics, such as particle size, surface charge and mucoadhesive properties [
11].
Curcumin (Cur) is the main curcuminoid, extracted mainly from the rhizome of
Curcuma longa. This polyphenolic compound is used both in the pharmaceutical and food industries for several centuries. Numerous studies have shown that Cur has numerous biological effects such as antioxidant, hypoglycemic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer through anti-angiogenic effect, neuro and cardio protective effects, as well as anti-obesity properties [
12,
13]. The effectiveness of this molecule is limited due to its instability and poor solubility in water. Also, in biological conditions it is rapid metabolized, the main sites being liver as well as intestine through microbiota. In a study of rats, a maximum 60 mg/mL was measured in serum, even after oral administration of 500 mg/kg of Cur [
14,
15]. To improve its stability, solubility and bioavailability, different nanoformulations, such as solid lipid NPs, nanogels, cyclodextrin complexes and nanoemulsions, have been developed [
16].
Chitosan (CS), is one of the most used polymers for nanocarrier formulations. It is a natural polymer derived from chitin, that possesses several beneficial properties, such as antibacterial activity, non-toxicity and biocompatibility, biodegradability, and permeability [
17].
The aim of this study was to develop of new co-delivery nanosystem, based on CS NPs loaded with Cur and Pio, as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), in order to target the optimal glycemic control and oxidative stress of T2DM. The co-delivery nanosystem (CS-Pio-Cur NPs) was fully physico-chemical characterized, in reference with simple naonosystems (CS-Pio/CS-Cur NPs), in order to highlight the advantages of co-delivery formulation. For simultaneously determination of APIs from co-delivery nanosystem, a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method was developed and validate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All chemicals used in this research were of analytical grade or HPLC p.a. quality, certified by the commercially available sources and were used without further purification unless otherwise specified. Curcumin (≥94% curcuminoid content, ≥80% curcumin), pioglitazone hydrochloride (MW=392.90 g/mol), chitosan low molecular weight (MW= 50–190 kDa, 75–85% deacetylation degree, viscosity 20-300 cP), pentasodium tripolyphosphate (TPP), acetic acid (min. 99.8%, p.a. ACS reagent), tween 80, were purchased from Sigma Aldrich.
2.2. Preparation of CS-APIs NPs
In order to find the best formulation, CS NPs loaded with different concentration of APIs (Cur, Pio and Cur-Pio combination) were developed and their preparation was reported in our previous work [
18]. Briefly, to 3 mL of CS low molecular weight 0.1% (wt/v), different concentrations of APIs (Pio: 0.2 mg/0.1485 mg/0.099 mg/0.0747 mg; Cur: 1.5mg/0.99 mg/0.72 mg/0.495 mg or Pio-Cur 0.2 mg-1.5 mg; 0.1485 mg-0.99 mg; 0.099 mg-0.72 mg; 0.0747 mg-0.495 mg) dissolved in 0.5 mL of methanol, were added. Then 1 mL of 0.1% (wt/v) TPP aqueous solution was added dropwise under stirring, when CS-APIs NPs were obtained.
2.3. Characterization of CS-APIs NPs
2.3.1. The physical parameters
The particles size (PS) and the polydispersity index (PI) measurements of the developed CS-based NPs (CS-Pio-Cur NPs, CS-Pio NPs, CS-Cur NPs) were determined by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) using a Easier Nano ZS90 instrument (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK). The Zeta Potential (ZP) was also performed using the same instrument employing the electrophoretic mobility of the NPs suspension. Each NPs formulation was suspended in distilled water at ambient temperature, homogenized at 10000 rpm and filled into a particle-sizing cell. All measurements were performed in triplicate.
2.3.2. X-ray diffraction
The physical state (crystalline of amorphous) of APIs (Cur, Pio, Pio-Cur physical mixture) unloaded and loaded into CS-APIs NPs (CS-Cur NPs, CS-Pio NPs, CS-Pio-Cur NPs) were analyzed using a X-ray diffraction instrument (Rigaku Miniflex 600, Japan) from 20 to 500 and the scan rate of 10/min.
2.3.3. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy
Fourier-transformed infrared (FTIR) spectra of APIs (Cur, Pio, Pio-Cur physical mixture), and CS-APIs NPs (CS-Cur NPs, CS-Pio NPs and CS-Pio-Cur NPs) were recorded using FTIR spectrophotometer (ABB-MB3000 FT-IR MIRacleTM Single Bounce ATR – cristalZnSe). The spectra processing was carried out with the Horizon MB™ FT-IR Software. The scanning range of 400–4000 cm-1 with 32 scans with the resolution at 4 cm-1 was applied.
2.3.4. The entrapment efficiency (EF) and loading capacity (LC)
The developed CS-APIs NPs, CS-Cur NPs (a: 1.5 mg, b: 0.99 mg, c: 0.72 mg, d: 0.495 mg), CS-Pio NPs (a: 0.2 mg, b: 0.148 mg, c: 0.099 mg, d: 0.0747 mg) and CS-Pio-Cur NPs (a: 0.2 mg-1.5 mg, b: 0.1485 mg-0.99 mg, c: 0.099 mg-0.72 mg, d: 0.0747 mg-0.495 mg, were studied in term od EE (%) and LC (%) in order to establish the optimal formulation.
The EE (%) and LC (%) of APIs into CS NPs was assessed using a UV spectrophotometric method (UVIKNO XL, BIOTECH Instruments) [
13]. After separation of CS-APIs NPs, the supernatant (TPP solution) was used to measure the absorbance, at 424 nm (for Cur) and at 272 nm (for Pio) respectively. In order to quantified the concentration of APIs (Pio and Cur respectively), the standard curve for Pio and Cur, using different concentrations, ranging of 9.9-47.619 μg/mL for Pio (R
2 = 0.999), and of 2.38-10 μg/mL for Cur (R
2 = 0.999) were plotted. The EE (%) was calculated using the following equation:
where:
The LC (%) of APIs (Cur, Pio) into CS NPs was measured based on the method reported in literature [
19]. A quantity of freeze-dried CS-APIs NPs (0.008 g CS-Pio NPs; 0.01 g CS-Cur NPs; 0.013 g CS-Pio-Cur NPs) was treated with ethanol (10 mL) The mixture was sonicated for 5 min and after that was centrifuged for 10 min at 15.000 rpm at 4
° C. Then, the supernatant was used to measure the absorbance at 424 nm (for Cur) and 272 nm (for Pio) respectively [
20,
21]. The LC (%) was calculated using the following equation:
where:
wAPIs = the quantity of APIs (Cur, Pio) loaded into CS NPs;
wCS-APIs NPs = the quantity of CS-APIs NPs.
