1. Introduction
1.1. Conceptualizations about Emotions
The concept of emotions has been addressed by several authors in the fields of psychology and philosophy. First, [
1] proposed that emotions have a biological basis and that the facial expressions of emotions have an evolutionary origin. According to [
2], emotions are the perception of specific bodily changes in response to an emotional stimulus. The authors [
3] worked in collaboration with William James in the development of the James-Lange theory, which proposed that emotions are the result of the perception of bodily responses that occur in emotional situations. For him, emotions are the awareness of our physiological reactions to an emotional event. For [
4], emotions are internal impulses that may be influenced by unconscious conflicts. In his theory [
5] proposed that emotions are the result of the cognitive evaluation we make of an event or situation in relation to our personal goals and values.
From the phenomenological perspective of Husserl [
6], emotions are regarded as the most intricate stratum of the affective experience. They exhibit a dual nature, encompassing a physical facet involving bodily changes in response to emotional states, and a cognitive facet characterized by to evaluate or appreciate the possibilities of a given situation" [
6]. These two dimensions are intricately interlaced, giving rise to four foundational attributes: (1) affective intentionality, (2) bodily resonance, (3) inclination towards action, and (4) function and significance.
Finally, Ekman’s theory of emotions has been widely studied and is considered one of the most influential theories of emotions. [
7] Focused on universal emotions and facial expressions. According to him, there are six basic universal emotions that are recognized in different cultures, such as happiness, sadness, surprise, fear, anger, and disgust. These basic emotions are discrete, meaning they comprise distinct patterns of psychological, physiological, and neurobiological features that distinguish them from one another. These emotions are basic for other complex emotional experiences and have evolved to be adaptive coping mechanisms for specific tasks and circumstances.
Ekman’s classification has been used in several practical applications, such as in the design of face and emotion recognition technologies. A standardised classification of emotions facilitates communication and information sharing among researchers. For these reasons, we detected students’ facial emotions using an ER code developed from Ekman’s theory with the addition of neutral emotion.
1.2. Emotions and Learning
Several authors have investigated how emotions influence the learning process. At the time, from to Vygotsky’s theory, the Russian term
perezhivanie refers to a deeply lived experience that is charged with emotional meaning and suggests that emotional experiences play a key role in the internalisation of knowledge and skills. Rich emotional experiences may enhance a deeper and more lasting internalisation of information, which may influence long-term academic performance [
8]. A theory of emotional intelligence [
9] highlights the importance of emotional skills in academic performance and learning. According to [
9], emotions have a significant impact on motivation, the ability to regulate stress and the ability to relate to others. [
10] Argues that emotions play a fundamental role in cognitive processes from the somatic theory of emotions. Emotional experiences are closely linked to decision making, memory formation and can facilitate the consolidation and retrieval of information, influencing the learning process.
Something to consider is that promoting students’ social-emotional well-being through emotion monitoring contributes to fostering a positive classroom climate and to the creation of healthier and more equitable educational communities, which is an important component of sustainable development [
11,
12].
The emotional dimension of the learning experience, specifically the feelings associated with perceiving and processing new information, becomes an essential component of the acquired knowledge and abilities [
12,
13].
The Pekrun’s theory of emotions [
14] provides a conceptual framework for understanding how emotions affect learning and academic performance, which distinguishes between two types of emotions in the academic context: activation emotions and value emotions. Activation emotions are related to perceptions of control and may include anxiety and boredom. Value emotions are linked to the importance and value of the task and include emotions such as joy and pride. Under this paradigm [
15] showed that students experience a wide range of emotions in the academic environment, except disgust. Anxiety constituted 15-27% of all emotional episodes in all three academic situations (study, class, tests and exams). However, the findings suggest that most emotions in academic situations are not anxiety related. Positive emotions, such as enjoyment, satisfaction, hope, pride, and relief, contrast with negative emotions like anger, anxiety, embarrassment, and boredom. Students also mentioned less frequently experienced emotions, such as hopelessness as well as social emotions such as gratitude, admiration, contempt and envy.
The studies linking positive emotions to achievement show that joy, hope, and pride positively correlate with students’ academic self-efficacy, academic interest and effort, and overall achievement [
16]. Positive emotions are hypothesized to facilitate approach-related activities, and these activities are likely to provide academic benefits, particularly as the student moves toward a desired goal [
17,
18]. Fredrickson [
19,
20] suggested that positive emotions enhance academic competence because they encourage exploring, integrating diverse materials, and broadening potential methods of solving problems.
About negative emotions, [
21] found that young children with negative emotionality struggle with higher order cognitive processes because of their lack of reflective planning and problem-solving skills. When a student’s experience of negative emotion leads to fixation on the object of the emotion (such as when a child dwells on the morning’s event that caused their anger), cognitive resources are redirected from educational materials to distractions that hinder learning. Negative emotions interfere with scholar activities by limiting cognitive resources necessary for integrating and recalling important details.
The anxiety and frustration from struggling with math exercises can cause a negative perception and dislike towards the topic [
22,
23]. Additionally, individuals experiencing negative emotions (such as sadness, frustration, or boredom) tend to process new information in a rigid and shallow manner [
24,
25].
Strong and persistent anxiety impairs learning, while occasional and mild anxiety has its benefits. The same goes for emotions and moods, as they have distinct learning purposes. According to [
26], a certain pessimism or seriousness can be advantageous for analytical and quantitative tasks, while a positive mood may be more beneficial for creative and heuristic thinking.
From another perspective some empirical findings support that the effect of emotionality on achievement might be indirect, through cognitive processes, interpersonal relationships with teacher and peers, and motivational mechanisms, such engagement, school liking, and staying on task [
27]. In this way, [
28] proposed a link between motivation and academic emotions, as motivational behaviours involve positive and negative academic emotions. Specifically, positive academic emotions are usually beneficial, but negative academic emotions, such as dissatisfaction and uneasiness, can have contradictory effects. Furthermore, it should be observed that students’ academic emotions often impact their performance.
