Submitted:
16 January 2024
Posted:
16 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
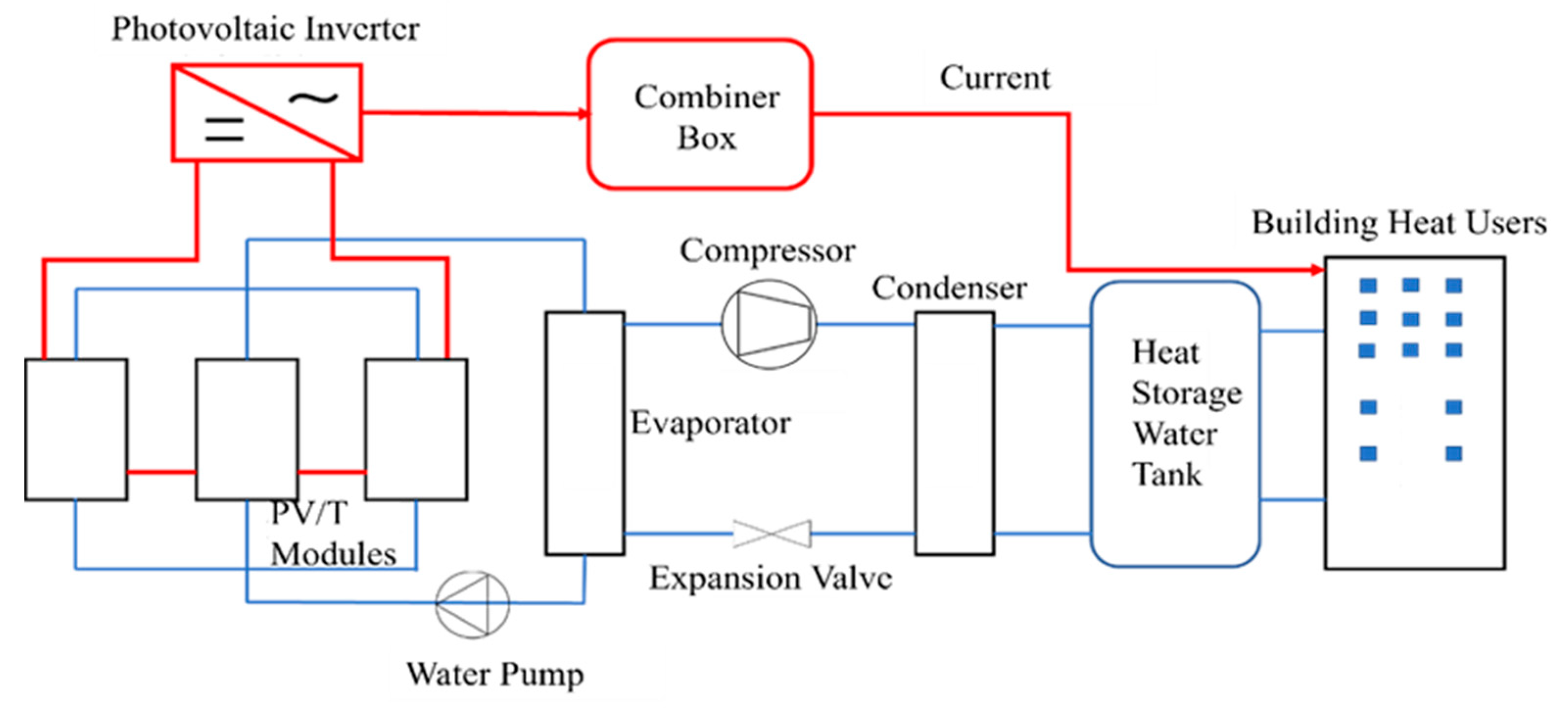
2. Establishment of Mathematical Model for PV/T Module
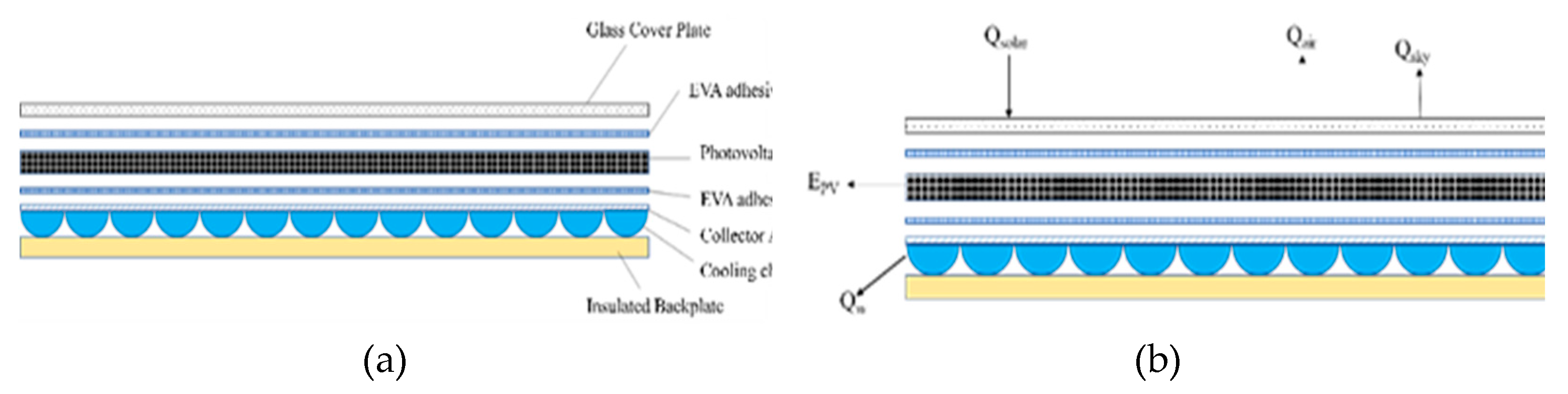
2.1. Mathematical Modeling of PV/T Module
2.2. Optoelectronic Effect Model
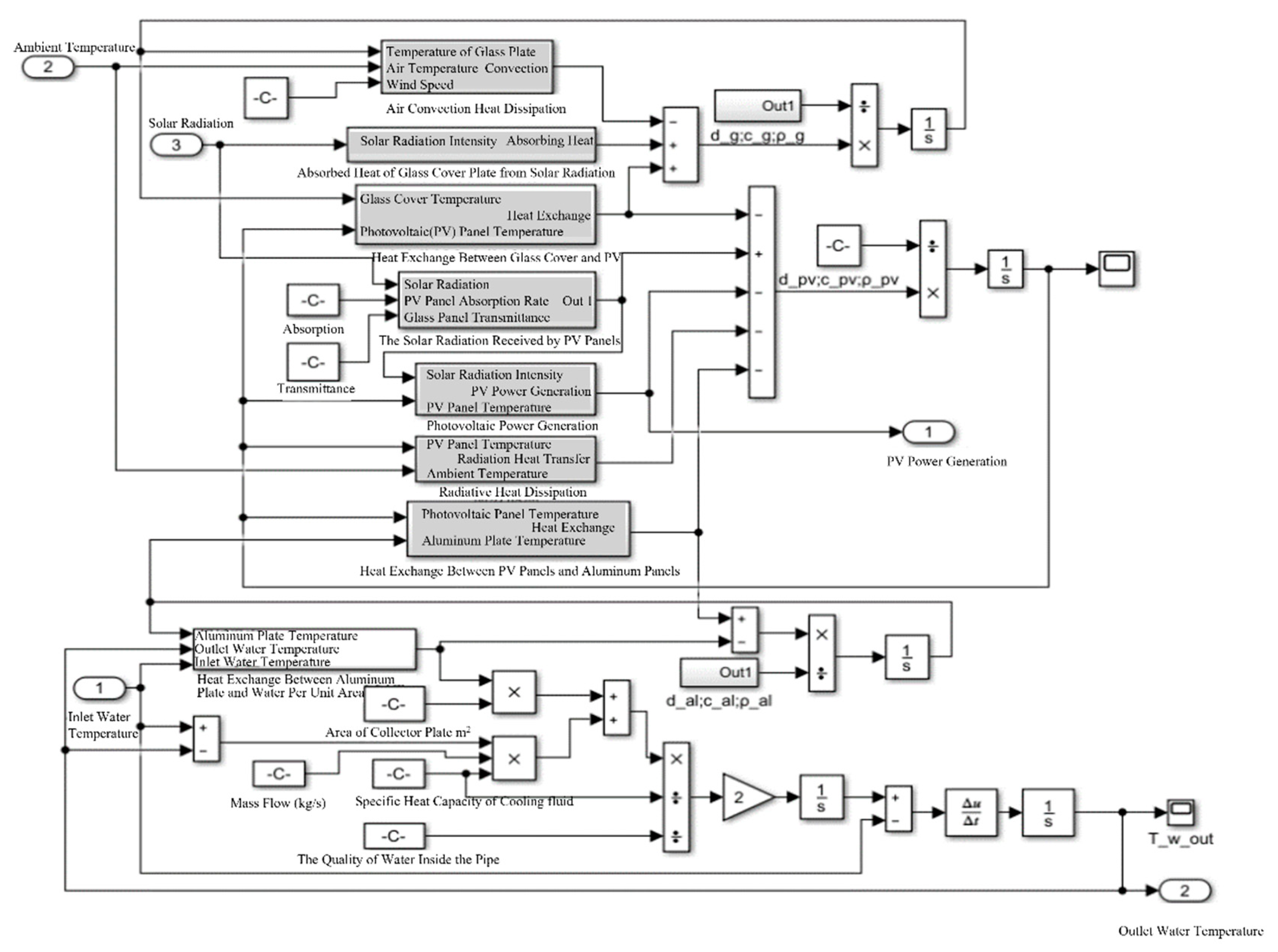
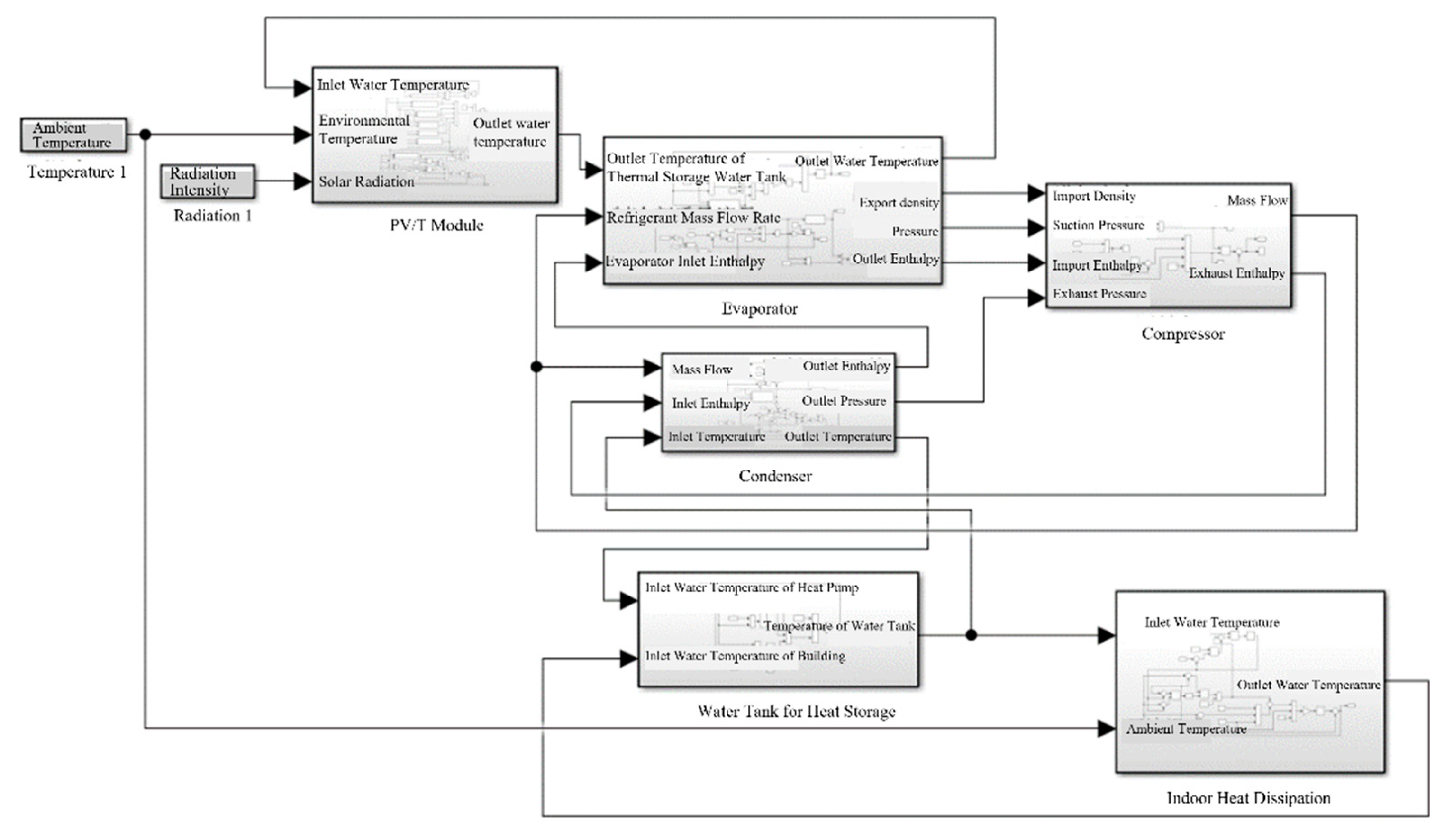
3. Dynamic Simulation Model of PV/T Modules
4. Analysis of Simulation Results
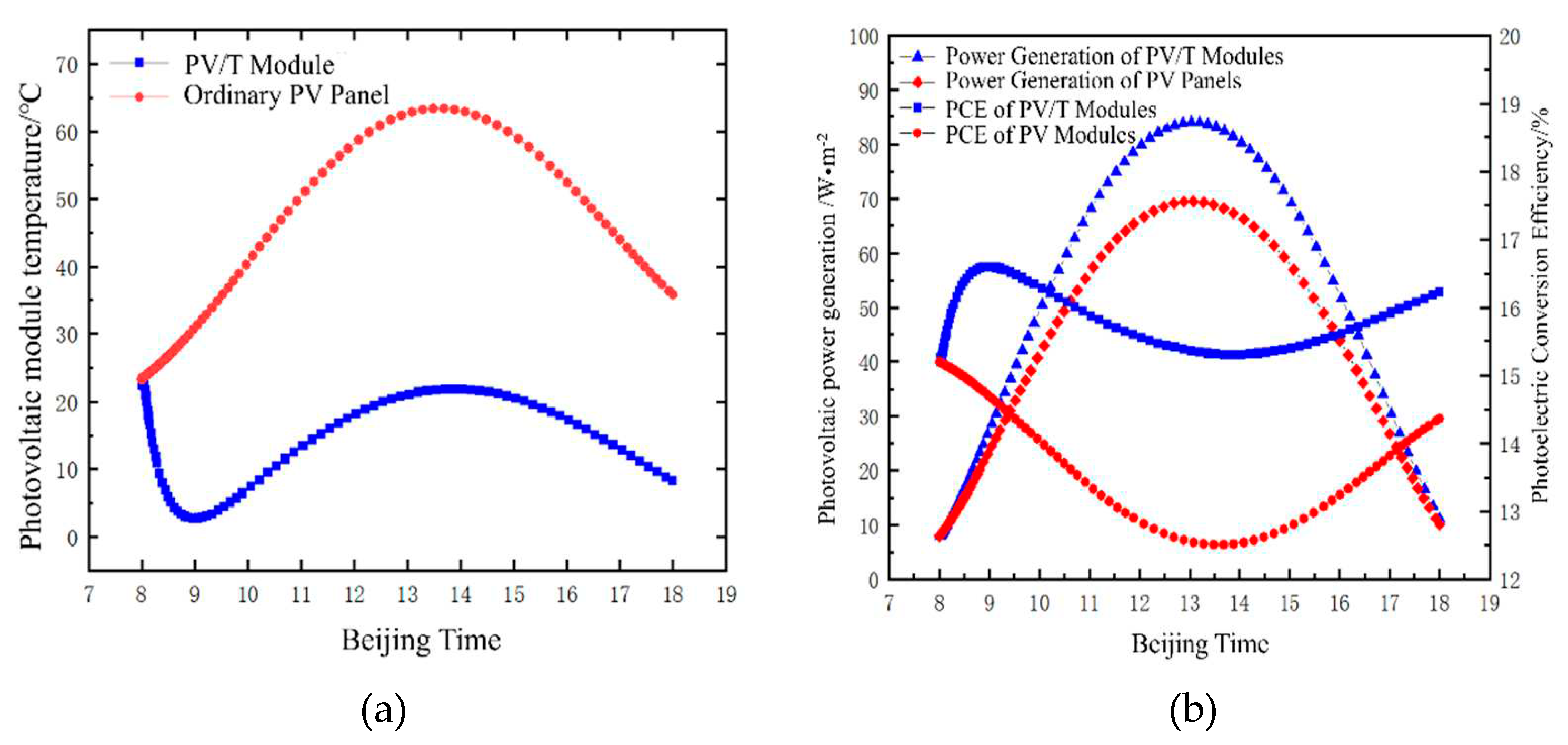
4.1. Simulation Analysis under Summer Heating Conditions
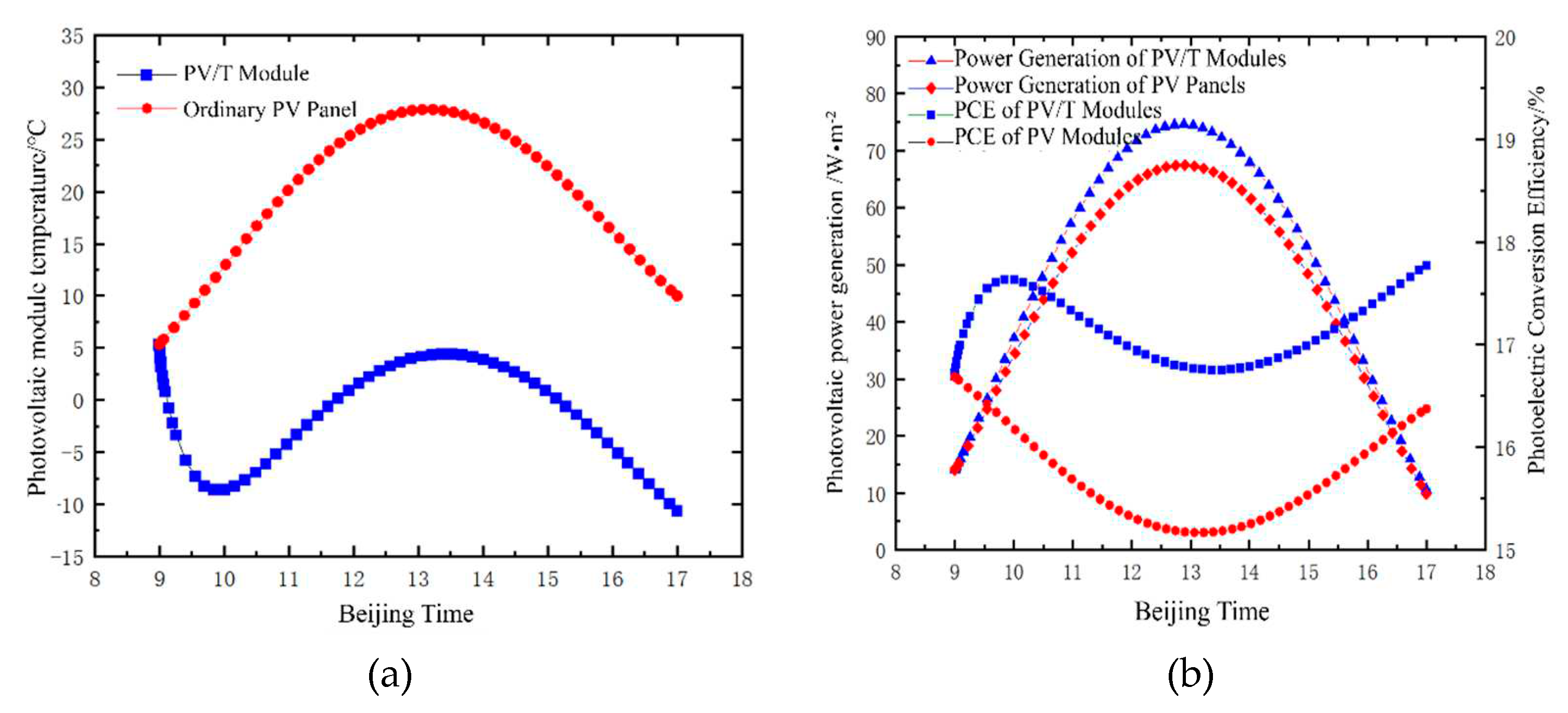
4.2. Simulation Analysis under Winter Heating Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, S.; Sarvaiya, J.N.; Seshadri, B. Temperature Dependent Photovoltaic (PV) Efficiency and Its Effect on PV Production in the World—A Review. Energy Procedia 2013, 33, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M. Performance analyses of combined heating and photovoltaic power systems for residences. Energy Convers. 