2.4. The APIs release study from CS-APIs NPs
2.4.1. Development and validation of HPLC method
To quantify the APIs (Pio, Cur), released from CS based NPs (CS-Cur/CS-Pio/CS-Pio-Cur NPs), a HPLC method was development, using a Shimadzu Nexera LC-40-XR system (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), equipped with a serial dual plunger pump, an autosampler (SIL 40 XR), an SPD-40V series UV-Vis and an RF-20Axs fluorescence detector. Chromatographic separation of APIs was achieved on a C18 column (2.1 x 100 mm, Waters CORTECS 2.7 μm), using two mobile phases: A (water/formic acid - 99.9/0.1, v/v) and B (tetrahydrofuran). Before use, the solvents were filtered through a 0.22 μm filter and degassed by ultrasonication. The injection sample was 10 μL, the run time was 20 min at isocratic mode (0.6 mL/min) and the optimal mobile phases ratio was A (62%): B (38%). The column temperature was kept at 30°C during chromatographic operation with UV-Vis detection for Pio (270 nm) and fluorescence detection for Cur (λex = 420 nm and λem = 550 nm).
The qualitative and quantitative analysis of APIs (Pio, Cur) was carried out based the retention times and peak areas, respectively. LabSolutionDB software was used for peak integration.
Plotting calibration curve for APIs
To plot the calibration curve, a stock solution (containing 2000 ppm) of standard APIs (Pio, Cur), was prepared by dissolving of 50.0 mg of Pio and Cur, respectively, in 25 mL acetonitrile. From stock solution, serial dilutions, (0.5, 1.5, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80 and 100 ppm of Pio and Cur, respectively), were prepared. The experiments were performed in triplicate.
The calibration curve is a plot of the area under the peak (AU) to the external standard, as a function of the drug concentration:
The slope and the intercept are determined from AU and concentration of APIs. Using this equation, the Cur and Pio released from CS based NPs (CS-Cur/CS-Pio/CS-Pio-Cur NPs) can be quantified.
2.4.2. In vitro APIs release model
To study the release of APIs (Cur, Pio) from CS-APIs NPs an
in vitro digestion model, was used. The release study was performed using simulated gastric fluid (SGF, pH 1.6), simulated intestinal fluid (SIF, pH 7.0), and simulated colonic fluid (SCF, pH 7.4), respectively (
Table 1).
A quantity of CS-APIs NPs: 13 mg of CS-Pio-Cur NPs (containing 2.66 mg Cur and 0.38 mg Pio), 9 mg of CS-Cur NPs (containing 2.47 mg Cur) and 8 mg of CS-Pio NPs (containing 0.38 mg Pio) was mixed with 50 mL of SGF (pH 1.6) and then shaken at 80 rpm at 37°C. Every 30 min (30 min, 60 min, 90 min), 300 μL of sample was collected, and centrifuged for 10 min at 15.000 rpm at 4° C. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter and then 10 μL of sample was injected using HPLC method conditions. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
After 1.5 h, the pH of mixture of CS-APIs NPs and SGF was adjusted at 7.0, by adding sodium taurocholate, lecithin, maleic acid, sodium chloride and sodium hydroxide, in order to simulate the SIF. The new mixture was shaken at 80 rpm at 37°C and every 30 min (120 min, 150 min, 180 min), 300 μL of sample was collected, and centrifuged for 10 min at 15.000 rpm at 4° C. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter and then 10 μL of sample was injected using HPLC method conditions. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
Finally, after other 1.5 h, the pH of mixture of CS-APIs NPs and SIF was adjusted at 7.4, by adding sodium taurocholate, lecithin, maleic acid, sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide and sodium oleate, in order to simulate the SCF. The new mixture was shaken at 80 rpm at 37°C and every 30 min (210 min, 240 min, 270 min), 300 μL of sample was collected, and centrifuged for 10 min at 15.000 rpm at 4° C. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter and then 10 μL of sample was injected using HPLC method conditions. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
The concentration (%) of APIs (Pio, Cur) released from the NPs into simulated fluids (SGF, SIF, SCF) was calculated using the following equation [
14]:
where:
C1 = the concentration of APIs (Cur, Pio) released in simulated fluid;
C0 = the concentration of APIs loaded into CS based NPs.
2.4.3. Statistical analysis
The results were expressed as mean value ± standard deviation (SD) and the analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 23 for Windows. The statistical significance of the results was assessed by the one-way and two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA’s test) followed by Tukey’s HSD test used to compare the differences among samples. A p value ˂ 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of CS-APIs NPs
3.1.1. The physical parameters
The developed CS-APIs NPs were characterized in terms of particle size (PS), polydispersity index (PI) and zeta potential (ZP), and the results are presented in
Table 2.
All CS-APIs NPs present small PS, between 214.40 and 294.20 nm, a proper PI and a high ZP value (11.13-32.44), that assure the physical stability of the developed nanosystems, through repulsion degree between the electrically charged and dispersed NPs.
