Submitted:
17 January 2024
Posted:
17 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Background
Computational Modeling to Study Field Shaping
Field Shaping by Modifying Electrode Properties
Conclusion
References
- N. M. Malešević et al., ‘A multi-pad electrode based functional electrical stimulation system for restoration of grasp’, J Neuroeng Rehabil, vol. 9, no. 1, p. 66, 2012. [CrossRef]
- A.D. Koutsou, J. C. Moreno, A. J. del Ama, E. Rocon, and J. L. Pons, ‘Advances in selective activation of muscles for non-invasive motor neuroprostheses’, J Neuroeng Rehabil, vol. 13, no. 1, p. 56, 2016. [CrossRef]
- D. A. Friedenberg et al., ‘Neuroprosthetic-enabled control of graded arm muscle contraction in a paralyzed human’, Sci Rep, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 1–10, 2017. [CrossRef]
- H. Usman, Y. Zhou, B. Metcalfe, and D. Zhang, ‘A Functional Electrical Stimulation System of High-Density Electrodes with Auto-Calibration for Optimal Selectivity’, IEEE Sens J, vol. 1748, no. c, pp. 1–1, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Crema, N. Malešević, I. Furfaro, F. Raschellà, A. Pedrocchi, and S. Micera, ‘A Wearable Multi-Site System for NMES-Based Hand Function Restoration’, IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 428–440, 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. Ravichandran, M. Y. Teo, A. Mcdaid, and K. Aw, ‘Conformable Electrode Arrays for Wearable Neuroprostheses’, Sensors, vol. 23, no. 6, p. 2982, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- N. RaviChandran, K. C. Aw, and A. McDaid, ‘Characterizing the Motor Points of Forearm Muscles for Dexterous Neuroprostheses’, IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, vol. 67, no. 1, pp. 50–59, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhou et al., ‘Stimulating the Comfort of Textile Electrodes in Wearable Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation’, Sensors, vol. 15, no. 7, pp. 17241–17257, Jul. 2015. [CrossRef]
- T. Keller and A. Kuhn, ‘Electrodes for transcutaneous (surface) electrical stimulation’, Journal of Automatic Control, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 35–45, 2008. [CrossRef]
- C. R. Butson and C. C. McIntyre, ‘Current steering to control the volume of tissue activated during deep brain stimulation’, Brain Stimul, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 7–15, Jan. 2008. [CrossRef]
- J. S. Brittain and H. Cagnan, ‘Recent Trends in the Use of Electrical Neuromodulation in Parkinson’s Disease’, Current Behavioral Neuroscience Reports, vol. 5, no. 2. Springer, pp. 170–178, Jun. 01, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Parazzini et al., ‘A computational model of the electric field distribution due to regional personalized or nonpersonalized electrodes to select transcranial electric stimulation target’, IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, vol. 64, no. 1, pp. 184–195, Jan. 2017. [CrossRef]
- L. Manola, J. Holsheimer, P. H. Veltink, K. Bradley, and D. Peterson, ‘Theoretical Investigation Into Longitudinal Cathodal Field Steering in Spinal Cord Stimulation’, Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 120–132, Apr. 2007. [CrossRef]
- L. N. Mishra, G. Kulkarni, and M. Gadgil, ‘A novel current steering method for targeted spinal cord stimulation’, Frontiers in Pain Research, vol. 4, p. 1028368, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Guidetti et al., ‘Modeling Electric Fields in Transcutaneous Spinal Direct Current Stimulation: A Clinical Perspective’, Biomedicines, vol. 11, no. 5. MDPI, May 01, 2023. [CrossRef]
- ‘Electric Field Shaping Via Separatrices For Focused Electric Retinal Stimulation Via Retinal Implants’.