1976, 16, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, J.E.C.; Russell, M.C. Combined photovoltaic and thermal hybrid collector systems. Conference Record of the IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists, Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- Ito, S.; Miura, N.; Takano, Y. Studies of Heat Pumps Using Direct Expansion Type Solar Collectors. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2005, 127, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, P.; Jie, J.; Wei, H.; et al. Performance of photovoltaic solar assisted heat pump system in typical climate zone. J Energy Environ. 2007, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Pei, G.; Chow, T.-T.; Liu, K.; He, H.; Lu, J.; Han, C. Experimental study of photovoltaic solar assisted heat pump system. Sol. Energy 2008, 82, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Smith, S.; et al. Review of R&D progress and practical application of the solar photovoltaic/thermal (PV/T) technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 599–617. [Google Scholar]
- Solanki, S.C.; Dubey, S.; Tiwari, A. Indoor simulation and testing of photovoltaic thermal (PV/T) air collectors. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyam; Tiwari, G.; Al-Helal, I. Analytical expression of temperature dependent electrical efficiency of N-PVT water collectors connected in series. Sol. Energy 2015, 114, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouhara, H.; Milko, J.; Danielewicz, J.; Sayegh, M.; Szulgowska-Zgrzywa, M.; Ramos, J.; Lester, S. The performance of a novel flat heat pipe based thermal and PV/T (photovoltaic and thermal systems) solar collector that can be used as an energy-active building envelope material. Energy 2016, 108, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Fu, X.S. ; A novel solar photovoltaic loop heat pipe/heat pump water heating system. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2020, 41, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.B.; Zhang, X.K.; Wang, C.C.; et al. An experimental research on energy-saving efficiency of a solar PV/T heat pump system based on micro heat pipe array. Renew. Energy Resour. 