3.1.2. X-ray diffraction
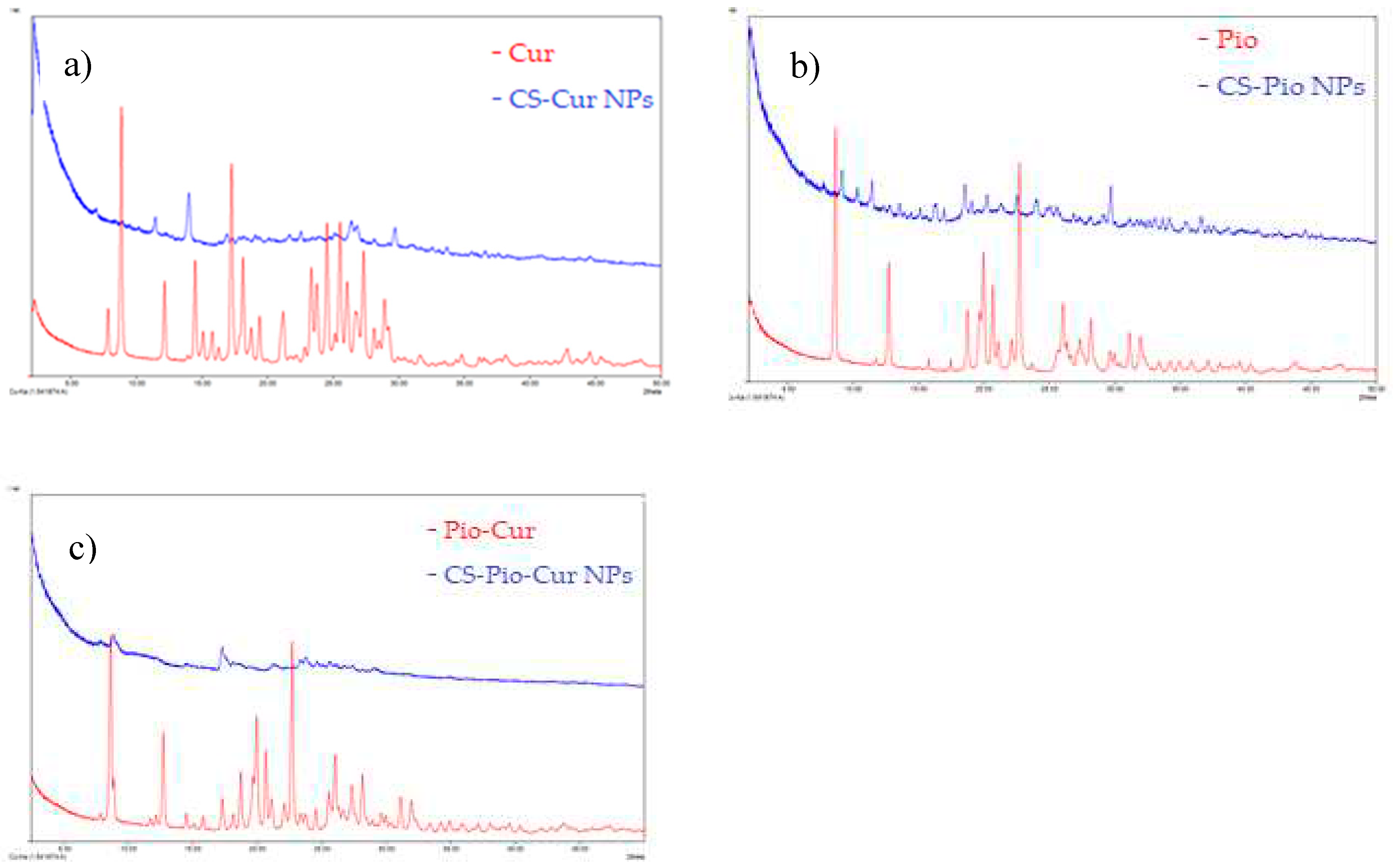
The crystalline state of APIs (Cur, Pio) greatly influences their stability, solubility and bioavailability. The XRD spectra of CS-Cur NPs, CS-Pio NPs and CS-Cur-Pio NPs in reference with Cur, Pio and physical mixture of Cur and Pio, are presented in
Figure 1.
The XRD spectrum of Cur (
Figure 1a) presents strong and sharps diffraction peaks at 2θ angles of 8.8°, 14.4°, 17.17°, 18.72°, 25.97°, etc., which means that Cur in pure state has a crystalline structure. In the CS-Cur NPs spectrum, only an intense peak la 14.4° and some small peaks between 20° to 30° are present, which means that Cur loaded into CS matrix has an amorphous form, which is due to CS.
Furthermore, the free Pio demonstrated multiple obvious sharp peaks at 2θ angles of 8.66°, 12.72°, 20.73°, 22.72° and more peaks at the angle range of 25° to 33°, indicating the crystal form (
Figure 1b). The characteristic peaks of Pio became wicker and wide in the spectrum of CS-Pio NPs, which means that Pio loaded into CS matrix, became amorphous.
The XRD spectrum of physical mixture of Cur and Pio (
Figure 1c) indicates multiple distinct characteristic sharp peaks at 2θ angles of 8.67°, 12.71°, 17.27°, 18.72°, 20.67°, 21.05°, 22.7°, 27.29°, 31.93°, which are associated with their crystalline state [
22]. In the XRD spectrum of CS-Pio-Cur NPs, only two peaks around 8.6° and 17.2°, were observed, weaker than characteristic peaks of Pio and Cur, which reinforces that APIs have changed their crystalline nature through nano-sizing in CS NPs.
Based on these results and correlated with physical parameters (PS, PI, ZP), it can be said that CS-APIs NPs can increase the solubility and bioavailability of APIs, by reducing the size of the particles and by changing the physical state.
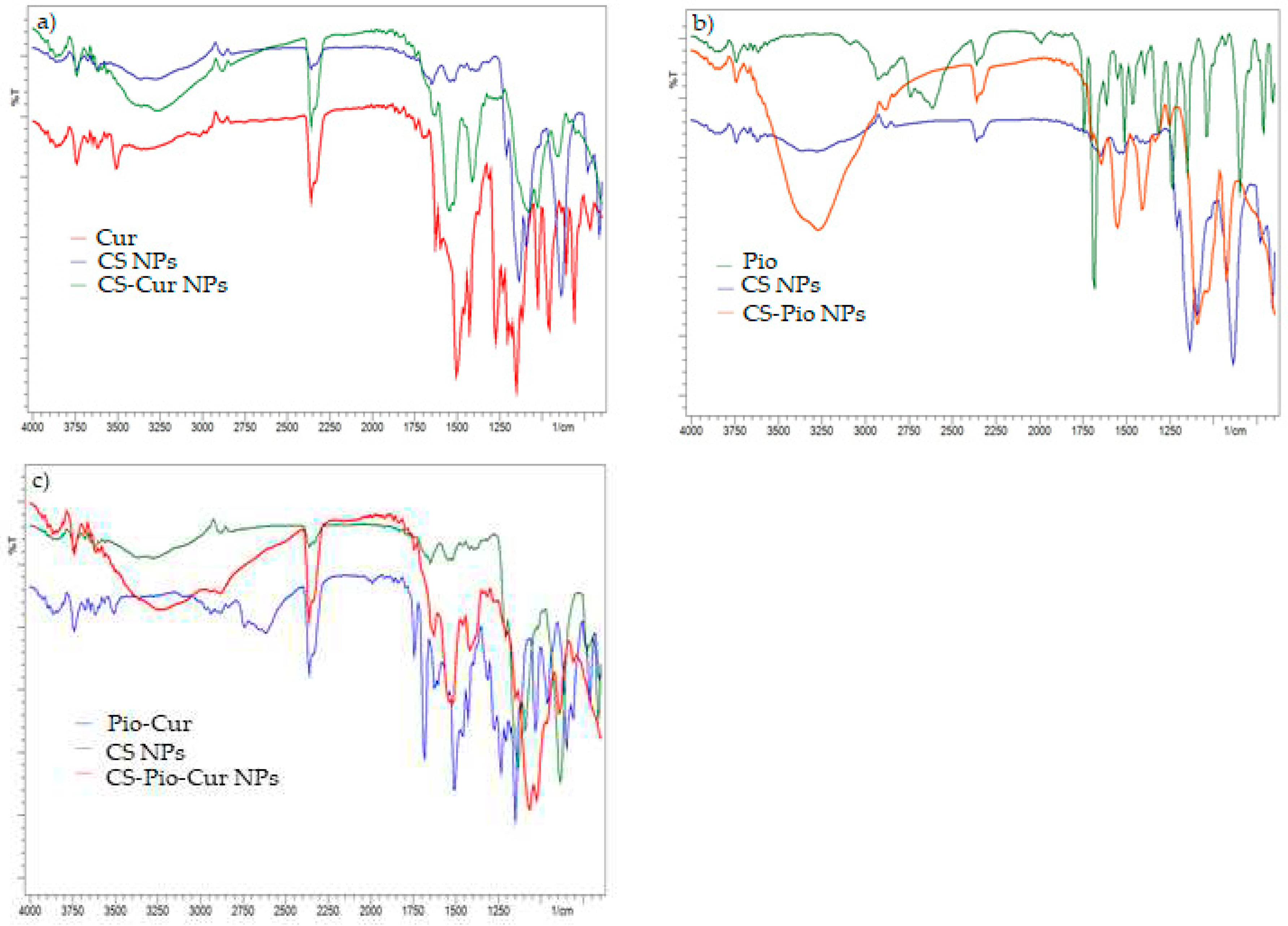
3.1.3. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy
In order to prove the loading of APIs (Cur, Pio) into polymeric matrix (CS NPs), FTIR spectroscopy was used.