- Z. Lu et al., ‘An in-silico analysis of retinal electric field distribution induced by different electrode design of trans-corneal electrical stimulation’, J Neural Eng, vol. 19, no. 5, p. 055004, Oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. H. Bonham and L. M. Litvak, ‘Current focusing and steering: Modeling, physiology, and psychophysics’, Hear Res, vol. 242, no. 1–2, p. 141, Aug. 2008. [CrossRef]
- C.-C. Wu and X. Luo, ‘Current Steering with Partial Tripolar Stimulation Mode in Cochlear Implants’, Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 213–231, Apr. 2013. [CrossRef]
- J. D. Falcone and P. T. Bhatti, ‘Current steering and current focusing with a high-density intracochlear electrode array’, in 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, IEEE, Aug. 2011, pp. 1049–1052. [CrossRef]
- C. D. Mørch, K. Hennings, and O. K. Andersen, ‘Estimating nerve excitation thresholds to cutaneous electrical stimulation by finite element modeling combined with a stochastic branching nerve fiber model’, Med Biol Eng Comput, vol. 49, no. 4, pp. 385–395, Apr. 2011. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Gaines, K. E. Finn, J. P. Slopsema, L. A. Heyboer, and K. H. Polasek, ‘A model of motor and sensory axon activation in the median nerve using surface electrical stimulation’, J Comput Neurosci, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 29–43, Aug. 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Agotici, K. Masani, and P. B. Yoo, ‘Computational Study on Spatially Distributed Sequential Stimulation for Fatigue Resistant Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation’, IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 29, pp. 2578–2586, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Kuhn, T. Keller, S. Micera, and M. Morari, ‘Array electrode design for transcutaneous electrical stimulation: A simulation study’, Med Eng Phys, vol. 31, no. 8, pp. 945–951, 2009. [CrossRef]
- N. RaviChandran, M. Y. Teo, K. Aw, and A. McDaid, ‘Design of Transcutaneous Stimulation Electrodes for Wearable Neuroprostheses’, IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 28, no. 7, pp. 1651–1660, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- N. Ravichandran, J. Hope, K. Aw, and A. Mcdaid, ‘Modeling the excitation of nerve axons under transcutaneous stimulation’, Comput Biol Med, vol. 165, p. 107463, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- C. R. Butson, S. E. Cooper, J. M. Henderson, and C. C. Mcintyre, ‘Patient-Specific Analysis of the Volume of Tissue Activated During Deep Brain Stimulation’. [CrossRef]
- K. Gunalan, B. Howell, and C. C. McIntyre, ‘Quantifying axonal responses in patient-specific models of subthalamic deep brain stimulation’, Neuroimage, vol. 172, no. January, pp. 263–277, 2018. [CrossRef]
- G. Duffley, D. N. Anderson, J. Vorwerk, A. D. Dorval, and C. R. Butson, ‘Evaluation of methodologies for computing the deep brain stimulation volume of tissue activated’, J Neural Eng, vol. 16, no. 6, Oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- N. Ravichandran, M. Y. Teo, K. Aw, and A. McDaid, ‘Design of Transcutaneous Stimulation Electrodes for Wearable Neuroprostheses’, IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 28, no. 7, pp. 1651–1660, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. C. Wu and X. Luo, ‘Current steering with partial tripolar stimulation mode in cochlear implants’, JARO - Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 213–231, Apr. 2013. [CrossRef]
- B. H. Bonham and L. M. Litvak, ‘Current focusing and steering: Modeling, physiology, and psychophysics’, Hear Res, vol. 242, no. 1–2, pp. 141–153, Aug. 2008. [CrossRef]
- V. Valente, A. Demosthenous, and R. Bayford, ‘A tripolar current-steering stimulator ASIC for field shaping in deep brain stimulation’, IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 197–207, 2012. [CrossRef]