The effects of emotions in learning were described as a hedonic affects [
29] can either facilitate or impede the acquisition of new knowledge, impacting its value and desirability. For example, the satisfaction of solving math problems enhances the acquired knowledge and skills, serving as motivation to continue the activity. In fact, students who are in a positive frame of mind are more likely to think creatively and learn a topic meaningfully [
30].
On the other hand, teachers also influence students’ emotions. The relationship between teachers’ social and affective strategy uses and students’ academic performance in English language class was explored by [
31]. Their argument is that language teachers should utilize affective strategies such as humour, positivity, fairness, encouragement, and politeness to effectively teach and enhance student achievement.
1.3. Emotions Assessment
Until now, the difficulty of recognize the student’s emotion has been obvious [
32]. Self-assessment is one of the most widely used ways to measure emotions [
33,
34,
35]. Individuals report their emotional experience using rating scales or questionnaires that request the rating of intensity, valence (positive or negative) and description of the emotions experienced. In clinical or research settings, direct observation of emotions through facial expressions and nonverbal language can be used [
36].
On the other hand, physiological responses, such as heart rate, skin conductance, and brain activation patterns, can be used to infer the presence and intensity of emotions [
37,
38]. These measurements could be obtained using technologies such as electrocardiograms (ECG), electrodermal activity (EDA) or neuroimaging techniques [
39].
In recent years, advancements in technology have allowed for the development of AI-based cameras that can detect and recognize facial expressions, enabling the assessment and monitoring of basic emotions in various settings, including the classroom [
40,
41].
Hence, the use of facial expression recognition technology has become a promising tool for assessing and monitoring emotions in real-time, providing valuable insights for both researchers and practitioners in the fields of psychology, education, and healthcare [
42].
With reference to [
43] facial expressions serve as a conduit for understanding individuals’ emotional states. In the educational field, employing AI-based methodologies enables continuous monitoring of students’ emotions. This approach facilitates the scrutiny of how diverse methodologies, educational scenarios, evaluative contexts, etc., impact emotions. Consequently, it allows for preemptive and targeted interventions to prevent and enhance emotional experiences. In that context, the general aim of the study is exploring how emotions change in secondary school students in the classroom context through continuous monitoring with a laptop camera. The specific objectives are:
- I.
Analyse the student’s emotions manifestations in the classroom.
- I.
Compare the emotions at the beginning and at the end of the class.
- I.
Relate the different emotions according to the subject and academic year.
2. Materials and Methods
This study adopted an exploratory observational design to monitor the emotions of secondary school students in six different class groups over 4 weeks.
The secondary school is located in Cambrils, a coastal town in north eastern Spain, which has three lines of four compulsory education courses, and two lines of two post compulsory education courses (bachelor’s degree). The average number of students per class is 32.
Table 1.
Students involved in the experiment.
Table 1.
Students involved in the experiment.
| Students |
Level |
Class |
|
16
24 |
First year secondary school
Fourth year secondary school |
2 groups
1 group |
| 24 |
First year bachelor’s degree |
2 groups |
| 12 |
Second year bachelor’s degree |
1 group |
Regarding the six different class groups recorded during the experiment, the first 2 groups are students of the first course of secondary school, who are 12-13 years old, and enrolled in the subject of Technology and an optative subject called Green project. The second group is students of the fourth course of secondary school, 15-16 years old, and enrolled in the subject of Robotics. The third and fourth groups belong to students of the first course of the bachelor’s degree, who were attending Technology and Robotics respectively and are 16-17 years old. The last group belongs to students of the second course of the bachelor’s degree, who are 17-18 years old and also enrolled in the subject of Technology. Each group of students has got a different teacher, in all these groups, teachers are female.
Figure 1.
Classroom arrangement.
Figure 1.
Classroom arrangement.
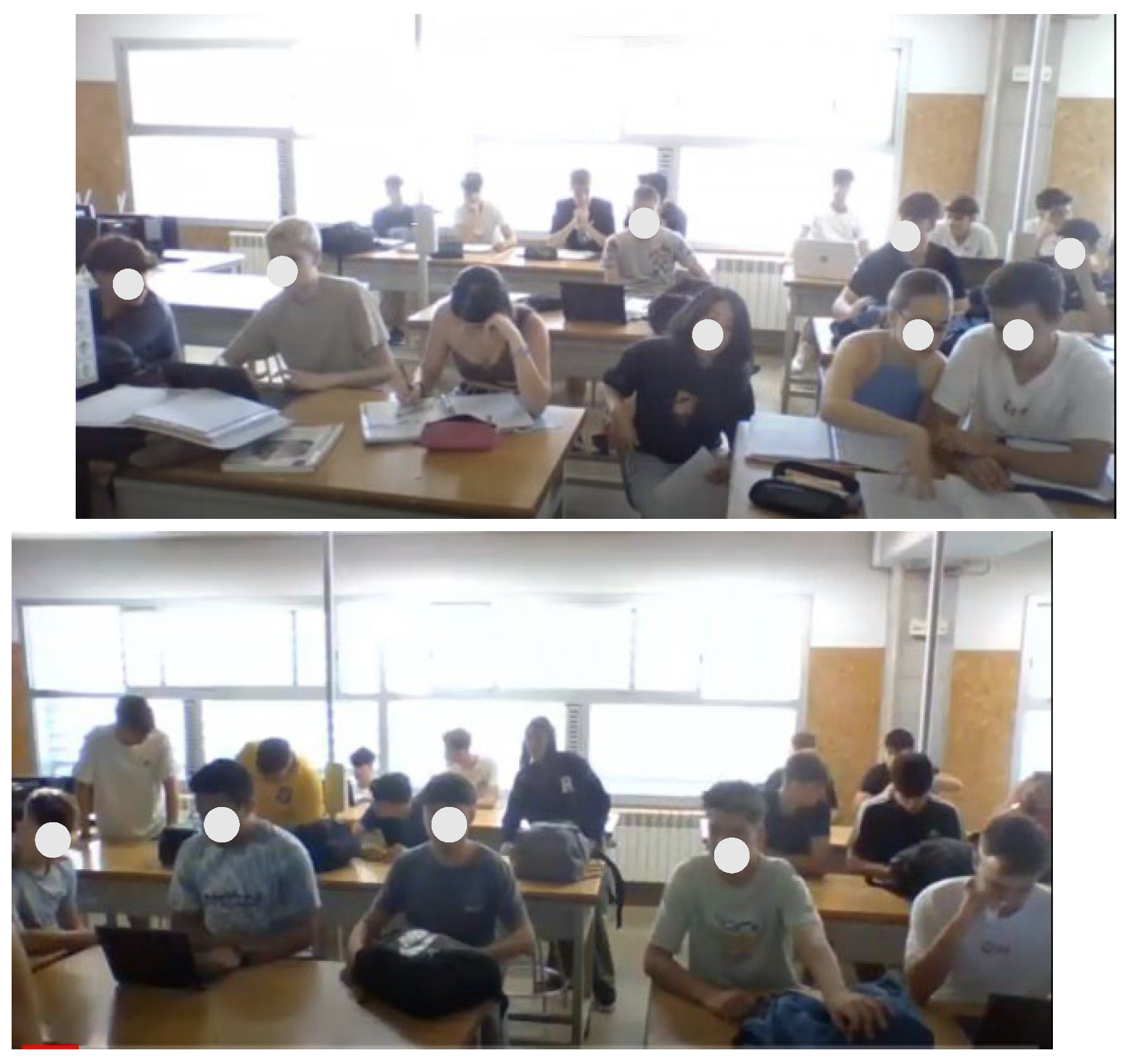
Figure 2.