The analysis of IR spectra of APIs (Cur, Pio) (
Figure 2) revealed the characteristic absorption bands, according to the literature data [
19,
22]. For Cur (
Figure 2a) the characteristic absorption peaks were recorded at 3510 cm
– 1 (phenolic O-H stretching vibration), 1628 cm
– 1 (stretching vibration of C=C and C=O of the inter-ring chain), 1597 cm
− 1 (symmetric stretching vibrations of the aromatic ring C=C), 1504 cm
– 1 (C=O stretching vibration), 1427 cm
– 1 (alkenyl =C-H bending vibration), 1273 cm
– 1 (aromatic C-O stretching vibration), 1026 cm
– 1 (C-O-C stretching vibration) and 856 cm
– 1 (bending vibration of CH of aromatic and skeletal CH).
The specific absorption peaks for Pio (
Figure 2b) was recorded at 1396 cm
-1 (asymmetric CH
3 vibration), 1466 cm
-1 (CH
2 vibration), 1551 cm
-1 and 1512 cm
-1 (asymmetric C=C stretching), 1744 cm
-1 and 1682 cm
-1 (asymmetric C=O stretching), 2924 cm
-1 and 2878 cm
-1 (C-H stretching of CH
2), and 3742 cm
-1 (N-H stretching), being in agreement with literature data [
9]. For CS, the specific vibration of pyranose units was recorded at 1095 cm
− 1.
The characteristic absorption peaks of APIs (Cur, Pio) were also identified in IR spectra recorded for CS-APIs NPs (CS-Cur NPs, CS-Pio NPs, CS-Pio-Cur NPs) (
Figure 2a, 2b, 2c), which proved the loading of APIs into polymer matrix. In addition, no notable change of the characteristic peaks was observed, that means there is no chemical interactions between APIs and CS, which support also the chemical stability of CS-APIs NPs.
3.1.4. The entrapment efficiency (EF) and loading capacity (LC)
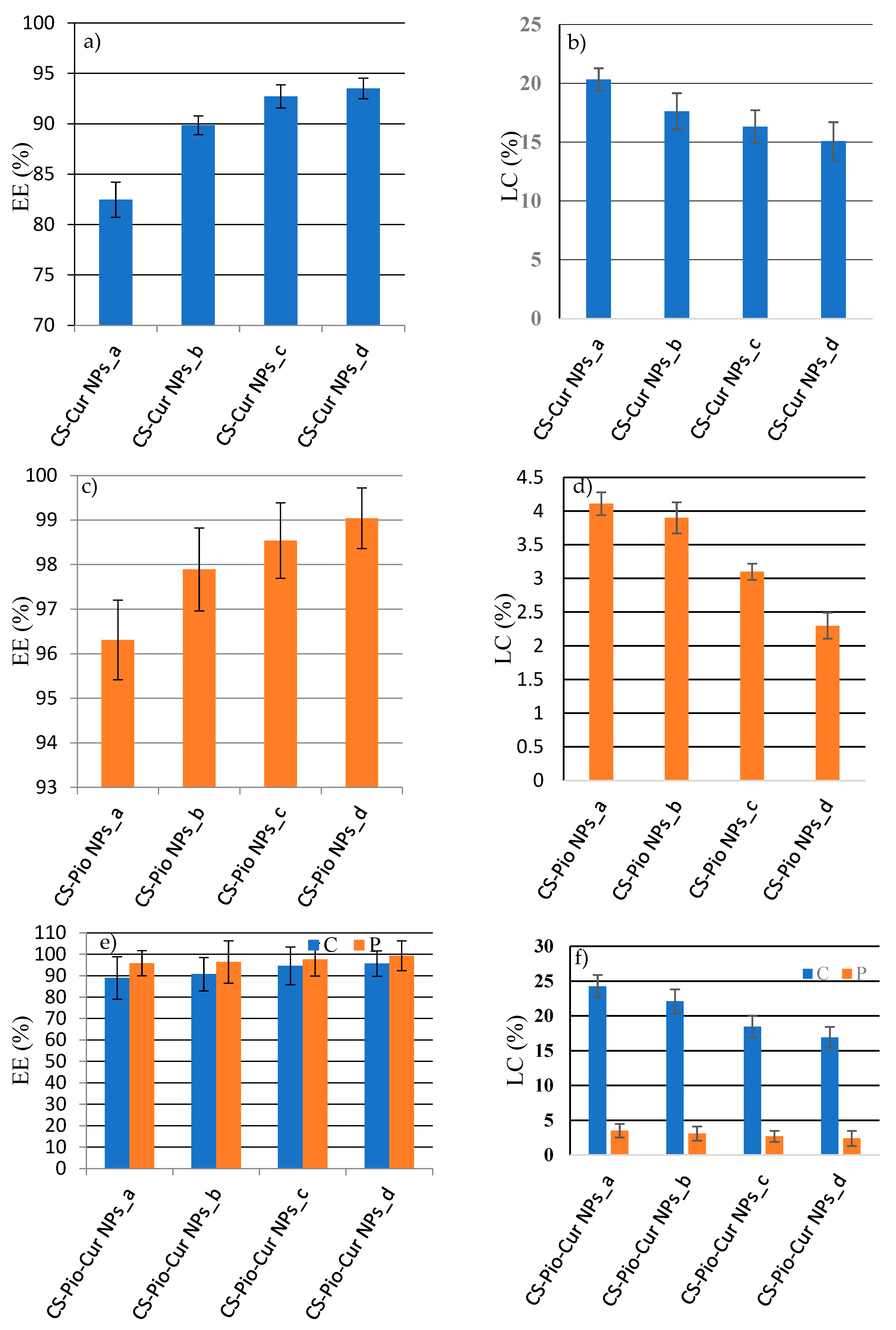
The analysis of the results (
Figure 3) revealed that EE (%) decrease with the concentration of APIs, while the LC (%) increase with it.