2021, 39, 611–617. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, L.C.; Zhao, S.G.; Gao, Y.Z.; et al. Experimental study on performance of photovoltaic direct-driven PV/T dual-source heat pump hot water system. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2023, 44, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Ding, G.L.; Zhang, C.L.; et al. Dynamic Simulation of Air-to-Water Dual-Mode Heat Pumps. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2003, 24, 725–728. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrullo, R.; Renno, C. A thermoeconomic model of a photovoltaic heat pump. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 1959–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelifa, A.; Touafek, K.; Ben Moussa, H.; Tabet, I. Modeling and detailed study of hybrid photovoltaic thermal (PV/T) solar collector. Sol. Energy 2016, 135, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.P.; Guo, X.X.; Liang, K.; et al. Research on the Performance of Flat-Box Photovoltaic/ Thermal Collector with Cooling Channels. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2017, 140, 021002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Ke, H.; Deng, X. Experimental and CFD investigation on temperature distribution of a serpentine tube type photovoltaic/thermal collector. Sol. Energy 2018, 174, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannemand, M.; Sifnaios, I.; Tian, Z.; Furbo, S. Simulation and optimization of a hybrid unglazed solar photovoltaic-thermal collector and heat pump system with two storage tanks. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 206, 112429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavian, S.; Aghanajafi, C.; Mosleh, H.J.; Nazari, A.; Nazari, A. Exergy, economic and environmental evaluation of an optimized hybrid photovoltaic-geothermal heat pump system. Appl. Energy 2020, 276, 115469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerdesh, Y.; Abdulina, Z.; Aliuly, A.; Belyayev, Y.; Mohanraj, M.; Kaltayev, A. Numerical simulation on solar collector and cascade heat pump combi water heating systems in Kazakhstan climates. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hamid, M.A.; Wei, G.; Sherin, M.; Cui, L.; Du, X. Comparative Study of Different Photovoltaic/Thermal Hybrid Configurations From Energetic and Exergetic Points of View: A Numerical Analysis. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2021, 143, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, A.; Rieberer, R. Energetic and economic analysis of a PV-assisted air-to-water heat pump system for renovated residential buildings with high-temperature heat emission system. Appl. Energy 2021, 293, 116953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.F. Study on dynamic simulation and optimization of PV/T-heat pump system. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Technological, 2018.
- Guo, G.Z.; Gou, Y.J. Simulation and Experimental Research on Integrated System of Photovoltaic and Photothermal Based on High-Efficiency Collector. Tangshan, North China University of Science and Technology, 2021.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




