Introduction
Today, toothpaste seems to improve every day. We have anti-cavity toothpaste, extra-whitening toothpaste, toothpaste with mouthwash, toothpaste for sensitive teeth, toothpaste with stripes, clear toothpaste, and even liver-flavored toothpaste for dogs (Chen, 2010). Modern toothpaste has many things to do. It must have abrasives to scour off bacterial films. It must have fluorides to harden the teeth against decay. It must have a strong enough flavor to hide the bad tastes of decaying bits of previous meals, and the awful taste of some of the other ingredients, such as detergents and phosphates (Simpson, 2005).
Most modern toothpastes used today cater for general oral hygiene and not for specific tooth mouth maladies like halitosis. According to Tonzetich (2015), some modern toothpaste used nowadays can also cause problems such as painful oral ulcers called canker sores of aphthous ulcers due to the presence of detergent in most toothpastes called Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS). Another common problem associated with modern toothpastes is tooth sensitivity. Sensitive teeth produce pain or discomfort when exposed to hot or cold foods, liquids, and sweets. Baking soda (found in some toothpaste) as well as, highly salted foods can also cause discomfort in people with sensitive teeth. The essence of this research is to make herbal toothpaste that takes care of the mouth majorly without any adverse effects on the patients’ health i.e. to produce herbal toothpaste for halitosis control.
Materials and Methods
Sample Collection
The two materials used for this study (Bridelia ferrugeinea and alum) were obtained from local market (Oja-Oje) in Ede Osun State. The reagents and equipment used for this study were obtained from the Science Laboratory Technology, Federal Polytechnic, Ede Osun State.
Production of Herbal Toothpaste
The required quantities of the ingredients were weighed and taken into mortal and grounded Calcium Carbonate, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, Glycerin, sodium fluoride and methyl cellulose were mixed in water. Sodium benzoate, hydrogen peroxide, peppermint, Bridelia ferrugeinea extract and alum were added into the above mixture. This mixture was titrated well until a paste consistency was formed. Six toothpaste samples were produced and labeled A,B, C,D,E and F respectively as shown in the table below.
Table 1.
Formulated constituents for the herbal toothpaste.
Table 1.
Formulated constituents for the herbal toothpaste.
| Toothpaste samples |
Constituents |
| A |
Calcium carbonate, Glycerin, Hydrogen peroxide, Sodium benzoate, Peppermint |
| B |
Calcium carbonate, Glycerin, Hydrogen peroxide, Sodium benzoate, Peppermint, Sodium fluoride, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate |
| C |
Calcium carbonate, Glycerin, Hydrogen peroxide, Sodium benzoate, Peppermint, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate |
| D |
Calcium carbonate, Glycerin, Hydrogen peroxide, Sodium benzoate, Peppermint, Sodium fluoride, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, Methyl cellulose |
| E |
Calcium carbonate, Glycerin, Hydrogen peroxide, Sodium benzoate, Peppermint, Sodium fluoride, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, Methyl cellulose, Bridelia ferrugeinea extract |
| F |
Calcium carbonate, Alum |
Culturing and Isolation of Bacteria from Test
The saliva of the ‘Halitosis’ patient was collected using cotton wool and transported into the laboratory for further analysis. Isolation, culturing and sensitivity tests were carried out according to standard methods.
Comparative Analysis between Commercial toothpaste and lab made toothpaste
For comparison between toothpaste the following physicochemical tests were carried out; Fineness, pH, foaming power, moisture and volatile matter.
Results
Properties of Lab. Made toothpaste and commercial toothpaste
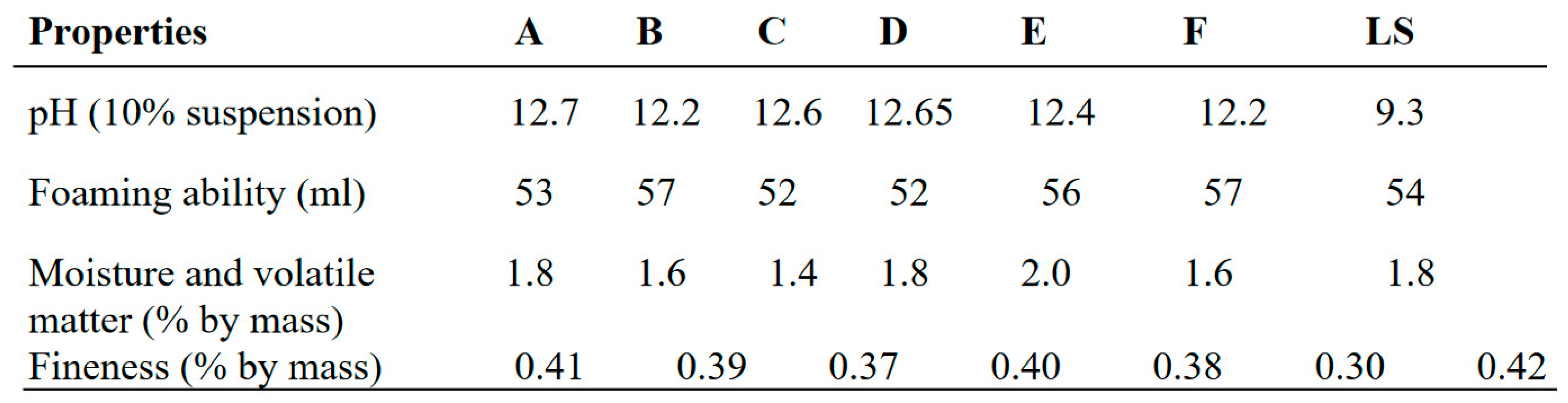
Table 2.