For CS-Cur NPs (
Figure 3a) the EE of Cur varied from 82.46% ± 1.74 (CS-Cur NPs_a) to 93.51% ± 1.01 (CS-Cur NPs_d), while the LC value decreased from 20.34% ± 0.94 (CS-Cur NPs_a) to 15.09% ± 1.61 (CS-Cur NPs_d). The most proper CS-Cur NPs formulation seems to be CS-Cur NPs_a, for which proper EE and LC values were recorded (EE = 82.46% ± 1.74; LC = 20.34% ± 0.94).
In case of CS-Pio NPs, the optimal formulation was CS-Pio NPs_a, for which the EE was 96.31% ± 0.68 and LC was of 4.11% ± 0.47 (
Figure 3b). The presence of Pio and Cur in the same NPs increase the EE of Cur. The results (
Figure 3c) showed that the optimal CS-Pio-Cur formulation is CS-Pio-Cur NPs_a (0.2 mg Pio/1.5 mg Cur), for which the EE (Cur: 88.95% ± 7.79, Pio: 94.83% ± 9.89) and LC (Cur: 24.25 % ± 1.62; Pio: 3.5% ± 0.98) were the highest.
3.2. The APIs release study
3.2.1. Development and validation of HPLC method
The developed HPLC method was validated according to the bio analytical guidelines [
23].
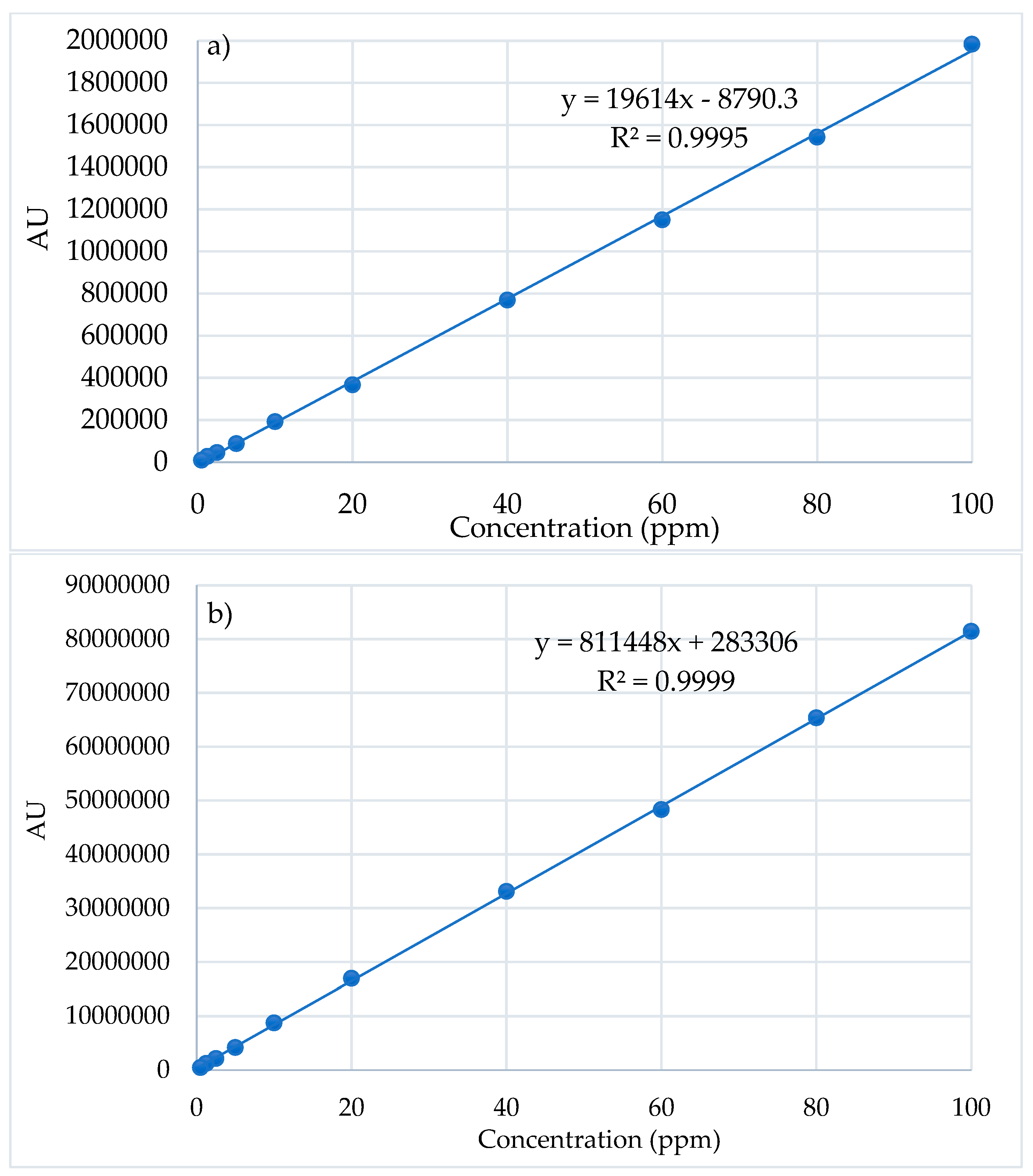
The linearity of the method was studied in the 0.5-100 ppm concentration range of Cur and Pio, respectively. The average value of the AU was calculated for each concentration and was plotted in relation to the concentration (
Figure 4). Statistical analysis of the results leads to regression line equations. The linear regression data for the calibration curve of APIs showed good linear relationship over the concentration range.
The accuracy of the method was calculated based on the experimental HPLC data and the regression curve equation. It was noted that recovery for Pio was between 98.34% and 101.96% (100±2%) while for Cur were between 99.5-101.43%.