Students attending in the classroom.
Figure 2.
Students attending in the classroom.
2.1. Materials
Having used a laptop, an Intel Core i5, PC Notebook HP ProBook 640 G2, with Intel Core i-5 6200U @ 2,3 GHz, RAM 8 GB with a webcam.
The laptop was placed in a high place in front of the class, in order to focus on the students’ faces, with the webcam camera facing them.
The experiment contains 47 videos. The dataset has been annotated in a semi-automatic procedure, manual and automatic annotations.
2.2. Experiment Procedure
This section describes our experiment using an improved system configuration and the scenario of more students. Previously, we investigated the effect of the emotions of two students attending class in two different subjects for several hours. It was to accomplish the aim, on developing and applying a code capable of detecting faces, ER and transfer the data into a database for further analysis, which consisted of establishing the first approximations to the relationship between students’ emotions and other conditions such as the subject, time of day and academic performance [
40].
This time the programming environment where the code has been developed and its relationship with the acquisition and processing of images (face detection, identification and ER) has been done thanks to Python. Besides the language itself, Python has a large number of instructions on libraries that can simplify complex tasks by introducing just a few lines of code. In addition, to facilitate programming, a code editor (IDEs) needed to create and execute the code, in this case, using Visual Studio Code.
On the other hand, Py-Feat (Python Facial Expression Analysis Toolbox) from a GitHub portal which has also been used, to promptly process, analyse, and visualize face expression data.
Therefore, during each class, students were recorded by the camera of the laptop for getting data, 50 minutes up to one hour video was recorded in mp4 file of each class, the video took as many students as there were in the field of view of the webcam, then uploaded and stored into the Google drive account. After that, videos were split every 10 seconds in consecutive frames; this was made possible through a code, by converting the images into png files for further data analysis.
A code capable of detecting and identifying faces and analysing facial expressions was developed, so Py-Feat was the chosen tool to obtain the emotions of the attending class’s students. Thereafter, the results were in a csv file with all emotions.
However, prior to the value of the emotions, the code gives the different action units (AUs) of every detected face, which is a quantitative method for describing facial movements. Thus, from the videos, the AUs of each facial part were extracted; intensity added to the code to obtain the value of each emotion and so on the data processing for each AU was performed independently for each face. The extracted AUs were represented as intensity information of continuous values from 0 to 1.
It should be noted that data processing for each ER will be performed as long as the student is in the focus of the webcam and is looking straight ahead or at least the camera detects enough face to extract data to analyse it.
AU detection task utilizes the unit defined by the Facial Action Coding System [
44] to capture and interpret facial muscle movements associated with different expressions [
45]. In this research, we particularly focus on the emotion detection task.
2.3. Computer Code
The code used for the experiment was the windows computer interpreter Command Prompt, that allowed us to convert the recorded videos of 50 to 60 minutes long in images, getting an image every 10 seconds as we ordered, thus achieving an average of 300-360 images per recorded class.
Then, these images with the help of a code editor, the one which is executable on the desktop of the computer, Visual Studio Code, were processed in the same command to be converted into AUs and emotions.
Figure 3.
Sample of the code on Command Prompt.
Figure 3.
Sample of the code on Command Prompt.
Figure 4.
Sample of the code on Visual Studio Code.
Figure 4.
Sample of the code on Visual Studio Code.
As a result, a csv file is given with all the emotions obtained from the students detected in the image.
Table 2.
Example of some of the emotions detected in a class.
Table 2.
Example of some of the emotions detected in a class.
| Anger |
Disgust |
Fear |
Happiness |
Sadness |
Surprise |
Neutral |
| 0.031168593 |
0.0024327133 |
0.13808474 |
0.1220372 |
0.18558967 |
0.08220446 |
0.43848264 |
| 0.002329524 |
0.0001936976 |
0.21880463 |
0.3955652 |
0.06304044 |
0.028335925 |
0.29173055 |
| 0.00045280394 |
0.00054282224 |
0.09731253 |
0.021843903 |
0.2380425 |
0.191383 |
0.4504225 |
| 0.0049407375 |
0.0026621392 |
0.230402 |
0.15494329 |
0.24908207 |
0.13208355 |
0.22588626 |
Before data collection and because this experiment involves contact with humans, and more precisely with minors, ethical approval was requested by the Ethics Committee of the Rovira i Virgili University. They reviewed and approved this experiment with the reference number: CEIPSA-2021-TD-0019. Written informed consent was obtained from all the students in it.