Evaluation tests for lab-made and commercial toothpaste.
Table 2.
Evaluation tests for lab-made and commercial toothpaste.
Figure 1.
pH value (%) and foam ability(ml) of lab made toothpaste and commercial toothpaste.
Figure 1.
pH value (%) and foam ability(ml) of lab made toothpaste and commercial toothpaste.
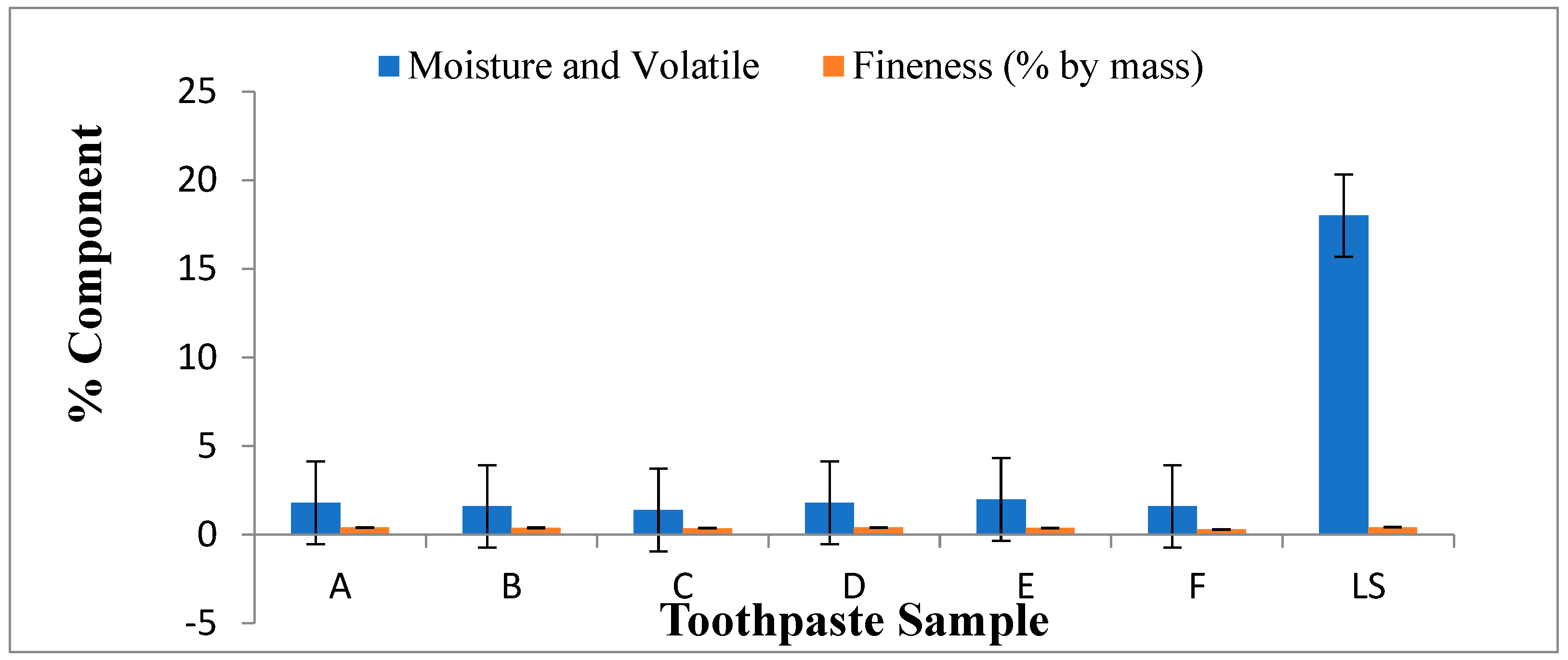
Figure 2.