The precision of the method could be expressed as the coefficient of variation (CV) or the relative standard deviation (RSD). The obtained results support the reproducibility of the method. The RSD (%) values were less than 2%, which confirm that the method has a high degree of accuracy and precision and so, can be applied for quantitative measurements of Cur and Pio from developed CS-APIs NPs.
The results strongly support that the developed HPLC method has good sensitivity, precision and accuracy, and can be applied for simultaneously determination of Cur and Pio from CS-APIs NPs.
3.2.2. In vitro APIs release
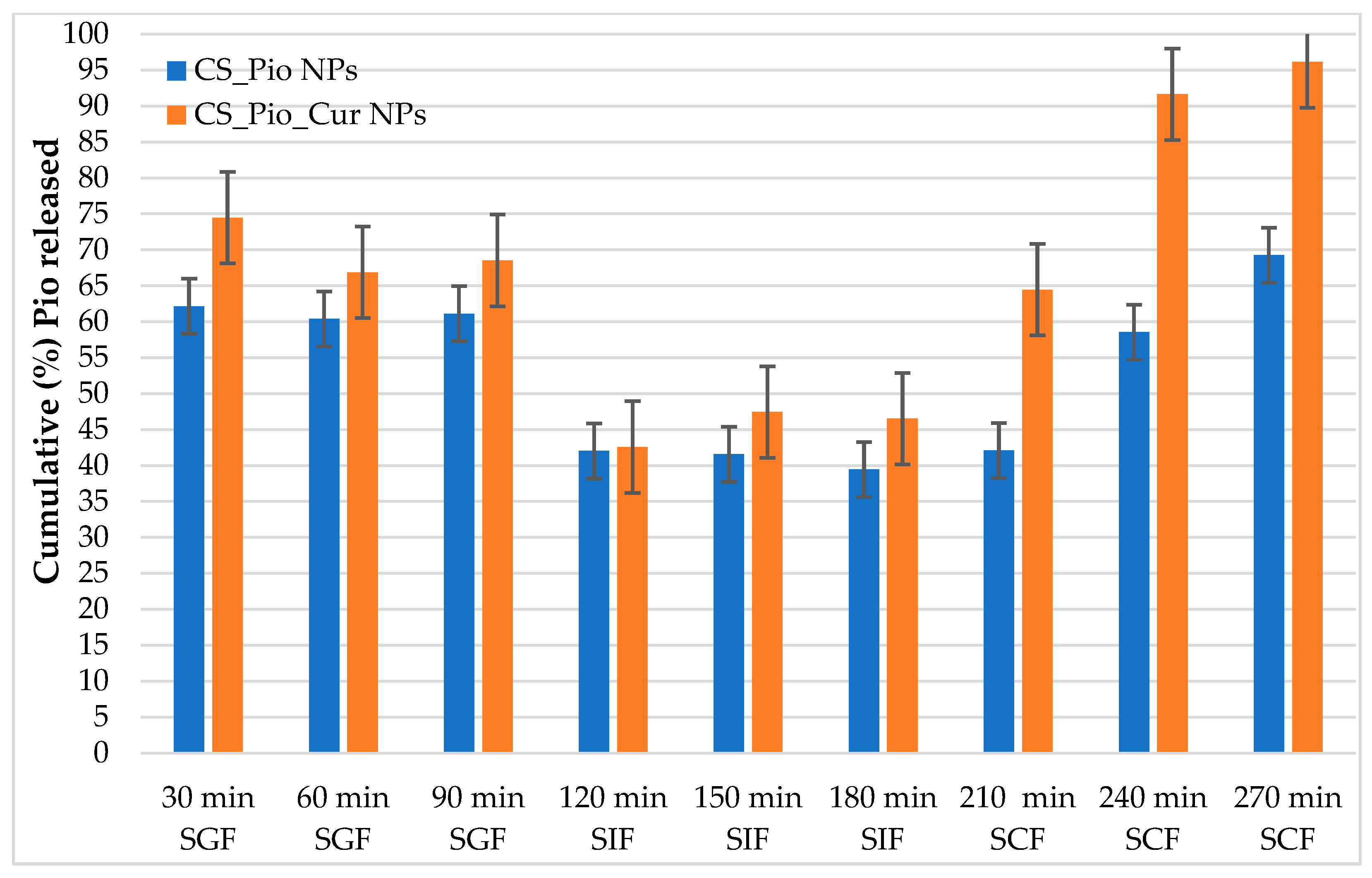
The Pio released from CS-APIs NPs
The cumulative release of Pio (%) from CS-Pio and CS-Pio-Cur NPs, using different simulated fluids (SGF, SIF and SCF), at different times, are presented in
Figure 5.
Using one way ANOVA analysis (F(1, 52)=10.185,
p<0.05) it was noted that, at the end of experiment (270 min) the cumulative Pio released from CS-Pio-Cur NPs (96.12±10.64%) was higher than Pio released from CS-Pio NPs (69.24±9.07%). Moreover, according to the literature data it was observed that the Pio release extensively depends on pH (p<0.05). So, the cumulative Pio release was higher in SCF (pH 7.4) (at 270 min, 69.24±9.07% from CS-Pio NPs and 96.12±10.64% from CS-Pio-Cur NPs) than the values recorded in SGF (pH 1.6) (at 90 min, 61.12±1.21% from CS-Pio NPs and 68.53±1.92% CS-Pio-Cur-NPs) [
24].