3. Results
We chose to apply nonparametric data analysis techniques because they are useful when data cannot be assumed to follow a specific parametric distribution, such as the normal distribution.
3.1. Analyse the Student’s Emotions Manifestations in the Classroom
The heatmap (
Figure 5) shows the correlations observed between the variables of interest. Pearson correlation coefficients were used to evaluate the strength and direction of the linear relationships between the variables. We found that all emotions correlate with each other, positively or negatively.
We highlight the positive correlations and significantly between the emotions disgust and anger (.447, p<.001) and sadness and fear (.417, p<.001). The negative and significant correlations were between anger and fear (-.321, p<.001) and between anger and sadness (-.291, p<.001).
3.2. Compare the Emotions at the Beginning and at the End of the Class
Comparing the emotions during the first five minutes of class and the last five minutes, using the nonparametric Mann Whitney U test, the results report that there are significant differences in emotions (Table 4).
Table 3.
Statistics of emotions according to the beginning and end of the class.
Table 3.
Statistics of emotions according to the beginning and end of the class.
| Descriptive Statistics |
| |
Anger |
disgust |
fear |
happiness |
sadness |
surprise |
| Mode |
|
0.004 |
ᵃ |
9.359×10-4 |
ᵃ |
0.036 |
ᵃ |
0.023 |
ᵃ |
0.046 |
ᵃ |
0.039 |
|
| Median |
|
0.011 |
|
0.002 |
|
0.120 |
|
0.056 |
|
0.122 |
|
0.160 |
|
| Mean |
|
0.081 |
|
0.012 |
|
0.146 |
|
0.112 |
|
0.163 |
|
0.223 |
|
| Std. D. |
|
0.172 |
|
0.047 |
|
0.122 |
|
0.151 |
|
0.140 |
|
0.211 |
|
| Min. |
|
2.410×10-5 |
|
1.920×10-5 |
|
1.800×10-4 |
|
1.680×10-4 |
|
2.674×10-4 |
|
6.730×10-5 |
|
| Max- |
|
0.995 |
|
0.876 |
|
0.868 |
|
0.942 |
|
0.933 |
|
0.950 |
|
| 25th percentile |
|
0.003 |
|
9.746×10-4 |
|
0.054 |
|
0.025 |
|
0.053 |
|
0.051 |
|
| 50th percentile |
|
0.011 |
|
0.002 |
|
0.120 |
|
0.056 |
|
0.122 |
|
0.160 |
|
| 75th percentile |
|
0.058 |
|
0.006 |
|
0.203 |
|
0.126 |
|
0.237 |
|
0.332 |
|
| |
| ᵃ More than one mode exists. For nominal and ordinal data, the first mode is reported. For continuous data, the mode with the highest density estimated is reported but multiple modes may exist. We recommend visualizing the data to check for multimodality. |
Table 4.
Mann Whitney U test.
Table 4.
Mann Whitney U test.
| Independent Samples T-Test |
|
| |
W |
df |
p |
|
| Anger |
|
1.607×10+6 |
|
|
|
0.002 |
|
| Disgust |
|
1.599×10+6 |
|
|
|
0.004 |
|
| Fear |
|
1.634×10+6 |
|
|
|
< .001 |
|
| Happiness |
|
1.658×10+6 |
|
|
|
< .001 |
|
| Sadness |
|
1.425×10+6 |
|
|
|
0.003 |
|
| Surprise |
|
1.488×10+6 |
|
|
|
0.413 |
|
| Neutral |
|
1.448×10+6 |
|
|
|
0.028 |
|
| |
|
|
Note. Mann-Whitney U test. |
|
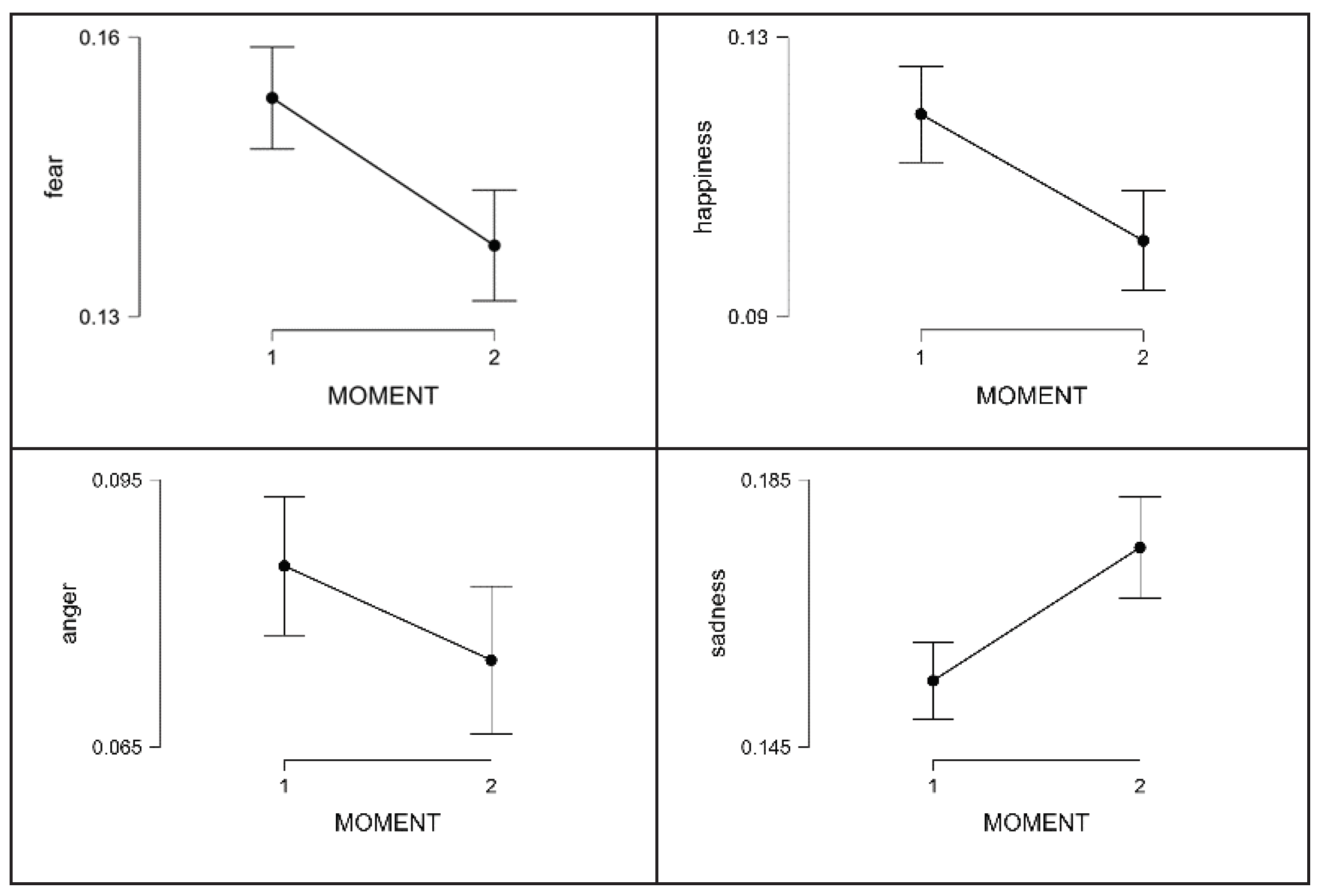
Specifically, the emotion of fear is presented with greater intensity at the beginning (1.634×10+6, p>.001) (
Figure 6). Happiness behaves in the same way, with greater intensity at the beginning than at the end (1.658×10+6, p< .001) and, to a lesser level, the same is true of anger. (.1.607×10+6, p=.002).