Moisture and volatile matter (%), fineness (%) of lab made and commercial toothpaste.
Figure 2.
Moisture and volatile matter (%), fineness (%) of lab made and commercial toothpaste.
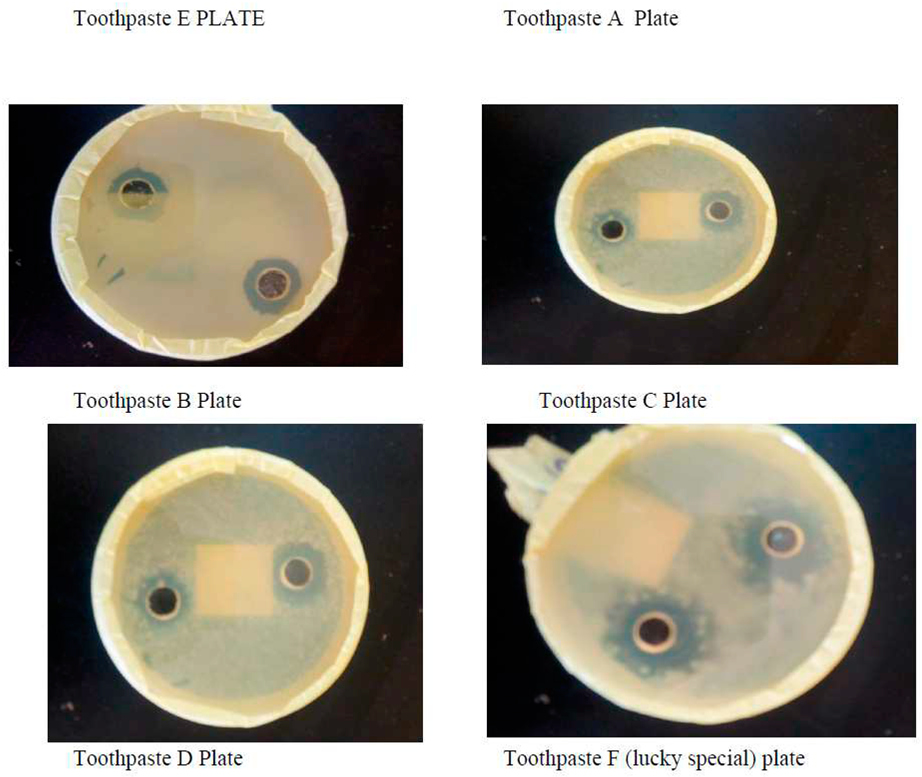
Zone Inhibition of Lab. Made toothpaste and Commercial toothpaste
Depending the morphological characterizes and biochemical test were identifying this type of bacteria which was Staphylococcus aureus. The microbial inhibition zones of toothpastes produced using natural source such as herbal resources. The results indicated that all tested toothpastes made in laboratory using natural source and selected commercial toothpaste (lucky commercial toothpaste) demonstrated a positive significant antimicrobial activity against the tested microorganism which was Staphylococcus aureus. This shows that both herbal toothpaste and commercial toothpaste selected for this study possessed antimicrobial activity against bacterial in the mouth.
The result in
Table 3 showed that the pH of the lab made toothpastes were alkaline compared to commercial toothpaste (lucky special) which was slightly alkaline. The pH value gives an indication of the inorganic constituents in toothpaste. High acidic pH encourages the growth of mouth bacterial that causes dental carries (Oyewale, 2005). Recommended pH for toothpaste is between 6.50 and 7.50 (NIS, 2006). The maximum fineness of the toothpaste is 0.5% by mass according to BIS (bureau of India Standards). The fineness of the evaluated toothpastes ranged from 0.30-0.42% by mass which complied with the BIS standard of the toothpaste. The foam formulation of toothpastes formulated and commercial toothpaste (lucky special) ranged from 52-57ml.The result showed that the foam formulation of the evaluated toothpastes is sufficient for its cleansing action, which also compared with the BIS standard which is 50ml.The moisture and volatile matter present in lucky special was significantly more than the rest of the formulations. The moisture and volatile matter of evaluated toothpastes complied with tolerable limit (50%) for the moisture and volatile matter in toothpaste as specified by SON (NIS, 2006). The preferable amount of residue has retained on sieve for Lab. made formulation which is better than the residue obtained by commercial toothpaste (lucky special).
More so, Simpson (2005) stated that herbal toothpaste are well know their ability in curing halitosis and other related mouth diseases due their abrasive properties present in the herbal toothpaste such as aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), various calcium hydrogen phosphates, various silicas and zeolites, and hydroxyapatite (Ca5(PO4)3OH) (Helen, 2010).Abrasives, like the dental polishing agents used in dentists’ offices, also because a small amount of enamel erosion which is termed "polishing" action. Simpson (2005) further stated that some herbal toothpastes now days contain powdered white mica, which acts as a mild abrasive, and also adds a cosmetically pleasing glittery shimmer to the paste. The polishing of teeth and removes stains from tooth surfaces.