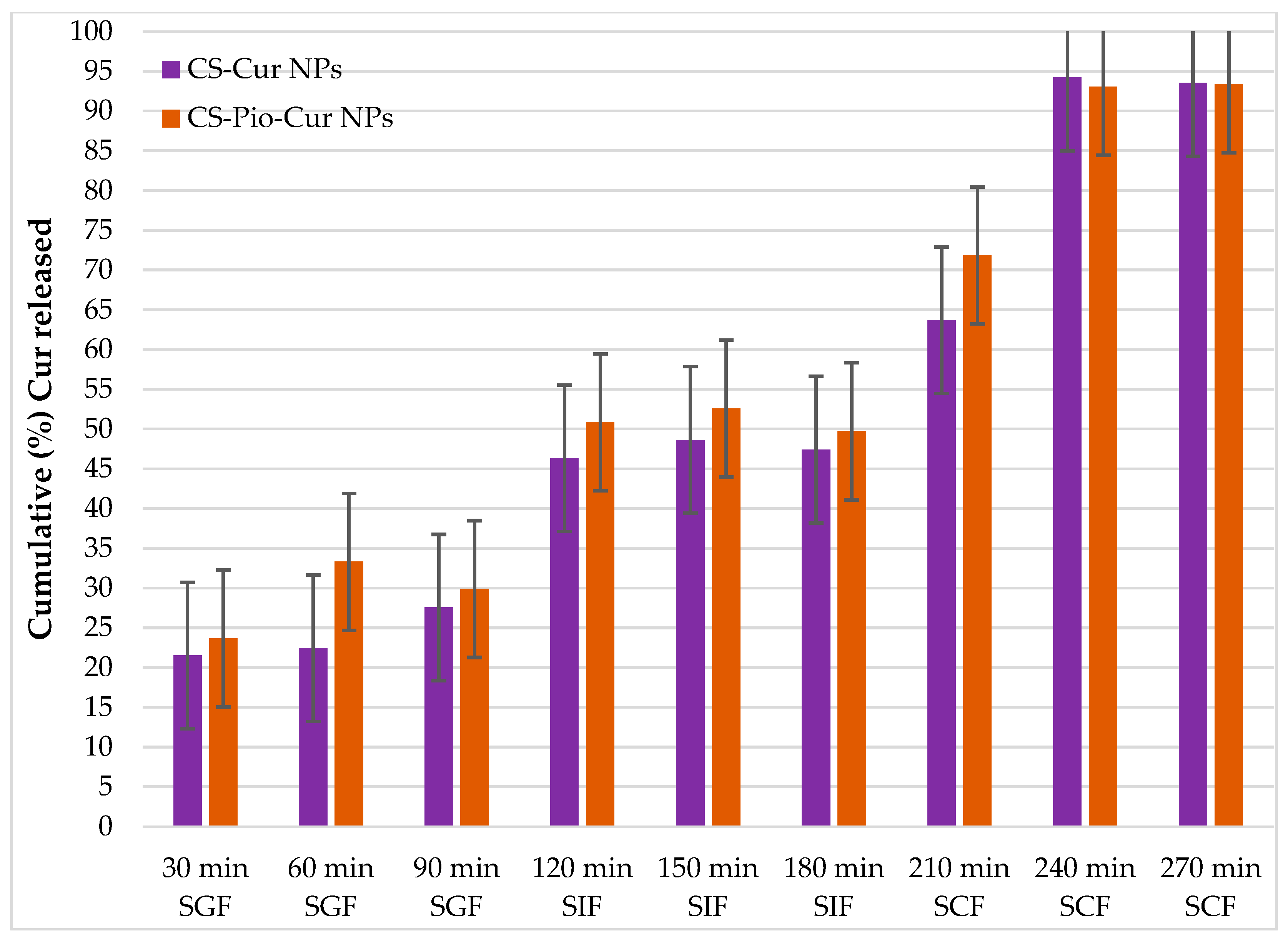
The Cur release from CS-APIs NPs
The value of cumulative Cur (%) released from CS-Cur/CS-Pio-Cur NPs, recorded in different simulated fluids (SGF, SIF and SCF), at different times, are presented in
Figure 6.
Analysis of the results using two-way ANOVA, revealed that the cumulative Cur (%) released from CS-APIs NPs (CS-Pio/CS-Pio-Cur NPs) is not influenced statistically significant (F(2, 48)=0.137, p=0.873), when exposure in simulated fluids (SGF, SIF, SCF) and type of formulation (CS-Pio NPs, CS-Pio-Cur NPs) are taken in consideration. In this situation, the presence of Pio in formulation do not influence de kinetic release of Cur from CS-APIs NPs.
Furthermore, as expected, a statistically significant difference (F(2,51)=237.922, p<0.05) was noted referring to cumulative Cur (%) released from CS-Cur NPs in simulated fluids. The average value of cumulative Cur release in SGF (27.55±0.38% at 90 min) was significantly less than the value recorded in SIF (47.42±0.76% at 180 min) and in SCF (93.53±2.26% at 270 min). A delivery similar manner was observed also for cumulative Cur released from CS-Pio-Cur NPs (29.87±0.37% at 90 min, in SGF; 49.72±1.42% at 180 min, in SIF and 93.36±1.85% at 270 min, in SCF). The low value recorded in SGF is explain based on that Cur is less soluble in acid conditions (SGF pH 1.6) than neutral conditions (SIF, SCF), which is in agreement with data from literature [
25,
26].
As general remarks, in vitro APIs (Cur, Pio) release assay showed that the developed co-delivery nanosystem, CS-Pio-Cur NPs, assure a controlled and prolonged release of Pio and Cur from polymer matrix along the GI tract.
4. Conclusions
In order to targeted the optimal hypoglycemic control and oxidative stress, which are involved both in onset and progression of T2DM, a new co-delivery nanosystem, CS-Pio-Cur NPs, was prepared. To find the optimal formulation conditions (CS concentration, Cur-Pio ratio), simple nanosystems (CS-Cur NPs and CS-Pio NPs), were also developed. The developed CS-APIs NPs (CS-Pio-Cur NPs, CS-Cur NPs, CS-Pio NPs) were fully characterized. The physical parameters (particle size, poly dispersity index, zeta potential) assure the physical stability of the developed nanosystems, through repulsion degree between the electrically charged and dispersed NPs.
The XRD study has demonstrated that APIs (Cur, Pio) loaded into CS NPs are in amorphous state, that could be an important advantage, because their solubility and bioavailability could be improved, in comparation with standard APIs, that are in crystalline state.
The analysis of FT-IR spectra supports the successful loading of APIs into CS matrix, as well as their chemical stability, which is very important for maintaining the drug’s efficiency.
The HPLC method developed for simultaneously quantification of APIs (Cur, Pio) from co-delivery nanosystem, has high sensitivity, precision and accuracy and was successful applied for release study. Based on in vitro release of APIs in different simulated fluids (SGF, SIF, SCF), it can be concluded that the developed CS-APIs NPs are suitable for oral administration, showing a good absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. According to the obtained results, the developed nanoformulations can be potential candidates for antidiabetic therapy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.G.L., A.S. and L.P.; methodology, F.G.L., A.S. and A.D.; validation, A.S., F.G.L. and L.P.; investigation, A.S., F.G.L., S.M.T., A.T.I., B.S.P., I.M.V. and M.A.; resources, L.P. and A.S.; data curation, B.S.P., I.M.V. and M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, F.G.L., A.S., B.S.P., S.M.T. and A.T.I.; writing—review and editing, L.P., A.S., B.S.P. and F.G.L.; supervision, L.P.; project administration, L.P. and A.S.; funding acquisition, L.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant of Romanian Ministry of Education and Research, CNCS-UEFISCDI, project number PN-III-P4-ID-PCE-2020-2687 (contract nr. 244/2021) within PNCDI IIII and by European Social Fund—the Human Capital Operational Programme, Project/Grant No: POCU/993/6/13/154722.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data could be requested from authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Vicente, A.B.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Siddiqi, H.; Uribe, K.B.; Ostolaza, H.; Martin. C. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6275.