- J. Krishnan, R. Joseph, M. C. Vayalappil, S. Krishnan, and A. Kishore, ‘A Review on Implantable Neuroelectrodes’, Crit Rev Biomed Eng, vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 21–39, 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. Flodin, R. Juthberg, and P. W. Ackermann, ‘Effects of electrode size and placement on comfort and efficiency during low-intensity neuromuscular electrical stimulation of quadriceps, hamstrings and gluteal muscles’, BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil, vol. 14, no. 1, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. D. Gomez-Tames, J. Gonzalez, and W. Yu, ‘A simulation study: Effect of the inter-electrode distance, electrode size and shape in Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation’, in Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, 2012, pp. 3576–3579. [CrossRef]
- A. Kuhn, T. Keller, M. Lawrence, and M. Morari, ‘The influence of electrode size on selectivity and comfort in transcutaneous electrical stimulation of the forearm’, IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 255–262, 2010. [CrossRef]
- A. Kuhn, T. Keller, M. Lawrence, and M. Morari, ‘The Influence of Electrode Size on Selectivity and Comfort in Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation of the Forearm’, IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 255–262, Jun. 2010. [CrossRef]
- N. RaviChandran, K. C. Aw, and A. McDaid, ‘Influence of Electrode Geometry on Selectivity and Comfort for Functional Electrical Stimulation’, in The International Functional Electrical Stimulation Society (IFESS), RehabWeek, Toronto, Canada: IFESS, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Datta, V. Bansal, J. Diaz, J. Patel, D. Reato, and M. Bikson, ‘Gyri-precise head model of transcranial direct current stimulation: Improved spatial focality using a ring electrode versus conventional rectangular pad’, Brain Stimul, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 201-207.e1, Oct. 2009. [CrossRef]
- M. Bortoletto, C. Rodella, R. Salvador, P. C. Miranda, and C. Miniussi, ‘Reduced Current Spread by Concentric Electrodes in Transcranial Electrical Stimulation (tES)’, Brain Stimul, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 525–528, 2016. [CrossRef]
- V. T. Krasteva and S. P. Papazov, ‘Estimation of current density distribution under electrodes for external defibrillation.’, Biomed Eng Online, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 7, Dec. 2002. [CrossRef]
- A. M. Sagi-Dolev, D. Prutchi, and R. H. Nathan, ‘Three-dimensional current density distribution under surface stimulation electrodes’, Med Biol Eng Comput, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 403–408, 1995. [CrossRef]
- A. Patriciu, K. Yoshida, J. J. Struijk, T. P. DeMonte, M. L. G. Joy, and H. Stodkilde-Jorgensen, ‘Current Density Imaging and Electrically Induced Skin Burns Under Surface Electrodes’, IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, vol. 52, no. 12, pp. 2024–2031, Dec. 2005. [CrossRef]
- C. Alon, G. Kantor, and H. S. Ho, ‘Effects of Electrode Size on Basic Excitatory Responses and on Selected Stimulus Parameters’, Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 29–35, Jul. 1994. [CrossRef]
- S. Papazov, K. Brandiski, and I. Daskalov, ‘Optimization of the defibrillation current density in the heart region by a two-layer segmented electrode’, J Med Eng Technol, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 28–33, 2001. [CrossRef]
- P. F. Meyer, P. D. Gadsby, D. Van Sickle, W. E. Schoenlein, K. S. Foster, and G. P. Graber, ‘Impedance-gradient electrode reduces skin irritation induced by transthoracic defibrillation’, Med Biol Eng Comput, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 225–229, 2005. [CrossRef]
- N. Sha, L. P. J. Kenney, B. W. Heller, A. T. Barker, D. Howard, and W. Wang, ‘The effect of the impedance of a thin hydrogel electrode on sensation during functional electrical stimulation’, Med Eng Phys, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 739–746, 2008. [CrossRef]
