Submitted:
17 January 2024
Posted:
18 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
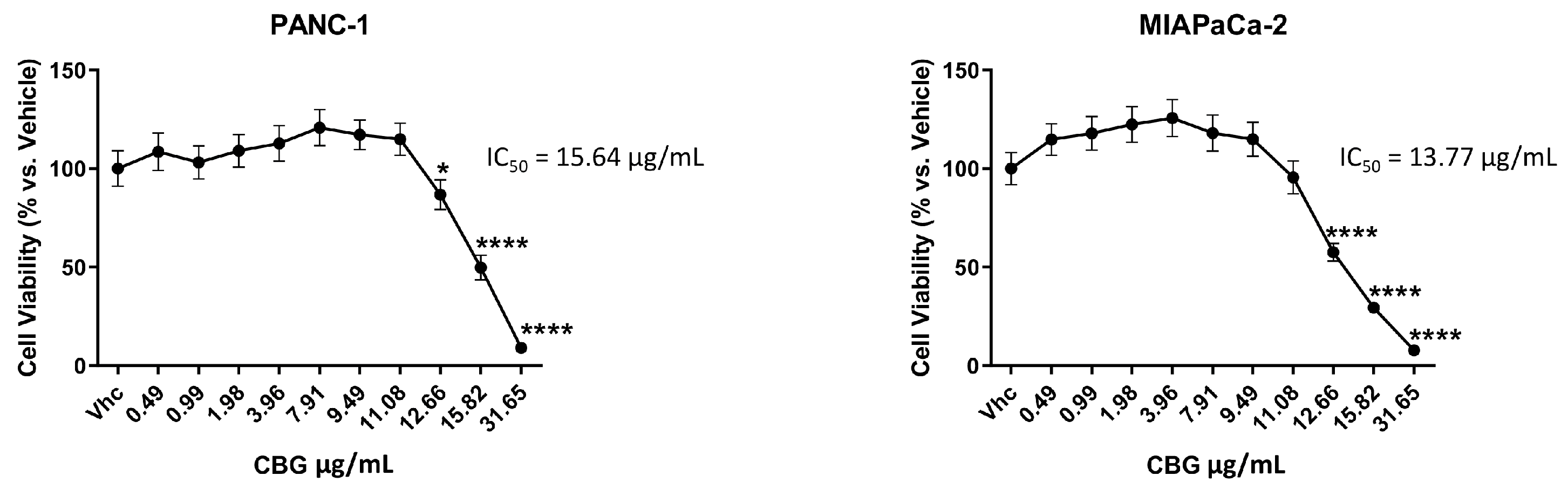
2.1. CBG inhibits cell growth of PDAC cell lines
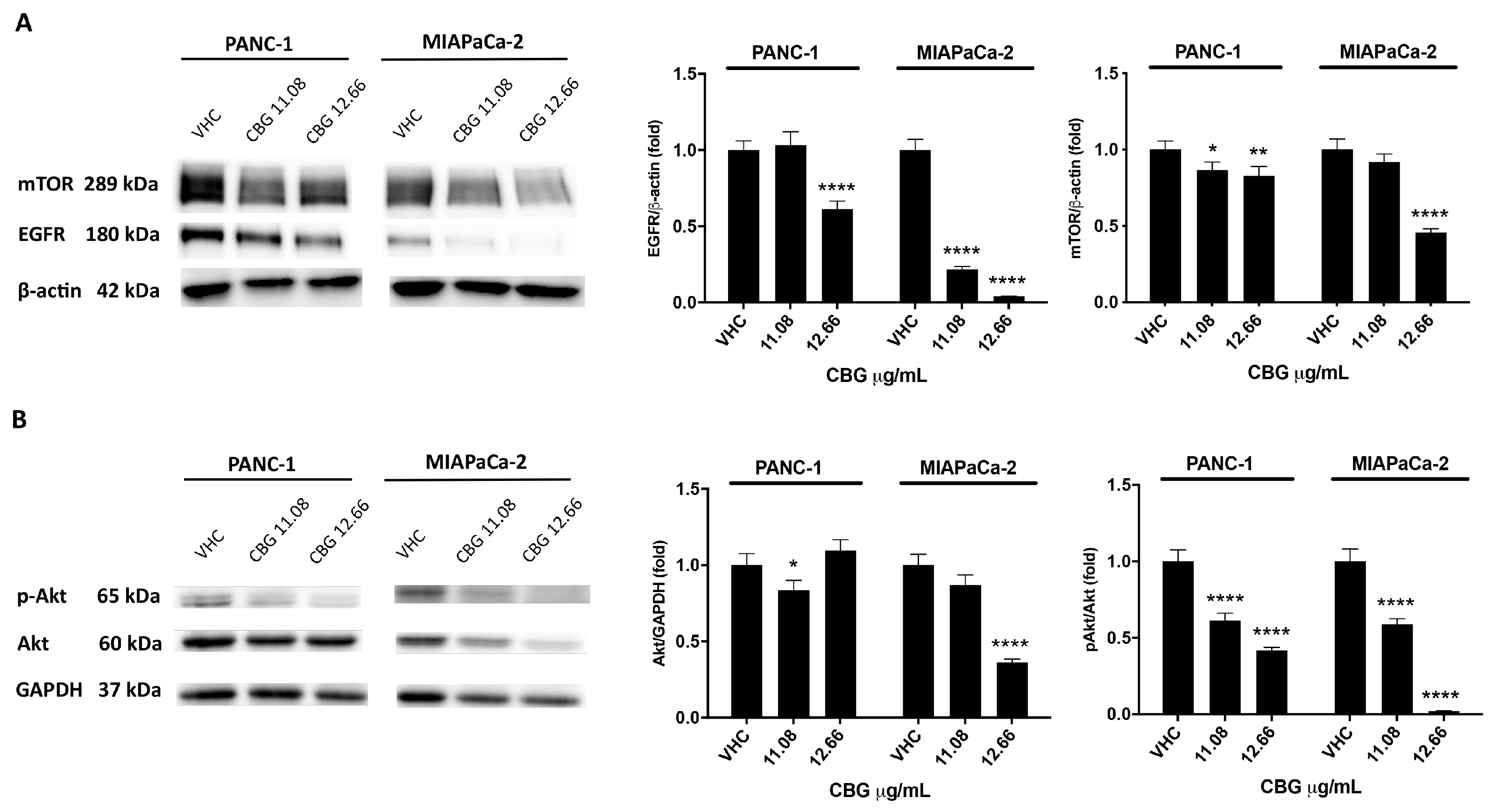
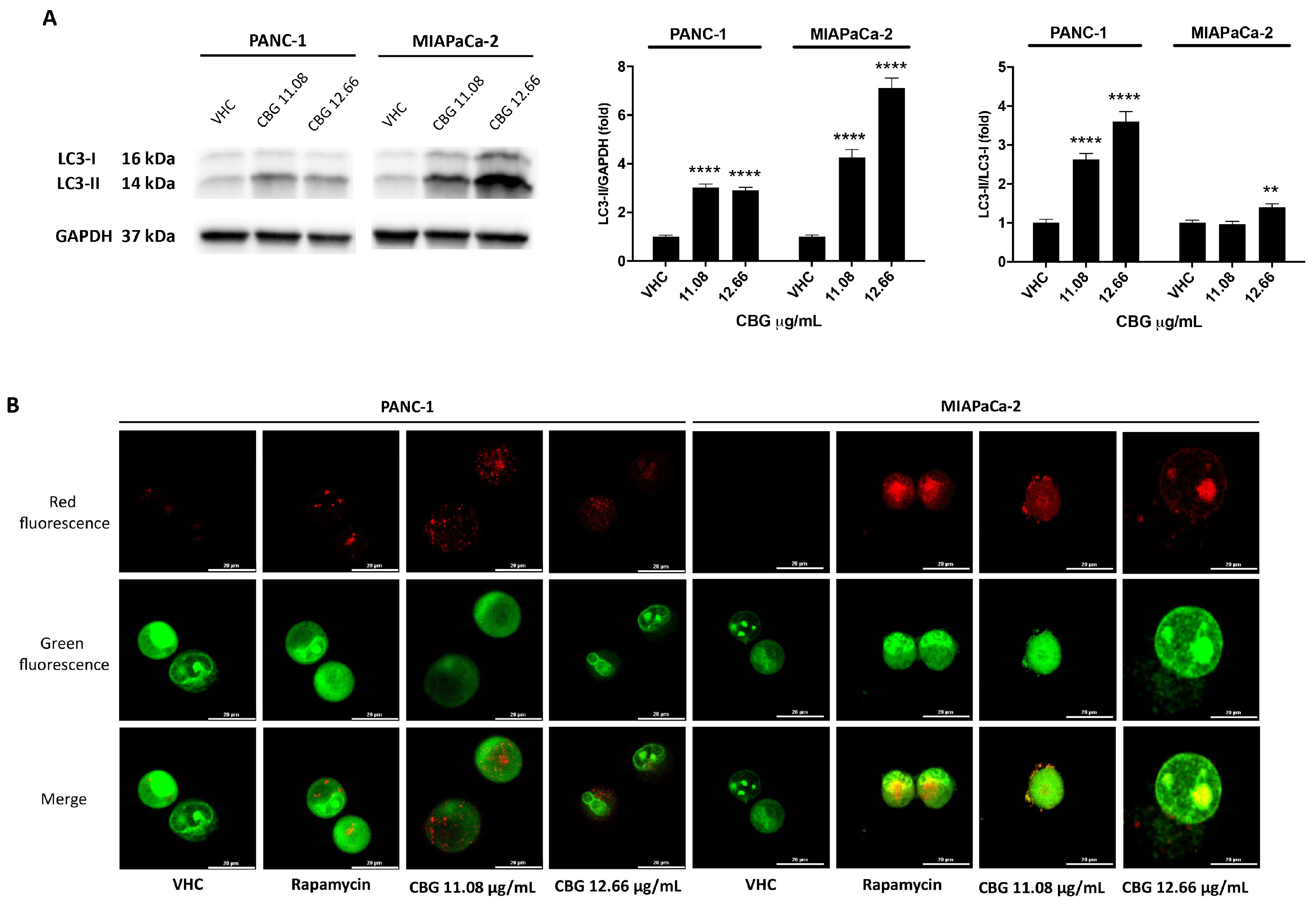
2.2. CBG induces autophagy by inhibition of EGFR and Akt/mTOR pathway in PDAC cell lines
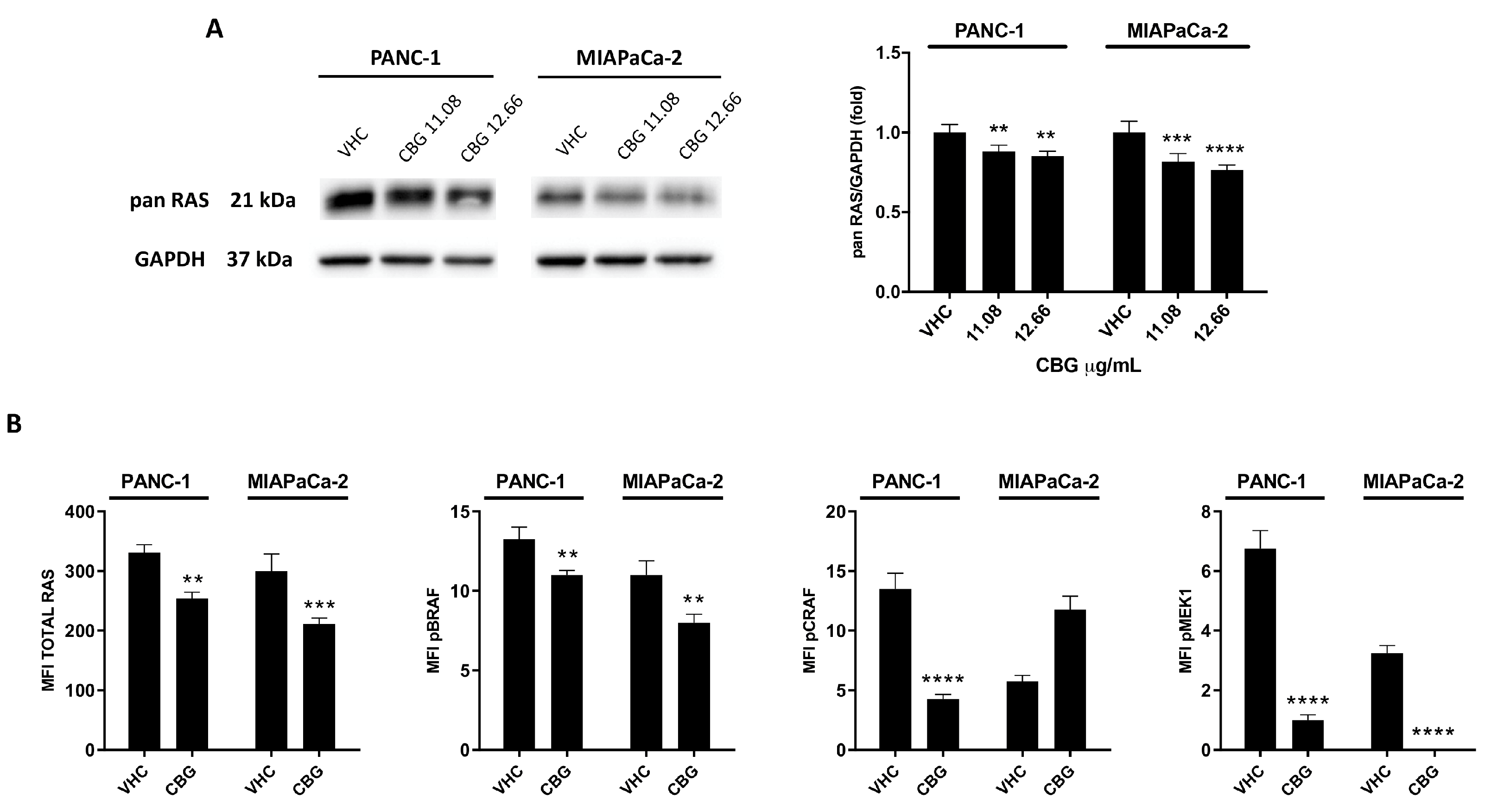
2.3. CBG reduces RAS downstream pathway in PDAC cell lines
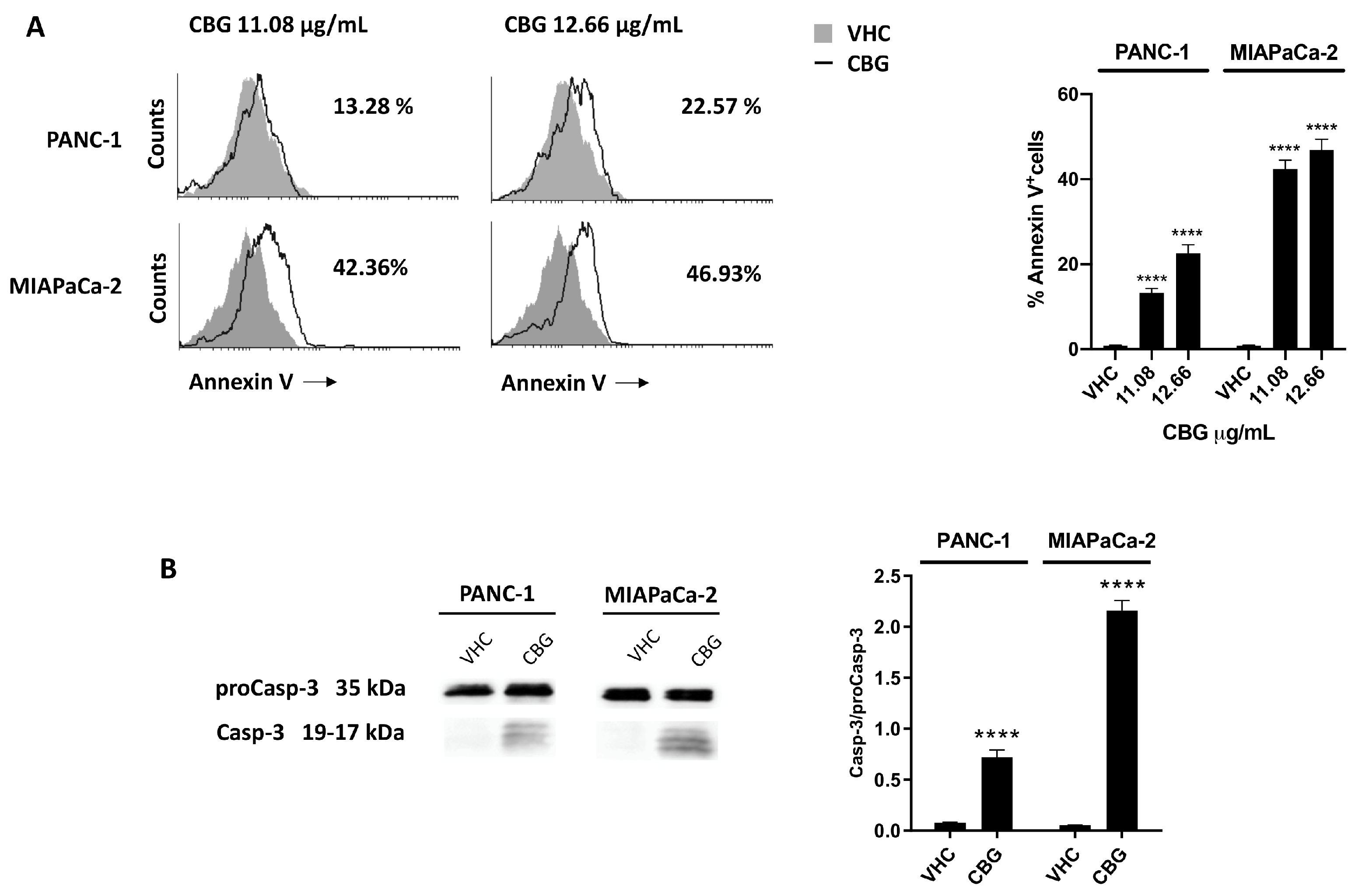
2.4. CBG induces apoptosis in PDAC cell lines
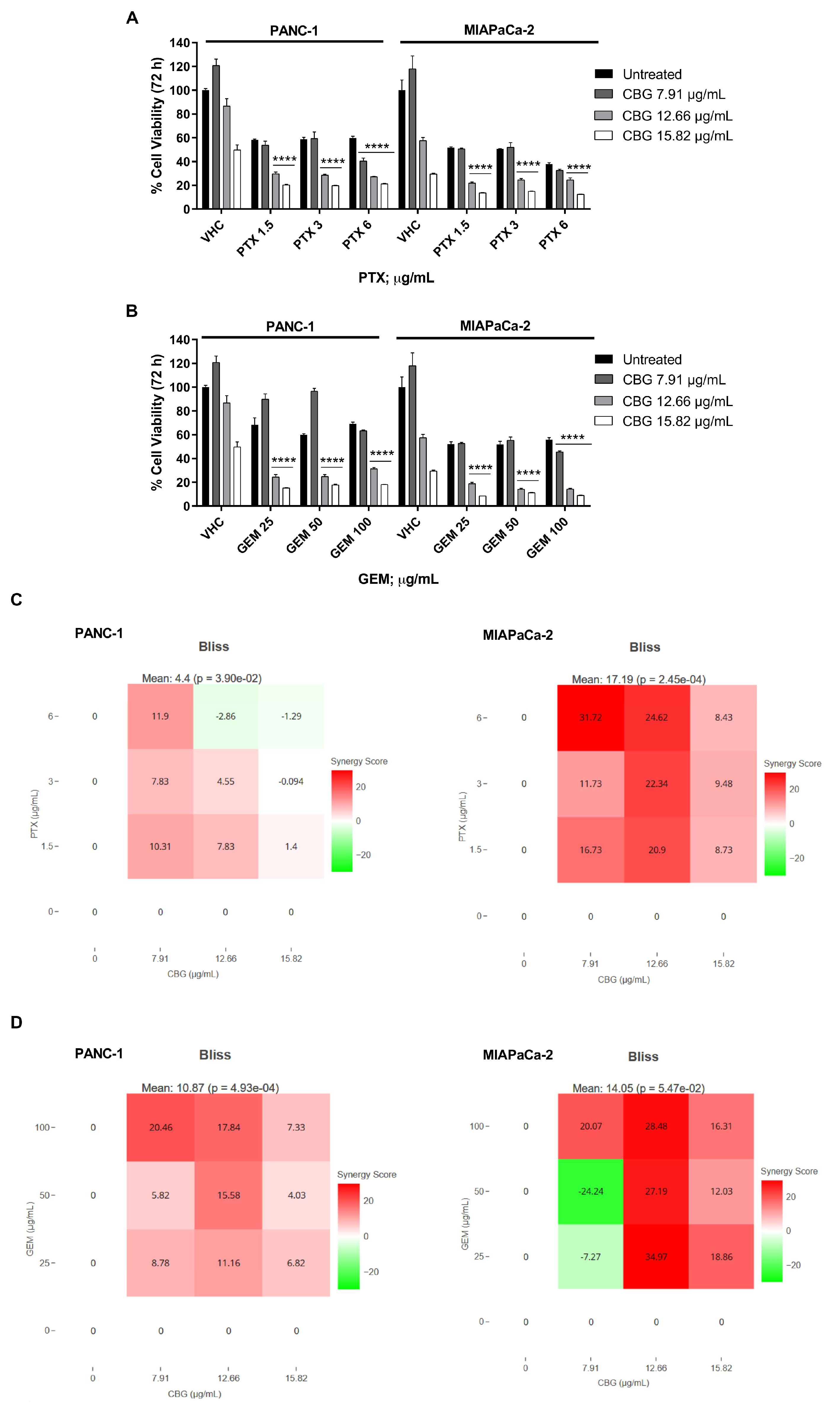
2.5. The combination of CBG with PTX or GEM induces higher cytotoxicity compared to administration of single drugs in PDAC cell lines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Reagents
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. Annexin V Staining
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Acridine Orange Staining
4.7. Milliplex multiplex assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
4.9. Drug interaction
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R. L.; Miller, K. D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamska, A.; Domenichini, A.; Falasca, M. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Current and Evolving Therapies. IJMS. 2017, 18, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M. A.; Bednar, F.; Zhang, Y.; Brisset, J. C.; Galbán, S.; Galbán, C. J.; Rakshit, S.; Flannagan, K. S.; Adsay, N. V.; Pasca di Magliano, M. Oncogenic Kras is required for both the initiation and maintenance of pancreatic cancer in mice. J Clin Invest. 2012, 122, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodoky, G.; Timcheva, C.; Spigel, D. R.; La Stella, P. J.; Ciuleanu, T. E.; Pover, G.; Tebbutt, N. C. A phase II open-label randomized study to assess the efficacy and safety of selumetinib (AZD6244 [ARRY-142886]) versus capecitabine in patients with advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who have failed first-line gemcitabine therapy. Invest New Drugs. 2012, 30, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, A. D.; Fesik, S. W.; Kimmelman, A. C.; Luo, J.; Der, C. J. Drugging the undruggable RAS: Mission possible? Nature reviews. Drug discovery. 2014, 13, 828–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, H. P.; Ming, M.; Mellon, M.; Young, S. H.; Han, L.; Sinnet-Smith, J.; Rozengurt, E. Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitors Induce Rapid Overactivation of the MEK/ERK Pathway in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Suppression of mTORC2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokinen, E.; Koivunen, J. P. MEK and PI3K inhibition in solid tumors: rationale and evidence to date. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2015, 7, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfaye, A. A.; Philip, P. A. Adjuvant treatment of surgically resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2019, 17, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Twelves, C.; Sabel, M.; Checketts, D.; Miller, S.; Tayo, B.; Jove, M.; Brazil, L.; Short, S. C. GWCA1208 study group. A phase 1b randomised, placebo-controlled trial of nabiximols cannabinoid oromucosal spray with temozolomide in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Br J Cancer. 2021, 124, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, M.; Aguzzi, C.; Fanelli, A.; Frassineti, A.; Zeppa, L.; Morelli, M.; Pastore, G.; Nabissi, M.; Luongo, M. The Effects of a Combination of Medical Cannabis, Melatonin, and Oxygen–Ozone Therapy on Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Case Report. Reports. 2023, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Wu, J. Antitumor mechanism of cannabidiol hidden behind cancer hallmarks. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023, 1878, 188905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łuczaj, W.; Dobrzyńska, I.; Skrzydlewska, E. Differences in the phospholipid profile of melanocytes and melanoma cells irradiated with UVA and treated with cannabigerol and cannabidiol. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 16121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lah, T. T.; Novak, M.; Pena Almidon, M. A.; Marinelli, O.; Žvar Baškovič, B.; Majc, B.; Mlinar, M.; Bošnjak, R.; Breznik, B.; Zomer, R.; Nabissi, M. Cannabigerol Is a Potential Therapeutic Agent in a Novel Combined Therapy for Glioblastoma. Cells. 2021, 10, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamtha, T.; Tabtimmai, L.; Songtawee, N.; Tansakul, N.; Choowongkomon, K. Structural analysis of cannabinoids against EGFR-TK leads a novel target against EGFR-driven cell lines. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022, 3, 100132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, G.; Seshacharyulu, P.; Rauth, S.; Nallasamy, P.; Rachagani, S.; Nimmakayala, R. K.; Vengoji, R.; Mallya, K.; Chirravuri-Venkata, R.; Singh, A. B.; et al. Selective inhibition of stemness through EGFR/FOXA2/SOX9 axis reduces pancreatic cancer metastasis. Oncogene. 2021, 40, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, O.; Morelli, M. B.; Annibali, D.; Aguzzi, C.; Zeppa, L.; Tuyaerts, S.; Amantini, C.; Amant, F.; Ferretti, B.; Maggi, F.; et al. The Effects of Cannabidiol and Prognostic Role of TRPV2 in Human Endometrial Cancer. IJMS. 2020, 21, 5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A. K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 2.0: visual analytics of multi-drug combination synergies. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48(W1), W488–W493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, M.; David, A.; Sapire, K.; Hausner, D. Complementary and Integrative Medicine in Pancreatic Cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2023, 25, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, F.; Chi, M.; Eamens, A. L.; Duchatel, R. J.; Douglas, A. M.; Schneider, J.; Gedye, C.; Woldu, A. S.; Dun, M. D. Can Hemp Help? Low-THC Cannabis and Non-THC Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Cancer. Cancers. 2020, 12, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, M.; Marinelli, O.; Zeppa, L.; Aguzzi, C.; Morelli, M. B.; Amantini, C.; Frassineti, A.; di Costanzo, M.; Fanelli, A.; Santoni, G.; Nabissi, M. Cannabidiol and Oxygen-Ozone Combination Induce Cytotoxicity in Human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines. Cancers. 2020, 12, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, R.; Adamska, A.; Lattanzio, R.; Mavrommati, I.; Edling, C. E.; Arifin, S. A.; Fyffe, C. A.; Sala, G.; Sacchetto, L.; Chiorino, G.; et al. GPR55 signalling promotes proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells and tumour growth in mice, and its inhibition increases effects of gemcitabine. Oncogene. 2018, 37, 6368–6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, M.; Carracedo, A.; Salanueva, I. J.; Hernández-Tiedra, S.; Lorente, M.; Egia, A.; Vázquez, P.; Blázquez, C.; Torres, S.; García, S.; et al. Cannabinoid action induces autophagy-mediated cell death through stimulation of ER stress in human glioma cells. J Clin Invest. 2009, 119, 1359–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, P. EGFR-mediated autophagy in tumourigenesis and therapeutic resistance. Cancer letters. 2020, 469, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, S.; Ionita-Radu, F.; Stefani, C.; Miricescu, D.; Stanescu-Spinu, I. I.; Greabu, M.; Ripszky Totan, A.; Jinga, M. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer: From Molecular to Clinical Aspects. IJMS. 2022, 23, 10132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Xu, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, Z.; He, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Davidson, D.; et al. Cannabidiol inhibits human glioma by induction of lethal mitophagy through activating TRPV4. Autophagy. 2021, 17, 3592–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vara, D.; Salazar, M.; Olea-Herrero, N.; Guzmán, M.; Velasco, G.; Díaz-Laviada, I. Anti-tumoral action of cannabinoids on hepatocellular