- Roy, B.; Ehlert, L.; Mullur, R.; Freeby, M.J.; Woo, M.A.; Kumar, R.; Choi, S. Regional Brain Gray Matter Changes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 109925.
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; Pavkov, M.E.; Ramachandaran, A.; Wild, S.H.; Jamesj, S.; Herman, W.H.; Zhang, P.; Bommer, C.; Kuo, S.; Boyko, E.; Magliano, D.J. Erratum to “IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045”. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 204, 110945.
- McCoy, M.A.; Theeke, L.A. A systematic review of the relationships among psychosocial factors and coping in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2019, 6 (4), 268-477.
- Halim, M.; Halim, A. The effects of inflammation, aging and oxidative stress on the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus (type 2 diabetes). Diab. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 1165-1172.
- McKeegan, K.; Mason, S.A.; Trewin, A.J.; Keske, M.A.; Wadley, G.D.; Gatta, P.A.D.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Parker, L. Reactive oxygen species in exercise and insulin resistance: Working towards personalized antioxidant treatment. Redox. Biol. 2021, 44, 102005.
- Khursheed, R.; Singh, S.K.; Wadhwa, S.; Kapoor, B.; Gulati, M.; Kumar, R.; Ramanunny, A.K.; Awasthi, A.; Dua, K. Treatment strategies against diabetes: Success so far and challenges ahead. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 862, 172625.
- Bansal, G.; Singh, S.; Monga, V.; Thanikachalam, P.V.; Chawla, P. Synthesis and biological evaluation of thiazolidine-2,4-dione-pyrazole conjugates as antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agents. Bio. Chem. 2019, 92, 103271.
- Sharma, D.K.; Pattnaik, G.; Behera, A. Development and in-vitro, in-vivo evaluation of Pioglitazone-loaded polymeric nanoparticles using central composite design surface response methodology. Open. Nano. 2023, 11, 100141.
- Egil, A.C.; Kesim, H.; Ustunkaya, B.; Kutlu, O.; Ince, G.O. Self-assembled albumin nanoparticles for redox responsive release of curcumin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103831.
- Chen, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Fang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Ding, Y. Application of Pickering emulsions stabilized by corn, potato and pea starch nanoparticles: Effect of environmental conditions and approach for curcumin release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 238, 124115.
- Idoudi, S.; Hiiji, Y.; Bedhiafi, T.; Korashy, H.M.; Uddin, S.; Merhi, M.; Dermime, S.; Billa, N. A novel approach of encapsulating curcumin and succinylated derivative in mannosylated-chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr.Polym. 2022, 297, 120034.
- Ai, C.; Zhao, C.; Xiang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhong, S.; Teng, H.; Chen, L. Gum arabic as a sole wall material for constructing nanoparticle to enhance the stability and bioavailability of curcumin. Food. Chem. 2023, 18, 100724.
- Huang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Luo, G.; Zeng, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, K. Curcumin encapsulated zein/caseinate-alginate nanoparticles: Release and antioxidant activity under in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food. Sci. 2023, 6, 100463.
- Niranjan, R.; Kaushik, M.; Prakash, J.; Venkataprasanna, K.S.; Prema, D.; Christy, A.; Pannerselvam, B.; Venkatasubbu, D. Chitosan based wound dressing patch loaded with curcumin tagged ZnO nanoparticles for potential wound healing application. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 154, 110885.
- Liu, W.; Pan, W.; Han, Y.; Li, D.; Chai, J. Solubilization, stability and antioxidant activity of curcumin in a novel surfactant-free microemulsion system. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 147, 111583.
- Ioneascu, O.M.; Iacob, A.T.; Mignon, A.; Vlierberghe, S.V.; Baican, M.; Danu, M.; Ibanescu, C.; Simionescu, N.; Profire, L. Design, preparation and in vitro characterization of biomimetic and bioactive chitosan/polyethylene oxide based nanofibers as wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 996-1000.
- Florentina, L.; Constantin, S.M.; Profire, B.S.; Vasincu, I.; Ionescu, O.M.; Iacob, A.T.; Iurascu, T.; Ababei, A.; Apotrosoaei, M.; Jitareanu, A.; Sava, A.; Profire, L. Med. Surg. J. 2022, 126(1): 126-134.
- Li, X.; Xu, T.; Wu, C.; Fan, G.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D. Fabrication and characterization of self-assembled whey protein isolate/ short linear glucan core–shell nanoparticles for sustained release of curcumin. Food. Chem. 2023, 407, 135124.
- Wasana, P.W.D.; Vajragupta, O.; Rojsitthisak, P.; Towiwat, P.; Rojsitthisak, P. Metformin and Curcumin co-encapsulated chitosan/alginate nanoparticles as effective oral carriers against pain-like behaviors in mice. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 640, 123037.
- Vakilinezhada, M.A.; Aminic, A.; Daraa, T.; Alipourb, S.; Methotrexate and Curcumin co-encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles as a potential breast cancer therapeutic system: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Colloids. Surf. 2019, 184, 110515.
- Ghobadi-Oghaz, N.; Asoodeh, A.; Mohammadi, M. Fabrication, characterization and in vitro cell exposure study of zein-chitosan nanoparticles for co-delivery of curcumin and berberine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 204, 576–586.
- Kaza, M.; Karazniewicz-Łada, M.; Kosicka, K.; Siemitkowska, A.; Rudzki, P.J. Bioanalytical method validation: new FDA guidance vs. EMA guideline. Better or worse?. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 165, 381–385.
- Sugita, M.; Kataoka, M.; Sugihara, M.; Takeuchi, S.; Yamashita, S. Effect of Excipients on the Particle Size of Precipitated Pioglitazone in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Impact on Bioequivalence. AAPS J. 2014, 16(5): 1119-27.
- Górnicka, J.; Mika, M.; Wróblewska, O.; Siudem, P.; Paradowska, K. Methods to Improve the Solubility of Curcumin from Turmeric. Life 2023, 13, 207.
- Kumavat, S.D.; Chaudhari, Y.; Borole, P.; Mishra, P.; Shenghani, K.; Duvvuri, P. Degradation Studies Of Curcumin. Pharm. Rev. Res. 2013, 3(2), 50-55.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).