- A. Kuhn, T. Keller, S. Micera, and M. Morari, ‘Array electrode design for transcutaneous electrical stimulation: A simulation study’, Med Eng Phys, vol. 31, no. 8, pp. 945–951, Oct. 2009. [CrossRef]
- G. Cooper, A. T. Barker, B. W. Heller, T. Good, L. P. J. Kenney, and D. Howard, ‘The use of hydrogel as an electrode-skin interface for electrode array FES applications’, Med Eng Phys, vol. 33, no. 8, pp. 967–972, Oct. 2011. [CrossRef]
- E. McAdams, ‘Biomedical Electrodes For Biopotential Monitoring and Electrostimulation’, in Bio-Medical CMOS ICs, H.-J. Yoo and C. van Hoof, Eds., in Integrated Circuits and Systems. , Boston, MA: Springer US, 2011, pp. 31–124. [CrossRef]
- G. Cooper, A. T. Barker, B. W. Heller, T. Good, L. P. J. Kenney, and D. Howard, ‘The use of hydrogel as an electrode-skin interface for electrode array FES applications’, Med Eng Phys, vol. 33, no. 8, pp. 967–972, 2011. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhou et al., ‘Stimulating the comfort of textile electrodes in wearable neuromuscular electrical stimulation’, Sensors (Switzerland), vol. 15, no. 7, pp. 17241–17257, Jul. 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. Gómez-Tames, J. González, and W. Yu, ‘Influence of different geometric representations of the volume conductor on nerve activation during electrical stimulation’, Comput Math Methods Med, vol. 2014, 2014. [CrossRef]
- J. H. K. Kim, M. L. Trew, A. J. Pullan, and O. Röhrle, ‘Simulating a dual-array electrode configuration to investigate the influence of skeletal muscle fatigue following functional electrical stimulation’, Comput Biol Med, vol. 42, no. 9, pp. 915–924, 2012. [CrossRef]
- C. D. Solomons, M. Slovak, B. Heller, and A. T. Barker, ‘Reducing the sensation of electrical stimulation with dry electrodes by using an array of constant current sources’, Med Eng Phys, vol. 51, pp. 91–95, 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. M. Malešević, L. Z. Popović, L. Schwirtlich, and D. B. Popović, ‘Distributed low-frequency functional electrical stimulation delays muscle fatigue compared to conventional stimulation’, Muscle Nerve, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 556–562, Oct. 2010. [CrossRef]
- N. RaviChandran, K. Aw, and A. McDaid, ‘Electrophysiologically-identified motor points of forearm muscles’, IEEE Dataport, 2019. [CrossRef]
- N. RaviChandran, K. Aw, and A. McDaid, ‘Automatic calibration of electrode arrays for dexterous neuroprostheses: a review’, Biomed Phys Eng Express, vol. 9, no. 5, p. 052001, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. David Gomez Tames, J. Gonzalez, and W. Yu, A Simulation Study: Effect of the Inter-Electrode Distance, Electrode Size and Shape in Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation. 2012. [CrossRef]
- E. P. Doheny, B. M. Caulfield, C. M. Minogue, and M. M. Lowery, ‘Effect of subcutaneous fat thickness and surface electrode configuration during neuromuscular electrical stimulation’, Med Eng Phys, vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 468–474, Jun. 2010. [CrossRef]
- L. Parisi and N. RaviChandran, ‘Evolutionary Denoising-Based Machine Learning for Detecting Knee Disorders’, Neural Process Lett, vol. 52, no. 3, pp. 2565–2581, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Parisi, N. RaviChandran, and M. Lanzillotta, ‘Artificial Intelligence for Clinical Gait Diagnostics of Knee Osteoarthritis: An Evidence - based Review and Analysis’, TechRxiv. Accessed: Apr. 16, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.techrxiv.org/doi/full/10.36227/techrxiv.11786511.v1. [CrossRef]
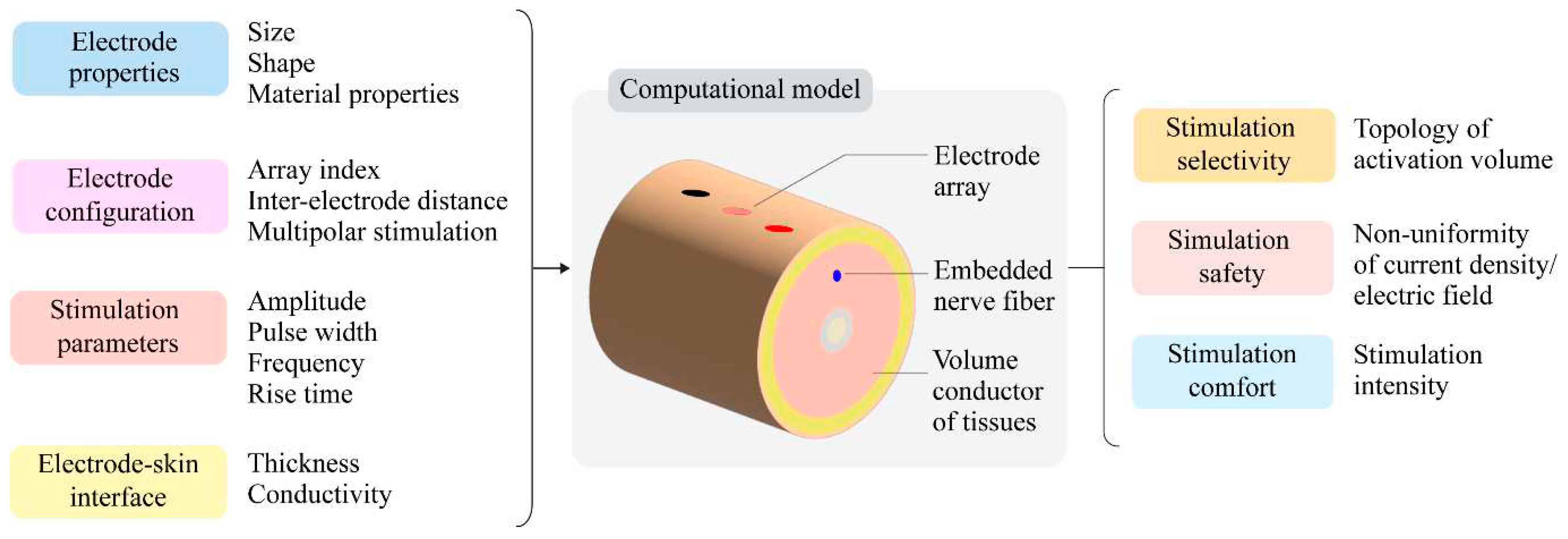
| Selectivity of stimulation | Activation volume¥ | Surface area Surface eccentricity Depth Volume Surface-to-volume ratio |
| Safety of stimulation | Non-uniformity coefficient |
Non-uniformity of current density Non-uniformity of electric field |
| Stimulation intensity | Stimulation amplitude | |
| Stimulation comfort | Stimulation intensity | Sensory threshold |
| Stimulation amplitude |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