On the contrary, sadness is somewhat less intense at the beginning and increases at the end (1.425×10+6, p=.003). Finally, there are emotions, including neutral emotion, for which no significant differences are observed; or in the case of disgust, this has no practical significance when analysing the descriptive information of the variable.
3.1. Relate the Different Emotions According to the Subject and Academic Year
The Kruskal-Wallis analysis indicated statistically significant differences in all emotional responses among courses. Specifically, anger varied significantly between courses (1, 5, 6) (H=215.711, p<.001), as did disgust (H=222.708, p<.001) in courses (5, 6). Fear showed significant differences (H=13.627, p<.001) in courses (1, 5), while happiness (H=556.320, p<.001) and sadness (H=190.068, p<.001) varied in courses (1, 5, 6). Surprise demonstrated significant differences (H=127.004, p< .001) in courses (1, 5).
Table 4.
Kruskal-Wallis results emotions by course.
Table 4.
Kruskal-Wallis results emotions by course.
| Emotion |
Factor |
Statistic |
df |
p |
| Anger |
Course |
215.711 |
2 |
< .001 |
| Disgust |
Course |
222.708 |
2 |
< .001 |
| Fear |
Course |
13.627 |
2 |
< .001 |
| Happiness |
Course |
556.320 |
2 |
< .001 |
| Sadness |
Course |
190.068 |
2 |
< .001 |
| Surprise |
Course |
127.004 |
2 |
< .001 |
Having identified differences among groups through Kruskal-Wallis analysis, subsequent post hoc comparisons were executed employing Dunn’s test with Bonferroni adjustment to evaluate specific variations between pairs of groups. The outcomes were:
− Anger: Differences are observed in all pairs of subjects, with the most pronounced difference (p<.001) between the first year of the bachelor (5) with the lowest presence of anger and the second year (6) with the highest presence of anger.
− Disgust: There are significant differences between the first year of secondary school (1) and first (5) and second year of bachelor (6), both comparisons with a significance of p<.001. The first year of secondary school has the lowest disgust and the second year of bachelor has the highest.
− Happiness: there are significant differences between the first year of secondary school (1) and the first year of bachelor (5) (p<.001), as well as with the second (6) (p<.001). The first year of secondary school showed less happiness than the other two courses.
− Fear: No significant differences are observed between the groups.
− Happiness: Significant differences exist between first year of secondary school (1) and first year of bachelor (5) (p <.001), as well as with second year (6) (p <.001). The first year of bachelor showed lower happiness compared to the other two courses.
− Sadness: There are significant differences between all pairs of courses (p <.001). First year of secondary school (1), which exhibits the highest level of sadness, differs significantly from Year 1 of bachelor (2) and Year 2 (6); to a lesser extent, there is a significant difference between Year 1 and Year 2 in bachelor’s degree, with a higher presence in the last.
− Surprise: Significant differences are observed between the first year of secondary school (1) and first year of bachelor, with a greater emotion of surprise. Similarly, differences exist between Year 1 and Year 2 of bachelor, with the highest surprise in Year 1.
Table 5.
Kruskal-Wallis results of emotions by subjects.
Table 5.
Kruskal-Wallis results of emotions by subjects.
| Emotion |
Factor |
Statistic |
df |
P |
| Anger |
Subject |
1915.681 |
2 |
< .001 |
| Disgust |
Subject |
592.134 |
2 |
< .001 |
| Fear |
Subject |
648.536 |
2 |
< .001 |
| Happiness |
Subject |
449.289 |
2 |
< .001 |
| Sadness |
Subject |
1813.724 |
2 |
< .001 |
| Surprise |
Subject |
18.857 |
2 |
< .001 |
After detecting significant differences between groups using Kruskal-Wallis analysis, post hoc comparisons were carried out using Dunn’s test with Bonferroni adjustment to assess specific differences between pairs of groups. The results highlighted:
− Disgust: differences between the subject pairs Glob and Green (p<.001), Glob and Tech (p<.001), as well as between Green and Tech (p<.001). The highest disgust is in Tech, followed by Glob and finally Green.
− Fear: differences between subject pairs; between Glob and Green (p<.001) and Green and Tech (p<.001). The highest fear was found in Green.