In addition, all lab-made toothpastes samples produced showed high level of antimicrobial activity and efficacy. This could be attributed to the presence of antimicrobial substances in toothpaste. Lab made toothpastes had a better activity on the test organisms as compared to lucky special toothpaste. Staphylococcus aureus (also known as golden staph) was the only bacteria isolated in the collected male and female saliva during the experiment. The herbal toothpastes produced for this study showed positive significant effects on growth of these bacteria. This shows no growth of Staphylococcus aureus when subjected to laboratory made toothpaste produced (herbal toothpaste) and selected commercial toothpaste (lucky toothpaste).
The possible antimicrobial effects of the herbal toothpaste produced and commercial toothpaste (lucky special) on the isolate were also ascertained. The results from the antibacterial screenings of lab made herbal toothpaste and commercial toothpaste (lucky special) (
Table 3) showed that the lab made herbal toothpastes have antimicrobial activity with zones of inhibition diameters (mm) in the range of 1.7mm. Though the zones of inhibition diameter (mm) were not within the range described by Kirby-Bauer which is 16-18m (Bauer
et al.,1966). This is because of the antimicrobial contents of the toothpaste used. If the concentrations were higher, the zone of inhibition would have been within or above that described by Kirby-Bauer. From the results of this investigation, the zone of inhibition diameters increased with increasing concentrations of the toothpastes but toothpastes are probably designed to be bacteriostatic not bacteriocidal because these oral bacteria form part of the oral flora but become pathogenic under favourable conditions. The population of these oral bacteria needs to be controlled rather than completely eradicated. The selected organism was more susceptible to the lab made herbal toothpastes with
Staphylococcus aureus having the highest mean zone of inhibition diameter (7.93mm) than Commercial toothpaste (lucky special) that had (0.06mm) zone diameter of inhibition. The difference could be as a result of their active ingredients. The herbal toothpaste had more active ingredients (
Sodium monofluorophosphate,
Bridellia ferruginea, extract, pepper mint extract, than the commercial toothpaste.
Conclusion
From the result of the tests carried out on herbal toothpaste produced in laboratory using natural ingredients, it can be concluded that the lab made toothpaste containing abrasive and antimicrobial properties can be considered as promising formulation for the prevention of halitosis caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
Recommendation
Individuals are encouraged to formulate herbal toothpaste in their home as formulated in this study to prevent diseases such as halitosis.
This study demonstrated the inhibitory effects of antimicrobial dentrifice on oral bacteria. Further investigations are needed to determine the effects of herbal extracts against oral pathogens with the goal to discover new antimicrobial agents mainly among plant extracts that will prevent halitosis.
References
- Chen, N. A meta-analysis of six-month studies of antiplaque and antigingivitis agents. Journal of the American Dental Association Journal 2010, 137, 1649–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, Z. Seventeen studies support the antiplaque, antigingivitis effects of dentifrices containing 0.30 percent triclosan, 2.0 percent Gantrez copolymer. Biochemistry Journal 2013, 12, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, S. Oral Hygiene Products. Industrial Chemistry Journal 2010, 3, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, P. The clinical effect of a stabilized stannous fluoride dentifrice on plaque formation, gingivitis and gingival bleeding. The Journal of Clinical Dentistry 2009, 11, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Lee M, Walsh T, Glenny A, Shi X. Fluoride toothpastes of different concentrations for preventing dental caries in children and adolescents. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, 106–111.
- Liu D, Zheng G, Zhang D, Lin H. Effect of desensitizing toothpastes on dentine Hypersensitivity. Journal of Dentistry 2013, 9, 10–15.
- Mamatha B, Naveen P. (2007). Effect to Apatite-containing Dentifrices on Dental Caries in School Children. Journal of Dental Health 2007, 39, 104–109.
- Oyewale, A. Stimation of the Essential Inorganic Constituents of Commercial Toothpaste. Journal of Science and industrial Research 2005, 64, 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, L. (2005). Topical applications of sodium fluoride and stannous fluoride. Public Health Reports 2005, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tonzetich, J. Production and origin of oral malodour: a review of mechanisms and methods of analysis. Journal of Periodontology 2015, 48, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wentworth, D. Dentifrice use help to remove plaque. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 2014, 43, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang G, Delgado E, Devizio W, Mateo LR, Li Y, Lee S. Hypersensitivity. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry Journal 2007, 10, 14–22.
- Zhao, W. National Library of Medicine. National Institutes of Health Retrieved Journal 2011, 8, 20–28. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).