carcinoma: role of AMPK-dependent activation of autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Kuzontkoski, P. M.; Groopman, J. E.; Prasad, A. Cannabidiol induces programmed cell death in breast cancer cells by coordinating the cross-talk between apoptosis and autophagy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, M. T.; Navas, C.; Martín-Serrano, G.; Graña-Castro, O.; Lechuga, C. G.; Martín-Díaz, L.; Djurec, M.; Li, J.; Morales-Cacho, L.; Esteban-Burgos, L.; et al. Complete Regression of Advanced Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas upon Combined Inhibition of EGFR and C-RAF. Cancer cell. 2019, 35, 573–587.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, M.; Nasser, M.W.; Ravi, J.; Wani, N.A.; Ahirwar, D.K.; Zhao, H.; Oghumu, S.; Satoskar, A.R.; Shilo, K.; Carson, W.E. 3rd; et al. Modulation of the tumor microenvironment and inhibition of EGF/EGFR pathway: novel anti-tumor mechanisms of Cannabidiol in breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2015, 9, 906–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viereckl, M. J.; Krutsinger, K.; Apawu, A.; Gu, J.; Cardona, B.; Barratt, D.; Han, Y. Cannabidiol and Cannabigerol Inhibit Cholangiocarcinoma Growth In Vitro via Divergent Cell Death Pathways. Biomolecules. 2022, 12, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