− Happiness: differences between all subject pairs. Between Glob and Green (p<.001), between Glob and Tech (p<.001), and between Green and Tech (p<.001). The highest happiness score appears in Tech.
− Sadness: differences between all subject pairs. Between Glob and Green (p<.001), between Glob and Tech (p<.001), and between Green and Tech (p<.001). The highest sadness score of sadness is in Green.
− Surprise: differences between some subject pairs. Between Glob and Green (p<.001), between Glob and Tech (p<.001), as well as between Green and Tech (p<.001). The highest surprise score is in Tech.
4. Discussion
After this research, it was observed that students experience a lot of emotions throughout a class session [
46]. Emotions significantly influence our cognitive functions [
47], linked to cognitive skills such as attention, working memory, planning, decision making, critical thinking, problem solving and reasoning [
48]. However, we did not find a clear pattern for associating emotions with a subject, yielding results that at first sight may seem contradictory. Likewise, a student might be frustrated with their poor understanding of the subject matter, or it has also been observed that stress, a negative emotional state, facilitates and/or impairs both learning and memory, depending on its intensity and duration.
Concerning learning performance, some positive emotions, such as enjoyment in learning, have been correlated with better performance on placement tests [
49]. In addition, research has shown that emotional-psychological satisfaction is a determinant variable in students’ academic performance. Regarding the presence of emotions according to the different school subjects, in the subject of Technology we observed that there is a higher level of disgust than in the other subjects, as well as positive emotions that would promote learning such as surprise and happiness. Although these results are not conclusive, it is important to highlight that emotions affect learning in Science, depending on the content of the subject. To interpret the result of negative emotions, we have found that in Physics and Chemistry subjects, similar to Technology, students show less interest as they consider it to be a difficult, boring and not very useful subject [
50]. In secondary education, emotions were more positive towards Natural Sciences and more negative towards Physics and Chemistry [
51]. Similarly, [
52] points out that students in compulsory secondary education more frequently experience negative emotions such as boredom, nervousness and worry towards learning Physics and Chemistry. However, it is important to consider that embracing pessimism or seriousness can be beneficial for analytical and quantitative tasks [
27]. In Green project’s subject, which would be more practical and holistic approach than Technology, there is a higher level of fear and sadness, which theoretically would not encourage learning. We would have to understand this result, considering the context as well as external or personal variables, not only the subject. The ability to detect and understand emotions in the classroom context could improve pedagogical practices, especially in subjects such as the ones studied Green project, allowing for a more effective education for sustainability by including topics of sustainability in the classroom.
Related to the classroom moment, the emotion of fear is more present at the beginning of the class sessions than at the end. This can be attributed to the process of adaptation of the students to their school environment and the initial lack of knowledge of what to expect from the class and the teacher. The same is true for happiness, which is more present at the beginning of the class sessions than at the end. This may be due to the excitement to join with peers and the positive expectation of learning new things but may diminish as the demands of academic tasks progress.
Regarding the relationship between emotions and academic years, there is no clear pattern and positive and negative emotions coexist in the different years. In the first year we found more anger and sadness, but more joy, in bachelor disgust and surprise. We think that perhaps the emotions are more strongly linked to the subject than to the year. Nevertheless, school and classroom climate are important factors influencing achievement emotions, as [
53] said, indeed, it can be assumed that classmates play an important role in students’ (achievement) emotions. Similarly, it can be expected that students’ valuation of subjects is influenced by parents who value that subject highly, those who like a particular subject, and teachers who teach these subjects with enthusiasm. The results are sample specific but show individual differences in emotional experiences in teaching and subjects. Therefore, more elaborate research is needed.
Regarding the relationship of the study with sustainability, the study maintains a connection to goals 3 and 4 of the Sustainable Development Goals, precisely because it is an interdisciplinary field. With Health and Well-being Goal 3, comprises ensuring healthy lives and promoting wellness for all at all ages. The tools we developed and applied have the potential to be used for the prevention of mental health problems, as they allow for the early identification of negative and positive emotions. Our research also contributes to the promotion of a healthy school environment by considering students’ emotions.
With Quality Education Goal 4, ensure inclusive, equitable and quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all. Understanding emotions can make it easier to support the participation of all students, which is essential to ensuring that everyone has equal opportunities to engage in and contribute to learning.
The implications of the study are several and could affect various stakeholders in the educational community: students, teachers, administrators, families, and mental health professionals. It could provide a deeper understanding of how emotions affect the learning experience of students in different subjects. This could help educators adapt their teaching methods to address students’ emotional needs. The study could help identify factors in each subject or moment that relate to certain emotions. This could lead to implementing strategies to mitigate emotions considered negative and encourage positive ones. Implications from the study could affect how the classroom’s emotional climate is assessed. Finally, from an educational technology point of view, the study could have implications for developing future monitoring tools to be integrated into the classroom, such as being applied with precision in other secondary schools, due to this system is based on a simple and successfully tested code.
Regarding the limitations of the study, we found several of them. First, the precision of the monitoring of emotions through the camera may be affected by environmental conditions such as lighting and camera quality, as well as by the movement and displacement of the students themselves.
Emotions, a complex phenomenon, can be produced not only by the classroom context but also by subject content or by prior, external, or personal factors. Related to this, emotional responses to an academic situation differ for each individual. However, here we have tried to find general tendencies.
Finally, the algorithm categorizes emotions but does not assign them to a specific individual. While this allows for student privacy, it prevents individual monitoring.
5. Conclusions
Considering the three aims of the study, analyse the student’s emotions manifestations in the classroom, compare the emotions at the beginning and at the end of the class and relate the different emotions according to the subject and academic year, we found that we were able to achieve all three. However, we have not obtained conclusive results for the second and third objectives because some results seem inconclusive or contradictory, perhaps evidencing the complexity of the emotional phenomenon and/or perhaps because more data is needed to analyse and find patterns that more clearly link emotions with the moments of the class, academic years, and the subjects.
From a technological point of view, the study is a very positive contribution because we developed and applied an innovative code system to detect students’ emotions during class session. The system uses a vision-based model, with a webcam that records the class period and then with the developed code detects and analyses the facial expressions, categorizing them into one of six basic emotions or neutral emotion. The developed emotional expression recognition software is accurate enough to identify the emotions of the learners; it is only possible to obtain suitable images of the participants in close-up, looking fully or partially at the camera.
Future research has promising scope to focus on specific aspects that seek to improve the integration and effectiveness of emotion monitoring in the classroom, considering ethics. A line could develop an interactive tools for teachers, such investigating how to design interfaces and tools that enable teachers to interpret and use emotional information effectively in the classroom, with the aim of improving student well-being and performance, or developing systems that provide specific suggestions (change of methodology, personalised attention) to address identified emotional needs.
Emotion monitoring is part of a holistic approach to education that considers academic development, but also the well-being of students and their readiness to contribute to a more sustainable society, while empowering the students themselves.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “Conceptualization, Palau, R.; methodology, Fretes, G.; software, Llurba. C.; validation, Llurba, C. and Fretes; formal analysis, Fretes, G.; investigation, Llurba. C. and Fretes, G.; resources, Llurba, C.; data curation, Fretes, G.; writing—original draft preparation, Llurba, C. and Fretes, G.; writing—review and editing, Palau, R.; visualization, Llurba. C. and Fretes, G.; supervision, Palau, R.; project administration, Palau, R.; funding acquisition, Y.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.” Please turn to the CRediT taxonomy for the term explanation. Authorship must be limited to those who have contributed substantially to the work reported.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
In this section, you should add the Institutional Review Board Statement and approval number, if relevant to your study. You might choose to exclude this statement if the study did not require ethical approval. Please note that the Editorial Office might ask you for further information. Please add “The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of NAME OF INSTITUTE (protocol code XXX and date of approval).” for studies involving humans. OR “The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of NAME OF INSTITUTE (protocol code XXX and date of approval).” for studies involving animals. OR “Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to REASON (please provide a detailed justification).” OR “Not applicable” for studies not involving humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent for publication must be obtained from participating patients who can be identified (including by the patients themselves). Please state “Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper” if applicable.
Data Availability Statement
We encourage all authors of articles published in MDPI journals to share their research data. In this section, please provide details regarding where data supporting reported results can be found, including links to publicly archived datasets analyzed or generated during the study. Where no new data were created, or where data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions, a statement is still required. Suggested Data Availability Statements are available in section “MDPI Research Data Policies” at
https://www.mdpi.com/ethics.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledge to NAIST (Nara Advance Institute of Science and Technology), specifically to Hiroki Tanaka, Kana Myamoto, Kazuhiro Shidara, Takeshi Saga and Satoshi Nakamura.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Darwin, C.R. The expression of the emotions in man and animals. London John Murray. 1st edition 1872.
- James, W. The principles of Psychology 1890, Volume II.
- Lange, C. The emotions. Baltimore, MD, 1885 William and Wilkins.
- Freud, S. A Project for a Scientific Psychology. London: Hogarth. 1895. (Standard Edition, Vol. 1, pp. 283-397).
- Lazarus, R. S. Thoughts on the relations between emotion and cognition 1982.
- Fuchs, T. Depression, intercorporeality, and interaffectivity. Journal of Consciousness Studies 2013. 20(7-8), 219–238.
- Ekman P., and Friesen, W.V. Facial action coding system. Environmental Psychology & Nonverbal Behavior 1978.
- Taype-Huarca, L.A., Zavalaga-del Carpio, A.L., Fernández-González, S.V. Usefulness of the Perezhivanie Construct in Affectivity and Learning: A Systematic Review. In Affectivity and Learning: Bridging the Gap Between Neurosciences, Cultural and Cognitive Psychology 2023.
- Goleman, D. Emotional intelligence. Bantam Books, Inc. 1995.
- Damasio, A. Descartes Error: Emotion, Reason, and the Human Brain. New York: Avon Books, 1994.
- Cristóvão, A.M., Valente, S., Rebelo, H., Ruivo, A.F. Front. Educ. 2023. 8 (June). Emotional education for sustainable development: A curriculum analysis of teacher training in Portugal and Spain. [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Educación para el Desarrollo Sostenible: Hojas de ruta. Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Educación, la Ciencia y la Cultura, Francia, 2020.
- Bower, G. H., & Forgas, J. P. Mood and social memory. In J. P. Forgas (Ed.), Handbook of affect and social cognition Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers. 2001 (pp. 95–120).
- Minsky, M. The Emotion Machine: Commonsense Thinking, Artificial Intelligence, and the Future of the Human Mind. Simon & Schuster 2007.
- Pekrun, R. The Control-Value Theory of Achievement Emotions: Assumptions, Corollaries, and Implications for Educational Research and Practice. Educ Psychol Rev 2006, 18, 315–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnenbrink-Garcia, L., Patall, E. A., & Pekrun, R. Adaptive Motivation and Emotion in Education: Research and Principles for Instructional Design. Policy Insights from the Behavioral and Brain Sciences 2016. 3(2), 228-236. [CrossRef]
- Stoeber, J. & Pekrun, R. Advances in test anxiety research. Anxiety Stress & Coping 2004. 17. 205-211. [CrossRef]
- Davidson RJ, Jackson DC, Kalin NH. Emotion, plasticity, context, and regulation: Perspectives from affective neuroscience. Psychol Bull. 2000 Nov;126(6):890-909. [CrossRef]
- Rothbart, M.K. and Bates, J.E. Temperament. In: Eisenberg, N., Damon, W. and Lerner, R.M., Eds., Handbook of Child Psychology, 6th Edition, Social, Emotional, and Personality Development, Wiley, New York, 2006. 99-166. [CrossRef]
- Fredrickson, B.L. What good are positive emotions? Review of General Psychology 1998, 2(3), 300–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredrickson, B.L. The role of positive emotions in positive psychology. The broaden-and-build theory of positive emotions. American Psychologist 2001. 56, 218-226. [CrossRef]
- Blair, C. School readiness: Integrating cognition and emotion in a neurobiological conceptualization of children’s functioning at school entry. American Psychologist 2002, 57(2), 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carver, C. S.; Carver, C. S., & Scheier, M. F. Origins and functions of positive and negative affect: A control-process view. Psychological Review 1990. 97(1), 19–35. [CrossRef]
- Goetz, T. Goetz, T., Pekrun, R., Hall, N., & Haag, L. Academic emotions from a social-cognitive perspective: Antecedents and domain specificity of students’ affect in the context of Latin instruction. British Journal of Educational Psychology 2006. 76(2), 289-308.
- Ahmed, W., van der Werf, G., Minnaert, A. Emotions, Self-Regulated Learning, and Achievement in Mathematics: A Growth Curve Analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology 2013, 105 (1), 150–161. [CrossRef]
- Efklides, A. Interactions of metacognition with motivation and affect in self-regulated learning: The MASRL model. Educational Psychologist 2011, 46(1), 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clore, G. L., Schiller, A. J., & Shaked, A. Affect and cognition: Three principles. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences 2018. 19, 78–82. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T., Lu, Y., Wang, B. Integrating TTF and UTAUT to explain mobile banking user adoption, Computers in Human Behavior 2010. 26 (4), pp 760-767. [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, Y. L2 selves, emotions, and motivated behaviors. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 2017, 39(4), 681–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormrod, J., Anderman, E., & Anderman, L. Educational psychology: Developing learners (10th ed.). Pearson Education. 2019.
- Saeidi, M., & Jabbarpour, N.. EFL Teachers Socio-Affective Strategy use in relation to students’ academic achievement. International Journal of Academic Research 2011. 3(3), 476-750.
- Fried, L. Teaching Teachers about Emotion Regulation in the Classroom. Australian Journal of Teacher Education 2011. 36(3). [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M., Lang, P. Measuring emotion: The self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential, Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry 1994. 25 (1), pp 49-59. [CrossRef]
- Harmon-Jones, C., Bastian, B., Harmon-Jones, E. The Discrete Emotions Questionnaire: A New Tool for Measuring State Self-Reported Emotions. PLoS ONE 2016. 11(8). [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, J.; Yue, T.; You, F. SAET: The Non-Verbal Measurement Tool in User Emotional Experience. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-M.; Hong, E.J.; Chung, K.; Park, R.C. Driver Facial Expression Analysis Using LFA-CRNN-Based Feature Extraction for Health-Risk Decisions. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landowska, A. Emotion Monitoring – Verification of Physiological Characteristics Measurement Procedures. Metrology and Measurement Systems 2014, 21(4), 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer AM, Zander TO, Van Erp JB, Korteling JE, Bronkhorst AW. Using neurophysiological signals that reflect cognitive or affective state: Six recommendations to avoid common pitfalls. Front Neurosci. 2015 30;9:136. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Li H, Ma L, Soong F. DEEMD-SPP: A Novel Framework for Emotion Recognition Based on EEG Signals. Front Psychiatry 2022. 13:885120. [CrossRef]
- Llurba, C., Fretes, G., Palau, R. Pilot study of real-time Emotional Recognition technology for Secondary school students. Interaction Design and Architecture 2022. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y., Li, Y., Yang, Y., & Zhai, X. Intelligent technology drives higher education reform: Key points and reflections on the 2023 Horizon report: Teaching and learning edition. Open Education Research 2023. 29(3), 19–30.
- Rößler, J.; Sun, J.; Gloor, P. Reducing Videoconferencing Fatigue through Facial Emotion Recognition. Future Internet 2021, 13, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumhuber, E. , Skora, L., Hill, H., Lander, K. The role of facial movements in emotion recognition. Nature Reviews Psychology. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P., & Friesen, W. V. Facial Action Coding System (FACS) [Database record]. APA PsycTests. 1978. [CrossRef]
- Vu, Tu & Huỳnh, V. T. & Kim, Soo. Vision Transformer for Action Units Detection. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Pekrun, R., & Stephens, E. J. Academic emotions. In K. R. Harris, S. Graham, T. Urdan, S. Graham, J. M. Royer, & M. Zeidner (Eds.). APA educational psychology handbook. Individual differences and cultural and contextual factors. American Psychological Association 2012. Vol. 2 (pp. 3–31). [CrossRef]
- Tyng, C. M., Amin, H. U., Saad, M. N. M., & Malik, A. S. The influences of emotion on learning and memory. Frontiers in Psychology 2017. 8, Article 1454. [CrossRef]
- Cristofori, I., Cohen-Zimerman, S., & Grafman, J. Executive Functions. In M. D’Esposito, & J. Grafman (Eds.). The Frontal Lobes. Handbook of Clinical Neurology Elsevier 2019. Volume 163, pp.197-219. [CrossRef]
- De la Fuente, J., Sander, P., Cardelle-Elawar, M., and Pignata, S. Effects of level of regulatory teaching on achievement emotion in the learning process: Anxiety and achievement emotions on higher education, in Teaching and Learning, ed. M. Vargas (New York, NY: Nova Science Publishers, Inc). 2016. 131–151.
- Solbes, J. Revisiting the teachers’ lounge: Reflections on emotional experience and teacher identify. Teaching and Teacher Education 2011, 26(3), 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brígido, M., Couso, D., Gutiérrez, C. y Mellado, V. The Emotions about Teaching and Learning Science: A Study of Prospective Primary Teachers in Three Spanish Universities. Journal of Baltic Science Education 2013. 12(3), 299-311. [CrossRef]
- Dávila, M.A. Las emociones y sus causas en el aprendizaje de Física y Química, en el alumnado de Educación Secundaria. Revista Eureka sobre enseñanza y divulgación de las ciencias 2017. 14(3), 570-586. /: 570-586. http, 1049.
- Gläser-Zikuda, M., Stuchlíková, I., Janík T. Theoretical and research papers. Emotional Aspects of Learning and Teaching: Reviewing the Field − Discussing the Issues. Orbis Scholae 2013. 7 (2) 7−22. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).